e9284821288a7dc0b1a585182ad3c188.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51

1 Section I Functional Business Systems 1

2 IT in Business • “Business managers are moving from a tradition where they could avoid, delegate, or ignore decisions about IT to one where they cannot create a marketing, product, international, organization, or financial plan that does not involve such decisions. ” – In all areas and functions of business. – That is what MIS is all about and that is why it is in the CBA upper division core. 2

Ahead 3 • Part 1 of chapter 5 – Functional business systems • Types of IS’s that support the business functions of: – – – Accting Finance Marketing Operations management HRM • Part 2 of chapter 5 – Cross-funtional enterprise systems • CRM, ERP, SCM 3

4 Introduction • E-business: – Use of the Internet, other networks, & IT to support • E-commerce • Enterprise communications & collaboration • Web-enabled business processes – E-business Again • E-commerce 4
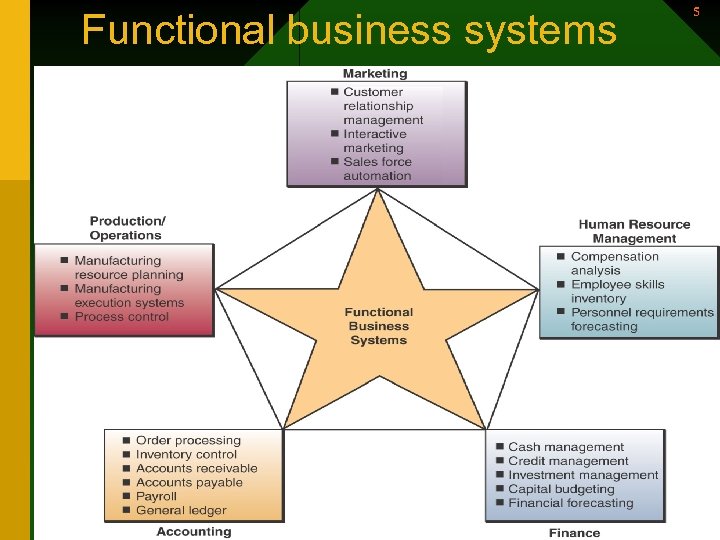
Functional business systems 5 5
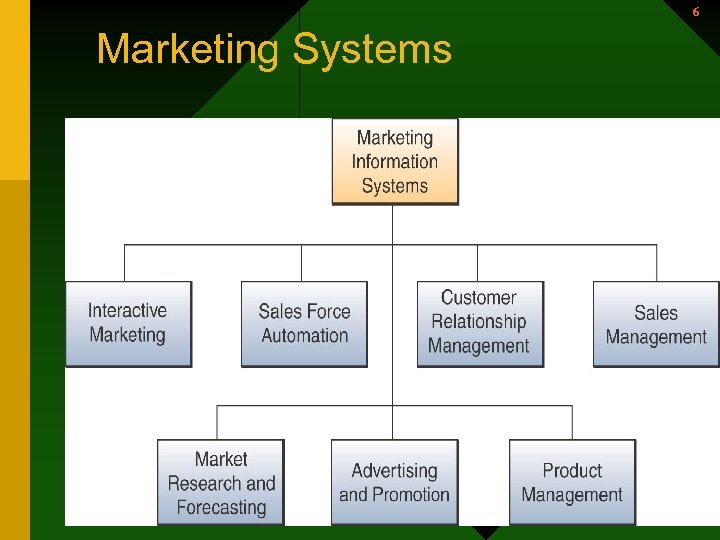
6 Marketing Systems 6

7 Marketing Information Systems • Pricing – A part of marketing • Imagine a marketing information system for an airline that helps determine price for tickets. 7

Marketing Systems 8 • Marketing Information Systems provide information technologies that support major components of the marketing function. – Interactive Marketing • Customer focused marketing process • Based on using Internet, intranets, & extranets to establish two-way communications between customers or potential customers and the business • Customers become involved in product development, delivery, & service issues 8

