0d5ba57446924344c880a56cd55412a5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 1 Speed and Velocity What is speed, velocity and acceleration? Speed and Velocity
1 Speed and Velocity What is speed, velocity and acceleration? Speed and Velocity
 2 Wendy runs 200 m east on a straight road and then turns west and runs 100 m back. What would be the distance she traveled and her displacement? A bus goes 500 km east from town A to town B in the morning and comes back halfway in the evening travelling west. What is the distance and displacement of the bus? Ashley travels 5 mi N to the nearest gas station. She then continues traveling in the same direction another 15 mi. What is the distance and displacement?
2 Wendy runs 200 m east on a straight road and then turns west and runs 100 m back. What would be the distance she traveled and her displacement? A bus goes 500 km east from town A to town B in the morning and comes back halfway in the evening travelling west. What is the distance and displacement of the bus? Ashley travels 5 mi N to the nearest gas station. She then continues traveling in the same direction another 15 mi. What is the distance and displacement?
 3 Speed is the distance traveled per unit of time. Speed (s) = distance (d) time (t) Each variable measured by units: Distance: meters (m), miles (mi) Time: seconds (s), hours (hr), minutes (min) Speed: meters per second (m/s), miles per hour (mi/hr), kilometers per hour (km/hr)
3 Speed is the distance traveled per unit of time. Speed (s) = distance (d) time (t) Each variable measured by units: Distance: meters (m), miles (mi) Time: seconds (s), hours (hr), minutes (min) Speed: meters per second (m/s), miles per hour (mi/hr), kilometers per hour (km/hr)
 4 3 TYPES OF SPEED Instantaneous, Average, Constant Pretend you are looking at your car's speedometer while you are driving. The reading you get from your speedometer is A. instantaneous speed… This is the speed that you are traveling at that moment.
4 3 TYPES OF SPEED Instantaneous, Average, Constant Pretend you are looking at your car's speedometer while you are driving. The reading you get from your speedometer is A. instantaneous speed… This is the speed that you are traveling at that moment.
