c35bc137f48a3c5e55eae241a4691784.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 1
1
 Party Structure Political Parties Not mentioned in the Constitution Two main parties: Republicans and Democrats Four levels: national, state, county and precinct Stratarchy Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 2
Party Structure Political Parties Not mentioned in the Constitution Two main parties: Republicans and Democrats Four levels: national, state, county and precinct Stratarchy Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 2
 Party Structure Temporary Party Organization Primaries and conventions where members of the major political parties select candidates for public office Precinct conventions Occur every even-numbered year on the first Tuesday in March Usually sparsely attended Select delegate for county convention Sometimes propositions are placed on the ballot Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 3
Party Structure Temporary Party Organization Primaries and conventions where members of the major political parties select candidates for public office Precinct conventions Occur every even-numbered year on the first Tuesday in March Usually sparsely attended Select delegate for county convention Sometimes propositions are placed on the ballot Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 3
 Party Structure Temporary Party Organization County and District Conventions Occur the third Saturday after the precinct conventions Elect state convention delegates Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 4
Party Structure Temporary Party Organization County and District Conventions Occur the third Saturday after the precinct conventions Elect state convention delegates Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 4
 Party Structure Temporary Party Organization State conventions June of even-numbered years Certify nominees from primaries Write the rules that govern the party Draft and adopt a party platform Select members of the party’s state executive committee If presidential election, select delegates to National Convention and electors Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 5
Party Structure Temporary Party Organization State conventions June of even-numbered years Certify nominees from primaries Write the rules that govern the party Draft and adopt a party platform Select members of the party’s state executive committee If presidential election, select delegates to National Convention and electors Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 5
 Party Structure Selection of National Convention Delegates Presidential preference primary and caucuses Democratic selection “Texas Two-Step” – Primary vote and caucus Republican selection Presidential preference primary Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 6
Party Structure Selection of National Convention Delegates Presidential preference primary and caucuses Democratic selection “Texas Two-Step” – Primary vote and caucus Republican selection Presidential preference primary Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 6
 Party Structure Permanent Party Organization Precinct Chair Organizes the party’s activities in a district County and District Executive Committees Conduct county primaries and arrange county conventions District executive committee nominates candidates to fill district vacancies Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 7
Party Structure Permanent Party Organization Precinct Chair Organizes the party’s activities in a district County and District Executive Committees Conduct county primaries and arrange county conventions District executive committee nominates candidates to fill district vacancies Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 7
 Party Structure Permanent Party Organization State Executive Committee Highest permanent party organization in state Members elected at party’s state convention Composed of a chair, vice chair, and two members from each senatorial district State party chair is chief fundraiser. Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 8
Party Structure Permanent Party Organization State Executive Committee Highest permanent party organization in state Members elected at party’s state convention Composed of a chair, vice chair, and two members from each senatorial district State party chair is chief fundraiser. Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 8
 Political Ideology Conservatism Belief in minimal government intervention in economic and social/welfare programs Gives high priority to reducing taxes and cutting public spending Neoconservative Fiscally conservative Accepts limited governmental role in solving social problems Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 9
Political Ideology Conservatism Belief in minimal government intervention in economic and social/welfare programs Gives high priority to reducing taxes and cutting public spending Neoconservative Fiscally conservative Accepts limited governmental role in solving social problems Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 9
