703507fcb3f72eff26dbba94c2a214d9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51

1

Programming and Budgeting Policies for Acquisition Programs Professor Gerry Land CPA, CDFM-A Defense Acquisition University Capital & Northeast Region Fort Belvoir, VA (703) 805 -3755; DSN 655 -3755 E-mail: gerry. land@dau. mil 2010 PDI – June 2010 2

Funding Policies Workshop Topics • Budgeting Building Blocks • Funding Policies - Annual Funding - Incremental Funding - Full Funding • Exceptions to Full Funding - Advance Procurement - Multiyear Procurement (economic order quantity) • Funding Policies for Unique Items - Communications and Information Systems - LRIP Articles - Product Improvements 3
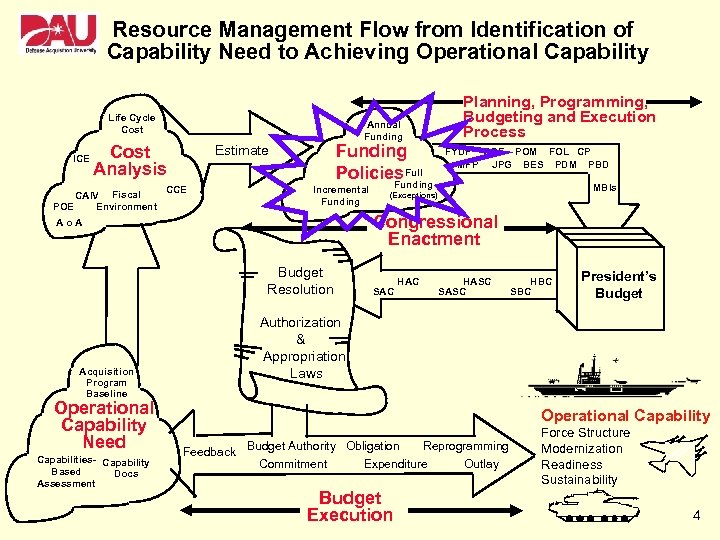
Resource Management Flow from Identification of Capability Need to Achieving Operational Capability Life Cycle Cost ICE Cost Analysis CAIV Fiscal Environment POE Annual Funding Policies Full Estimate CCE Incremental Funding Budget Resolution Funding MBIs (Exceptions) SAC HASC SASC HBC SBC President’s Budget Authorization & Appropriation Laws Acquisition Program Baseline Capabilities- Capability Based Docs Assessment FYDP GDF POM FOL CP MFP JPG BES PDM PBD Congressional Enactment Ao. A Operational Capability Need Planning, Programming, Budgeting and Execution Process Operational Capability Feedback Budget Authority Obligation Commitment Reprogramming Expenditure Budget Execution Outlay Force Structure Modernization Readiness Sustainability 4

What is Needed to Build a Program Budget? Program Direction: A statement of what the program manager is expected to do – the Acquisition Program Baseline (APB) Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): A translation of the program direction into a statement of the tasks required to achieve the program objectives Schedule: The sequence of tasks in the WBS – • Showing when each task begins and ends • How tasks are related to each other • How workload/cost for each task is distributed within the time period 5

Appropriation Categories vs. Appropriation Accounts • Appropriation Categories • Definition: Broad, generic terms pertaining to general “types” of Federal Government funds. • Examples of interest to Acquisition Community: • Research, Development, Test and Evaluation (RDT&E) • Procurement • Military Construction (MILCON) • Appropriation Accounts • Definition: Specific designation of Federal Government funds as contained in an Appropriations Act passed by Congress and signed into law by President. Each account has a unique four digit code preceded by a two digit prefix. • Examples of interest to Acquisition Community: • Research, Development, Test and Evaluation (RDT&E), Army (2040) • Aircraft Procurement, Navy (1506) • Operations & Maintenance (O&M), Air Force (3400) 6
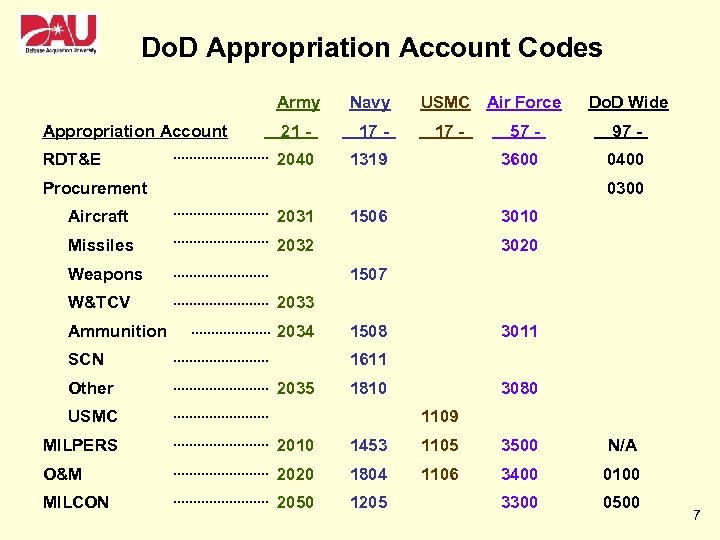
Do. D Appropriation Account Codes Army Navy Appropriation Account 21 - 17 - RDT&E 2040 USMC Air Force 1319 17 - Do. D Wide 57 - 97 - 3600 0400 Procurement 0300 Aircraft 2031 Missiles 2032 Weapons 1506 3010 3020 1507 W&TCV 2033 Ammunition 2034 SCN Other 1508 3011 1611 2035 1810 USMC 3080 1109 MILPERS 2010 1453 1105 3500 N/A O&M 2020 1804 1106 3400 0100 MILCON 2050 1205 3300 0500 7

Underlying Assumptions in Budgeting • “Color of money” (i. e. , Appropriation) requested in the budget is based on type of work to be performed • Normally, funding is requested for a 12 month fiscal year (1 October – 30 September of following year) • Correct level of funding requested (i. e. , budgeted) for a fiscal year is based on required level of work effort plus application of proper funding policy for that Appropriation • Funding is requested (i. e. , budgeted) for the fiscal year when the organization honestly “requires” the funds in accordance with proper funding policy • Application of proper funding policy implies that funds will be obligated during the first year of availability 8

