69e2b2ae985d62bc63f483d884ea052c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 10 Management: Principles and Practices Griffin © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Student Version Power. Point Presentation by Charlie Cook The University of West Alabama
10 Management: Principles and Practices Griffin © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Student Version Power. Point Presentation by Charlie Cook The University of West Alabama
 The Nature of Entrepreneurship • Entrepreneurship Ø The process of planning, organizing, operating, and assuming the risk of a business. • Entrepreneur Ø Someone who engages in entrepreneurship. • Small Business Ø A business that is privately owned by one individual or a small group of individuals; it has sales and assets that are not large enough to influence its environment. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 2
The Nature of Entrepreneurship • Entrepreneurship Ø The process of planning, organizing, operating, and assuming the risk of a business. • Entrepreneur Ø Someone who engages in entrepreneurship. • Small Business Ø A business that is privately owned by one individual or a small group of individuals; it has sales and assets that are not large enough to influence its environment. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 2
 The Role of Entrepreneurship in Society • Research Findings: Ø Most new businesses fail, those that survive often do so because the entrepreneur works for little income. Ø More than 98% of U. S. businesses have fewer than 100 employees. Ø Most U. S. workers work for small businesses. Ø The majority of small businesses are owner operated. Ø Small business is a strong presence in both mature and emerging economies Ø Small businesses have a strong effect on job creation, innovation, and are important to big businesses. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 3
The Role of Entrepreneurship in Society • Research Findings: Ø Most new businesses fail, those that survive often do so because the entrepreneur works for little income. Ø More than 98% of U. S. businesses have fewer than 100 employees. Ø Most U. S. workers work for small businesses. Ø The majority of small businesses are owner operated. Ø Small business is a strong presence in both mature and emerging economies Ø Small businesses have a strong effect on job creation, innovation, and are important to big businesses. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 3
 Entrepreneurship’s Role in Society • Small Businesses’ Role in Job Creation Ø Create many of the new jobs in the U. S. Ø Dominate sectors that have added the most jobs. Ø Represent 92% of all U. S. exporters. • Innovation Ø Major innovations are as likely to come from small businesses as from large firms. Ø Much of what is created in the high-technology sectors comes from start-up companies. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 4
Entrepreneurship’s Role in Society • Small Businesses’ Role in Job Creation Ø Create many of the new jobs in the U. S. Ø Dominate sectors that have added the most jobs. Ø Represent 92% of all U. S. exporters. • Innovation Ø Major innovations are as likely to come from small businesses as from large firms. Ø Much of what is created in the high-technology sectors comes from start-up companies. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 4
 Entrepreneurship’s Role in Society (cont’d) • Importance to Large Businesses Ø Most products made by large manufacturers are sold to customers by small businesses. Ø Small businesses as suppliers provide large firms with essential services, supplies, and raw materials. Ø Large businesses outsource many routine business operations such as packaging, delivery, and distribution to small businesses. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 5
