6d4fa81c10f92c1191d850f58abdf92e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 11 th Edition TODAY AND TOMORROW n 4 Input and Output CHAPTER Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition
11 th Edition TODAY AND TOMORROW n 4 Input and Output CHAPTER Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition
 Learning Objectives n n Chapter 4 Explain the purpose of a computer keyboard and the types of keyboards widely used today. List several different pointing devices and describe their functions. Describe the purposes of scanners and readers and list some types of scanners and readers in use today. Understand how digital cameras differ from conventional cameras. Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 2
Learning Objectives n n Chapter 4 Explain the purpose of a computer keyboard and the types of keyboards widely used today. List several different pointing devices and describe their functions. Describe the purposes of scanners and readers and list some types of scanners and readers in use today. Understand how digital cameras differ from conventional cameras. Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 2
 Learning Objectives, Cont’d. n Explain how audio input is accomplished. n Describe the characteristics of a display device. n List several types of printers and explain their function. n Chapter 4 Understand which hardware devices are used for audio output. Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 3
Learning Objectives, Cont’d. n Explain how audio input is accomplished. n Describe the characteristics of a display device. n List several types of printers and explain their function. n Chapter 4 Understand which hardware devices are used for audio output. Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 3
 Overview n Chapter 4 This chapter covers: n Different types of keyboards and pointing devices n Types of scanners, readers, and digital cameras n What audio input is n Types of display devices and how they work n Types of printers and how they work n What audio output is Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 4
Overview n Chapter 4 This chapter covers: n Different types of keyboards and pointing devices n Types of scanners, readers, and digital cameras n What audio input is n Types of display devices and how they work n Types of printers and how they work n What audio output is Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 4
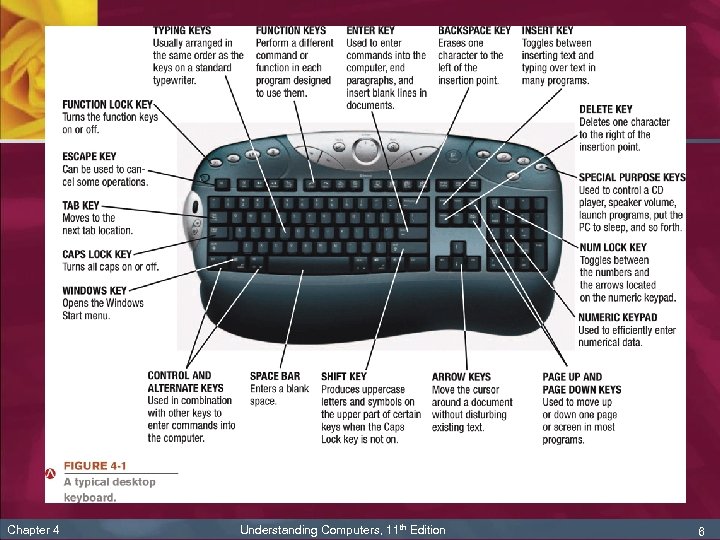
 Keyboards n n n Chapter 4 Keyboard: input device containing keys, arranged in a typewriter type of configuration, that can be used to input letters, numbers, and other symbols Most PCs today are designed to be used with a keyboard Contains: n Standard alphanumeric keys n Numeric keypad n Function keys n Directional keys and special keys Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 5
Keyboards n n n Chapter 4 Keyboard: input device containing keys, arranged in a typewriter type of configuration, that can be used to input letters, numbers, and other symbols Most PCs today are designed to be used with a keyboard Contains: n Standard alphanumeric keys n Numeric keypad n Function keys n Directional keys and special keys Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 5
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 6
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 6
 Keyboards, Cont’d n n Chapter 4 Can be: n Wireless n Portable n Foldable Handheld PCs and mobile devices today often have a built-in keyboard or thumb pad (keyboard designed to be pressed with just the thumbs) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 7
Keyboards, Cont’d n n Chapter 4 Can be: n Wireless n Portable n Foldable Handheld PCs and mobile devices today often have a built-in keyboard or thumb pad (keyboard designed to be pressed with just the thumbs) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 7
