c38b39506428e041499050cc628e602a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

10 tips for building your own TAVR research program Issi Barbash, MD Med. Star Washington Hospital Center

Israel M. Barbash, MD I/we have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report.
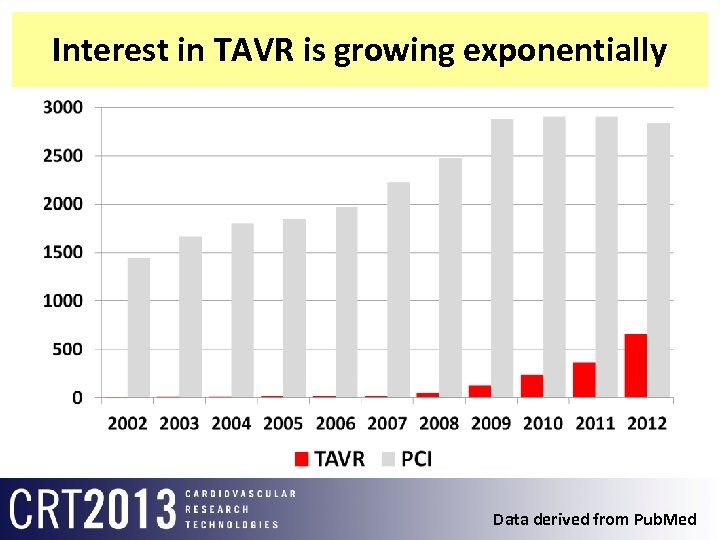
Interest in TAVR is growing exponentially Data derived from Pub. Med

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments

Procedure volumes • Key to obtaining meaningful data • Requires significant procedure volumes • Consider multi-center collaborations

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments
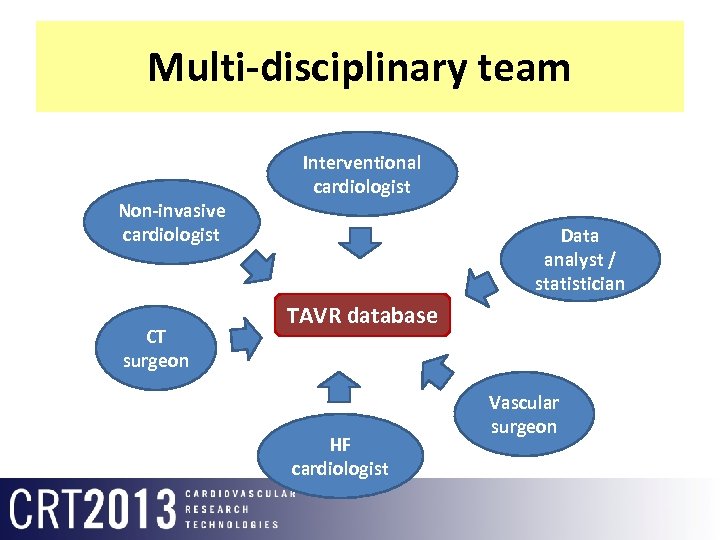
Multi-disciplinary team Non-invasive cardiologist CT surgeon Interventional cardiologist Data analyst / statistician TAVR database HF cardiologist Vascular surgeon

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments

Excel sheet - Cheap but risky

Web-based database – No tech support needed • Build web-based databases quickly and securely • Flexible • Export data to common data analysis packages • Ad Hoc custom queries • Advanced features - Autovalidation, calculated fields • FREE http: //project-redcap. org/

Web-based database – tech support needed • 100% flexible • Secure

Web-based database - 2 • Requires dedicated personnel to build, maintain, troubleshoot

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments

Categories of data to collect • • Baseline demographics & medical history Baseline medications Echo studies CT data Procedural data and complications In hospital course and complications Long term follow up (survival, hospitalizations, pacemaker, compliance with medications)

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments
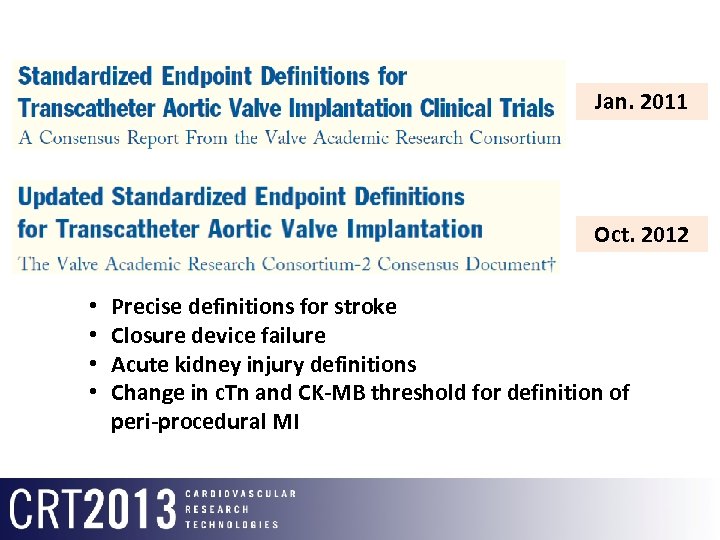
Jan. 2011 Oct. 2012 • • Precise definitions for stroke Closure device failure Acute kidney injury definitions Change in c. Tn and CK-MB threshold for definition of peri-procedural MI

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments

Which parameters not to collect ? • Collecting excessive parameters may exhaust the system • Some parameters are impossible to collect

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments
Data entry method Manual data collection Automated export mechanism from EMR

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments

Patient pool resource • Evaluation process of AS patients from initial referral to TAVR is complicated and prolonged • Having all the data per patient in a single location can: – Search for qualifying patients for new protocols / devices – Minimize losing track of patients – Enhance communication with ref MDs

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments

Long term follow up program • Mortality data is the most crucial • Other parameters: – HF symptoms – Hospitalizations – Pacemaker implantation – Bleeding events – Stroke and intracranial bleeds • Mechanism – Phone calls – Office visits

1. Procedure volumes - Key to a successful program 2. Create broadened “Heart-Team” 3. Choose appropriate database platform 4. Create the right categories of data to be collected 5. Parameters you want to collect 6. Parameters you do not want to collect 7. Enter data to the database the right way 8. Collect data Prospectively 9. Establish follow up mechanisms 10. Perform quality control assessments

Final remarks • Creating database requires multi-disciplinary collaboration and various resources • Putting sufficient efforts in the planning phase would save pain later • The advantages of having a AVR database are beyond research
c38b39506428e041499050cc628e602a.ppt