 5 B. Constant Speed is when the object covers equal distances in equal amounts of time. C. Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time. It can be calculated using the following formula: speed = distance time . . . or shortened: Average Speed is: Total distance = distance traveled all over Total time = final time (end) minus initial time (beginning)
5 B. Constant Speed is when the object covers equal distances in equal amounts of time. C. Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time. It can be calculated using the following formula: speed = distance time . . . or shortened: Average Speed is: Total distance = distance traveled all over Total time = final time (end) minus initial time (beginning)
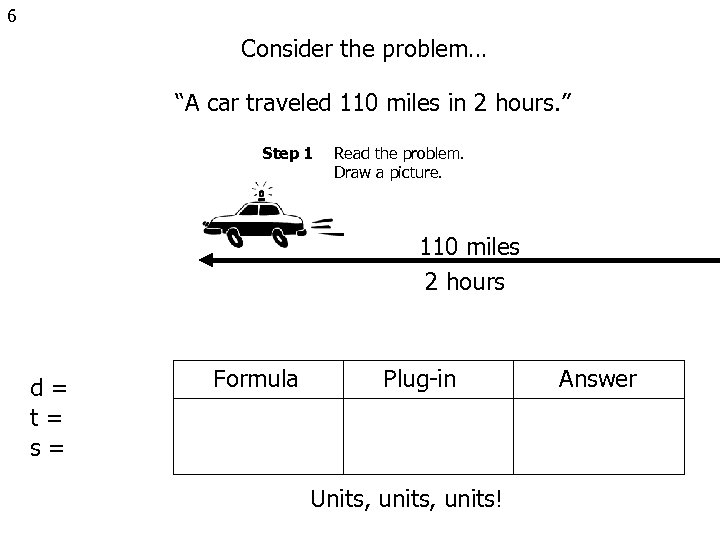 6 Consider the problem… “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. 110 miles 2 hours d= t= s= Formula Plug-in Units, units! Answer
6 Consider the problem… “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. 110 miles 2 hours d= t= s= Formula Plug-in Units, units! Answer
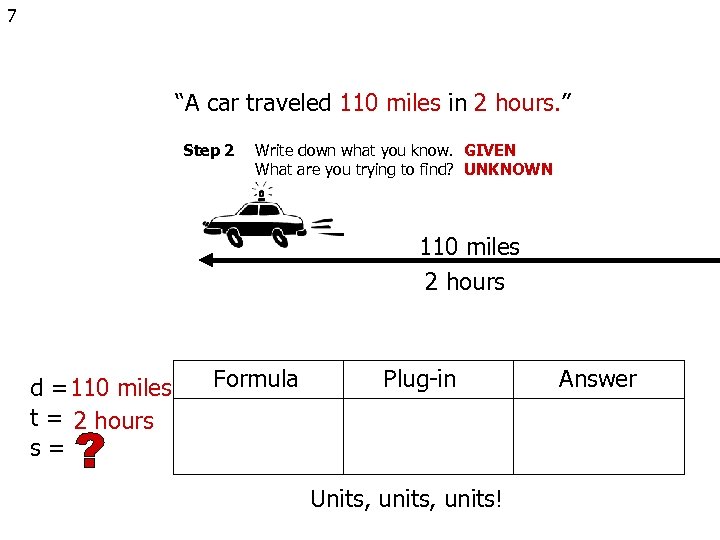 7 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 2 Write down what you know. GIVEN What are you trying to find? UNKNOWN 110 miles 2 hours d = 110 miles t = 2 hours s= Formula Plug-in Units, units! Answer
7 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 2 Write down what you know. GIVEN What are you trying to find? UNKNOWN 110 miles 2 hours d = 110 miles t = 2 hours s= Formula Plug-in Units, units! Answer
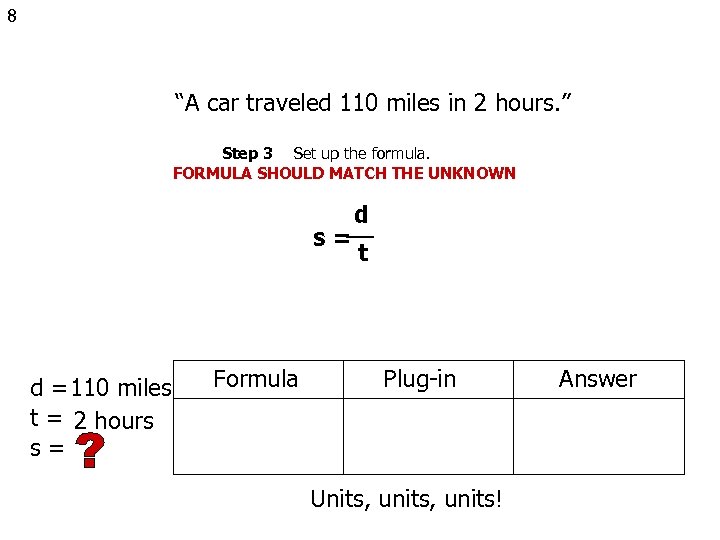 8 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 3 Set up the formula. FORMULA SHOULD MATCH THE UNKNOWN s= d = 110 miles t = 2 hours s= Formula d t Plug-in Units, units! Answer
8 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 3 Set up the formula. FORMULA SHOULD MATCH THE UNKNOWN s= d = 110 miles t = 2 hours s= Formula d t Plug-in Units, units! Answer
 9 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 3 Formula d = 110 miles d t = 2 hours S= s= t Set up the formula. EQUATION Plug-in Units, units! Answer
9 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 3 Formula d = 110 miles d t = 2 hours S= s= t Set up the formula. EQUATION Plug-in Units, units! Answer
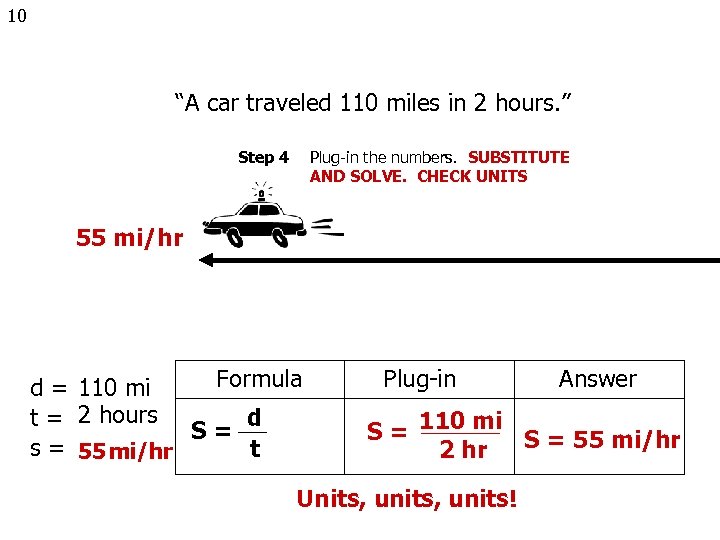 10 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 4 Plug-in the numbers. SUBSTITUTE AND SOLVE. CHECK UNITS 55 mi/hr Formula d = 110 mi d t = 2 hours S= s = 55 mi/hr t Plug-in Answer S = 110 mi S = 55 mi/hr 2 hr Units, units!
