Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 11 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
11 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
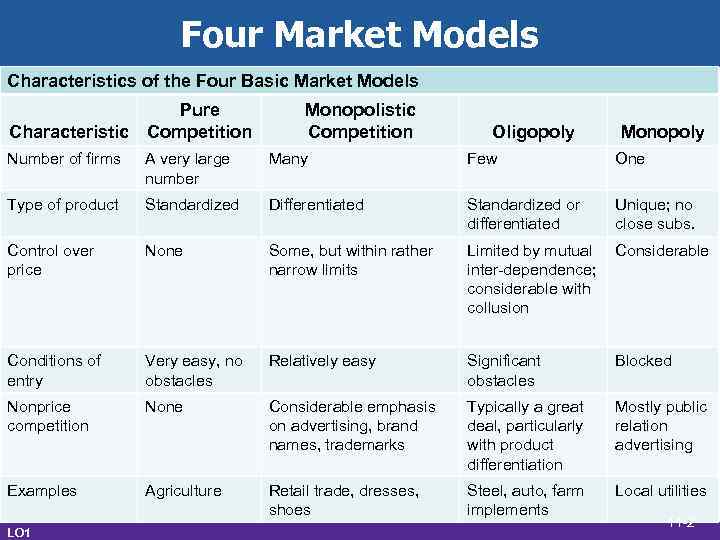 Four Market Models Characteristics of the Four Basic Market Models Characteristic Pure Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Monopoly Number of firms A very large number Many Few One Type of product Standardized Differentiated Standardized or differentiated Unique; no close subs. Control over price None Some, but within rather narrow limits Limited by mutual inter-dependence; considerable with collusion Considerable Conditions of entry Very easy, no obstacles Relatively easy Significant obstacles Blocked Nonprice competition None Considerable emphasis on advertising, brand names, trademarks Typically a great deal, particularly with product differentiation Mostly public relation advertising Examples Agriculture Retail trade, dresses, shoes Steel, auto, farm implements Local utilities LO 1 11 -2
Four Market Models Characteristics of the Four Basic Market Models Characteristic Pure Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Monopoly Number of firms A very large number Many Few One Type of product Standardized Differentiated Standardized or differentiated Unique; no close subs. Control over price None Some, but within rather narrow limits Limited by mutual inter-dependence; considerable with collusion Considerable Conditions of entry Very easy, no obstacles Relatively easy Significant obstacles Blocked Nonprice competition None Considerable emphasis on advertising, brand names, trademarks Typically a great deal, particularly with product differentiation Mostly public relation advertising Examples Agriculture Retail trade, dresses, shoes Steel, auto, farm implements Local utilities LO 1 11 -2
 Monopolistic Competition • Relatively large number of sellers • Differentiated products • Easy entry and exit • Advertising LO 1 11 -3
Monopolistic Competition • Relatively large number of sellers • Differentiated products • Easy entry and exit • Advertising LO 1 11 -3
 Monopolistically Competitive • Industry concentration • Measured by: • Four-firm concentration ratios • Percentage of 4 largest firms 4 -Firm CR = Output of four largest firms Total output in the industry • Herfindahl index • Sum of squared market shares HI = (%S 1)2 + (%S 2)2 + (%S 3)2 + …. + (%Sn)2 LO 1 11 -4