 Pointing Devices n n n Chapter 4 Pointing device: input device that moves an onscreen pointer (arrow or insertion point) to allow the user to select objects on the screen. Usually buttons on the device are used to select objects Common types of pointing devices: n Mouse n Electronic pen n Touch screen Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 8
Pointing Devices n n n Chapter 4 Pointing device: input device that moves an onscreen pointer (arrow or insertion point) to allow the user to select objects on the screen. Usually buttons on the device are used to select objects Common types of pointing devices: n Mouse n Electronic pen n Touch screen Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 8
 The Mouse n Chapter 4 Mouse: common pointing device that the user slides along a flat surface to move a pointer around the screen and clicks its buttons to make selections n Rests on the desk or other flat surface close to the user’s PC n Older mechanical mice have a ball exposed on the bottom surface n Most mice today are optical mice that track movements with light n Can be wireless Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 9
The Mouse n Chapter 4 Mouse: common pointing device that the user slides along a flat surface to move a pointer around the screen and clicks its buttons to make selections n Rests on the desk or other flat surface close to the user’s PC n Older mechanical mice have a ball exposed on the bottom surface n Most mice today are optical mice that track movements with light n Can be wireless Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 9
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 10
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 10
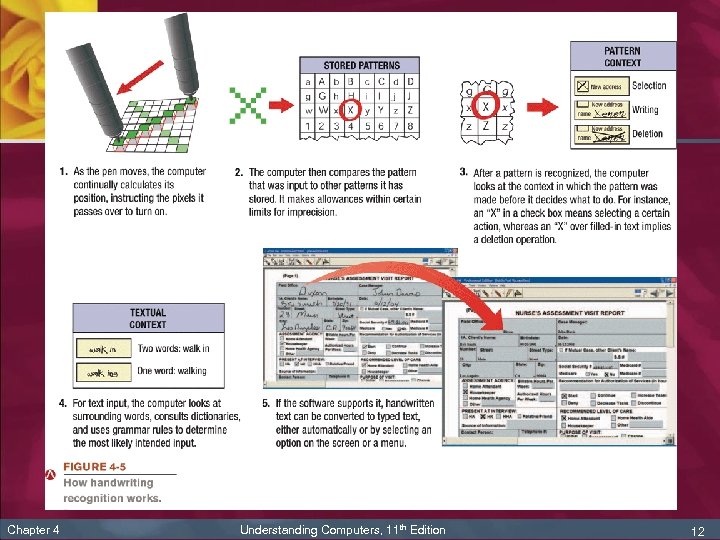
 Electronic Pens n n Electronic pen (stylus or digital pen): used instead of a mouse to select objects, as well as to draw or write electronically on the screen Commonly used with pen-based PCs n n Chapter 4 To issue commands and input data If handwriting recognition is used, written text can be converted to editable typed text Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 11
Electronic Pens n n Electronic pen (stylus or digital pen): used instead of a mouse to select objects, as well as to draw or write electronically on the screen Commonly used with pen-based PCs n n Chapter 4 To issue commands and input data If handwriting recognition is used, written text can be converted to editable typed text Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 11
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 12
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 12
 Electronic Pens, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Also used with n Digital writing systems n Graphics tablets n Signature capture devices Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 13
Electronic Pens, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Also used with n Digital writing systems n Graphics tablets n Signature capture devices Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 13
 Touch Screens n n Chapter 4 Touch screen: display device that is touched with the finger to issue commands or otherwise generate input to the connected PC Touch screen kiosks are found in retail stores, movie theaters, courthouses, fast-food restaurants, airports, and point-of-sale (POS) systems Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 14
Touch Screens n n Chapter 4 Touch screen: display device that is touched with the finger to issue commands or otherwise generate input to the connected PC Touch screen kiosks are found in retail stores, movie theaters, courthouses, fast-food restaurants, airports, and point-of-sale (POS) systems Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 14
