6db4719a77a85c18c746f75fcbde1e8c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
1 Valuation and Characteristics of Bonds Chapter 7

General Valuation: The following comments are valid for all kind of assets. 3 v Book Value v. Stated value from the firm’s Balance Sheet v Market Value v. The price for the asset at any given time--determined by supply and demand in the marketplace. Asset can be bought or sold at this price. v Intrinsic Value v. Present value of the asset’s expected cash flow v. Investor estimates cash flows v. Investor determines required rate based on risk of asset and market conditions.

4 In a perfect market where all investors have the same expectations & risk aversion: Market Value = Intrinsic Value

Bonds v Debt Instruments v Bondholders are lending to the corporation (or, governments) money for some stated period of time. v Liquid Asset v Corporate Bonds can be traded in the secondary market. v Price at which a given bond trades is determined by market conditions and terms of the bond. 5

Bond Terminology 6 v Par Value v. Usually $1, 000. Also called the Face Value v Coupon Interest Rate v. Borrowers (firms) typically make periodic payments to the bondholders. Coupon rate is the percent of face value paid every year. v Maturity v. Time at which the maturity value (Par Value) is paid to the bondholder. v Indenture v. Document which details the legal obligation of the corporation to the bondholders. The indenture lists all the terms and conditions of the bond.

Types of Bonds v Debentures v Subordinated Debenture v Mortgage Bond v Eurobond v Convertible Bond v Zero Coupon Bonds v Junk Bond 7
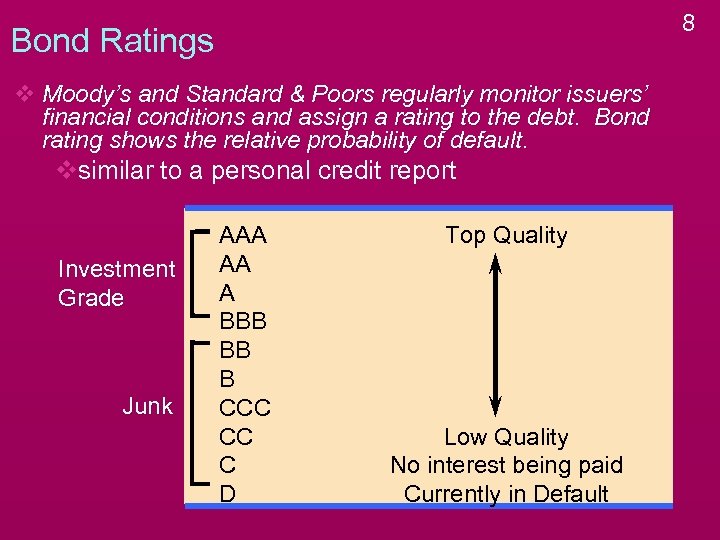
8 Bond Ratings v Moody’s and Standard & Poors regularly monitor issuers’ financial conditions and assign a rating to the debt. Bond rating shows the relative probability of default. vsimilar to a personal credit report Investment Grade Junk AAA AA A BBB BB B CCC CC C D Top Quality Low Quality No interest being paid Currently in Default
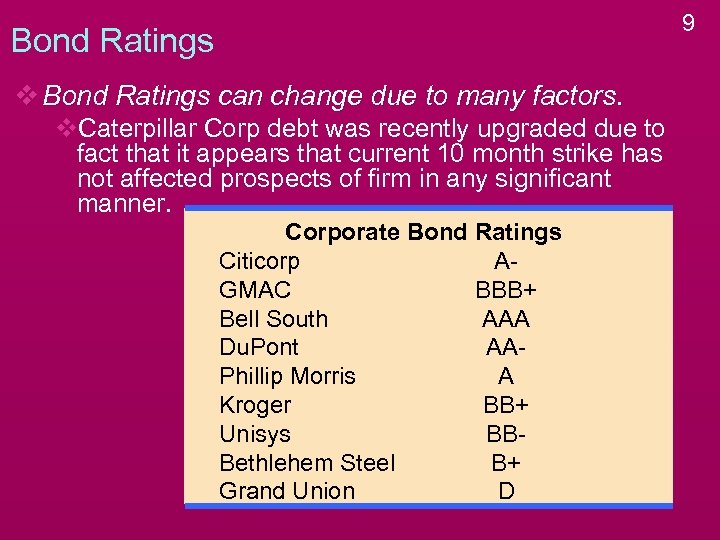
9 Bond Ratings v Bond Ratings can change due to many factors. v. Caterpillar Corp debt was recently upgraded due to fact that it appears that current 10 month strike has not affected prospects of firm in any significant manner. Corporate Bond Ratings Citicorp AGMAC BBB+ Bell South AAA Du. Pont AAPhillip Morris A Kroger BB+ Unisys BBBethlehem Steel B+ Grand Union D

10 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Company Issuing the Bond

11 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Coupon Interest Rate
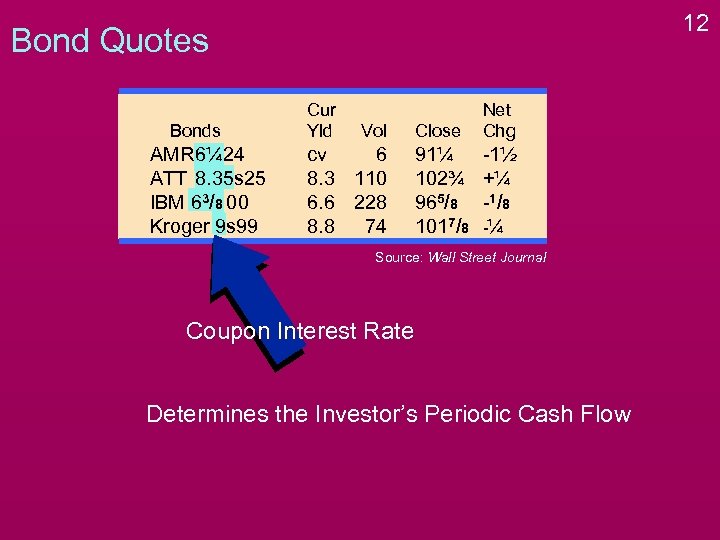
12 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Coupon Interest Rate Determines the Investor’s Periodic Cash Flow

13 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Coupon Interest Rate Determines the Investor’s Periodic Cash Flow = Interest Payment = Coupon Rate x Par =. 06375 x 1000 = $63. 75/Year

