f3fe68eb97e2e30d8ababdfc284ee41c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 1
1
 Part 1 Marketing Dynamics Chapter 2 Business Basics 2
Part 1 Marketing Dynamics Chapter 2 Business Basics 2
 Chapter Objectives ¾ Identify economic needs and wants. ¾ Describe three uses of money. ¾ Explain how business satisfies economic needs. ¾ Describe three forms of business ownership. (Continued) 3
Chapter Objectives ¾ Identify economic needs and wants. ¾ Describe three uses of money. ¾ Explain how business satisfies economic needs. ¾ Describe three forms of business ownership. (Continued) 3
 Chapter Objectives ¾ Describe the difference between a forprofit corporation and a nonprofit corporation. ¾ List the four functions of business and give an example of each. ¾ Explain the role of marketing in business. 4
Chapter Objectives ¾ Describe the difference between a forprofit corporation and a nonprofit corporation. ¾ List the four functions of business and give an example of each. ¾ Explain the role of marketing in business. 4
 Marketing Terms ¾ need ¾ want ¾ economic needs and wants ¾ economic goods and services ¾ exchange ¾ money ¾ value ¾ time value of money ¾ business ¾ profit ¾ sole proprietorship ¾ partnership ¾ corporation ¾ nonprofit corporation ¾ production ¾ finance ¾ management 5
Marketing Terms ¾ need ¾ want ¾ economic needs and wants ¾ economic goods and services ¾ exchange ¾ money ¾ value ¾ time value of money ¾ business ¾ profit ¾ sole proprietorship ¾ partnership ¾ corporation ¾ nonprofit corporation ¾ production ¾ finance ¾ management 5
 Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Need ¤ necessary for survival ¾ Want ¤ something you desire, but could function without (Continued) 6
Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Need ¤ necessary for survival ¾ Want ¤ something you desire, but could function without (Continued) 6
 Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Economic needs and wants can be satisfied by buying something What are some of your economic needs and wants? (Continued) 7
Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Economic needs and wants can be satisfied by buying something What are some of your economic needs and wants? (Continued) 7
 Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Economic goods and services are the items you buy to satisfy economic needs and wants Name some economic goods and services. (Continued) 8
Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Economic goods and services are the items you buy to satisfy economic needs and wants Name some economic goods and services. (Continued) 8
 Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Some needs and wants cannot be satisfied by buying something What are some needs and wants that cannot be satisfied by buying something? 9
Economic Needs and Wants ¾ Some needs and wants cannot be satisfied by buying something What are some needs and wants that cannot be satisfied by buying something? 9
 The Exchange ¾ An exchange is a trade ¾ Exchanges are the basis of all business Describe an exchange you made. 10
The Exchange ¾ An exchange is a trade ¾ Exchanges are the basis of all business Describe an exchange you made. 10
 Money ¾ Money is a consistent item that people accept in exchange for goods or work Describe American money. How is it consistent? (Continued) 11
Money ¾ Money is a consistent item that people accept in exchange for goods or work Describe American money. How is it consistent? (Continued) 11
 Money ¾ Without money, modern business could not exist ¾ Money is used in three ways ¤ medium of exchange ¤ unit of value ¤ store of wealth 12
Money ¾ Without money, modern business could not exist ¾ Money is used in three ways ¤ medium of exchange ¤ unit of value ¤ store of wealth 12
 Medium of Exchange ¾ Money is a convenient medium of exchange ¾ Paper money and coins are easy to carry 13
Medium of Exchange ¾ Money is a convenient medium of exchange ¾ Paper money and coins are easy to carry 13