 Other Pointing Devices n n Trackballs n Pointing sticks n Chapter 4 Joysticks Touch pads Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 15
Other Pointing Devices n n Trackballs n Pointing sticks n Chapter 4 Joysticks Touch pads Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 15
 Scanners, Readers, and Digital Cameras n n n Chapter 4 Source documents: documents containing data that already exists in physical form (order form, photograph, invoice, check, or price label) Source data automation: capturing data directly from a source document Most common devices used in source data automation: scanning or reading devices Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 16
Scanners, Readers, and Digital Cameras n n n Chapter 4 Source documents: documents containing data that already exists in physical form (order form, photograph, invoice, check, or price label) Source data automation: capturing data directly from a source document Most common devices used in source data automation: scanning or reading devices Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 16
 Scanners n Scanner (optical scanner): input device that reads printed text and graphics and transfers them to a computer in digital form n Can scan photos, documents, drawings, etc. n Data is typically input as a single image n Chapter 4 If optical character recognition (OCR) is used, text is input as editable, typed text Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 17
Scanners n Scanner (optical scanner): input device that reads printed text and graphics and transfers them to a computer in digital form n Can scan photos, documents, drawings, etc. n Data is typically input as a single image n Chapter 4 If optical character recognition (OCR) is used, text is input as editable, typed text Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 17
 Scanners n n n Chapter 4 Types of scanners: n Flatbed n Sheetfed n Handheld n Drum n Three-dimensional (3 D) Quality of scanned images indicated by optical resolution, measured in number of dots per inch (dpi) Resolution can often be specified Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 18
Scanners n n n Chapter 4 Types of scanners: n Flatbed n Sheetfed n Handheld n Drum n Three-dimensional (3 D) Quality of scanned images indicated by optical resolution, measured in number of dots per inch (dpi) Resolution can often be specified Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 18
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 19
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 19
 Readers n Barcode readers: input devices that read barcodes n n Chapter 4 Barcode: machine-readable code that represents data as a set of bars Common types: n Universal Product Code (UPC) n Code 39 n POSTNET code Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 20
Readers n Barcode readers: input devices that read barcodes n n Chapter 4 Barcode: machine-readable code that represents data as a set of bars Common types: n Universal Product Code (UPC) n Code 39 n POSTNET code Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 20
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 21
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 21
 Readers, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Radio frequency identification (RFID) readers n Radio frequency identification (RFID): technology used to store and transmit data located in RFID tags n RFID tag: device containing tiny chips and radio antennas that is attached to objects that will be identified using RFID technology n Applications: tracking inventory pallets and shipping containers, tracking or locating livestock and other animals, tagging tractors and other large assets to keep track of their locations Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 22