9 Targeted Marketing 9

Marketing Systems (continued) 10 – Sales Force Automation • The sales force is connected to marketing websites on the Internet, extranets, & the company intranet • Increases productivity of sales force • Speeds up the capture & analysis of sales data • Allows management to provide improved delivery information & better support of the sales force. 10

11 Manufacturing Systems • Support the production/operations function • Assists firms in planning, monitoring, & controlling inventories, purchases, & the flow of goods and services 11

12 Manufacturing Systems (continued) • Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) – Simplify – Automate – Integrate • Supports the concepts of flexible manufacturing systems, agile manufacturing, & total quality management – Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) – Computer-Aided Design (CAD) – Material Requirements Planning (MRP) 12
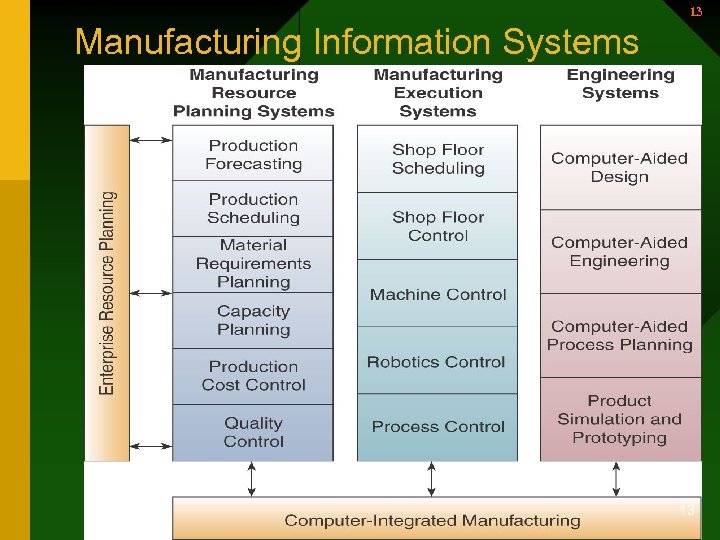
13 Manufacturing Information Systems 13
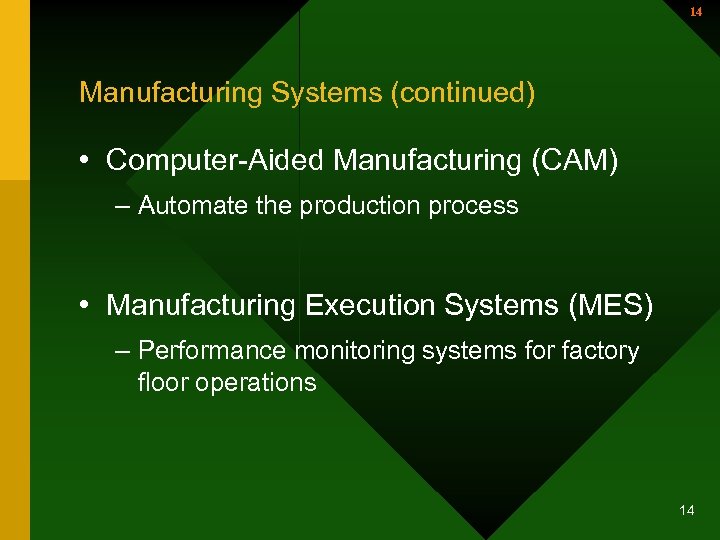
14 Manufacturing Systems (continued) • Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) – Automate the production process • Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) – Performance monitoring systems for factory floor operations 14
15 Manufacturing Systems (continued) • Process Control – The use of computers to control an ongoing physical process – Machine Control – The use of a computer to control the actions of a machine. 15

