c62bebaed054121e0faf5a519ff05eee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 10. Information Management in Tourism Destinations World Tourism Organization Manila, 20 – 22 March 2006 M Fabricius
10. Information Management in Tourism Destinations World Tourism Organization Manila, 20 – 22 March 2006 M Fabricius
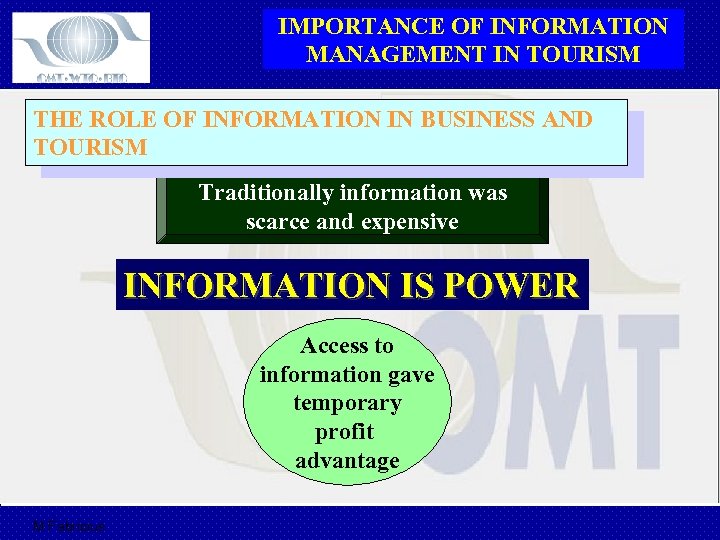 IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM THE ROLE OF INFORMATION IN BUSINESS AND TOURISM Traditionally information was scarce and expensive INFORMATION IS POWER Access to information gave temporary profit advantage M Fabricius
IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM THE ROLE OF INFORMATION IN BUSINESS AND TOURISM Traditionally information was scarce and expensive INFORMATION IS POWER Access to information gave temporary profit advantage M Fabricius
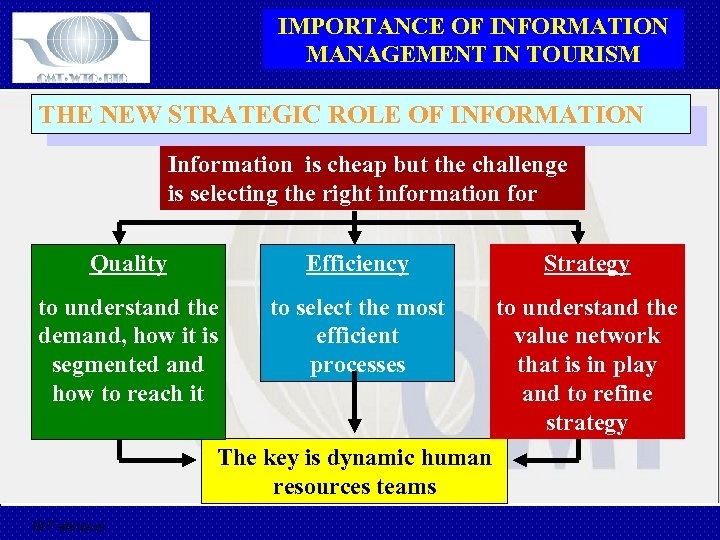 IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM THE NEW STRATEGIC ROLE OF INFORMATION Information is cheap but the challenge is selecting the right information for Quality Efficiency Strategy to understand the demand, how it is segmented and how to reach it to select the most efficient processes to understand the value network that is in play and to refine strategy The key is dynamic human resources teams M Fabricius
IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM THE NEW STRATEGIC ROLE OF INFORMATION Information is cheap but the challenge is selecting the right information for Quality Efficiency Strategy to understand the demand, how it is segmented and how to reach it to select the most efficient processes to understand the value network that is in play and to refine strategy The key is dynamic human resources teams M Fabricius
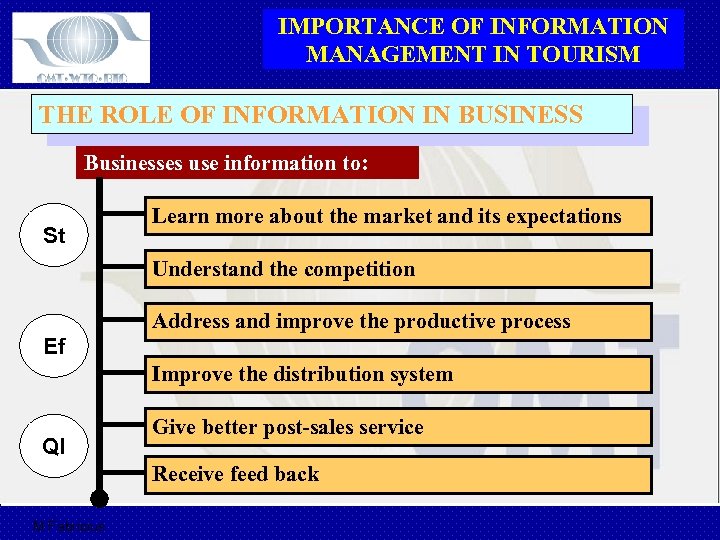 IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM THE ROLE OF INFORMATION IN BUSINESS Businesses use information to: St Learn more about the market and its expectations Understand the competition Address and improve the productive process Ef Improve the distribution system Ql Give better post-sales service Receive feed back M Fabricius
IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM THE ROLE OF INFORMATION IN BUSINESS Businesses use information to: St Learn more about the market and its expectations Understand the competition Address and improve the productive process Ef Improve the distribution system Ql Give better post-sales service Receive feed back M Fabricius
 IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR MARKETING Information for Marketing Consumer research Market analysis and forecasting Product and price studies Promotions and sales research Distribution research Evaluating and performance monitoring studies Data mining M Fabricius
IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR MARKETING Information for Marketing Consumer research Market analysis and forecasting Product and price studies Promotions and sales research Distribution research Evaluating and performance monitoring studies Data mining M Fabricius
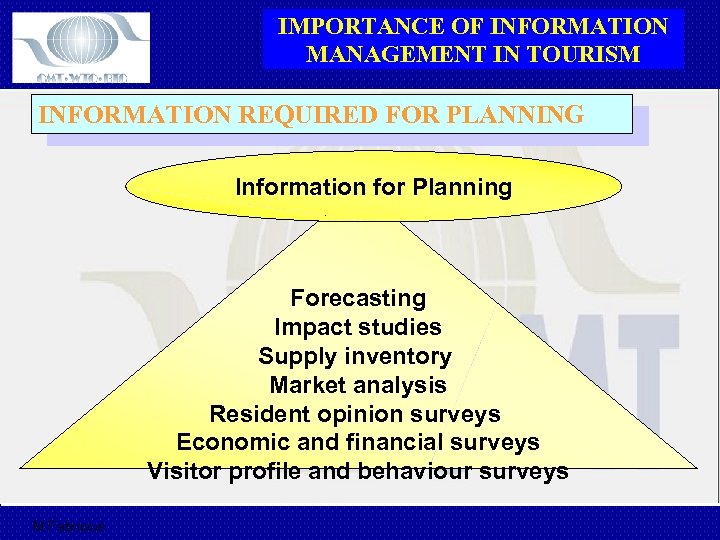 IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR PLANNING Information for Planning Forecasting Impact studies Supply inventory Market analysis Resident opinion surveys Economic and financial surveys Visitor profile and behaviour surveys M Fabricius
IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM INFORMATION REQUIRED FOR PLANNING Information for Planning Forecasting Impact studies Supply inventory Market analysis Resident opinion surveys Economic and financial surveys Visitor profile and behaviour surveys M Fabricius
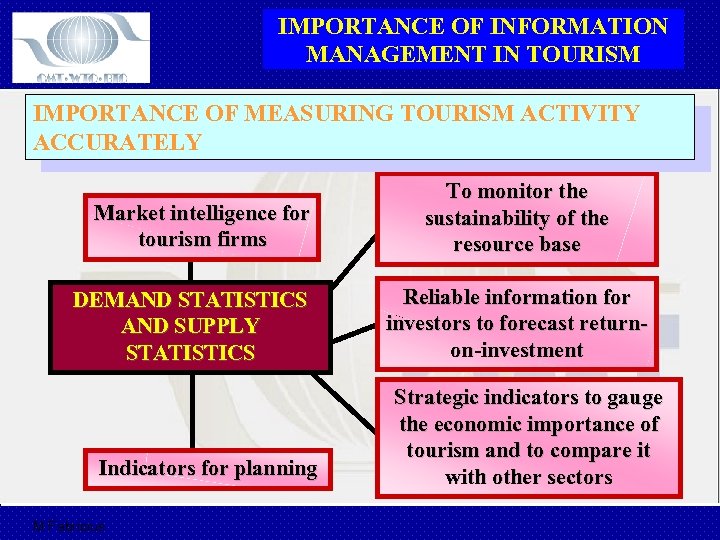 IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM IMPORTANCE OF MEASURING TOURISM ACTIVITY ACCURATELY Market intelligence for tourism firms DEMAND STATISTICS AND SUPPLY STATISTICS Indicators for planning M Fabricius To monitor the sustainability of the resource base Reliable information for investors to forecast returnon-investment Strategic indicators to gauge the economic importance of tourism and to compare it with other sectors
IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN TOURISM IMPORTANCE OF MEASURING TOURISM ACTIVITY ACCURATELY Market intelligence for tourism firms DEMAND STATISTICS AND SUPPLY STATISTICS Indicators for planning M Fabricius To monitor the sustainability of the resource base Reliable information for investors to forecast returnon-investment Strategic indicators to gauge the economic importance of tourism and to compare it with other sectors
 INFORMATION COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES (TOURISM E-BUSINESS) MAKING THE MOST OF ICT-BASED OPPORTUNITIES FOR DEVELOPING TOURISM IN DESTINATIONS • Key trends in the use of ICT in general and for travel and tourism • Key roles for ICT/e-business in destination management and marketing • E-business model for tourism destination communities • Options for acquiring ICT/e-business systems Acknowledgement: TEAM Tourism Enterprise and Management Dr Roger Carter M Fabricius
INFORMATION COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES (TOURISM E-BUSINESS) MAKING THE MOST OF ICT-BASED OPPORTUNITIES FOR DEVELOPING TOURISM IN DESTINATIONS • Key trends in the use of ICT in general and for travel and tourism • Key roles for ICT/e-business in destination management and marketing • E-business model for tourism destination communities • Options for acquiring ICT/e-business systems Acknowledgement: TEAM Tourism Enterprise and Management Dr Roger Carter M Fabricius
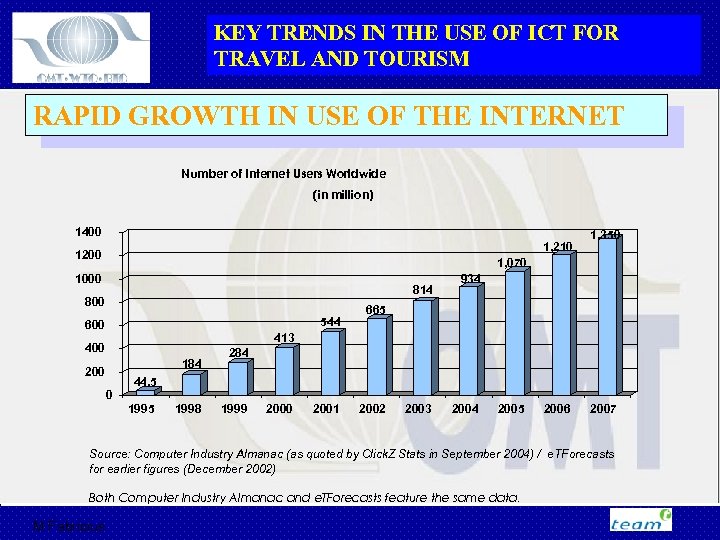 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM RAPID GROWTH IN USE OF THE INTERNET Number of Internet Users Worldwide (in million) 1400 1, 210 1200 1, 350 1, 070 1000 814 800 544 600 934 665 413 400 184 200 0 284 44. 5 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Source: Computer Industry Almanac (as quoted by Click. Z Stats in September 2004) / e. TForecasts for earlier figures (December 2002) Both Computer Industry Almanac and e. TForecasts feature the same data. M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM RAPID GROWTH IN USE OF THE INTERNET Number of Internet Users Worldwide (in million) 1400 1, 210 1200 1, 350 1, 070 1000 814 800 544 600 934 665 413 400 184 200 0 284 44. 5 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Source: Computer Industry Almanac (as quoted by Click. Z Stats in September 2004) / e. TForecasts for earlier figures (December 2002) Both Computer Industry Almanac and e. TForecasts feature the same data. M Fabricius
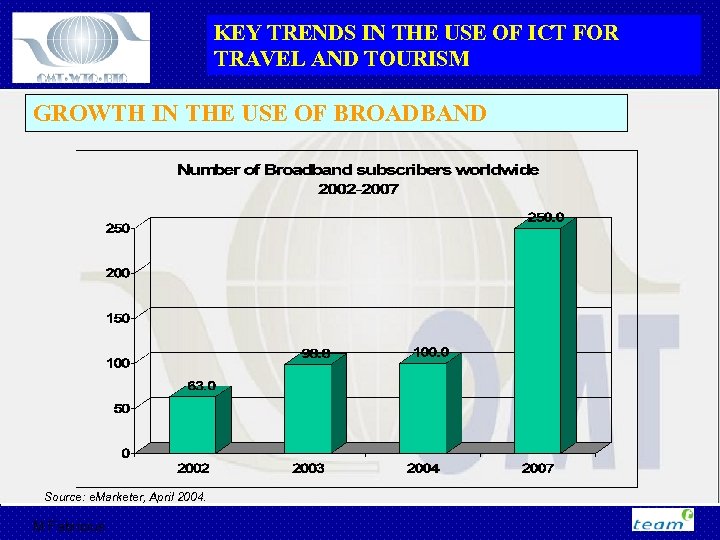 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM GROWTH IN THE USE OF BROADBAND Source: e. Marketer, April 2004. M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM GROWTH IN THE USE OF BROADBAND Source: e. Marketer, April 2004. M Fabricius
