8e7d3f43c6dcce901c9771720818e387.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 113

 11: 15 -12: 00 – Friday 11 March 2011 The role of the National Programme Manager in advocacy and partnerships Профилактика неинфекционных заболеваний и борьба с ними 预防和控制非传染病 Prevención y control de las enfermedades no transmisibles ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻤﺮﺍﺽ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺪﻳﺔ ﻭﻣﻜﺎﻓﺤﺘﻬﺎ Prévention et maîtrise des maladies non Prevention and control of non-communicable transmissibles diseases
11: 15 -12: 00 – Friday 11 March 2011 The role of the National Programme Manager in advocacy and partnerships Профилактика неинфекционных заболеваний и борьба с ними 预防和控制非传染病 Prevención y control de las enfermedades no transmisibles ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻤﺮﺍﺽ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺪﻳﺔ ﻭﻣﻜﺎﻓﺤﺘﻬﺎ Prévention et maîtrise des maladies non Prevention and control of non-communicable transmissibles diseases
 Dr Ashley Bloomfield, Partnership Adviser, NCDnet Mr Paul Garwood, Communications Officer Mr Menno van Hilten, External Relations Officer World Health Organization Профилактика неинфекционных заболеваний и борьба с ними 预防和控制非传染病 Prevención y control de las enfermedades no transmisibles ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻤﺮﺍﺽ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺪﻳﺔ ﻭﻣﻜﺎﻓﺤﺘﻬﺎ Prévention et maîtrise des maladies non Prevention and control of non-communicable transmissibles diseases
Dr Ashley Bloomfield, Partnership Adviser, NCDnet Mr Paul Garwood, Communications Officer Mr Menno van Hilten, External Relations Officer World Health Organization Профилактика неинфекционных заболеваний и борьба с ними 预防和控制非传染病 Prevención y control de las enfermedades no transmisibles ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻤﺮﺍﺽ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺪﻳﺔ ﻭﻣﻜﺎﻓﺤﺘﻬﺎ Prévention et maîtrise des maladies non Prevention and control of non-communicable transmissibles diseases
 People remember. . . • 20% of what they hear • 40% of what they hear and see • 80% of what they discover for themselves 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
People remember. . . • 20% of what they hear • 40% of what they hear and see • 80% of what they discover for themselves 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Rules of engagement Format: • 5 exercises • A bit of theory in between • Interactive • Informal • Interruptions encouraged Time management: • 11: 15 – 12: 00 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Rules of engagement Format: • 5 exercises • A bit of theory in between • Interactive • Informal • Interruptions encouraged Time management: • 11: 15 – 12: 00 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Setting expectations After this session, you'll have the basic tools (and skills) to convince decision-makers that: • NCDs merit increased investment • NCD action carries substantial benefits 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Setting expectations After this session, you'll have the basic tools (and skills) to convince decision-makers that: • NCDs merit increased investment • NCD action carries substantial benefits 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Exercise 1 If you had a chance to speak to US President Obama (*) for 2 minutes, what would you tell him about NCDs? * Or any other President or Prime-Minister from a G-20 country 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Exercise 1 If you had a chance to speak to US President Obama (*) for 2 minutes, what would you tell him about NCDs? * Or any other President or Prime-Minister from a G-20 country 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Challenge 1 What is the point? We are not always clear WHY we speak, write or make a presentation 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Challenge 1 What is the point? We are not always clear WHY we speak, write or make a presentation 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Challenge 2 We are trained to be logical, complete, accurate, evidence-based and fear being misunderstood. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Challenge 2 We are trained to be logical, complete, accurate, evidence-based and fear being misunderstood. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Challenge 3 We tend to concentrate on what we know and don't always think of why our message is important to listeners, viewers or the audience …now 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Challenge 3 We tend to concentrate on what we know and don't always think of why our message is important to listeners, viewers or the audience …now 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Challenge 4 Scientists, experts and programme managers speak like this "I need 30 minutes of your time to share 40 years of my accumulated technical expertise" "Yesterday's article in the Lancet discusses the prevention of preeclampsia in diabetic women. " 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Ministers and decision-makers speak like this "We must make the prevention and control NCDs and the improvement of maternal health top priorities on the development agenda"
Challenge 4 Scientists, experts and programme managers speak like this "I need 30 minutes of your time to share 40 years of my accumulated technical expertise" "Yesterday's article in the Lancet discusses the prevention of preeclampsia in diabetic women. " 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Ministers and decision-makers speak like this "We must make the prevention and control NCDs and the improvement of maternal health top priorities on the development agenda"
 "Dear President Obama" 1. In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. 2. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. 3. At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. 4. You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly in New York in September 2011, which will be attended by Heads of State and Government. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"Dear President Obama" 1. In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. 2. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. 3. At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. 4. You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly in New York in September 2011, which will be attended by Heads of State and Government. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 "Communications 101" Elements of communication: • Sender • Message • Target Audience • Proof points • Channel • Time 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"Communications 101" Elements of communication: • Sender • Message • Target Audience • Proof points • Channel • Time 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Me s s a g e : th e fo u r O ' s "Communications 101" Ongoing situation Opportunities One recommendation Operationalization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Me s s a g e : th e fo u r O ' s "Communications 101" Ongoing situation Opportunities One recommendation Operationalization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
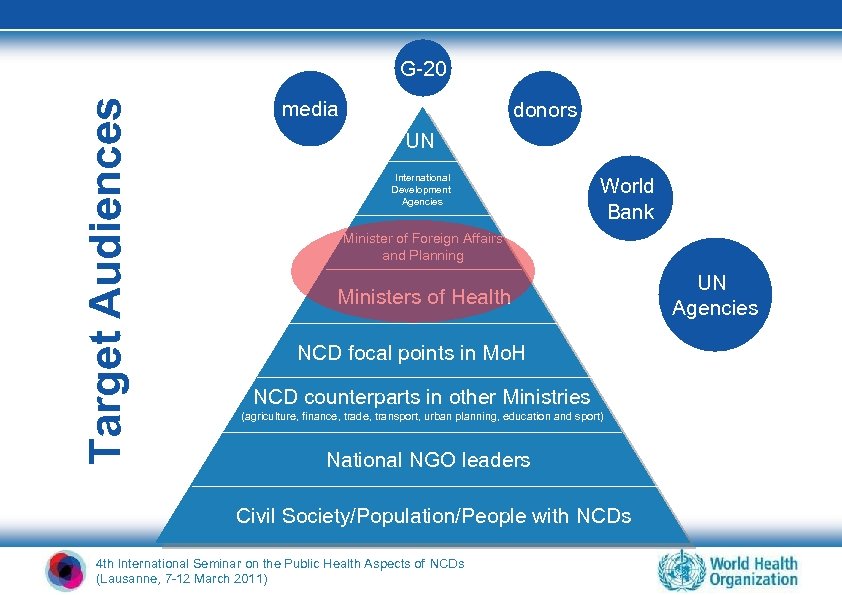
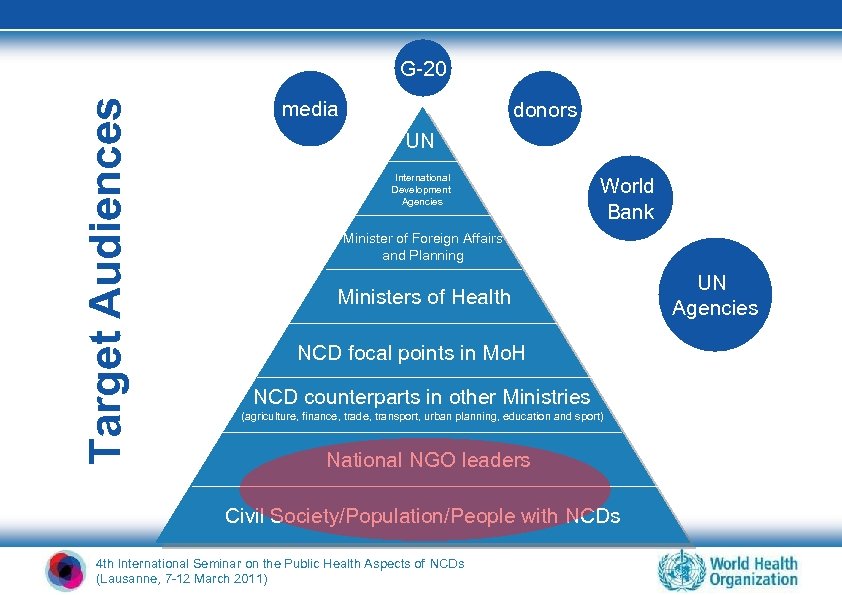
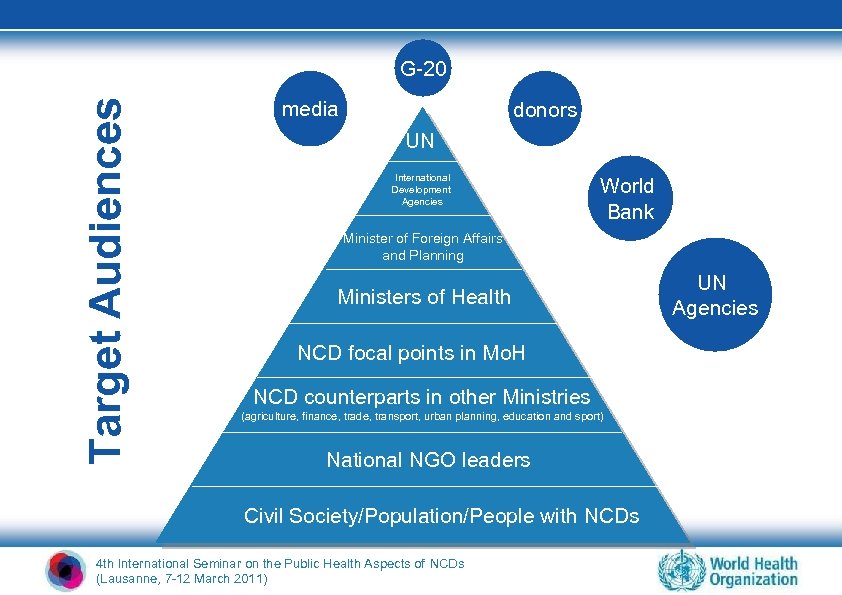 Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
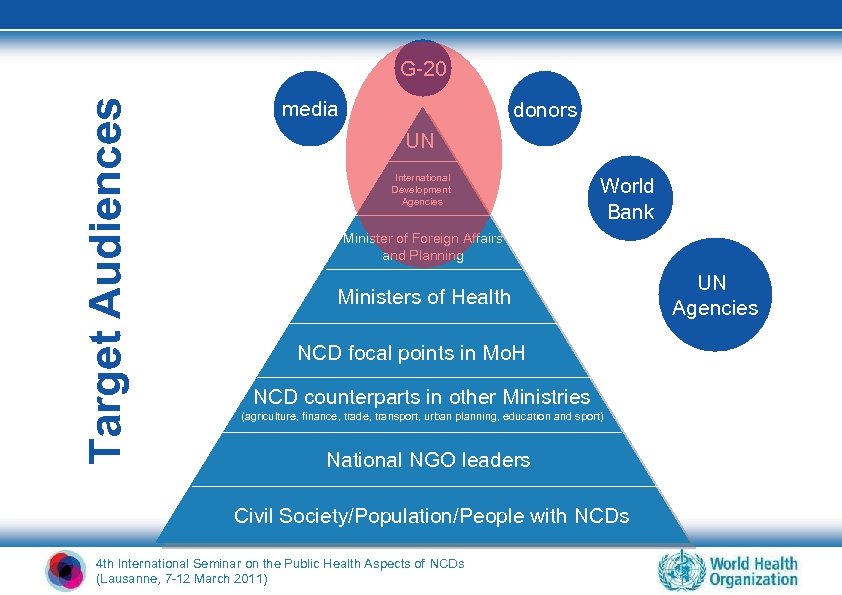 Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
 "Dear President Obama" (Key message on NCDs to international leaders) Ongoing situation Opportunities One recommendation Operationalization 1. In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. 2. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. 3. At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. 4. You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly in New York in September 2011, which will be attended by Heads of State and Government. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"Dear President Obama" (Key message on NCDs to international leaders) Ongoing situation Opportunities One recommendation Operationalization 1. In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. 2. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. 3. At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. 4. You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly in New York in September 2011, which will be attended by Heads of State and Government. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Translating key messages into a presentation In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Translating key messages into a presentation In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
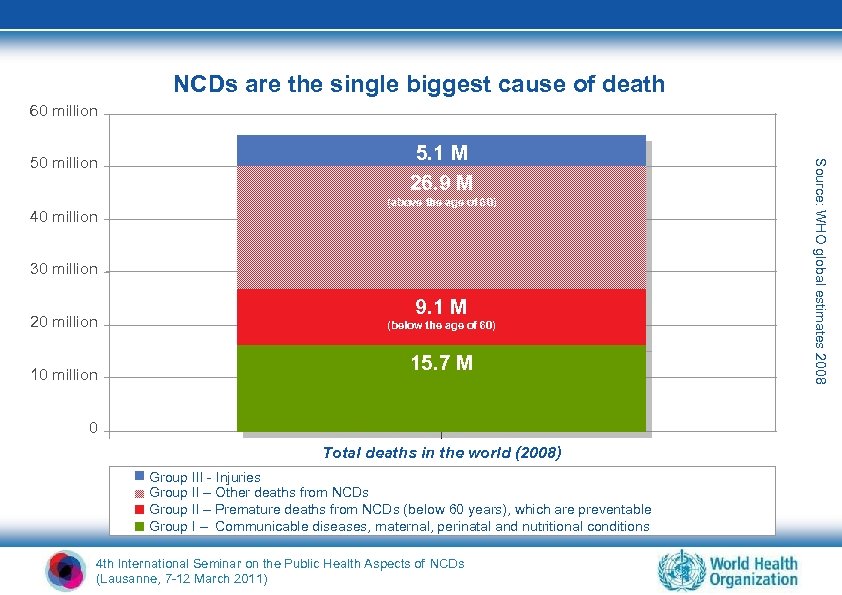 NCDs are the single biggest cause of death 10% 60 million 40 million 5. 1 M 26. 9 M (above the age of 60) 30 million 20 million 10 million 9. 1 M (below the age of 60) 15. 7 M 0 Total deaths in the world (2008) Group III - Injuries Low-income countries Group II – Other deaths from NCDs Group II – Premature deaths from NCDs (below 60 years), which are preventable Group I – Communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Source: WHO global estimates 2008 50 million
NCDs are the single biggest cause of death 10% 60 million 40 million 5. 1 M 26. 9 M (above the age of 60) 30 million 20 million 10 million 9. 1 M (below the age of 60) 15. 7 M 0 Total deaths in the world (2008) Group III - Injuries Low-income countries Group II – Other deaths from NCDs Group II – Premature deaths from NCDs (below 60 years), which are preventable Group I – Communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Source: WHO global estimates 2008 50 million
 90% of global premature deaths from NCDs occur in low- and middle-income countries 2. 9 M 13. 6 M Total deaths (2008) 20 million 15 million 5. 3 M 10 million 8. 3 M 0. 5 M 6. 6 M 1 M 2. 3 M 0. 8 M 1. 4 M 4. 4 M 1 M 0. 6 M High-income countries 5. 6 M 1. 4 M 1. 2 M Upper middle-income Low-income countries Group III - Injuries Low-income countries Group II – Other deaths from NCDs Group II – Premature deaths from NCDs (below 60 years), which are preventable Group I – Communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Source: WHO global estimates 2008 25 million
90% of global premature deaths from NCDs occur in low- and middle-income countries 2. 9 M 13. 6 M Total deaths (2008) 20 million 15 million 5. 3 M 10 million 8. 3 M 0. 5 M 6. 6 M 1 M 2. 3 M 0. 8 M 1. 4 M 4. 4 M 1 M 0. 6 M High-income countries 5. 6 M 1. 4 M 1. 2 M Upper middle-income Low-income countries Group III - Injuries Low-income countries Group II – Other deaths from NCDs Group II – Premature deaths from NCDs (below 60 years), which are preventable Group I – Communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Source: WHO global estimates 2008 25 million
 Four types of NCDs account for most deaths in all regions 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% WHO Region for Africa WHO Region for the Americas WHO Region for the Eastern Mediterranean WHO Region for Europe Other NCDs Diabetes Respiratory diseases Cancers Cardiovascular diseases 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) WHO Region for South-East Asia WHO Region for the Western Pacific
Four types of NCDs account for most deaths in all regions 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% WHO Region for Africa WHO Region for the Americas WHO Region for the Eastern Mediterranean WHO Region for Europe Other NCDs Diabetes Respiratory diseases Cancers Cardiovascular diseases 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) WHO Region for South-East Asia WHO Region for the Western Pacific