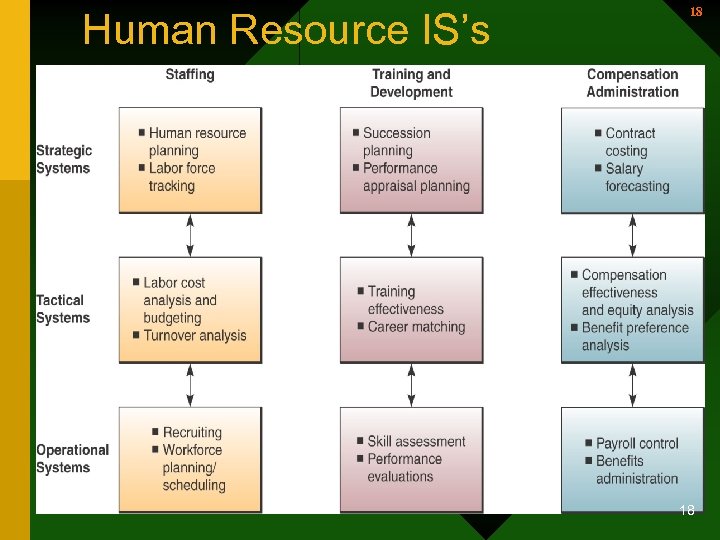
16 Human Resource Systems • Human Resource Information Systems – Support • Planning to meet the personnel needs of the business • Development of employees to their full potential • Recruitment, selection, & hiring • Job placement 16

Human Resource Systems (continued) 17 • Human Resource Information Systems – Support • Performance appraisals • Employee benefits analysis • Training and development – – – Who needs training Who will do the training What type of training Where will the training be Cost effective? How does work continue with personnel in training • Health, safety, & security 17
Human Resource IS’s 18 18

19 Human Resource Systems (continued) • HRM and the Internet – Allows companies to process most common HRM applications over their intranets. – Allows companies to provide around-theclock services to their employees. – Allows companies to disseminate valuable information faster. – Allows employees to perform HRM tasks online. 19

20 HRM & Corporate Intranets • Most HRM applications can be run over the firm’s intranet. 24 X 7 • Provides services to the customers; employees. • Faster than previous channels • Intranet can collect information on-line for input to their employee files. NAU • Enable employees to perform HRM tasks with little or no intervention 20

21 HRM & Corporate Intranets • Enable employees to perform HRM tasks with little or no intervention – Employee Self Service (ESS) – View benefits – Enter travel & expense reports – Access & update personal information • The first intranets developed were for HRM functions. 21

Human Resource Systems (continued) 22 – Staffing • Supported by information systems that record and track human resources to maximize their use – Training and Development • Help human resource managers plan and monitor employee recruitment, training, and development programs 22

23 Accounting Systems • Record and report business transactions and other economic events – Who is interested in this ? ? ? • Online Accounting Systems 23

Widely Used Accounting IS’s 24 24
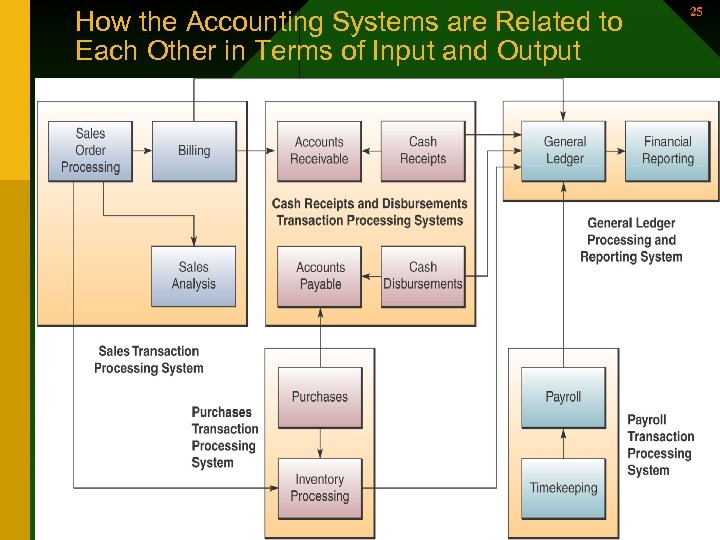
How the Accounting Systems are Related to Each Other in Terms of Input and Output 25 25