“Notional” Example of Preparing Input for FY 2012 Budget - Applying Escalation Year Budget Prepared FY 10 Price Today (Base Yr $ ) Outlay Rate (%) Cumulative Inflation (%) Dollar “Value” ( $ ) When Outlaid “Required Budget” Estimate (Current/Then Yr $ ) Target Fiscal Year FY 11 FY 12 FY 13 FY 14 TOTAL $$ To go from “Price Today” to “Required Budget”, multiple “ Price Today” by proper Weighted (Composite) Index of Appropriation Account $$$ Budget Estimate = “Price Today in Base Yr $” plus inflation plus economic effects of outlays occurring in future years 9
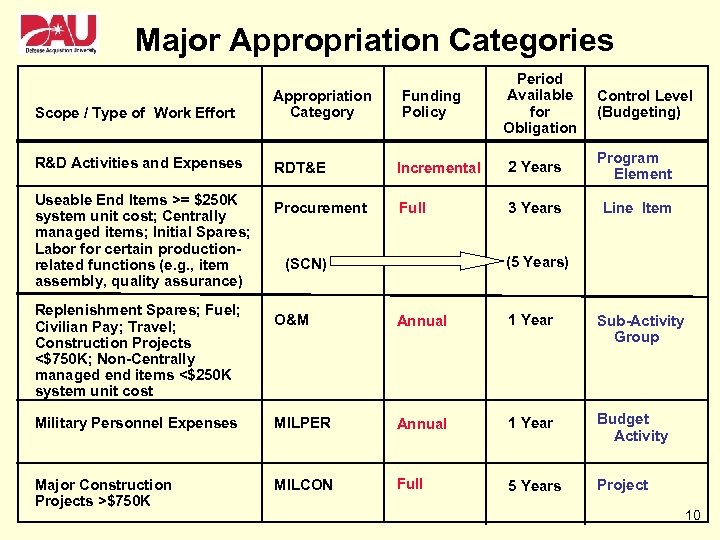
Major Appropriation Categories Funding Policy Period Available for Obligation Control Level (Budgeting) Scope / Type of Work Effort Appropriation Category R&D Activities and Expenses RDT&E Incremental 2 Years Program Element Procurement Full 3 Years Line Item Useable End Items >= $250 K system unit cost; Centrally managed items; Initial Spares; Labor for certain productionrelated functions (e. g. , item assembly, quality assurance) Replenishment Spares; Fuel; Civilian Pay; Travel; Construction Projects <$750 K; Non-Centrally managed end items <$250 K system unit cost (5 Years) (SCN) O&M Annual 1 Year Sub-Activity Group Military Personnel Expenses MILPER Annual 1 Year Budget Activity Major Construction Projects >$750 K MILCON Full 5 Years Project 10

Annual Funding Policy • Appropriations: • Operations and Maintenance • Military Personnel • Budgeting Policy: • Annual budget request will be limited to obligation authority necessary to cover all expenses during a 12 month budget period (usually the fiscal year). 11

Service Contract Exception to Annual Funding Policy • Exception to budgeting for “Fiscal Year” period • U. S. Code, Title 10, Section 2410 a provides authority for Do. D to budget for and obligate funds for severable service contracts for periods crossing fiscal years -provided the contract period does not exceed 12 months 12
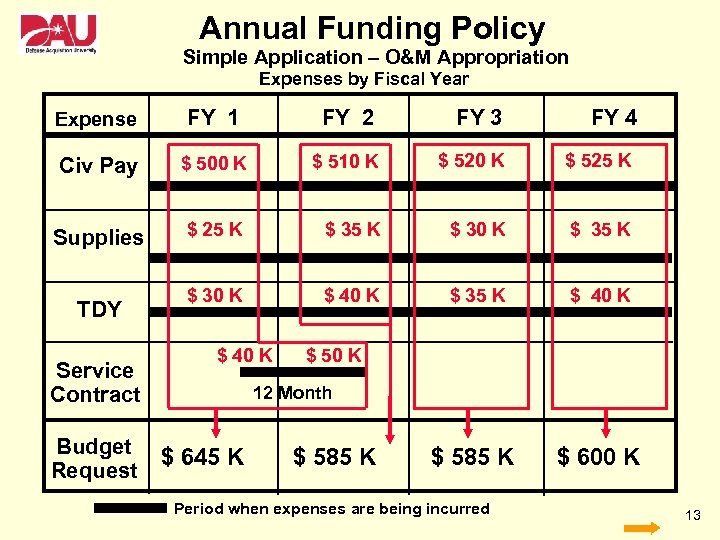
Annual Funding Policy Simple Application – O&M Appropriation Expenses by Fiscal Year Expense FY 1 FY 2 FY 3 FY 4 Civ Pay $ 500 K $ 510 K $ 525 K Supplies $ 25 K $ 30 K $ 35 K $ 30 K $ 40 K $ 35 K $ 40 K $ 585 K $ 600 K TDY Service Contract Budget Request $ 40 K $ 50 K 12 Month $ 645 K $ 585 K Period when expenses are being incurred 13

Incremental Funding Policy • Appropriation: Research, Development, Test & Evaluation (RDT&E) • Budgeting Policy: • Annual budget request will be limited to budget authority necessary to cover all costs expected to be incurred during that fiscal year • Incremental Funding Policy provides flexibility to the government in the uncertain environment of RDT&E 14

Purposes of the Incremental Funding Policy • Allows Congress to review progress of every R&D project – each year – and decide if the project should continue and, if so, at what dollar amount • Does not require one Congress to “tie the hands” of a future Congress • Provides Do. D flexibility to fund R&D projects on a year-by-year basis 15

18 Month Exception to Incremental Funding Policy • For requirements with no logical way to divide the work to limit contract to a shorter period, or • If the planned technical effort is such that no responsible contractor will accept a contract for less than completion of the total requirement • For these types of efforts that take longer than 12 months, but less than 18 months, the Service or Defense Agency Comptroller may approve financing the total requirement in one fiscal year 16