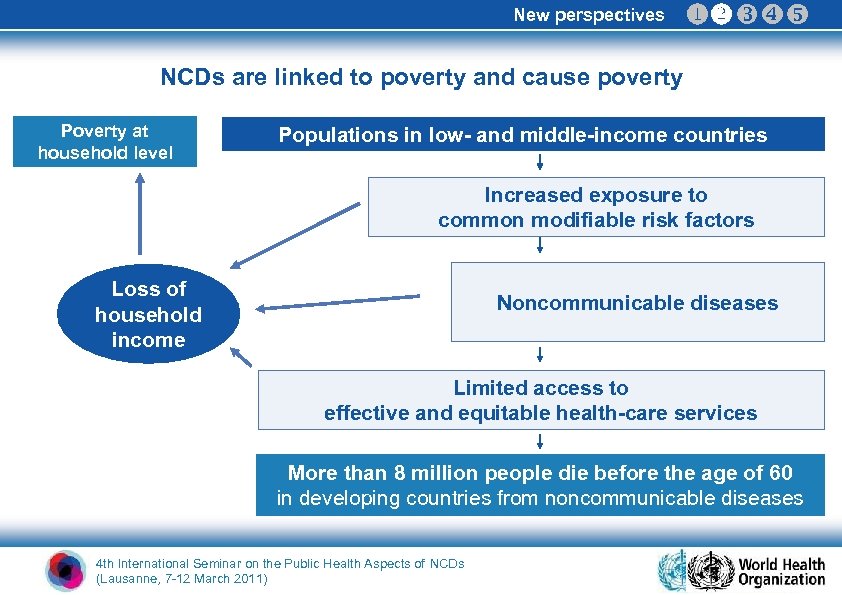 New perspectives NCDs are linked to poverty and cause poverty Poverty at household level Populations in low- and middle-income countries Increased exposure to common modifiable risk factors Loss of household income Noncommunicable diseases Limited access to effective and equitable health-care services More than 8 million people die before the age of 60 in developing countries from noncommunicable diseases 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
New perspectives NCDs are linked to poverty and cause poverty Poverty at household level Populations in low- and middle-income countries Increased exposure to common modifiable risk factors Loss of household income Noncommunicable diseases Limited access to effective and equitable health-care services More than 8 million people die before the age of 60 in developing countries from noncommunicable diseases 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
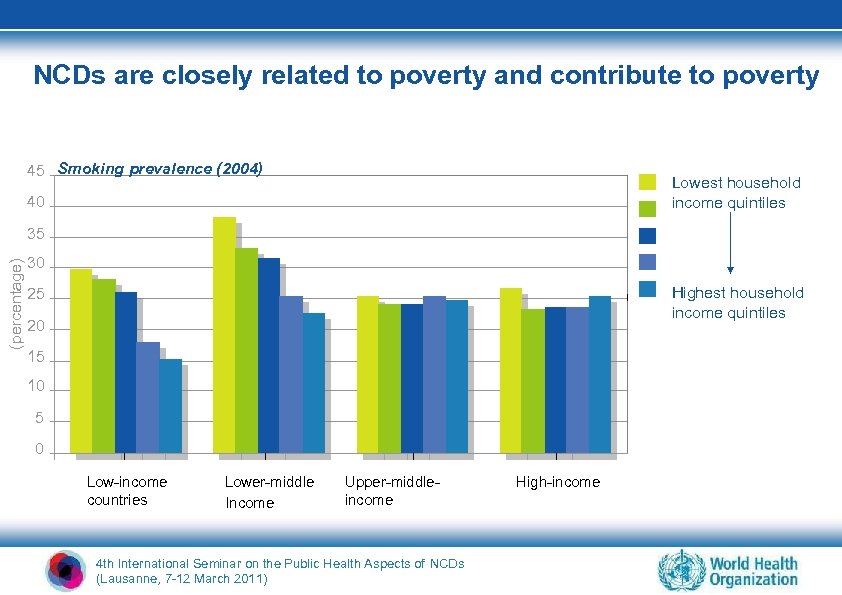 NCDs are closely related to poverty and contribute to poverty 45 Smoking prevalence (2004) Lowest household income quintiles 40 (percentage) 35 30 Highest household income quintiles 25 20 15 10 5 0 Low-income countries Lower-middle Income Upper-middleincome 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) High-income
NCDs are closely related to poverty and contribute to poverty 45 Smoking prevalence (2004) Lowest household income quintiles 40 (percentage) 35 30 Highest household income quintiles 25 20 15 10 5 0 Low-income countries Lower-middle Income Upper-middleincome 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) High-income
 Translating key messages into a presentation A sound global vision and concrete road map exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Translating key messages into a presentation A sound global vision and concrete road map exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 World Health Assembly in 2000: There is a clear vision on how to address NCDs *Surveillance* Mapping the epidemic of NCDs *Prevention* Reducing the level of exposure to risk factors 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) *Management* Strengthen health care for people with NCDs
World Health Assembly in 2000: There is a clear vision on how to address NCDs *Surveillance* Mapping the epidemic of NCDs *Prevention* Reducing the level of exposure to risk factors 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) *Management* Strengthen health care for people with NCDs
 World Health Assembly in 2008: There is a clear roadmap for all countries and partners Six objectives: 1. Raising the priority accorded to NCDs in development work at global and national levels, and integrating prevention and control of NCDs into policies across all government departments 2. Establishing and strengthening national policies and programmes 3. Reducing and preventing risk factors 4. Prioritizing research on prevention and health care 5. Strengthening partnerships 6. Monitoring NCD trends and assessing progress made at country level 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
World Health Assembly in 2008: There is a clear roadmap for all countries and partners Six objectives: 1. Raising the priority accorded to NCDs in development work at global and national levels, and integrating prevention and control of NCDs into policies across all government departments 2. Establishing and strengthening national policies and programmes 3. Reducing and preventing risk factors 4. Prioritizing research on prevention and health care 5. Strengthening partnerships 6. Monitoring NCD trends and assessing progress made at country level 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 In May 2000, WHO Member States began mobilizing a global response to address NCDs, with a particular focus on developing countries 2000 Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases Global Strategy on Infant and Young Child Feeding 2002 WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health 2003 WHA resolution on cancer prevention and control 2004 Action Plan on the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs 2005 Set of recommendations on the marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children 2008 2010 2011 Global Strategy to Reduce the Harmful Use of Alcohol High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
In May 2000, WHO Member States began mobilizing a global response to address NCDs, with a particular focus on developing countries 2000 Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases Global Strategy on Infant and Young Child Feeding 2002 WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health 2003 WHA resolution on cancer prevention and control 2004 Action Plan on the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs 2005 Set of recommendations on the marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children 2008 2010 2011 Global Strategy to Reduce the Harmful Use of Alcohol High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Translating key messages into a presentation At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included yet in the MDGs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Translating key messages into a presentation At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included yet in the MDGs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) The eight MDGs break down into 21 quantifiable targets that are measured by 60 indicators. www. undp. org/mdg 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) The eight MDGs break down into 21 quantifiable targets that are measured by 60 indicators. www. undp. org/mdg 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
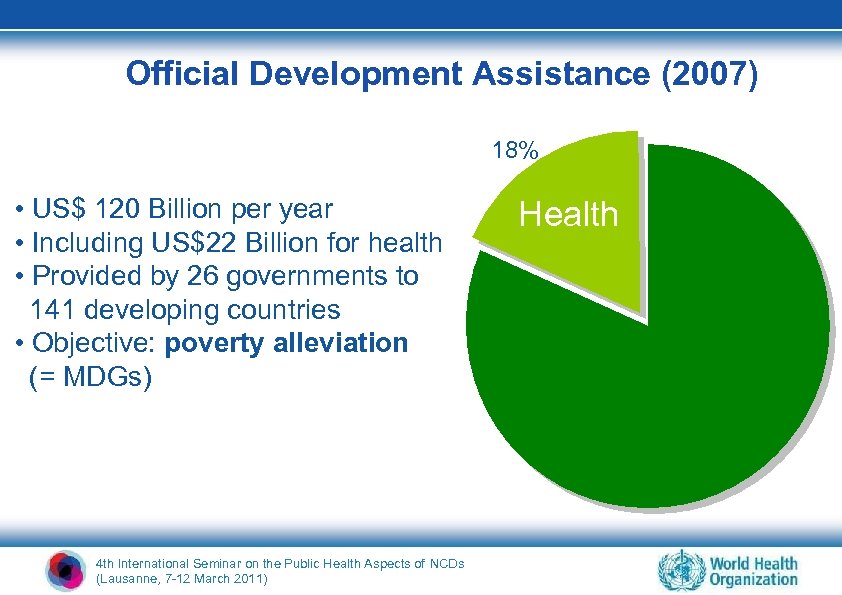 Official Development Assistance (2007) 18% • US$ 120 Billion per year • Including US$22 Billion for health • Provided by 26 governments to 141 developing countries • Objective: poverty alleviation (= MDGs) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Health
Official Development Assistance (2007) 18% • US$ 120 Billion per year • Including US$22 Billion for health • Provided by 26 governments to 141 developing countries • Objective: poverty alleviation (= MDGs) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) Health
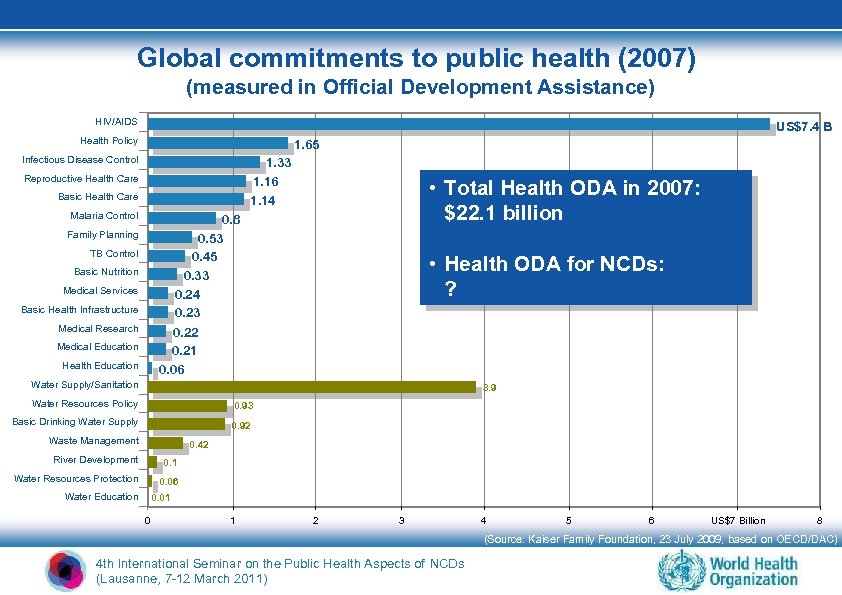 Global commitments to public health (2007) (measured in Official Development Assistance) HIV/AIDS US$7. 4 B Health Policy 1. 65 Infectious Disease Control 1. 33 1. 16 1. 14 Reproductive Health Care Basic Health Care Malaria Control • Total Health ODA in 2007: $22. 1 billion 0. 8 0. 53 0. 45 0. 33 0. 24 0. 23 Family Planning TB Control Basic Nutrition Medical Services Basic Health Infrastructure Medical Research • Health ODA for NCDs: ? 0. 22 0. 21 0. 06 Medical Education Health Education Water Supply/Sanitation 3. 9 Water Resources Policy 0. 93 Basic Drinking Water Supply 0. 92 Waste Management 0. 42 River Development 0. 1 Water Resources Protection 0. 06 Water Education 0. 01 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 US$7 Billion 8 (Source: Kaiser Family Foundation, 23 July 2009, based on OECD/DAC) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Global commitments to public health (2007) (measured in Official Development Assistance) HIV/AIDS US$7. 4 B Health Policy 1. 65 Infectious Disease Control 1. 33 1. 16 1. 14 Reproductive Health Care Basic Health Care Malaria Control • Total Health ODA in 2007: $22. 1 billion 0. 8 0. 53 0. 45 0. 33 0. 24 0. 23 Family Planning TB Control Basic Nutrition Medical Services Basic Health Infrastructure Medical Research • Health ODA for NCDs: ? 0. 22 0. 21 0. 06 Medical Education Health Education Water Supply/Sanitation 3. 9 Water Resources Policy 0. 93 Basic Drinking Water Supply 0. 92 Waste Management 0. 42 River Development 0. 1 Water Resources Protection 0. 06 Water Education 0. 01 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 US$7 Billion 8 (Source: Kaiser Family Foundation, 23 July 2009, based on OECD/DAC) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
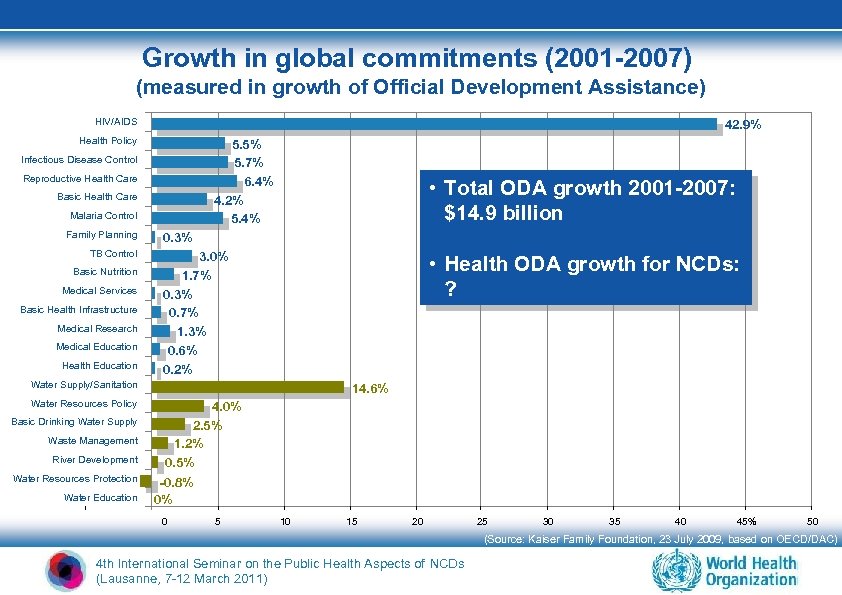 Growth in global commitments (2001 -2007) (measured in growth of Official Development Assistance) HIV/AIDS 42. 9% Health Policy 5. 5% 5. 7% 6. 4% 4. 2% 5. 4% Infectious Disease Control Reproductive Health Care Basic Health Care Malaria Control Family Planning TB Control Basic Nutrition Medical Services Basic Health Infrastructure Medical Research Medical Education Health Education • Total ODA growth 2001 -2007: $14. 9 billion 0. 3% 3. 0% 1. 7% 0. 3% 0. 7% 1. 3% 0. 6% 0. 2% • Health ODA growth for NCDs: ? Water Supply/Sanitation Water Resources Policy Basic Drinking Water Supply Waste Management River Development Water Resources Protection Water Education 14. 6% 4. 0% 2. 5% 1. 2% 0. 5% -0. 8% 0% 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45% 50 (Source: Kaiser Family Foundation, 23 July 2009, based on OECD/DAC) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Growth in global commitments (2001 -2007) (measured in growth of Official Development Assistance) HIV/AIDS 42. 9% Health Policy 5. 5% 5. 7% 6. 4% 4. 2% 5. 4% Infectious Disease Control Reproductive Health Care Basic Health Care Malaria Control Family Planning TB Control Basic Nutrition Medical Services Basic Health Infrastructure Medical Research Medical Education Health Education • Total ODA growth 2001 -2007: $14. 9 billion 0. 3% 3. 0% 1. 7% 0. 3% 0. 7% 1. 3% 0. 6% 0. 2% • Health ODA growth for NCDs: ? Water Supply/Sanitation Water Resources Policy Basic Drinking Water Supply Waste Management River Development Water Resources Protection Water Education 14. 6% 4. 0% 2. 5% 1. 2% 0. 5% -0. 8% 0% 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45% 50 (Source: Kaiser Family Foundation, 23 July 2009, based on OECD/DAC) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 The Paris Declaration invites donors to base their support on demand from developing countries Pending 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
The Paris Declaration invites donors to base their support on demand from developing countries Pending 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Translating key messages into a presentation You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly in New York (19 -20 September 2011) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Translating key messages into a presentation You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly in New York (19 -20 September 2011) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Raising the priority of NCDs in development work 13 May 2010 United Nations General Assembly resolution A/RES/64/265 Cameroon on behalf of Member States who are members of the Group of African States Member States which sponsored the draft resolution 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Raising the priority of NCDs in development work 13 May 2010 United Nations General Assembly resolution A/RES/64/265 Cameroon on behalf of Member States who are members of the Group of African States Member States which sponsored the draft resolution 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 2009 ECOSOC High-level Segment: Russian Federation announced the First Global Ministerial Conference on NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