10 “A car traveled 110 miles in 2 hours. ” Step 4 Plug-in the numbers. SUBSTITUTE AND SOLVE. CHECK UNITS 55 mi/hr Formula d = 110 mi d t = 2 hours S= s = 55 mi/hr t Plug-in Answer S = 110 mi S = 55 mi/hr 2 hr Units, units!
 11 Do the problems 1 -3 on your notes.
11 Do the problems 1 -3 on your notes.
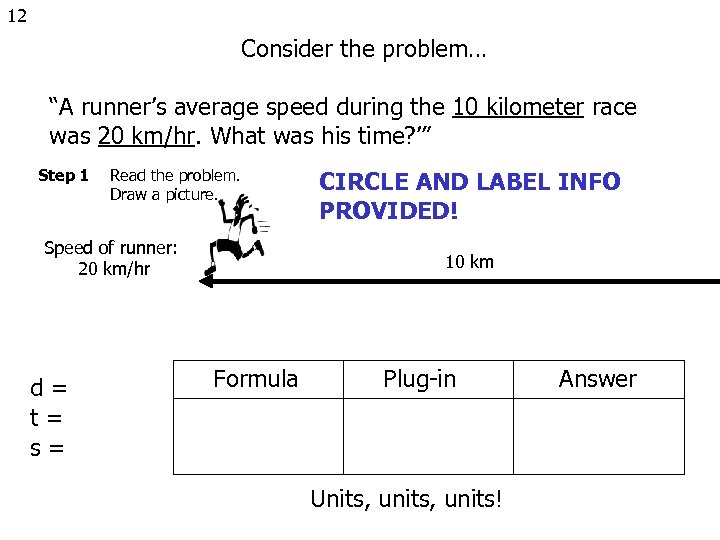 12 Consider the problem… “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ’” Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. Speed of runner: 20 km/hr d= t= s= CIRCLE AND LABEL INFO PROVIDED! 10 km Formula Plug-in Units, units! Answer
12 Consider the problem… “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ’” Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. Speed of runner: 20 km/hr d= t= s= CIRCLE AND LABEL INFO PROVIDED! 10 km Formula Plug-in Units, units! Answer
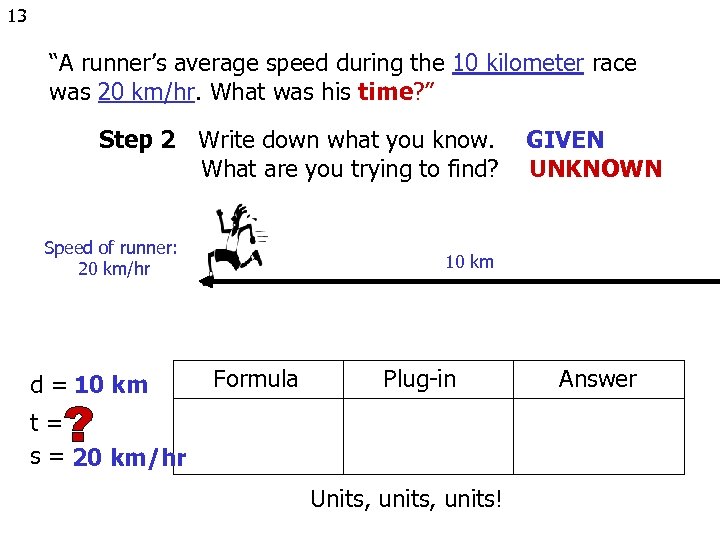 13 “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ” Step 2 Write down what you know. What are you trying to find? Speed of runner: 20 km/hr d = 10 km GIVEN UNKNOWN 10 km Formula Plug-in t= s = 20 km/hr Units, units! Answer
13 “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ” Step 2 Write down what you know. What are you trying to find? Speed of runner: 20 km/hr d = 10 km GIVEN UNKNOWN 10 km Formula Plug-in t= s = 20 km/hr Units, units! Answer
 14 “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ’” Step 3 Set up the formula. FORMULA MUST MATCH UNKNOWN t= d = 10 km Formula t= t (hr) = s = 20 km/hr d s Plug-in d (km) s (km/hr) Units, units! Answer
14 “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ’” Step 3 Set up the formula. FORMULA MUST MATCH UNKNOWN t= d = 10 km Formula t= t (hr) = s = 20 km/hr d s Plug-in d (km) s (km/hr) Units, units! Answer
