9dcf9e2b187e6d025ccd8feb239aaf43.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 148

 § 1. The atmosphere in a tank might be too lean if it is: § A. Capable of supporting combustion because the hydrocarbon content is above the UFL (Upper Flammable Limit) § B. Capable of supporting a fire once started § C. Incapable of supporting combustion because the hydrocarbon content is below the (LFL) Lower Flammable Limit § D. Not safe for ballasting
§ 1. The atmosphere in a tank might be too lean if it is: § A. Capable of supporting combustion because the hydrocarbon content is above the UFL (Upper Flammable Limit) § B. Capable of supporting a fire once started § C. Incapable of supporting combustion because the hydrocarbon content is below the (LFL) Lower Flammable Limit § D. Not safe for ballasting
 Flammable Limit or Explosive Range If the oxygen is less than 10% inside a tank, the hydrocarbon vapor will not burn and therefore it will be classified as Too Lean But if oxygen is more than 10% inside the tank there will be a chance the hydrocarbon vapor will ignite and it is called Too Rich
Flammable Limit or Explosive Range If the oxygen is less than 10% inside a tank, the hydrocarbon vapor will not burn and therefore it will be classified as Too Lean But if oxygen is more than 10% inside the tank there will be a chance the hydrocarbon vapor will ignite and it is called Too Rich
 § 2. Keeping the draft at or below the load line mark will insure that the unit has adequate: § A. Lightweight displacement § B. Reserve buoyancy § C. Reserve ballast § D. Critical motions
§ 2. Keeping the draft at or below the load line mark will insure that the unit has adequate: § A. Lightweight displacement § B. Reserve buoyancy § C. Reserve ballast § D. Critical motions
 § 3. Your vessel is floating in water whose density is 1010. Your fresh water allowance is 8 inches. How far below her mark may she be loaded so as to float at her mark in salt water whose density is 1025? § A. 4. 8 inches § B. 6. 4 inches § C. 3. 2 inches § D. 8. 0 inches
§ 3. Your vessel is floating in water whose density is 1010. Your fresh water allowance is 8 inches. How far below her mark may she be loaded so as to float at her mark in salt water whose density is 1025? § A. 4. 8 inches § B. 6. 4 inches § C. 3. 2 inches § D. 8. 0 inches
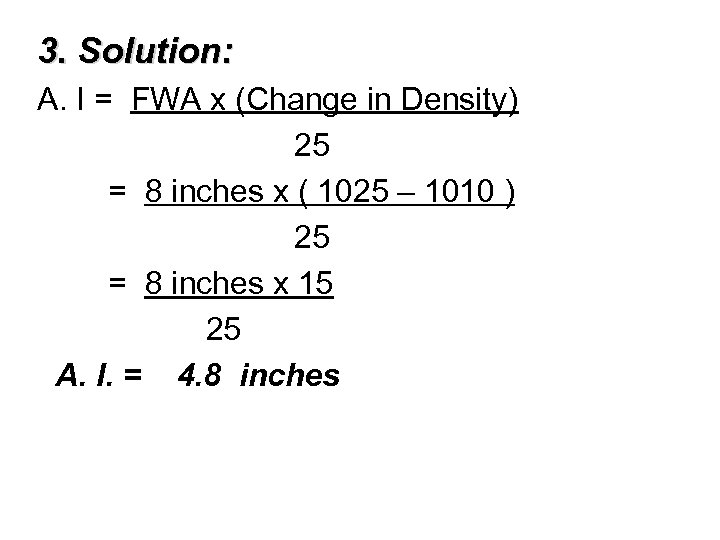 3. Solution: A. I = FWA x (Change in Density) 25 = 8 inches x ( 1025 – 1010 ) 25 = 8 inches x 15 25 A. I. = 4. 8 inches
3. Solution: A. I = FWA x (Change in Density) 25 = 8 inches x ( 1025 – 1010 ) 25 = 8 inches x 15 25 A. I. = 4. 8 inches
 4. A vessel is to lift a cargo weighing 30 tons with her boom whose head is 30 feet from center line. The ship’s displacement excluding the weight to be lifted is 8, 700 tons. KM is 21. 5 ft; KG is 20. 5 ft. What will be the list of the vessel when the cargo is lifted? A. 1. 4 B. 3. 4 C. 2. 8 D. 5. 8
4. A vessel is to lift a cargo weighing 30 tons with her boom whose head is 30 feet from center line. The ship’s displacement excluding the weight to be lifted is 8, 700 tons. KM is 21. 5 ft; KG is 20. 5 ft. What will be the list of the vessel when the cargo is lifted? A. 1. 4 B. 3. 4 C. 2. 8 D. 5. 8
 • INCLINING • GM = Weight x Distance Displ. x Tan List Dist. = GM x Displ. x Tan List Weight = GM x Displ x Tan List Distance Tan List = Weight x Distance Displ. x GM • • EXPERIMENT
• INCLINING • GM = Weight x Distance Displ. x Tan List Dist. = GM x Displ. x Tan List Weight = GM x Displ x Tan List Distance Tan List = Weight x Distance Displ. x GM • • EXPERIMENT
 GM = KM – KG GM = 21. 5 ft – 20. 5 ft. GM = 1. 0 foot TAN LIST = W x D GM x = 30 t x 30 ft. 1 ft x 8, 700 t = 900 / 8, 700 = 0. 1030927 inv. Tan LIST = 5. 88°
GM = KM – KG GM = 21. 5 ft – 20. 5 ft. GM = 1. 0 foot TAN LIST = W x D GM x = 30 t x 30 ft. 1 ft x 8, 700 t = 900 / 8, 700 = 0. 1030927 inv. Tan LIST = 5. 88°
 § 5. The change in trim of a vessel may be found by: § A. Looking at the hydrostatic properties table for the draft of the vessel § B. Dividing the trim moments by MTI § C. Subtracting the LCF from the LCB § D. Dividing longitudinal moments by the
§ 5. The change in trim of a vessel may be found by: § A. Looking at the hydrostatic properties table for the draft of the vessel § B. Dividing the trim moments by MTI § C. Subtracting the LCF from the LCB § D. Dividing longitudinal moments by the
 § 6. Your vessel measures 119 ft. long by 17 ft. in beam. If the natural rolling period at a draft of 5’ 05” is 6 seconds, what is the GM? § A. 1. 55 ft. § B. 1. 36 ft. § C. 1. 14 ft. § D. 1. 96 ft.
§ 6. Your vessel measures 119 ft. long by 17 ft. in beam. If the natural rolling period at a draft of 5’ 05” is 6 seconds, what is the GM? § A. 1. 55 ft. § B. 1. 36 ft. § C. 1. 14 ft. § D. 1. 96 ft.
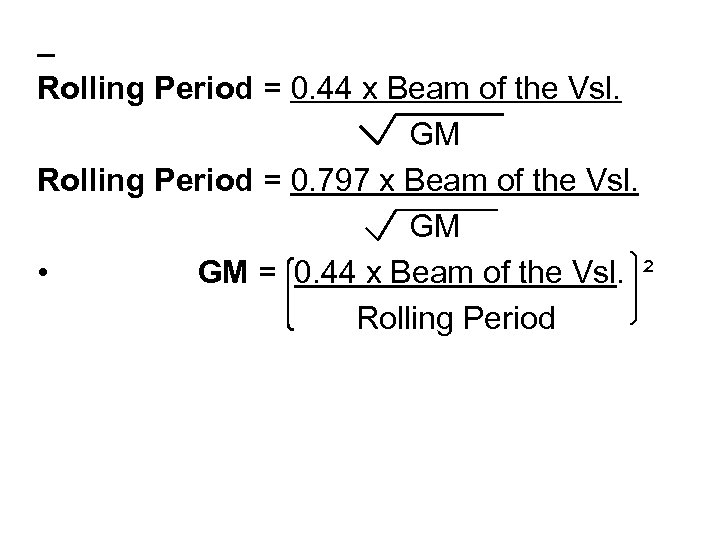 Rolling Period = 0. 44 x Beam of the Vsl. GM Rolling Period = 0. 797 x Beam of the Vsl. GM • GM = 0. 44 x Beam of the Vsl. ² Rolling Period
Rolling Period = 0. 44 x Beam of the Vsl. GM Rolling Period = 0. 797 x Beam of the Vsl. GM • GM = 0. 44 x Beam of the Vsl. ² Rolling Period
