939f3aa786828dfab54646cefe35f6fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 10 Chapter 10: The Traditional Approach to Design Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition
10 Chapter 10: The Traditional Approach to Design Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition
 10 Learning Objectives u Develop a system flowchart u Develop a structure chart using transaction analysis and transform analysis u Write pseudocode for structured modules Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2
10 Learning Objectives u Develop a system flowchart u Develop a structure chart using transaction analysis and transform analysis u Write pseudocode for structured modules Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 2
 10 Overview u Traditional approach to designing software l Overview of structured models, model development process, related terminology l How data flow diagrams are annotated with automation boundary information l How analysis phase models are transformed into design models using system flowcharts, structure charts, and module pseudocode l Integration into other design phase activities l Applying approach to a three-layer architecture Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 3
10 Overview u Traditional approach to designing software l Overview of structured models, model development process, related terminology l How data flow diagrams are annotated with automation boundary information l How analysis phase models are transformed into design models using system flowcharts, structure charts, and module pseudocode l Integration into other design phase activities l Applying approach to a three-layer architecture Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 3
 The Structured Approach to Designing the Application Architecture u Application 10 software programs l Designed in conjunction with database and user interface l Hierarchy of modules u Design internal logic of individual modules u Top-down approach l DFDs with automation boundaries l System flowcharts, structure charts, pseudocode Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 4