 15 “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ’” Step 4 SUBSTITUTE AND SOLVE Plug-in the numbers and do the math. Check units for answer. Time: 0. 5 Hour d = 10 km t = 0. 5 hr s = 20 km/hr Formula t= d s Plug-in t = 10 km (hr) 20 km/hr Units, units! Answer 10 km =0. 5 20 km/hr hr
15 “A runner’s average speed during the 10 kilometer race was 20 km/hr. What was his time? ’” Step 4 SUBSTITUTE AND SOLVE Plug-in the numbers and do the math. Check units for answer. Time: 0. 5 Hour d = 10 km t = 0. 5 hr s = 20 km/hr Formula t= d s Plug-in t = 10 km (hr) 20 km/hr Units, units! Answer 10 km =0. 5 20 km/hr hr
 16 Do the problems 4 -5 on your notes.
16 Do the problems 4 -5 on your notes.
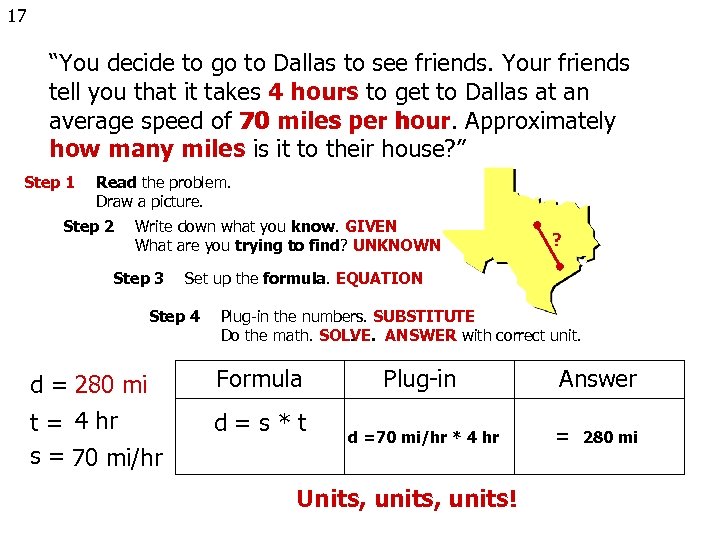 17 “You decide to go to Dallas to see friends. Your friends tell you that it takes 4 hours to get to Dallas at an average speed of 70 miles per hour. Approximately hour how many miles is it to their house? ” Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. Step 2 Write down what you know. GIVEN What are you trying to find? UNKNOWN Step 3 ? Set up the formula. EQUATION Step 4 Plug-in the numbers. SUBSTITUTE Do the math. SOLVE. ANSWER with correct unit. d = 280 mi Formula t = 4 hr s = 70 mi/hr d=s*t Plug-in Answer d =70 mi/hr * 4 hr = 280 mi Units, units!
17 “You decide to go to Dallas to see friends. Your friends tell you that it takes 4 hours to get to Dallas at an average speed of 70 miles per hour. Approximately hour how many miles is it to their house? ” Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. Step 2 Write down what you know. GIVEN What are you trying to find? UNKNOWN Step 3 ? Set up the formula. EQUATION Step 4 Plug-in the numbers. SUBSTITUTE Do the math. SOLVE. ANSWER with correct unit. d = 280 mi Formula t = 4 hr s = 70 mi/hr d=s*t Plug-in Answer d =70 mi/hr * 4 hr = 280 mi Units, units!