 Unit of Value ¾ Money can express the exact value of an item ¤ the dollar is the unit of value in the United States ¾ The value of a product expressed in dollars is the price ¤ marketers use price to set the value of a product 14
Unit of Value ¾ Money can express the exact value of an item ¤ the dollar is the unit of value in the United States ¾ The value of a product expressed in dollars is the price ¤ marketers use price to set the value of a product 14
 Time Value of Money ¾ Time value of money is the notion that a sum of money has greater potential worth in the future than it does today 15
Time Value of Money ¾ Time value of money is the notion that a sum of money has greater potential worth in the future than it does today 15
 Store of Wealth ¾ Money is easy to store ¾ You can save money until you need it Why do people save money? 16
Store of Wealth ¾ Money is easy to store ¾ You can save money until you need it Why do people save money? 16
 What Is Business? ¾ Business ¤ general term for activities involved in the development and exchange of products ¾ The term business also refers to ¤a person or group of people who are involved in the development and exchange of products (Continued) 17
What Is Business? ¾ Business ¤ general term for activities involved in the development and exchange of products ¾ The term business also refers to ¤a person or group of people who are involved in the development and exchange of products (Continued) 17
 What Is Business? ¾ Other terms for business ¤ firm, company, organization, corporation, and enterprise Describe some businesses in your neighborhood. (Continued) 18
What Is Business? ¾ Other terms for business ¤ firm, company, organization, corporation, and enterprise Describe some businesses in your neighborhood. (Continued) 18
 What Is Business? ¾ Business powers the economy ¾ Money flows from businesses to workers ¤ then from the workers back to the businesses ¾ Business provides ¤ goods and services you use every day ¤ wages (money) people use to buy goods and services (Continued) 19
What Is Business? ¾ Business powers the economy ¾ Money flows from businesses to workers ¤ then from the workers back to the businesses ¾ Business provides ¤ goods and services you use every day ¤ wages (money) people use to buy goods and services (Continued) 19
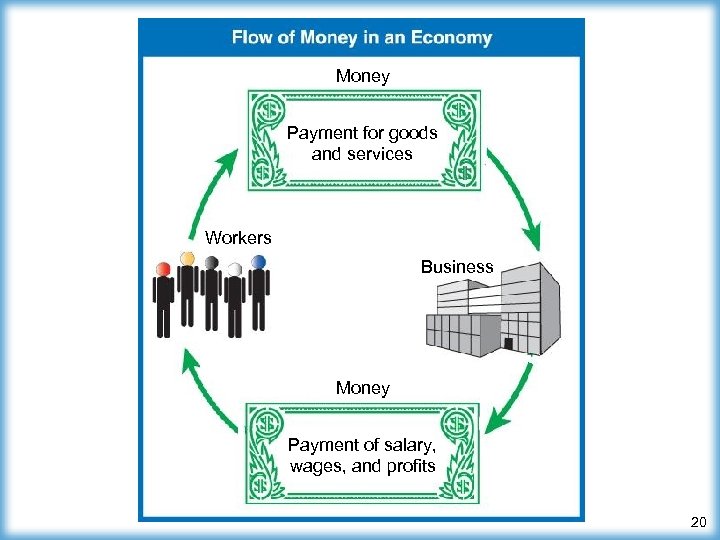 Money Payment for goods and services Workers Business Money Payment of salary, wages, and profits 20
Money Payment for goods and services Workers Business Money Payment of salary, wages, and profits 20
 Making a Profit ¾ Businesses aim to make a profit Sales Costs and Expenses Profit What is profit? 21
Making a Profit ¾ Businesses aim to make a profit Sales Costs and Expenses Profit What is profit? 21
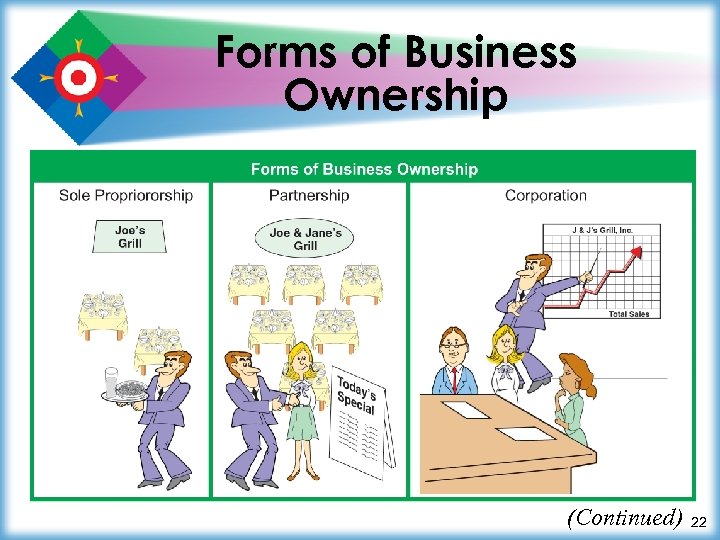 Forms of Business Ownership (Continued) 22
Forms of Business Ownership (Continued) 22
 Forms of Business Ownership ¾ Sole proprietorship is a business owned by one person ¤ who gets all profits and bears all risks ¾ Partnership is a business owned by a small number of people, usually two or three ¤ partners share profits and risks 23
Forms of Business Ownership ¾ Sole proprietorship is a business owned by one person ¤ who gets all profits and bears all risks ¾ Partnership is a business owned by a small number of people, usually two or three ¤ partners share profits and risks 23
 What Is a Corporation? ¾ A corporation is a legal entity established for the purpose of doing business ¤ exists separate from the people who own it ¤ is owned by stockholders (Continued) 24
What Is a Corporation? ¾ A corporation is a legal entity established for the purpose of doing business ¤ exists separate from the people who own it ¤ is owned by stockholders (Continued) 24