 6. Solution: GM = 0. 44 x Beam ² R. P. GM = 0. 44 x 17 ft ² 6 secs. GM = 1. 55 ft.
6. Solution: GM = 0. 44 x Beam ² R. P. GM = 0. 44 x 17 ft ² 6 secs. GM = 1. 55 ft.
 § 7. Repairing damage to the hull at or above the waterline reduces the threat of: § A. Free surface effects § B. Wind overturning moments § C. Continued progressive flooding § D. Capsizing the vessel
§ 7. Repairing damage to the hull at or above the waterline reduces the threat of: § A. Free surface effects § B. Wind overturning moments § C. Continued progressive flooding § D. Capsizing the vessel
 § 8. Cargoes that gives off fumes that may contaminate other cargo is known as a: § A. Delicate cargo § B. Toxic cargo § C. Dirty cargo § D. Odorous cargo
§ 8. Cargoes that gives off fumes that may contaminate other cargo is known as a: § A. Delicate cargo § B. Toxic cargo § C. Dirty cargo § D. Odorous cargo
 § 9. A vessel is fitted with deep tanks with a capacity of 1, 000 tons of fresh water. What quantity of peanut oil with specific gravity of 0. 92 could be carried in such tanks? § A. 920 tons § B. 907 tons § C. 840 tons § D. 850 tons
§ 9. A vessel is fitted with deep tanks with a capacity of 1, 000 tons of fresh water. What quantity of peanut oil with specific gravity of 0. 92 could be carried in such tanks? § A. 920 tons § B. 907 tons § C. 840 tons § D. 850 tons
 9. Solution: WT. = R. D of Peanut Oil x Cap. Of FW R. D of FW WT = 0. 92 ton/m³ x 1, 000 tons 1, 000 ton/m³ WT = 920 tons
9. Solution: WT. = R. D of Peanut Oil x Cap. Of FW R. D of FW WT = 0. 92 ton/m³ x 1, 000 tons 1, 000 ton/m³ WT = 920 tons
 § 10. You are loading a cargo of canned goods with a stowage factor of 65. If you allow 15% for broken stowage, how many tons can be loaded in a space of 55, 000 cubic feet? § A. 719 § B. 846 § C. 687 § D. 973
§ 10. You are loading a cargo of canned goods with a stowage factor of 65. If you allow 15% for broken stowage, how many tons can be loaded in a space of 55, 000 cubic feet? § A. 719 § B. 846 § C. 687 § D. 973
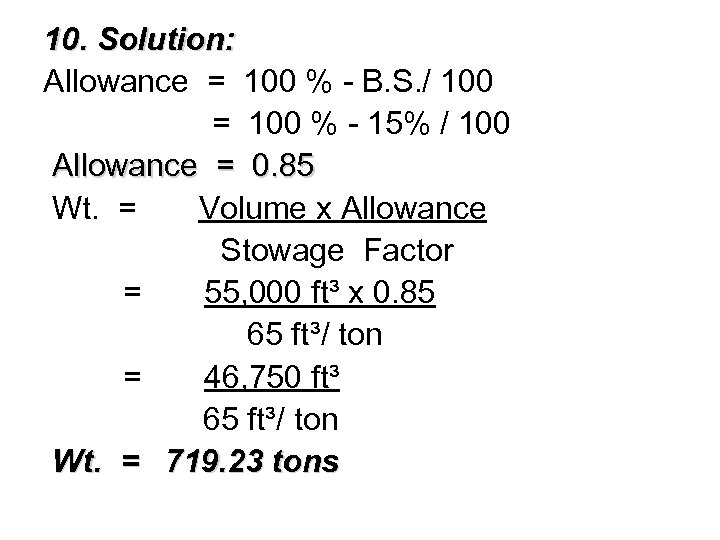 10. Solution: Allowance = 100 % - B. S. / 100 = 100 % - 15% / 100 Allowance = 0. 85 Wt. = Volume x Allowance Stowage Factor = 55, 000 ft³ x 0. 85 65 ft³/ ton = 46, 750 ft³ 65 ft³/ ton Wt. = 719. 23 tons
10. Solution: Allowance = 100 % - B. S. / 100 = 100 % - 15% / 100 Allowance = 0. 85 Wt. = Volume x Allowance Stowage Factor = 55, 000 ft³ x 0. 85 65 ft³/ ton = 46, 750 ft³ 65 ft³/ ton Wt. = 719. 23 tons
 § 11. The difference between the starboard and port drafts caused by shifting a weight transversely is: § A. List § B. Trim § C. Heel § D. Flotation
§ 11. The difference between the starboard and port drafts caused by shifting a weight transversely is: § A. List § B. Trim § C. Heel § D. Flotation
 § 12. Non-flammable gases should have what kind of label? § A. Green § B. Skull and crossbones § C. White § D. Red
§ 12. Non-flammable gases should have what kind of label? § A. Green § B. Skull and crossbones § C. White § D. Red

 Indicate dangerous goods that must be stored at a safe distance from explosive goods
Indicate dangerous goods that must be stored at a safe distance from explosive goods
 § 13. An unstable upright equilibrium position on a vessel means that the metacenter is: § A. Higher than the baseline § B. At the same height as the center of gravity § C. Lower than the center of gravity § D. On the longitudinal centerline
§ 13. An unstable upright equilibrium position on a vessel means that the metacenter is: § A. Higher than the baseline § B. At the same height as the center of gravity § C. Lower than the center of gravity § D. On the longitudinal centerline
 § 14. Corrosive liquids and acids should have what kind of label? § A. Skull and cross bone § B. Red § C. Yellow § D. White
§ 14. Corrosive liquids and acids should have what kind of label? § A. Skull and cross bone § B. Red § C. Yellow § D. White

 § 15. A consignment of lumber is to be loaded, each piece measures 3 inches thick, 12 inches wide and 16 feet long. There are 30, 000 pieces to be loaded. How many board feet is the shipment? shipment § A. 96, 000 § B. 1, 440, 000 § C. 1, 200, 000 § D. 14, 400, 000
§ 15. A consignment of lumber is to be loaded, each piece measures 3 inches thick, 12 inches wide and 16 feet long. There are 30, 000 pieces to be loaded. How many board feet is the shipment? shipment § A. 96, 000 § B. 1, 440, 000 § C. 1, 200, 000 § D. 14, 400, 000
 1. 2. 3. BF = L' x W' x H' x 12 BF = L' x W' x H" BF = L' x W" x H" / 12 BF = L‘ x W“ x H“ / 12 BF = 16‘ x 12“ x 3“ / 12 BF = 576 / 12 BF = 48 x 30, 000 pcs. BF = 1, 440, 000
1. 2. 3. BF = L' x W' x H' x 12 BF = L' x W' x H" BF = L' x W" x H" / 12 BF = L‘ x W“ x H“ / 12 BF = 16‘ x 12“ x 3“ / 12 BF = 576 / 12 BF = 48 x 30, 000 pcs. BF = 1, 440, 000
 § 16. In which case may metacentric height be considered an indication of a vessel’s stability? § A. For all angles of inclination § B. For small angles of inclination § C. In no case § D. For large angles of inclination
§ 16. In which case may metacentric height be considered an indication of a vessel’s stability? § A. For all angles of inclination § B. For small angles of inclination § C. In no case § D. For large angles of inclination
 § 17. Containers of flammable solids should be conspicuously labeled by the shipper with a: § A. Red and white label § B. Orange label § C. Green label § D. Yellow label
§ 17. Containers of flammable solids should be conspicuously labeled by the shipper with a: § A. Red and white label § B. Orange label § C. Green label § D. Yellow label

 Indicate dangerous goods that must be separated from flammable solids, spontaneously combustible agents or agents that are dangerous when wet by a wet longitudinal intermediate spaceor on deck by at least 24 metres.
Indicate dangerous goods that must be separated from flammable solids, spontaneously combustible agents or agents that are dangerous when wet by a wet longitudinal intermediate spaceor on deck by at least 24 metres.
 § 18. In handling break bulk hazardous materials, it is forbidden to use: § A. Pallets § B. Cargo nets § C. Slings § D. Metal bale hooks
§ 18. In handling break bulk hazardous materials, it is forbidden to use: § A. Pallets § B. Cargo nets § C. Slings § D. Metal bale hooks
 § 19. A vessel displacing 18, 000 tons has a KG of 50 feet. A crane is used to lift cargo weighing 20 tons from a supply vessel. When lifting, the head of the crane boom is 150 feet above the keel. What is the change in KG? § A. 0. 11 foot § B. 0. 17 foot § C. 0. 32 foot § D. 0. 25 foot
§ 19. A vessel displacing 18, 000 tons has a KG of 50 feet. A crane is used to lift cargo weighing 20 tons from a supply vessel. When lifting, the head of the crane boom is 150 feet above the keel. What is the change in KG? § A. 0. 11 foot § B. 0. 17 foot § C. 0. 32 foot § D. 0. 25 foot
 19. Solution: GG‘ = Wt x Dist = 20 tons x (150 ft – 50 ft ) 18, 000 tons = 20 tons x 100 ft 18, 000 tons = 2, 000 ft/ton 18, 000 tons GG‘ = 0. 11 ft.
19. Solution: GG‘ = Wt x Dist = 20 tons x (150 ft – 50 ft ) 18, 000 tons = 20 tons x 100 ft 18, 000 tons = 2, 000 ft/ton 18, 000 tons GG‘ = 0. 11 ft.
