cf5a95799bcda623f5bc10b1a690f904.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61
 1
1
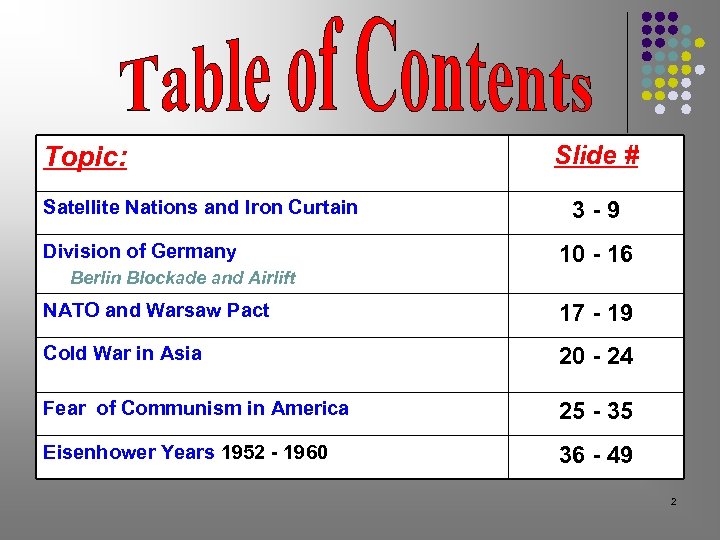 Topic: Satellite Nations and Iron Curtain Division of Germany Slide # 3 -9 10 - 16 Berlin Blockade and Airlift NATO and Warsaw Pact 17 - 19 Cold War in Asia 20 - 24 Fear of Communism in America 25 - 35 Eisenhower Years 1952 - 1960 36 - 49 2
Topic: Satellite Nations and Iron Curtain Division of Germany Slide # 3 -9 10 - 16 Berlin Blockade and Airlift NATO and Warsaw Pact 17 - 19 Cold War in Asia 20 - 24 Fear of Communism in America 25 - 35 Eisenhower Years 1952 - 1960 36 - 49 2
 • • “Cold War” describes the conflict between the USSR and the “Western Powers” in the period following WWII Period of tension characterized by conflict at diplomatic, economic, and all levels short of actual armed conflict between the principals on either side 3
• • “Cold War” describes the conflict between the USSR and the “Western Powers” in the period following WWII Period of tension characterized by conflict at diplomatic, economic, and all levels short of actual armed conflict between the principals on either side 3
 Breakdown of wartime cooperation between the Allies Mutual Suspicion l l Roosevelt had idealistic aims ‘four freedoms´: f. from want, f. of speech, f. of religious belief, and f. from fear l. Stalin had more concrete aims lregaining of Russian territory lost in WWI, control over E. E. for SECURITY 4
Breakdown of wartime cooperation between the Allies Mutual Suspicion l l Roosevelt had idealistic aims ‘four freedoms´: f. from want, f. of speech, f. of religious belief, and f. from fear l. Stalin had more concrete aims lregaining of Russian territory lost in WWI, control over E. E. for SECURITY 4
 Background: l l After WW II, the US and USSR emerged as rival superpowers. Each nation was strong enough to greatly influence world events. 5
Background: l l After WW II, the US and USSR emerged as rival superpowers. Each nation was strong enough to greatly influence world events. 5
 Yalta Conference l l Feb 4 -11, 1945 – Yalta Conference – Churchill, FDR, and Stalin meet: agree Stalin could control countries of Eastern Europe though Stalin promises to hold elections in occupied countries (Korea was divided at 38 th II) Roosevelt had to secure Russian assistance in ending war with Japan 6
Yalta Conference l l Feb 4 -11, 1945 – Yalta Conference – Churchill, FDR, and Stalin meet: agree Stalin could control countries of Eastern Europe though Stalin promises to hold elections in occupied countries (Korea was divided at 38 th II) Roosevelt had to secure Russian assistance in ending war with Japan 6
 Potsdam Conference July 1945 l l Final wartime conference Big Three l l England = Attlee USA = Truman USSR = Stalin promised to allow free elections in Eastern Europe 7