How does a Program Office Prepare its Budget under Incremental Funding ? • Create a good estimate of expected future costs to be incurred (even though system design may be unstable and contractor may not be chosen) • Use 9 -months or less of effort for first year increment of a “new start” program (due to nature/timing of budget approval) • For second and succeeding yearly increments, budget for entire year, taking into account any changes (slippages) that may have occurred from previous budget submission Note: Service or Agency comptroller may approve up to 15 months of costs for second and succeeding fiscal years (i. e. , 3 months beyond end of fiscal year) 17
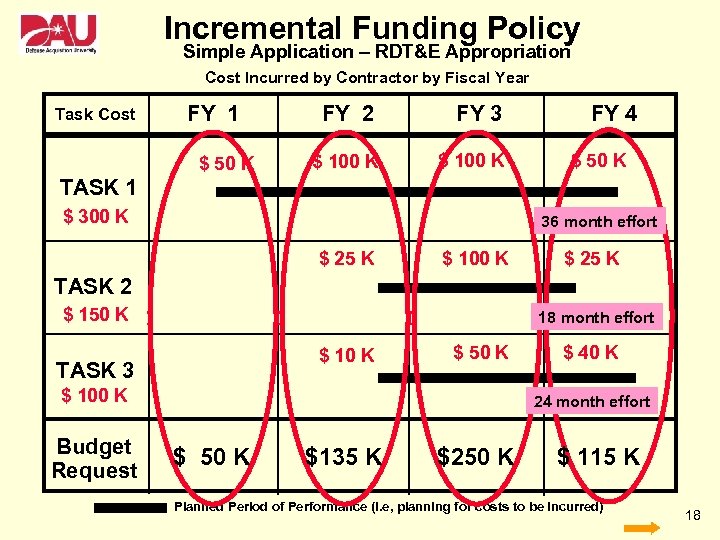
Incremental Funding Policy Simple Application – RDT&E Appropriation Cost Incurred by Contractor by Fiscal Year Task Cost FY 1 $ 50 K FY 2 FY 3 $ 100 K FY 4 $ 50 K TASK 1 $ 300 K 36 month effort $ 25 K $ 100 K $ 25 K TASK 2 $ 150 K 18 month effort $ 10 K TASK 3 $ 50 K $ 100 K Budget Request $ 40 K 24 month effort $ 50 K $135 K $250 K $ 115 K Planned Period of Performance (i. e, planning for costs to be incurred) 18

Full Funding Policy • Applies to Procurement and Military Construction Appropriations • Annual budget request must cover the total cost to deliver a given quantity of complete, militarily usable end items in a 12 month funded delivery period • Governing Concepts • Usable End Items - Piecemeal procurement of systems is not permitted • Funded Delivery Period - 12 month period starting with projected delivery of first item • Exceptions to Policy • Advanced Procurement (For Long Lead Items) • Economic Order Quantity (With Multiyear Procurement) 19

Purposes of Full Funding Policy • Allows Congress to understand the full cost of a complete weapon system through budget process • Does not require one Congress to “tie the hands” of a future Congress • Avoids purchase of a large number of partially completed systems, followed by the need for more money to complete these systems • Achieves better program stability - but on a year by year basis 20