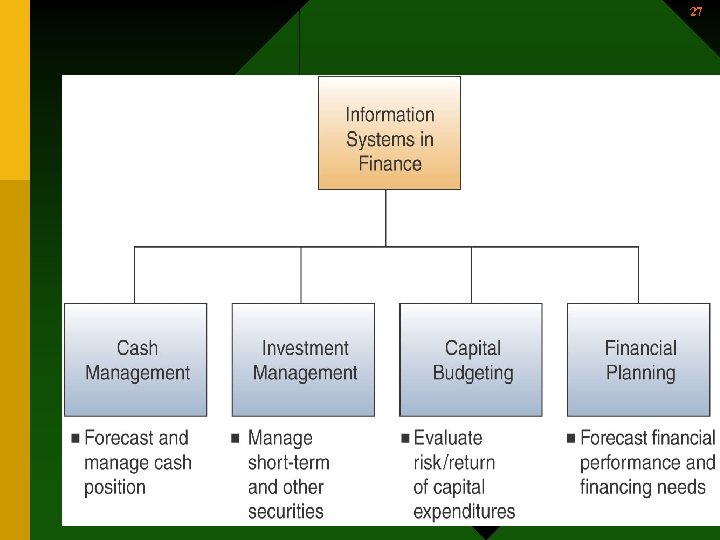
26 Financial Management Systems • Supports financial managers in decisions concerning – The financing of the business – The allocation & control of financial resources within the business. 26
27 27
28 Section II Cross-Functional Enterprise Systems 28
29 Cross-Functional Enterprise Applications • Integrated combinations of information subsystems that share information resources and support business processes across the functional units • A strategic way to use IT to share information resources & improve efficiency & effectiveness 29
30 Cross-Functional Enterprise Applications • They also extend beyond to: v. Customers v. Suppliers v. Other business partners 30
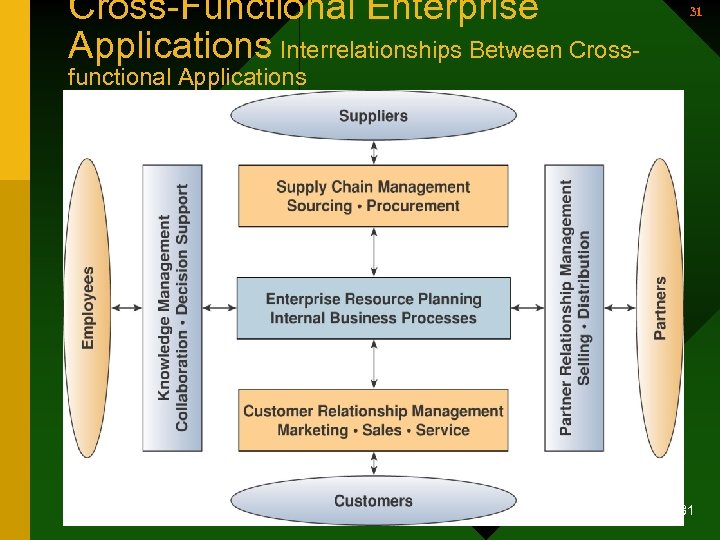
Cross-Functional Enterprise Applications Interrelationships Between Cross- 31 functional Applications • Enterprise Application Architecture 31
32 Cross-Functional Enterprise Applications – Focused on accomplishing fundamental business processes in concert with the company’s customer, supplier, partner, & employee stakeholders – Business processes 32
33 Cross Functional Enterprise Systems • To cross the boundaries of traditional business functions • To reengineer and improve vital business processes all across the enterprise. • A strategic way to use IT to share infor. resources and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes • To develop strategic relationships with customers, suppliers, and business partners. 33