Potsdam Conference July 1945 l l Final wartime conference Big Three l l England = Attlee USA = Truman USSR = Stalin promised to allow free elections in Eastern Europe 7
 The turning point of WWII and the symbolic beginning of the Cold War occurred at the Battle of 1. 2. 3. 4. Leningrad Moscow Stalingrad Berlin 8
The turning point of WWII and the symbolic beginning of the Cold War occurred at the Battle of 1. 2. 3. 4. Leningrad Moscow Stalingrad Berlin 8
 Which was NOT a provision of the Yalta Conference? 1. divided Germany into occupation zones 2. guaranteed Poles a broader based democratic government 3. gave Soviet Union control of Eastern Europe 4. Soviet Union promised to enter war against Japan 9
Which was NOT a provision of the Yalta Conference? 1. divided Germany into occupation zones 2. guaranteed Poles a broader based democratic government 3. gave Soviet Union control of Eastern Europe 4. Soviet Union promised to enter war against Japan 9
 Satellite Nations… l l l Stalin never allowed truly free elections. Instead, communist governments were installed in many Eastern European nations. Main Purpose? l Protect USSR from invasion from the West 10
Satellite Nations… l l l Stalin never allowed truly free elections. Instead, communist governments were installed in many Eastern European nations. Main Purpose? l Protect USSR from invasion from the West 10
 Yugoslavia – Josef Tito breaks from Stalin, though still communist • • The U. S. sent economic assistance “The Yugoslav dictator might be a “son-of-a-bitch, ” the new Secretary of State Dean Acheson acknowledged in 1949, but he was now “our son-of-a-bitch. ” 11
Yugoslavia – Josef Tito breaks from Stalin, though still communist • • The U. S. sent economic assistance “The Yugoslav dictator might be a “son-of-a-bitch, ” the new Secretary of State Dean Acheson acknowledged in 1949, but he was now “our son-of-a-bitch. ” 11
 Containment Policy l l George Kennan, career Foreign Service Officer Formulated the policy of “containment”: l l US would not get rid of communism, but would not allow it to spread. US would “contain” communism where is already existed. 12
Containment Policy l l George Kennan, career Foreign Service Officer Formulated the policy of “containment”: l l US would not get rid of communism, but would not allow it to spread. US would “contain” communism where is already existed. 12
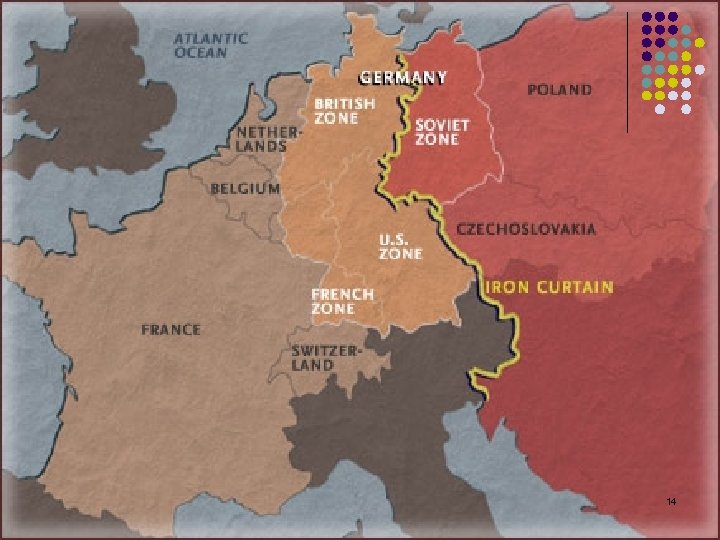
 The Iron Curtain l l l Winston Churchill coined this term. Famous speech on March 5, 1946 at Westminster College, in Fulton, Missouri. CLICK for text and video of speech 13
The Iron Curtain l l l Winston Churchill coined this term. Famous speech on March 5, 1946 at Westminster College, in Fulton, Missouri. CLICK for text and video of speech 13
 14
14
 Churchill’s Warning… l Churchill felt that behind the Iron Curtain, the USSR was planning to attack and conquer Western Europe. 15