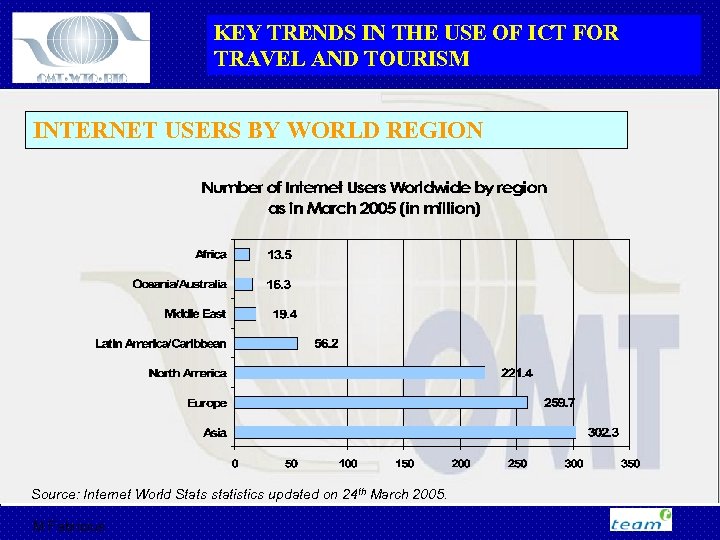 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM INTERNET USERS BY WORLD REGION Source: Internet World Stats statistics updated on 24 th March 2005. M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM INTERNET USERS BY WORLD REGION Source: Internet World Stats statistics updated on 24 th March 2005. M Fabricius
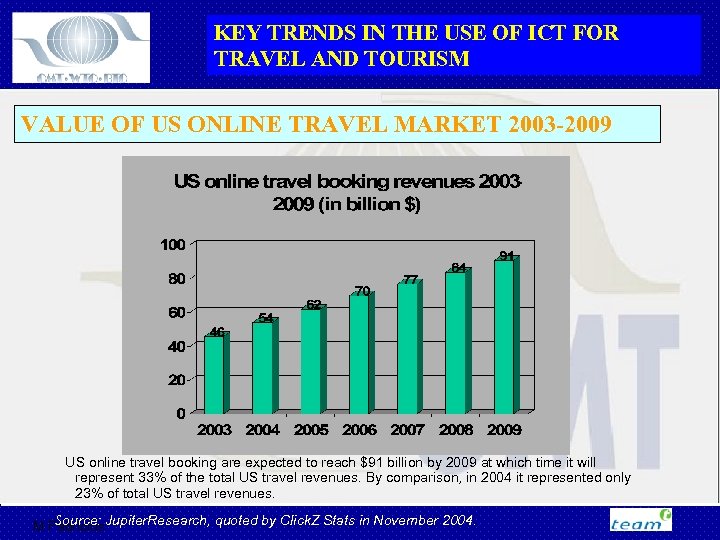 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM VALUE OF US ONLINE TRAVEL MARKET 2003 -2009 US online travel booking are expected to reach $91 billion by 2009 at which time it will represent 33% of the total US travel revenues. By comparison, in 2004 it represented only 23% of total US travel revenues. Source: M Fabricius. Jupiter. Research, quoted by Click. Z Stats in November 2004.
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM VALUE OF US ONLINE TRAVEL MARKET 2003 -2009 US online travel booking are expected to reach $91 billion by 2009 at which time it will represent 33% of the total US travel revenues. By comparison, in 2004 it represented only 23% of total US travel revenues. Source: M Fabricius. Jupiter. Research, quoted by Click. Z Stats in November 2004.
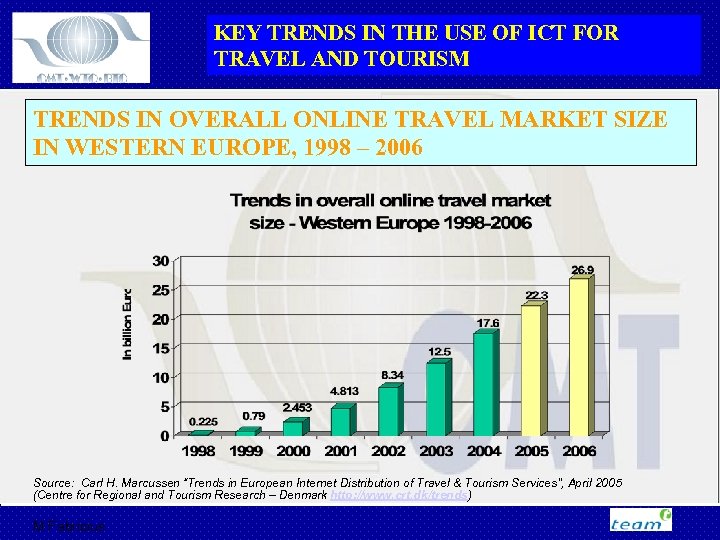 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM TRENDS IN OVERALL ONLINE TRAVEL MARKET SIZE IN WESTERN EUROPE, 1998 – 2006 Source: Carl H. Marcussen “Trends in European Internet Distribution of Travel & Tourism Services”, April 2005 (Centre for Regional and Tourism Research – Denmark http: //www. crt. dk/trends) M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM TRENDS IN OVERALL ONLINE TRAVEL MARKET SIZE IN WESTERN EUROPE, 1998 – 2006 Source: Carl H. Marcussen “Trends in European Internet Distribution of Travel & Tourism Services”, April 2005 (Centre for Regional and Tourism Research – Denmark http: //www. crt. dk/trends) M Fabricius
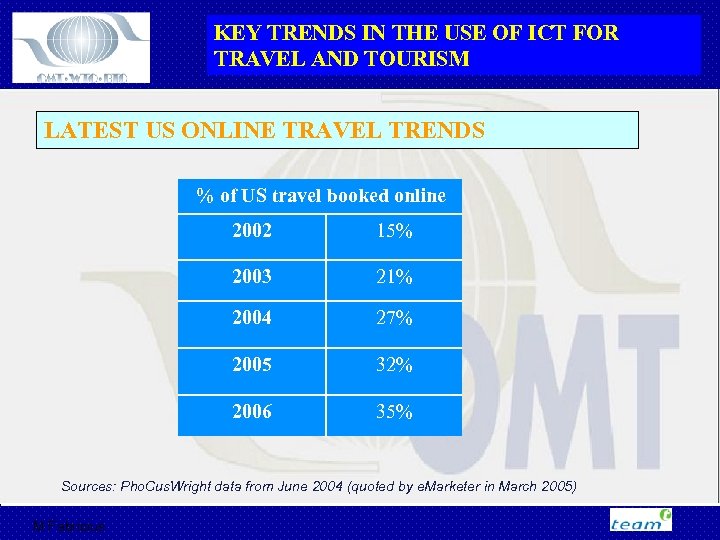 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM LATEST US ONLINE TRAVEL TRENDS % of US travel booked online 2002 15% 2003 21% 2004 27% 2005 32% 2006 35% Sources: Pho. Cus. Wright data from June 2004 (quoted by e. Marketer in March 2005) M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM LATEST US ONLINE TRAVEL TRENDS % of US travel booked online 2002 15% 2003 21% 2004 27% 2005 32% 2006 35% Sources: Pho. Cus. Wright data from June 2004 (quoted by e. Marketer in March 2005) M Fabricius
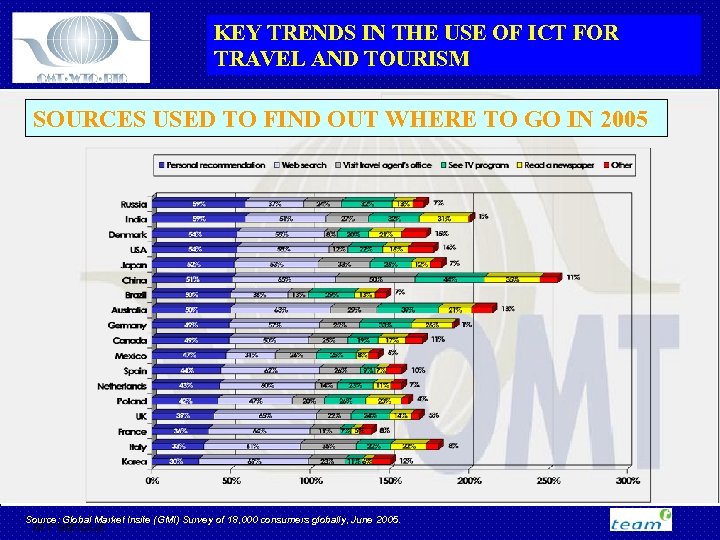 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM SOURCES USED TO FIND OUT WHERE TO GO IN 2005 Source: Global Market Insite (GMI) Survey of 18, 000 consumers globally, June 2005. M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM SOURCES USED TO FIND OUT WHERE TO GO IN 2005 Source: Global Market Insite (GMI) Survey of 18, 000 consumers globally, June 2005. M Fabricius
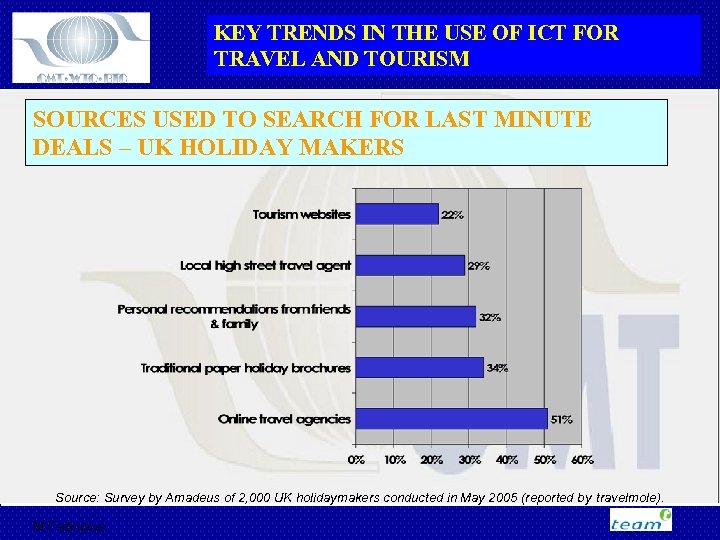 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM SOURCES USED TO SEARCH FOR LAST MINUTE DEALS – UK HOLIDAY MAKERS Source: Survey by Amadeus of 2, 000 UK holidaymakers conducted in May 2005 (reported by travelmole). M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM SOURCES USED TO SEARCH FOR LAST MINUTE DEALS – UK HOLIDAY MAKERS Source: Survey by Amadeus of 2, 000 UK holidaymakers conducted in May 2005 (reported by travelmole). M Fabricius