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) 34 • Software enables users to model the business processes involved in the interactions that should occur between business applications. • Also provides middleware that – Performs data conversion & coordination – Provides application communication & messaging services – Provides access to the application interfaces 34
35 Enterprise Application Integration (continued) • Business value – Integrates front-office and back-office applications to allow for quicker, more effective response to business events and customer demands – Improves customer and suppler experience with the business because of its responsiveness. 35
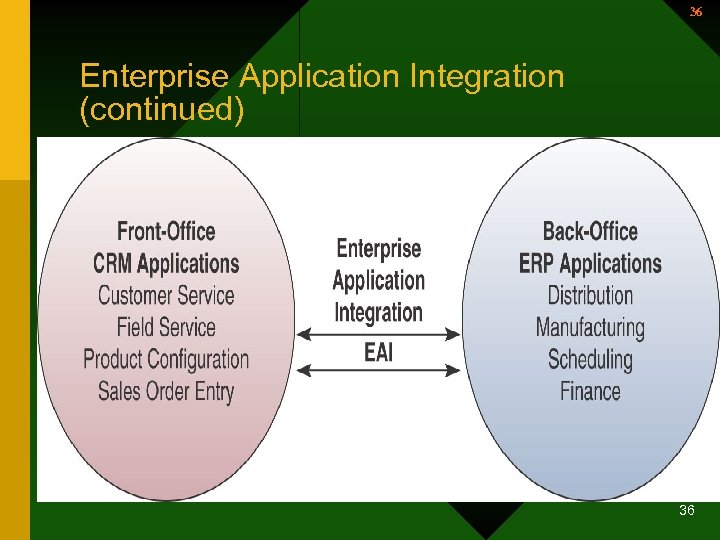
36 Enterprise Application Integration (continued) 36
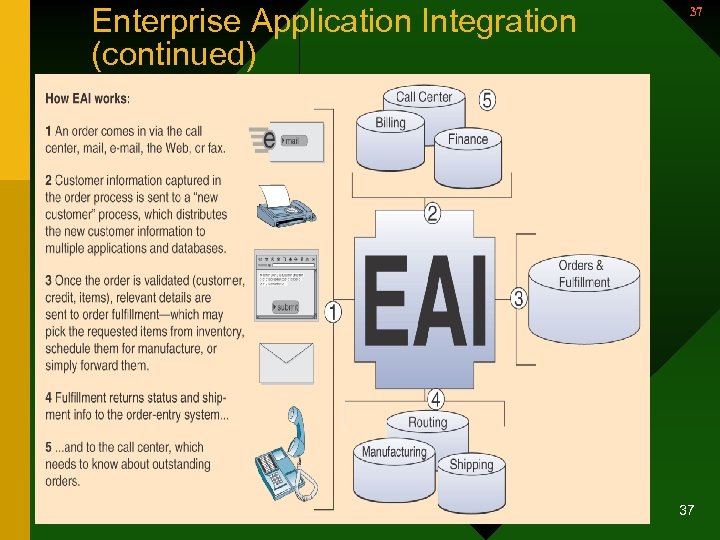
Enterprise Application Integration (continued) 37 37
38 Transaction Processing Systems • One of the major application categories of IS’s in business. • Cross-functional information system. • Processes data resulting from the occurrence of business transactions – Transactions – events that occur as part of doing business • Sales • Purchases • Deposits • Withdrawals • Refunds • Payments 38