2009 ECOSOC High-level Segment: Russian Federation announced the First Global Ministerial Conference on NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 ECOSOC 2009 Ministerial Declaration: NCDs are a leading threat to development 18. We also recognize that the emergence of non-communicable diseases is imposing a heavy burden on society, one with serious social and economic consequences, and that there is a need to respond to cardiovascular diseases, cancers, diabetes and chronic respiratory diseases, which represent a leading threat to human health and development. • • In this regard, we: Call for urgent action to implement the World Health Organization Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases and its related Action Plan; Recognize that diabetes is a chronic, debilitating and costly disease associated with severe complications; Stress the need to scale up care for mental health conditions, including prevention, treatment and rehabilitation; Reaffirm the importance of the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control within the sphere of global public health and call upon States parties to the Convention to fully implement it. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
ECOSOC 2009 Ministerial Declaration: NCDs are a leading threat to development 18. We also recognize that the emergence of non-communicable diseases is imposing a heavy burden on society, one with serious social and economic consequences, and that there is a need to respond to cardiovascular diseases, cancers, diabetes and chronic respiratory diseases, which represent a leading threat to human health and development. • • In this regard, we: Call for urgent action to implement the World Health Organization Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases and its related Action Plan; Recognize that diabetes is a chronic, debilitating and costly disease associated with severe complications; Stress the need to scale up care for mental health conditions, including prevention, treatment and rehabilitation; Reaffirm the importance of the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control within the sphere of global public health and call upon States parties to the Convention to fully implement it. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 United Nations General Assembly Resolution 64/265 adopted on 13 May 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 64/265 adopted on 13 May 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 United Nations General Assembly in September 2010: Address the developmental challenges posed by NCDs We, Heads of State and Government, commit ourselves to. . . 63. k. Strengthening the effectiveness of health systems and proven interventions to address. . . the increased incidence of noncommunicable diseases. . . 76. i Undertaking concerted action and a coordinated response at the national, regional and global levels in order to adequately address the developmental and other challenges posed by non-communicable diseases, namely cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes, and working towards a successful high-level meeting of the General Assembly in 2011. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
United Nations General Assembly in September 2010: Address the developmental challenges posed by NCDs We, Heads of State and Government, commit ourselves to. . . 63. k. Strengthening the effectiveness of health systems and proven interventions to address. . . the increased incidence of noncommunicable diseases. . . 76. i Undertaking concerted action and a coordinated response at the national, regional and global levels in order to adequately address the developmental and other challenges posed by non-communicable diseases, namely cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes, and working towards a successful high-level meeting of the General Assembly in 2011. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 United Nations General Assembly Resolution 65/238 adopted on 13 December 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 65/238 adopted on 13 December 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 WHO's role in the preparatory process leading towards the UN High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO's role in the preparatory process leading towards the UN High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Mandate from the United Nations General Assembly Resolutions A/RES/64/265 and A/RES/65/238 Dates Monday 19 and Tuesday 20 September 2011 Venue United Nations in New York Participants • Member States' delegations led by Heads of State and Government • Heads of UN Agencies, World Bank, IGOs • Selected representatives from NGOs and the private sector Aim To address the prevention and control of NCDs worldwide, with a particular focus on developmental and other challenges and social and economic impacts, particularly for developing countries Structure • Formal plenary meetings chaired by the President of the General Assembly • Three round tables Outcome Document ("We, Heads of State and Government, commit ourselves to. . . ") 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Mandate from the United Nations General Assembly Resolutions A/RES/64/265 and A/RES/65/238 Dates Monday 19 and Tuesday 20 September 2011 Venue United Nations in New York Participants • Member States' delegations led by Heads of State and Government • Heads of UN Agencies, World Bank, IGOs • Selected representatives from NGOs and the private sector Aim To address the prevention and control of NCDs worldwide, with a particular focus on developmental and other challenges and social and economic impacts, particularly for developing countries Structure • Formal plenary meetings chaired by the President of the General Assembly • Three round tables Outcome Document ("We, Heads of State and Government, commit ourselves to. . . ") 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Who is in charge? Mr Joseph Deiss President of the UN General Assembly Co-Facilitators Ambassador Raymond Wolfe Permanent Representative of Jamaica (New York) Ambassador Sylvie Lucas Permanent Representative of Luxembourg (New York) Member States 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Who is in charge? Mr Joseph Deiss President of the UN General Assembly Co-Facilitators Ambassador Raymond Wolfe Permanent Representative of Jamaica (New York) Ambassador Sylvie Lucas Permanent Representative of Luxembourg (New York) Member States 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 WHO's role in the preparatory process leading towards the UN High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) Regional consultations The UN General Assembly invites WHO to continue to hold regional multisectoral consultations Report of the UNSG The UN General Assembly decided that the report of the UNSG, in collaboration with WHO (and other UN Agencies), on the global status of NCDs, with a particular focus on the developmental challenges faced by developing countries, shall be submitted no later than May 2011 to the General Assembly. 19 September 2011 The formal plenary on 19 September 2011 shall feature an opening statement by the WHO Director-General 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO's role in the preparatory process leading towards the UN High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) Regional consultations The UN General Assembly invites WHO to continue to hold regional multisectoral consultations Report of the UNSG The UN General Assembly decided that the report of the UNSG, in collaboration with WHO (and other UN Agencies), on the global status of NCDs, with a particular focus on the developmental challenges faced by developing countries, shall be submitted no later than May 2011 to the General Assembly. 19 September 2011 The formal plenary on 19 September 2011 shall feature an opening statement by the WHO Director-General 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
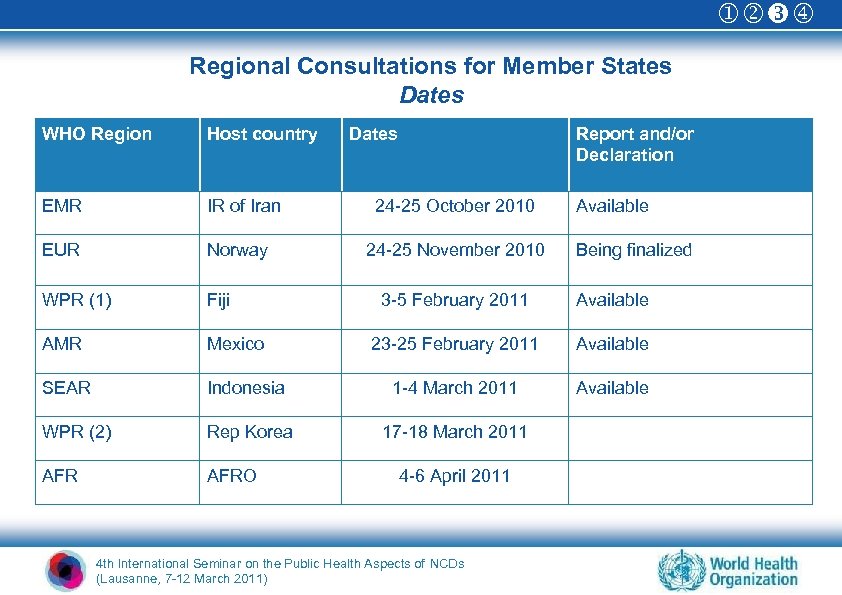 Regional Consultations for Member States Dates WHO Region Host country EMR IR of Iran EUR Norway WPR (1) Fiji AMR Mexico SEAR Dates Report and/or Declaration 24 -25 October 2010 24 -25 November 2010 Available Being finalized 3 -5 February 2011 Available 23 -25 February 2011 Available Indonesia 1 -4 March 2011 Available WPR (2) Rep Korea 17 -18 March 2011 AFRO 4 -6 April 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Regional Consultations for Member States Dates WHO Region Host country EMR IR of Iran EUR Norway WPR (1) Fiji AMR Mexico SEAR Dates Report and/or Declaration 24 -25 October 2010 24 -25 November 2010 Available Being finalized 3 -5 February 2011 Available 23 -25 February 2011 Available Indonesia 1 -4 March 2011 Available WPR (2) Rep Korea 17 -18 March 2011 AFRO 4 -6 April 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Regional Consultation for Member States Eastern Mediterranean Region (Tehran, 25 -26 October 2010) • Include the prevention and control of NCDs among the top priorities in national health strategies and plans, and in global development initiatives and in related investment decisions. • Focus on galvanizing action to accelerate the implementation of the Action Plan of the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs. • Global goal, targets and indicators should be established and monitored. • Heads of State and Government should establish mechanisms to ensure the effective involvement of (public and private) sectors outside health, and uphold their accountability in relation to the impact of their policies on health. • Countries should develop standards, rules and regulations, for marketing and advertising of tobacco, food and non-alcoholic beverages, and other unhealthy goods, according to their needs and local contexts. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Regional Consultation for Member States Eastern Mediterranean Region (Tehran, 25 -26 October 2010) • Include the prevention and control of NCDs among the top priorities in national health strategies and plans, and in global development initiatives and in related investment decisions. • Focus on galvanizing action to accelerate the implementation of the Action Plan of the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs. • Global goal, targets and indicators should be established and monitored. • Heads of State and Government should establish mechanisms to ensure the effective involvement of (public and private) sectors outside health, and uphold their accountability in relation to the impact of their policies on health. • Countries should develop standards, rules and regulations, for marketing and advertising of tobacco, food and non-alcoholic beverages, and other unhealthy goods, according to their needs and local contexts. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Regional Consultation for Member States European Region (Oslo, 25 -26 November 2010) • Generate global commitment and momentum to implement the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs and its Action Plan • Scale up technical support for low- and middle-income countries (including as part of priorities for Official Development Assistance) • Establish global targets and indicators in order to halt and begin to reverse premature deaths from NCDs • Acknowledge that NCDs are a threat to socio-economic development that the developed world nor the developing world can afford. • Also acknowledge that NCDs are a development issue and intimately linked to poverty and the MDGs. • Promote approaches that involve all government departments • Measures must also address the social determinants 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Regional Consultation for Member States European Region (Oslo, 25 -26 November 2010) • Generate global commitment and momentum to implement the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs and its Action Plan • Scale up technical support for low- and middle-income countries (including as part of priorities for Official Development Assistance) • Establish global targets and indicators in order to halt and begin to reverse premature deaths from NCDs • Acknowledge that NCDs are a threat to socio-economic development that the developed world nor the developing world can afford. • Also acknowledge that NCDs are a development issue and intimately linked to poverty and the MDGs. • Promote approaches that involve all government departments • Measures must also address the social determinants 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Subregional Consultation for Pacific Island Member States (Nadi, Fiji, 3 -5 February 2011) • Demonstrate political leadership at the highest level to take responsibility for and address the NCD crisis at national and regional levels • Ensure the right multi-sectoral policy environment to mainstream the response • Support priority cost-effective interventions, monitor their implementation and expand the evidence base through research and surveillance • Resource and sustain the response adequately • Ensure full accountability of all sectors for their respective contributions • Significantly strengthen advocacy and community engagement to maintain a focus on the NCD crisis • Strengthen health systems to effectively respond to the crisis. