Kozlov_SM_5_11_10_16_environment.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 1 MODERN STRATEGIC ANALYSIS Theme 3. Process of Strategic Management AVK Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov 11/10/16 SPb. PU
1 MODERN STRATEGIC ANALYSIS Theme 3. Process of Strategic Management AVK Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov 11/10/16 SPb. PU
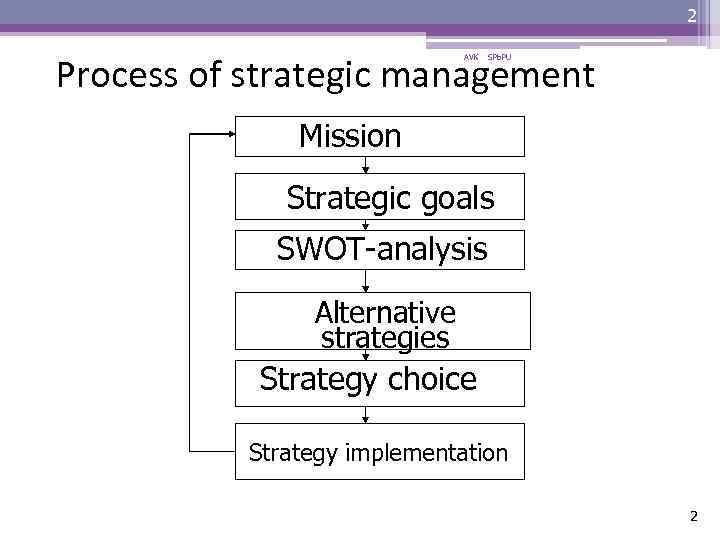 2 Process of strategic management AVK SPb. PU Mission Strategic goals SWOT-analysis Alternative strategies Strategy choice Strategy implementation 2
2 Process of strategic management AVK SPb. PU Mission Strategic goals SWOT-analysis Alternative strategies Strategy choice Strategy implementation 2
 3 AVK SPb. PU Strategic goals • Express more precisely the mission statement • Give standards of performance for the business • Give clear direction for development 3
3 AVK SPb. PU Strategic goals • Express more precisely the mission statement • Give standards of performance for the business • Give clear direction for development 3
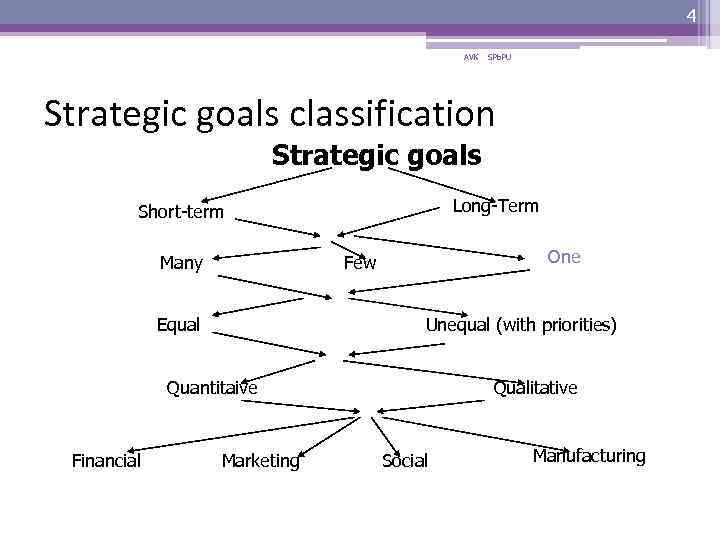 4 AVK SPb. PU Strategic goals classification Strategic goals Long-Term Short-term Many One Few Equal Unequal (with priorities) Quantitaive Financial Marketing Qualitative Social Manufacturing
4 AVK SPb. PU Strategic goals classification Strategic goals Long-Term Short-term Many One Few Equal Unequal (with priorities) Quantitaive Financial Marketing Qualitative Social Manufacturing
 5 AVK SMART model • Goals are to be ▫ Specific ▫ Measurable ▫ Achievable (Attainable) ▫ Realistic (Relevant) ▫ Time-Tabled (Time-bound) SPb. PU
5 AVK SMART model • Goals are to be ▫ Specific ▫ Measurable ▫ Achievable (Attainable) ▫ Realistic (Relevant) ▫ Time-Tabled (Time-bound) SPb. PU
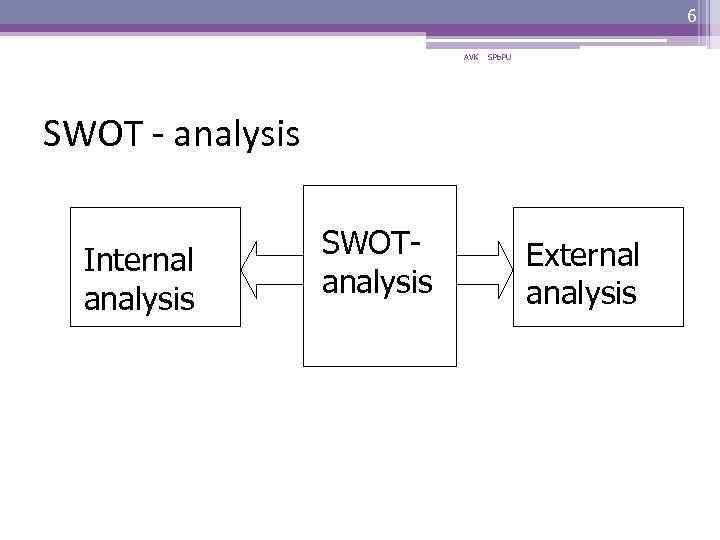 6 AVK SPb. PU SWOT - analysis Internal analysis SWOTanalysis External analysis
6 AVK SPb. PU SWOT - analysis Internal analysis SWOTanalysis External analysis
 7 External analysis AVK SPb. PU GETS model • Government (Taxation, Licensing, Subsidies, Budget and Non-Budget Funding) • Economy (Economic trends, currency stability, capital availability, prices for land premises rent. . . ) • Technology (depending on the industry) • Society (public sensitivity to the situation, price policy firstly, in this particular field, public institutions, mass-media attitude)
7 External analysis AVK SPb. PU GETS model • Government (Taxation, Licensing, Subsidies, Budget and Non-Budget Funding) • Economy (Economic trends, currency stability, capital availability, prices for land premises rent. . . ) • Technology (depending on the industry) • Society (public sensitivity to the situation, price policy firstly, in this particular field, public institutions, mass-media attitude)
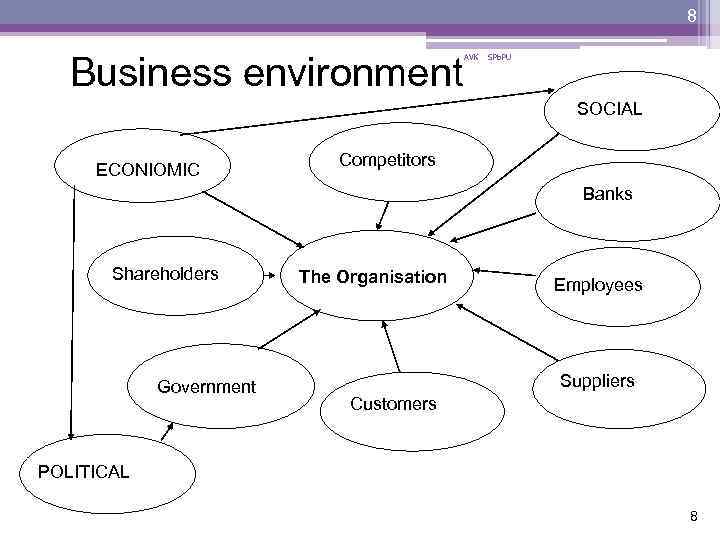 8 Business environment AVK SPb. PU SOCIAL ECONIOMIC Competitors Banks Shareholders Government The Organisation Employees Suppliers Customers POLITICAL 8