Monopolistically Competitive • Industry concentration • Measured by: • Four-firm concentration ratios • Percentage of 4 largest firms 4 -Firm CR = Output of four largest firms Total output in the industry • Herfindahl index • Sum of squared market shares HI = (%S 1)2 + (%S 2)2 + (%S 3)2 + …. + (%Sn)2 LO 1 11 -4
 Price and Output in Monopolistic Comp • Demand is highly elastic • Short run profit or loss • Produce where MR=MC • Long run normal profit • Entry and exit • Inefficient • Product variety LO 2 11 -5
Price and Output in Monopolistic Comp • Demand is highly elastic • Short run profit or loss • Produce where MR=MC • Long run normal profit • Entry and exit • Inefficient • Product variety LO 2 11 -5
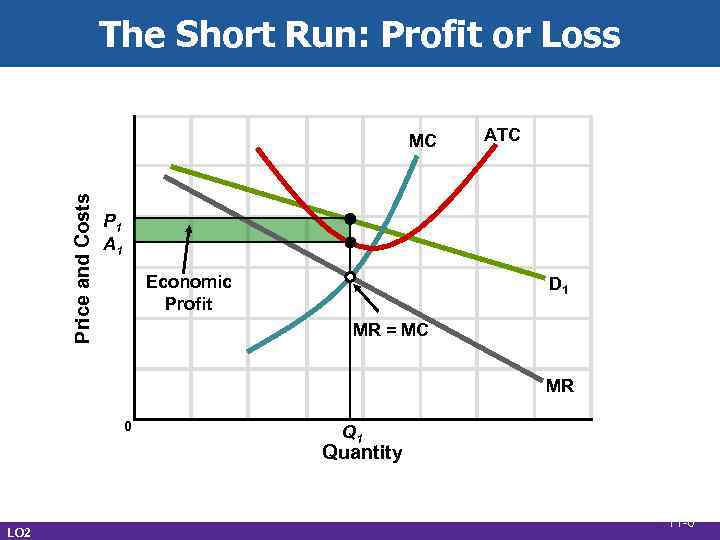 The Short Run: Profit or Loss Price and Costs MC ATC P 1 A 1 Economic Profit D 1 MR = MC MR 0 Q 1 Quantity LO 2 11 -6
The Short Run: Profit or Loss Price and Costs MC ATC P 1 A 1 Economic Profit D 1 MR = MC MR 0 Q 1 Quantity LO 2 11 -6
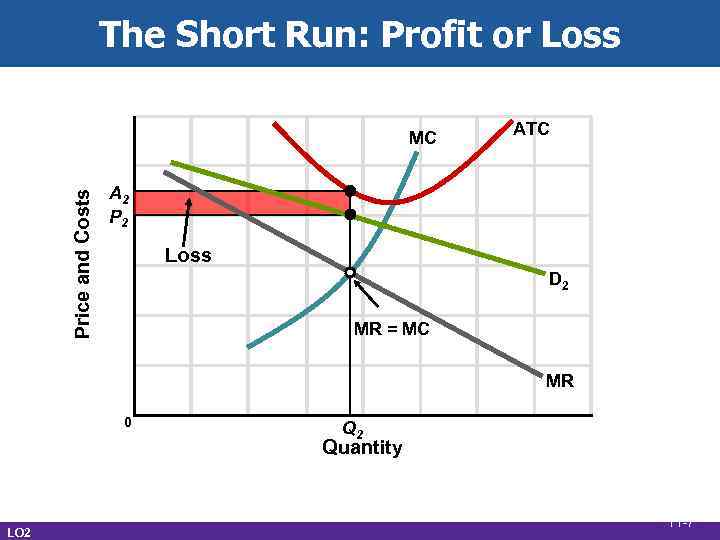 The Short Run: Profit or Loss Price and Costs MC ATC A 2 P 2 Loss D 2 MR = MC MR 0 Q 2 Quantity LO 2 11 -7
The Short Run: Profit or Loss Price and Costs MC ATC A 2 P 2 Loss D 2 MR = MC MR 0 Q 2 Quantity LO 2 11 -7
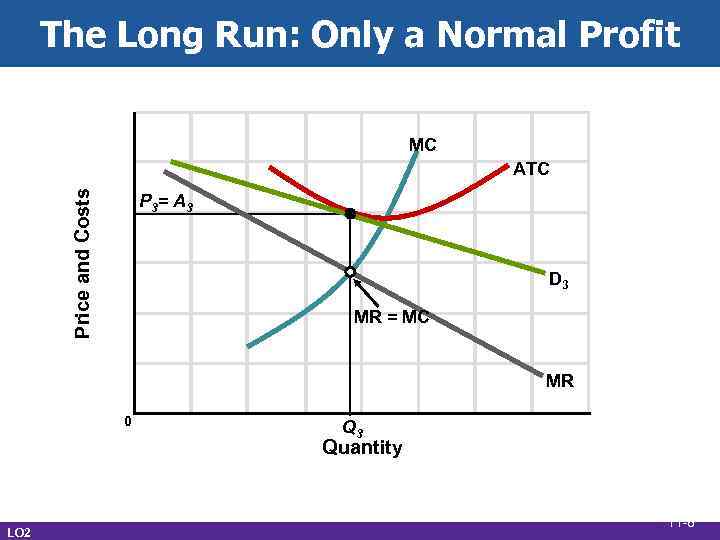 The Long Run: Only a Normal Profit MC Price and Costs ATC P 3= A 3 D 3 MR = MC MR 0 Q 3 Quantity LO 2 11 -8
The Long Run: Only a Normal Profit MC Price and Costs ATC P 3= A 3 D 3 MR = MC MR 0 Q 3 Quantity LO 2 11 -8
 Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency • Inefficient • Productive inefficiency • P > ATC • Allocative inefficiency • P > MC LO 2 11 -9
Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency • Inefficient • Productive inefficiency • P > ATC • Allocative inefficiency • P > MC LO 2 11 -9
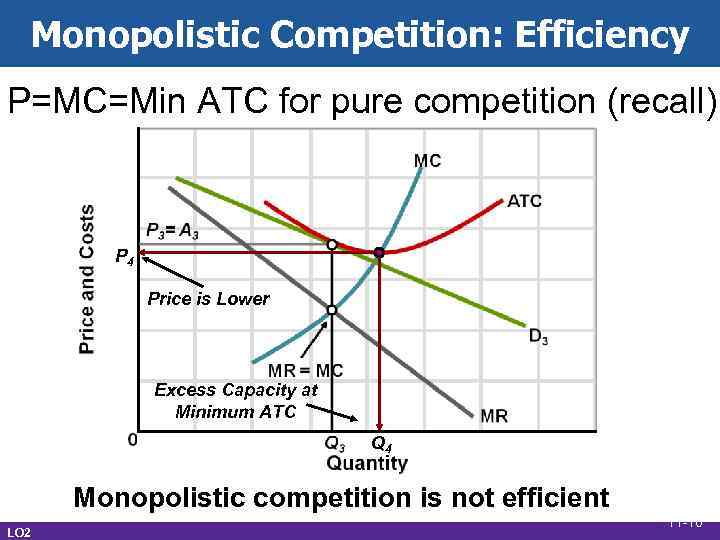 Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency P=MC=Min ATC for pure competition (recall) P 4 Price is Lower Excess Capacity at Minimum ATC Q 4 Monopolistic competition is not efficient LO 2 11 -10
Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency P=MC=Min ATC for pure competition (recall) P 4 Price is Lower Excess Capacity at Minimum ATC Q 4 Monopolistic competition is not efficient LO 2 11 -10
 Product Variety • The firm constantly manages price, • LO 2 product, and advertising • Better product differentiation • Better advertising The consumer benefits by greater array of choices and better products • Types and styles • Brands and quality 11 -11
Product Variety • The firm constantly manages price, • LO 2 product, and advertising • Better product differentiation • Better advertising The consumer benefits by greater array of choices and better products • Types and styles • Brands and quality 11 -11
 Oligopoly • A few large producers • Homogeneous or differentiated • • • LO 3 products Limited control over price • Mutual interdependence • Strategic behavior Entry barriers Mergers 11 -12
Oligopoly • A few large producers • Homogeneous or differentiated • • • LO 3 products Limited control over price • Mutual interdependence • Strategic behavior Entry barriers Mergers 11 -12
 Oligopolistic Industries • Four-firm concentration ratio • 40% or more to be oligopoly • Shortcomings • Localized markets • Inter-industry competition • World price • Dominant firms LO 3 11 -13
Oligopolistic Industries • Four-firm concentration ratio • 40% or more to be oligopoly • Shortcomings • Localized markets • Inter-industry competition • World price • Dominant firms LO 3 11 -13
 Game Theory Overview • Oligopolies display strategic pricing behavior • Mutual interdependence • Collusion • Incentive to cheat • Prisoner’s dilemma LO 4 11 -14
Game Theory Overview • Oligopolies display strategic pricing behavior • Mutual interdependence • Collusion • Incentive to cheat • Prisoner’s dilemma LO 4 11 -14
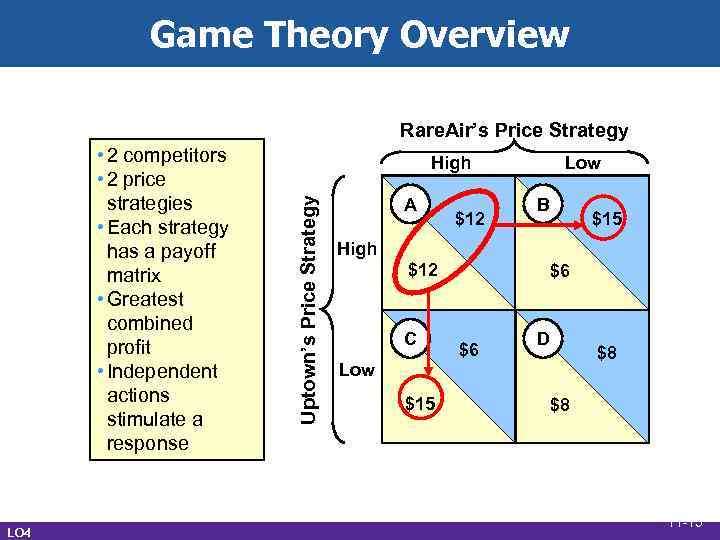 Game Theory Overview Rare. Air’s Price Strategy LO 4 High Uptown’s Price Strategy • 2 competitors • 2 price strategies • Each strategy has a payoff matrix • Greatest combined profit • Independent actions stimulate a response A $12 Low B $15 High $12 C $6 $6 D $8 Low $15 $8 11 -15
Game Theory Overview Rare. Air’s Price Strategy LO 4 High Uptown’s Price Strategy • 2 competitors • 2 price strategies • Each strategy has a payoff matrix • Greatest combined profit • Independent actions stimulate a response A $12 Low B $15 High $12 C $6 $6 D $8 Low $15 $8 11 -15