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Subregional Consultation for Pacific Island Member States (Nadi, Fiji, 3 -5 February 2011) • Demonstrate political leadership at the highest level to take responsibility for and address the NCD crisis at national and regional levels • Ensure the right multi-sectoral policy environment to mainstream the response • Support priority cost-effective interventions, monitor their implementation and expand the evidence base through research and surveillance • Resource and sustain the response adequately • Ensure full accountability of all sectors for their respective contributions • Significantly strengthen advocacy and community engagement to maintain a focus on the NCD crisis • Strengthen health systems to effectively respond to the crisis. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Ministerial Declaration adopted at the Regional Consultation for the Americas (Mexico, 24 -25 February 2011) The Ministers of Health and their representatives: • Promote recognition of the rising prevalence of NCDs on the national, as well as the international development agenda • Reaffirm their commitment to strengthen policies and programmes for the prevention and control of NCDs • Call on WHO to propose to Member States targets for the Action Plan for the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs against which countries' progress will be measured, with a view to future inclusion in the MDGs • Promote access to comprehensive and cost-effective prevention, treatment and care for integrated management of NCDs • Provide leadership in promoting active participation of all sector of government and civil soetiy in implementing measures to prevent and control NCDs • Promote collaborative efforts and partnerships among key multisectoral stakeholders in public and private sector 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Ministerial Declaration adopted at the Regional Consultation for the Americas (Mexico, 24 -25 February 2011) The Ministers of Health and their representatives: • Promote recognition of the rising prevalence of NCDs on the national, as well as the international development agenda • Reaffirm their commitment to strengthen policies and programmes for the prevention and control of NCDs • Call on WHO to propose to Member States targets for the Action Plan for the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs against which countries' progress will be measured, with a view to future inclusion in the MDGs • Promote access to comprehensive and cost-effective prevention, treatment and care for integrated management of NCDs • Provide leadership in promoting active participation of all sector of government and civil soetiy in implementing measures to prevent and control NCDs • Promote collaborative efforts and partnerships among key multisectoral stakeholders in public and private sector 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Ministerial Meeting on Health and Developmental Challenges of NCDs (Jakarta, 1 -4 March 2011) We call upon global leaders, donor partners and UN Agencies to: • Include NCD prevention and control in internationally agreed developmental goals, including the MDGs. • Assist countries in integrating NCD control in their primary health-care based health systems strengthening initiatives in a harmonized manner. • In accordance with national priorities enhance capacity building, technical and financial support to Member States to supplement national efforts for sustainable NCD prevention and control programmes. • Support countries for research for control and prevention of NCDs. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Ministerial Meeting on Health and Developmental Challenges of NCDs (Jakarta, 1 -4 March 2011) We call upon global leaders, donor partners and UN Agencies to: • Include NCD prevention and control in internationally agreed developmental goals, including the MDGs. • Assist countries in integrating NCD control in their primary health-care based health systems strengthening initiatives in a harmonized manner. • In accordance with national priorities enhance capacity building, technical and financial support to Member States to supplement national efforts for sustainable NCD prevention and control programmes. • Support countries for research for control and prevention of NCDs. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Informal Dialogue NGOs (Geneva, 1 November 2010) • Governments should be accountable and measured on NCD plans through (global and national) goals, targets and indicators • The WHO Framework Convention for Tobacco Control should be fully implemented by all countries • Member States should give a commitment to prevent the preventable • Globally-agreed approaches to NCD treatment and care should be implemented • Technical support, through resources and expertise, should be made available to enable low- and middle-income countries to deliver NCD interventions • NCDs need to be included in the successor goals to the MDGs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Informal Dialogue NGOs (Geneva, 1 November 2010) • Governments should be accountable and measured on NCD plans through (global and national) goals, targets and indicators • The WHO Framework Convention for Tobacco Control should be fully implemented by all countries • Member States should give a commitment to prevent the preventable • Globally-agreed approaches to NCD treatment and care should be implemented • Technical support, through resources and expertise, should be made available to enable low- and middle-income countries to deliver NCD interventions • NCDs need to be included in the successor goals to the MDGs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Informal Dialogue Private Sector (Geneva, 2 November 2010) • Elevate NCDs to agendas of Heads of State and Government • Mainstream the need to address NCDs into the public debate • Disseminate information which allows individuals and populations to change their behaviours • Demonstrate progress • Bring a sense of urgency and accountability to the public debate • Highlight that NCDs are a critical development issue • Provide accountable measure and commitments • Promote collaboration across sectors • Reinforce complementarity to existing priorities 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Informal Dialogue Private Sector (Geneva, 2 November 2010) • Elevate NCDs to agendas of Heads of State and Government • Mainstream the need to address NCDs into the public debate • Disseminate information which allows individuals and populations to change their behaviours • Demonstrate progress • Bring a sense of urgency and accountability to the public debate • Highlight that NCDs are a critical development issue • Provide accountable measure and commitments • Promote collaboration across sectors • Reinforce complementarity to existing priorities 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 WHO Global Forum 2011: • NGOs • Private sector • Academia • Member States A short report • Member States • UN Agencies and IGOs • Selected speakers from NGOs and Academia Moscow Declaration 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO Global Forum 2011: • NGOs • Private sector • Academia • Member States A short report • Member States • UN Agencies and IGOs • Selected speakers from NGOs and Academia Moscow Declaration 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Goals and Objectives of the Conference • Goals: – To raise political awareness about the importance and potential of prevention and control of NCDs and place them higher on the global and national political agendas – To strengthen international cooperation for the prevention and control of NCDs with a particular focus on promoting the upcoming high level debate at the High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) and beyond • Objectives: – To highlight evidence relating to the impact of NCDs on health and socioeconomic outcomes – To profile available effective instruments, strategies and policies both within as well as outside of the health sector to address the epidemic of NCDs – To accelerate integration of the prevention and control of NCDs into the global development cooperation agenda – To articulate a road map for action in the Moscow Declaration on NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Goals and Objectives of the Conference • Goals: – To raise political awareness about the importance and potential of prevention and control of NCDs and place them higher on the global and national political agendas – To strengthen international cooperation for the prevention and control of NCDs with a particular focus on promoting the upcoming high level debate at the High-level Meeting on NCDs (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) and beyond • Objectives: – To highlight evidence relating to the impact of NCDs on health and socioeconomic outcomes – To profile available effective instruments, strategies and policies both within as well as outside of the health sector to address the epidemic of NCDs – To accelerate integration of the prevention and control of NCDs into the global development cooperation agenda – To articulate a road map for action in the Moscow Declaration on NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 WHO Global Forum (Moscow, 27 April 2011) Preliminary Objectives • Provide an opportunity for a wide range of stakeholders to discuss global NCD issues to inform and support the Moscow Ministerial Conference, as well as the discussions on the NCD agenda item of the Sixty-fourth World Health Assembly. • Understand expectations, roles and contributions of the different stakeholders in support of the High-level Meeting and its expected outcomes and activities post the HLM. • Update knowledge and share experience on the progress in addressing NCDs, including through implementing the Action Plan for the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs • Promote ways of accelerating the implementation of actions for "international partners" under each objective of the Action Plan. • Mobilize a broader base of stakeholders in support of NCD prevention and control in particular in developing countries. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO Global Forum (Moscow, 27 April 2011) Preliminary Objectives • Provide an opportunity for a wide range of stakeholders to discuss global NCD issues to inform and support the Moscow Ministerial Conference, as well as the discussions on the NCD agenda item of the Sixty-fourth World Health Assembly. • Understand expectations, roles and contributions of the different stakeholders in support of the High-level Meeting and its expected outcomes and activities post the HLM. • Update knowledge and share experience on the progress in addressing NCDs, including through implementing the Action Plan for the Global Strategy for the Prevention and Control of NCDs • Promote ways of accelerating the implementation of actions for "international partners" under each objective of the Action Plan. • Mobilize a broader base of stakeholders in support of NCD prevention and control in particular in developing countries. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