 18 Do problem 6 on your notes.
18 Do problem 6 on your notes.
 19 Instantaneous speed (Reading on your speedometer) and Average speed distance traveled over (Total time) Both do not involve direction.
19 Instantaneous speed (Reading on your speedometer) and Average speed distance traveled over (Total time) Both do not involve direction.
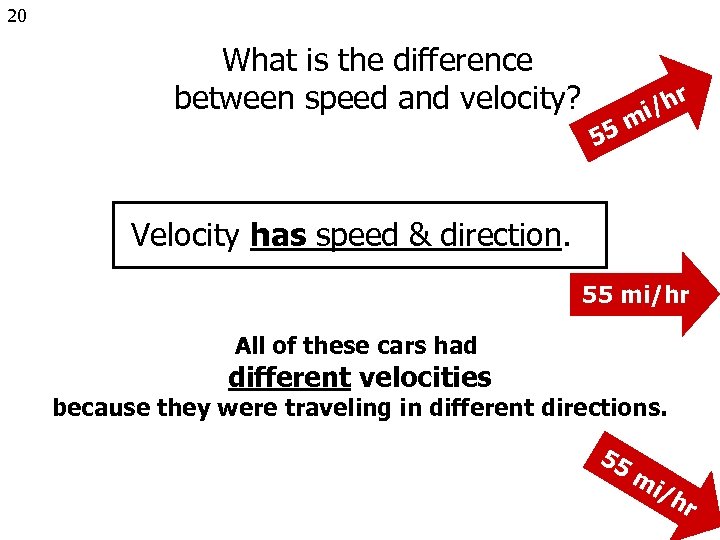 20 What is the difference between speed and velocity? r i/h 5 m 5 Velocity has speed & direction. 55 mi/hr All of these cars had different velocities because they were traveling in different directions. 55 mi /h r
20 What is the difference between speed and velocity? r i/h 5 m 5 Velocity has speed & direction. 55 mi/hr All of these cars had different velocities because they were traveling in different directions. 55 mi /h r
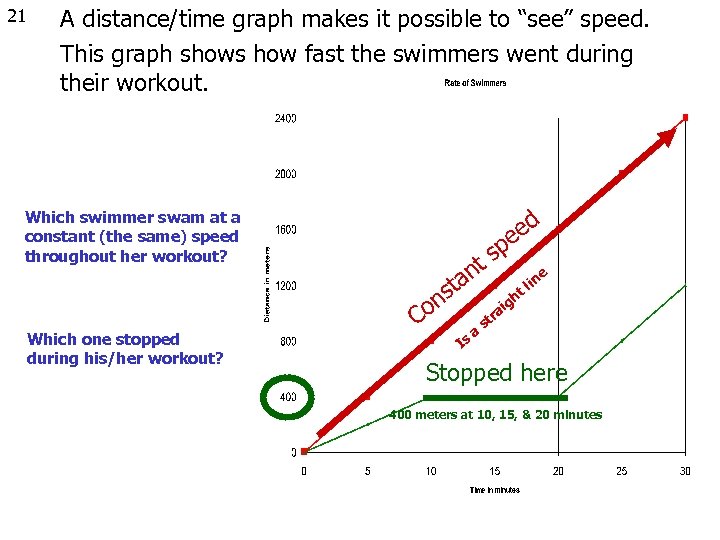 21 A distance/time graph makes it possible to “see” speed. This graph shows how fast the swimmers went during their workout. ed e Which swimmer swam at a constant (the same) speed throughout her workout? sp nt a st n Which one stopped during his/her workout? Co Is a g ai in tl e h r st Stopped here 400 meters at 10, 15, & 20 minutes
21 A distance/time graph makes it possible to “see” speed. This graph shows how fast the swimmers went during their workout. ed e Which swimmer swam at a constant (the same) speed throughout her workout? sp nt a st n Which one stopped during his/her workout? Co Is a g ai in tl e h r st Stopped here 400 meters at 10, 15, & 20 minutes
