bf38a02a13a3fc33b602e1af7a197bed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 1 Trial Lecture Vertical and Horizontal Handoff in Wireless Internet Access Tor K Moseng Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Networks Dept. of Telematics, NTNU 19. 06. 09 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
1 Trial Lecture Vertical and Horizontal Handoff in Wireless Internet Access Tor K Moseng Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Networks Dept. of Telematics, NTNU 19. 06. 09 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 2 Outline • Introduction • Horizontal Handover – Handover in GSM – Handover in Wi. Fi • Vertical Handover – Handover UMTS-Wi. Fi • Handover Approaches • Standards – IEEE 802. 21 – UMA – CALM • Visions Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
2 Outline • Introduction • Horizontal Handover – Handover in GSM – Handover in Wi. Fi • Vertical Handover – Handover UMTS-Wi. Fi • Handover Approaches • Standards – IEEE 802. 21 – UMA – CALM • Visions Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 3 Introduction Wireless Internet Access • Different wireless networks available – E. g. GSM/GPRS, UMTS, Wi. Fi, Wi. MAX • Mobility is Essential Internet – Changes the users’ behavior – Internet access from any wireless device • Always best connected – Multi-mode equipment Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
3 Introduction Wireless Internet Access • Different wireless networks available – E. g. GSM/GPRS, UMTS, Wi. Fi, Wi. MAX • Mobility is Essential Internet – Changes the users’ behavior – Internet access from any wireless device • Always best connected – Multi-mode equipment Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 4 Introduction Wireless Internet Access • What is handover? – Changing the point of connection while communicating • Why is handover needed? – Mobility – User preferences • What is the objective? – Handover procedure without a users notice Seamless handover Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
4 Introduction Wireless Internet Access • What is handover? – Changing the point of connection while communicating • Why is handover needed? – Mobility – User preferences • What is the objective? – Handover procedure without a users notice Seamless handover Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
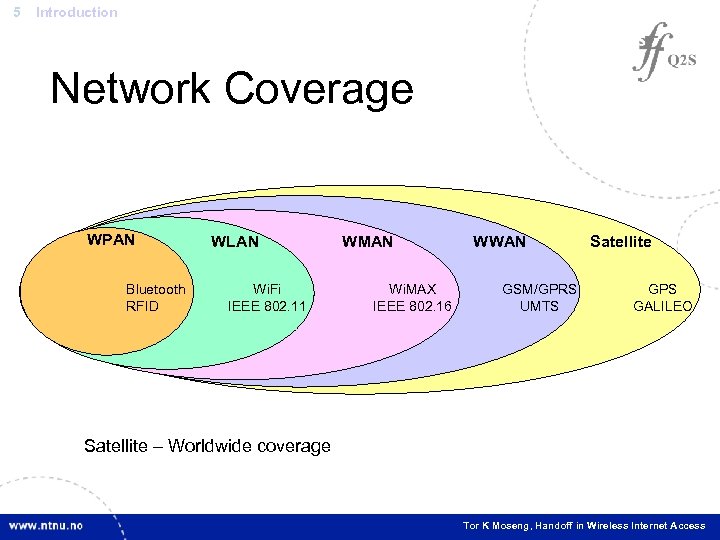 5 Introduction Network Coverage WPAN Bluetooth RFID WLAN Wi. Fi IEEE 802. 11 WMAN Wi. MAX IEEE 802. 16 WWAN GSM/GPRS UMTS Satellite GPS GALILEO Metropolitancoverage Local Area Network – Home, Hotel, Airport Satellite Personal Area Network – In–a. City wide proximity Wireless– Worldwide. Network – Regional, Cellular systems Wide Area Network person’s Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
5 Introduction Network Coverage WPAN Bluetooth RFID WLAN Wi. Fi IEEE 802. 11 WMAN Wi. MAX IEEE 802. 16 WWAN GSM/GPRS UMTS Satellite GPS GALILEO Metropolitancoverage Local Area Network – Home, Hotel, Airport Satellite Personal Area Network – In–a. City wide proximity Wireless– Worldwide. Network – Regional, Cellular systems Wide Area Network person’s Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