14 Bond Quotes Cur Yld Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Year of Maturity

15 Bond Quotes Cur Yld Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Year of Maturity Determines the Time frame for the Investment 00 = year 2000, therefore in 1995 this is a 5 year investment
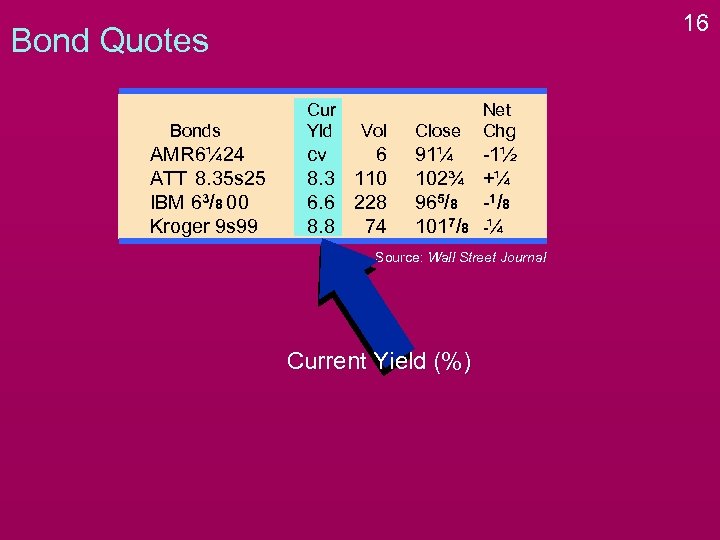
16 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Current Yield (%)
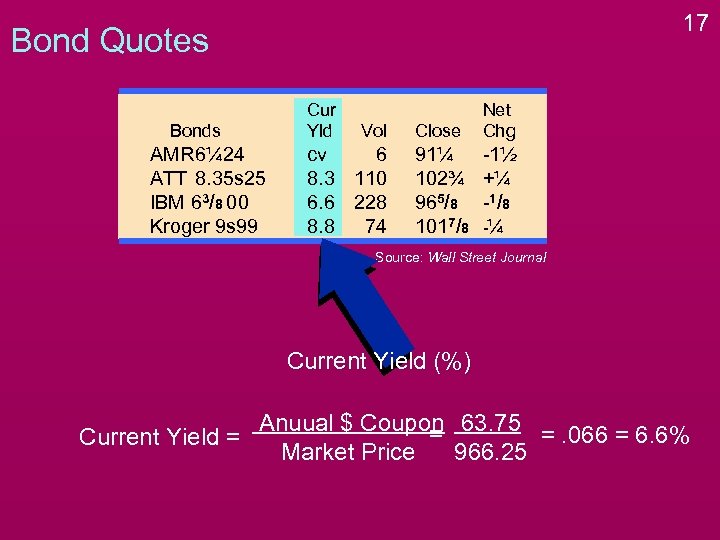
17 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Current Yield (%) Anuual $ Coupon 63. 75 = =. 066 = 6. 6% Current Yield = Market Price 966. 25

18 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Daily Trading Volume

19 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Daily Closing Market Price

20 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Daily Closing Market Price Expressed as a % of Par

21 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Daily Closing Market Price Expressed as a % of Par $Price = 965/8 x 10 = $966. 25