 § 20. A cargo of 75 tons is to be lifted with a boom located 50 feet from the ship centerline. The ship’s displacement including the suspended cargo is 6, 000 tons and GM six feet. The list of the ship with the cargo suspended from the boom will be: § A. 5. 40 § B. 5. 00 § C. 6. 50 § D. 5. 94
§ 20. A cargo of 75 tons is to be lifted with a boom located 50 feet from the ship centerline. The ship’s displacement including the suspended cargo is 6, 000 tons and GM six feet. The list of the ship with the cargo suspended from the boom will be: § A. 5. 40 § B. 5. 00 § C. 6. 50 § D. 5. 94
 20. Solution: TAN LIST = W x D GM x = 75 t x 50 ft 6 ft. x 6, 000 t = 3, 750 36, 000 LIST = 0. 104166 inv Tan LIST = 5. 94°
20. Solution: TAN LIST = W x D GM x = 75 t x 50 ft 6 ft. x 6, 000 t = 3, 750 36, 000 LIST = 0. 104166 inv Tan LIST = 5. 94°
 § 21. When the height of the metacenter is greater than the height of the center of gravity, the upright equilibrium position is stable and stability is: § A. Neutral § B. Unstable § C. Negative § D. Positive
§ 21. When the height of the metacenter is greater than the height of the center of gravity, the upright equilibrium position is stable and stability is: § A. Neutral § B. Unstable § C. Negative § D. Positive
 § 22. In preparation for receiving chilled reefer cargo, the reefer space has been pre-cooled for over 24 hours. You may begin loading when the space has been cooled to a temperature between: between § A. – 10 F and +10 F § B. 42 F and 55 F § C. 12 F and 20 F § D. 28 F and 40 F OR -2º C and 4º C
§ 22. In preparation for receiving chilled reefer cargo, the reefer space has been pre-cooled for over 24 hours. You may begin loading when the space has been cooled to a temperature between: between § A. – 10 F and +10 F § B. 42 F and 55 F § C. 12 F and 20 F § D. 28 F and 40 F OR -2º C and 4º C
 § 23. When a vessel is inclined at a small angle the center of buoyancy will: § A. Remain stationary § B. Move towards the high side § C. Move to the height of the metacenter § D. Move towards the low side
§ 23. When a vessel is inclined at a small angle the center of buoyancy will: § A. Remain stationary § B. Move towards the high side § C. Move to the height of the metacenter § D. Move towards the low side
 § 24. A tank is loaded with 9, 000 barrels of gasoline. The temperature of the product is 80 F, and it has a coefficient of expansion of. 0008. The net amount of cargo loaded is: § A. 8, 856 barrels § B. 8, 944 barrels § C. 9, 144 barrels § D. 9, 072 barrels
§ 24. A tank is loaded with 9, 000 barrels of gasoline. The temperature of the product is 80 F, and it has a coefficient of expansion of. 0008. The net amount of cargo loaded is: § A. 8, 856 barrels § B. 8, 944 barrels § C. 9, 144 barrels § D. 9, 072 barrels
 24. Solution: Standard Loading Temp. = 60° F Net bbls = Gross +/- ( Gross x Coefficient x ( Diff. In temperature )) = 9, 000 +/- (9, 000 x 0. 0008 (80°F - 60°F)) = 9, 000 +/- ( 7. 2 x 20°F ) = 9, 000 - 144 Net bbls. = 8, 856
24. Solution: Standard Loading Temp. = 60° F Net bbls = Gross +/- ( Gross x Coefficient x ( Diff. In temperature )) = 9, 000 +/- (9, 000 x 0. 0008 (80°F - 60°F)) = 9, 000 +/- ( 7. 2 x 20°F ) = 9, 000 - 144 Net bbls. = 8, 856
 § § § 25. Bilge soundings indicate: A. Whether the ship is taking on water B. Whether the cargo is leaking or not C. The amount of condensation in the hold D. All of these
§ § § 25. Bilge soundings indicate: A. Whether the ship is taking on water B. Whether the cargo is leaking or not C. The amount of condensation in the hold D. All of these
 § 26. If the metacentric height is large, a vessel will: § A. Have a slow and easy motion § B. Be stiff § C. Be tender § D. Have a tendency to yaw
§ 26. If the metacentric height is large, a vessel will: § A. Have a slow and easy motion § B. Be stiff § C. Be tender § D. Have a tendency to yaw
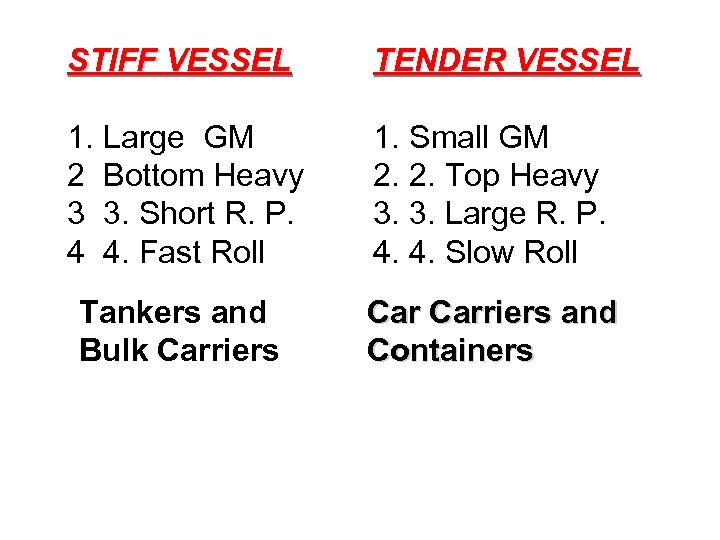 STIFF VESSEL TENDER VESSEL 1. Large GM 2 Bottom Heavy 3 3. Short R. P. 4 4. Fast Roll 1. Small GM 2. 2. Top Heavy 3. 3. Large R. P. 4. 4. Slow Roll Tankers and Bulk Carriers and Containers
STIFF VESSEL TENDER VESSEL 1. Large GM 2 Bottom Heavy 3 3. Short R. P. 4 4. Fast Roll 1. Small GM 2. 2. Top Heavy 3. 3. Large R. P. 4. 4. Slow Roll Tankers and Bulk Carriers and Containers
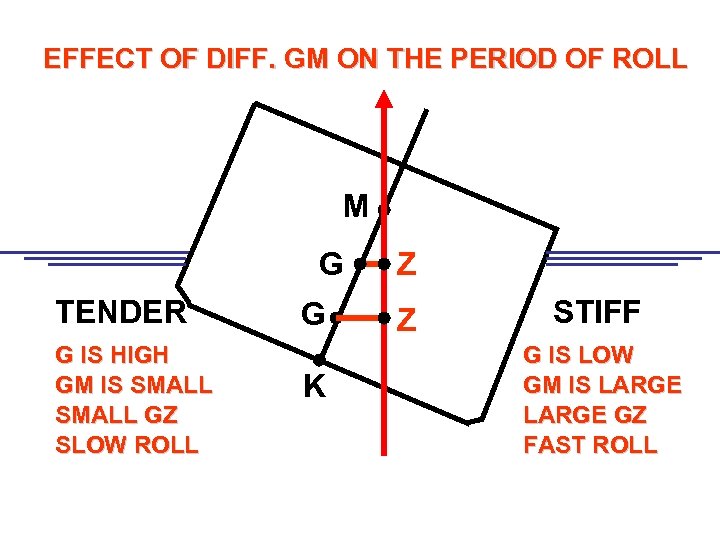 EFFECT OF DIFF. GM ON THE PERIOD OF ROLL M G TENDER G IS HIGH GM IS SMALL GZ SLOW ROLL G K Z Z STIFF G IS LOW GM IS LARGE GZ FAST ROLL
EFFECT OF DIFF. GM ON THE PERIOD OF ROLL M G TENDER G IS HIGH GM IS SMALL GZ SLOW ROLL G K Z Z STIFF G IS LOW GM IS LARGE GZ FAST ROLL
 STIFF VESSEL
STIFF VESSEL
 STIFF VESSEL
STIFF VESSEL
 TENDER VESSEL
TENDER VESSEL
 TENDER SHIP
TENDER SHIP
 27. Certain cargoes must be segregated because of their: § A. Inherent characteristics § B. Weight § C. Danger to human § D. Destination
27. Certain cargoes must be segregated because of their: § A. Inherent characteristics § B. Weight § C. Danger to human § D. Destination
 § 28. The shearing stress on a ship’s structure are usually GREATEST at: § A. Midships § B. The stem § C. The bow § D. Ships quarter length points
§ 28. The shearing stress on a ship’s structure are usually GREATEST at: § A. Midships § B. The stem § C. The bow § D. Ships quarter length points
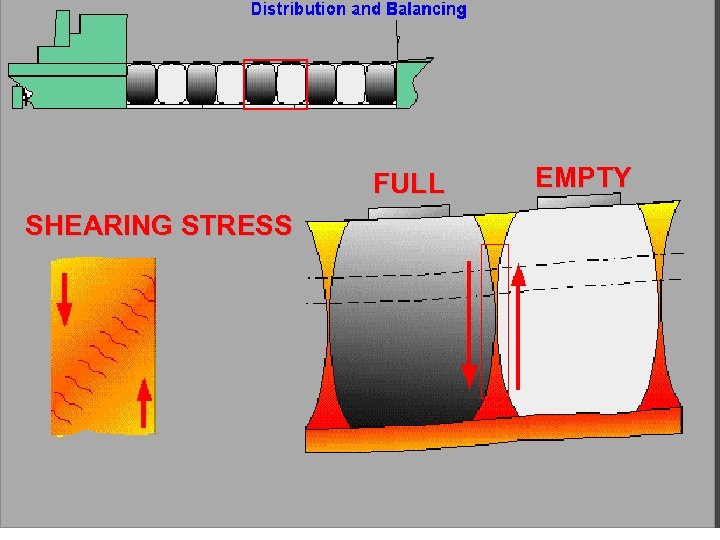 FULL SHEARING STRESS EMPTY
FULL SHEARING STRESS EMPTY
 § 29. If a vessel is loaded in such a manner that she is said to be sagging, what kind of stress is placed on the sheer strakes? § A. Thrust § B. Compression § C. Tension § D. Racking
§ 29. If a vessel is loaded in such a manner that she is said to be sagging, what kind of stress is placed on the sheer strakes? § A. Thrust § B. Compression § C. Tension § D. Racking
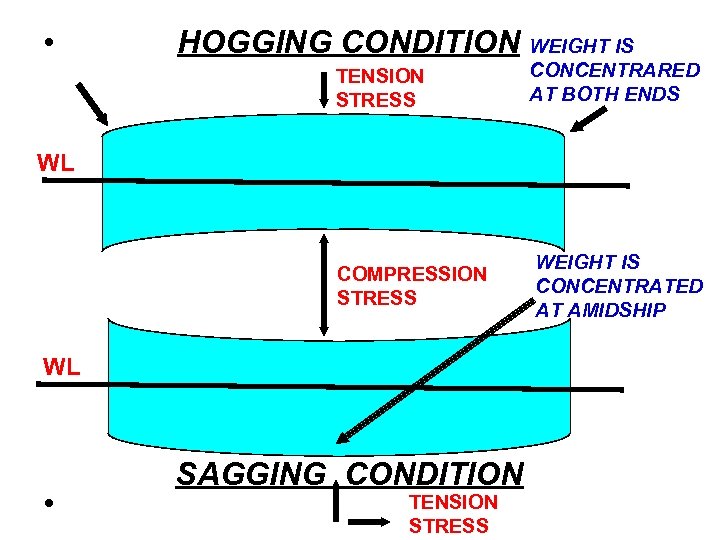 • HOGGING CONDITION WEIGHT IS TENSION STRESS CONCENTRARED AT BOTH ENDS COMPRESSION STRESS WEIGHT IS CONCENTRATED AT AMIDSHIP WL WL SAGGING CONDITION TENSION • STRESS
• HOGGING CONDITION WEIGHT IS TENSION STRESS CONCENTRARED AT BOTH ENDS COMPRESSION STRESS WEIGHT IS CONCENTRATED AT AMIDSHIP WL WL SAGGING CONDITION TENSION • STRESS

 § 30. How much force would be required to lift a weight of 200 lbs. , using a gun tackle rigged to disadvantage disregarding friction? § A. 150 lbs. § B. 100 lbs. § C. 50 lbs. § D. 200 lbs.