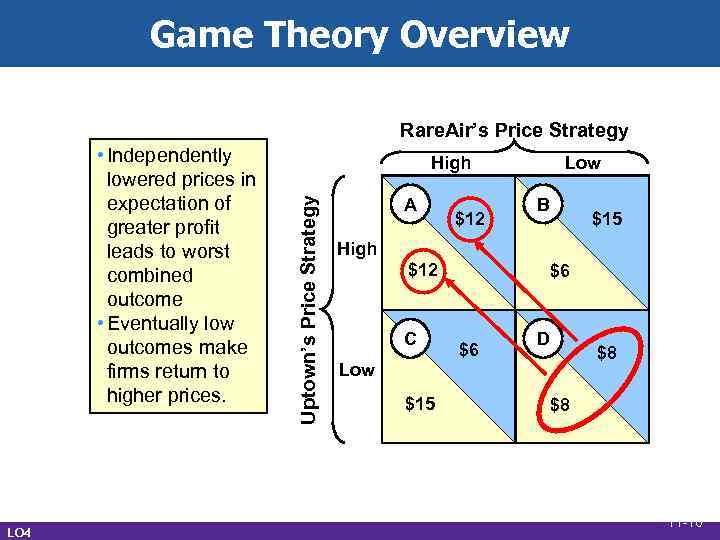 Game Theory Overview Rare. Air’s Price Strategy LO 4 High Uptown’s Price Strategy • Independently lowered prices in expectation of greater profit leads to worst combined outcome • Eventually low outcomes make firms return to higher prices. A $12 Low B $15 High $12 C $6 $6 D $8 Low $15 $8 11 -16
Game Theory Overview Rare. Air’s Price Strategy LO 4 High Uptown’s Price Strategy • Independently lowered prices in expectation of greater profit leads to worst combined outcome • Eventually low outcomes make firms return to higher prices. A $12 Low B $15 High $12 C $6 $6 D $8 Low $15 $8 11 -16
 Three Oligopoly Models • Kinked-demand curve • Collusive pricing • Price leadership • Reasons for 3 models • Diversity of oligopolies • Complications of interdependence LO 5 11 -17
Three Oligopoly Models • Kinked-demand curve • Collusive pricing • Price leadership • Reasons for 3 models • Diversity of oligopolies • Complications of interdependence LO 5 11 -17
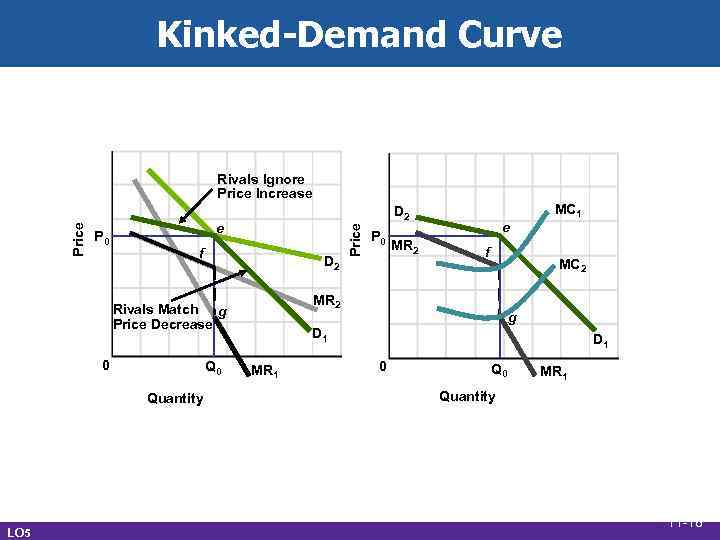 Kinked-Demand Curve P 0 e f D 2 Q 0 Quantity LO 5 P 0 MR 2 e f MC 2 MR 2 Rivals Match g Price Decrease 0 MC 1 D 2 Price Rivals Ignore Price Increase g D 1 MR 1 D 1 0 Q 0 MR 1 Quantity 11 -18
Kinked-Demand Curve P 0 e f D 2 Q 0 Quantity LO 5 P 0 MR 2 e f MC 2 MR 2 Rivals Match g Price Decrease 0 MC 1 D 2 Price Rivals Ignore Price Increase g D 1 MR 1 D 1 0 Q 0 MR 1 Quantity 11 -18
 Kinked-Demand Curve • Criticisms • Explains inflexibility, not price • Prices are not that rigid • Price wars LO 6 11 -19
Kinked-Demand Curve • Criticisms • Explains inflexibility, not price • Prices are not that rigid • Price wars LO 6 11 -19
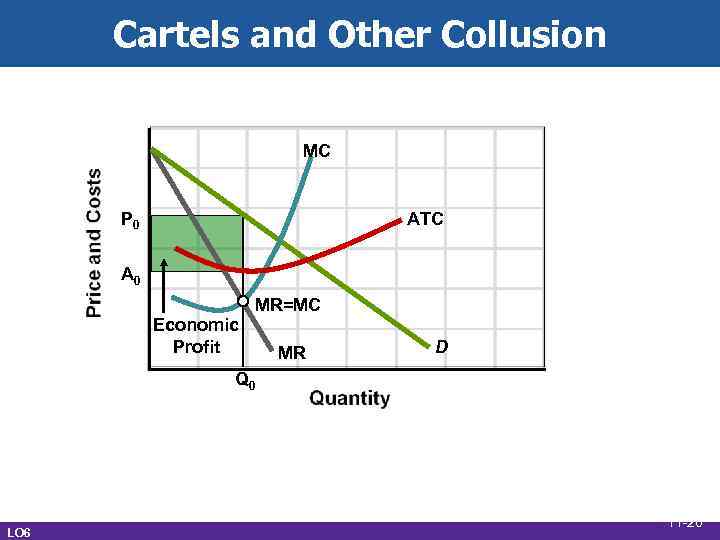 Cartels and Other Collusion MC P 0 ATC A 0 Economic Profit MR=MC MR D Q 0 LO 6 11 -20
Cartels and Other Collusion MC P 0 ATC A 0 Economic Profit MR=MC MR D Q 0 LO 6 11 -20
 Overt Collusion • Cartels - a group of firms or nations • • LO 6 that collude • Formally agreeing to the price • Sets output levels for members Collusion is illegal in the United States OPEC 11 -21
Overt Collusion • Cartels - a group of firms or nations • • LO 6 that collude • Formally agreeing to the price • Sets output levels for members Collusion is illegal in the United States OPEC 11 -21