22 Bond Quotes Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Change from Previous Day’s Closing Price
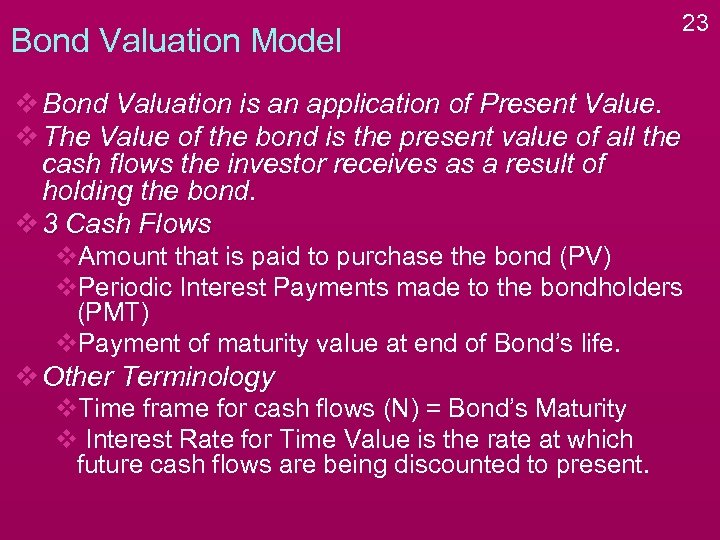
Bond Valuation Model 23 v Bond Valuation is an application of Present Value. v The Value of the bond is the present value of all the cash flows the investor receives as a result of holding the bond. v 3 Cash Flows v. Amount that is paid to purchase the bond (PV) v. Periodic Interest Payments made to the bondholders (PMT) v. Payment of maturity value at end of Bond’s life. v Other Terminology v. Time frame for cash flows (N) = Bond’s Maturity v Interest Rate for Time Value is the rate at which future cash flows are being discounted to present.
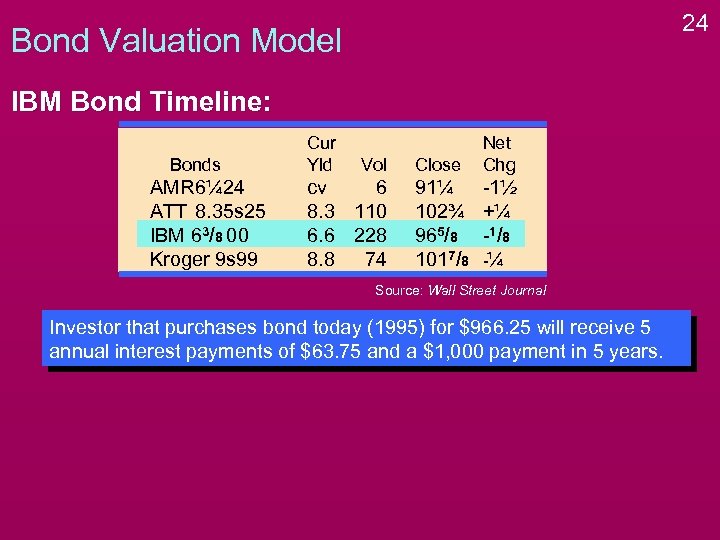
24 Bond Valuation Model IBM Bond Timeline: Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Cur Yld Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Investor that purchases bond today (1995) for $966. 25 will receive 5 annual interest payments of $63. 75 and a $1, 000 payment in 5 years.
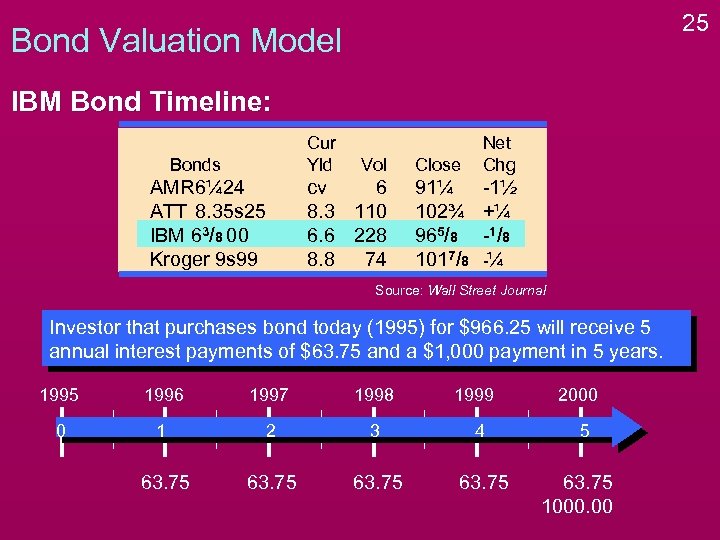
25 Bond Valuation Model IBM Bond Timeline: Cur Yld Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal Investor that purchases bond today (1995) for $966. 25 will receive 5 annual interest payments of $63. 75 and a $1, 000 payment in 5 years. 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 0 1 2 3 4 63. 75 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00
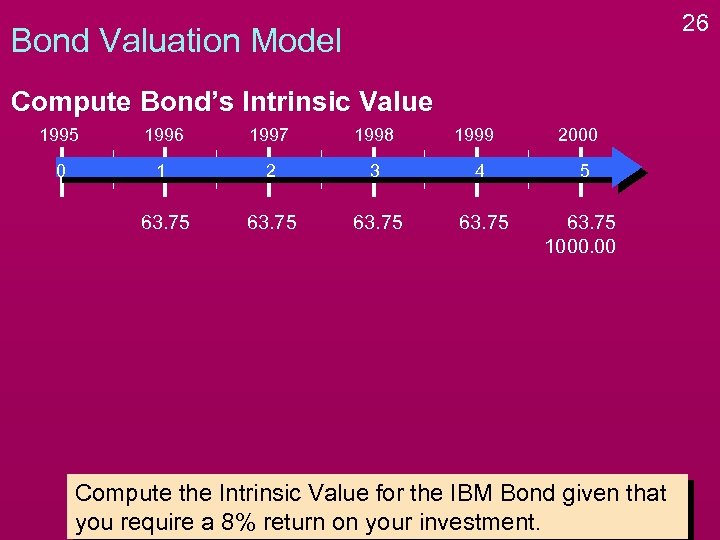
26 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the IBM Bond given that you require a 8% return on your investment.
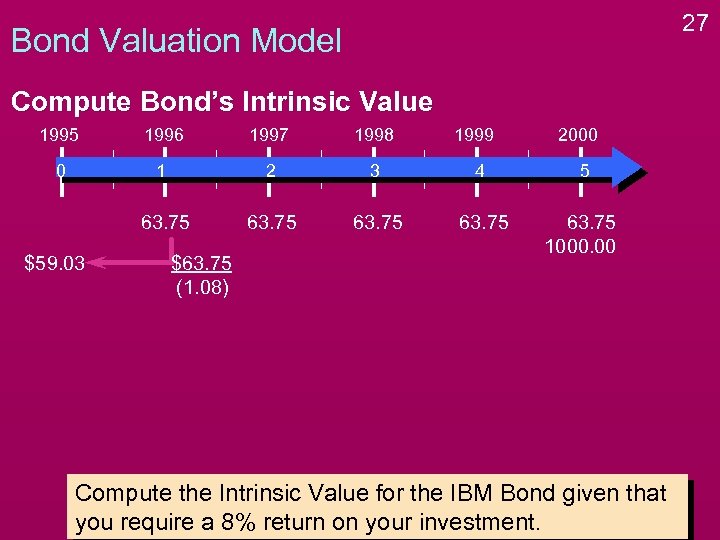
27 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $59. 03 $63. 75 (1. 08) 1999 2000 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the IBM Bond given that you require a 8% return on your investment.
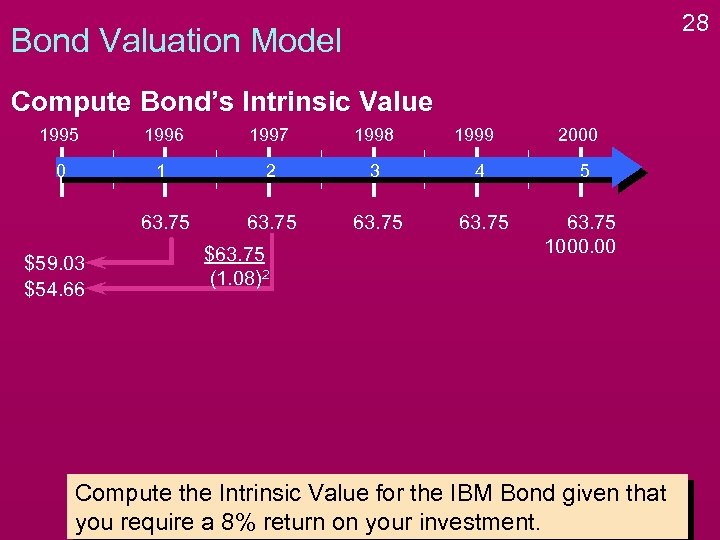
28 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $59. 03 $54. 66 $63. 75 (1. 08)2 1999 2000 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the IBM Bond given that you require a 8% return on your investment.
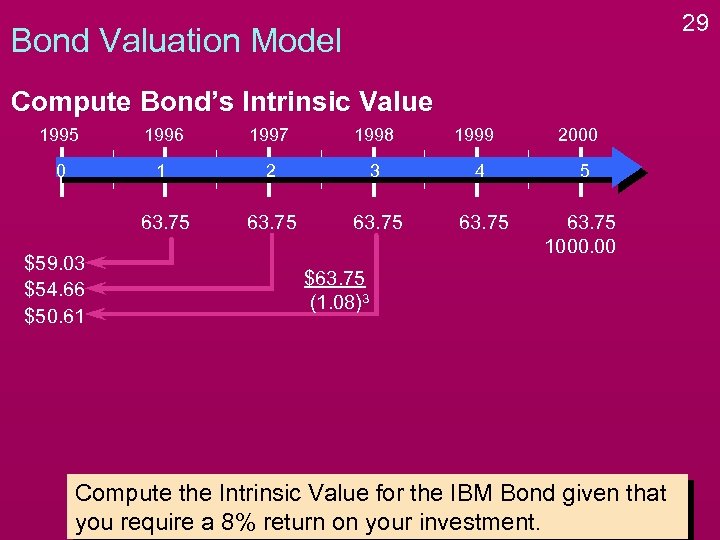
29 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $59. 03 $54. 66 $50. 61 1999 2000 $63. 75 (1. 08)3 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the IBM Bond given that you require a 8% return on your investment.
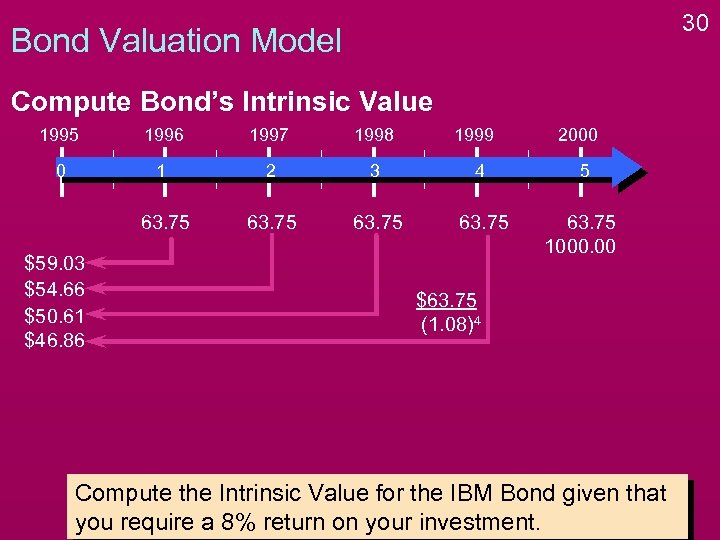