§ 30. How much force would be required to lift a weight of 200 lbs. , using a gun tackle rigged to disadvantage disregarding friction? § A. 150 lbs. § B. 100 lbs. § C. 50 lbs. § D. 200 lbs.
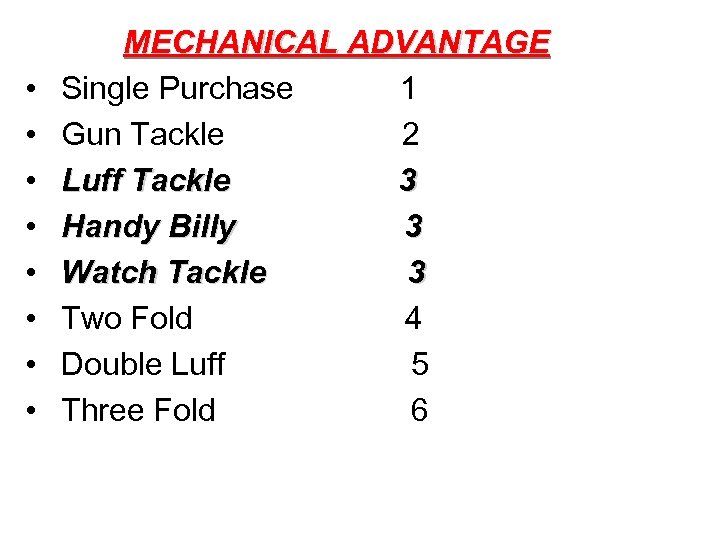 MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE • Single Purchase 1 • Gun Tackle 2 • Luff Tackle 3 • Handy Billy 3 • Watch Tackle 3 • Two Fold 4 • Double Luff 5 • Three Fold 6
MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE • Single Purchase 1 • Gun Tackle 2 • Luff Tackle 3 • Handy Billy 3 • Watch Tackle 3 • Two Fold 4 • Double Luff 5 • Three Fold 6
 30. Solution: Force = Wt x (1 + 10% nos of Sheaves) Mechanical Advantage Force = Weight Mechanical Advantage = 200 lbs. 2 Force = 100 lbs
30. Solution: Force = Wt x (1 + 10% nos of Sheaves) Mechanical Advantage Force = Weight Mechanical Advantage = 200 lbs. 2 Force = 100 lbs
 § 31. You are loading bagged coffee beams, to keep cargo leakage from being contaminated by ships structure, you should: § A. Hose down the deck before loading the cargo § B. Place the cargo on a layer of spaced dunnage § C. Use separation cloths between the deck and cargo § D. Use bag-on-bag stowage
§ 31. You are loading bagged coffee beams, to keep cargo leakage from being contaminated by ships structure, you should: § A. Hose down the deck before loading the cargo § B. Place the cargo on a layer of spaced dunnage § C. Use separation cloths between the deck and cargo § D. Use bag-on-bag stowage
 § 32. The wave period and the apparent rolling period of a vessel are the same: § A. Rolling period decreases § B. Rolling period increases § C. Synchronous rolling occurs § D. Roll period is dampened
§ 32. The wave period and the apparent rolling period of a vessel are the same: § A. Rolling period decreases § B. Rolling period increases § C. Synchronous rolling occurs § D. Roll period is dampened
 § 33. In order to check your vessel’s stability a weight of 40 tons is lifted with the jumbo boom, the boom head being 50 feet from the ship’s centerline. The clinometer is then carefully read and shows a list of 5º. The vessel’s displacement is 8, 000 tons including the suspended weight. What will be the metacentric height of the vessel at this time? § A. 2. 74 feet GM § B. 2. 86 feet GM § C. 2. 80 feet GM § D. 2. 93 feet GM
§ 33. In order to check your vessel’s stability a weight of 40 tons is lifted with the jumbo boom, the boom head being 50 feet from the ship’s centerline. The clinometer is then carefully read and shows a list of 5º. The vessel’s displacement is 8, 000 tons including the suspended weight. What will be the metacentric height of the vessel at this time? § A. 2. 74 feet GM § B. 2. 86 feet GM § C. 2. 80 feet GM § D. 2. 93 feet GM
 33. Solution: Tan List = W x D GM x GM = W x D Tan List x = 40 t x 50 ft. Tan 5° x 8, 000 t GM = 2. 86 ft.
33. Solution: Tan List = W x D GM x GM = W x D Tan List x = 40 t x 50 ft. Tan 5° x 8, 000 t GM = 2. 86 ft.
 § 34. What can be used to measure the percentage of oxygen inside a chain locker? § A. Combustible gas indicator § B. Oxygen indicator § C. Flame safety lamp § D. H 2 S meter
§ 34. What can be used to measure the percentage of oxygen inside a chain locker? § A. Combustible gas indicator § B. Oxygen indicator § C. Flame safety lamp § D. H 2 S meter
 § 35. A vessel behaves as if all of its weight is acting downward through the center of gravity, and all its support is acting upward through the: § A. Center of buoyancy § B. Tipping center § C. Keel § D. Amidships
§ 35. A vessel behaves as if all of its weight is acting downward through the center of gravity, and all its support is acting upward through the: § A. Center of buoyancy § B. Tipping center § C. Keel § D. Amidships
 § 36. A slow and easy motion in a seaway is an indication of a: § A. Low center of gravity § B. Small GM § C. Stiff vessel § D. Large GZ
§ 36. A slow and easy motion in a seaway is an indication of a: § A. Low center of gravity § B. Small GM § C. Stiff vessel § D. Large GZ
 § 37. When loading a container vessel, the operation is basically that of vertical loading. The important factors to be considered when loading containers are port of discharge: § A. Availability of dunnage, and docking § B. Crushability, and inherent vice § C. Sweat, and weight § D. Weight and refrigeration
§ 37. When loading a container vessel, the operation is basically that of vertical loading. The important factors to be considered when loading containers are port of discharge: § A. Availability of dunnage, and docking § B. Crushability, and inherent vice § C. Sweat, and weight § D. Weight and refrigeration
 § 38. The lashing of a stack of containers with interlocking fittings restrain the forces that causes: A. Toppling B. Crushing C. Racking D. Buckling
§ 38. The lashing of a stack of containers with interlocking fittings restrain the forces that causes: A. Toppling B. Crushing C. Racking D. Buckling
 § 39. When loading or discharging dry mud or cement, crew members should use goggles and: § A. Ear plug § B. Rubberized boots § C. Facial respirator mask § D. Fireman’s outfit
§ 39. When loading or discharging dry mud or cement, crew members should use goggles and: § A. Ear plug § B. Rubberized boots § C. Facial respirator mask § D. Fireman’s outfit

 § 40. The important stability parameter, KG is defined as the: § A. Height of the metacenter above the keel § B. Height of the center of buoyancy above the keel § C. Metacentric height § D. Height of the center of gravity above the keel
§ 40. The important stability parameter, KG is defined as the: § A. Height of the metacenter above the keel § B. Height of the center of buoyancy above the keel § C. Metacentric height § D. Height of the center of gravity above the keel
 § 41. Which of the following steps is NOT generally taken when gas-freeing a tank? § A. Washing the tank interior with sea water § B. Fresh air ventilation § C. Application of degreasing solvents § D. Removal of sludge and corrosion products
§ 41. Which of the following steps is NOT generally taken when gas-freeing a tank? § A. Washing the tank interior with sea water § B. Fresh air ventilation § C. Application of degreasing solvents § D. Removal of sludge and corrosion products
 § 42. Reid vapor pressure is: § A. The lowest temperature and pressure that will cause a flammable liquid to give off vapors § B. Exerted by liquid cargo on a cargo hose body § C. Exerted by liquid cargo on the sides of a tank § D. A measurement of the amount of flammable vapors given off by a liquid at a certain temperature
§ 42. Reid vapor pressure is: § A. The lowest temperature and pressure that will cause a flammable liquid to give off vapors § B. Exerted by liquid cargo on a cargo hose body § C. Exerted by liquid cargo on the sides of a tank § D. A measurement of the amount of flammable vapors given off by a liquid at a certain temperature
