 1. What is Management? Who is a manager? 2. Four Managerial Functions Lectures # 1 2 Aida Zakirova, associate professor, c. e. s. , MPA,
1. What is Management? Who is a manager? 2. Four Managerial Functions Lectures # 1 2 Aida Zakirova, associate professor, c. e. s. , MPA,
 Management is • the process of dealing with or controlling things or people; • the control and organizing of a business or other organization; • getting work done through others. • The managers also have to be concerned with efficiency and effectiveness in the work process.
Management is • the process of dealing with or controlling things or people; • the control and organizing of a business or other organization; • getting work done through others. • The managers also have to be concerned with efficiency and effectiveness in the work process.
 Efficiency (КПД) • Efficiency is getting work done with a minimum of effort, expense, or waste.
Efficiency (КПД) • Efficiency is getting work done with a minimum of effort, expense, or waste.
 Effectiveness Managers must also strive for effectiveness, which is accomplishing tasks that help fulfill organizational objectives.
Effectiveness Managers must also strive for effectiveness, which is accomplishing tasks that help fulfill organizational objectives.
 Management is • The process of using organizational resources to achieve organizational objectives through the functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. • Specific discipline (our course) • People who manage (Top-management). • Career choice (major 5 M 050700 Management).
Management is • The process of using organizational resources to achieve organizational objectives through the functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. • Specific discipline (our course) • People who manage (Top-management). • Career choice (major 5 M 050700 Management).
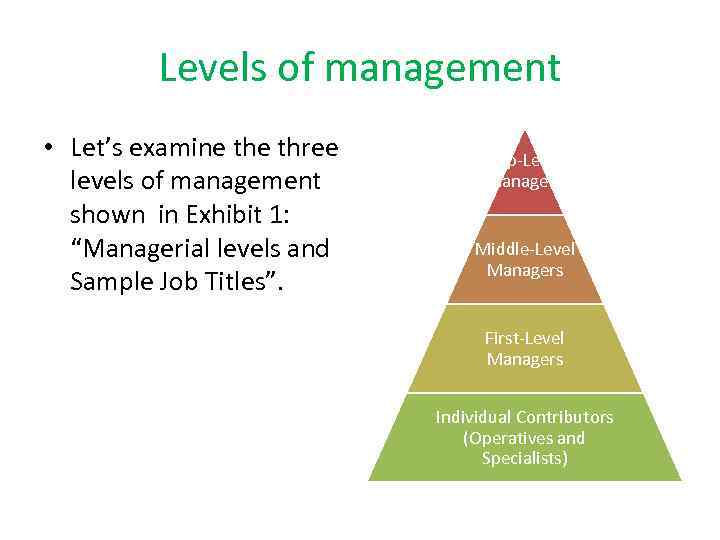 Levels of management • Let’s examine three levels of management shown in Exhibit 1: “Managerial levels and Sample Job Titles”. Top Level managers Middle Level Managers First Level Managers Individual Contributors (Operatives and Specialists)
Levels of management • Let’s examine three levels of management shown in Exhibit 1: “Managerial levels and Sample Job Titles”. Top Level managers Middle Level Managers First Level Managers Individual Contributors (Operatives and Specialists)
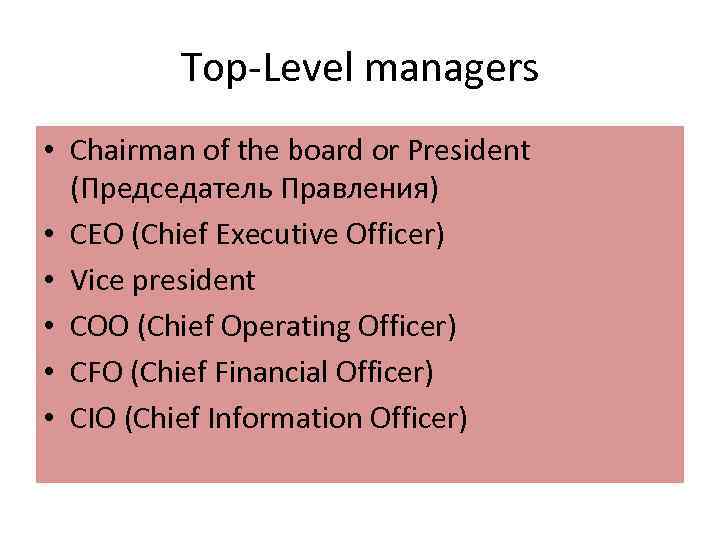 Top Level managers • Chairman of the board or President (Председатель Правления) • CEO (Chief Executive Officer) • Vice president • COO (Chief Operating Officer) • CFO (Chief Financial Officer) • CIO (Chief Information Officer)