Churchill’s Warning… l Churchill felt that behind the Iron Curtain, the USSR was planning to attack and conquer Western Europe. 15
 Truman Doctrine l l l As Communist uprising started to develop in various parts of Western Europe Truman felt that it was necessary to take action. It will be the policy of the U. S. to assist free people anywhere who are resisting attempted takeover by an outside force or by an armed minority from within (rebellion) Example of Truman Doctrine in action: Greek and Turkish Aid Bill 16
Truman Doctrine l l l As Communist uprising started to develop in various parts of Western Europe Truman felt that it was necessary to take action. It will be the policy of the U. S. to assist free people anywhere who are resisting attempted takeover by an outside force or by an armed minority from within (rebellion) Example of Truman Doctrine in action: Greek and Turkish Aid Bill 16
 Truman Doctrine 1947 $400 million in economic aid to Greece and Turkey Truman hoped to stop spread of communism 17
Truman Doctrine 1947 $400 million in economic aid to Greece and Turkey Truman hoped to stop spread of communism 17
 1947, George C. Marshall visited Stalin in Moscow “All the way back to Washington, ” he talked “of the importance of finding some initiative to prevent the complete breakdown of Western Europe. ” 18
1947, George C. Marshall visited Stalin in Moscow “All the way back to Washington, ” he talked “of the importance of finding some initiative to prevent the complete breakdown of Western Europe. ” 18
 Marshall Plan - 1947 • Massive Aid package that offered food and economic assistance to European countries • To strengthen democracies • Also called the European Recovery Plan • Offered to the Soviet Union and its Satellites. • $17 Billion in Aid • In what 2 ways does this benefit America? 19
Marshall Plan - 1947 • Massive Aid package that offered food and economic assistance to European countries • To strengthen democracies • Also called the European Recovery Plan • Offered to the Soviet Union and its Satellites. • $17 Billion in Aid • In what 2 ways does this benefit America? 19
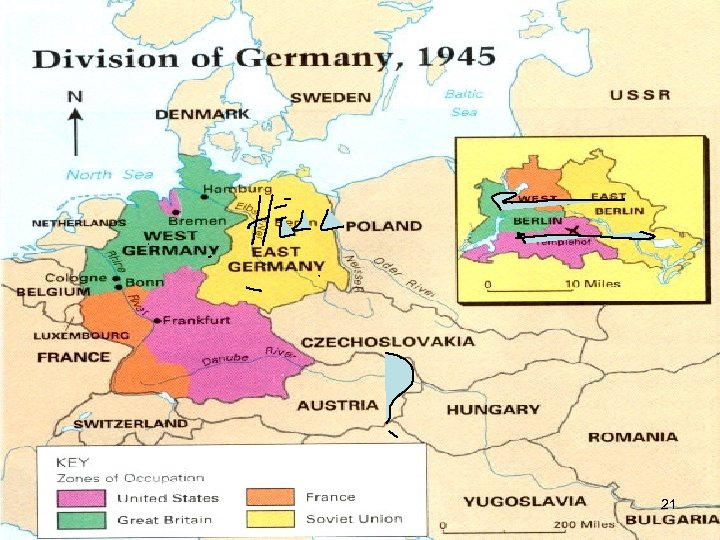
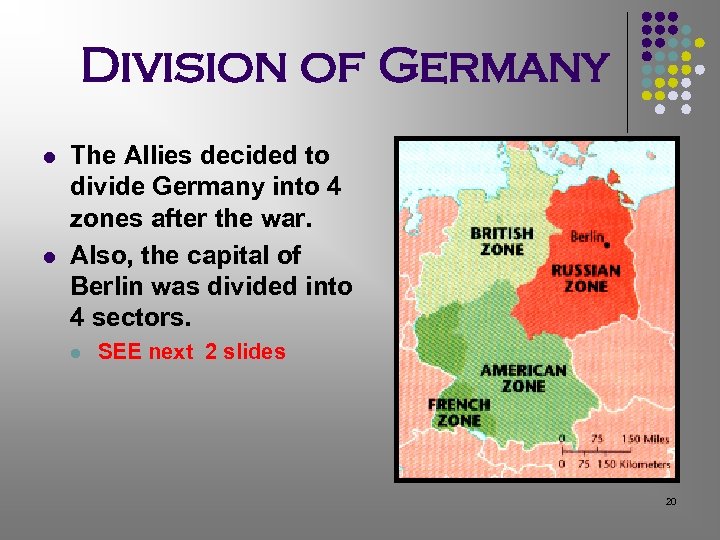 Division of Germany l l The Allies decided to divide Germany into 4 zones after the war. Also, the capital of Berlin was divided into 4 sectors. l SEE next 2 slides 20
Division of Germany l l The Allies decided to divide Germany into 4 zones after the war. Also, the capital of Berlin was divided into 4 sectors. l SEE next 2 slides 20
 21
21
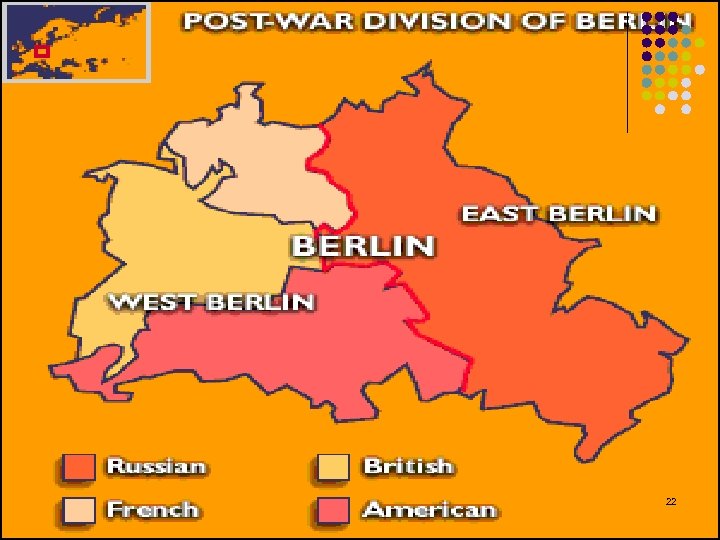 22
22
 Problem with Berlin? l Berlin was in the Soviet Sector. l Stalin was not happy with a “small piece” of democracy in Eastern Europe. l What did he do? 23
Problem with Berlin? l Berlin was in the Soviet Sector. l Stalin was not happy with a “small piece” of democracy in Eastern Europe. l What did he do? 23