Concept of “Usable End Items” Which Program is Correct Under Full Funding? Program A Year 1 Year 2 Program B Year 2 21
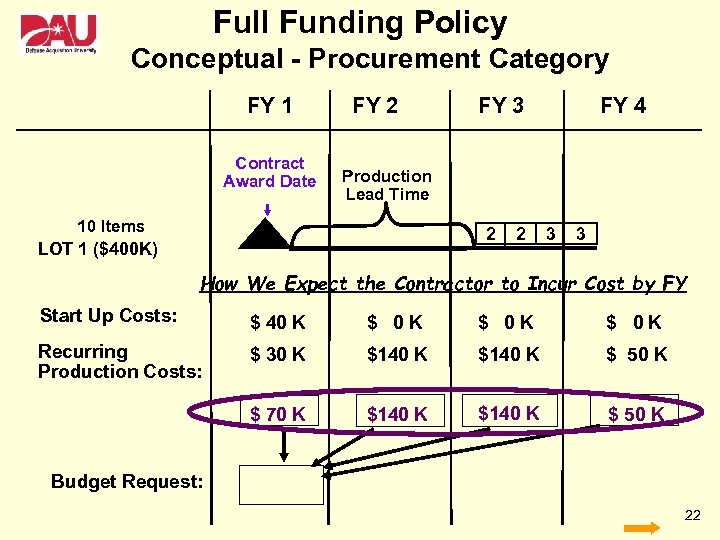
Full Funding Policy Conceptual - Procurement Category FY 1 Contract Award Date FY 2 FY 3 FY 4 Production Lead Time 10 Items 2 LOT 1 ($400 K) 2 3 3 How We Expect the Contractor to Incur Cost by FY Start Up Costs: $ 40 K $ 0 K Recurring Production Costs: $ 30 K $140 K $ 50 K $ 70 K $140 K $ 50 K Budget Request: 22
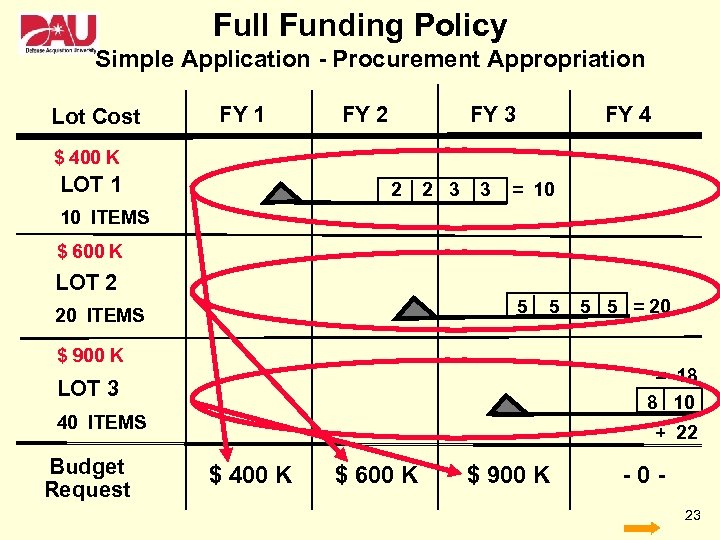
Full Funding Policy Simple Application - Procurement Appropriation Lot Cost FY 1 FY 2 FY 3 FY 4 $ 400 K LOT 1 2 2 3 3 = 10 10 ITEMS $ 600 K LOT 2 5 20 ITEMS 5 $ 900 K = 18 8 10 LOT 3 40 ITEMS Budget Request 5 5 = 20 + 22 $ 400 K $ 600 K $ 900 K -023
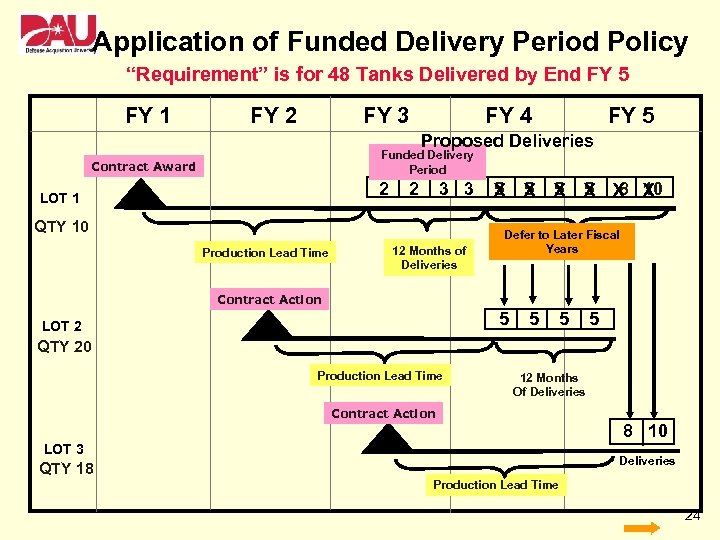
Application of Funded Delivery Period Policy “Requirement” is for 48 Tanks Delivered by End FY 5 FY 1 FY 2 FY 3 FY 4 FY 5 Proposed Deliveries Funded Delivery Period Contract Award 2 LOT 1 2 3 3 QTY 10 Production Lead Time 12 Months of Deliveries 5 5 8 10 X X X Defer to Later Fiscal Years Contract Action 5 LOT 2 5 5 5 QTY 20 Production Lead Time 12 Months Of Deliveries Contract Action 8 10 LOT 3 Deliveries QTY 18 Production Lead Time 24
Advance Procurement Long Lead-time Items • Exception to Full Funding Policy – Explanation why an exception: the PMO is not buying usable end items – Shown in Acquisition Strategy – Approved in Milestone Decision • Circumstances that justify use: – When necessary to maintain (protect) planned production schedule – Lead-time of component greater than life of the appropriation – Lead-time of component significantly longer than remainder of end item • Budgetary Implications: – Minimum amount budgeted = termination liability of total cost of long lead-time items being procured – Budgeted amount generally requested one fiscal year in advance of related end item contract – Budgeted amount is shown as a separate line entry on various budget exhibits (e. g. , P-1, P-5, P-40) 25
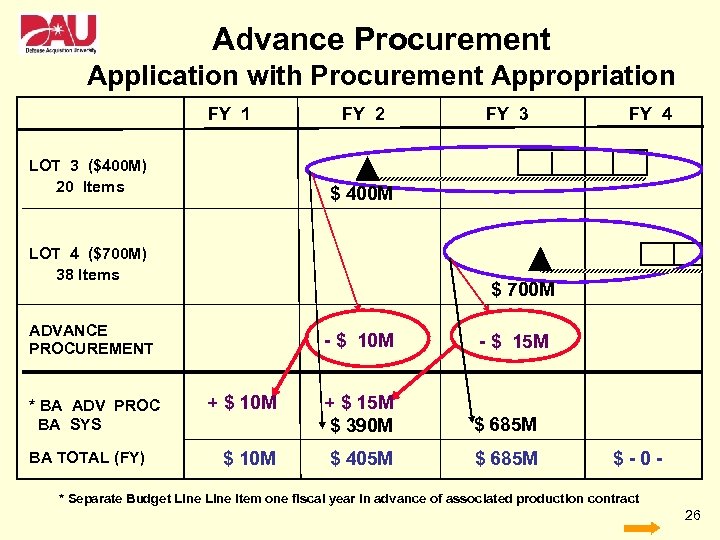
Advance Procurement Application with Procurement Appropriation FY 1 LOT 3 ($400 M) 20 Items FY 2 $ 700 M ADVANCE PROCUREMENT BA TOTAL (FY) FY 4 $ 400 M LOT 4 ($700 M) 38 Items * BA ADV PROC BA SYS FY 3 - $ 10 M + $ 10 M - $ 15 M + $ 15 M $ 390 M $ 685 M $ 405 M $ 685 M $-0 - * Separate Budget Line Item one fiscal year in advance of associated production contract 26
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Associated with Multiyear Procurement (MYP) • Exception to Full Funding Policy – Explanation why an exception: Contracted deliveries will exceed the 12 month funded delivery period • Definition of MYP – A generic term that describes the process, planning and ultimate contract by which the government may contract for the purchase of supplies or services that satisfy requirements for more than one but normally not more than five years. Source: Do. D 7000. 14 -R, Vol 2 A, Chap 1, Section 010203 27