30 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $59. 03 $54. 66 $50. 61 $46. 86 1999 2000 $63. 75 (1. 08)4 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the IBM Bond given that you require a 8% return on your investment.
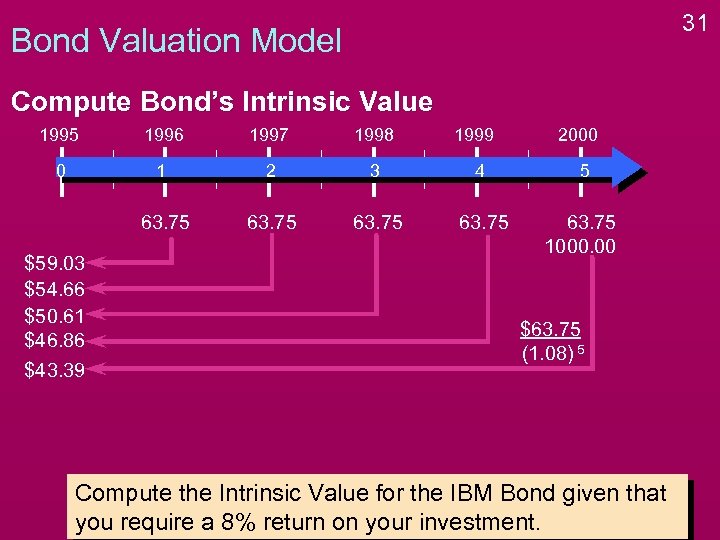
31 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $59. 03 $54. 66 $50. 61 $46. 86 $43. 39 1999 2000 $63. 75 (1. 08) 5 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the IBM Bond given that you require a 8% return on your investment.
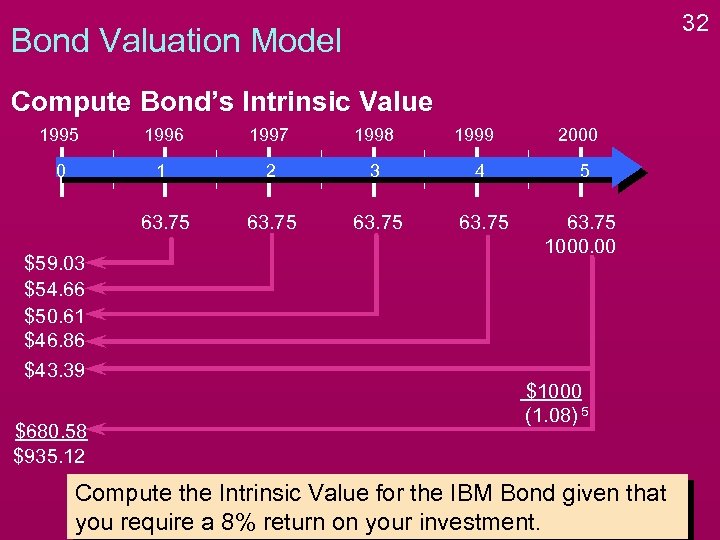
32 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $59. 03 $54. 66 $50. 61 $46. 86 $43. 39 $680. 58 $935. 12 1999 2000 $1000 (1. 08) 5 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the IBM Bond given that you require a 8% return on your investment.
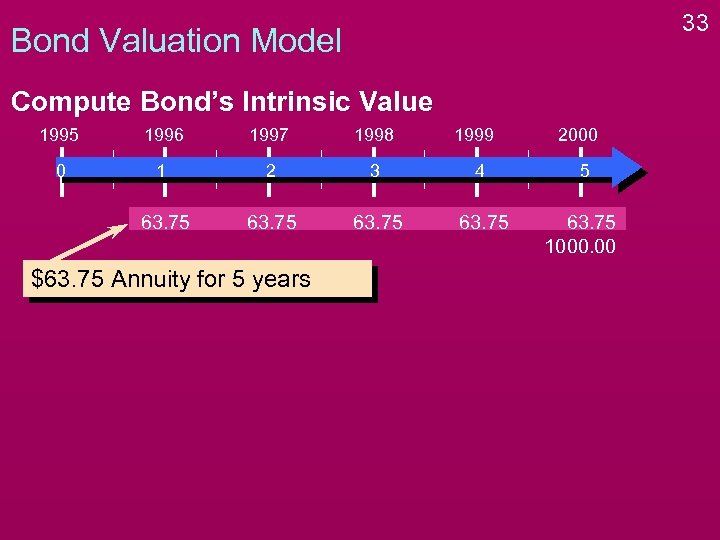
33 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $63. 75 Annuity for 5 years 1999 2000
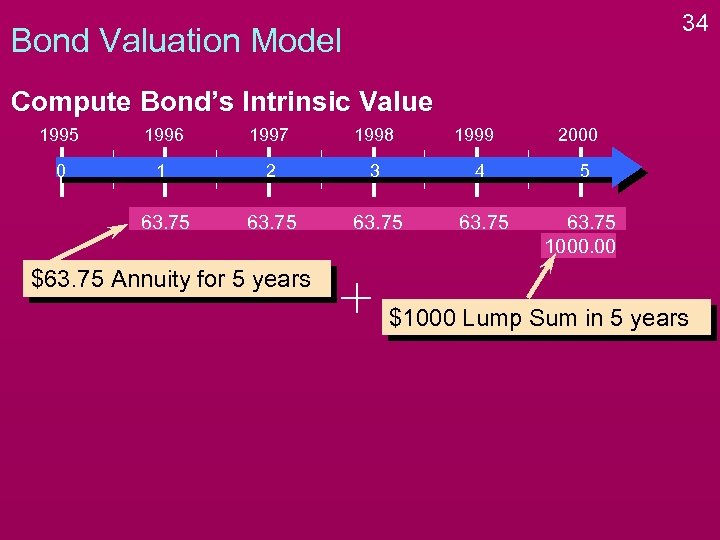
34 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $63. 75 Annuity for 5 years $1000 Lump Sum in 5 years
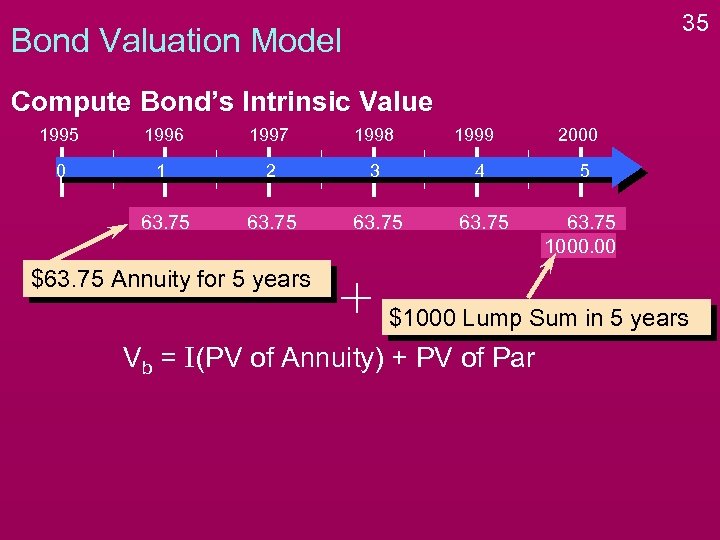
35 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $63. 75 Annuity for 5 years $1000 Lump Sum in 5 years Vb = I(PV of Annuity) + PV of Par
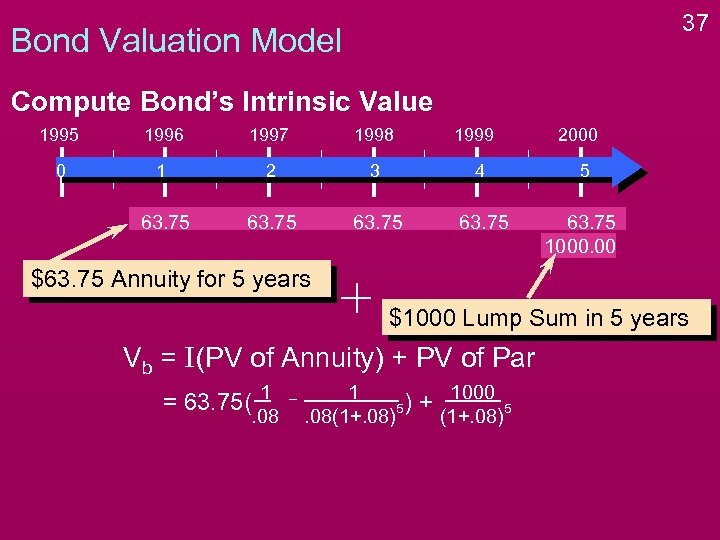
37 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $63. 75 Annuity for 5 years $1000 Lump Sum in 5 years Vb = I(PV of Annuity) + PV of Par = 63. 75( 1 . 08 1 5). 08(1+. 08) + 1000 (1+. 08) 5
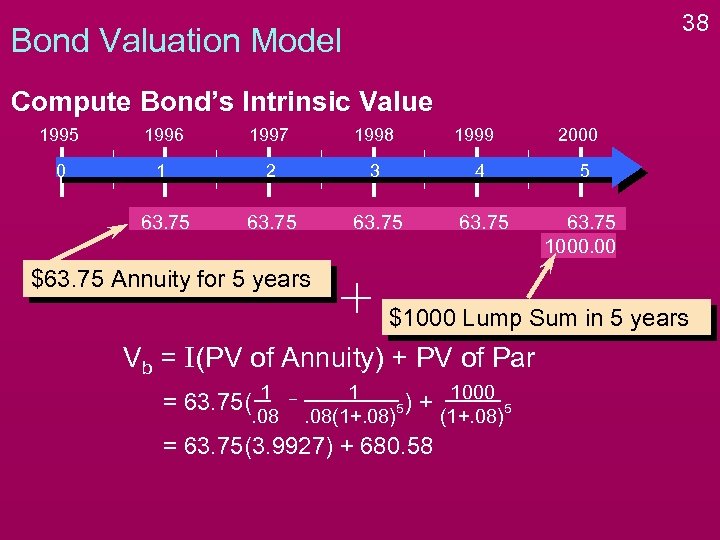
38 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $63. 75 Annuity for 5 years $1000 Lump Sum in 5 years Vb = I(PV of Annuity) + PV of Par = 63. 75( 1 . 08 1 5). 08(1+. 08) + 1000 = 63. 75(3. 9927) + 680. 58 (1+. 08) 5
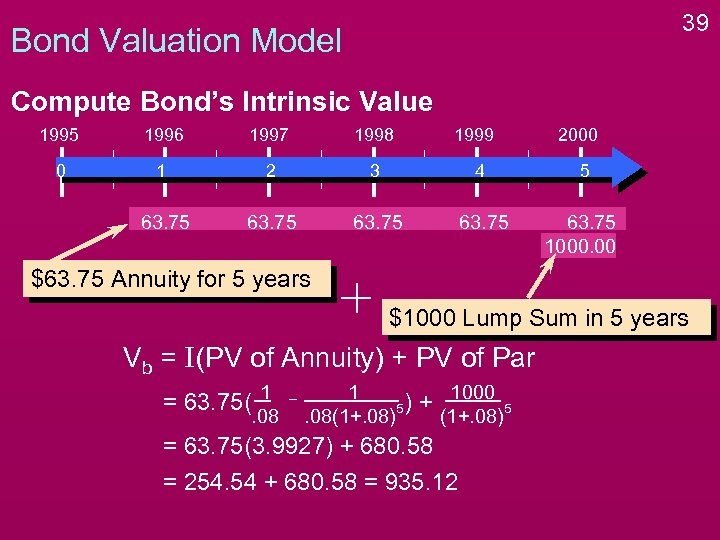
39 Bond Valuation Model Compute Bond’s Intrinsic Value 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 0 1 2 3 4 5 63. 75 1000. 00 $63. 75 Annuity for 5 years $1000 Lump Sum in 5 years Vb = I(PV of Annuity) + PV of Par = 63. 75( 1 . 08 1 5). 08(1+. 08) + 1000 (1+. 08) = 63. 75(3. 9927) + 680. 58 = 254. 54 + 680. 58 = 935. 12 5
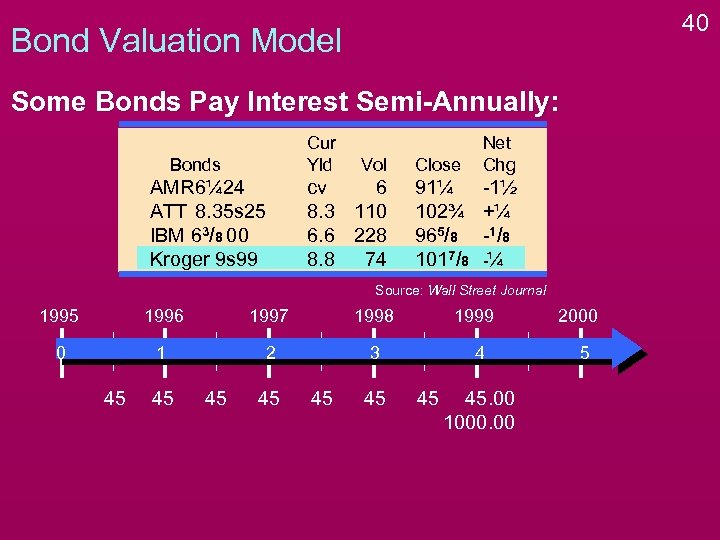
40 Bond Valuation Model Some Bonds Pay Interest Semi-Annually: Cur Yld Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 45 45 45 1999 4 45 45. 00 1000. 00 2000 5
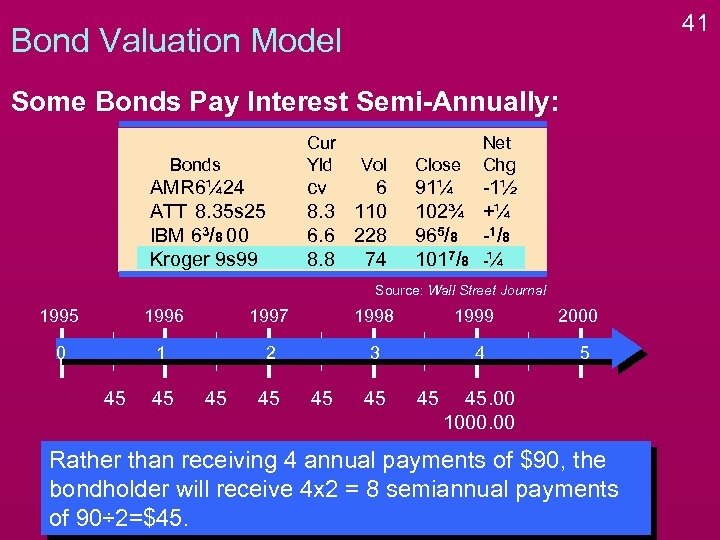