 § 43. When loading bulk liquid cargo, what is the first action you should take if a cargo valve jammed open? § A. Trip the pump relief valve § B. Order the dock man to shut down § C. Run out the vessel’s or terminal firehose § D. Call the owner, operator, or terminal supervisor
§ 43. When loading bulk liquid cargo, what is the first action you should take if a cargo valve jammed open? § A. Trip the pump relief valve § B. Order the dock man to shut down § C. Run out the vessel’s or terminal firehose § D. Call the owner, operator, or terminal supervisor
 § 44. It is possible, and sometimes necessary to strengthen the deck of a vessel for carriage of deck cargo by: § A. Welding steel “feet” to the deck, on which the cargo is placed § B. Placing bunker on the deck § C. Building a stage on which to place the cargo § D. Erecting vertical pillars under the deck to support the cargo
§ 44. It is possible, and sometimes necessary to strengthen the deck of a vessel for carriage of deck cargo by: § A. Welding steel “feet” to the deck, on which the cargo is placed § B. Placing bunker on the deck § C. Building a stage on which to place the cargo § D. Erecting vertical pillars under the deck to support the cargo
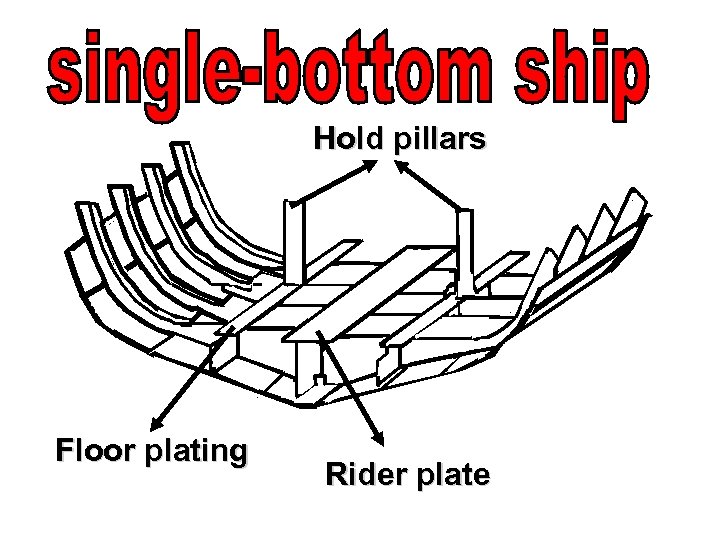 Hold pillars Floor plating Rider plate
Hold pillars Floor plating Rider plate
 § 45. Which of the following statements about ventilation of bulk coal is TRUE? § A. Coal should not be ventilated, all oxygen should be excluded from the cargo § B. Coal should be surface ventilated only § C. Coal should be through ventilated only if temperature in the center of the cargo exceed 125ºF § D. Coal should be through ventilated to remove methane and reduce the heat of spontaneous combustion
§ 45. Which of the following statements about ventilation of bulk coal is TRUE? § A. Coal should not be ventilated, all oxygen should be excluded from the cargo § B. Coal should be surface ventilated only § C. Coal should be through ventilated only if temperature in the center of the cargo exceed 125ºF § D. Coal should be through ventilated to remove methane and reduce the heat of spontaneous combustion
 § 46. A vessel’s bottom will be subjected to tension when weight is concentrated: § A. At both ends of the vessel § B. Amidships. § C. Aft § D. Forward
§ 46. A vessel’s bottom will be subjected to tension when weight is concentrated: § A. At both ends of the vessel § B. Amidships. § C. Aft § D. Forward
 § 47. Hygroscopic cargoes should be ventilated in cases when: § A. The dew point of the air in the hold is very low § B. Going from a warm to a cold climate § C. The dew point of the outside air is greater than the dew point of the air in the hold § D. The outside dew point is 60º F and the cargo temperature is 54º F
§ 47. Hygroscopic cargoes should be ventilated in cases when: § A. The dew point of the air in the hold is very low § B. Going from a warm to a cold climate § C. The dew point of the outside air is greater than the dew point of the air in the hold § D. The outside dew point is 60º F and the cargo temperature is 54º F
 § 48. Segregation of cargoes refers to: § A. Separation of cargoes by destination § B. Classifying cargoes according to their toxicity § C. Separating cargoes so that one cannot damage the other because of its inherent characteristics § D. Listing of cargoes in order of their flammability
§ 48. Segregation of cargoes refers to: § A. Separation of cargoes by destination § B. Classifying cargoes according to their toxicity § C. Separating cargoes so that one cannot damage the other because of its inherent characteristics § D. Listing of cargoes in order of their flammability
 § 49. Which of the following weld faults can only be detected by a method that examines the internal structure of a weld? § A. Under cut § B. Lack of penetration § C. Overlap § D. Lack of reinforcement
§ 49. Which of the following weld faults can only be detected by a method that examines the internal structure of a weld? § A. Under cut § B. Lack of penetration § C. Overlap § D. Lack of reinforcement
 § 50. The amount of strain on each runner of a married fall system lifting 2, 000 lbs. When the angle made by the legs is 90º would be: § A. 1, 414 lbs. § B. 1, 000 lbs. § C. 2, 000 lbs. § D. 1, 154 lbs.
§ 50. The amount of strain on each runner of a married fall system lifting 2, 000 lbs. When the angle made by the legs is 90º would be: § A. 1, 414 lbs. § B. 1, 000 lbs. § C. 2, 000 lbs. § D. 1, 154 lbs.
 50. Solution: Strain = Weight 2 x ½ Cos = 2, 000 lbs. 2 x Cos 45° = 2, 000 lbs 1. 41421 Strain = 1. 414 lbs.
50. Solution: Strain = Weight 2 x ½ Cos = 2, 000 lbs. 2 x Cos 45° = 2, 000 lbs 1. 41421 Strain = 1. 414 lbs.
 § 51. What is the area of a circle with a radius of 4 feet after a sector of 111 degrees has been removed? § A. 3. 90 feet § B. 8. 67 feet § C. 34. 77 feet § D. 50. 27 feet
§ 51. What is the area of a circle with a radius of 4 feet after a sector of 111 degrees has been removed? § A. 3. 90 feet § B. 8. 67 feet § C. 34. 77 feet § D. 50. 27 feet
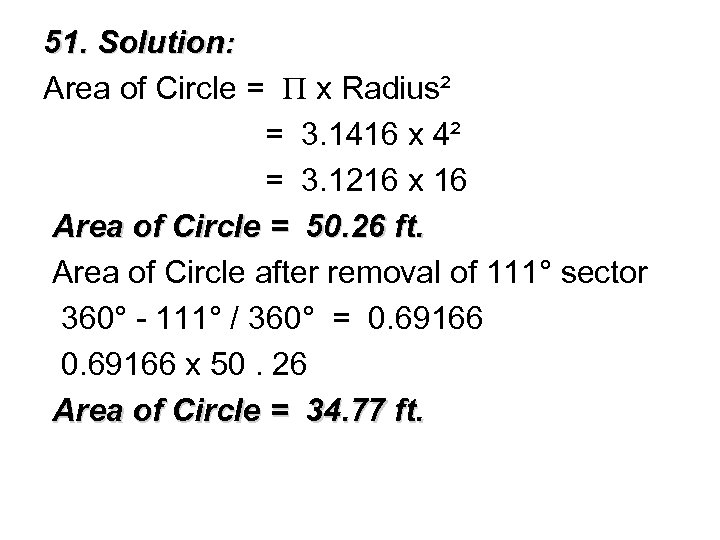 51. Solution: Area of Circle = x Radius² = 3. 1416 x 4² = 3. 1216 x 16 Area of Circle = 50. 26 ft. Area of Circle after removal of 111° sector 360° - 111° / 360° = 0. 69166 x 50. 26 Area of Circle = 34. 77 ft.
51. Solution: Area of Circle = x Radius² = 3. 1416 x 4² = 3. 1216 x 16 Area of Circle = 50. 26 ft. Area of Circle after removal of 111° sector 360° - 111° / 360° = 0. 69166 x 50. 26 Area of Circle = 34. 77 ft.
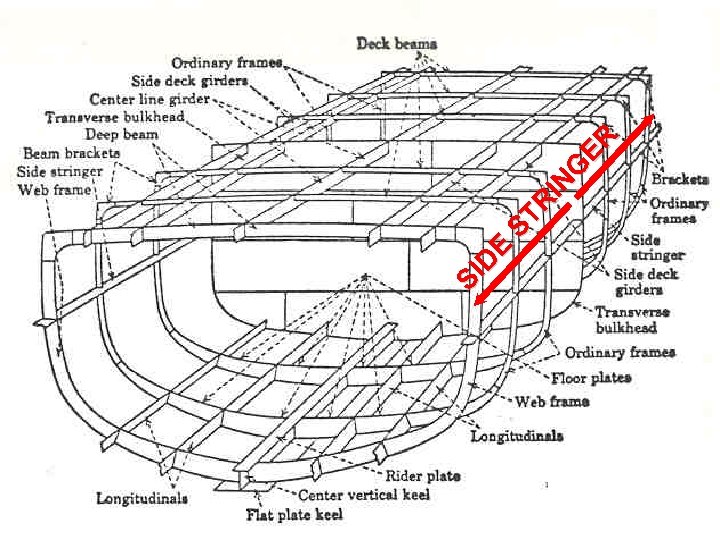
 § 52. A term applied to a fore and aft girder running along the side of the ship and also to the outboard strake of plating on any deck: § A. Stringer § B. Camber § C. Keel § D. Frames
§ 52. A term applied to a fore and aft girder running along the side of the ship and also to the outboard strake of plating on any deck: § A. Stringer § B. Camber § C. Keel § D. Frames
 SI D E ST R IN G ER
SI D E ST R IN G ER
 § 53. If additional weight is added above the center of gravity, the vessel will: § A. Reduce reserve buoyancy § B. Increase GM § C. Reduce righting moments § D. All of these
§ 53. If additional weight is added above the center of gravity, the vessel will: § A. Reduce reserve buoyancy § B. Increase GM § C. Reduce righting moments § D. All of these
 § 54. It is a form of longitudinal deformation under stress by which the middle part of the vessel structure sinks below the extremities: § A. Sagging § B. Racking § C. Hogging § D. Torsion
§ 54. It is a form of longitudinal deformation under stress by which the middle part of the vessel structure sinks below the extremities: § A. Sagging § B. Racking § C. Hogging § D. Torsion
 • 55. When a weight of 800 lbs. is suspended, what is the stress on the hauling part when using a gun tackle rove to least advantage? • A. 320 lbs. • B. 347 lbs. • C. 400 lbs. • D. 480 lbs.