The Structured Approach to Designing the Application Architecture u Application 10 software programs l Designed in conjunction with database and user interface l Hierarchy of modules u Design internal logic of individual modules u Top-down approach l DFDs with automation boundaries l System flowcharts, structure charts, pseudocode Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 4
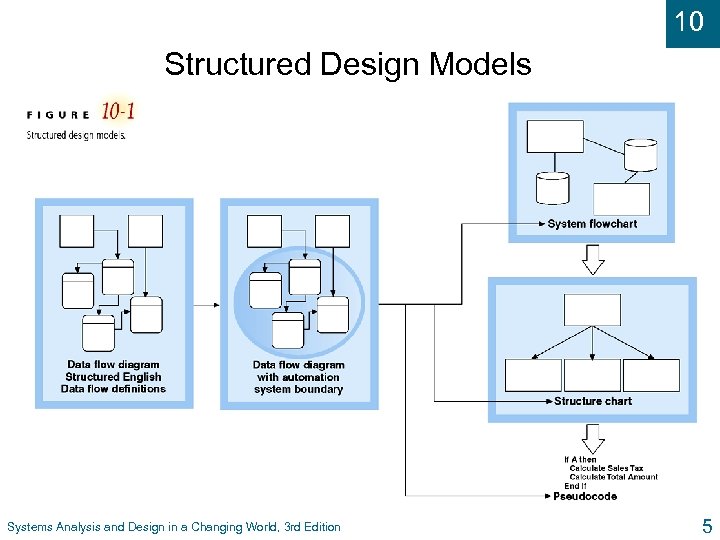 10 Structured Design Models Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 5
10 Structured Design Models Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 5
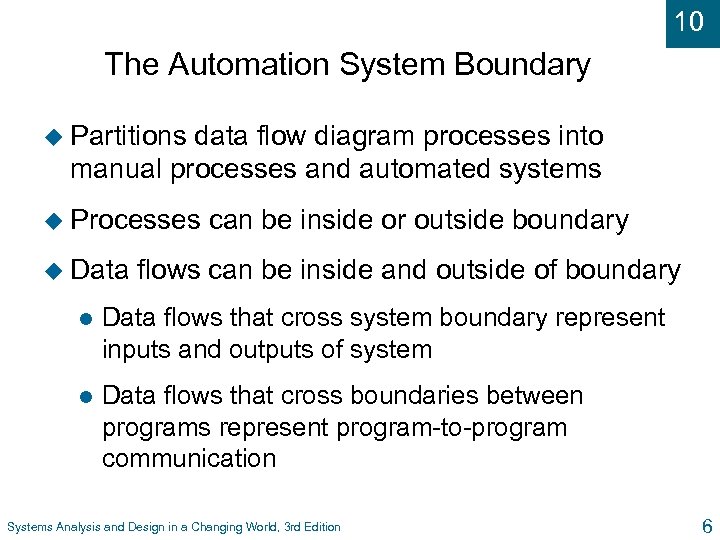 10 The Automation System Boundary u Partitions data flow diagram processes into manual processes and automated systems u Processes u Data can be inside or outside boundary flows can be inside and outside of boundary l Data flows that cross system boundary represent inputs and outputs of system l Data flows that cross boundaries between programs represent program-to-program communication Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 6
10 The Automation System Boundary u Partitions data flow diagram processes into manual processes and automated systems u Processes u Data can be inside or outside boundary flows can be inside and outside of boundary l Data flows that cross system boundary represent inputs and outputs of system l Data flows that cross boundaries between programs represent program-to-program communication Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 6
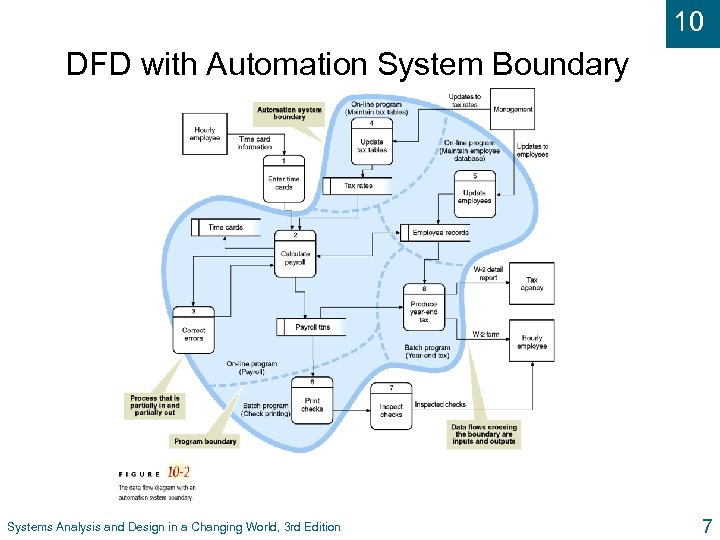 10 DFD with Automation System Boundary Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 7
10 DFD with Automation System Boundary Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 7
 10 The System Flowchart u Representation of various computer programs, files, databases, and associated manual processes that make up complete system u Frequently constructed during analysis activities u Graphically describes organization of subsystems into automated and manual components u Can show type of transaction processing system l Batch l Real time Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 8