Readers, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Radio frequency identification (RFID) readers n Radio frequency identification (RFID): technology used to store and transmit data located in RFID tags n RFID tag: device containing tiny chips and radio antennas that is attached to objects that will be identified using RFID technology n Applications: tracking inventory pallets and shipping containers, tracking or locating livestock and other animals, tagging tractors and other large assets to keep track of their locations Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 22
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 23
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 23
 Readers, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Optical mark readers (OMRs): input data from special forms to score or tally exams, questionnaires, ballots, and so forth n Use pencil to fill in small circles/shapes on the form to indicate their selections n Forms are inserted into an optical mark reader to be scored or tallied Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 24
Readers, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Optical mark readers (OMRs): input data from special forms to score or tally exams, questionnaires, ballots, and so forth n Use pencil to fill in small circles/shapes on the form to indicate their selections n Forms are inserted into an optical mark reader to be scored or tallied Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 24
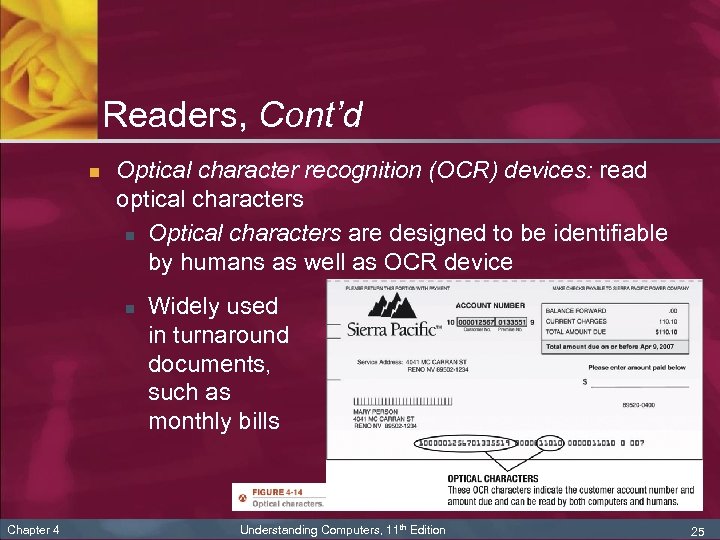 Readers, Cont’d n Optical character recognition (OCR) devices: read optical characters n Optical characters are designed to be identifiable by humans as well as OCR device n Chapter 4 Widely used in turnaround documents, such as monthly bills Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 25
Readers, Cont’d n Optical character recognition (OCR) devices: read optical characters n Optical characters are designed to be identifiable by humans as well as OCR device n Chapter 4 Widely used in turnaround documents, such as monthly bills Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 25
 Readers, Cont’d n Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) readers: read MICR characters n n Chapter 4 Used primarily for banking MICR readers read the special magnetic characters and sort/process checks Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 26
Readers, Cont’d n Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) readers: read MICR characters n n Chapter 4 Used primarily for banking MICR readers read the special magnetic characters and sort/process checks Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 26
 Readers, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Biometric readers: used to input biometric data n Biometric data is based on unique physiological characteristics (fingerprint, hand geometry, face, iris of the eye) or personal traits (voice, signature) n Readers can be stand-alone or built into another piece of hardware (keyboard, mouse) n Also being built into computers and storage devices to allow access only by authorized individuals n Most often used for access control and to verify transactions Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 27
Readers, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Biometric readers: used to input biometric data n Biometric data is based on unique physiological characteristics (fingerprint, hand geometry, face, iris of the eye) or personal traits (voice, signature) n Readers can be stand-alone or built into another piece of hardware (keyboard, mouse) n Also being built into computers and storage devices to allow access only by authorized individuals n Most often used for access control and to verify transactions Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 27