• 55. When a weight of 800 lbs. is suspended, what is the stress on the hauling part when using a gun tackle rove to least advantage? • A. 320 lbs. • B. 347 lbs. • C. 400 lbs. • D. 480 lbs.
 55. Solution: Force = Weight x ( 1 + 10% N. O. S ) Mechanical Advantage Force = Weight Mechanical Advantage Force = 800 lbs 2 Force = 400 lbs
55. Solution: Force = Weight x ( 1 + 10% N. O. S ) Mechanical Advantage Force = Weight Mechanical Advantage Force = 800 lbs 2 Force = 400 lbs
 • 56. The definition “A” mixture of hydrocarbon products composed predominantly of propane, butylene or butadiene which is liquefied by compression at normal atmospheric temperature for storage, transport and handling refers to: • A. LPG • B. Grade A products • C. Grade B products • D. LNG
• 56. The definition “A” mixture of hydrocarbon products composed predominantly of propane, butylene or butadiene which is liquefied by compression at normal atmospheric temperature for storage, transport and handling refers to: • A. LPG • B. Grade A products • C. Grade B products • D. LNG
 § 57. When working cargo with a Burton or married fall arrangement, the part of the cargo gear most likely to fail would be the: § A. Guy § B. Topping lift § C. Boom § D. Gooseneck
§ 57. When working cargo with a Burton or married fall arrangement, the part of the cargo gear most likely to fail would be the: § A. Guy § B. Topping lift § C. Boom § D. Gooseneck
 § 58. What term indicates the midship portion of a vessel that has a constant cross section? § A. Middle body § B. Amidship § C. Half of length § D. Moulded length
§ 58. What term indicates the midship portion of a vessel that has a constant cross section? § A. Middle body § B. Amidship § C. Half of length § D. Moulded length
 59. Spontaneous heating of coal rapidly accelerate at the approximate minimum temperature of: A. 88° F B. 100° F C. 111° F D. 119° F
59. Spontaneous heating of coal rapidly accelerate at the approximate minimum temperature of: A. 88° F B. 100° F C. 111° F D. 119° F
 • 60. Transverse frames are more widely spaced on a ship that is designed with the: • A. Longitudinally system of framing • B. Isometric system of framing • C. Centerline system of framing • D. Transverse system of framing
• 60. Transverse frames are more widely spaced on a ship that is designed with the: • A. Longitudinally system of framing • B. Isometric system of framing • C. Centerline system of framing • D. Transverse system of framing
 § 61. This is the ratio of the immersed volume to the area of the load waterplane multiplied by the mean draught: § A. Vertical prismatic coefficient § B. Prismatic coefficient § C Waterplane area coefficient § D. Midship section area coefficient
§ 61. This is the ratio of the immersed volume to the area of the load waterplane multiplied by the mean draught: § A. Vertical prismatic coefficient § B. Prismatic coefficient § C Waterplane area coefficient § D. Midship section area coefficient

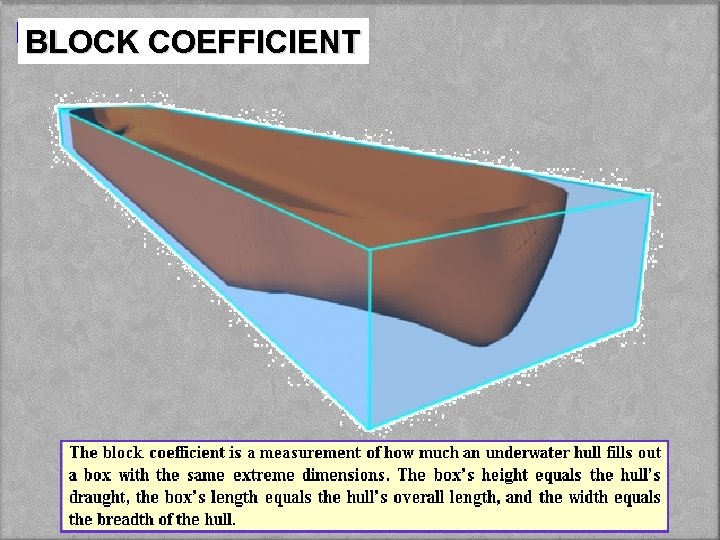
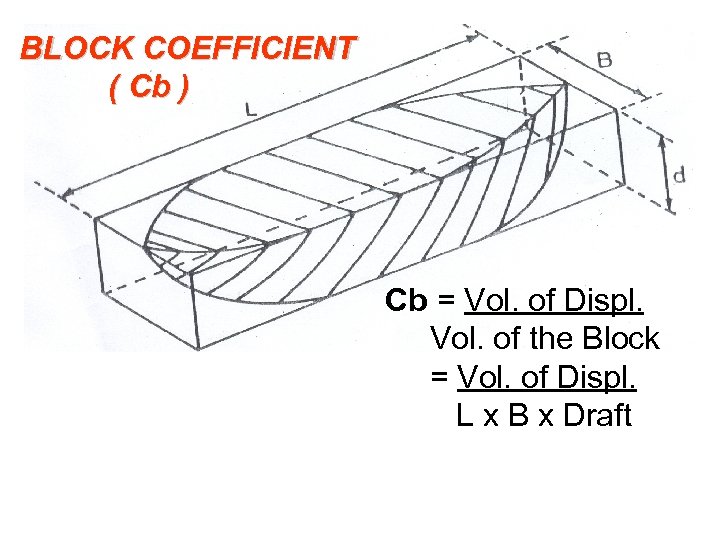 BLOCK COEFFICIENT ( Cb ) Cb = Vol. of Displ. Vol. of the Block = Vol. of Displ. L x B x Draft
BLOCK COEFFICIENT ( Cb ) Cb = Vol. of Displ. Vol. of the Block = Vol. of Displ. L x B x Draft
 BLOCK COEFFICIENT
BLOCK COEFFICIENT
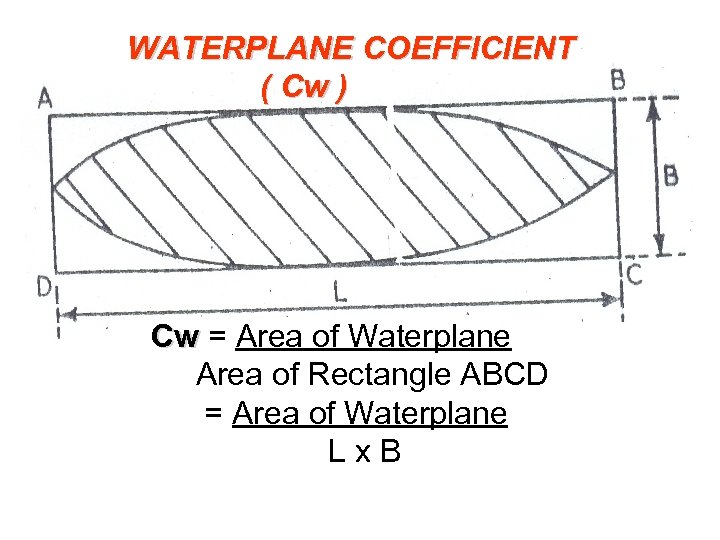 WATERPLANE COEFFICIENT ( Cw ) Cw = Area of Waterplane Cw Area of Rectangle ABCD = Area of Waterplane L x B
WATERPLANE COEFFICIENT ( Cw ) Cw = Area of Waterplane Cw Area of Rectangle ABCD = Area of Waterplane L x B

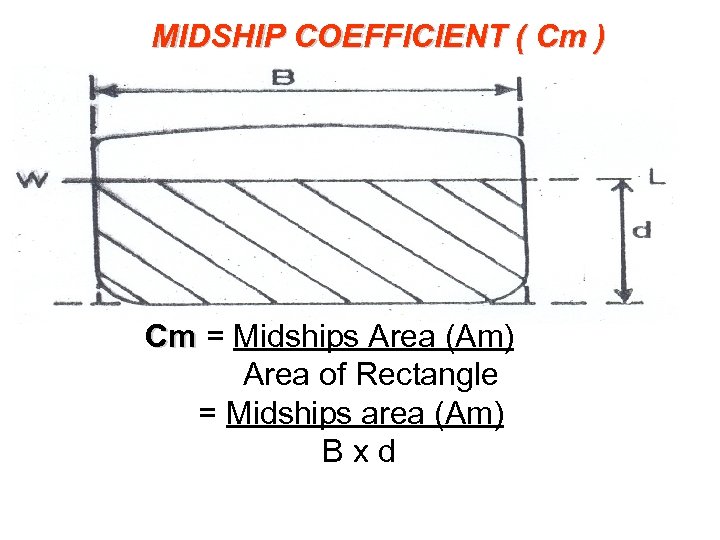 MIDSHIP COEFFICIENT ( Cm ) Cm = Midships Area (Am) Cm Area of Rectangle = Midships area (Am) B x d
MIDSHIP COEFFICIENT ( Cm ) Cm = Midships Area (Am) Cm Area of Rectangle = Midships area (Am) B x d

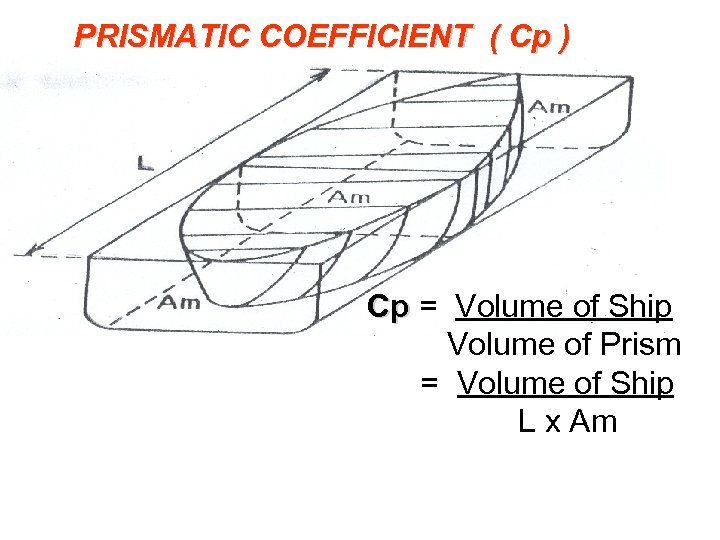 PRISMATIC COEFFICIENT ( Cp ) Cp = Volume of Ship Cp Volume of Prism = Volume of Ship L x Am
PRISMATIC COEFFICIENT ( Cp ) Cp = Volume of Ship Cp Volume of Prism = Volume of Ship L x Am
 § 62. On tank vessels that use an automatic tape well, free movement of the tape is normally checked by: § A. Operating the hand clutch § B. Comparing with a hand tape § C. Removing the side plate § D. Using litmus paste
§ 62. On tank vessels that use an automatic tape well, free movement of the tape is normally checked by: § A. Operating the hand clutch § B. Comparing with a hand tape § C. Removing the side plate § D. Using litmus paste
 § 63. The advantage in using a single whip tackle is: I. The strain on the hauling part is less than the weight II. The direction of the pull of force needed to lift the weight is changed § A. I only § B. II only § C. Both I and II § D. Neither I nor II
§ 63. The advantage in using a single whip tackle is: I. The strain on the hauling part is less than the weight II. The direction of the pull of force needed to lift the weight is changed § A. I only § B. II only § C. Both I and II § D. Neither I nor II
 64. “Block Stowage” means: § A. Storing all cargo for a port in the same area § B. Having the cargo on pallets § C. Using separation cloths to separate different kinds of cargo § D. Using port marks on the cargo
64. “Block Stowage” means: § A. Storing all cargo for a port in the same area § B. Having the cargo on pallets § C. Using separation cloths to separate different kinds of cargo § D. Using port marks on the cargo
 § 65. When a vessel is stationary and in a hogging condition, the main deck is in under: § A. Tension stress § B. Compression stress § C. Racking stress § D. Shear stress
§ 65. When a vessel is stationary and in a hogging condition, the main deck is in under: § A. Tension stress § B. Compression stress § C. Racking stress § D. Shear stress
 § 66. A vessel is drawing 38’ 08” in salt water. What would she have to do in order to maintain the same draft in brackish water? § A. Discharge cargo and lighten up before proceeding § B. Load additional cargo § C. Proceed slowly with no change to deadweight tons § D. Load clean ballast
§ 66. A vessel is drawing 38’ 08” in salt water. What would she have to do in order to maintain the same draft in brackish water? § A. Discharge cargo and lighten up before proceeding § B. Load additional cargo § C. Proceed slowly with no change to deadweight tons § D. Load clean ballast
 • 67. If a vessel goes from salt water to fresh water and wishes to keep the same draft, you would: • A. Discharged ballast • B. Take on ballast • C. Do nothing as it does remain the same • D. None of these
• 67. If a vessel goes from salt water to fresh water and wishes to keep the same draft, you would: • A. Discharged ballast • B. Take on ballast • C. Do nothing as it does remain the same • D. None of these
 § 68. If the cargo to be loaded in the hold is bulk grain, the limber boards should be: § A. Covered with tarpaulin with battens § B. Disinfected with bitumastic § C. Caulked with oakum § D. Cleaned and limed washed
§ 68. If the cargo to be loaded in the hold is bulk grain, the limber boards should be: § A. Covered with tarpaulin with battens § B. Disinfected with bitumastic § C. Caulked with oakum § D. Cleaned and limed washed
 § 69. All lines in the loadline are _______ in thickness. § A. 16 mms § B. 20 mms § C. 24 mms § D. 25 mms