Multiyear Procurement (MYP) Continued • Commitment to buy a specific quantity of useable end items of a weapon system over a specified number of years (normally, maximum of five years) • Annual Appropriation by Congress for same specified number of years • Purpose: - To reduce program cost growth - To counteract adverse effects of the annual budget and procurement process - To bring stability to acquisition process 28
Multiyear Procurement (MYP) Continued • Benefits: – Provides assurance to contractor of future years procurement – Encourages contractor investment – Facilitates economic order quantities – Increases contractor productivity • Potential problems: – Government liable for a penalty (in a decreasing amount) for early cancellation of contract – Can not budget for that cancellation/termination liability – Controversial concept (both in Congress & OSD) 29
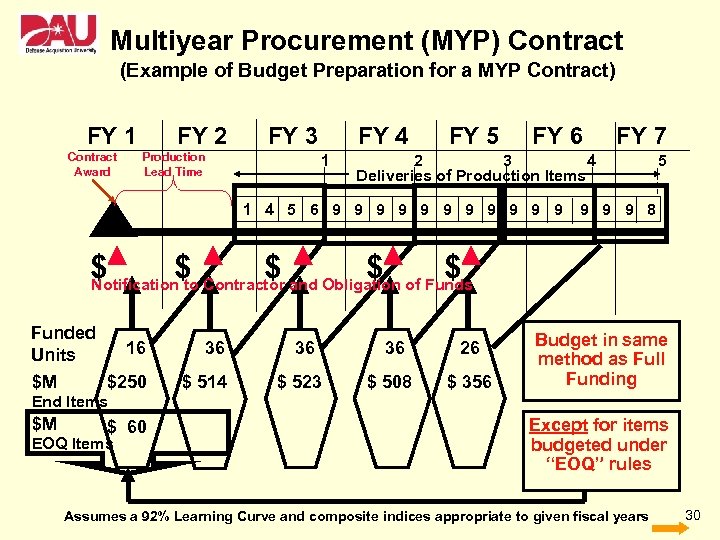
Multiyear Procurement (MYP) Contract (Example of Budget Preparation for a MYP Contract) FY 1 Contract Award FY 2 FY 3 Production Lead Time FY 4 1 FY 5 FY 6 FY 7 2 3 4 Deliveries of Production Items 1 4 5 6 9 9 9 5 9 9 9 8 $ $ $ Notification to Contractor and Obligation of Funds Funded Units $M 16 36 $250 $ 514 36 $ 523 36 $ 508 26 $ 356 Budget in same method as Full Funding End Items $M $ 60 EOQ Items Except for items budgeted under “EOQ” rules Assumes a 92% Learning Curve and composite indices appropriate to given fiscal years 30

Multiyear Procurement (MYP) Recent Example • • • Program: F/A-18 Super Hornet and E/A-18 Growler Proposed quantity of aircraft: 124 total Time period: FY 2010 through FY 2013 Contractor: Boeing Projected contract award: NLT 30 Sep 2010 Potential savings compared to annual contract actions: $590 Million (approximately 10% of basic contract with annual options) • Congress provided conditional authority in FY 2010 NDAA and FY 2010 Defense Appropriations Act • On 14 May 2010 OSD notified Congressional leaders of intent to award the MYP contract for aircraft 31