Top Level managers • Chairman of the board or President (Председатель Правления) • CEO (Chief Executive Officer) • Vice president • COO (Chief Operating Officer) • CFO (Chief Financial Officer) • CIO (Chief Information Officer)
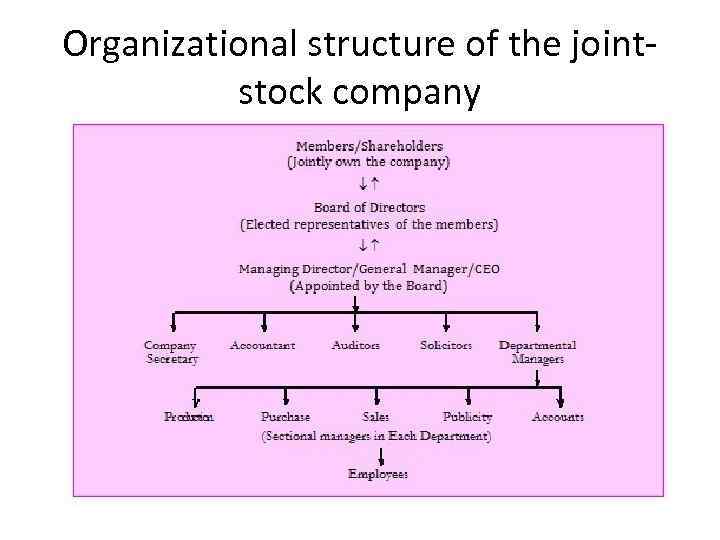 Organizational structure of the joint stock company
Organizational structure of the joint stock company
 Middle Level Managers • Director (руководитель) • Branch director (руководитель подразделения) • Department chairperson (председатель) • Chief of surgery (подразделение) • Team leader
Middle Level Managers • Director (руководитель) • Branch director (руководитель подразделения) • Department chairperson (председатель) • Chief of surgery (подразделение) • Team leader
 First Level Managers • Supervisor • Office manager • Crew chief
First Level Managers • Supervisor • Office manager • Crew chief
 Individual Contributors (Operatives and Specialists) • Tool and die maker (инструментальщик) • Cook (повар) • Word processing technician (спец по текстообработке) • Assembler (рабочий сборщик)
Individual Contributors (Operatives and Specialists) • Tool and die maker (инструментальщик) • Cook (повар) • Word processing technician (спец по текстообработке) • Assembler (рабочий сборщик)
 Types of managers • • Functional and General managers Administrators Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners Team Leader
Types of managers • • Functional and General managers Administrators Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners Team Leader
 Functional and General managers • Functional managers supervise the work of employees engaged in specialized activities, such accounting, engineering, information systems, food preparation, marketing, and sales. A functional manager is a manager of specialists and of their support team, such as office assistants. • General managers are responsible for the work of several different groups that perform a variety of functions, e. g. a plant general manager. Reporting to the plant general manager are various departments engaged in both specialized an generalized work, such as manufacturing, engineering, labor relations, quality control, safety, and information systems.
Functional and General managers • Functional managers supervise the work of employees engaged in specialized activities, such accounting, engineering, information systems, food preparation, marketing, and sales. A functional manager is a manager of specialists and of their support team, such as office assistants. • General managers are responsible for the work of several different groups that perform a variety of functions, e. g. a plant general manager. Reporting to the plant general manager are various departments engaged in both specialized an generalized work, such as manufacturing, engineering, labor relations, quality control, safety, and information systems.