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 28
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 28
 Digital Cameras n Digital camera: input device that takes pictures and records them as digital data (instead of film or videotaped) images n Chapter 4 Usually designated as: n Still cameras (take individual still photos) n Video cameras (capture moving video images) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 29
Digital Cameras n Digital camera: input device that takes pictures and records them as digital data (instead of film or videotaped) images n Chapter 4 Usually designated as: n Still cameras (take individual still photos) n Video cameras (capture moving video images) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 29
 Digital Cameras, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Digital still cameras n Available in a wide variety of sizes and capabilities n Images are immediately available for viewing or printing n Typically use flash memory for storage n Photos can be transferred to a PC or printer n Digital photos can be retouched with image editing software, posted to a Web page, or burned onto a CD or DVD disc n Camera quality is measured in megapixels Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 30
Digital Cameras, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Digital still cameras n Available in a wide variety of sizes and capabilities n Images are immediately available for viewing or printing n Typically use flash memory for storage n Photos can be transferred to a PC or printer n Digital photos can be retouched with image editing software, posted to a Web page, or burned onto a CD or DVD disc n Camera quality is measured in megapixels Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 30
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 31
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 31
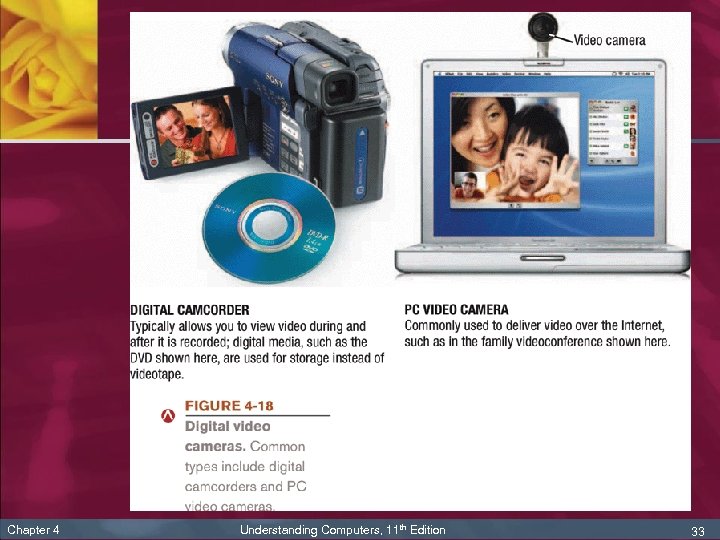
 Digital Cameras, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Digital video cameras: include digital camcorders and small PC video cameras n Digital camcorders: similar to analog camcorders, but they store images on digital media—typically either on mini digital video (DV) tape cartridges or rewritable DVDs n PC video cameras (PC cams, Web cam): designed to transmit video images over the Internet, such as during a videoconference or video phone call Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 32
Digital Cameras, Cont’d n Chapter 4 Digital video cameras: include digital camcorders and small PC video cameras n Digital camcorders: similar to analog camcorders, but they store images on digital media—typically either on mini digital video (DV) tape cartridges or rewritable DVDs n PC video cameras (PC cams, Web cam): designed to transmit video images over the Internet, such as during a videoconference or video phone call Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 32
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 33
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 33
 Audio Input n Chapter 4 Audio input: process of entering audio data into the computer (voice and music) n Voice input systems (speech recognition systems): enable a computer to recognize the human voice n Consist of a microphone or headset and appropriate software n Can be used to dictate text or commands into a PC n Music input systems: can input and record music (either original compositions or via a CD or DVD player) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 34
Audio Input n Chapter 4 Audio input: process of entering audio data into the computer (voice and music) n Voice input systems (speech recognition systems): enable a computer to recognize the human voice n Consist of a microphone or headset and appropriate software n Can be used to dictate text or commands into a PC n Music input systems: can input and record music (either original compositions or via a CD or DVD player) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 34