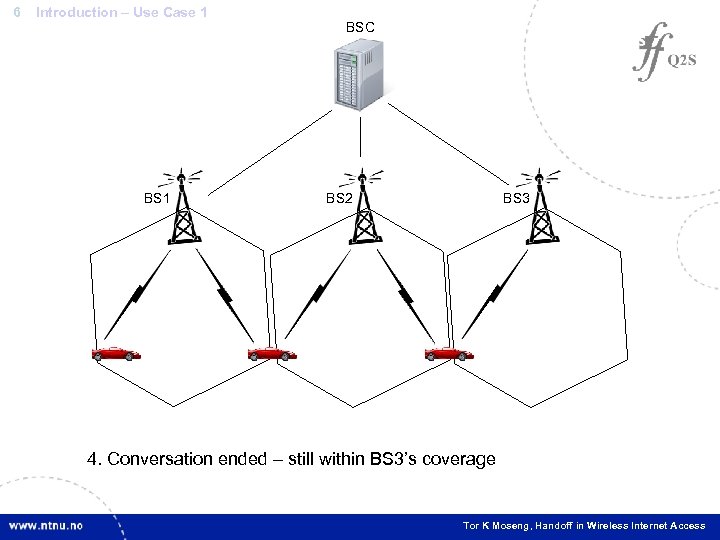 6 Introduction – Use Case 1 BSC BS 2 BS 3 2. Conversation BS 1’s – still within BS 3’s 1. Moving out of ended start conversation coverage 4. 3. Connect to BS 1 and coverage – connect to BS 2’s BS 3 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
6 Introduction – Use Case 1 BSC BS 2 BS 3 2. Conversation BS 1’s – still within BS 3’s 1. Moving out of ended start conversation coverage 4. 3. Connect to BS 1 and coverage – connect to BS 2’s BS 3 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
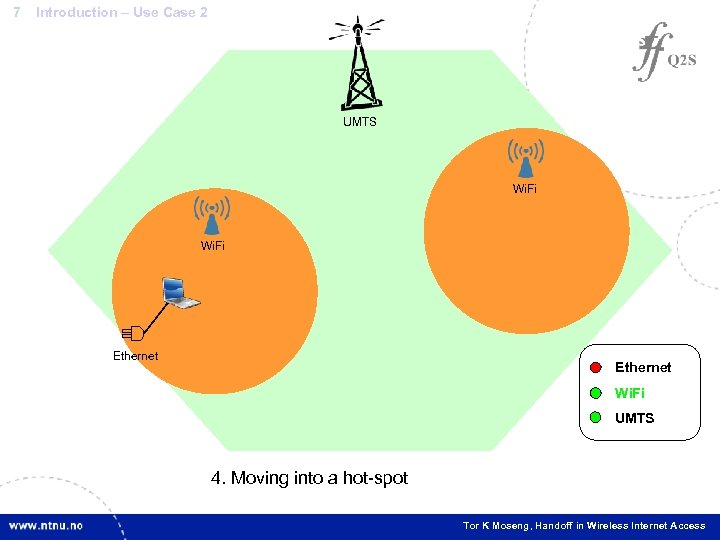 7 Introduction – Use Case 2 UMTS Wi. Fi Ethernet Wi. Fi UMTS 4. 3. 2. Moving indoorhot-spot 1. Wired connection at the working desk into a outdoor Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
7 Introduction – Use Case 2 UMTS Wi. Fi Ethernet Wi. Fi UMTS 4. 3. 2. Moving indoorhot-spot 1. Wired connection at the working desk into a outdoor Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
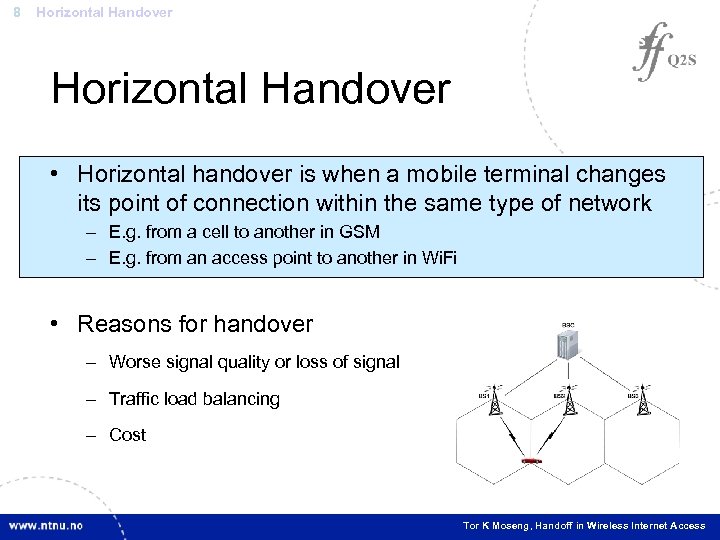 8 Horizontal Handover • Horizontal handover is when a mobile terminal changes its point of connection within the same type of network – E. g. from a cell to another in GSM – E. g. from an access point to another in Wi. Fi • Reasons for handover – Worse signal quality or loss of signal – Traffic load balancing – Cost Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
8 Horizontal Handover • Horizontal handover is when a mobile terminal changes its point of connection within the same type of network – E. g. from a cell to another in GSM – E. g. from an access point to another in Wi. Fi • Reasons for handover – Worse signal quality or loss of signal – Traffic load balancing – Cost Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
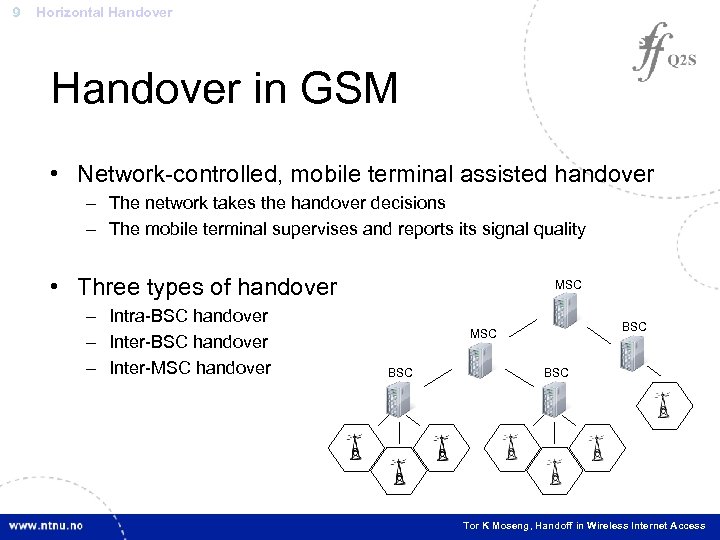 9 Horizontal Handover in GSM • Network-controlled, mobile terminal assisted handover – The network takes the handover decisions – The mobile terminal supervises and reports its signal quality • Three types of handover – Intra-BSC handover – Inter-MSC handover MSC BSC BSC Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
9 Horizontal Handover in GSM • Network-controlled, mobile terminal assisted handover – The network takes the handover decisions – The mobile terminal supervises and reports its signal quality • Three types of handover – Intra-BSC handover – Inter-MSC handover MSC BSC BSC Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
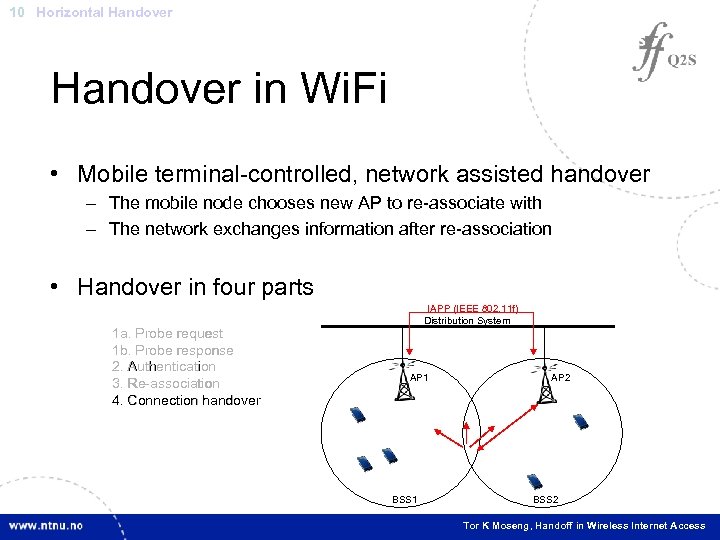 10 Horizontal Handover in Wi. Fi • Mobile terminal-controlled, network assisted handover – The mobile node chooses new AP to re-associate with – The network exchanges information after re-association • Handover in four parts 1 a. Probe request 1 b. Probe response 2. Authentication 3. Re-association 4. Connection handover IAPP (IEEE 802. 11 f) Distribution System AP 1 BSS 1 AP 2 BSS 2 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