Entrepreneurship’s Role in Society (cont’d) • Importance to Large Businesses Ø Most products made by large manufacturers are sold to customers by small businesses. Ø Small businesses as suppliers provide large firms with essential services, supplies, and raw materials. Ø Large businesses outsource many routine business operations such as packaging, delivery, and distribution to small businesses. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 5
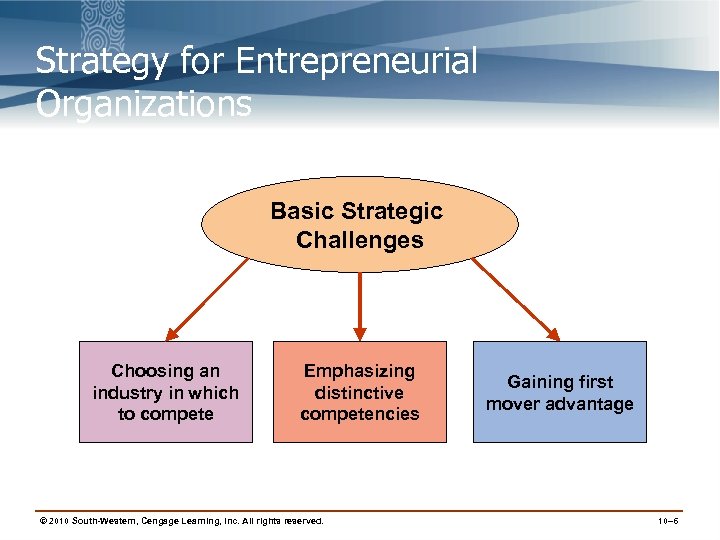 Strategy for Entrepreneurial Organizations Basic Strategic Challenges Choosing an industry in which to compete Emphasizing distinctive competencies © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Gaining first mover advantage 10– 6
Strategy for Entrepreneurial Organizations Basic Strategic Challenges Choosing an industry in which to compete Emphasizing distinctive competencies © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Gaining first mover advantage 10– 6
 Writing a Business Plan • Business Plan Ø is a document that summarizes the business strategy and structure. It should include: v v v business goals and objectives. strategies used to achieve these goals and objectives. a plan of how the entrepreneur will implement these strategies. • Entrepreneurship and International Management Ø Expansion and growth potential in foreign markets. Ø Entering a foreign country’s market can be an important catalyst for success. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 7
Writing a Business Plan • Business Plan Ø is a document that summarizes the business strategy and structure. It should include: v v v business goals and objectives. strategies used to achieve these goals and objectives. a plan of how the entrepreneur will implement these strategies. • Entrepreneurship and International Management Ø Expansion and growth potential in foreign markets. Ø Entering a foreign country’s market can be an important catalyst for success. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 7
 Entrepreneurial Organization Structure • Starting the New Business Ø Buying an Existing Business v Business has a proven ability to draw customers and make a profit (the business is a going concern). v Networks (e. g. , customers and suppliers) are established. v Negative: New owners inherit any existing problems. Ø Starting from Scratch v Avoids problems associated with previous owners. v Freedom to choose suppliers, equipment, location, and workers. v Negative: More business risk and uncertainty. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 8
Entrepreneurial Organization Structure • Starting the New Business Ø Buying an Existing Business v Business has a proven ability to draw customers and make a profit (the business is a going concern). v Networks (e. g. , customers and suppliers) are established. v Negative: New owners inherit any existing problems. Ø Starting from Scratch v Avoids problems associated with previous owners. v Freedom to choose suppliers, equipment, location, and workers. v Negative: More business risk and uncertainty. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 8
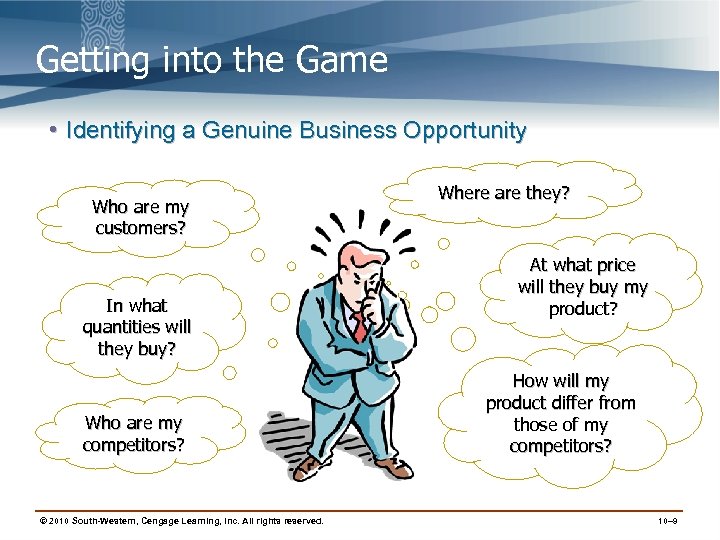 Getting into the Game • Identifying a Genuine Business Opportunity Who are my customers? In what quantities will they buy? Who are my competitors? © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Where are they? At what price will they buy my product? How will my product differ from those of my competitors? 10– 9
Getting into the Game • Identifying a Genuine Business Opportunity Who are my customers? In what quantities will they buy? Who are my competitors? © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Where are they? At what price will they buy my product? How will my product differ from those of my competitors? 10– 9
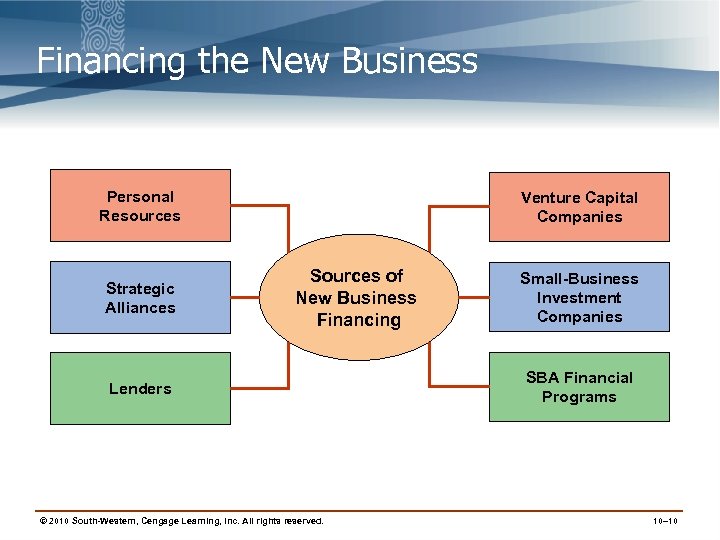 Financing the New Business Personal Resources Strategic Alliances Venture Capital Companies Sources of New Business Financing Lenders © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Small-Business Investment Companies SBA Financial Programs 10– 10