Funding Rules for Communications and Information Systems • RDT&E - Development, test and evaluation costs - Development of major upgrades - Hardware/Software for RDT&E facilities • Procurement - Investment - New equipment / SW > $250 K - Upgrades / replacement equipment > $250 K • O&M - Expenses - New equipment / SW < $250 K - Upgrades / replacement equipment < $250 K - Routine maintenance - Equipment leases 32
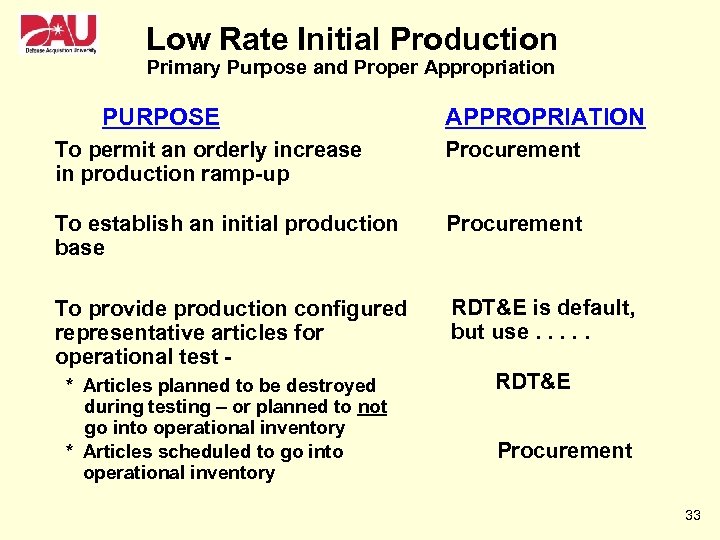
Low Rate Initial Production Primary Purpose and Proper Appropriation PURPOSE APPROPRIATION To permit an orderly increase in production ramp-up Procurement To establish an initial production base Procurement To provide production configured representative articles for operational test - RDT&E is default, but use. . . * Articles planned to be destroyed during testing – or planned to not go into operational inventory * Articles scheduled to go into operational inventory RDT&E Procurement 33
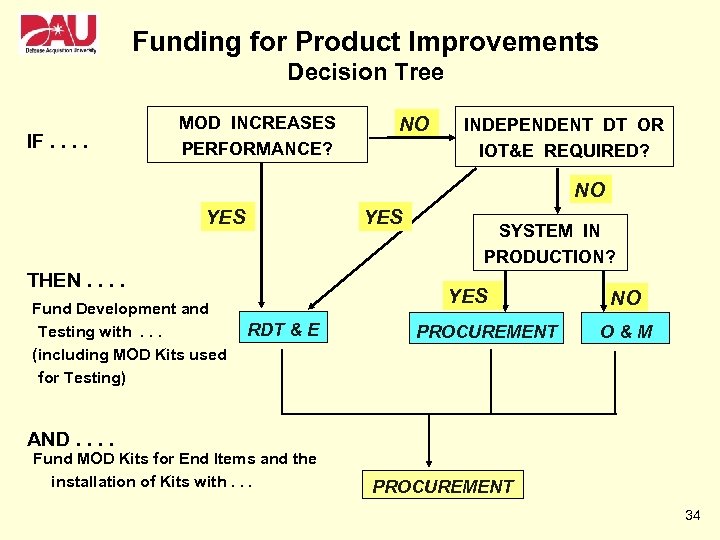
Funding for Product Improvements Decision Tree IF. . MOD INCREASES PERFORMANCE? NO INDEPENDENT DT OR IOT&E REQUIRED? NO YES THEN. . Fund Development and Testing with. . . (including MOD Kits used for Testing) SYSTEM IN PRODUCTION? YES RDT & E PROCUREMENT NO O&M AND. . Fund MOD Kits for End Items and the installation of Kits with. . . PROCUREMENT 34
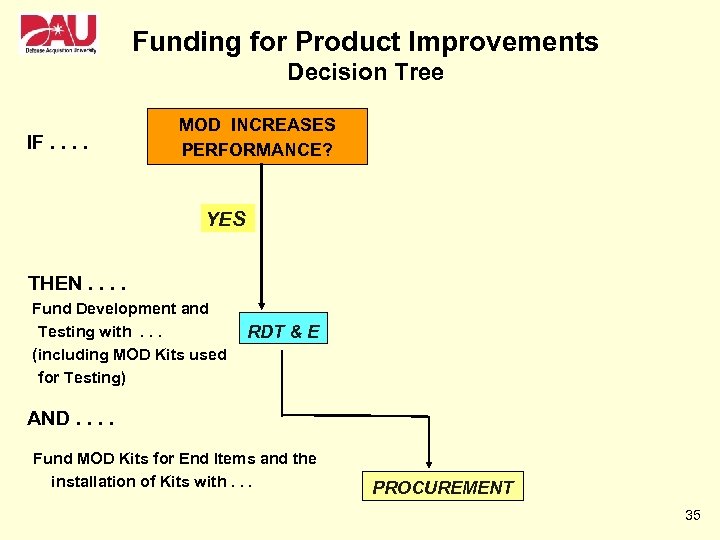
Funding for Product Improvements Decision Tree IF. . MOD INCREASES PERFORMANCE? YES THEN. . Fund Development and Testing with. . . (including MOD Kits used for Testing) RDT & E AND. . Fund MOD Kits for End Items and the installation of Kits with. . . PROCUREMENT 35
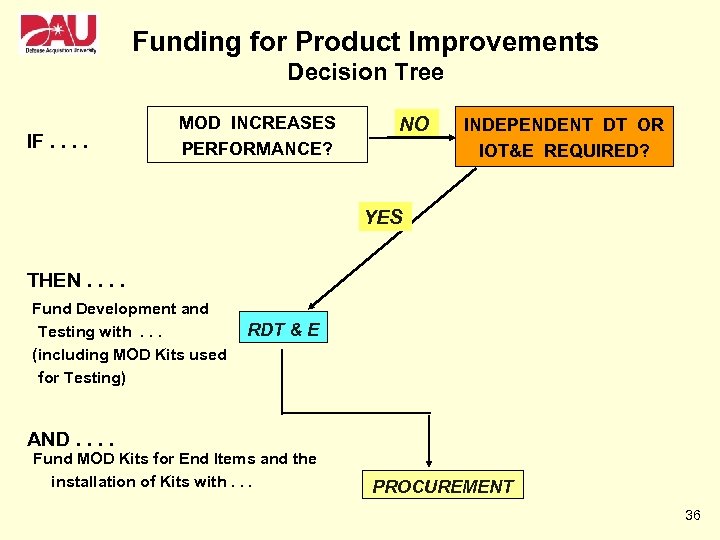
Funding for Product Improvements Decision Tree IF. . MOD INCREASES PERFORMANCE? NO INDEPENDENT DT OR IOT&E REQUIRED? YES THEN. . Fund Development and Testing with. . . (including MOD Kits used for Testing) RDT & E AND. . Fund MOD Kits for End Items and the installation of Kits with. . . PROCUREMENT 36
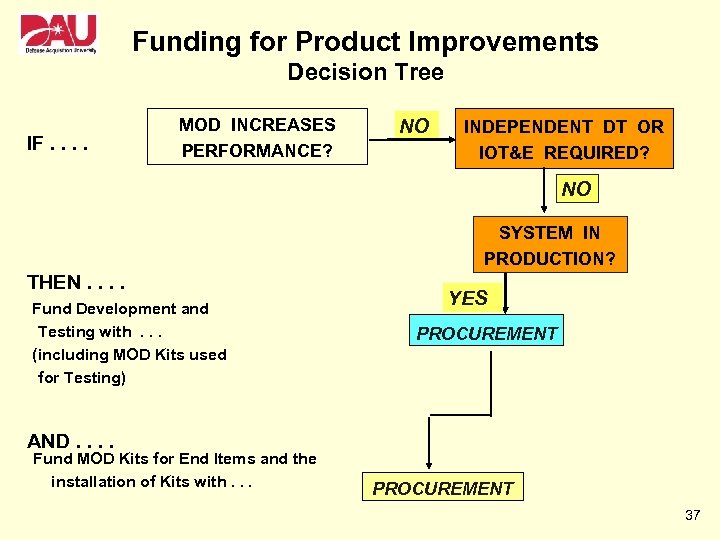
Funding for Product Improvements Decision Tree IF. . MOD INCREASES PERFORMANCE? NO INDEPENDENT DT OR IOT&E REQUIRED? NO SYSTEM IN PRODUCTION? THEN. . Fund Development and Testing with. . . (including MOD Kits used for Testing) YES PROCUREMENT AND. . Fund MOD Kits for End Items and the installation of Kits with. . . PROCUREMENT 37
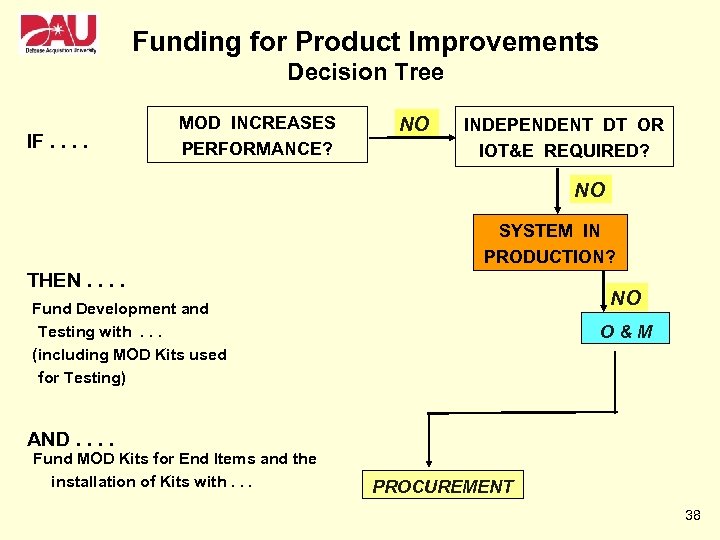
Funding for Product Improvements Decision Tree IF. . MOD INCREASES PERFORMANCE? NO INDEPENDENT DT OR IOT&E REQUIRED? NO SYSTEM IN PRODUCTION? THEN. . NO Fund Development and Testing with. . . (including MOD Kits used for Testing) O&M AND. . Fund MOD Kits for End Items and the installation of Kits with. . . PROCUREMENT 38
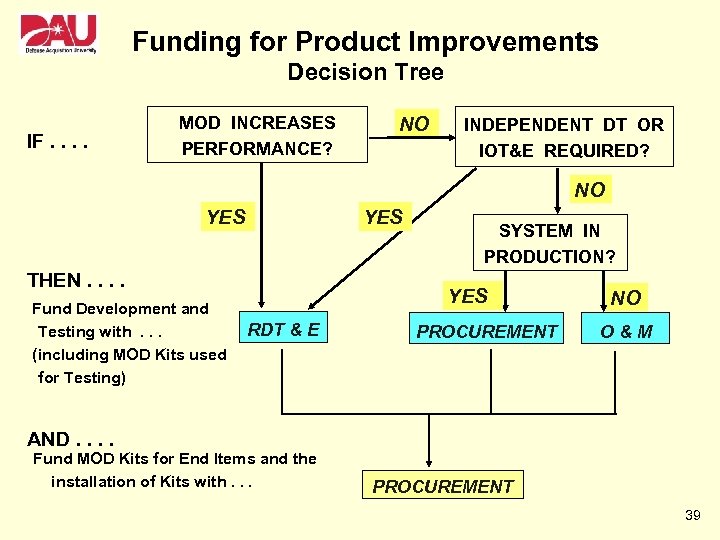
Funding for Product Improvements Decision Tree IF. . MOD INCREASES PERFORMANCE? NO INDEPENDENT DT OR IOT&E REQUIRED? NO YES THEN. . Fund Development and Testing with. . . (including MOD Kits used for Testing) SYSTEM IN PRODUCTION? YES RDT & E PROCUREMENT NO O&M AND. . Fund MOD Kits for End Items and the installation of Kits with. . . PROCUREMENT 39