 Political Ideology Liberalism Favor government regulation of economy to achieve more equal distribution of wealth Favor government involvement in social programs Protect individual freedoms and rights Neoliberal Less government regulation of business and economy, but greater government involvement in social programs Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 10
Political Ideology Liberalism Favor government regulation of economy to achieve more equal distribution of wealth Favor government involvement in social programs Protect individual freedoms and rights Neoliberal Less government regulation of business and economy, but greater government involvement in social programs Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 10
 An Overview of Texas Political History 1840 s to 1870 s: Origin of the Party System Pro-Houston faction Jackson Democrats Anti-Houston faction Calhoun Democrats Reconstruction Republicans – E. J. Davis Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 11
An Overview of Texas Political History 1840 s to 1870 s: Origin of the Party System Pro-Houston faction Jackson Democrats Anti-Houston faction Calhoun Democrats Reconstruction Republicans – E. J. Davis Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 11
 Texas Political History 1870 s to 1970 s: A One-Party Dominant System Strong Democratic Party Populist Party Agrarian based Conservative Democrats v. Liberal Democrats Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 12
Texas Political History 1870 s to 1970 s: A One-Party Dominant System Strong Democratic Party Populist Party Agrarian based Conservative Democrats v. Liberal Democrats Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 12
 Texas Political History 1970 s to 1990 s: An Emerging Two-Party System Resurgence of Republican Party 2000 to 2012: Republican Dominance Controlled all state-wide elections George Bush wins presidency in 2000 Republicans take control of the Texas House in 2002 Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 13
Texas Political History 1970 s to 1990 s: An Emerging Two-Party System Resurgence of Republican Party 2000 to 2012: Republican Dominance Controlled all state-wide elections George Bush wins presidency in 2000 Republicans take control of the Texas House in 2002 Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 13
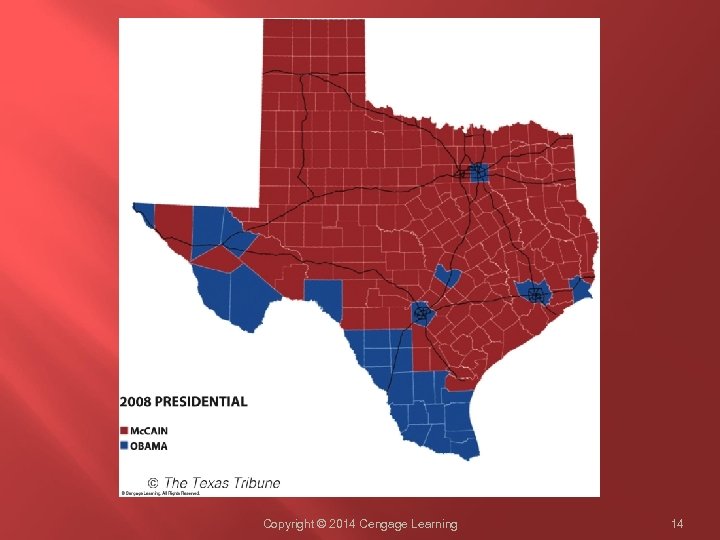 Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 14
Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 14
 Electoral Trends Dealignment Realignment Voters trend away from allegiance to political parties Voters shift away from one political party to another Straight-Ticket Voting for all the candidates of one party Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 15
Electoral Trends Dealignment Realignment Voters trend away from allegiance to political parties Voters shift away from one political party to another Straight-Ticket Voting for all the candidates of one party Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 15
 Electoral Trends Third Parties Any political party other than the Democratic or Republican Party Achieve success in making the public aware of their issues, persuading major parties adopt some of their issues La Raza Unida Reform Party Libertarian Party Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 16
Electoral Trends Third Parties Any political party other than the Democratic or Republican Party Achieve success in making the public aware of their issues, persuading major parties adopt some of their issues La Raza Unida Reform Party Libertarian Party Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 16
 Electoral Trends Independents Applies to candidates who have no party affiliation Limited success due to no campaign organization or fundraising abilities, difficulty gaining ballot access Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 17
Electoral Trends Independents Applies to candidates who have no party affiliation Limited success due to no campaign organization or fundraising abilities, difficulty gaining ballot access Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 17
 Chapter 4 Learning Objectives 1. 2. Describe the structure of political parties in Texas, distinguishing between the temporary party structure and the permanent party structure. Compare and contrast the different political ideologies found in the Lone Star State. Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 18
Chapter 4 Learning Objectives 1. 2. Describe the structure of political parties in Texas, distinguishing between the temporary party structure and the permanent party structure. Compare and contrast the different political ideologies found in the Lone Star State. Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 18
 Chapter 4 Learning Objectives 3. 4. Trace the history of political parties in Texas Identify the roles that minor parties and independents have played in Texas. Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 19
Chapter 4 Learning Objectives 3. 4. Trace the history of political parties in Texas Identify the roles that minor parties and independents have played in Texas. Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning 19