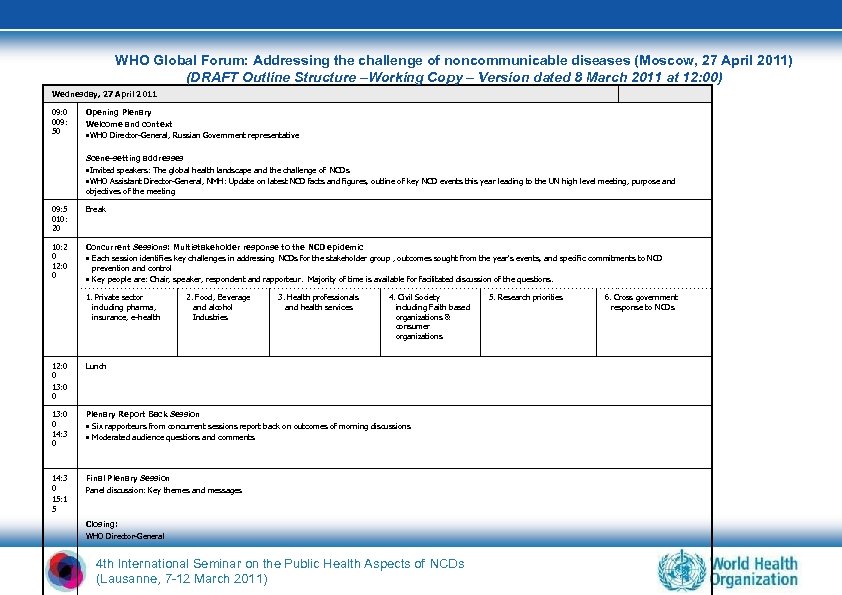 WHO Global Forum: Addressing the challenge of noncommunicable diseases (Moscow, 27 April 2011) (DRAFT Outline Structure –Working Copy – Version dated 8 March 2011 at 12: 00) Wednesday, 27 April 2011 09: 0 009: 50 Opening Plenary Welcome and context • WHO Director-General, Russian Government representative Scene-setting addresses • Invited speakers: The global health landscape and the challenge of NCDs • WHO Assistant Director-General, NMH: Update on latest NCD facts and figures, outline of key NCD events this year leading to the UN high level meeting, purpose and objectives of the meeting 09: 5 010: 20 Break 10: 2 0 12: 0 0 Concurrent Sessions: Multistakeholder response to the NCD epidemic • Each session identifies key challenges in addressing NCDs for the stakeholder group , outcomes sought from the year's events, and specific commitments to NCD prevention and control • Key people are: Chair, speaker, respondent and rapporteur. Majority of time is available for facilitated discussion of the questions. 1. Private sector including pharma, insurance, e-health 2. Food, Beverage and alcohol Industries 3. Health professionals and health services 4. Civil Society including Faith based organizations & consumer organizations 12: 0 0 13: 0 0 Lunch 13: 0 0 14: 3 0 Plenary Report Back Session • Six rapporteurs from concurrent sessions report back on outcomes of morning discussions • Moderated audience questions and comments 14: 3 0 15: 1 5 Final Plenary Session Panel discussion: Key themes and messages Closing: WHO Director-General 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) 5. Research priorities 6. Cross government response to NCDs
WHO Global Forum: Addressing the challenge of noncommunicable diseases (Moscow, 27 April 2011) (DRAFT Outline Structure –Working Copy – Version dated 8 March 2011 at 12: 00) Wednesday, 27 April 2011 09: 0 009: 50 Opening Plenary Welcome and context • WHO Director-General, Russian Government representative Scene-setting addresses • Invited speakers: The global health landscape and the challenge of NCDs • WHO Assistant Director-General, NMH: Update on latest NCD facts and figures, outline of key NCD events this year leading to the UN high level meeting, purpose and objectives of the meeting 09: 5 010: 20 Break 10: 2 0 12: 0 0 Concurrent Sessions: Multistakeholder response to the NCD epidemic • Each session identifies key challenges in addressing NCDs for the stakeholder group , outcomes sought from the year's events, and specific commitments to NCD prevention and control • Key people are: Chair, speaker, respondent and rapporteur. Majority of time is available for facilitated discussion of the questions. 1. Private sector including pharma, insurance, e-health 2. Food, Beverage and alcohol Industries 3. Health professionals and health services 4. Civil Society including Faith based organizations & consumer organizations 12: 0 0 13: 0 0 Lunch 13: 0 0 14: 3 0 Plenary Report Back Session • Six rapporteurs from concurrent sessions report back on outcomes of morning discussions • Moderated audience questions and comments 14: 3 0 15: 1 5 Final Plenary Session Panel discussion: Key themes and messages Closing: WHO Director-General 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) 5. Research priorities 6. Cross government response to NCDs
 WHO Global Forum (Moscow, 27 April 2011) Draft structure (for discussion) 09: 00 -10: 30 Opening Plenary 1030 -11: 00 Coffee 11: 00 -13: 00 Concurrent Sessions – Challenges, Outcomes, Commitments/Actions • Private sector involved in producing or delivery of health-related goods and services (e. g. pharmaceuticals, ICT) • Industry organizations (possibly separate for alcohol and food industries) • Civil society, including NCDAlliance, faith-based organizations, health professional bodies • Researchers, collaborating centres and research alliances • Global health initiatives, funds, partnerships, philanthropic organizations 13: 00 -14: 00 Lunch 14: 00 -15: 30 Plenary – Report back from concurrent sessions 15: 30 -16: 00 Coffee break 16: 00 -16: 45 Final Plenary – Selected NCDnet IAC Members 16: 45 -17: 00 Closing remarks Timing is being changed to accommodate the EURO Consultation on the summary report of the Regional Consultation 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO Global Forum (Moscow, 27 April 2011) Draft structure (for discussion) 09: 00 -10: 30 Opening Plenary 1030 -11: 00 Coffee 11: 00 -13: 00 Concurrent Sessions – Challenges, Outcomes, Commitments/Actions • Private sector involved in producing or delivery of health-related goods and services (e. g. pharmaceuticals, ICT) • Industry organizations (possibly separate for alcohol and food industries) • Civil society, including NCDAlliance, faith-based organizations, health professional bodies • Researchers, collaborating centres and research alliances • Global health initiatives, funds, partnerships, philanthropic organizations 13: 00 -14: 00 Lunch 14: 00 -15: 30 Plenary – Report back from concurrent sessions 15: 30 -16: 00 Coffee break 16: 00 -16: 45 Final Plenary – Selected NCDnet IAC Members 16: 45 -17: 00 Closing remarks Timing is being changed to accommodate the EURO Consultation on the summary report of the Regional Consultation 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
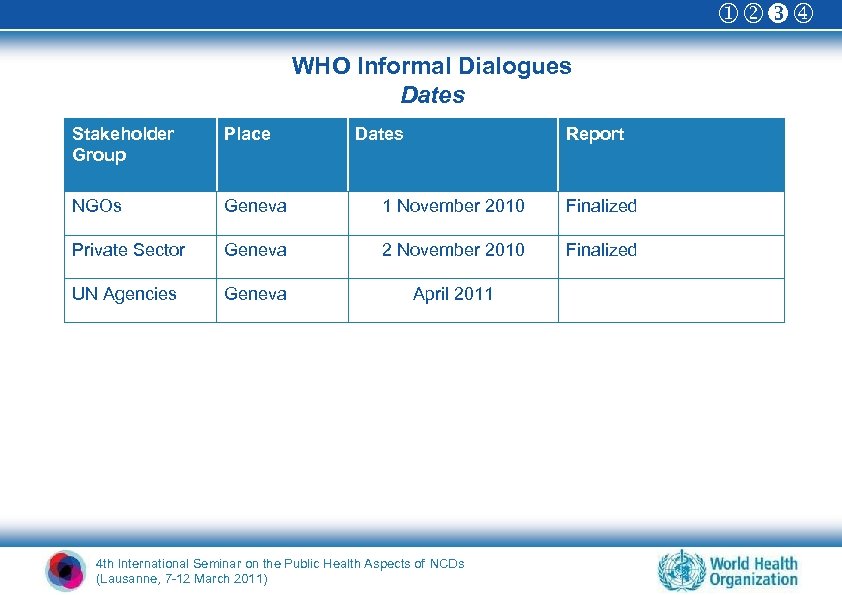 WHO Informal Dialogues Dates Stakeholder Group Place Dates Report NGOs Geneva 1 November 2010 Finalized Private Sector Geneva 2 November 2010 Finalized UN Agencies Geneva April 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO Informal Dialogues Dates Stakeholder Group Place Dates Report NGOs Geneva 1 November 2010 Finalized Private Sector Geneva 2 November 2010 Finalized UN Agencies Geneva April 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
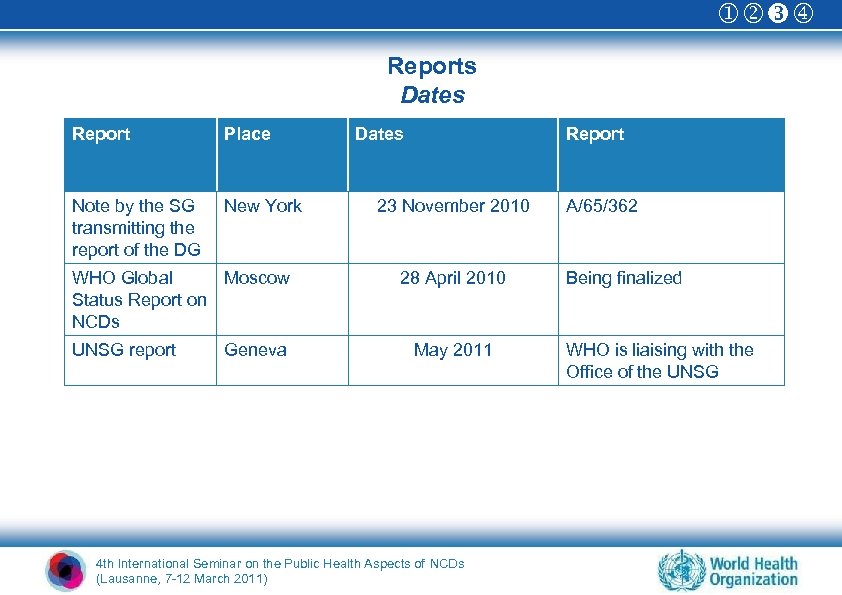 Reports Dates Report Place Note by the SG transmitting the report of the DG New York WHO Global Moscow Status Report on NCDs UNSG report Geneva Dates Report 23 November 2010 28 April 2010 May 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) A/65/362 Being finalized WHO is liaising with the Office of the UNSG
Reports Dates Report Place Note by the SG transmitting the report of the DG New York WHO Global Moscow Status Report on NCDs UNSG report Geneva Dates Report 23 November 2010 28 April 2010 May 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) A/65/362 Being finalized WHO is liaising with the Office of the UNSG
 Informal Interactive Hearings with NGOs and the private sector June 2011 A/RES/65/238: • "Requests the President of the General Assembly to organize, no later than June 2011 and in consultation with representatives of NGOs in consultative status with ECOSOC, civil society organizations, the private sector and academia, an informal interactive hearing with NGOs, civil society organizations, the private sector and academia to provide an input to the preparatory process for the High-level Meeting" • "Decides that the President of the General Assembly shall preside over the abovementioned informal interactive hearing, and requests the President of the General Assembly to prepare a summary of the hearing, to be issued as a document of the Assembly prior to the High-level meeting. " 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Informal Interactive Hearings with NGOs and the private sector June 2011 A/RES/65/238: • "Requests the President of the General Assembly to organize, no later than June 2011 and in consultation with representatives of NGOs in consultative status with ECOSOC, civil society organizations, the private sector and academia, an informal interactive hearing with NGOs, civil society organizations, the private sector and academia to provide an input to the preparatory process for the High-level Meeting" • "Decides that the President of the General Assembly shall preside over the abovementioned informal interactive hearing, and requests the President of the General Assembly to prepare a summary of the hearing, to be issued as a document of the Assembly prior to the High-level meeting. " 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 WHO Executive Board January 2011 Report by the WHO Secretariat Draft resolution proposed by Barbados, Norway, Russian Federation and Trinidad & Tobago For further discussion during the World Health Assembly in May 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO Executive Board January 2011 Report by the WHO Secretariat Draft resolution proposed by Barbados, Norway, Russian Federation and Trinidad & Tobago For further discussion during the World Health Assembly in May 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 "The summit in September in New York is our chance to broker an international commitment that puts NCDs high on the development agenda, where they belong" Mr Ban Ki-Moon, UN Secretary-General, World Economic Forum, 27 January 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"The summit in September in New York is our chance to broker an international commitment that puts NCDs high on the development agenda, where they belong" Mr Ban Ki-Moon, UN Secretary-General, World Economic Forum, 27 January 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Dr Margaret Chan, WHO Director-General "We must make the prevention and control of chronic noncommunicable diseases and the improvement of maternal health top priorities on the development agenda. " 6 July 2009 Economic and Social Council 2009 High-level Segment Dr Margaret Chan WHO Director-General 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Dr Margaret Chan, WHO Director-General "We must make the prevention and control of chronic noncommunicable diseases and the improvement of maternal health top priorities on the development agenda. " 6 July 2009 Economic and Social Council 2009 High-level Segment Dr Margaret Chan WHO Director-General 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Mr Ban Ki-Moon UN Secretary-General World Economic Forum 27 January 2011 "Certainly, we want to work more closely with pharmaceutical companies to make medicines more affordable and accessible. But we will also look to food companies to cut back on the salt, transfats and sugar and be more responsible in marketing products to children and York is our chance to "The summit in September in New providing accurate information on their products. broker an international commitment that puts NCDs high And virtually all industries can help reduce pollution and on the development agenda, where they belong" promote healthy lifestyles. To the business executives here, let me say: the well-being of your workforces, your very productivity and reputation are all at stake in working for global public health. " 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Mr Ban Ki-Moon UN Secretary-General World Economic Forum 27 January 2011 "Certainly, we want to work more closely with pharmaceutical companies to make medicines more affordable and accessible. But we will also look to food companies to cut back on the salt, transfats and sugar and be more responsible in marketing products to children and York is our chance to "The summit in September in New providing accurate information on their