Summary • Each appropriation category has a specific set of policies pertaining to budget formulation. • Budgeting policies are based on agreements between Congress and OSD. • Budget requests in the Budget Estimate Submission (BES) and the President’s Budget (PB) should be prepared in accordance with applicable policies. 40

Questions? Now for the DAU optional “commercial” 41

Briefing for DAU Students Learn. Perform. Succeed. #1 ’ 02 ’ 06 ’ 05 ’ 06 ’ 07 ’ 04 ’ 06 ’ 07 ’ 09 ’ 03 ’ 04 Jan 2010

DAU Mission Provide a global learning environment to support a mission-ready Defense Acquisition Workforce that develops, delivers, and sustains effective and affordable warfighting capabilities. Impact acquisition excellence through: ü Acquisition certification and leadership training ü Mission assistance to acquisition organizations ü Online knowledge sharing resources ü Continuous learning assets ü Strategic workforce planning

AT&L Performance Learning Model Training Courses Classroom & online DAWIA, Core Plus, & Executive Continuous Learning CL Modules - Online, self-paced learning modules Conferences - PEO / SYSCOM, Business Managers, DAU Acquisition Community Symposium Knowledge Sharing DAP - Online portal to Big A & HCI knowledge ACC - Do. D's online collaborative communities Virtual Library - Online connection to DAU research collection Formal & informal learning at the point of Mission Assistance Consulting - Helping organizations solve complex acquisition problems Targeted Training - Tailored organizational training Rapid Deployment Training - On-site & online training on the latest AT&L policies

Located with our Customers Region Location Workforce Capital/Northeast Fort Belvoir, VA 31, 566 Mid-Atlantic California, MD 23, 110 Midwest Kettering, OH 18, 604 South Huntsville, AL 28, 360 West San Diego, CA 25, 465 We are part of the community, not just a place to take classes.