10 Horizontal Handover in Wi. Fi • Mobile terminal-controlled, network assisted handover – The mobile node chooses new AP to re-associate with – The network exchanges information after re-association • Handover in four parts 1 a. Probe request 1 b. Probe response 2. Authentication 3. Re-association 4. Connection handover IAPP (IEEE 802. 11 f) Distribution System AP 1 BSS 1 AP 2 BSS 2 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 11 Vertical Handover • Vertical handover is when a mobile terminal changes its point of connection in a different type of network – E. g. from a wired Ethernet connection to an access point in Wi. Fi – E. g. from an access point in Wi. Fi to a cell in UMTS • Reasons for handover – – Worse signal quality or loss of signal Performance requirements (e. g. bandwidth) Cost Power consumption Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
11 Vertical Handover • Vertical handover is when a mobile terminal changes its point of connection in a different type of network – E. g. from a wired Ethernet connection to an access point in Wi. Fi – E. g. from an access point in Wi. Fi to a cell in UMTS • Reasons for handover – – Worse signal quality or loss of signal Performance requirements (e. g. bandwidth) Cost Power consumption Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 12 Vertical Handover Challenges in Vertical Handover • Multi-mode devices • Power consumption • Qo. S – Available capacity – Security • Timing • The business model • Session continuity Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
12 Vertical Handover Challenges in Vertical Handover • Multi-mode devices • Power consumption • Qo. S – Available capacity – Security • Timing • The business model • Session continuity Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 13 Vertical Handover UMTS-Wi. Fi 1. Open coupling – No common subscriber database and billing – Poor handover performance 2. Loose coupling – Common subscriber database and billing – Improved handover performance 3. Tight coupling – UMTS core network interface must be supported single operator – Improved handover performance Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
13 Vertical Handover UMTS-Wi. Fi 1. Open coupling – No common subscriber database and billing – Poor handover performance 2. Loose coupling – Common subscriber database and billing – Improved handover performance 3. Tight coupling – UMTS core network interface must be supported single operator – Improved handover performance Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
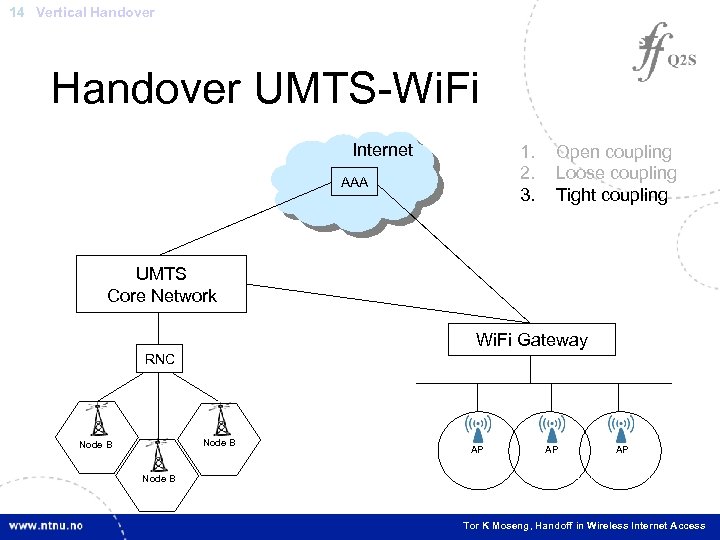 14 Vertical Handover UMTS-Wi. Fi Internet 1. 2. 3. AAA Open coupling Loose coupling Tight coupling UMTS Core Network Wi. Fi Gateway RNC Node B AP AP AP Node B Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
14 Vertical Handover UMTS-Wi. Fi Internet 1. 2. 3. AAA Open coupling Loose coupling Tight coupling UMTS Core Network Wi. Fi Gateway RNC Node B AP AP AP Node B Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 15 Handover Approaches • Handover objective is a seamless handover – Smooth handover: low loss – Fast handover: low delay Smooth and fast handover gives a seamless handover • Lower layers handover – Hard handover – Soft handover • Network layer mobility – Mobile IP Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