 Berlin Blockade l l June 1948, Stalin attempts to starve West Berliners into submission. All rail and street access was blocked. 24
Berlin Blockade l l June 1948, Stalin attempts to starve West Berliners into submission. All rail and street access was blocked. 24
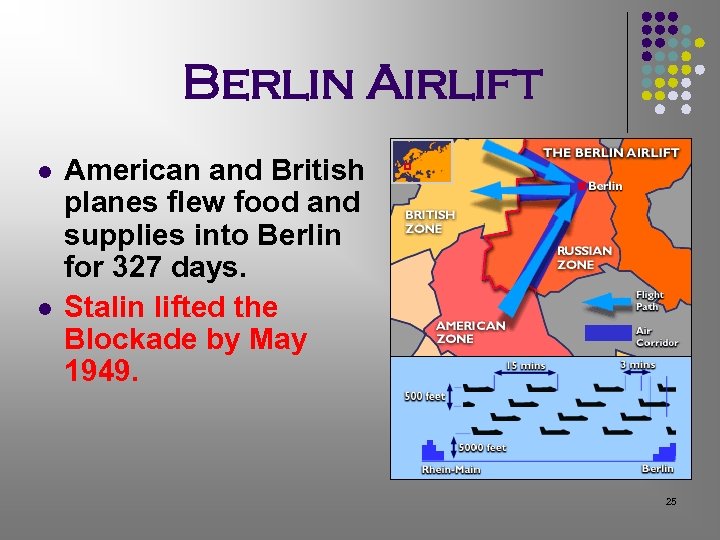 Berlin Airlift l l American and British planes flew food and supplies into Berlin for 327 days. Stalin lifted the Blockade by May 1949. 25
Berlin Airlift l l American and British planes flew food and supplies into Berlin for 327 days. Stalin lifted the Blockade by May 1949. 25
 26
26
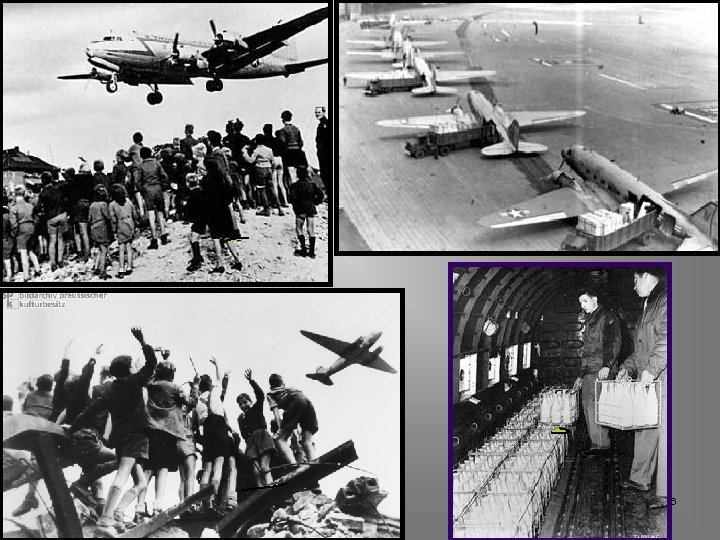
 Operation “Little Vittles” l l During the Berlin Airlift a group of pilots decided to help boost the spirits of the German children. They organized a mission to drop candy to the children using parachutes made of handkerchiefs. 27
Operation “Little Vittles” l l During the Berlin Airlift a group of pilots decided to help boost the spirits of the German children. They organized a mission to drop candy to the children using parachutes made of handkerchiefs. 27
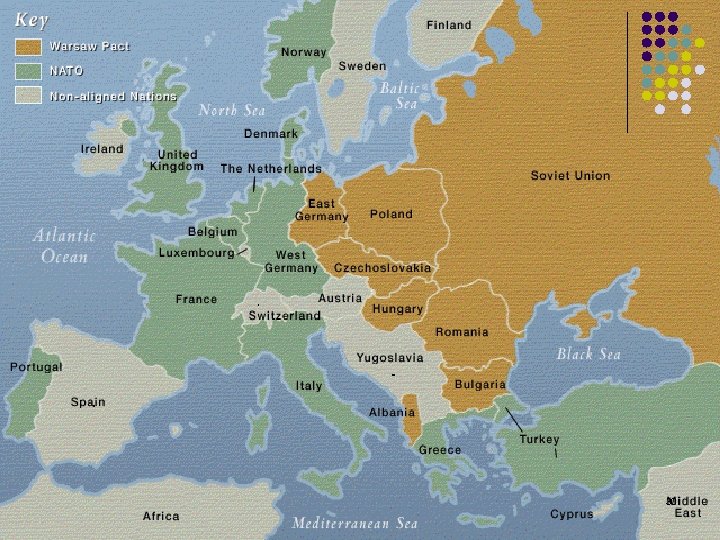
 North Atlantic Treaty Organization l l l NATO was established by a treaty in 1949 This organization established a system of collective defense whereby its member states agree to mutual defense in response to an attack by any external party. Original members were: l l United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, France, Denmark, Iceland, Italy, Norway, Portugal, Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg. Greece (1952), West Germany (1955) join also 28
North Atlantic Treaty Organization l l l NATO was established by a treaty in 1949 This organization established a system of collective defense whereby its member states agree to mutual defense in response to an attack by any external party. Original members were: l l United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, France, Denmark, Iceland, Italy, Norway, Portugal, Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg. Greece (1952), West Germany (1955) join also 28
 The Warsaw Pact l Communist Response to NATO. l l l Signed on May 1, 1955 in Warsaw, Poland Military treaty, which bound its signatories to come to the aid of the others, should any one of them be the victim of foreign aggression. Original Members: l Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary, East Germany, Poland, Rumania, the USSR, and the Czechoslovak Republic. 29
The Warsaw Pact l Communist Response to NATO. l l l Signed on May 1, 1955 in Warsaw, Poland Military treaty, which bound its signatories to come to the aid of the others, should any one of them be the victim of foreign aggression. Original Members: l Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary, East Germany, Poland, Rumania, the USSR, and the Czechoslovak Republic. 29