§ 69. All lines in the loadline are _______ in thickness. § A. 16 mms § B. 20 mms § C. 24 mms § D. 25 mms
 § § § 70. Safety shackles are fitted with: A. A threaded bolt, locknuts, cotter pins B. A threaded bolt C. A round pin with a cotter pin D. Round pins and locknuts
§ § § 70. Safety shackles are fitted with: A. A threaded bolt, locknuts, cotter pins B. A threaded bolt C. A round pin with a cotter pin D. Round pins and locknuts
 § 71. Loadline markings indicate the drafts at which, for various conditions and types or classes of vessels, there will still be left a sufficient percentage of ______ to ensure the vessel’s safety. § A. Reserve buoyancy § B. Intact buoyancy § C. Longitudinal stability § D. Transverse
§ 71. Loadline markings indicate the drafts at which, for various conditions and types or classes of vessels, there will still be left a sufficient percentage of ______ to ensure the vessel’s safety. § A. Reserve buoyancy § B. Intact buoyancy § C. Longitudinal stability § D. Transverse
 § 72. The result of two forces acting in opposite directions and along parallel lines, is an example of what type of stress? § A. Shear § B. Tensile § C. Compression § D. Strain
§ 72. The result of two forces acting in opposite directions and along parallel lines, is an example of what type of stress? § A. Shear § B. Tensile § C. Compression § D. Strain
 § 73. Which of the following is an advantage gained by building a vessel by Isherwood system of construction? § A. It provided a great deal of longitudinal strength § B. It provides for transverse strength than any other system § C. It reduces the need for a large amount of longitudinals § D. It eliminates the need for any transverse framing
§ 73. Which of the following is an advantage gained by building a vessel by Isherwood system of construction? § A. It provided a great deal of longitudinal strength § B. It provides for transverse strength than any other system § C. It reduces the need for a large amount of longitudinals § D. It eliminates the need for any transverse framing
 § 74. Which of the following most important in prevention of sweat damage to cargo in the hold? § A. Dew point of the outside air § B. Dew point of the air in the cargo hold § C. Outside temperature § D. Temperature of the cargo
§ 74. Which of the following most important in prevention of sweat damage to cargo in the hold? § A. Dew point of the outside air § B. Dew point of the air in the cargo hold § C. Outside temperature § D. Temperature of the cargo
 § 75. What is the simplest member of the olefin family, the largest volume organic chemical and is used in more than 30% of all petrochemical products? § A. Ethylene Use as raw material in organic industry § B. Aromatics Use in manufacture of resin, § C. Propylene fibres and elastomers § D. Butadiene Use for production of synthetic rubber
§ 75. What is the simplest member of the olefin family, the largest volume organic chemical and is used in more than 30% of all petrochemical products? § A. Ethylene Use as raw material in organic industry § B. Aromatics Use in manufacture of resin, § C. Propylene fibres and elastomers § D. Butadiene Use for production of synthetic rubber
 § § 76. Barium cyanide solid is classed as “poison B” and cannot be stowed near: near A. Acids B. Flammable solids C. Flammable liquids D. Benzene
§ § 76. Barium cyanide solid is classed as “poison B” and cannot be stowed near: near A. Acids B. Flammable solids C. Flammable liquids D. Benzene
 § 77. What do you call the principle of separating the oil residues from water? The seawater is discharged at sea while the oil residue is retained on board. § A. Decantation § B. Separation § C. Division § D. Segregation
§ 77. What do you call the principle of separating the oil residues from water? The seawater is discharged at sea while the oil residue is retained on board. § A. Decantation § B. Separation § C. Division § D. Segregation
 § 78. What do you call the plan showing the longitudinal, vertical section passing through the meridian line of vessel? § A. Sheer plan § B. Docking arrangement § C. Stowage plan § D. Bon jean curve
§ 78. What do you call the plan showing the longitudinal, vertical section passing through the meridian line of vessel? § A. Sheer plan § B. Docking arrangement § C. Stowage plan § D. Bon jean curve
 § 79. Where would you find the draft marks on a ship? § A. Area of water line near stem and stern § B. Midships near the waterline § C. Voids § D. Deep tanks
§ 79. Where would you find the draft marks on a ship? § A. Area of water line near stem and stern § B. Midships near the waterline § C. Voids § D. Deep tanks
 § 80. Your draft at the dock is 27’ 06”. What will be your draft when at sea? § A. 26’ 10” § B. 26 ’ 08” § C. 26’ 11” § D. 28’ 02”
§ 80. Your draft at the dock is 27’ 06”. What will be your draft when at sea? § A. 26’ 10” § B. 26 ’ 08” § C. 26’ 11” § D. 28’ 02”
 80. Solution: New Draft Old Density Old Draft New Density New Draft 1, 000 kgs/m³ 27. 5‘ 1, 025 kgs/m³ New Draft = 27. 5‘ x 1, 000 kgs/m³ 1, 025 kgs/m³ New Draft = 26. 829 or 26‘ 10"
80. Solution: New Draft Old Density Old Draft New Density New Draft 1, 000 kgs/m³ 27. 5‘ 1, 025 kgs/m³ New Draft = 27. 5‘ x 1, 000 kgs/m³ 1, 025 kgs/m³ New Draft = 26. 829 or 26‘ 10"
 § 81. On the vessel cargo hold a gasoline powered forklift truck is used, what precaution should you take? § A. See that ventilation is supplied on account to truck poisonous exhaust § B. See to it that hold are well lighted during the night time § C. Trucks are operated by experience stevedore § D. All of the above
§ 81. On the vessel cargo hold a gasoline powered forklift truck is used, what precaution should you take? § A. See that ventilation is supplied on account to truck poisonous exhaust § B. See to it that hold are well lighted during the night time § C. Trucks are operated by experience stevedore § D. All of the above
 82. What are “liquefied flammables”? A. Toxic B. Poison C. Completely odorless in their pure natural state D. Odorized to help detect leaks
82. What are “liquefied flammables”? A. Toxic B. Poison C. Completely odorless in their pure natural state D. Odorized to help detect leaks
 § 83. What do you mean by the term “cargo tank length” as used in part 157 of the pollution regulations? § A. Length from the collision bulkhead to the forward bulkhead of the machinery spaces § B. Length of any individual cargo space, from bulkhead to bulkhead § C. Diagonal measurement of a cargo tank § D. Greatest distance between two opposite cargo tank bulkhead
§ 83. What do you mean by the term “cargo tank length” as used in part 157 of the pollution regulations? § A. Length from the collision bulkhead to the forward bulkhead of the machinery spaces § B. Length of any individual cargo space, from bulkhead to bulkhead § C. Diagonal measurement of a cargo tank § D. Greatest distance between two opposite cargo tank bulkhead
 § 84. What would you do first when you notice oil on the water near vessel while taking on fuel? § A. Stop loading § B. Notify the terminal superintendent § C. Notify the senior deck officer § D. Determine whether your vessel is the source