 Administrators • An administrator is typically a manager who works in a public (government) or nonprofit organization rather than in a business firm. Among these man agerial positions are hospital administrator and housing administrator. • An employee is not an administrator in the managerial sense unless he or she supervises others.
Administrators • An administrator is typically a manager who works in a public (government) or nonprofit organization rather than in a business firm. Among these man agerial positions are hospital administrator and housing administrator. • An employee is not an administrator in the managerial sense unless he or she supervises others.
 Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners • An entrepreneur is a person who founds and operates an innovative business. You need an innovative idea to be an entrepreneur. • Similar to an entrepreneur, the owner of a small business becomes a manager when the firm grows to include several employees.
Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners • An entrepreneur is a person who founds and operates an innovative business. You need an innovative idea to be an entrepreneur. • Similar to an entrepreneur, the owner of a small business becomes a manager when the firm grows to include several employees.
 Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners • A major characteristic of both entrepreneurs and small business owners is their passion for the work. • These types of managers will usually have a single minded drive to solve a problem. single-minded - целеустремлённый
Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners • A major characteristic of both entrepreneurs and small business owners is their passion for the work. • These types of managers will usually have a single minded drive to solve a problem. single-minded - целеустремлённый
 The process of management • To understand what managers do is to regard (рассмотреть) their work as a process. • A process is a series of actions that achieve something (making a profit, provide a service, etc. ) • To achieve an objective, the manager uses resources and carry out four major managerial functions.
The process of management • To understand what managers do is to regard (рассмотреть) their work as a process. • A process is a series of actions that achieve something (making a profit, provide a service, etc. ) • To achieve an objective, the manager uses resources and carry out four major managerial functions.
 A manager’s resources Can be divided into four types: • Human • Financial • Physical • Informational
A manager’s resources Can be divided into four types: • Human • Financial • Physical • Informational
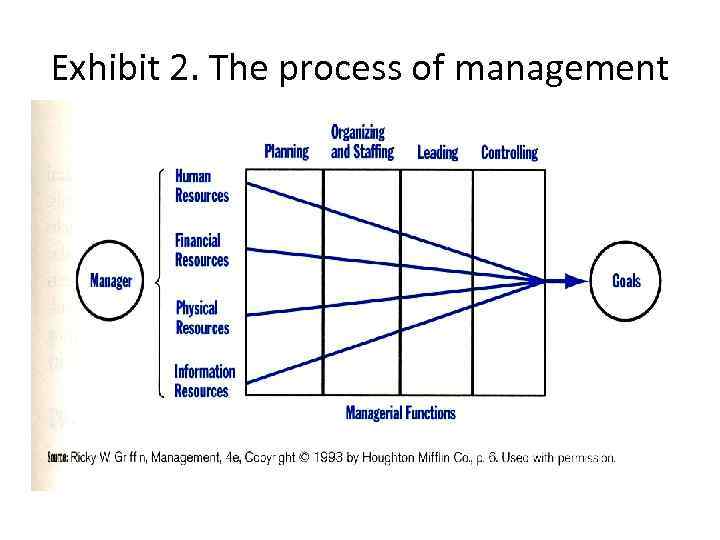 Exhibit 2. The process of management
Exhibit 2. The process of management
 The Four Managerial Functions • Exhibit 2 shows the 4 major resources in the context of the management process. To accomplish goals, the manager performs four managerial functions. • These functions are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
The Four Managerial Functions • Exhibit 2 shows the 4 major resources in the context of the management process. To accomplish goals, the manager performs four managerial functions. • These functions are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
 Planning • Planning involves setting goals and figuring out ways of reaching them. Planning, considered the central function of management, pervades (наполняет) every thing a manager does. In planning, a manager looks to the future, saying, “Here is what we want to achieve, and here is how we are going to do it. ”
Planning • Planning involves setting goals and figuring out ways of reaching them. Planning, considered the central function of management, pervades (наполняет) every thing a manager does. In planning, a manager looks to the future, saying, “Here is what we want to achieve, and here is how we are going to do it. ”
 Planning • Decision making is usually a component of planning, because choices have to be made in the process of finalizing plans. • The importance of planning expands as it contributes heavily (в большей степени) to performing the other management functions. For example, managers must make plans to do an effective job of staffing the organization. Planning is also part of marketing.