 30
30
 Cold War in Asia 31
Cold War in Asia 31
 Struggle for China l Mao Zedong wanted China to become a communist state after WW II. l Chang Kai Shek fought to stop the communists but was unsuccessful. 32
Struggle for China l Mao Zedong wanted China to become a communist state after WW II. l Chang Kai Shek fought to stop the communists but was unsuccessful. 32
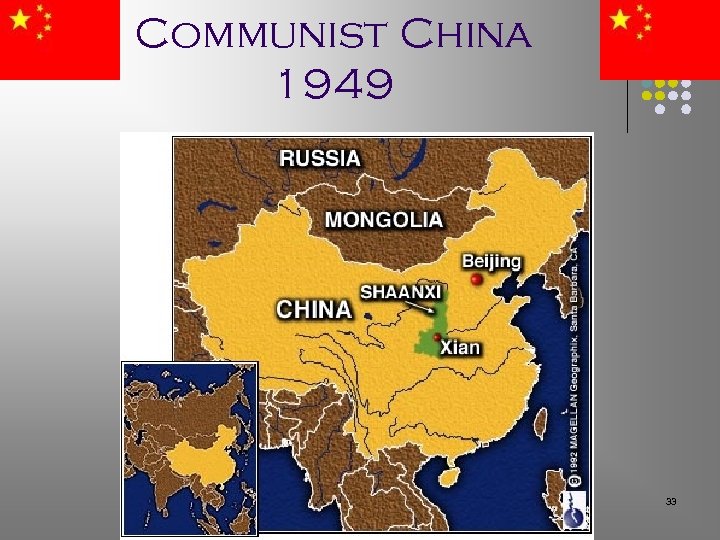 Communist China 1949 33
Communist China 1949 33
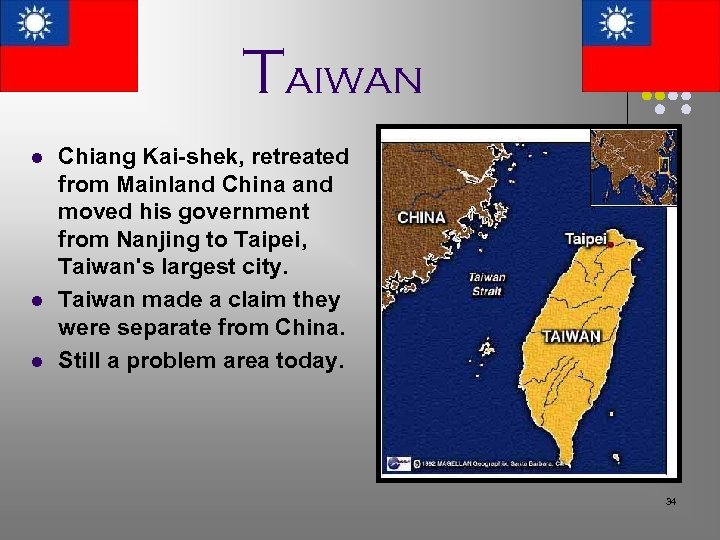 Taiwan l l l Chiang Kai-shek, retreated from Mainland China and moved his government from Nanjing to Taipei, Taiwan's largest city. Taiwan made a claim they were separate from China. Still a problem area today. 34
Taiwan l l l Chiang Kai-shek, retreated from Mainland China and moved his government from Nanjing to Taipei, Taiwan's largest city. Taiwan made a claim they were separate from China. Still a problem area today. 34
 1949 l l Not a very good year #1 – The Soviet Union tested an atomic bomb. (This happened years ahead of what we had predicted) #2 – China, the most populated country in the world fell to Communism Who do you think took much of the blam for this? 35
1949 l l Not a very good year #1 – The Soviet Union tested an atomic bomb. (This happened years ahead of what we had predicted) #2 – China, the most populated country in the world fell to Communism Who do you think took much of the blam for this? 35
 Cold War in America (1945 -1960) l Was there reason to be concerned? YES! l l Soviet domination of Eastern Europe Soviets had tested a bomb China turned Communist – 1 billion people! 80, 000 Americans members of Communist party 36
Cold War in America (1945 -1960) l Was there reason to be concerned? YES! l l Soviet domination of Eastern Europe Soviets had tested a bomb China turned Communist – 1 billion people! 80, 000 Americans members of Communist party 36
 Loyalty Review Board l l Set up by President Truman in March 1947. Purpose? l l Investigate Federal government employees and dismiss those disloyal to US 212 dismissed 37
Loyalty Review Board l l Set up by President Truman in March 1947. Purpose? l l Investigate Federal government employees and dismiss those disloyal to US 212 dismissed 37
 House on Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) l 1947= House of Representatives l Investigate Communist influence in the movie industry 38
House on Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) l 1947= House of Representatives l Investigate Communist influence in the movie industry 38
 ‘Hollywood Ten’ l l l 10 Hollywood screenwriters and directors who refused to testify before HUAC. Charged with contempt of Congress. Claimed 1 st Amendment right of free speech 39