10 The System Flowchart u Representation of various computer programs, files, databases, and associated manual processes that make up complete system u Frequently constructed during analysis activities u Graphically describes organization of subsystems into automated and manual components u Can show type of transaction processing system l Batch l Real time Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 8
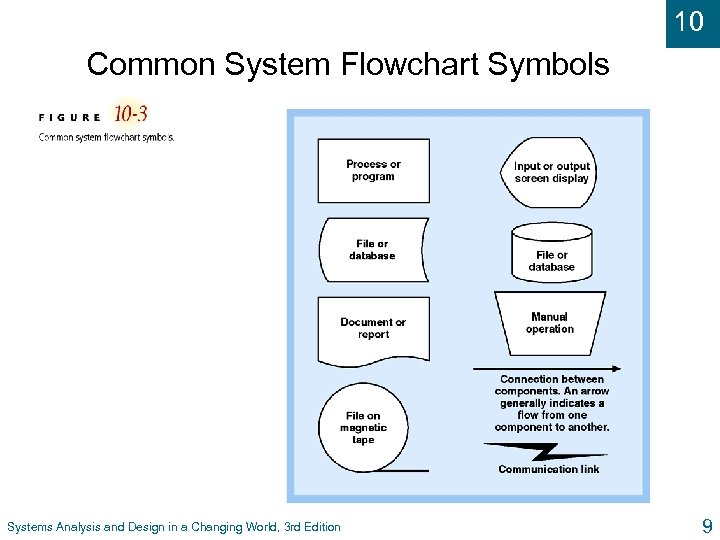 10 Common System Flowchart Symbols Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 9
10 Common System Flowchart Symbols Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 9
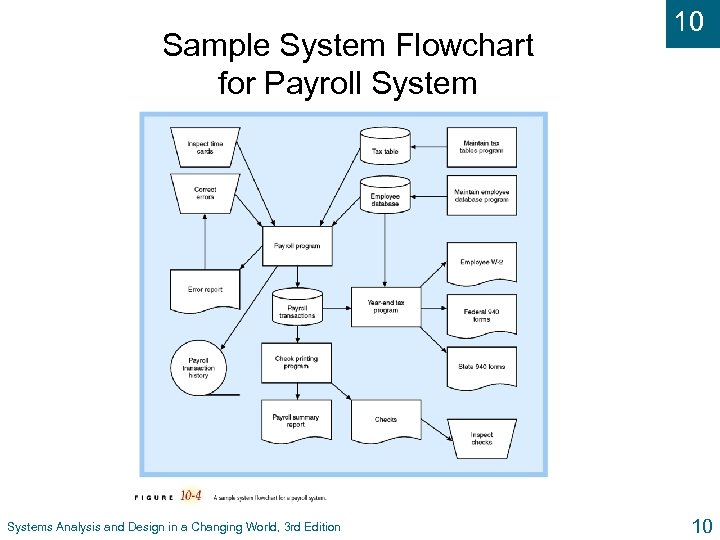 Sample System Flowchart for Payroll Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 10
Sample System Flowchart for Payroll Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 10
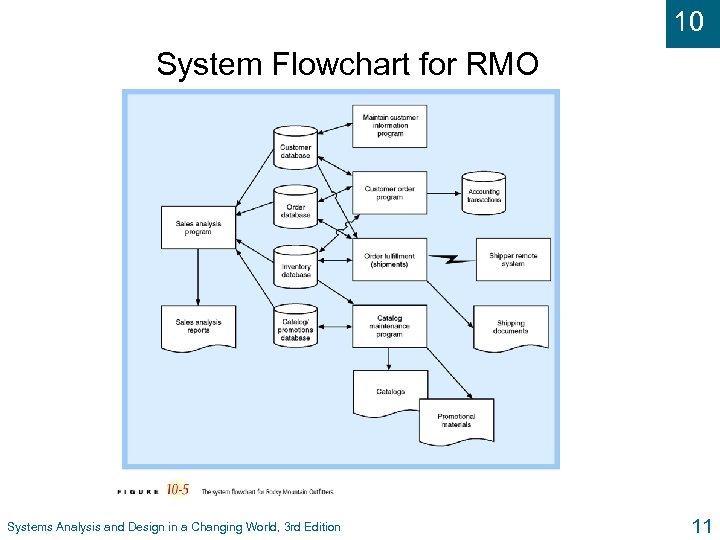 10 System Flowchart for RMO Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 11
10 System Flowchart for RMO Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 11
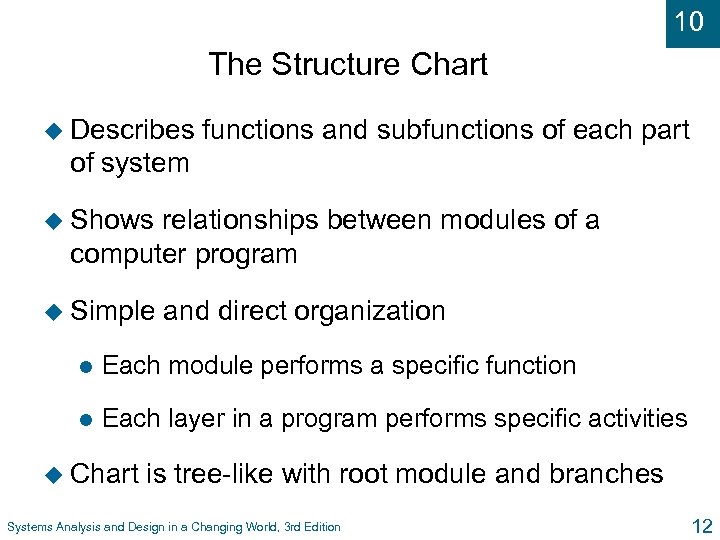 10 The Structure Chart u Describes functions and subfunctions of each part of system u Shows relationships between modules of a computer program u Simple and direct organization l Each module performs a specific function l Each layer in a program performs specific activities u Chart is tree-like with root module and branches Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 12
10 The Structure Chart u Describes functions and subfunctions of each part of system u Shows relationships between modules of a computer program u Simple and direct organization l Each module performs a specific function l Each layer in a program performs specific activities u Chart is tree-like with root module and branches Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 12
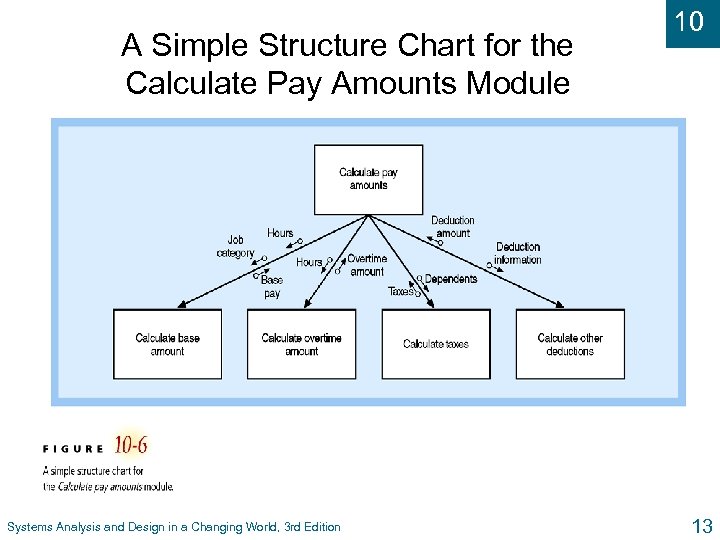 A Simple Structure Chart for the Calculate Pay Amounts Module Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 13
A Simple Structure Chart for the Calculate Pay Amounts Module Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 13