15 Handover Approaches • Handover objective is a seamless handover – Smooth handover: low loss – Fast handover: low delay Smooth and fast handover gives a seamless handover • Lower layers handover – Hard handover – Soft handover • Network layer mobility – Mobile IP Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 16 Handover Approaches Hard Handover ”break before make” • Old connection is broken before a new connection is activated • Primarily used in FDMA and TDMA systems (e. g. GSM) – Different frequency ranges used in adjacent cells to minimize the interference • When to perform hard handover? – E. g. based on measurements of the signal quality – Different schemes to avoid unnecessary handovers Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
16 Handover Approaches Hard Handover ”break before make” • Old connection is broken before a new connection is activated • Primarily used in FDMA and TDMA systems (e. g. GSM) – Different frequency ranges used in adjacent cells to minimize the interference • When to perform hard handover? – E. g. based on measurements of the signal quality – Different schemes to avoid unnecessary handovers Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 17 Handover Approaches Soft Handover ”make before break” • New connection is activated before the old is broken • Used in UMTS to improve the signal quality – Uplink and downlink signals may be combined for better signal – A mobile may in UMTS spend a large part of the connection time in soft handover – Better connection reliability • More seamless handover Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
17 Handover Approaches Soft Handover ”make before break” • New connection is activated before the old is broken • Used in UMTS to improve the signal quality – Uplink and downlink signals may be combined for better signal – A mobile may in UMTS spend a large part of the connection time in soft handover – Better connection reliability • More seamless handover Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 18 Handover Approaches Mobile IP • Changing the point of connection may change the IP-address – Disrupting the on-going session • Mobile IP is a network-layer mobility management solution – Hides the mobile node’s movement from its corresponding node • Two IP-addresses involved – Home Address: the point of contact for corresponding nodes – Care-of-Address: the current point of connection • Two agents involved – Home Agent: acts as a proxy and forwards packets to the Co. A – Foreign Agent: allows mobile nodes to register in ”foreign” subnets Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
18 Handover Approaches Mobile IP • Changing the point of connection may change the IP-address – Disrupting the on-going session • Mobile IP is a network-layer mobility management solution – Hides the mobile node’s movement from its corresponding node • Two IP-addresses involved – Home Address: the point of contact for corresponding nodes – Care-of-Address: the current point of connection • Two agents involved – Home Agent: acts as a proxy and forwards packets to the Co. A – Foreign Agent: allows mobile nodes to register in ”foreign” subnets Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