products. broker an international commitment that puts NCDs high And virtually all industries can help reduce pollution and on the development agenda, where they belong" promote healthy lifestyles. To the business executives here, let me say: the well-being of your workforces, your very productivity and reputation are all at stake in working for global public health. " 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 "Dear President Obama" (Key message on NCDs to international leaders) Ongoing situation 1. Opportunities 2. One recommendation 3. Operationalization 4. In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly on NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"Dear President Obama" (Key message on NCDs to international leaders) Ongoing situation 1. Opportunities 2. One recommendation 3. Operationalization 4. In all developing countries, and by any metric, NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to prevent 8 million premature deaths from NCDs in developing countries each year. At WHO, we witness how programme managers in developing countries are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. Donors, like USAID, should start considering their requests for technical assistance, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. You and the other leaders of the G-20 have a unique opportunity to include NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions at the upcoming High-level Meeting of the United Nations General Assembly on NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Exercise 2 If your team had a chance to speak to a Minister in your country for 2 minutes, what would your team plan tell her/him about NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Exercise 2 If your team had a chance to speak to a Minister in your country for 2 minutes, what would your team plan tell her/him about NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
 "Dear Minister of Planning" 1. 2. 3. 4. Based on current data, we know that NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty in our country to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to address risk factors and enhance primary care to prevent up to [x] million premature deaths from NCDs per year. We are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. We should seek technical assistance from donors, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. We should ensure that our domestic efforts are placed at the forefront of any international efforts, in particular at the upcoming High-level Meeting on NCDs (September 2011). 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"Dear Minister of Planning" 1. 2. 3. 4. Based on current data, we know that NCDs now account for a large enough share of premature deaths and poverty in our country to merit a concerted and coordinated public policy response. A global vision and affordable solutions exist to address risk factors and enhance primary care to prevent up to [x] million premature deaths from NCDs per year. We are increasingly challenged to formulate effective strategies to address NCDs. We should seek technical assistance from donors, even if these problems are not included (yet) in the MDGs. We should ensure that our domestic efforts are placed at the forefront of any international efforts, in particular at the upcoming High-level Meeting on NCDs (September 2011). 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Exercise 3 If you had a chance to meet with a school class of children today, what would you tell them in 2 minutes about NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Exercise 3 If you had a chance to meet with a school class of children today, what would you tell them in 2 minutes about NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
 Main Challenge • Stand-alone public health messages are very hard to convey to individuals • Reducing the level of exposure to communities to risk factors, while strengthening the capacity of individuals to make healthier choices that foster good health 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Main Challenge • Stand-alone public health messages are very hard to convey to individuals • Reducing the level of exposure to communities to risk factors, while strengthening the capacity of individuals to make healthier choices that foster good health 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 "Dear Children" 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"Dear Children" 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 www. who. int/tobacco 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
www. who. int/tobacco 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 The seven C's of social mobilization 1. Command attention 2. Clarify message Ongoing situation 3. Communicate a benefit 4. Consistency counts Opportunities 5. Cater to the heart and the head 6. Create trust One recommendation 7. Call to action Operationalization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
The seven C's of social mobilization 1. Command attention 2. Clarify message Ongoing situation 3. Communicate a benefit 4. Consistency counts Opportunities 5. Cater to the heart and the head 6. Create trust One recommendation 7. Call to action Operationalization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 The seven C's of social mobilization 1. Command attention 2. Clarify message Ongoing situation 3. Communicate a benefit 4. Consistency counts Opportunities 5. Cater to the heart and the head 6. Create trust One recommendation 7. Call to action Operationalization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
The seven C's of social mobilization 1. Command attention 2. Clarify message Ongoing situation 3. Communicate a benefit 4. Consistency counts Opportunities 5. Cater to the heart and the head 6. Create trust One recommendation 7. Call to action Operationalization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 What is social mobilization? • A broad scale movement to engage people's participation in achieving a specific development goal through self-reliant efforts. • It involves all relevant segments of society: decision and policy makers, opinion leaders, bureaucrats and technocrats, professional groups, religious associations, commerce and industry, communities and individuals. • Decentralized process involving a range of players engaged in interrelated and complementary efforts and takes into account the felt needs of the people • Seeks to empower individuals and groups for action (as defined by UNICEF) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
What is social mobilization? • A broad scale movement to engage people's participation in achieving a specific development goal through self-reliant efforts. • It involves all relevant segments of society: decision and policy makers, opinion leaders, bureaucrats and technocrats, professional groups, religious associations, commerce and industry, communities and individuals. • Decentralized process involving a range of players engaged in interrelated and complementary efforts and takes into account the felt needs of the people • Seeks to empower individuals and groups for action (as defined by UNICEF) 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 What are the components of social mobilization? • The "community" as a whole is mobilized around a particular programme or innovation and comes to incorporate its offerings into felt needs and expectations. – – – Political mobilization Government mobilization Community mobilization Corporate mobilization Beneficiary mobilization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
What are the components of social mobilization? • The "community" as a whole is mobilized around a particular programme or innovation and comes to incorporate its offerings into felt needs and expectations. – – – Political mobilization Government mobilization Community mobilization Corporate mobilization Beneficiary mobilization 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Aims of social mobilization • Increase people's awareness, knowledge and ability to organize for self-reliance • To help people to be motivated and to know about their rights and duties, and to begin to demand satisfaction of their needs • To understand modify people's ideas and beliefs • To mobilize all available resources. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Aims of social mobilization • Increase people's awareness, knowledge and ability to organize for self-reliance • To help people to be motivated and to know about their rights and duties, and to begin to demand satisfaction of their needs • To understand modify people's ideas and beliefs • To mobilize all available resources. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Five integrated communications actions essential for "Communications for behavioural impact" 1. Public Relations/Advocacy/Administrative Mobilization, for putting the particular healthy behaviour on the public and administrative/programme management agenda via the mass media: news coverage, talk shows, soap operas, celebrity spokespersons, discussion programmes; meetings/discussions with various categories of government and community leadership, service providers, administrators; official memoranda; partnership meetings. 2. Community Mobilization, including use of participatory research, community group meetings, partnership meetings, traditional media, music, song and dance, road shows, community drama, leaflets, posters, pamphlets, videos, home visits. 3. Sustained Appropriate Advertising, (in MRIP fashion – Massive, Repetitive, Intense, Persistent), via radio, television, newspapers and other available media, engaging people in reviewing the merits of the recommended behaviour vis-à-vis the “cost” of carrying it out. 4. Personal Selling/Interpersonal Communication/Counselling, at the community level, in homes and particularly at service points, with appropriate informational literature and additional incentives, and allowing for careful listening to people’s concerns and addressing them. 5. Point-of-Service Promotion, emphasising easily accessible and readily available solutions to health problems. The key in planning COMBI programmes is to strive for an integrated approach with a judicious blending and selection of communication actions appropriate to the behavioural outcome desired, and not to believe that one single kind of communication intervention is all-powerful. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Five integrated communications actions essential for "Communications for behavioural impact" 1. Public Relations/Advocacy/Administrative Mobilization, for putting the particular healthy behaviour on the public and administrative/programme management agenda via the mass media: news coverage, talk shows, soap operas, celebrity spokespersons, discussion programmes; meetings/discussions with various categories of government and community leadership, service providers, administrators; official memoranda; partnership meetings. 2. Community Mobilization, including use of participatory research, community group meetings, partnership meetings, traditional media, music, song and dance, road shows, community drama, leaflets, posters, pamphlets, videos, home visits. 3. Sustained Appropriate Advertising, (in MRIP fashion – Massive, Repetitive, Intense, Persistent), via radio, television, newspapers and other available media, engaging people in reviewing the merits of the recommended behaviour vis-à-vis the “cost” of carrying it out. 4. Personal Selling/Interpersonal Communication/Counselling, at the community level, in homes and particularly at service points, with appropriate informational literature and additional incentives, and allowing for careful listening to people’s concerns and addressing them. 5. Point-of-Service Promotion, emphasising easily accessible and readily available solutions to health problems. The key in planning COMBI programmes is to strive for an integrated approach with a judicious blending and selection of communication actions appropriate to the behavioural outcome desired, and not to believe that one single kind of communication intervention is all-powerful. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Example 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Example 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Example 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Example 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Example 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Example 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Exercise 4 If you could meet a donor representative today, what would you tell him/her in 2 minutes about NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Exercise 4 If you could meet a donor representative today, what would you tell him/her in 2 minutes about NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