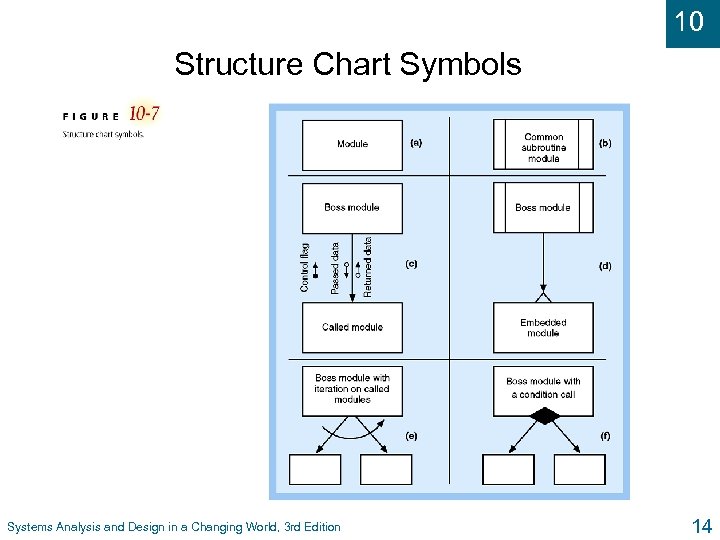 10 Structure Chart Symbols Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 14
10 Structure Chart Symbols Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 14
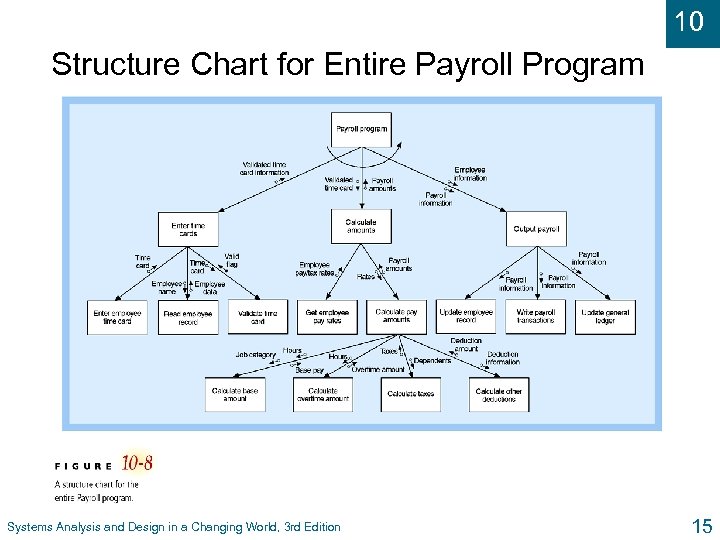 10 Structure Chart for Entire Payroll Program Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 15
10 Structure Chart for Entire Payroll Program Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 15
 10 Developing a Structure Chart u Transaction Analysis l Uses system flow chart and event table inputs l Upper-level modules developed first l Identifies each transaction supported by program u Transform Analysis l Uses DFD fragments for inputs l Computer program ‘transforms’ inputs into outputs l Charts have input, calculate, and output subtrees Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 16
10 Developing a Structure Chart u Transaction Analysis l Uses system flow chart and event table inputs l Upper-level modules developed first l Identifies each transaction supported by program u Transform Analysis l Uses DFD fragments for inputs l Computer program ‘transforms’ inputs into outputs l Charts have input, calculate, and output subtrees Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 16
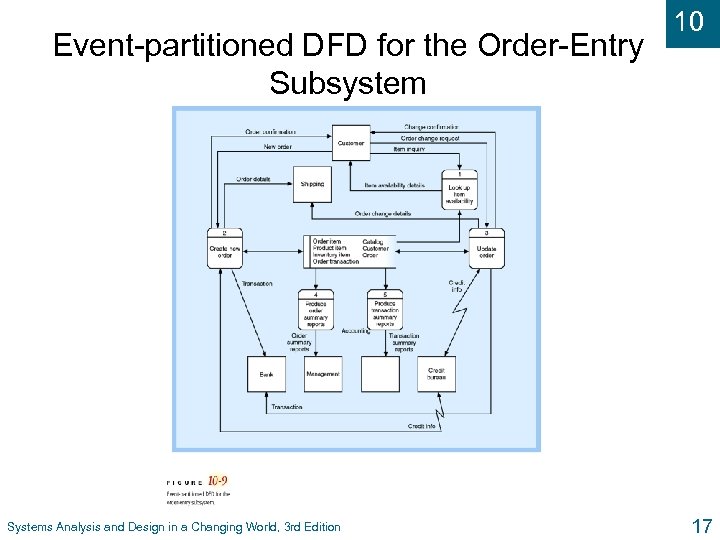 Event-partitioned DFD for the Order-Entry Subsystem Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 17
Event-partitioned DFD for the Order-Entry Subsystem Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 17
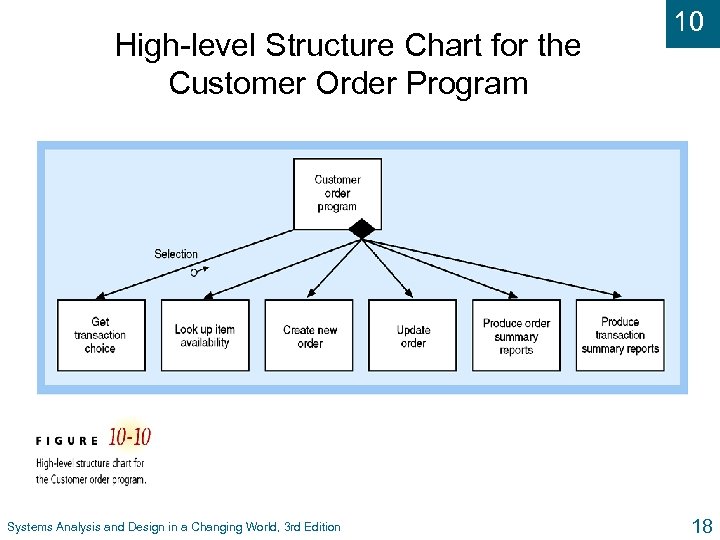 High-level Structure Chart for the Customer Order Program Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 18
High-level Structure Chart for the Customer Order Program Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 18
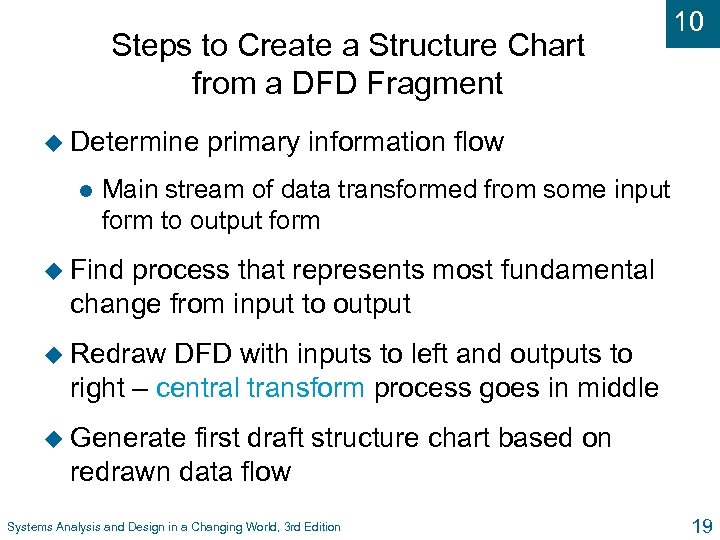 Steps to Create a Structure Chart from a DFD Fragment u Determine l 10 primary information flow Main stream of data transformed from some input form to output form u Find process that represents most fundamental change from input to output u Redraw DFD with inputs to left and outputs to right – central transform process goes in middle u Generate first draft structure chart based on redrawn data flow Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 19