 Audio Input, Cont’d Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 35
Audio Input, Cont’d Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 35
 Display Devices n n Chapter 4 Display device: output device that presents output visually Soft copy: output that appears on a display device Monitor: display device for a desktop PC Display screen: screen built into the unit of all-in -one PCs, notebook computers, handheld PCs, smart phones, consumer devices, and many other devices Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 36
Display Devices n n Chapter 4 Display device: output device that presents output visually Soft copy: output that appears on a display device Monitor: display device for a desktop PC Display screen: screen built into the unit of all-in -one PCs, notebook computers, handheld PCs, smart phones, consumer devices, and many other devices Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 36
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 37
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 37
 Display Device Characteristics n n Chapter 4 Usually color, but can be monochrome Can be a CRT monitor or a flat-panel display n CRT monitor: projects images onto a display screen using technology similar to that of TVs n Flat-panel display: forms images by manipulating electronically charged chemicals or gases sandwiched between thin panes of glass Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 38
Display Device Characteristics n n Chapter 4 Usually color, but can be monochrome Can be a CRT monitor or a flat-panel display n CRT monitor: projects images onto a display screen using technology similar to that of TVs n Flat-panel display: forms images by manipulating electronically charged chemicals or gases sandwiched between thin panes of glass Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 38
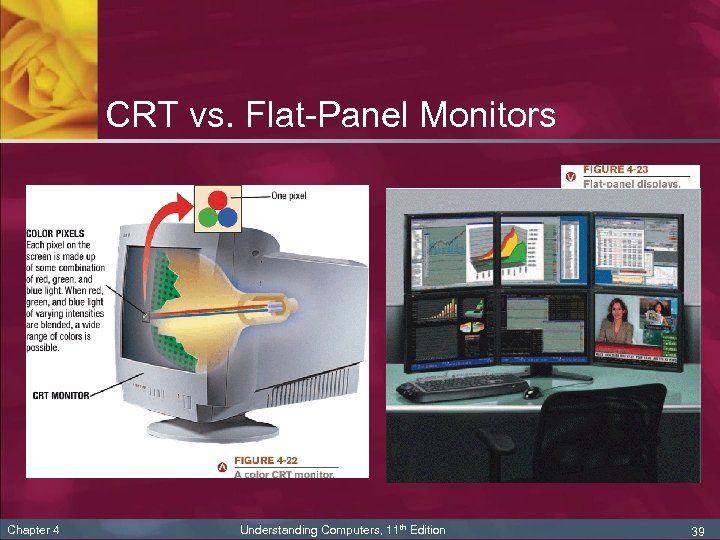 CRT vs. Flat-Panel Monitors Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 39
CRT vs. Flat-Panel Monitors Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 39
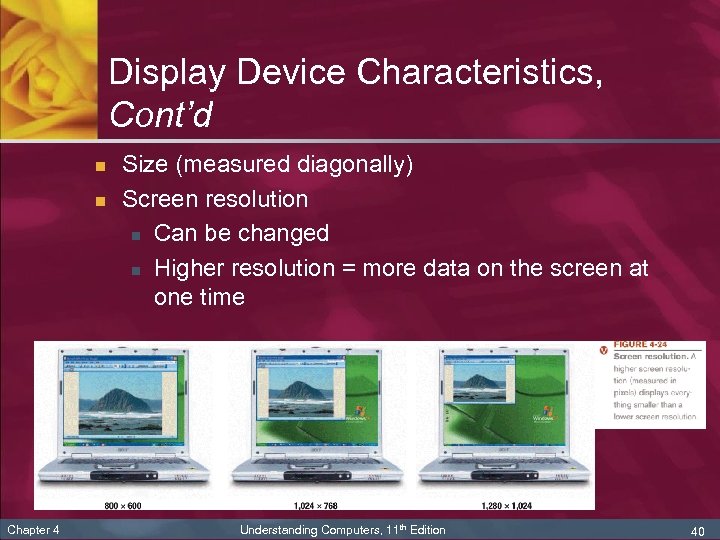 Display Device Characteristics, Cont’d n n Chapter 4 Size (measured diagonally) Screen resolution n Can be changed n Higher resolution = more data on the screen at one time Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 40
Display Device Characteristics, Cont’d n n Chapter 4 Size (measured diagonally) Screen resolution n Can be changed n Higher resolution = more data on the screen at one time Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 40
 Display Device Characteristics, Cont’d n n Chapter 4 Video card (determines display characteristics and how monitor can connect to the PC) Monitors can be also be: n Wired or wireless n 2 D or 3 D Displays n Digital TV and/or HDTV ready or capable Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 41
Display Device Characteristics, Cont’d n n Chapter 4 Video card (determines display characteristics and how monitor can connect to the PC) Monitors can be also be: n Wired or wireless n 2 D or 3 D Displays n Digital TV and/or HDTV ready or capable Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 41
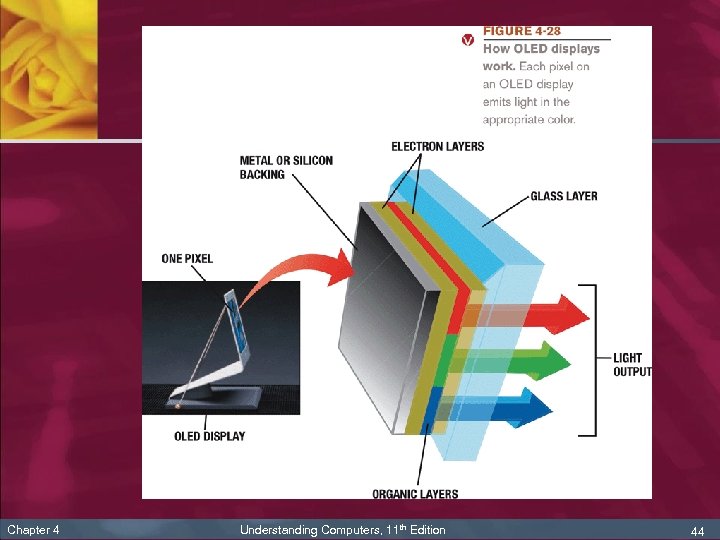
 Flat-Panel Display Technologies n n n Chapter 4 Liquid crystal displays (LCDs): use charged liquid crystals to display images Organic light emitting diode (OLED) displays: use emissive organic material to display brighter and sharper images n Flexible OLEDs (FOLEDs) n Transparent OLEDs (TOLEDs) n Phosphorescent OLEDs (PHOLEDs) Plasma displays: use layers of gas to display images; most often used on large displays Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 42