Planning • Decision making is usually a component of planning, because choices have to be made in the process of finalizing plans. • The importance of planning expands as it contributes heavily (в большей степени) to performing the other management functions. For example, managers must make plans to do an effective job of staffing the organization. Planning is also part of marketing.
 Organizing and Staffing • Organizing is the process of making sure the necessary human and physical resources are available to carry out a plan and achieve organizational goals. Organizing also involves assigning activities, dividing work into specific jobs and tasks, and specifying who has the authority to accomplish certain tasks.
Organizing and Staffing • Organizing is the process of making sure the necessary human and physical resources are available to carry out a plan and achieve organizational goals. Organizing also involves assigning activities, dividing work into specific jobs and tasks, and specifying who has the authority to accomplish certain tasks.
 Organizing and Staffing • Another major aspect of organizing is grouping activities into departments or some other logical subdivision. The staffing function ensures the avail ability of necessary human resources to achieve organizational goals. Hiring people for jobs is a typical staffing activity. Staffing is such a major activity that it is sometimes classified as a function separate from organizing.
Organizing and Staffing • Another major aspect of organizing is grouping activities into departments or some other logical subdivision. The staffing function ensures the avail ability of necessary human resources to achieve organizational goals. Hiring people for jobs is a typical staffing activity. Staffing is such a major activity that it is sometimes classified as a function separate from organizing.
 Leading • Leading means influencing others to achieve organizational objectives. As a consequence, it involves energizing, directing, persuading others, and creating a vision. Leadership involves dozens of interpersonal processes: motivating, communicating, coaching, and showing group members how they can reach their goals.
Leading • Leading means influencing others to achieve organizational objectives. As a consequence, it involves energizing, directing, persuading others, and creating a vision. Leadership involves dozens of interpersonal processes: motivating, communicating, coaching, and showing group members how they can reach their goals.
 Leading • Leadership is such a key component of managerial work that management is sometimes seen as accomplishing results through people. The leadership aspect of management focuses on inspiring people and bringing about change, whereas the other three functions focus more on maintaining a stable system.
Leading • Leadership is such a key component of managerial work that management is sometimes seen as accomplishing results through people. The leadership aspect of management focuses on inspiring people and bringing about change, whereas the other three functions focus more on maintaining a stable system.
 Leading • Although leadership deals heavily with persuasion and inspiration, the leader also executes the visions and other ideas for change he or she formu lates. As explained by business executive Larry Bossidy and consultant Ram Charan, visionaries often fail because they do not translate their strategies (master plans) into results. "
Leading • Although leadership deals heavily with persuasion and inspiration, the leader also executes the visions and other ideas for change he or she formu lates. As explained by business executive Larry Bossidy and consultant Ram Charan, visionaries often fail because they do not translate their strategies (master plans) into results. "
 Controlling • Controlling generally involves comparing actual performance to a prede termined standard. Any significant difference between actual and desired performance would prompt (побуждать) a manager to take corrective action. He or she might, for example, increase advertising to boost lower than anticipated (низкие) sales.
Controlling • Controlling generally involves comparing actual performance to a prede termined standard. Any significant difference between actual and desired performance would prompt (побуждать) a manager to take corrective action. He or she might, for example, increase advertising to boost lower than anticipated (низкие) sales.
 Controlling • A secondary aspect of controlling is determining whether the original plan needs revision, given the realities of the day. The controlling function sometimes causes a manager to return to the planning function temporarily to fine tune (настроить, отлаживать) the original plan.
Controlling • A secondary aspect of controlling is determining whether the original plan needs revision, given the realities of the day. The controlling function sometimes causes a manager to return to the planning function temporarily to fine tune (настроить, отлаживать) the original plan.