 What Is a Corporation? ¾ A corporation can buy property, manufacture products, earn money, lose money, sue, and be sued ¾ A corporation offers limited liability to its shareholders ¤ if a corporation is sued, the corporation pays damages from its income – the shareholders (owners) do not pay Name some corporations. 25
What Is a Corporation? ¾ A corporation can buy property, manufacture products, earn money, lose money, sue, and be sued ¾ A corporation offers limited liability to its shareholders ¤ if a corporation is sued, the corporation pays damages from its income – the shareholders (owners) do not pay Name some corporations. 25
 What Is a Nonprofit Corporation? ¾ There are two types of corporations ¤ for-profit ¤ nonprofit ¾ Goal of a for-profit corporation is to make a profit for its owners ¾ Goal of a nonprofit is to benefit society (Continued) 26
What Is a Nonprofit Corporation? ¾ There are two types of corporations ¤ for-profit ¤ nonprofit ¾ Goal of a for-profit corporation is to make a profit for its owners ¾ Goal of a nonprofit is to benefit society (Continued) 26
 What Is a Nonprofit Corporation? ¾ A nonprofit corporation ¤ is a legal entity, like a for-profit corporation ¤ is established to provide a benefit to society ¤ can make a profit, but any profit that a nonprofit corporation earns goes back to support its cause or benefit ¾ Examples of benefits or causes ¤ charity, education, medical research, youth activities, religion, and the arts (Continued) 27
What Is a Nonprofit Corporation? ¾ A nonprofit corporation ¤ is a legal entity, like a for-profit corporation ¤ is established to provide a benefit to society ¤ can make a profit, but any profit that a nonprofit corporation earns goes back to support its cause or benefit ¾ Examples of benefits or causes ¤ charity, education, medical research, youth activities, religion, and the arts (Continued) 27
 What Is a Nonprofit Corporation? ¾ Examples ¤ DECA ¤ American Cancer Society ¤ Goodwill Name some other nonprofit corporations. 28
What Is a Nonprofit Corporation? ¾ Examples ¤ DECA ¤ American Cancer Society ¤ Goodwill Name some other nonprofit corporations. 28
 The Functions of Business ¾ Four functions of business ¤ production – making products ¤ finance – handling money ¤ marketing – focusing on customers ¤ management – planning, coordinating, monitoring 29
The Functions of Business ¾ Four functions of business ¤ production – making products ¤ finance – handling money ¤ marketing – focusing on customers ¤ management – planning, coordinating, monitoring 29
 Production ¾ For goods, production includes ¤ farming ¤ mining ¤ construction ¤ manufacturing (Continued) 30
Production ¾ For goods, production includes ¤ farming ¤ mining ¤ construction ¤ manufacturing (Continued) 30
 Production ¾ For services, production is often the service itself ¤ Examples – TV production – hairstyling Describe production that you have seen. 31
Production ¾ For services, production is often the service itself ¤ Examples – TV production – hairstyling Describe production that you have seen. 31
 Finance ¾ Finance includes ¤ planning and budgeting ¤ accounting – paying bills – receiving payments – keeping track of transactions 32
Finance ¾ Finance includes ¤ planning and budgeting ¤ accounting – paying bills – receiving payments – keeping track of transactions 32
 Marketing ¾ Marketing helps the business focus on the customer ¾ Marketing includes ¤ selling ¤ promotion ¤ pricing ¤ learning about customers 33
Marketing ¾ Marketing helps the business focus on the customer ¾ Marketing includes ¤ selling ¤ promotion ¤ pricing ¤ learning about customers 33
 Management ¾ Management includes ¤ planning ¤ coordinating ¤ monitoring ¤ supervising ¾ Managers look at the big picture and lead workers to make the business better 34
Management ¾ Management includes ¤ planning ¤ coordinating ¤ monitoring ¤ supervising ¾ Managers look at the big picture and lead workers to make the business better 34
 Review ¾ Explain the three uses of money. ¾ What are three forms of business ownership? ¾ What are the four functions of business? ¾ What is the role of marketing in business? 35