§ 84. What would you do first when you notice oil on the water near vessel while taking on fuel? § A. Stop loading § B. Notify the terminal superintendent § C. Notify the senior deck officer § D. Determine whether your vessel is the source
 § 85. What distance will a weight of 152. 4 tons have to be moved in order to remove a 2 degrees list from a vessel of displacement 9, 144 tons and GM 1. 03 m? § A. 2. 16 m § B. 2. 29 m § C. 3. 20 m § D. 5. 52 m
§ 85. What distance will a weight of 152. 4 tons have to be moved in order to remove a 2 degrees list from a vessel of displacement 9, 144 tons and GM 1. 03 m? § A. 2. 16 m § B. 2. 29 m § C. 3. 20 m § D. 5. 52 m
 85. Solution: Tan List = W x D GM x Dist = Tan List x GM x Weight = Tan 2° x 1. 03 m x 9, 144 tons 152. 4 tons Distance = 2. 16 m
85. Solution: Tan List = W x D GM x Dist = Tan List x GM x Weight = Tan 2° x 1. 03 m x 9, 144 tons 152. 4 tons Distance = 2. 16 m
 § 86. Which part provides for the vertical control and positioning of the boom in a yard and stay rig? § A. Topping lift § B. Cargo whip § C. Back stay § D. Spider block
§ 86. Which part provides for the vertical control and positioning of the boom in a yard and stay rig? § A. Topping lift § B. Cargo whip § C. Back stay § D. Spider block
 § 87. What do you call a rope ladder with a wooden rung? § A. Jacob’s ladder § B. Pilot ladder § C. Jury ladder § D. Life ladder
§ 87. What do you call a rope ladder with a wooden rung? § A. Jacob’s ladder § B. Pilot ladder § C. Jury ladder § D. Life ladder
 § 88. What are these devices which secure standing and running rigging that includes cleats, bitts, chocks, fair leads and pad eye? § A. Deck fittings § B. Deck devices § C. Deck stores § D. Deck gears
§ 88. What are these devices which secure standing and running rigging that includes cleats, bitts, chocks, fair leads and pad eye? § A. Deck fittings § B. Deck devices § C. Deck stores § D. Deck gears
 § 89. What do you call the cargo gear mode of 4 legs of equal length of either rope or wire, one end of each leg being spliced into an iron ring, the other end into the eye of a hook? § A. Bridle § B. Chain sling § C. Bull rope § D. Sling
§ 89. What do you call the cargo gear mode of 4 legs of equal length of either rope or wire, one end of each leg being spliced into an iron ring, the other end into the eye of a hook? § A. Bridle § B. Chain sling § C. Bull rope § D. Sling
 § 90. When a double bottom tank is full of fresh water, it holds 120 tons. Find how many tons of oil of relative density 0. 84 it will hold? § A. 100. 8 tons § B. 108. 0 tons § C. 110. 7 tons § D. 112. 8 tons
§ 90. When a double bottom tank is full of fresh water, it holds 120 tons. Find how many tons of oil of relative density 0. 84 it will hold? § A. 100. 8 tons § B. 108. 0 tons § C. 110. 7 tons § D. 112. 8 tons
 90. Solution: Weight = R. D. of Oil x Cap. Of FW R. D. of FW Weight = 0. 84 x 120 tons 1. 000 Weight = 100. 8 tons
90. Solution: Weight = R. D. of Oil x Cap. Of FW R. D. of FW Weight = 0. 84 x 120 tons 1. 000 Weight = 100. 8 tons
 § 91. After discharging refrigerated cargo, what are the advantages of thoroughly airing the cold storage compartment? § A. To remove bad smell § B. To dry the holds flooring and bilges § C. To clean the cargo hold § D. For removal of CO 2 and other gases, odors and dampness
§ 91. After discharging refrigerated cargo, what are the advantages of thoroughly airing the cold storage compartment? § A. To remove bad smell § B. To dry the holds flooring and bilges § C. To clean the cargo hold § D. For removal of CO 2 and other gases, odors and dampness
 92. Which of the following conditions will cause a vessel’s bottom to be subjected to tension stresses? § A. Concentration of weight amidship § B. Concentration of weight forward § C. Concentration of weight aft § D. Concentration of weight at both end of the vessels
92. Which of the following conditions will cause a vessel’s bottom to be subjected to tension stresses? § A. Concentration of weight amidship § B. Concentration of weight forward § C. Concentration of weight aft § D. Concentration of weight at both end of the vessels
 § 93. What is the use of the dunnage in bagged of rice and other goods that was closely packed? § A. Air passage § B. Division § C. Drainage § D. Spacing
§ 93. What is the use of the dunnage in bagged of rice and other goods that was closely packed? § A. Air passage § B. Division § C. Drainage § D. Spacing
 § 94. Metacentric height is a measure of: I. The righting arm of the vessel II. Initial stability of a vessel § A. I only § B. II only § C. Both I and II § D. Neither I nor II
§ 94. Metacentric height is a measure of: I. The righting arm of the vessel II. Initial stability of a vessel § A. I only § B. II only § C. Both I and II § D. Neither I nor II
 § 95. It is customarily stated as the number of cubic feet one ton of 2, 240 pounds (long ton) of a particular lot of cargo will occupy: § A. Stowage factor § B. Deadweight cargo § C. Insured cargo § D. Measurement cargo
§ 95. It is customarily stated as the number of cubic feet one ton of 2, 240 pounds (long ton) of a particular lot of cargo will occupy: § A. Stowage factor § B. Deadweight cargo § C. Insured cargo § D. Measurement cargo
 § 96. The highest deck which runs the full length of the ship is: § A. Main deck § B. Poop deck § C. Deck house § D. Shelter deck
§ 96. The highest deck which runs the full length of the ship is: § A. Main deck § B. Poop deck § C. Deck house § D. Shelter deck
 § 97. What do you call the metal chimney or passage through which the smoke and gases are led from the uptakes to the open air? § A. Smokestack § B. Smoke pipe § C. Funnel § D. Chimney
§ 97. What do you call the metal chimney or passage through which the smoke and gases are led from the uptakes to the open air? § A. Smokestack § B. Smoke pipe § C. Funnel § D. Chimney
 § 98. Your vessel measures 30 meters long by 5 meters in beam. If the rolling period is 6 seconds, find the GM: § A. 0. 44 m § B. 0. 56 m § C. 0. 48 m § D. 0. 58 m
§ 98. Your vessel measures 30 meters long by 5 meters in beam. If the rolling period is 6 seconds, find the GM: § A. 0. 44 m § B. 0. 56 m § C. 0. 48 m § D. 0. 58 m
 • 98. Solution: • GM = 0. 797 x Beam ² R. P. • GM = 0. 797 x 5 m ² 6 secs. • GM = 0. 44 m
• 98. Solution: • GM = 0. 797 x Beam ² R. P. • GM = 0. 797 x 5 m ² 6 secs. • GM = 0. 44 m
 § 99. Which of the following are essential parts of the keel? I. Middle line keelson II. Side keelson § A. I only § B. II only § C. Both I and II § D. Neither I nor II
§ 99. Which of the following are essential parts of the keel? I. Middle line keelson II. Side keelson § A. I only § B. II only § C. Both I and II § D. Neither I nor II
 § 100. In British Harbor, the Department of Transportation has given authority to any person to inspect the oil record book of a ship: § A. Harbor Master § B. Representative of the Agent § C. Marine Surveyor § D. Port State Control
§ 100. In British Harbor, the Department of Transportation has given authority to any person to inspect the oil record book of a ship: § A. Harbor Master § B. Representative of the Agent § C. Marine Surveyor § D. Port State Control