‘Hollywood Ten’ l l l 10 Hollywood screenwriters and directors who refused to testify before HUAC. Charged with contempt of Congress. Claimed 1 st Amendment right of free speech 39
 Blacklisted l l l Following a meeting of film industry executives at New York's Waldorf. Astoria hotel, MPAA president Johnston issued a press release on the executives' behalf that is today referred to as the Waldorf Statement. The statement declared that the ten would be fired or suspended without pay and not reemployed until they were cleared of contempt charges and had sworn that they were not Communists. The first Hollywood blacklist was now in effect. 40
Blacklisted l l l Following a meeting of film industry executives at New York's Waldorf. Astoria hotel, MPAA president Johnston issued a press release on the executives' behalf that is today referred to as the Waldorf Statement. The statement declared that the ten would be fired or suspended without pay and not reemployed until they were cleared of contempt charges and had sworn that they were not Communists. The first Hollywood blacklist was now in effect. 40
 Spy Cases Shock the US l During the late 1940 s and early 1950 s, America was rocked by sensational stories of Americans spying for the Soviet Union. 41
Spy Cases Shock the US l During the late 1940 s and early 1950 s, America was rocked by sensational stories of Americans spying for the Soviet Union. 41
 Alger Hiss l l Hiss worked for the US State Department. Accused of being a spy for the USSR. Found guilty of perjury. Later (1990 s) Hiss was proven to be a spy for the USSR (or maybe not) 42
Alger Hiss l l Hiss worked for the US State Department. Accused of being a spy for the USSR. Found guilty of perjury. Later (1990 s) Hiss was proven to be a spy for the USSR (or maybe not) 42
 The Rosenbergs l l American Communists who were found guilty of conspiracy to commit espionage in relation to passing information on the American nuclear bomb to the Soviet Union. The couple were executed at sundown in the electric chair at Sing Correctional Facility in Ossining, New York, on June 19, 1953. 43
The Rosenbergs l l American Communists who were found guilty of conspiracy to commit espionage in relation to passing information on the American nuclear bomb to the Soviet Union. The couple were executed at sundown in the electric chair at Sing Correctional Facility in Ossining, New York, on June 19, 1953. 43
 Other Spies David Greenglass: Courier Harry Gold: Courier Klaus Fuchs: Scientist/Spy
Other Spies David Greenglass: Courier Harry Gold: Courier Klaus Fuchs: Scientist/Spy
 Mc. Carthyism l l Senator Joe Mc. Carthy became the most famous anti. Communist activist. Used the issue to help win re-election in 1950. 45
Mc. Carthyism l l Senator Joe Mc. Carthy became the most famous anti. Communist activist. Used the issue to help win re-election in 1950. 45