39 Transaction Processing Systems • These systems play an important role in supporting the operations of a business 39
Transaction Processing Systems (continued) 40 • Online transaction processing systems – Play a strategic role in e-commerce. – Real-time systems – Can use the Internet or extranets for OLTP – Real-time systems that capture and process transactions immediately • Adds value to product or service through superior customer service • For differentiation 40
Online Transaction Processing Systems-- Syntellect 41 • A Cable pay-per-view system • Use phone or WWW • Then transported to db applica. Server • Order is processed. DB is updated • Approval order is relayed back to the cable video server • Transmits the video to customer • 700 cable companies. Very profitable 41
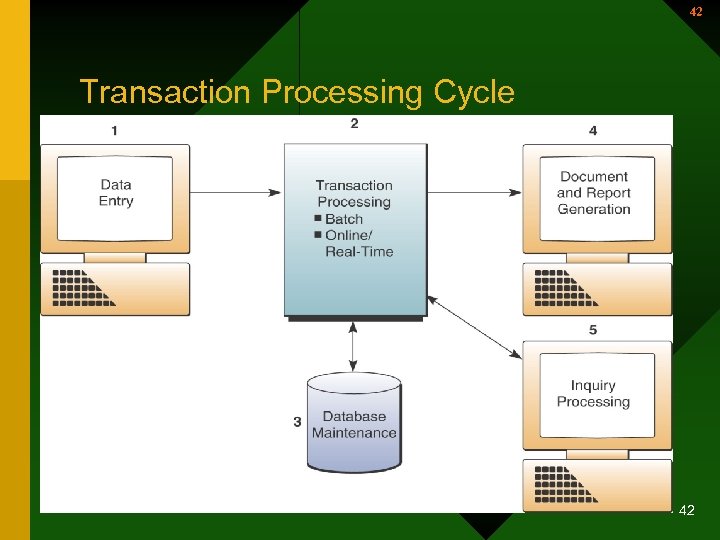
42 Transaction Processing Cycle 42
43 Transaction Processing Systems (continued) • Transaction Processing Cycle – Data entry • The capture of business data – Transaction processing • Two basic ways – Batch processing where transaction data are accumulated & processed periodically – Real-time processing where data are processed immediately after a transaction occurs 43
44 Transaction Processing Cycle (continued) • Transaction Processing Cycle (continued) – Database maintenance • Corporate databases are updated to reflect the day-to-day business transactions – Document and report generation • A variety of documents and reports are produced 44
45 Transaction Processing Cycle (continued) • Transaction Processing Cycle (continued – Inquiry processing • Inquiries and responses concerning the results of transaction processing activity 45
46 Enterprise Collaboration Systems • Cross-functional e-business systems that enhance communication, coordination, & collaboration – Communicate – share information with each other – Coordinate – coordinate individual work efforts & use of resources with each other. – Collaborate – work together cooperatively on joint projects and assignments • Allows virtual teams 46
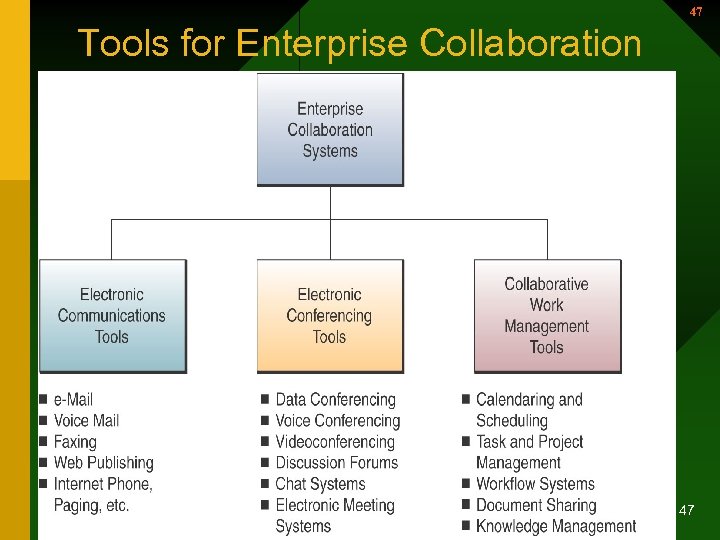
47 Tools for Enterprise Collaboration 47

Tools for Enterprise Collaboration 48 • Tools for Enterprise Collaboration – Electronic communication • • E-mail Voice mail Fax Web publishing Bulletin boards Paging Internet phone systems 48

49 Tools for Enterprise Collaboration • Electronic conferencing – Data & voice conferencing – Videoconferencing – Chat systems – Discussion forums – Electronic meeting systems • Synchronous. Team members can meet at the same time and place in a “decision room” setting 49

50 Tools for Enterprise Collaboration • Collaborative work management – Calendaring & scheduling – Task & project management – Workflow systems – Knowledge management 50

General Electric Committed to Collaboration 51 • Use Lotus development tools – Web-based work spaces – Realtime online meetings – 18, 000 workspaces for 250, 000 employees – Company wide knowledge mgt. System • Database of employee areas of expertise – So others can contact – Faster workflow and quicker, smarter decisions 51
e9284821288a7dc0b1a585182ad3c188.ppt