 22 Make the speed graph & answer the questions.
22 Make the speed graph & answer the questions.
 23 Acceleration
23 Acceleration
 24 Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity over time. Any time an object's velocity is changing, we say that the object is accelerating. This brings up an important point. In common language, when things speed up, we say that they are "accelerating, " and, when they slow down, we say that they are "decelerating. "
24 Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity over time. Any time an object's velocity is changing, we say that the object is accelerating. This brings up an important point. In common language, when things speed up, we say that they are "accelerating, " and, when they slow down, we say that they are "decelerating. "
 25 However, in the language of physics, we say that both objects are accelerating, not because both objects are speeding up, but because both objects have changing velocities. • POSITIVE ACCELERATION (SPEEDING UP) * NEGATIVE ACCELERATION (DECELERATING) SLOW DOWN
25 However, in the language of physics, we say that both objects are accelerating, not because both objects are speeding up, but because both objects have changing velocities. • POSITIVE ACCELERATION (SPEEDING UP) * NEGATIVE ACCELERATION (DECELERATING) SLOW DOWN
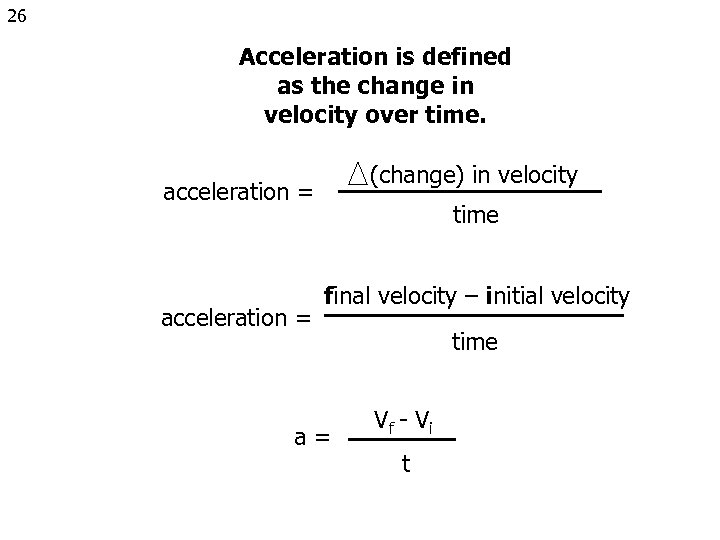 26 Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity over time. (change) in velocity acceleration = time final velocity – initial velocity a= time Vf - V i t
26 Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity over time. (change) in velocity acceleration = time final velocity – initial velocity a= time Vf - V i t
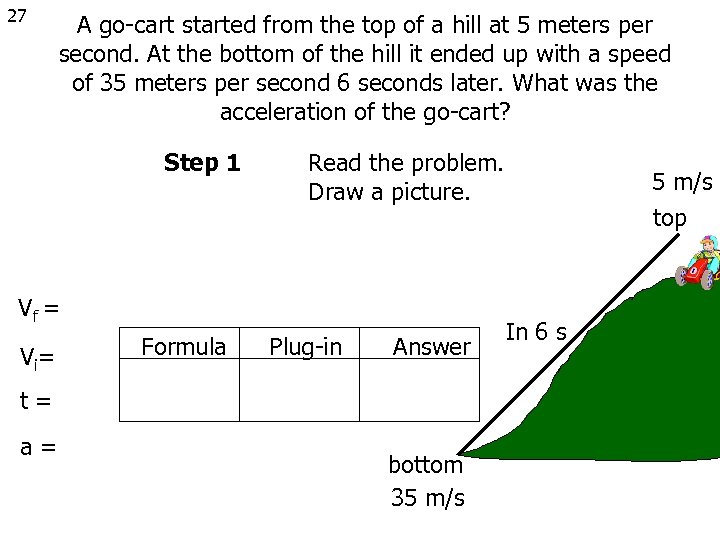 27 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. Vf = V i= Formula Plug-in Answer t= a= bottom 35 m/s top In 6 s
27 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Step 1 Read the problem. Draw a picture. Vf = V i= Formula Plug-in Answer t= a= bottom 35 m/s top In 6 s