41 Bond Valuation Model Some Bonds Pay Interest Semi-Annually: Cur Yld Bonds AMR 6¼ 24 ATT 8. 35 s 25 IBM 63/8 00 Kroger 9 s 99 Vol cv 6 8. 3 110 6. 6 228 8. 8 74 Close Net Chg 91¼ 102¾ 965/8 1017/8 -1½ +¼ -1 / 8 -¼ Source: Wall Street Journal 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 45 45 45 1999 4 45 2000 5 45. 00 1000. 00 Rather than receiving 4 annual payments of $90, the bondholder will receive 4 x 2 = 8 semiannual payments of 90÷ 2=$45.
42 Bond Valuation Model Some Bonds Pay Interest Semi-Annually: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 45 45 45 1999 4 45 2000 5 45. 00 1000. 00 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the Kroger Bond given that you require a 10% return on your investment.
43 Bond Valuation Model Some Bonds Pay Interest Semi-Annually: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 45 45 45 1999 4 45 2000 5 45. 00 1000. 00 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the Kroger Bond given that you require a 10% return on your investment. Since interest is received every 6 months, need to use semi-annual compounding
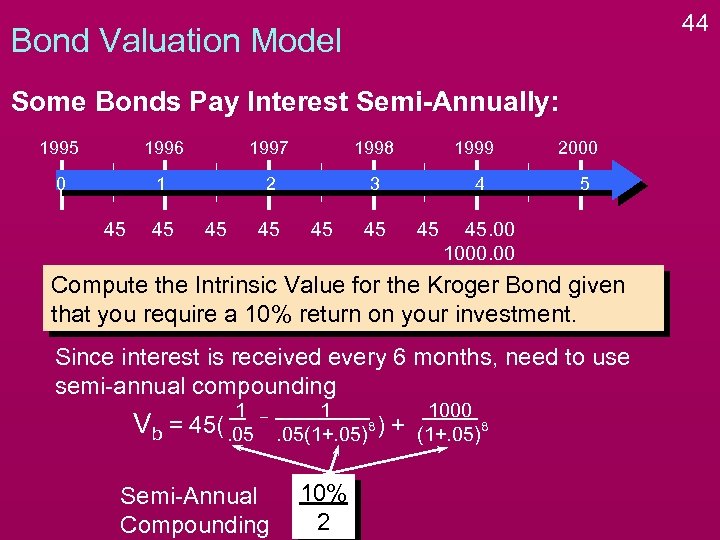
44 Bond Valuation Model Some Bonds Pay Interest Semi-Annually: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 45 45 45 1999 4 45 45 2000 5 45. 00 1000. 00 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the Kroger Bond given that you require a 10% return on your investment. Since interest is received every 6 months, need to use semi-annual compounding Vb = 1 45(. 05 Semi-Annual Compounding 1 8. 05(1+. 05) ) 10% 2 + 1000 8 (1+. 05)
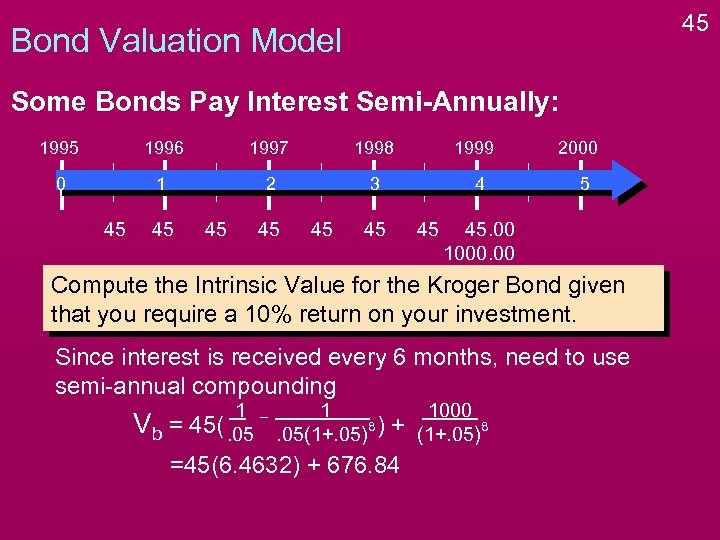
45 Bond Valuation Model Some Bonds Pay Interest Semi-Annually: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 45 45 45 1999 4 45 45 2000 5 45. 00 1000. 00 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the Kroger Bond given that you require a 10% return on your investment. Since interest is received every 6 months, need to use semi-annual compounding Vb = 1 45(. 05 1 8. 05(1+. 05) ) + =45(6. 4632) + 676. 84 1000 8 (1+. 05)
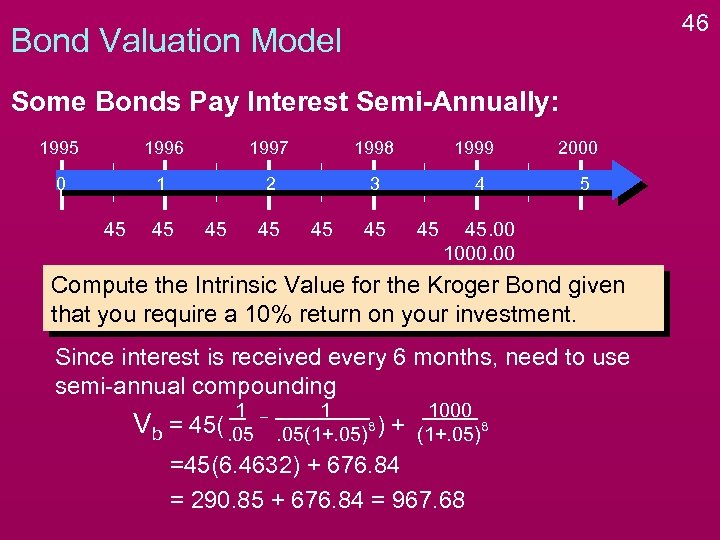
46 Bond Valuation Model Some Bonds Pay Interest Semi-Annually: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 45 45 45 1999 4 45 45 2000 5 45. 00 1000. 00 Compute the Intrinsic Value for the Kroger Bond given that you require a 10% return on your investment. Since interest is received every 6 months, need to use semi-annual compounding Vb = 1 45(. 05 1 8. 05(1+. 05) ) + 1000 8 (1+. 05) =45(6. 4632) + 676. 84 = 290. 85 + 676. 84 = 967. 68