Steps to Create a Structure Chart from a DFD Fragment u Determine l 10 primary information flow Main stream of data transformed from some input form to output form u Find process that represents most fundamental change from input to output u Redraw DFD with inputs to left and outputs to right – central transform process goes in middle u Generate first draft structure chart based on redrawn data flow Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 19
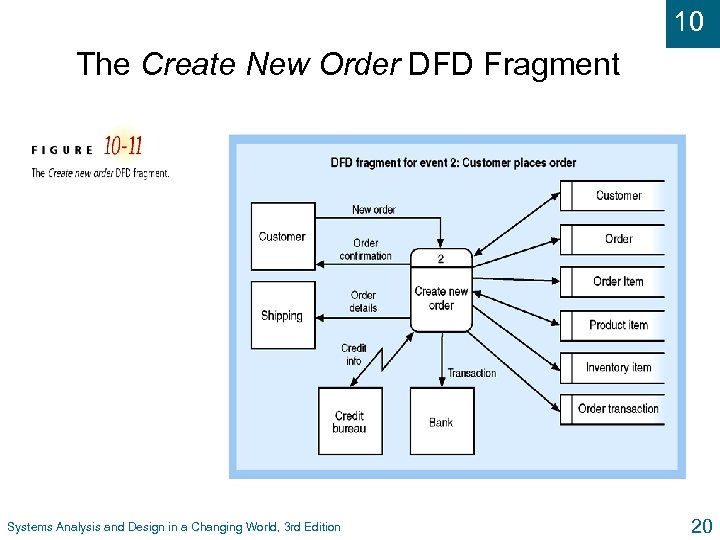 10 The Create New Order DFD Fragment Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 20
10 The Create New Order DFD Fragment Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 20
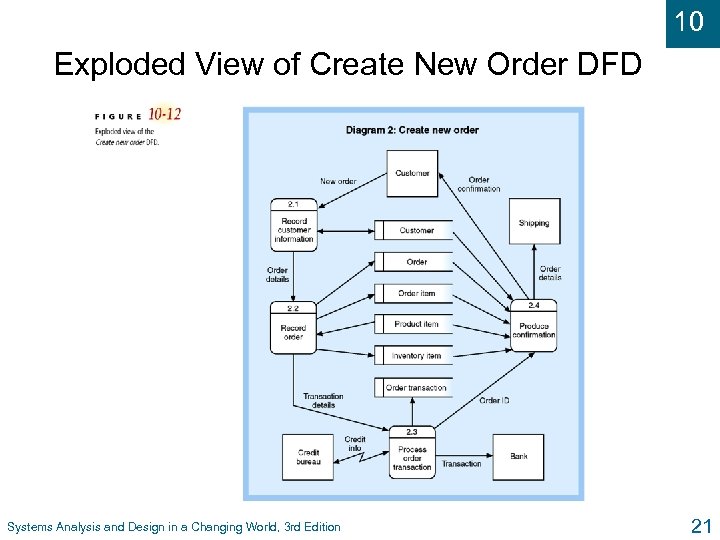 10 Exploded View of Create New Order DFD Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 21
10 Exploded View of Create New Order DFD Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 21
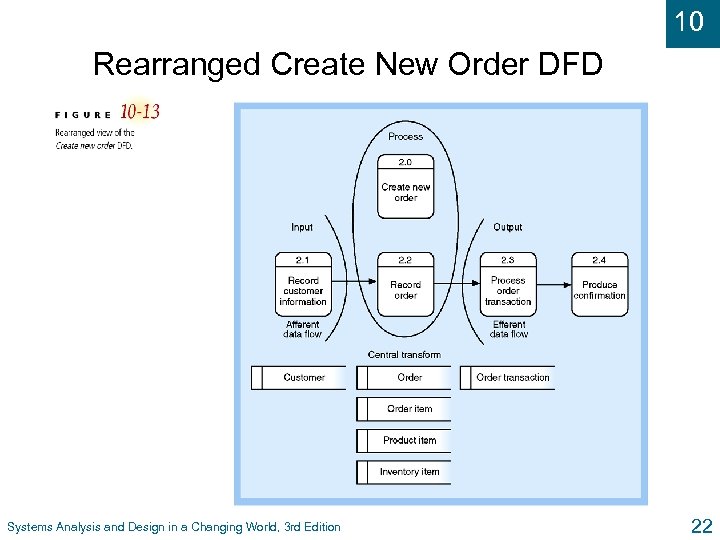 10 Rearranged Create New Order DFD Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 22
10 Rearranged Create New Order DFD Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 22
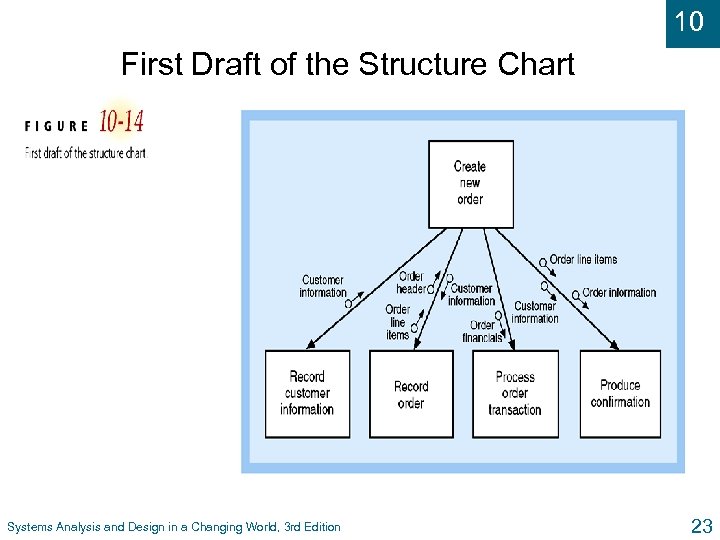 10 First Draft of the Structure Chart Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 23
10 First Draft of the Structure Chart Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 23
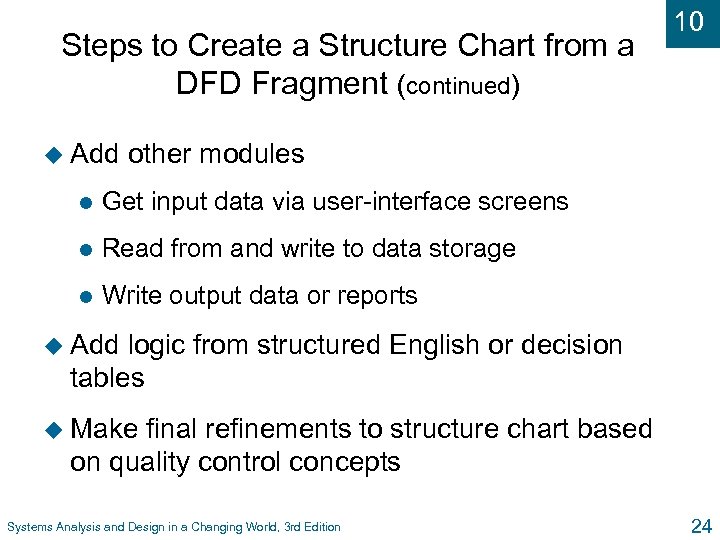 Steps to Create a Structure Chart from a DFD Fragment (continued) u Add 10 other modules l Get input data via user-interface screens l Read from and write to data storage l Write output data or reports u Add logic from structured English or decision tables u Make final refinements to structure chart based on quality control concepts Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 24
Steps to Create a Structure Chart from a DFD Fragment (continued) u Add 10 other modules l Get input data via user-interface screens l Read from and write to data storage l Write output data or reports u Add logic from structured English or decision tables u Make final refinements to structure chart based on quality control concepts Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 24