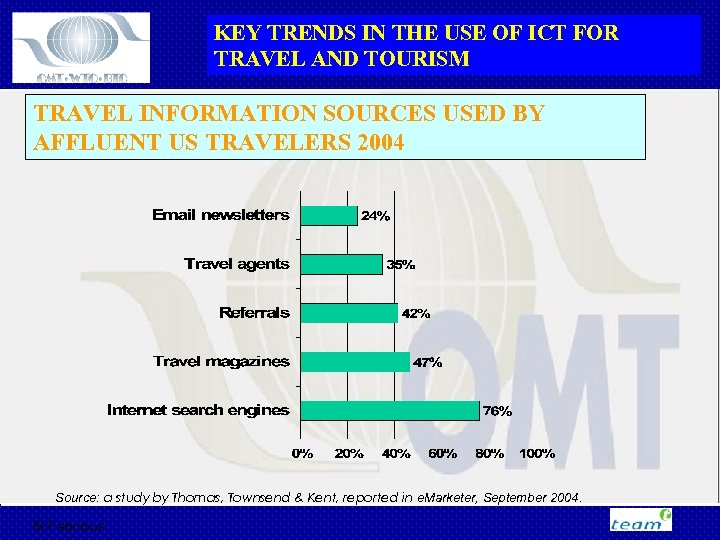 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM TRAVEL INFORMATION SOURCES USED BY AFFLUENT US TRAVELERS 2004 Source: a study by Thomas, Townsend & Kent, reported in e. Marketer, September 2004. M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM TRAVEL INFORMATION SOURCES USED BY AFFLUENT US TRAVELERS 2004 Source: a study by Thomas, Townsend & Kent, reported in e. Marketer, September 2004. M Fabricius
 KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM THE NEW TOURIST • Takes more and shorter holidays • Makes decisions later, reducing the lead time • Seeks more individual offers; self-enrichment; better, immediate information about the product and the destination; better service • Is more mobile and critical; more brand aware but less loyal; more price sensitive • Is more knowledgeable about international travel And • Has access to the Internet to obtain instant, in-depth information and booking And • Has access to low cost international air travel M Fabricius
KEY TRENDS IN THE USE OF ICT FOR TRAVEL AND TOURISM THE NEW TOURIST • Takes more and shorter holidays • Makes decisions later, reducing the lead time • Seeks more individual offers; self-enrichment; better, immediate information about the product and the destination; better service • Is more mobile and critical; more brand aware but less loyal; more price sensitive • Is more knowledgeable about international travel And • Has access to the Internet to obtain instant, in-depth information and booking And • Has access to low cost international air travel M Fabricius
 KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING FUNCTIONS • • • Destination marketing, including branding and image Marketing campaigns to drive business, particularly to SMEs Unbiased information services Operation/facilitation of bookings Destination coordination & management for visitor ‘quality of experience’ + involvement in the daily operation Visitor information and reservations Strategy, research and development Training and education Business advice Product “start-ups” Events development and management Attractions development and management M Fabricius
KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING FUNCTIONS • • • Destination marketing, including branding and image Marketing campaigns to drive business, particularly to SMEs Unbiased information services Operation/facilitation of bookings Destination coordination & management for visitor ‘quality of experience’ + involvement in the daily operation Visitor information and reservations Strategy, research and development Training and education Business advice Product “start-ups” Events development and management Attractions development and management M Fabricius
 KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING DESTINATION MARKETING • • • Destination marketing, including branding and image Marketing campaigns to drive business Unbiased information services Operation/facilitation of bookings Destination coordination & management for visitor ‘quality of experience’ + involvement in the daily operation Visitor information and reservations Research and development Training and education Business advice Product “start-ups” Events development and management Attractions development and management M Fabricius
KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING DESTINATION MARKETING • • • Destination marketing, including branding and image Marketing campaigns to drive business Unbiased information services Operation/facilitation of bookings Destination coordination & management for visitor ‘quality of experience’ + involvement in the daily operation Visitor information and reservations Research and development Training and education Business advice Product “start-ups” Events development and management Attractions development and management M Fabricius
 KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING DESTINATION MANAGEMENT • • • Destination marketing, including branding and image Marketing campaigns to drive business Unbiased information services Operation/facilitation of bookings Destination coordination & management for visitor ‘quality of experience’ + involvement in the daily operation Visitor information and reservations Research and development Training and education Business advice Product “start-ups” Events development and management Attractions development and management M Fabricius
KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING DESTINATION MANAGEMENT • • • Destination marketing, including branding and image Marketing campaigns to drive business Unbiased information services Operation/facilitation of bookings Destination coordination & management for visitor ‘quality of experience’ + involvement in the daily operation Visitor information and reservations Research and development Training and education Business advice Product “start-ups” Events development and management Attractions development and management M Fabricius
 KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING COMMUNICATION LIFE-CYCLE (CLC) – LEISURE TOURISM • • …. or ‘the customer journey’ Let us consider the leisure consumer perspective first Dream/ select Plan Book Visit Dream again V • This represents a key conceptual framework for the application of new media by DMOs • DMOs must optimise their opportunities by responding effectively to the requirements of the visitor at each stage in the cycle • Media for communication between DMO and consumers will vary at each stage in the life cycle M Fabricius
KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING COMMUNICATION LIFE-CYCLE (CLC) – LEISURE TOURISM • • …. or ‘the customer journey’ Let us consider the leisure consumer perspective first Dream/ select Plan Book Visit Dream again V • This represents a key conceptual framework for the application of new media by DMOs • DMOs must optimise their opportunities by responding effectively to the requirements of the visitor at each stage in the cycle • Media for communication between DMO and consumers will vary at each stage in the life cycle M Fabricius
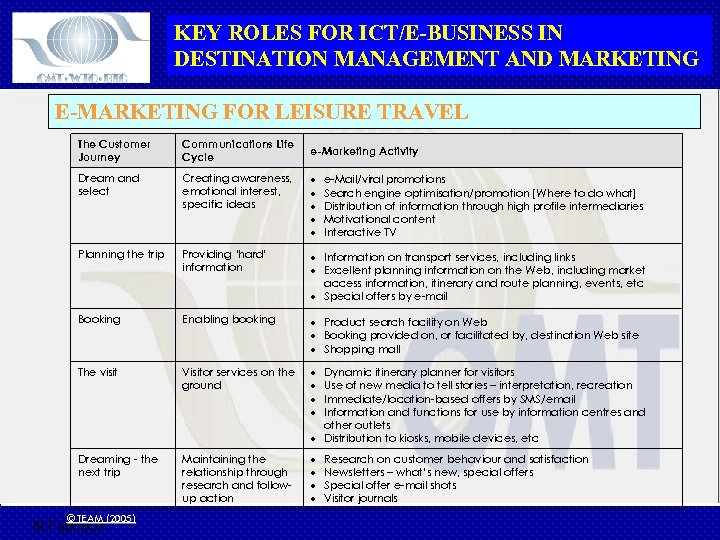 KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING E-MARKETING FOR LEISURE TRAVEL The Customer Journey Communications Life Cycle Dream and select Creating awareness, emotional interest, specific ideas Planning the trip Providing ‘hard’ information Information on transport services, including links Excellent planning information on the Web, including market access information, itinerary and route planning, events, etc Special offers by e-mail Booking Enabling booking Product search facility on Web Booking provided on, or facilitated