 Mc. Carthy’s Tactics l l l Made one unsupported accusation after another. He would bully witnesses. Mc. Carthyism = tactics used to advance your career. 46
Mc. Carthy’s Tactics l l l Made one unsupported accusation after another. He would bully witnesses. Mc. Carthyism = tactics used to advance your career. 46
 Mc. Carthy’s Downfall l l In 1954 Mc. Carthy made accusations against the US Army. Led to televised Senate investigation; and American people did not like Mc. Carthy’s tactics. His popularity dropped greatly. 47
Mc. Carthy’s Downfall l l In 1954 Mc. Carthy made accusations against the US Army. Led to televised Senate investigation; and American people did not like Mc. Carthy’s tactics. His popularity dropped greatly. 47
 Change in Leaders l l l The early 1950 s saw a change in leaders in both the US and USSR. USA = Dwight Eisenhower wins the election of 1952. USSR = Nikita Khruschev takes over when Stalin dies in 1953. 48
Change in Leaders l l l The early 1950 s saw a change in leaders in both the US and USSR. USA = Dwight Eisenhower wins the election of 1952. USSR = Nikita Khruschev takes over when Stalin dies in 1953. 48
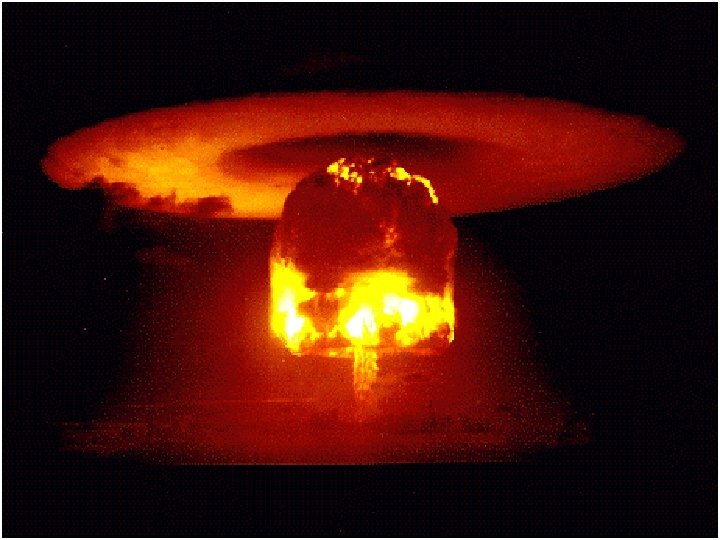
 Hydrogen Bomb l US exploded the 1 st Hbomb on November 1, 1952 in South Pacific. l l That bomb completely destroyed one island left a crater 175 feet deep. Russians exploded on in August of 1953. 49
Hydrogen Bomb l US exploded the 1 st Hbomb on November 1, 1952 in South Pacific. l l That bomb completely destroyed one island left a crater 175 feet deep. Russians exploded on in August of 1953. 49
 50
50
 Brinkmanship l l Defined as willingness to push nation to the “brink” of nuclear war to keep peace. Policy advocated by John Foster Dulles; Secretary of State. 51
Brinkmanship l l Defined as willingness to push nation to the “brink” of nuclear war to keep peace. Policy advocated by John Foster Dulles; Secretary of State. 51
 Central Intelligence Agency - CIA l l Used spies to gather information abroad Began to carry out covert operations to weaken or overthrow governments unfriendly to the United States. 52
Central Intelligence Agency - CIA l l Used spies to gather information abroad Began to carry out covert operations to weaken or overthrow governments unfriendly to the United States. 52
 Iran l l One of the CIAs first covert actions tool place in Iran when Iran’s Prime minister Mohammed Mossadegh nationalized Iran’s oil fields. CIA worked to remove Mossadegh 53
Iran l l One of the CIAs first covert actions tool place in Iran when Iran’s Prime minister Mohammed Mossadegh nationalized Iran’s oil fields. CIA worked to remove Mossadegh 53
 Shah of Iran l l CIA “Operation Ajax” caused the downfall of Mossadegh from office. The Shah, backed by the US, formed a government friendly to the US. 54
Shah of Iran l l CIA “Operation Ajax” caused the downfall of Mossadegh from office. The Shah, backed by the US, formed a government friendly to the US. 54