Learning assets at www. dau. mil DAU Training & CL Courses http: //icatalog. dau. mil/ Mission Assistance Acquisition Best Practices Clearinghouse http: //www. dau. mil/images/Pages/mission_assistance. aspx Defense Acquisition Portal Acquisition Community Connection https: //dap. dau. mil https: //acc. dau. mil/ https: //bpch. dau. mil/ DAU Acker Library http: //www. dau. mil/Library/
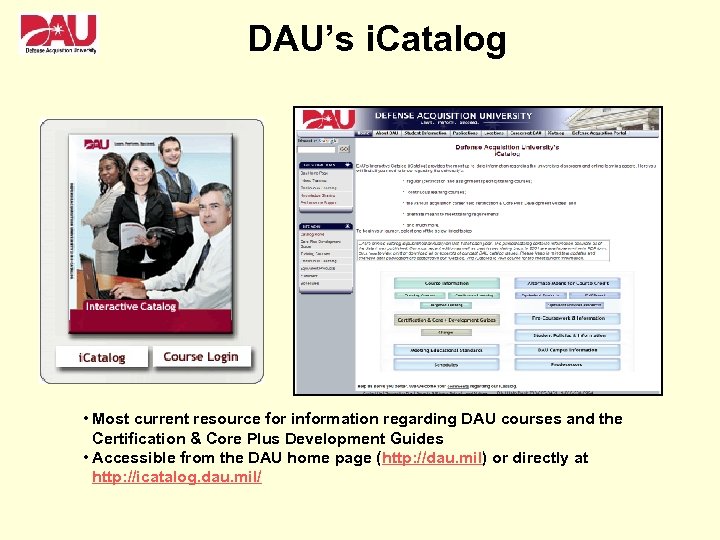
DAU’s i. Catalog • Most current resource for information regarding DAU courses and the Certification & Core Plus Development Guides • Accessible from the DAU home page (http: //dau. mil) or directly at http: //icatalog. dau. mil/
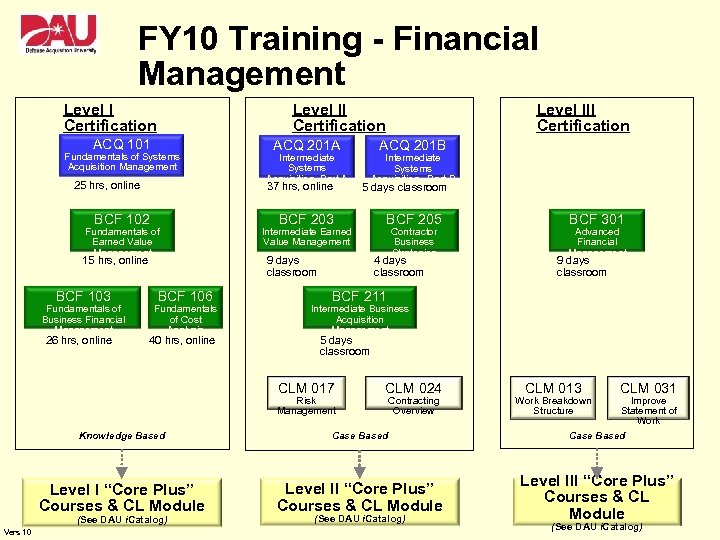
FY 10 Training - Financial Management Level I Certification Level II Certification ACQ 101 Fundamentals of Systems Acquisition Management 25 hrs, online BCF 102 15 hrs, online BCF 103 26 hrs, online Intermediate Systems Acquisition, Part A 37 hrs, online Fundamentals of Earned Value Management Fundamentals of Business Financial Management ACQ 201 A BCF 106 Fundamentals of Cost Analysis 40 hrs, online Level III Certification ACQ 201 B Intermediate Systems Acquisition , Part B 5 days classroom BCF 203 Intermediate Earned Value Management 9 days classroom BCF 205 Contractor Business Strategies 4 days classroom BCF 301 Advanced Financial Management 9 days classroom BCF 211 Intermediate Business Acquisition Management 5 days classroom CLM 017 Risk Management CLM 024 Contracting Overview CLM 013 Work Breakdown Structure CLM 031 Improve Statement of Work Knowledge Based Case Based Level I “Core Plus” Courses & CL Module Level III “Core Plus” Courses & CL Module (See DAU i. Catalog) Vers 10 (See DAU i. Catalog)
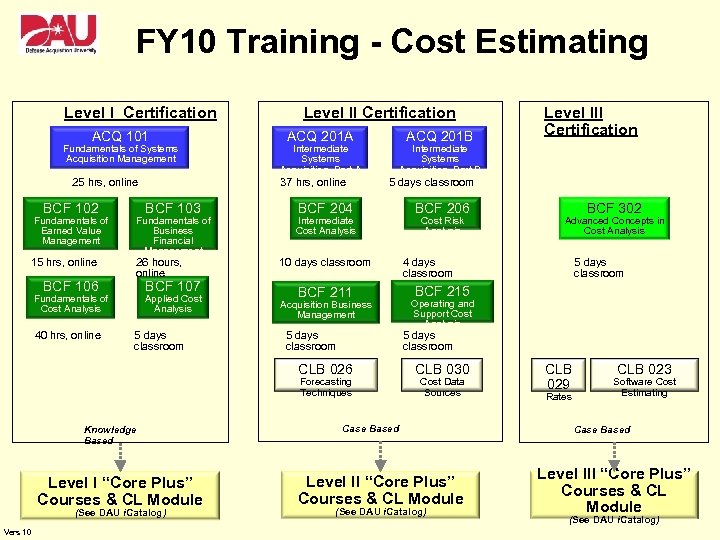
FY 10 Training - Cost Estimating Level I Certification ACQ 101 Fundamentals of Systems Acquisition Management BCF 102 15 hrs, online BCF 106 BCF 103 Fundamentals of Business Financial Management 26 hours, online BCF 107 Fundamentals of Cost Analysis 40 hrs, online ACQ 201 A Applied Cost Analysis 5 days classroom ACQ 201 B Intermediate Systems Acquisition, Part A 37 hrs, online 25 hrs, online Fundamentals of Earned Value Management Level II Certification Intermediate Systems Acquisition, Part B 5 days classroom BCF 204 Intermediate Cost Analysis 10 days classroom BCF 211 Acquisition Business Management 5 days classroom Forecasting Techniques Level I “Core Plus” Courses & CL Module (See DAU i. Catalog) Vers 10 BCF 206 Cost Risk Analysis BCF 302 Advanced Concepts in Cost Analysis 4 days classroom 5 days classroom BCF 215 Operating and Support Cost Analysis 5 days classroom CLB 026 Knowledge Based Level III Certification CLB 030 Cost Data Sources Case Based Level II “Core Plus” Courses & CL Module (See DAU i. Catalog) CLB 029 Rates CLB 023 Software Cost Estimating Case Based Level III “Core Plus” Courses & CL Module (See DAU i. Catalog)

DAU’s Commitment to the Defense Acquisition Workforce • Training - 24 / 7 learning assets: in the classroom and in the workplace • Continuous Learning - Helping you learn in the workplace: what you need to know , when you need to know it • Mission Assistance - Supporting your organization • Knowledge Sharing - Connecting you – the Engaged Learner - with the experts, resources and materials you need to do your job Shaping a culture of engagement and career-

51
703507fcb3f72eff26dbba94c2a214d9.ppt