by, destination Web site Shopping mall The visit Visitor services on the ground Dreaming - the next trip Maintaining the relationship through research and followup action © TEAM (2005) M Fabricius e-Marketing Activity e-Mail/viral promotions Search engine optimisation/promotion [Where to do what] Distribution of information through high profile intermediaries Motivational content Interactive TV Dynamic itinerary planner for visitors Use of new media to tell stories – interpretation, recreation Immediate/location-based offers by SMS/email Information and functions for use by information centres and other outlets Distribution to kiosks, mobile devices, etc Research on customer behaviour and satisfaction Newsletters – what’s new, special offers Special offer e-mail shots Visitor journals
KEY ROLES FOR ICT/E-BUSINESS IN DESTINATION MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING E-MARKETING FOR LEISURE TRAVEL The Customer Journey Communications Life Cycle Dream and select Creating awareness, emotional interest, specific ideas Planning the trip Providing ‘hard’ information Information on transport services, including links Excellent planning information on the Web, including market access information, itinerary and route planning, events, etc Special offers by e-mail Booking Enabling booking Product search facility on Web Booking provided on, or facilitated by, destination Web site Shopping mall The visit Visitor services on the ground Dreaming - the next trip Maintaining the relationship through research and followup action © TEAM (2005) M Fabricius e-Marketing Activity e-Mail/viral promotions Search engine optimisation/promotion [Where to do what] Distribution of information through high profile intermediaries Motivational content Interactive TV Dynamic itinerary planner for visitors Use of new media to tell stories – interpretation, recreation Immediate/location-based offers by SMS/email Information and functions for use by information centres and other outlets Distribution to kiosks, mobile devices, etc Research on customer behaviour and satisfaction Newsletters – what’s new, special offers Special offer e-mail shots Visitor journals
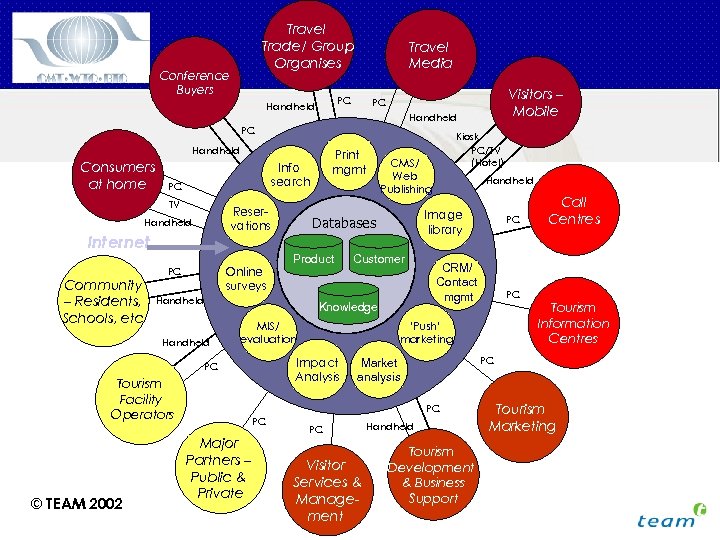
 E-BUSINESS MODEL FOR DESTINATION COMMUNITIES THE DESTINATION E-BUSINESS SYSTEM • • • The destination represents the focal point for all the players in tourism whose interests are interdependent – government, residents, suppliers, carriers, major corporations, intermediaries, consumers A core role for DMOs is bring together those players to work together in a meaningful way The DMO’s ICT/e-business systems potentially provide key media for these players to work together in destination management and marketing These systems enable the DMO to communicate with all the players – but also, for the players to communicate with each other The destination community e-business system may be represented like this …… M Fabricius
E-BUSINESS MODEL FOR DESTINATION COMMUNITIES THE DESTINATION E-BUSINESS SYSTEM • • • The destination represents the focal point for all the players in tourism whose interests are interdependent – government, residents, suppliers, carriers, major corporations, intermediaries, consumers A core role for DMOs is bring together those players to work together in a meaningful way The DMO’s ICT/e-business systems potentially provide key media for these players to work together in destination management and marketing These systems enable the DMO to communicate with all the players – but also, for the players to communicate with each other The destination community e-business system may be represented like this …… M Fabricius