Financing the New Business Personal Resources Strategic Alliances Venture Capital Companies Sources of New Business Financing Lenders © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Small-Business Investment Companies SBA Financial Programs 10– 10
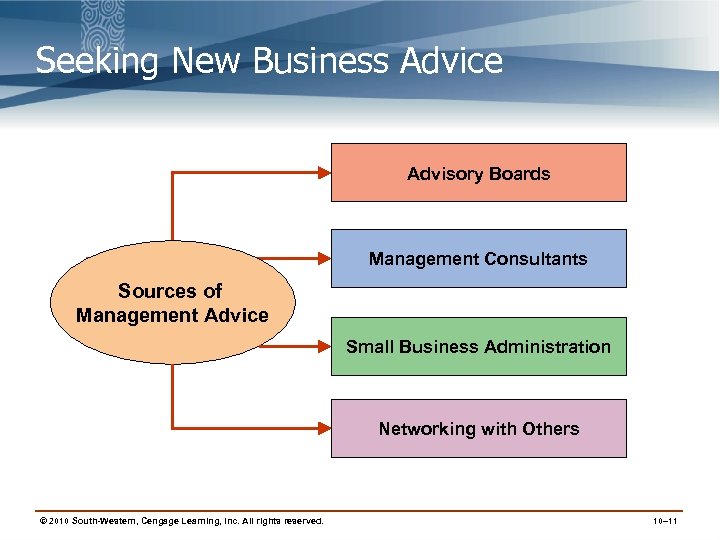 Seeking New Business Advice Advisory Boards Management Consultants Sources of Management Advice Small Business Administration Networking with Others © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 11
Seeking New Business Advice Advisory Boards Management Consultants Sources of Management Advice Small Business Administration Networking with Others © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 11
 Franchising • The Franchising Agreement Ø Governs the operation of a franchise business by the entrepreneur (the franchisee) under a license by a parent company (the franchiser). Ø The entrepreneur pays the parent company for use of trademarks, products, formulas, and business plans. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 12
Franchising • The Franchising Agreement Ø Governs the operation of a franchise business by the entrepreneur (the franchisee) under a license by a parent company (the franchiser). Ø The entrepreneur pays the parent company for use of trademarks, products, formulas, and business plans. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 12
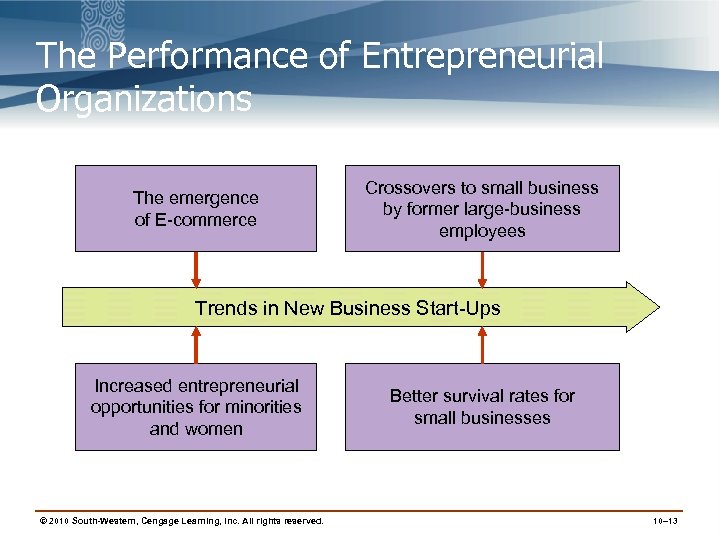 The Performance of Entrepreneurial Organizations The emergence of E-commerce Crossovers to small business by former large-business employees Trends in New Business Start-Ups Increased entrepreneurial opportunities for minorities and women © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Better survival rates for small businesses 10– 13
The Performance of Entrepreneurial Organizations The emergence of E-commerce Crossovers to small business by former large-business employees Trends in New Business Start-Ups Increased entrepreneurial opportunities for minorities and women © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. Better survival rates for small businesses 10– 13
 Success in Entrepreneurial Organizations • Reasons for Success Ø Hard work, drive, and dedication by the entrepreneur. Ø Careful analysis of market conditions provides insights about business conditions Ø Managerial competence through training and experience contributes to success. Ø Luck sometimes plays a role. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. • Reasons for Failure Ø Managerial incompetence/ inexperience of the entrepreneur. Ø Neglect in not devoting sufficient time and effort to the business. Ø Weak control systems that do not warn of impending problems. Ø Insufficient capital to sustain the business until it starts to turn a profit. 10– 14
Success in Entrepreneurial Organizations • Reasons for Success Ø Hard work, drive, and dedication by the entrepreneur. Ø Careful analysis of market conditions provides insights about business conditions Ø Managerial competence through training and experience contributes to success. Ø Luck sometimes plays a role. © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. • Reasons for Failure Ø Managerial incompetence/ inexperience of the entrepreneur. Ø Neglect in not devoting sufficient time and effort to the business. Ø Weak control systems that do not warn of impending problems. Ø Insufficient capital to sustain the business until it starts to turn a profit. 10– 14
 Key Terms • • • entrepreneurship entrepreneur small business established market niche first-mover advantage business plan venture capital company franchisee franchisor franchising agreement © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 15
Key Terms • • • entrepreneurship entrepreneur small business established market niche first-mover advantage business plan venture capital company franchisee franchisor franchising agreement © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning, Inc. All rights reserved. 10– 15