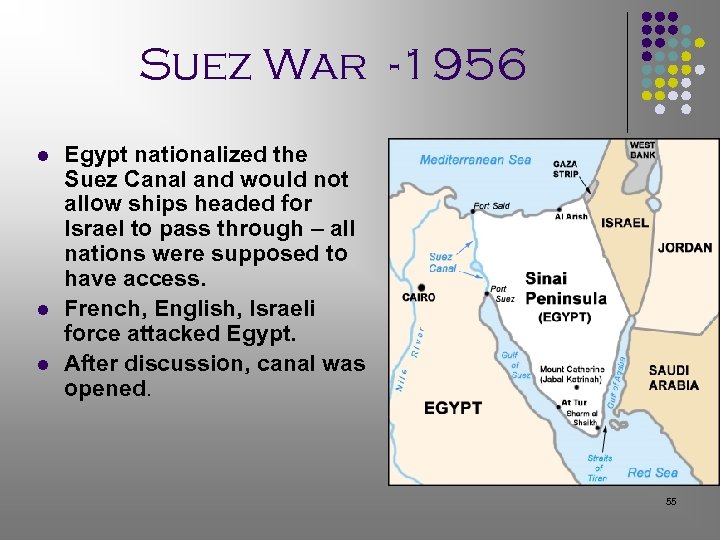 Suez War -1956 l l l Egypt nationalized the Suez Canal and would not allow ships headed for Israel to pass through – all nations were supposed to have access. French, English, Israeli force attacked Egypt. After discussion, canal was opened. 55
Suez War -1956 l l l Egypt nationalized the Suez Canal and would not allow ships headed for Israel to pass through – all nations were supposed to have access. French, English, Israeli force attacked Egypt. After discussion, canal was opened. 55
 Hungarian Uprising 1956 l l The Hungarian people, tired of Soviet domination in their country, rose in revolt and called for a democratic government. The Soviet response was swift and brutal: 56
Hungarian Uprising 1956 l l The Hungarian people, tired of Soviet domination in their country, rose in revolt and called for a democratic government. The Soviet response was swift and brutal: 56
 USSR Crushes Rebellion l Soviet tanks rolled into Hungary and killed 30, 000 Hungarians and executed the resistance leader – Imre Nagy. l US and UN did nothing to help. 57
USSR Crushes Rebellion l Soviet tanks rolled into Hungary and killed 30, 000 Hungarians and executed the resistance leader – Imre Nagy. l US and UN did nothing to help. 57
 Space Race l l l On October 4, 1957 the Soviet Union successfully launched Sputnik I. The world's first artificial satellite was about the size of a beach ball. Orbited the earth in 98 minutes. Race to control space was on! 58
Space Race l l l On October 4, 1957 the Soviet Union successfully launched Sputnik I. The world's first artificial satellite was about the size of a beach ball. Orbited the earth in 98 minutes. Race to control space was on! 58
 U-2 Incident l l U-2 was designed to be high altitude reconnaissance plane. CIA used these to spy on USSR and one was shot down on May 1, 1960. 59
U-2 Incident l l U-2 was designed to be high altitude reconnaissance plane. CIA used these to spy on USSR and one was shot down on May 1, 1960. 59
 Francis Gary Powers l l l Recruited by CIA to fly spy missions. Shot down in U 2 over USSR and convicted of espionage. Exchanged for a KGB colonel the US had captured. 60
Francis Gary Powers l l l Recruited by CIA to fly spy missions. Shot down in U 2 over USSR and convicted of espionage. Exchanged for a KGB colonel the US had captured. 60
 Conclusion… l Moving into the 1960’s, the Cold War was really starting to heat up with no end in sight. l The Cold War will continue in the 1960 s with the world moving closer to an open conflict between the US and USSR. 61
Conclusion… l Moving into the 1960’s, the Cold War was really starting to heat up with no end in sight. l The Cold War will continue in the 1960 s with the world moving closer to an open conflict between the US and USSR. 61