 Travel Trade/ Group Organises Conference Buyers Travel Media PC Handheld Consumers at home TV Reservations Handheld Internet Community – Residents, Schools, etc Online surveys PC Customer Impact Analysis CRM/ Contact mgmt Major Partners – Public & Private PC PC Visitor Services & Management Call Centres Tourism Information Centres PC Market analysis PC PC PC ‘Push’ marketing MIS/ evaluation Tourism Facility Operators Handheld Image library Knowledge PC M Fabricius Product Kiosk PC/TV (Hotel) CMS/ Web Publishing Databases Handheld © TEAM 2002 Print mgmt Info search PC Visitors – Mobile PC Handheld Tourism Marketing Tourism Development & Business Support © TEAM 2000
Travel Trade/ Group Organises Conference Buyers Travel Media PC Handheld Consumers at home TV Reservations Handheld Internet Community – Residents, Schools, etc Online surveys PC Customer Impact Analysis CRM/ Contact mgmt Major Partners – Public & Private PC PC Visitor Services & Management Call Centres Tourism Information Centres PC Market analysis PC PC PC ‘Push’ marketing MIS/ evaluation Tourism Facility Operators Handheld Image library Knowledge PC M Fabricius Product Kiosk PC/TV (Hotel) CMS/ Web Publishing Databases Handheld © TEAM 2002 Print mgmt Info search PC Visitors – Mobile PC Handheld Tourism Marketing Tourism Development & Business Support © TEAM 2000
 OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS BROAD APPROACHES FOR OBTAINING DESTINATION SYSTEM • Incremental – Start with product database(s) and one or two Web interfaces – Buy-in or develop the functionality and add in new interfaces over time in response to expressed user requirements • Planned system – Work towards the concept of a fully integrated system, normally for multiple user groups – even if it is implemented in phases M Fabricius
OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS BROAD APPROACHES FOR OBTAINING DESTINATION SYSTEM • Incremental – Start with product database(s) and one or two Web interfaces – Buy-in or develop the functionality and add in new interfaces over time in response to expressed user requirements • Planned system – Work towards the concept of a fully integrated system, normally for multiple user groups – even if it is implemented in phases M Fabricius
 OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS PLANNED APPROACH - OPTIONS • Buy a fully integrated software system - e. g. World. net, TIScover, Visit - as a package ‘offthe-shelf’, with some customisation and/or highly flexible templates. • Buy or develop a purpose designed system, built from components: – Generic and/or – Tourism specific M Fabricius
OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS PLANNED APPROACH - OPTIONS • Buy a fully integrated software system - e. g. World. net, TIScover, Visit - as a package ‘offthe-shelf’, with some customisation and/or highly flexible templates. • Buy or develop a purpose designed system, built from components: – Generic and/or – Tourism specific M Fabricius
 OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS PLANNING FOR AN INTEGRATED DMS • E-Business strategy – defines the wider ebusiness network, provides the framework for action and basis for buy-in; principal focus is on opportunities to make existing activities more cost-effective • Specification of user requirements – a two-way process • Functional specification • Project scoping/Business case analysis • It is an iterative approach M Fabricius
OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS PLANNING FOR AN INTEGRATED DMS • E-Business strategy – defines the wider ebusiness network, provides the framework for action and basis for buy-in; principal focus is on opportunities to make existing activities more cost-effective • Specification of user requirements – a two-way process • Functional specification • Project scoping/Business case analysis • It is an iterative approach M Fabricius
 OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS PLANNING FOR AN INTEGRATED DMS • ‘Request for Information’ from system suppliers or integrator – optional but educational – may result in changes to the specifications or the business case analysis and short listing of potential suppliers • ‘Request for Proposals’ (or ITT) – which should result in an evaluation of the options based on a variety of factors, including a systematic assessment of the extent to which the products will meet the DMO’s detailed requirements • Implementation Plan – not only the role-out of the ICT, but also the information management plan, the training plan and so on…. • As early as possible in this process, appoint the Project Manager, to contribute to the evolving process M Fabricius
OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS PLANNING FOR AN INTEGRATED DMS • ‘Request for Information’ from system suppliers or integrator – optional but educational – may result in changes to the specifications or the business case analysis and short listing of potential suppliers • ‘Request for Proposals’ (or ITT) – which should result in an evaluation of the options based on a variety of factors, including a systematic assessment of the extent to which the products will meet the DMO’s detailed requirements • Implementation Plan – not only the role-out of the ICT, but also the information management plan, the training plan and so on…. • As early as possible in this process, appoint the Project Manager, to contribute to the evolving process M Fabricius
 OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS RESUMè • Key market trends, the factors that make it essential for DMOs to take the use of new media seriously and recognise its dynamic nature • Review of destination management and marketing functions and the way that may be supported by a ebusiness • Concept of destinations as communities, and the way that may be supported by a destination e-business system • Analysis of the options for acquiring ICT/e-business systems M Fabricius
OPTIONS FOR ACQUIRING DESTINATION EBUSINESS SYSYEMS RESUMè • Key market trends, the factors that make it essential for DMOs to take the use of new media seriously and recognise its dynamic nature • Review of destination management and marketing functions and the way that may be supported by a ebusiness • Concept of destinations as communities, and the way that may be supported by a destination e-business system • Analysis of the options for acquiring ICT/e-business systems M Fabricius
 Thank You! M Fabricius
Thank You! M Fabricius


