 1
1
 Overview of this Lecture 2
Overview of this Lecture 2
 3
3
 4
4
 TAs
TAs
 Grades 6
Grades 6
 Homework 7
Homework 7
 Textbook 8
Textbook 8
 Overview of this Lecture 9
Overview of this Lecture 9
 10
10
 Discrete vs. Continuous Mathematics 11
Discrete vs. Continuous Mathematics 11
 Discrete vs. Continuous Mathematics 12
Discrete vs. Continuous Mathematics 12
 13
13
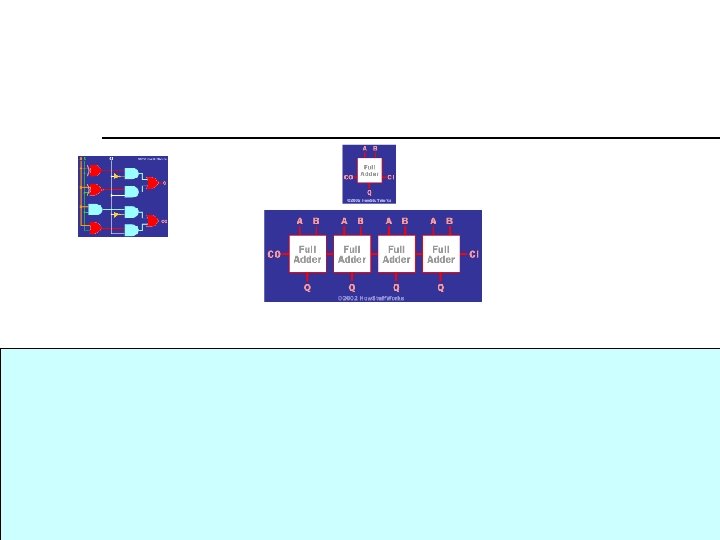 14
14
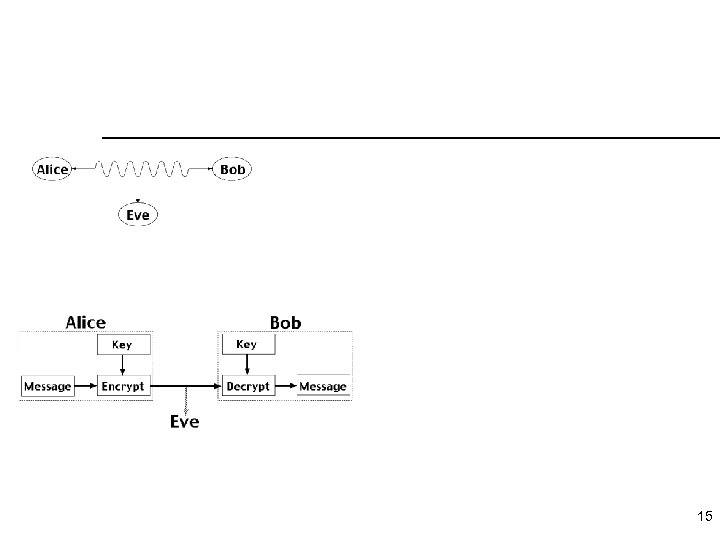 15
15
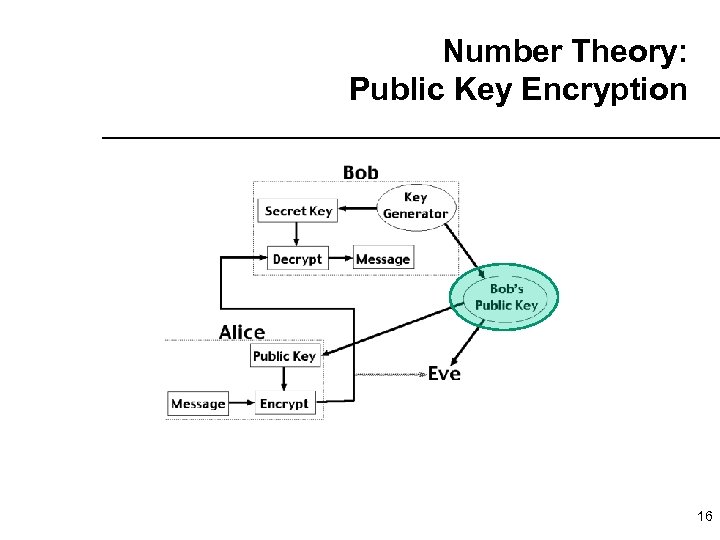 Number Theory: Public Key Encryption 16
Number Theory: Public Key Encryption 16
 RSA Approach
RSA Approach
 18
18
 19
19
 Graphs and Networks 20
Graphs and Networks 20
 21
21
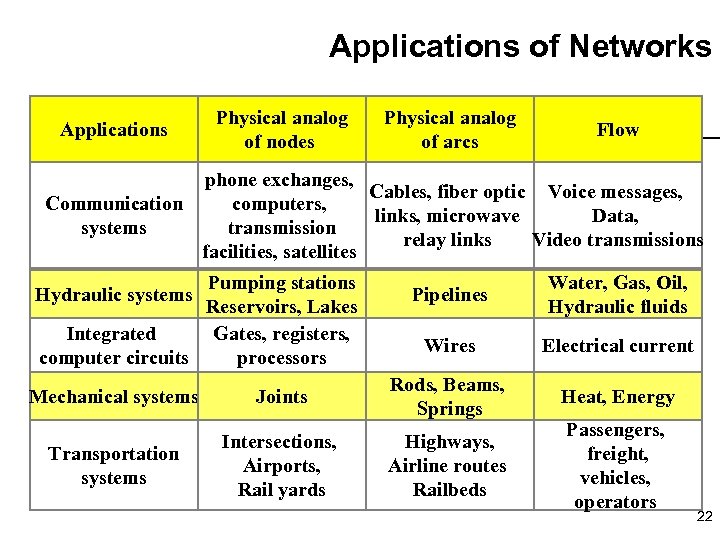 Applications of Networks Applications Physical analog of nodes Physical analog of arcs Flow phone exchanges, Cables, fiber optic Voice messages, Communication computers, links, microwave Data, systems transmission relay links Video transmissions facilities, satellites