Yield to Maturity v Bondholder’s Expected Rate of Return. v. If an investor purchases bond at today’s price and hold it until maturity, what is the annual rate of return that is earned? 47

Yield to Maturity v Bondholder’s Expected Rate of Return. v. If an investor purchases bond at today’s price and hold it until maturity, what is the annual rate of return that is earned? Substitute the Market Price (P 0) for Vb and solve for kb where kb = Annual YTM 48
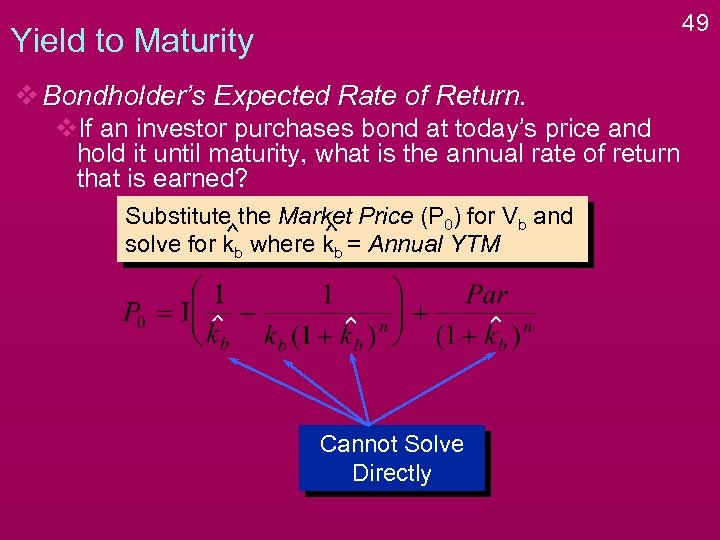
49 Yield to Maturity v Bondholder’s Expected Rate of Return. v. If an investor purchases bond at today’s price and hold it until maturity, what is the annual rate of return that is earned? Substitute the Market Price (P 0) for Vb and solve for kb where kb = Annual YTM Cannot Solve Directly
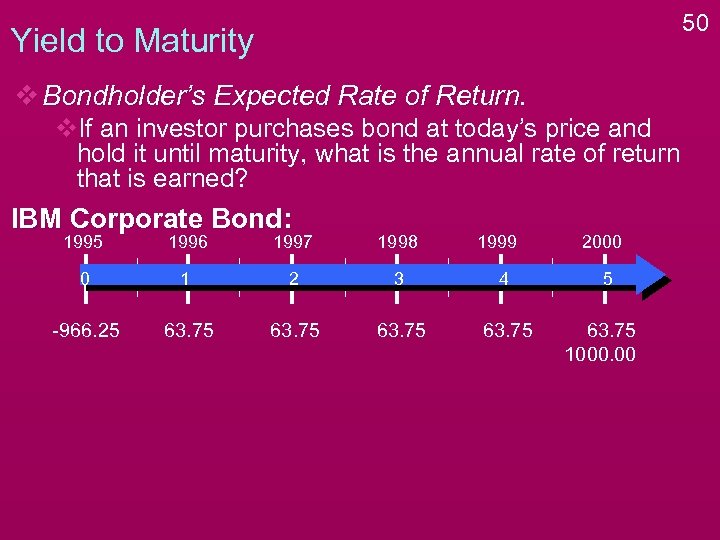
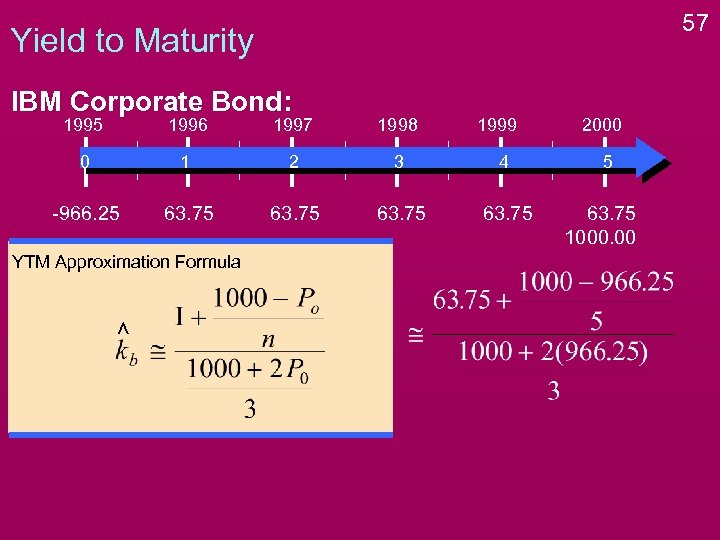
50 Yield to Maturity v Bondholder’s Expected Rate of Return. v. If an investor purchases bond at today’s price and hold it until maturity, what is the annual rate of return that is earned? IBM Corporate Bond: 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 0 1 2 3 4 -966. 25 63. 75 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00
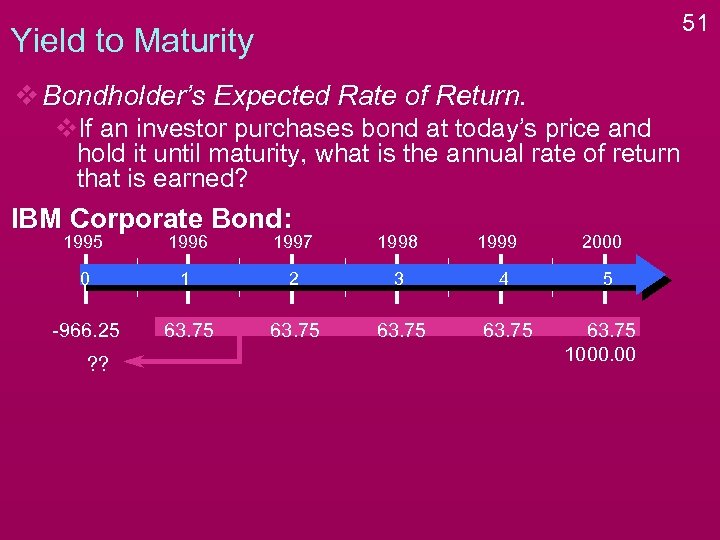
51 Yield to Maturity v Bondholder’s Expected Rate of Return. v. If an investor purchases bond at today’s price and hold it until maturity, what is the annual rate of return that is earned? IBM Corporate Bond: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 -966. 25 63. 75 ? ? + ? ? 966. 25 1999 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00
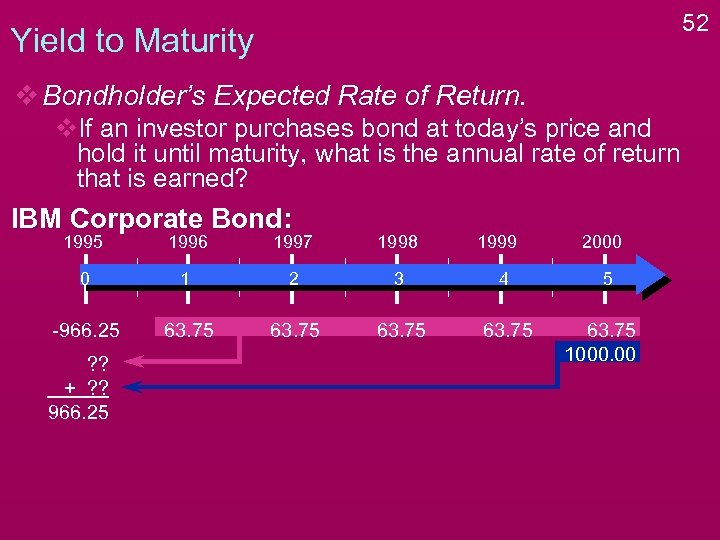
52 Yield to Maturity v Bondholder’s Expected Rate of Return. v. If an investor purchases bond at today’s price and hold it until maturity, what is the annual rate of return that is earned? IBM Corporate Bond: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 -966. 25 63. 75 ? ? + ? ? 966. 25 1999 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00
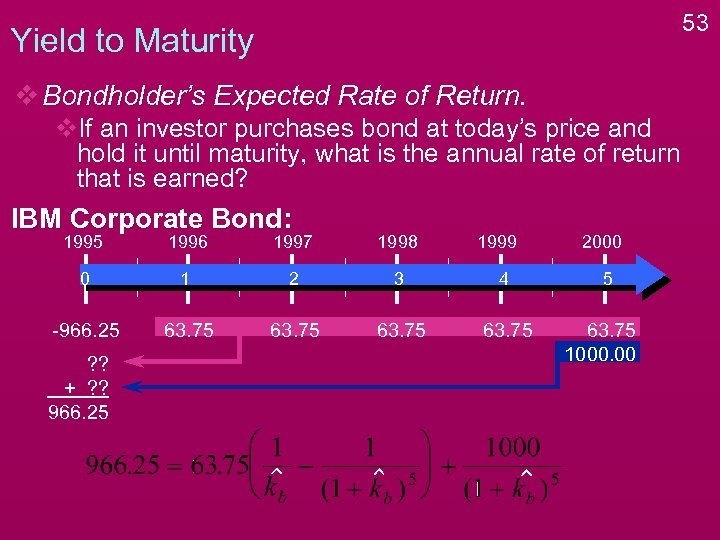
53 Yield to Maturity v Bondholder’s Expected Rate of Return. v. If an investor purchases bond at today’s price and hold it until maturity, what is the annual rate of return that is earned? IBM Corporate Bond: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 -966. 25 63. 75 ? ? + ? ? 966. 25 1999 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00