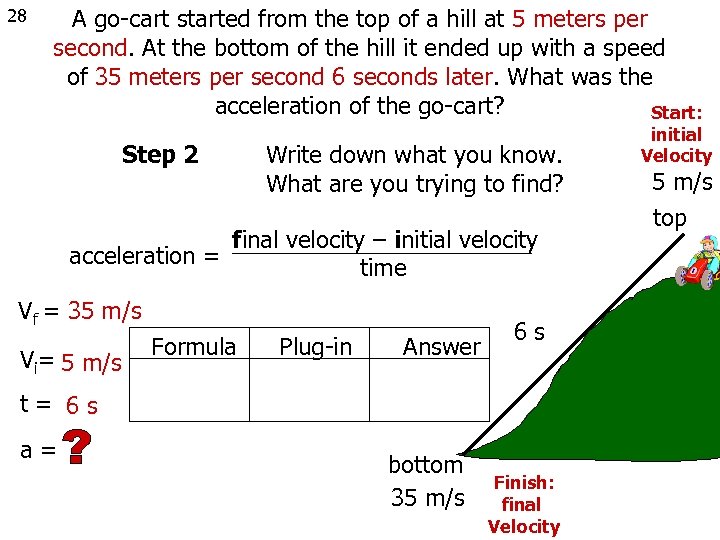 28 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Start: Step 2 acceleration = Write down what you know. What are you trying to find? final velocity – initial velocity time Vf = 35 m/s Vi= 5 m/s Formula Plug-in Answer 6 s t= 6 s a= bottom 35 m/s Finish: final Velocity initial Velocity 5 m/s top
28 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Start: Step 2 acceleration = Write down what you know. What are you trying to find? final velocity – initial velocity time Vf = 35 m/s Vi= 5 m/s Formula Plug-in Answer 6 s t= 6 s a= bottom 35 m/s Finish: final Velocity initial Velocity 5 m/s top
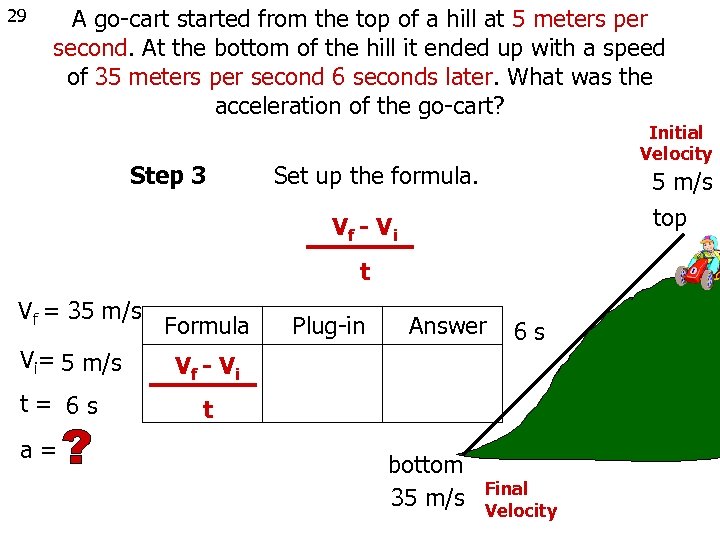 29 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Step 3 Initial Velocity Set up the formula. 5 m/s top Vf - V i t Vf = 35 m/s Vi= 5 m/s t= 6 s a= Formula Plug-in Answer 6 s Vf - V i t bottom 35 m/s Final Velocity
29 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Step 3 Initial Velocity Set up the formula. 5 m/s top Vf - V i t Vf = 35 m/s Vi= 5 m/s t= 6 s a= Formula Plug-in Answer 6 s Vf - V i t bottom 35 m/s Final Velocity
 30 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Step 4 Vf = 35 m/s Vi= 5 m/s t= 6 s a = 5 m/s 2 Formula Vf - V i t Plug-in the numbers. Solve. Plug-in 35 m/s – 5 m/s 6 s Answer 30 m/s 6 s = 5 m/s 2
30 A go-cart started from the top of a hill at 5 meters per second. At the bottom of the hill it ended up with a speed of 35 meters per second 6 seconds later. What was the acceleration of the go-cart? Step 4 Vf = 35 m/s Vi= 5 m/s t= 6 s a = 5 m/s 2 Formula Vf - V i t Plug-in the numbers. Solve. Plug-in 35 m/s – 5 m/s 6 s Answer 30 m/s 6 s = 5 m/s 2
 31 5 m/sec 2 • • 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 m/sec sec increase in speed every second. 0 m/sec 5 m/sec 10 m/sec 15 m/sec 20 m/sec 25 m/sec 30 m/sec
31 5 m/sec 2 • • 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 m/sec sec increase in speed every second. 0 m/sec 5 m/sec 10 m/sec 15 m/sec 20 m/sec 25 m/sec 30 m/sec