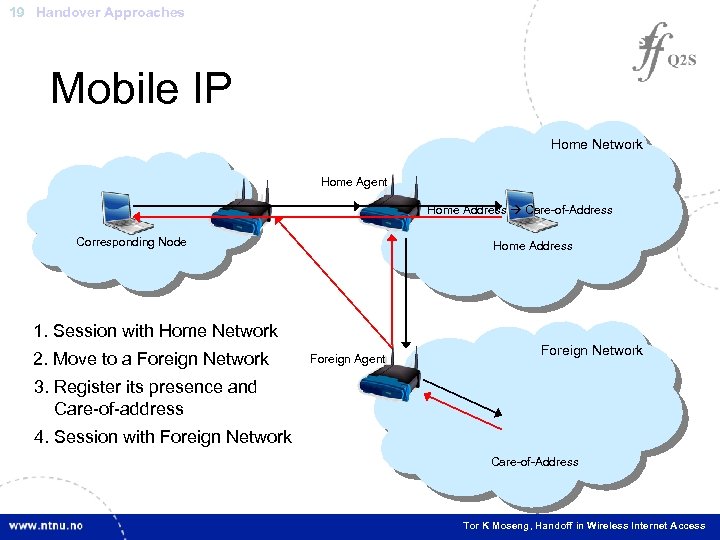 19 Handover Approaches Mobile IP Home Network Home Agent Home Address Care-of-Address Corresponding Node Home Address 1. Session with Home Network 2. Move to a Foreign Network Foreign Agent Foreign Network 3. Register its presence and Care-of-address 4. Session with Foreign Network Care-of-Address Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
19 Handover Approaches Mobile IP Home Network Home Agent Home Address Care-of-Address Corresponding Node Home Address 1. Session with Home Network 2. Move to a Foreign Network Foreign Agent Foreign Network 3. Register its presence and Care-of-address 4. Session with Foreign Network Care-of-Address Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 20 Standards for vertical handover • IEEE 802. 21 • Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) • Continous Air-Interface for Long and Medium range (CALM) Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
20 Standards for vertical handover • IEEE 802. 21 • Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) • Continous Air-Interface for Long and Medium range (CALM) Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 21 Standards – IEEE 802. 21 • Support seamless vertical handover – Media Independent Handover (IEEE Std 802. 21 -2008, January 2009) – Assess on-going work related to handover in IEEE, IETF and 3 GPP – GSM/GPRS, UMTS, IEEE 802. 3/11/15. 3/16/20 • Goals – Framework for vertical handover – Different vendors, operators and users • Not covered – Handover policy – Security What about the business model? Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
21 Standards – IEEE 802. 21 • Support seamless vertical handover – Media Independent Handover (IEEE Std 802. 21 -2008, January 2009) – Assess on-going work related to handover in IEEE, IETF and 3 GPP – GSM/GPRS, UMTS, IEEE 802. 3/11/15. 3/16/20 • Goals – Framework for vertical handover – Different vendors, operators and users • Not covered – Handover policy – Security What about the business model? Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 22 Standards – UMA Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) • 3 GPP standard for cellular systems and unlicensed wireless networks handover – A mobile centric version of IEEE 802. 21 • The UMA Network Controller (UNC) – Provides an interface into mobile operators core network – Secure transport of mobile signaling over IP • Extends a mobile operator’s services over IP-based access networks – Use Wi. Fi to improve coverage and performance of 3 G services Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