Yield to Maturity Cannot Solve directly, must use a Financial Calculator or the following Approximation Formula for YTM: 54
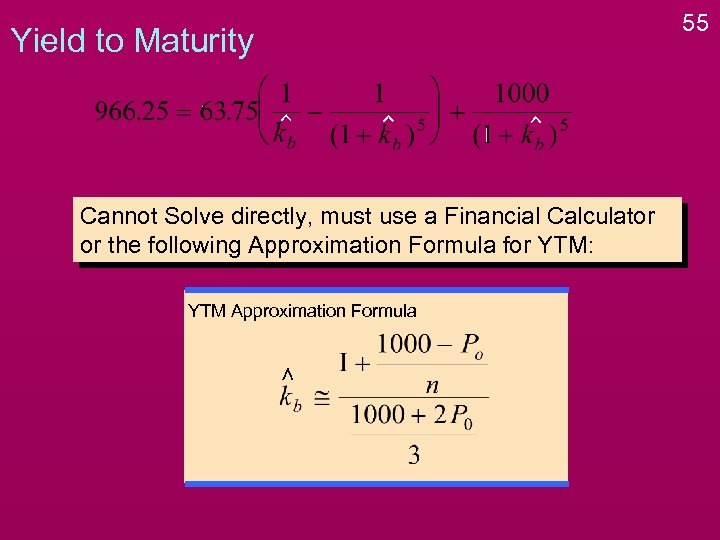
Yield to Maturity Cannot Solve directly, must use a Financial Calculator or the following Approximation Formula for YTM: YTM Approximation Formula 55
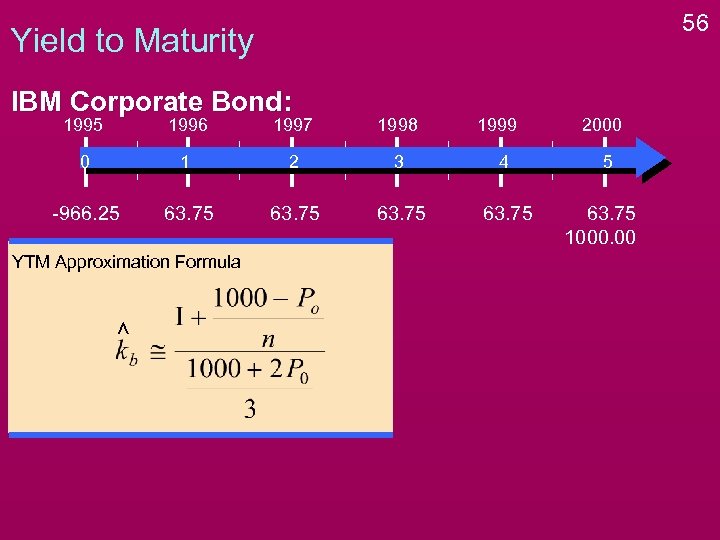
56 Yield to Maturity IBM Corporate Bond: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 -966. 25 63. 75 YTM Approximation Formula 1999 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00
57 Yield to Maturity IBM Corporate Bond: 1995 1996 1997 1998 0 1 2 3 4 -966. 25 63. 75 YTM Approximation Formula 1999 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00
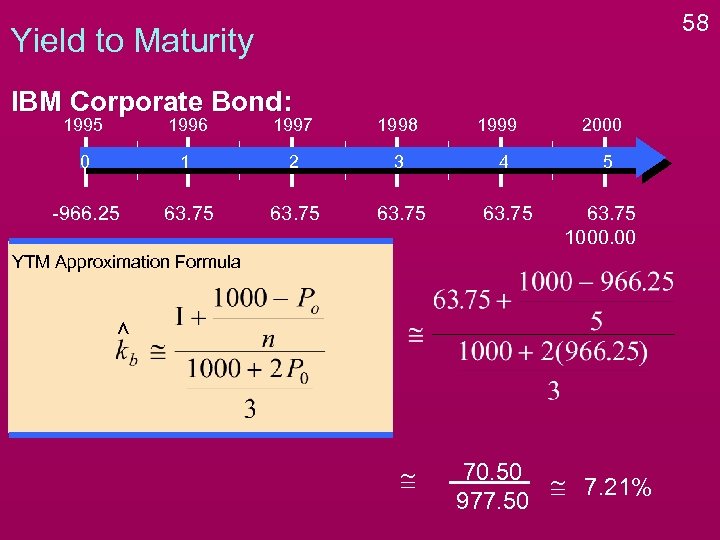
58 Yield to Maturity IBM Corporate Bond: 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 0 1 2 3 4 -966. 25 63. 75 2000 5 63. 75 1000. 00 YTM Approximation Formula @ 70. 50 @ 7. 21% 977. 50
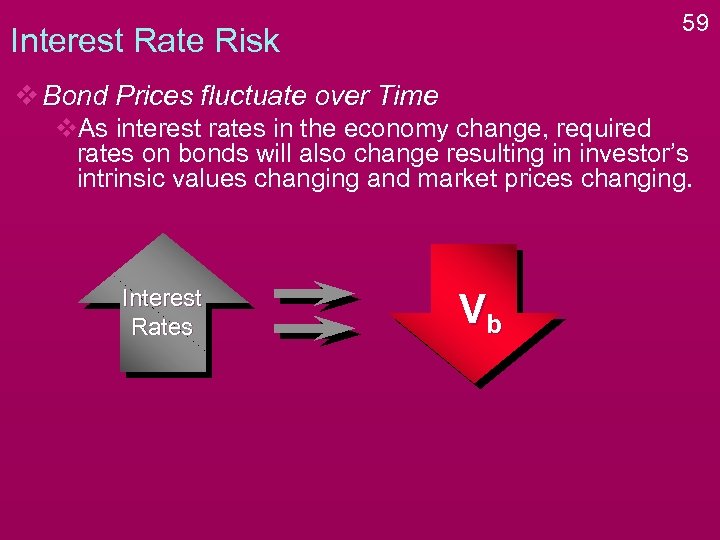
59 Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time v. As interest rates in the economy change, required rates on bonds will also change resulting in investor’s intrinsic values changing and market prices changing. Interest Rates Vb