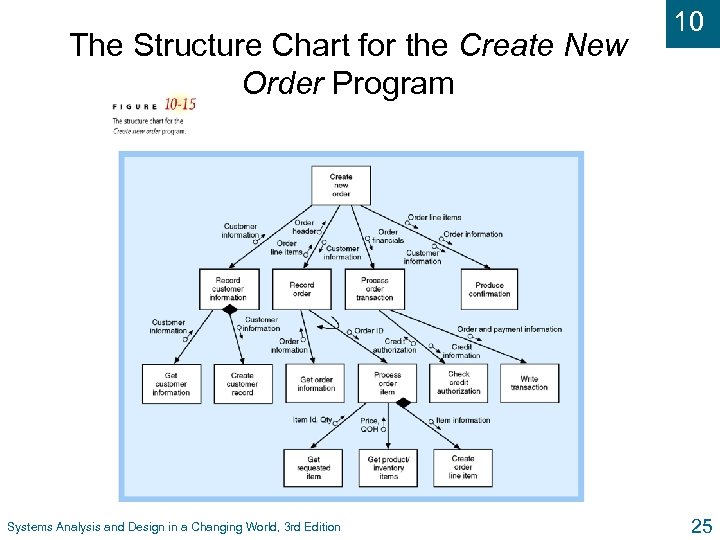 The Structure Chart for the Create New Order Program Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 25
The Structure Chart for the Create New Order Program Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 25
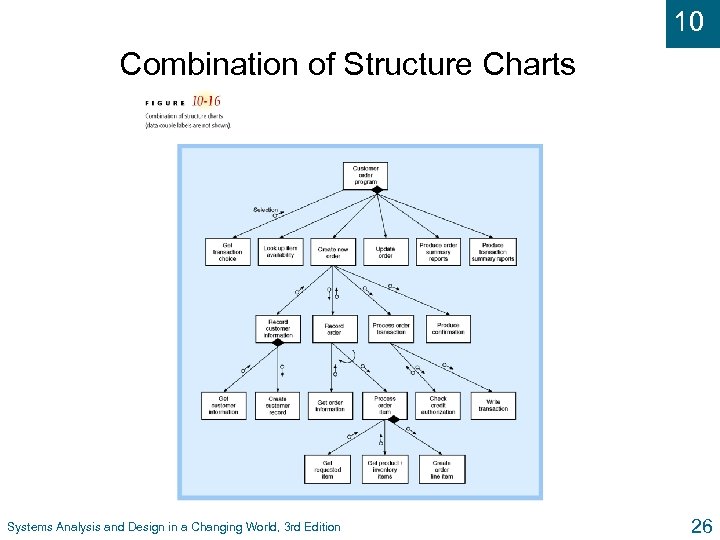 10 Combination of Structure Charts Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 26
10 Combination of Structure Charts Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 26
 10 Evaluating the Quality of a Structure Chart u Module coupling l Measure of how module is connected to other modules in program l Goal is to be loosely coupled u Module cohesion l Measure of internal strength of module l Module performs one defined task l Goal is to be highly cohesive Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 27
10 Evaluating the Quality of a Structure Chart u Module coupling l Measure of how module is connected to other modules in program l Goal is to be loosely coupled u Module cohesion l Measure of internal strength of module l Module performs one defined task l Goal is to be highly cohesive Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 27
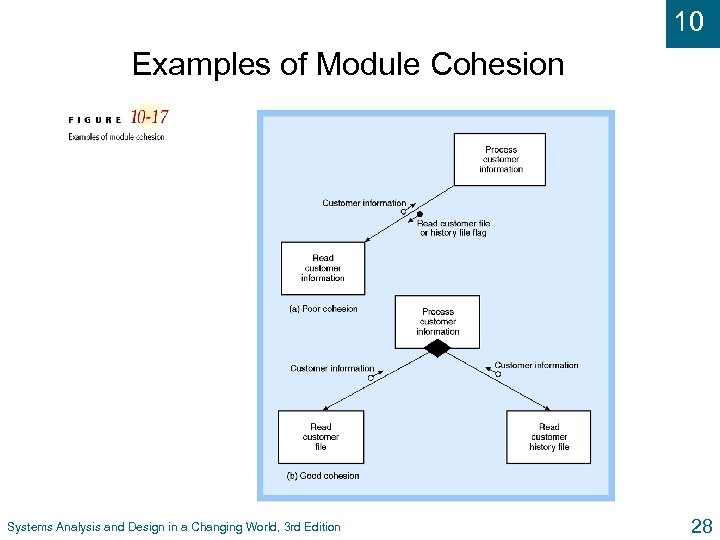 10 Examples of Module Cohesion Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 28
10 Examples of Module Cohesion Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 28
 10 Module Algorithm Design: Pseudocode u Describes internal logic of software modules u Variation of structured English that is closer to programming code u Syntax should mirror development language u Three types of control statements used in structured programming: l Sequence: sequence of executable statements l Decision: if-then-else logic l Iteration: do-until or do-while Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 29
10 Module Algorithm Design: Pseudocode u Describes internal logic of software modules u Variation of structured English that is closer to programming code u Syntax should mirror development language u Three types of control statements used in structured programming: l Sequence: sequence of executable statements l Decision: if-then-else logic l Iteration: do-until or do-while Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 29