Flat-Panel Display Technologies n n n Chapter 4 Liquid crystal displays (LCDs): use charged liquid crystals to display images Organic light emitting diode (OLED) displays: use emissive organic material to display brighter and sharper images n Flexible OLEDs (FOLEDs) n Transparent OLEDs (TOLEDs) n Phosphorescent OLEDs (PHOLEDs) Plasma displays: use layers of gas to display images; most often used on large displays Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 42
 Flat-Panel Display Technologies, Cont’d Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 43
Flat-Panel Display Technologies, Cont’d Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 43
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 44
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 44
 Data and Multimedia Projectors n n n Chapter 4 Data projector: display device that projects all computer output to a wall or projection screen Most data projectors today can project video, in addition to computer output. Can be wireless projectors Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 45
Data and Multimedia Projectors n n n Chapter 4 Data projector: display device that projects all computer output to a wall or projection screen Most data projectors today can project video, in addition to computer output. Can be wireless projectors Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 45
 Printers n n Chapter 4 Printer: output device that produces output on paper n Produce hard copy n Can be used with both desktop and portable PCs Printer characteristics n Impact vs. nonimpact printing n Most printers are nonimpact n Impact printers (like dot-matrix printers) are still used for printing multipart forms and shipping documents Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 46
Printers n n Chapter 4 Printer: output device that produces output on paper n Produce hard copy n Can be used with both desktop and portable PCs Printer characteristics n Impact vs. nonimpact printing n Most printers are nonimpact n Impact printers (like dot-matrix printers) are still used for printing multipart forms and shipping documents Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 46
 Printers n Chapter 4 Printer characteristics, cont’d n Can print in color or black-and white only n Can be a personal or network printer n Quality is called print resolution and measured in dots per inch (dpi) n Print speed is measured in pages per minute (ppm) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 47
Printers n Chapter 4 Printer characteristics, cont’d n Can print in color or black-and white only n Can be a personal or network printer n Quality is called print resolution and measured in dots per inch (dpi) n Print speed is measured in pages per minute (ppm) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 47
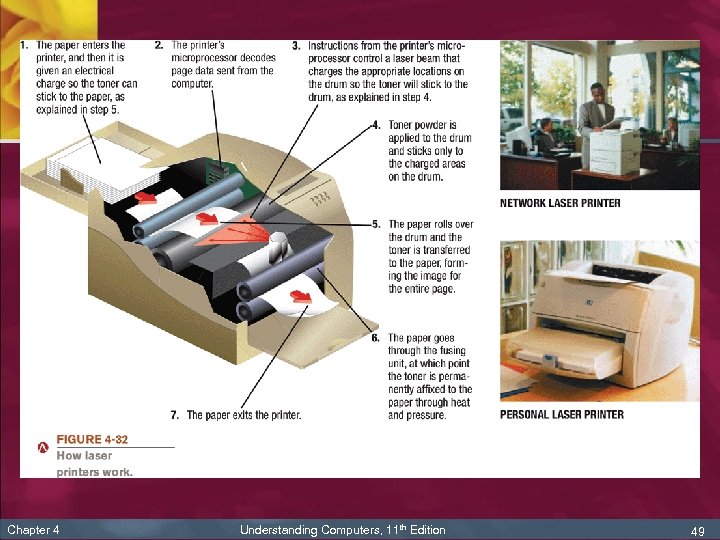
 Laser Printers n Laser printer: output device that uses toner powder and technology similar to that of a photocopier to produce images on paper n The standard for business documents n Print one entire page at a time n Usually black and white, though color printers are available n Chapter 4 Common print resolution for laser printers is between 600 and 2, 400 dpi Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 48
Laser Printers n Laser printer: output device that uses toner powder and technology similar to that of a photocopier to produce images on paper n The standard for business documents n Print one entire page at a time n Usually black and white, though color printers are available n Chapter 4 Common print resolution for laser printers is between 600 and 2, 400 dpi Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 48
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 49