 Obstacles to Collusion • Demand cost differences • Number of firms • Cheating • Recession • New entrants • Legal obstacles LO 6 11 -22
Obstacles to Collusion • Demand cost differences • Number of firms • Cheating • Recession • New entrants • Legal obstacles LO 6 11 -22
 Price Leadership Model • Price Leadership • Dominant firm initiates price • • LO 6 changes • Other firms follow the leader Use limit pricing to block entry of new firms Possible price war 11 -23
Price Leadership Model • Price Leadership • Dominant firm initiates price • • LO 6 changes • Other firms follow the leader Use limit pricing to block entry of new firms Possible price war 11 -23
 Oligopoly and Advertising • Prevalent to compete with product development and advertising • Less easily duplicated than a price change • Financially able to advertise LO 7 11 -24
Oligopoly and Advertising • Prevalent to compete with product development and advertising • Less easily duplicated than a price change • Financially able to advertise LO 7 11 -24
 Advertising Positive Effects Negative Effects Low-cost way of providing information to consumers Can be manipulative Enhances competition Contains misleading claims that confuse consumers Speeds up technological progress Consumers pay high prices for a good while forgoing a better, lower priced, unadvertised version of the product Can help firms obtain economies of scale LO 7 11 -25
Advertising Positive Effects Negative Effects Low-cost way of providing information to consumers Can be manipulative Enhances competition Contains misleading claims that confuse consumers Speeds up technological progress Consumers pay high prices for a good while forgoing a better, lower priced, unadvertised version of the product Can help firms obtain economies of scale LO 7 11 -25
 Oligopoly and Efficiency • Oligopolies are inefficient • Productively inefficient P > min. ATC • Allocatively inefficient P > MC • Qualifications • Increased foreign competition • Limit pricing • Technological advance LO 7 11 -26
Oligopoly and Efficiency • Oligopolies are inefficient • Productively inefficient P > min. ATC • Allocatively inefficient P > MC • Qualifications • Increased foreign competition • Limit pricing • Technological advance LO 7 11 -26