 Integrating Structured Application Design with Other Design Tasks 10 u Structure chart must be modified or enhanced to integrate design of user interface and database l Are additional modules needed? l Does pseudocode in modules need modification? l Are additional data couples needed to pass data? u Structure charts and system flowcharts must correspond to planned network architecture l Required protocols, capacity, and security Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 30
Integrating Structured Application Design with Other Design Tasks 10 u Structure chart must be modified or enhanced to integrate design of user interface and database l Are additional modules needed? l Does pseudocode in modules need modification? l Are additional data couples needed to pass data? u Structure charts and system flowcharts must correspond to planned network architecture l Required protocols, capacity, and security Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 30
 10 Three-Layer Design u Three-layer l architecture: View layer, business logic layer, and data layer u Structure charts and system flowcharts describe design decisions and software structuring u Employs multiple programs for user interface, business logic, and data access modules u Modules in different layers communicate over real -time links using well-defined protocols Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 31
10 Three-Layer Design u Three-layer l architecture: View layer, business logic layer, and data layer u Structure charts and system flowcharts describe design decisions and software structuring u Employs multiple programs for user interface, business logic, and data access modules u Modules in different layers communicate over real -time links using well-defined protocols Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 31
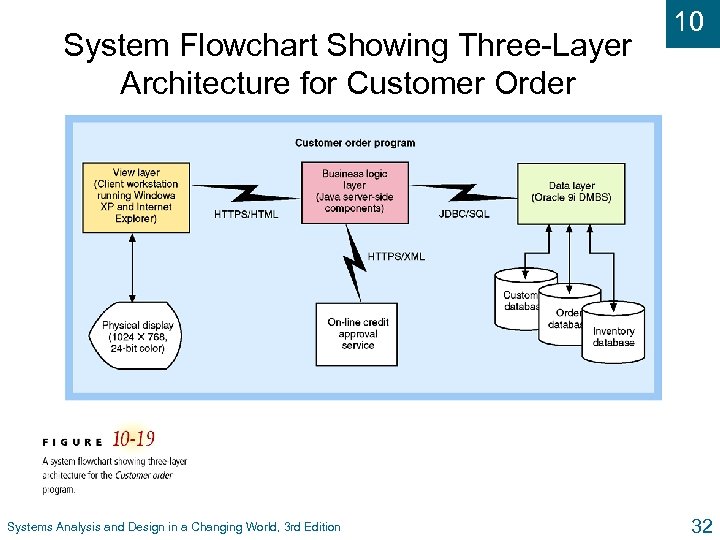 System Flowchart Showing Three-Layer Architecture for Customer Order Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 32