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 49
 Ink-Jet Printers n Ink-jet printer: output device that sprays droplets of ink to produce images on paper n n Often the choice for home use n Print fairly slowly, one line at a time n Chapter 4 Typically print in color Quality not quite as good as a laser printer Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 50
Ink-Jet Printers n Ink-jet printer: output device that sprays droplets of ink to produce images on paper n n Often the choice for home use n Print fairly slowly, one line at a time n Chapter 4 Typically print in color Quality not quite as good as a laser printer Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 50
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 51
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 51
 Special Purpose Printers n n Photo printers (designed to print photographs) Barcode printers (print barcodes; some can encode RFID tags) n Label printers (print labels, electronic postage, etc. ) n Portable printers (designed to be carried with you) n Chapter 4 Plotters and wide-format ink-jet printers (print on large paper or other large materials) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 52
Special Purpose Printers n n Photo printers (designed to print photographs) Barcode printers (print barcodes; some can encode RFID tags) n Label printers (print labels, electronic postage, etc. ) n Portable printers (designed to be carried with you) n Chapter 4 Plotters and wide-format ink-jet printers (print on large paper or other large materials) Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 52
 Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 53
Chapter 4 Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 53
 Multifunction Devices n n Chapter 4 Multifunction device: device that offers some combination of printing, copying, scanning, and faxing capabilities Most commonly, these types of devices are based on color ink-jet printer technology, although laser multifunction devices are available Advantage: takes up less space and is less expensive than purchasing multiple machines Disadvantage: Lose all devices if it needs to be repaired Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 54
Multifunction Devices n n Chapter 4 Multifunction device: device that offers some combination of printing, copying, scanning, and faxing capabilities Most commonly, these types of devices are based on color ink-jet printer technology, although laser multifunction devices are available Advantage: takes up less space and is less expensive than purchasing multiple machines Disadvantage: Lose all devices if it needs to be repaired Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 54
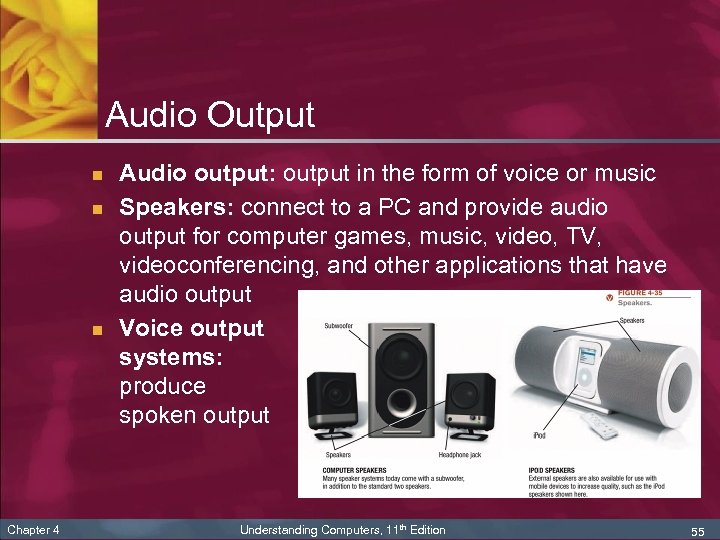 Audio Output n n n Chapter 4 Audio output: output in the form of voice or music Speakers: connect to a PC and provide audio output for computer games, music, video, TV, videoconferencing, and other applications that have audio output Voice output systems: produce spoken output Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 55
Audio Output n n n Chapter 4 Audio output: output in the form of voice or music Speakers: connect to a PC and provide audio output for computer games, music, video, TV, videoconferencing, and other applications that have audio output Voice output systems: produce spoken output Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 55
 Summary n n n n Chapter 4 Keyboards Pointing Devices Scanners, Readers, and Digital Cameras Audio Input Display Devices Printers Audio Output Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 56
Summary n n n n Chapter 4 Keyboards Pointing Devices Scanners, Readers, and Digital Cameras Audio Input Display Devices Printers Audio Output Understanding Computers, 11 th Edition 56