22 Standards – UMA Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) • 3 GPP standard for cellular systems and unlicensed wireless networks handover – A mobile centric version of IEEE 802. 21 • The UMA Network Controller (UNC) – Provides an interface into mobile operators core network – Secure transport of mobile signaling over IP • Extends a mobile operator’s services over IP-based access networks – Use Wi. Fi to improve coverage and performance of 3 G services Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 23 Standards – CALM • ISO approved framework for continuous communication across various interfaces and media for vehicular users – ISO TC 204/WG 16 – Wide Area Communications – IEEE 802. 11/11 p/15/16 e/20, 2 G/3 G, and ITS systems • Application support – In-vehicle Internet access – ITS applications (focus on Vehicle Safety Communication) – V 2 V communication • Vertical handover based on IPv 6 protocols (ISO 21210) Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
23 Standards – CALM • ISO approved framework for continuous communication across various interfaces and media for vehicular users – ISO TC 204/WG 16 – Wide Area Communications – IEEE 802. 11/11 p/15/16 e/20, 2 G/3 G, and ITS systems • Application support – In-vehicle Internet access – ITS applications (focus on Vehicle Safety Communication) – V 2 V communication • Vertical handover based on IPv 6 protocols (ISO 21210) Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 24 Visions • 4 G network: Universal wireless access with much higher data rates than today ”Anytime, Anywhere” • Collection of technologies and protocols – Not just one single standard – Seamless handover and roaming – Qo. S support • Prediction of availability is 2015 (ref: Phil Redman, Gartner) Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
24 Visions • 4 G network: Universal wireless access with much higher data rates than today ”Anytime, Anywhere” • Collection of technologies and protocols – Not just one single standard – Seamless handover and roaming – Qo. S support • Prediction of availability is 2015 (ref: Phil Redman, Gartner) Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
 25 Visions • The Wireless World Research Forum (WWRF) formulates visions on strategic future research directions in the wireless field Networks for the Wireless World must enable application- and service-independent end-to-end reachability in the global network environment. Networks for the Wireless World should be capable to support both existing and new mobility mechanisms that enable terminals and networks to move around without being closely tied to so-called ”home” networks. Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
25 Visions • The Wireless World Research Forum (WWRF) formulates visions on strategic future research directions in the wireless field Networks for the Wireless World must enable application- and service-independent end-to-end reachability in the global network environment. Networks for the Wireless World should be capable to support both existing and new mobility mechanisms that enable terminals and networks to move around without being closely tied to so-called ”home” networks. Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