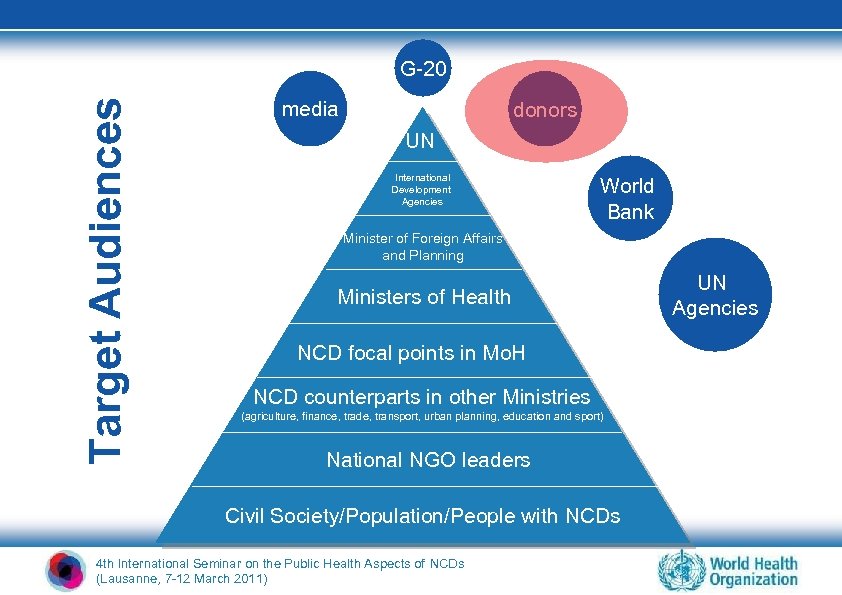 Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
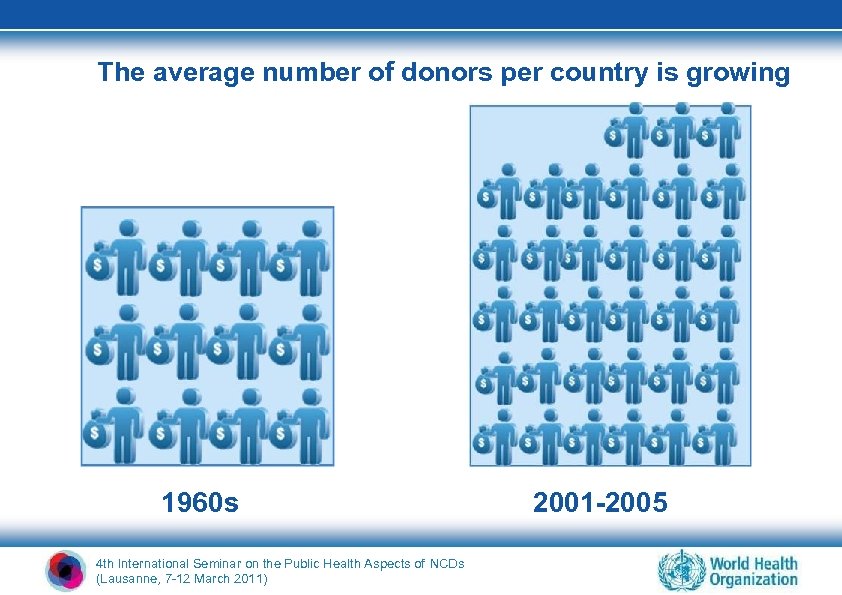 The average number of donors per country is growing 1960 s 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) 2001 -2005
The average number of donors per country is growing 1960 s 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) 2001 -2005
 WHO Country Cooperation Strategy UN Common Country Assessment UN Development Assistance Framework 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
WHO Country Cooperation Strategy UN Common Country Assessment UN Development Assistance Framework 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 "Dear Donor" 1. The rapidly rising burden of NCDs, in particular amoung the poorest and the most vulnerable ones, may increase the level of malnutrition and reversing the achievement of MDG 1 (Eradicate extreme hunger and poverty) and the health-related goals of the MDGs and the progress made in the past two decades. 2. A national vision and affordable solutions exist to address risk factors and enhance primary care to prevent up to [x] million premature deaths from NCDs per year in our country. MDGs provides opportunities for synergy, as do strategies for poverty alleviation. 3. We should include the prevention and control of NCDs as an integral part of work on national development and in related investment decisions. 4. We can start doing so by expanding the technical capacity of the Ministry of Health in the area of NCDs, so that NCDs will be included in national development plans. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
"Dear Donor" 1. The rapidly rising burden of NCDs, in particular amoung the poorest and the most vulnerable ones, may increase the level of malnutrition and reversing the achievement of MDG 1 (Eradicate extreme hunger and poverty) and the health-related goals of the MDGs and the progress made in the past two decades. 2. A national vision and affordable solutions exist to address risk factors and enhance primary care to prevent up to [x] million premature deaths from NCDs per year in our country. MDGs provides opportunities for synergy, as do strategies for poverty alleviation. 3. We should include the prevention and control of NCDs as an integral part of work on national development and in related investment decisions. 4. We can start doing so by expanding the technical capacity of the Ministry of Health in the area of NCDs, so that NCDs will be included in national development plans. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 The resource mobilization cycle 1. Assessing • Analysis based on international and national support • CCA, UNDAF • Thematic donor group (e. g. health, poverty) 2. Positioning • Programmatic vision of national NCDs programme (not a project) • Focus on national ownership • Focus on your Ministry's core comparative advantage • Focus on links to poverty (NCDs are closely related to poverty and contribute to poverty) 3. Mobilizing • Developing a project proposal (follow the "logical framework") • Emphasis on capacity building and sustainability (how will the project continue? ) • Clarity about accountabilities and responsibilities 4. Delivering 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
The resource mobilization cycle 1. Assessing • Analysis based on international and national support • CCA, UNDAF • Thematic donor group (e. g. health, poverty) 2. Positioning • Programmatic vision of national NCDs programme (not a project) • Focus on national ownership • Focus on your Ministry's core comparative advantage • Focus on links to poverty (NCDs are closely related to poverty and contribute to poverty) 3. Mobilizing • Developing a project proposal (follow the "logical framework") • Emphasis on capacity building and sustainability (how will the project continue? ) • Clarity about accountabilities and responsibilities 4. Delivering 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Frequently Asked Questions by Donors about NCDs • How does the magnitude and trends of NCDs have a major socio-economic impact in developing countries? • How are the poorest quintiles within developing countries are disproportionally affected by NCDs, their risk factors and their socio-economic impact? • Which evidence-based interventions to prevent and control NCDs are cost-effective for developing countries? • When implemented in developing countries, will these interventions (a) improve health outcomes from NCDs among the lowest income quintile; (2) contribute to poverty reduction among the lowest income quintile? • Are technical assistance packages available which are aimed at building institutional capacities within developing countries to prevent and control NCDs? • Are estimates on a national "price tag" national funding gaps are available (i. e. difference between costed national plans, and available domestic and international resources)? • What is the self-enlightened interested of tax payers in OECD/DAC donor countries to support their international development agencies in addressing NCDs in developing countries? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Frequently Asked Questions by Donors about NCDs • How does the magnitude and trends of NCDs have a major socio-economic impact in developing countries? • How are the poorest quintiles within developing countries are disproportionally affected by NCDs, their risk factors and their socio-economic impact? • Which evidence-based interventions to prevent and control NCDs are cost-effective for developing countries? • When implemented in developing countries, will these interventions (a) improve health outcomes from NCDs among the lowest income quintile; (2) contribute to poverty reduction among the lowest income quintile? • Are technical assistance packages available which are aimed at building institutional capacities within developing countries to prevent and control NCDs? • Are estimates on a national "price tag" national funding gaps are available (i. e. difference between costed national plans, and available domestic and international resources)? • What is the self-enlightened interested of tax payers in OECD/DAC donor countries to support their international development agencies in addressing NCDs in developing countries? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Exercise 5 If you could speak to a journalist of a leading newspaper today, what would you tell him/her in two minutes on NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Exercise 5 If you could speak to a journalist of a leading newspaper today, what would you tell him/her in two minutes on NCDs? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
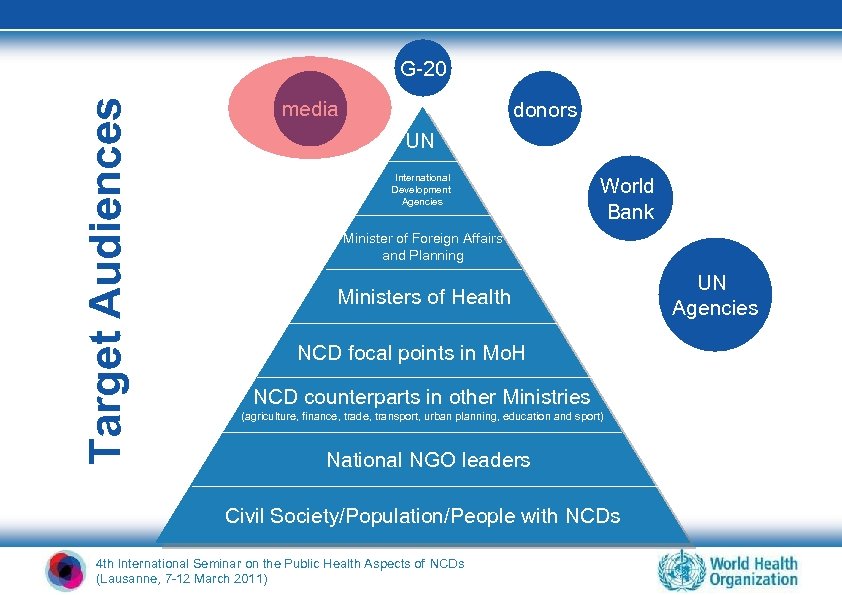 Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs and Planning Ministers of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD counterparts in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/People with NCDs 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
 What are your talking points? • Interviews are not conversations • Prepare 4 key messages (four O's) to be used repeatedly as the cornerstone of your responses • Double-check that the key messages explain – So what? – Why is this so compelling? – Why now? – The reasons or benefits 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
What are your talking points? • Interviews are not conversations • Prepare 4 key messages (four O's) to be used repeatedly as the cornerstone of your responses • Double-check that the key messages explain – So what? – Why is this so compelling? – Why now? – The reasons or benefits 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 10 golden rules 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Never, never lie Never say "No comment" There is never a "off the record" Be short, get to the point and always think of the audience Stay clam, confident and in charge Use simple language, avoid jargon Stay in control It's OK to say "I don't know, but I'll find out" Don't speculate Beware of reporters' tactics 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
10 golden rules 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Never, never lie Never say "No comment" There is never a "off the record" Be short, get to the point and always think of the audience Stay clam, confident and in charge Use simple language, avoid jargon Stay in control It's OK to say "I don't know, but I'll find out" Don't speculate Beware of reporters' tactics 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Reporters' tactics • • Speculative questions Hearsay questions Negative repeat questions Putting words into your mouth Presupposition questions False facts and incorrect information Feeding the mike 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Reporters' tactics • • Speculative questions Hearsay questions Negative repeat questions Putting words into your mouth Presupposition questions False facts and incorrect information Feeding the mike 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 What is WHO doing? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
What is WHO doing? 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 NCDnet Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs (developing countries) Minister of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD focal points in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/Patients 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
NCDnet Target Audiences G-20 media donors UN International Development Agencies World Bank Minister of Foreign Affairs (developing countries) Minister of Health NCD focal points in Mo. H NCD focal points in other Ministries (agriculture, finance, trade, transport, urban planning, education and sport) National NGO leaders Civil Society/Population/Patients 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) UN Agencies
 o b ject ive Promoting partnerships www. who. int/ncdnet Objective: • Facilitate the implementation of the NCD Global Strategy Action Plan Goals: • Raise awareness through collective advocacy • Increase resource availability through innovative financing mechanisms • Catalyze countrylevel implementation 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
o b ject ive Promoting partnerships www. who. int/ncdnet Objective: • Facilitate the implementation of the NCD Global Strategy Action Plan Goals: • Raise awareness through collective advocacy • Increase resource availability through innovative financing mechanisms • Catalyze countrylevel implementation 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 www. who. int/ncdnet WHO International Advisory Council Global Forum Meetings Regional Forum Meetings National Forum Meetings Advocacy and Communications Innovative Resourcing Mechanisms Monitoring and evaluation Working groups 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