Review ¾ Explain the three uses of money. ¾ What are three forms of business ownership? ¾ What are the four functions of business? ¾ What is the role of marketing in business? 35
 Glossary Back ¾ business. General term for all the activities involved in the development and exchange of products. Also used to refer to a specific person or group of people who are involved in the development and exchange of products; also called firm, company, organization, corporation, or enterprise. ¾ corporation. Legal entity established for the purpose of doing business. (Continued) 36
Glossary Back ¾ business. General term for all the activities involved in the development and exchange of products. Also used to refer to a specific person or group of people who are involved in the development and exchange of products; also called firm, company, organization, corporation, or enterprise. ¾ corporation. Legal entity established for the purpose of doing business. (Continued) 36
 Glossary Back ¾ economic goods and services. Products that you buy to satisfy economic needs. ¾ economic needs and wants. Needs and wants that you can satisfy by buying something. ¾ exchange. To trade something of value for something you want. ¾ finance. The function of business that includes all activities involving money. (Continued) 37
Glossary Back ¾ economic goods and services. Products that you buy to satisfy economic needs. ¾ economic needs and wants. Needs and wants that you can satisfy by buying something. ¾ exchange. To trade something of value for something you want. ¾ finance. The function of business that includes all activities involving money. (Continued) 37
 Glossary Back ¾ management. The function of business that includes all the activities required to plan, coordinate, and monitor a business. ¾ money. A consistent item that people accept in exchange for goods or work. ¾ need. Something that is necessary for survival. (Continued) 38
Glossary Back ¾ management. The function of business that includes all the activities required to plan, coordinate, and monitor a business. ¾ money. A consistent item that people accept in exchange for goods or work. ¾ need. Something that is necessary for survival. (Continued) 38
 Glossary Back ¾ nonprofit corporation. Legal entity, like a for-profit corporation; however, instead of profit, its main goal is to achieve something to benefit society; also called nonprofit, nonprofit organization, or notfor-profit organization. ¾ partnership. Business owned by a small number of people, usually two or three. (Continued) 39
Glossary Back ¾ nonprofit corporation. Legal entity, like a for-profit corporation; however, instead of profit, its main goal is to achieve something to benefit society; also called nonprofit, nonprofit organization, or notfor-profit organization. ¾ partnership. Business owned by a small number of people, usually two or three. (Continued) 39
 Glossary Back ¾ production. Any activity related to making a product (good, service, or idea). ¾ profit. Money that a business has left after all the expenses and costs of running the business are paid. ¾ sole proprietorship. Business owned by one person. (Continued) 40
Glossary Back ¾ production. Any activity related to making a product (good, service, or idea). ¾ profit. Money that a business has left after all the expenses and costs of running the business are paid. ¾ sole proprietorship. Business owned by one person. (Continued) 40
 Glossary Back ¾ time value of money. The notion that a sum of money has greater potential worth in the future than it does today. ¾ value. How much something is worth. ¾ want. Something you desire but you could function without. 41
Glossary Back ¾ time value of money. The notion that a sum of money has greater potential worth in the future than it does today. ¾ value. How much something is worth. ¾ want. Something you desire but you could function without. 41