![26 References • • • • 3 GPP, [Online]: www. 3 gpp. org Jacques 26 References • • • • 3 GPP, [Online]: www. 3 gpp. org Jacques](https://present5.com/presentation/bf38a02a13a3fc33b602e1af7a197bed/image-26.jpg) 26 References • • • • 3 GPP, [Online]: www. 3 gpp. org Jacques De Kegel, IBM & Wireless 2004, Presentation WIreless e-business EBO, [Online]: http: //www. ti. kviv. be/Ittelecom/EBO_overview. pdf Knut Evensen, CALM Architecture and CALM M 5 Convenor, Presentation at IEEE 802 Plenary Tutorials, November 2006 Hussain et al. , Mobility Management Challenges and Issues in 4 G Heterogeneous Networks, In Proceedings of Inter. Sense'06, May 2006 IEEE, [Online]: www. ieee. org IETF, [Online]: www. ietf. org Juha Korhonen, Introduction to 3 G Mobile Communications, 2 nd Ed, Artech House, 2003 Lim et al. , SHARE: Seamless Handover Architecture for 3 G-WLAN Roaming Environment, Wireless Networks, 15: 353 -363, 2009 Network World, [Online]: www. networkworld. com Charles Perkins, Presentation at an IEEE 802 Handoff Tutorial, November 2002, [Online]: http: //ieee 802. org/16/tutorial/T 80216 -02_04. zip Bjørn Rønning, UMTS og WLAN - konkurrerende eller komplimentære systemer, Norsk UMTS-forum, Oktober 2001, [Online]: http: //www. umts. no/files/30 Okt 01 -Bj%C 3%B 8 rn. R%C 3%B 8 nning-%20 UMTS%20 forum. pdf Sharma et al. , Omni. Con: A Mobile IP-based Vertical Handoff System for Wireless LAN and GPRS Links, In Proceedings of ICPP 2004 Workshops, 2004 UMA Today, [Online]: www. umatoday. com Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, [Online]: http: //en. wikipedia. org Wireless World Research Forum, [Online]: http: //www. wireless-world-research. org/ Qing-An Zeng and D. P. Agrawal, Handoff in Wireless Mobile Networks, Chapter 1, Handbook of Wireless Networks and Mobile Computing, 2002 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access
26 References • • • • 3 GPP, [Online]: www. 3 gpp. org Jacques De Kegel, IBM & Wireless 2004, Presentation WIreless e-business EBO, [Online]: http: //www. ti. kviv. be/Ittelecom/EBO_overview. pdf Knut Evensen, CALM Architecture and CALM M 5 Convenor, Presentation at IEEE 802 Plenary Tutorials, November 2006 Hussain et al. , Mobility Management Challenges and Issues in 4 G Heterogeneous Networks, In Proceedings of Inter. Sense'06, May 2006 IEEE, [Online]: www. ieee. org IETF, [Online]: www. ietf. org Juha Korhonen, Introduction to 3 G Mobile Communications, 2 nd Ed, Artech House, 2003 Lim et al. , SHARE: Seamless Handover Architecture for 3 G-WLAN Roaming Environment, Wireless Networks, 15: 353 -363, 2009 Network World, [Online]: www. networkworld. com Charles Perkins, Presentation at an IEEE 802 Handoff Tutorial, November 2002, [Online]: http: //ieee 802. org/16/tutorial/T 80216 -02_04. zip Bjørn Rønning, UMTS og WLAN - konkurrerende eller komplimentære systemer, Norsk UMTS-forum, Oktober 2001, [Online]: http: //www. umts. no/files/30 Okt 01 -Bj%C 3%B 8 rn. R%C 3%B 8 nning-%20 UMTS%20 forum. pdf Sharma et al. , Omni. Con: A Mobile IP-based Vertical Handoff System for Wireless LAN and GPRS Links, In Proceedings of ICPP 2004 Workshops, 2004 UMA Today, [Online]: www. umatoday. com Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, [Online]: http: //en. wikipedia. org Wireless World Research Forum, [Online]: http: //www. wireless-world-research. org/ Qing-An Zeng and D. P. Agrawal, Handoff in Wireless Mobile Networks, Chapter 1, Handbook of Wireless Networks and Mobile Computing, 2002 Tor K Moseng, Handoff in Wireless Internet Access