www. who. int/ncdnet WHO International Advisory Council Global Forum Meetings Regional Forum Meetings National Forum Meetings Advocacy and Communications Innovative Resourcing Mechanisms Monitoring and evaluation Working groups 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 www. who. int/ncdnet NCDnet was established July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
www. who. int/ncdnet NCDnet was established July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
 www. who. int/ncdnet First NCDnet Planning Meeting: Consensus reached on the scope and purpose of three working groups Working Groups: July 2009 Oct 2009 ● Advocacy and communications ● Innovative financing mechanisms ● Monitoring and evaluation Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
www. who. int/ncdnet First NCDnet Planning Meeting: Consensus reached on the scope and purpose of three working groups Working Groups: July 2009 Oct 2009 ● Advocacy and communications ● Innovative financing mechanisms ● Monitoring and evaluation Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
 www. who. int/ncdnet (1) First NCDnet Global Forum Meeting: Consensus reached on priority activities for each working group (2) First meeting of the NCDnet International Advisory Council July 2009 Oct 2009 • Raise awareness at high-level forums • Develop a joint methodology and conduct needs and constraints analyses • Feasibility study on earmarking tobacco taxes for health financing • Estimate global resourcing needs • Organize donor forums • Establish an ODA baseline for NCDs • Establish an evaluation framework • Develop national monitoring and evaluation tools Feb Sept April Sept 2010 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
www. who. int/ncdnet (1) First NCDnet Global Forum Meeting: Consensus reached on priority activities for each working group (2) First meeting of the NCDnet International Advisory Council July 2009 Oct 2009 • Raise awareness at high-level forums • Develop a joint methodology and conduct needs and constraints analyses • Feasibility study on earmarking tobacco taxes for health financing • Estimate global resourcing needs • Organize donor forums • Establish an ODA baseline for NCDs • Establish an evaluation framework • Develop national monitoring and evaluation tools Feb Sept April Sept 2010 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 www. who. int/ncdnet • Second meeting of the NCDnet International Advisory Council • Side-event on NCDs during the MDG Summit July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
www. who. int/ncdnet • Second meeting of the NCDnet International Advisory Council • Side-event on NCDs during the MDG Summit July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
 www. who. int/ncdnet (1) First Global Ministerial Meeting on NCDs and Healthy Lifestyles (Moscow) (2) Second NCDnet Global Forum Meeting (Moscow) (3) Third meeting of the NCD International Advisory Council July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
www. who. int/ncdnet (1) First Global Ministerial Meeting on NCDs and Healthy Lifestyles (Moscow) (2) Second NCDnet Global Forum Meeting (Moscow) (3) Third meeting of the NCD International Advisory Council July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
 www. who. int/ncdnet NCD Summit 2011 (New York) July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
www. who. int/ncdnet NCD Summit 2011 (New York) July 2009 Oct 2009 Feb 2010 Sept 2010 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) April 2011 Sept 2011
 Criteria for WHO's engagement in partnerships (1) • The partnership demonstrates a clear added value for public health • The partnership has a clear goal that concerns a priority area of work for WHO • Partnerships are guided by the technical norms and standards established by WHO • The partnership supports national development objectives • The partnership ensures appropriate and adequate participation of stakeholders 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Criteria for WHO's engagement in partnerships (1) • The partnership demonstrates a clear added value for public health • The partnership has a clear goal that concerns a priority area of work for WHO • Partnerships are guided by the technical norms and standards established by WHO • The partnership supports national development objectives • The partnership ensures appropriate and adequate participation of stakeholders 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Criteria for WHO's engagement in partnerships (2) • The roles of partners are clear • Transaction costs related to a partnership must be evaluated, along with the potential benefits and risks • Pursuit of public-health goals takes precedence over the special interests of participants. • The structure of the partnership corresponds to the proposed functions • The partnership has an independent external evaluation and/or self-monitoring mechanism More info at: http: //apps. who. int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA 63/A 63_44 -en. pdf 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Criteria for WHO's engagement in partnerships (2) • The roles of partners are clear • Transaction costs related to a partnership must be evaluated, along with the potential benefits and risks • Pursuit of public-health goals takes precedence over the special interests of participants. • The structure of the partnership corresponds to the proposed functions • The partnership has an independent external evaluation and/or self-monitoring mechanism More info at: http: //apps. who. int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA 63/A 63_44 -en. pdf 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 To take home 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
To take home 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 NCD Heads of State Summit 2011 (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) www. who. int/nmh 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
NCD Heads of State Summit 2011 (New York, 19 -20 September 2011) www. who. int/nmh 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Including NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions needs to be the number one priority of the NCD Summit 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Including NCDs in global development initiatives and related investment decisions needs to be the number one priority of the NCD Summit 2011 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Further references for self-study • • • WHO – www. who. int/ncd UNDP -The blue book: a hands-on approach to advocating for the MDGs http: //www. undp. or. id/mdg/documents/The%20 Blue%20 Book%20 A%20 Hands%20 on%20 Appro ach%20 to%20 Advocating%20 for%20 the%20 MDGs. pdf World Bank – Public policy and the challenge of NCDs http: //siteresources. worldbank. org/INTPH/Resources/Public. Policyand. NCDs. World. Bank 2007 Full. R eport. pdf Public Health Advocacy Toolkit from the Public Health Alliance for the Island of Ireland http: //advocacy. phaii. org/. Contains interactive learning modules, a useful advocacy model, case studies and competencies list Bruce S. Jansson. Improving Healthcare Through Advocacy: A Guide for the Health and Helping Professions. ISBN: 978 -0 -470 -50529 -8. Wiley, February 2011. This new book contains over 100 case studies from the perspective of patients, healthcare providers, and others, and practical tips on how to provide effective advocacy. Stafford J, Mitchell H, Stoneham M, Daube M. Advocacy in Action: a toolkit for public health professionals. 2 nd Edition. Public Health Advocacy Institute of Western Australia, 2011 http: //www. phaiwa. org. au/index. php/component/attachments/download/35 Institute for Social Marketing, University of Stirling, Scotland. http: //www. management. stir. ac. uk/about-us/institute-of-social-marketing w The Institute's Director, Professor Gerard Hastings, is a leading researcher and practitioner on public health social marketing. The website includes the Centre for Tobacco Control Research, which is part of the Institute, and also contains a number of useful case studies, including on the effects of food promotion to children. Hastings has also published a textbook on social marketing, Social Marketing: why should the devil have all the best tunes? published in 2007 by Butterworth Heinemann - ISBN: 978 -07506 -8350 -0. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
Further references for self-study • • • WHO – www. who. int/ncd UNDP -The blue book: a hands-on approach to advocating for the MDGs http: //www. undp. or. id/mdg/documents/The%20 Blue%20 Book%20 A%20 Hands%20 on%20 Appro ach%20 to%20 Advocating%20 for%20 the%20 MDGs. pdf World Bank – Public policy and the challenge of NCDs http: //siteresources. worldbank. org/INTPH/Resources/Public. Policyand. NCDs. World. Bank 2007 Full. R eport. pdf Public Health Advocacy Toolkit from the Public Health Alliance for the Island of Ireland http: //advocacy. phaii. org/. Contains interactive learning modules, a useful advocacy model, case studies and competencies list Bruce S. Jansson. Improving Healthcare Through Advocacy: A Guide for the Health and Helping Professions. ISBN: 978 -0 -470 -50529 -8. Wiley, February 2011. This new book contains over 100 case studies from the perspective of patients, healthcare providers, and others, and practical tips on how to provide effective advocacy. Stafford J, Mitchell H, Stoneham M, Daube M. Advocacy in Action: a toolkit for public health professionals. 2 nd Edition. Public Health Advocacy Institute of Western Australia, 2011 http: //www. phaiwa. org. au/index. php/component/attachments/download/35 Institute for Social Marketing, University of Stirling, Scotland. http: //www. management. stir. ac. uk/about-us/institute-of-social-marketing w The Institute's Director, Professor Gerard Hastings, is a leading researcher and practitioner on public health social marketing. The website includes the Centre for Tobacco Control Research, which is part of the Institute, and also contains a number of useful case studies, including on the effects of food promotion to children. Hastings has also published a textbook on social marketing, Social Marketing: why should the devil have all the best tunes? published in 2007 by Butterworth Heinemann - ISBN: 978 -07506 -8350 -0. 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011)
 Thank you bloomfielda@who. int garwoodp@who. int vanhiltenm@who. int Профилактика неинфекционных заболеваний и борьба с ними 预防和控制非传染病 Prevención y control de las enfermedades no transmisibles ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻤﺮﺍﺽ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺪﻳﺔ ﻭﻣﻜﺎﻓﺤﺘﻬﺎ 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects Prévention et maîtrise des maladies non Prevention and control of non-communicable of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) transmissibles diseases
Thank you bloomfielda@who. int garwoodp@who. int vanhiltenm@who. int Профилактика неинфекционных заболеваний и борьба с ними 预防和控制非传染病 Prevención y control de las enfermedades no transmisibles ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻤﺮﺍﺽ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺪﻳﺔ ﻭﻣﻜﺎﻓﺤﺘﻬﺎ 4 th International Seminar on the Public Health Aspects Prévention et maîtrise des maladies non Prevention and control of non-communicable of NCDs (Lausanne, 7 -12 March 2011) transmissibles diseases