 32 Do the problems 8 -9 on your notes.
32 Do the problems 8 -9 on your notes.
 33 i/h m m 70 i/h 70 70 i/h m Velocity involves both speed and direction. Changing velocity does not have to necessarily involve a change in speed. It could just involve a change in direction. 70 m i/h
33 i/h m m 70 i/h 70 70 i/h m Velocity involves both speed and direction. Changing velocity does not have to necessarily involve a change in speed. It could just involve a change in direction. 70 m i/h
 34 Think Differently About Acceleration 1. Consider a car moving at a constant speed of 55 mph while turning in a circle. 2. The car's velocity is not constant, even though the speed is constant. Constant Speed of 55 mph 3. WHY? This is because the direction of motion is constantly changing while the car is turning around the track. 4. Since the direction is changing, even though the speed is not, the velocity is changing (velocity involves both speed and direction).
34 Think Differently About Acceleration 1. Consider a car moving at a constant speed of 55 mph while turning in a circle. 2. The car's velocity is not constant, even though the speed is constant. Constant Speed of 55 mph 3. WHY? This is because the direction of motion is constantly changing while the car is turning around the track. 4. Since the direction is changing, even though the speed is not, the velocity is changing (velocity involves both speed and direction).
 35 Think Differently About Acceleration 5. The car is accelerating because its velocity is changing. Constant Speed of 55 mph 6. As a result, the car is accelerating, even though it is neither speeding up nor slowing down.
35 Think Differently About Acceleration 5. The car is accelerating because its velocity is changing. Constant Speed of 55 mph 6. As a result, the car is accelerating, even though it is neither speeding up nor slowing down.
 36 Speed of Sound • If you shout at a wall that is 40 meters away how long will it take before you hear the echo of your voice. (The speed of sound = 343 m/sec)
36 Speed of Sound • If you shout at a wall that is 40 meters away how long will it take before you hear the echo of your voice. (The speed of sound = 343 m/sec)
 37 Speed of Sound • If you shout at a wall that is 40 meters away how long will it take before you hear the echo of your voice. (The speed of sound = 343 m/sec) • V=D 343 = 80 343 T = 80 T T 343 T =. 23 seconds
37 Speed of Sound • If you shout at a wall that is 40 meters away how long will it take before you hear the echo of your voice. (The speed of sound = 343 m/sec) • V=D 343 = 80 343 T = 80 T T 343 T =. 23 seconds
 38 Speed of Sound • A lightening bolt flashes in the distance and 5 seconds later you hear the clash of thunder. How far away was the lightening? (Speed of sounds = 343 m/sec)
38 Speed of Sound • A lightening bolt flashes in the distance and 5 seconds later you hear the clash of thunder. How far away was the lightening? (Speed of sounds = 343 m/sec)
 39 Speed of Sound • A lightening bolt flashes in the distance and 5 seconds later you hear the clash of thunder. How far away was the lightening? (Speed of sounds = 343 m/sec) • V=D 343 = D D = 1715 m T 5
39 Speed of Sound • A lightening bolt flashes in the distance and 5 seconds later you hear the clash of thunder. How far away was the lightening? (Speed of sounds = 343 m/sec) • V=D 343 = D D = 1715 m T 5
 40 Speed of Light • Light from the sun is traveling at a speed of 186, 000 miles/sec. It takes light 8 minutes to reach the Earth. Calculate the distance from the Earth to the sun.
40 Speed of Light • Light from the sun is traveling at a speed of 186, 000 miles/sec. It takes light 8 minutes to reach the Earth. Calculate the distance from the Earth to the sun.
 41 Speed of Light • Light from the sun is traveling at a speed of 186, 000 miles/sec. It takes light 8 minutes to reach the Earth. Calculate the distance from the Earth to the sun. • V=D 186, 000 = D T 480 D = 89, 280, 000 miles
41 Speed of Light • Light from the sun is traveling at a speed of 186, 000 miles/sec. It takes light 8 minutes to reach the Earth. Calculate the distance from the Earth to the sun. • V=D 186, 000 = D T 480 D = 89, 280, 000 miles