System Flowchart Showing Three-Layer Architecture for Customer Order Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 32
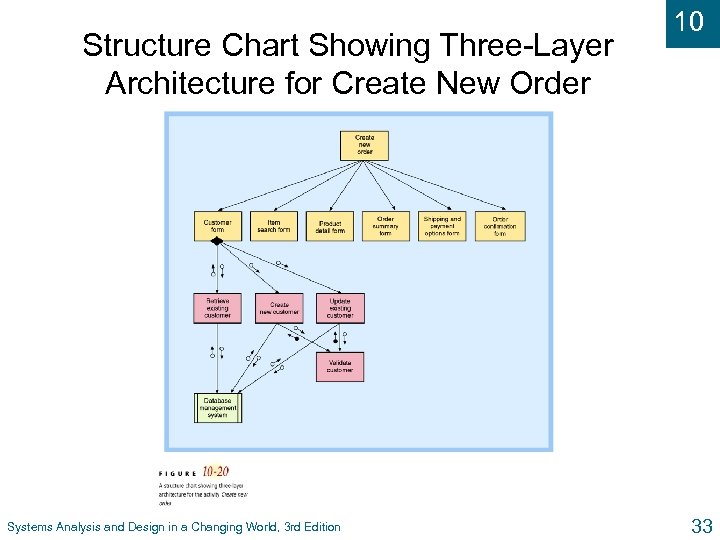 Structure Chart Showing Three-Layer Architecture for Create New Order Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 33
Structure Chart Showing Three-Layer Architecture for Create New Order Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 10 33
 10 Summary u For traditional structured approach to systems design, primary input is data flow diagram l DFD is enhanced by adding system boundary l Designer describes processes within each DFD boundary using one or more structure charts u Structure charts developed using: l Transaction analysis – multiple transaction types l Transform analysis – single transaction from input to output Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 34
10 Summary u For traditional structured approach to systems design, primary input is data flow diagram l DFD is enhanced by adding system boundary l Designer describes processes within each DFD boundary using one or more structure charts u Structure charts developed using: l Transaction analysis – multiple transaction types l Transform analysis – single transaction from input to output Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 34
 10 Summary (continued) u Structure charts may be based on three-layer architecture l Modules will be clearly identified by layer l Structure chart may be decomposed if layers execute on multiple systems u Structured design may also include: l System flowcharts to show data movement l Module pseudocode to describe internal logic of structure chart module Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 35
10 Summary (continued) u Structure charts may be based on three-layer architecture l Modules will be clearly identified by layer l Structure chart may be decomposed if layers execute on multiple systems u Structured design may also include: l System flowcharts to show data movement l Module pseudocode to describe internal logic of structure chart module Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 3 rd Edition 35