Pumping stations Reservoirs, Lakes Integrated Gates, registers, computer circuits processors Hydraulic systems Pipelines Water, Gas, Oil, Hydraulic fluids Wires Electrical current Heat, Energy Mechanical systems Joints Rods, Beams, Springs Transportation systems Intersections, Airports, Rail yards Highways, Airline routes Railbeds Passengers, freight, vehicles, operators 22
Applications of Networks Applications Physical analog of nodes Physical analog of arcs Flow phone exchanges, Cables, fiber optic Voice messages, Communication computers, links, microwave Data, systems transmission relay links Video transmissions facilities, satellites Pumping stations Reservoirs, Lakes Integrated Gates, registers, computer circuits processors Hydraulic systems Pipelines Water, Gas, Oil, Hydraulic fluids Wires Electrical current Heat, Energy Mechanical systems Joints Rods, Beams, Springs Transportation systems Intersections, Airports, Rail yards Highways, Airline routes Railbeds Passengers, freight, vehicles, operators 22
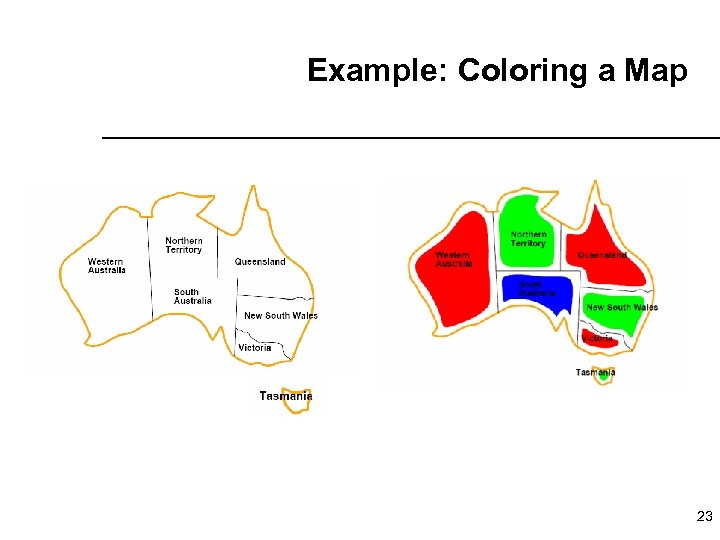 Example: Coloring a Map 23
Example: Coloring a Map 23
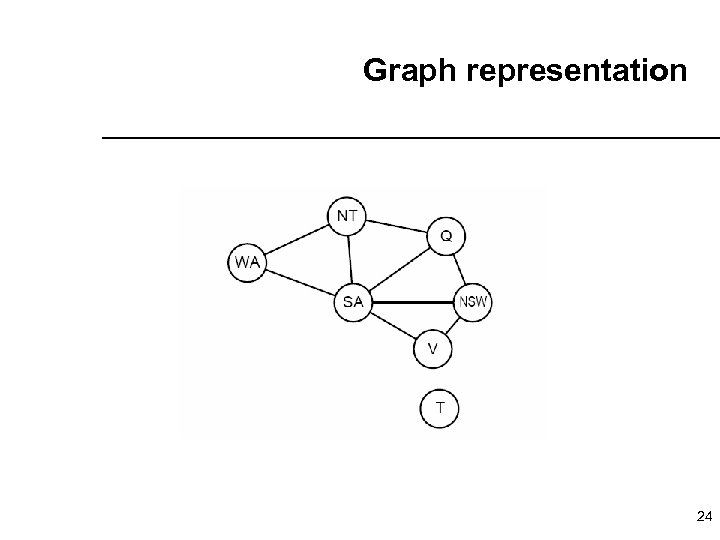 Graph representation 24
Graph representation 24
 Four Color Theorem 25
Four Color Theorem 25
 26
26
 Scheduling of Final Exams 27
Scheduling of Final Exams 27
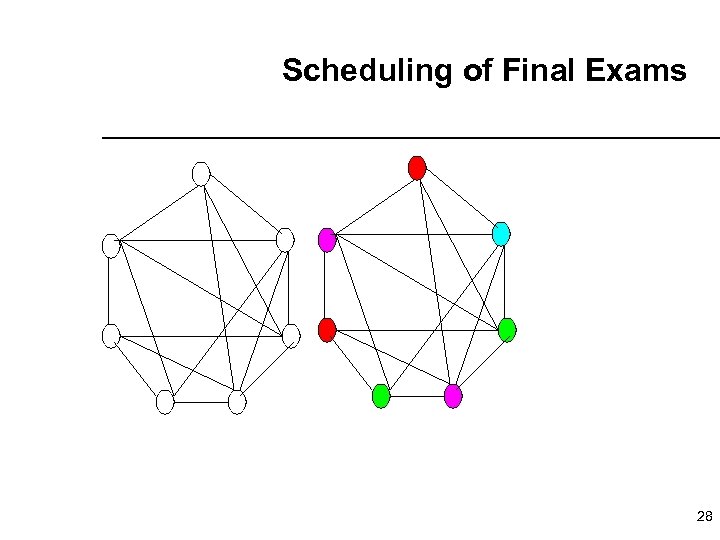 Scheduling of Final Exams 28
Scheduling of Final Exams 28
 Frequency Assignments 29
Frequency Assignments 29
 Index Registers 30
Index Registers 30
 Example 2: Traveling Salesman 31
Example 2: Traveling Salesman 31
 32
32
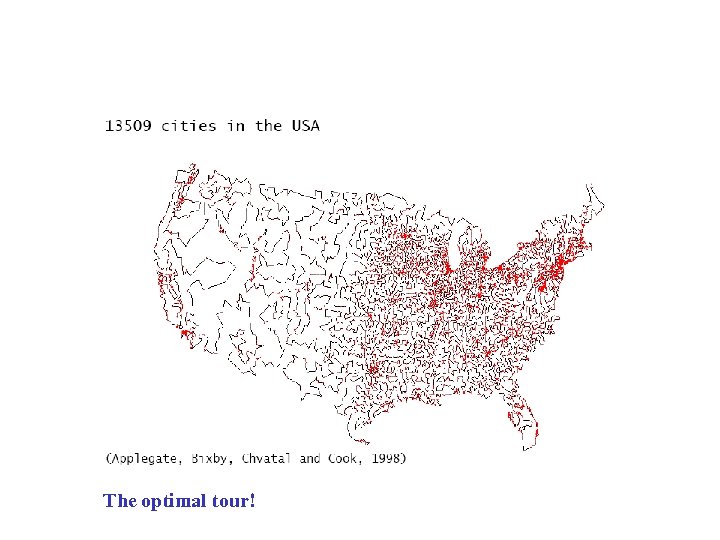 The optimal tour!
The optimal tour!
 Probability and Chance 34
Probability and Chance 34
 Probability: Bayesian Reasoning 35
Probability: Bayesian Reasoning 35
 Probability and Chance, cont. 36
Probability and Chance, cont. 36
 38
38
 Goals of CS 280
Goals of CS 280
 Topics CS 280
Topics CS 280
 Topics CS 280
Topics CS 280
 42
42