60 Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time v. As interest rates in the economy change, required rates on bonds will also change resulting in investor’s intrinsic values changing and market prices changing. Interest Rates Vb Vb

Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time 61

Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time v. When bonds are originally issued, the coupon rate is set to match current prevailing rates. 62

Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time v. When bonds are originally issued, the coupon rate is set to match current prevailing rates. v. Over time, the prevailing rates may change, but the coupon rate is fixed. 63

Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time v. When bonds are originally issued, the coupon rate is set to match current prevailing rates. v. Over time, the prevailing rates may change, but the coupon rate is fixed. v. Resulting in the actual price of the bond changing. 64

Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time v. When bonds are originally issued, the coupon rate is set to match current prevailing rates. v. Over time, the prevailing rates may change, but the coupon rate is fixed. v. Resulting in the actual price of the bond changing. 1995 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 6% Purchase ATT 6 s 2015 Bond for $1000. 00 65

Interest Rate Risk v Bond Prices fluctuate over Time v. When bonds are originally issued, the coupon rate is set to match current prevailing rates. v. Over time, the prevailing rates may change, but the coupon rate is fixed. v. Resulting in the actual price of the bond changing. 1995 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 6% Purchase ATT 6 s 2015 Bond for $1000. 00 1 1 1000 Vb = 60(. 06(1+. 06)20 ) + (1+. 06)20 = $1, 000 66

Interest Rate Risk 1995 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 6% Purchase ATT 6 s 2015 Bond for $1000. 00 1998 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 9% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 9%) 67

Interest Rate Risk 1995 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 6% Purchase ATT 6 s 2015 Bond for $1000. 00 1998 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 9% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 9%) 1 1 1000 Vb = 60(. 09(1+. 09)17 ) + (1+. 09)17 = $743. 69 68

Interest Rate Risk 1995 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 6% Purchase ATT 6 s 2015 Bond for $1000. 00 1998 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 9% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 9%) Market Price for ATT 6 s 2015 is now $743. 69 2001 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 5% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 5%) 69

Interest Rate Risk 1995 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 6% Purchase ATT 6 s 2015 Bond for $1000. 00 1998 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 9% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 9%) Market Price for ATT 6 s 2015 is now $743. 69 2001 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 5% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 5%) 1000 1 1 Vb = 60(. 05(1+. 05)14) + (1+. 05)14 = $1, 098. 99 70

71 Interest Rate Risk 1995 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 6% Purchase ATT 6 s 2015 Bond for $1000. 00 1998 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 9% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 9%) Market Price for ATT 6 s 2015 is now $743. 69 2001 AAA Bonds are currently yielding 5% If you want to sell the ATT 6 s 2015 Bond, it must be priced to earn the purchaser a competitive rate (required rate = 5%) Market Price for ATT 6 s 2015 is now $1, 098. 99 Bond Prices fall during periods of rising interest rates and rise during periods of falling interest rates.

Bond Relationships Bond Price changes in the opposite direction of the interest rate changes 73

Bond Relationships 74 Bond Price changes in the opposite direction of the interest rate changes If the coupon rate of a bond is less than the required rate of investors, the bond will sell at a discount. Fig. 7 -3. As the maturity date approaches, the market value of the bond approaches its par value. Fig 7 -4, Table 72. Everything else being equal, a bond with longer maturity is more price sensitive to changes in interest rates than a bond with shorter maturity.

Bond Relationships 75 Bond Price changes in the opposite direction of the interest rate changes. If the coupon rate of a bond is less than the required rate of investors, the bond will sell at a discount. Fig. 7 -3. As the maturity date approaches, the market value of the bond approaches its par value. Fig 7 -4, Table 72. Everything else being equal, a bond with longer maturity is more price sensitive to changes in interest rates than a bond with shorter maturity. Everything else being equal, a bond with higher coupon is less price sensitive to changes in interest rates than a bond with lower coupon.

76
6db4719a77a85c18c746f75fcbde1e8c.ppt