8 Business environment AVK SPb. PU SOCIAL ECONIOMIC Competitors Banks Shareholders Government The Organisation Employees Suppliers Customers POLITICAL 8
 9 Government AVK SPb. PU • Most dangerous pressure group for Russian business through ▫ Control inspections (tax insp. , fire insp. , sanitary insp. ) ▫ Custom service ▫ Licensing, and certification procedures ▫ Influence upon arbitrage ▫ Growing state order ▫ Reprivatisation of key industries 9
9 Government AVK SPb. PU • Most dangerous pressure group for Russian business through ▫ Control inspections (tax insp. , fire insp. , sanitary insp. ) ▫ Custom service ▫ Licensing, and certification procedures ▫ Influence upon arbitrage ▫ Growing state order ▫ Reprivatisation of key industries 9
 10 AVK SPb. PU Government • Taxation system ▫ Moderate level of tax rates Income tax – 13 % Corporate tax (on profit) - 24 % VAT - 18 % Social taxes (health, pension, unemployment, incident insurance) - 30 % 10
10 AVK SPb. PU Government • Taxation system ▫ Moderate level of tax rates Income tax – 13 % Corporate tax (on profit) - 24 % VAT - 18 % Social taxes (health, pension, unemployment, incident insurance) - 30 % 10
 11 Banks AVK SPb. PU Russian aspects • Small size (too many banks) before 1998 - app. 4000, now - app. 1000. • Loans for companies only for guarantee (real estate, goods in stock, equipment, stocks) • Low protection of Information • High Interest Rate -25 % in Rubles, 8 -12 % in USD) (20 • Risk of Bankruptcy (Crisis of year 1998, troubles of summer 2004, crisis of the 2008 -09 political situation of the year 2014/16 ) • State guarantee for deposits of individuals App. 20000 USD • Preferences for Quick Money in giving loans (not for industrial companies, mostly trade, currency exchange, stocks) 11
11 Banks AVK SPb. PU Russian aspects • Small size (too many banks) before 1998 - app. 4000, now - app. 1000. • Loans for companies only for guarantee (real estate, goods in stock, equipment, stocks) • Low protection of Information • High Interest Rate -25 % in Rubles, 8 -12 % in USD) (20 • Risk of Bankruptcy (Crisis of year 1998, troubles of summer 2004, crisis of the 2008 -09 political situation of the year 2014/16 ) • State guarantee for deposits of individuals App. 20000 USD • Preferences for Quick Money in giving loans (not for industrial companies, mostly trade, currency exchange, stocks) 11
 12 AVK SPb. PU Banks Russian aspects • Assets of the biggest Russian Banks (01/01/2015), bln USD • Sberbank – 366, 0 (477, 0 in 2014, 313, 7 in 2011) • VTB– 137, 1 (160, 0 in 2014, 96, 8 in 2011) • Gasprombank – 77, 4 (104, 8 in 2014, 64, 3 in 2011) • The # 1 in 2014 in the World • Industrial and Commercial Bank of China 3124, 0 • Total assets of Russian banking system – • less. 1000 bln USD • Assets of ING Group, (Netherlands), 26 th place in the world bank ranking – 1082, 0 bln USD 12
12 AVK SPb. PU Banks Russian aspects • Assets of the biggest Russian Banks (01/01/2015), bln USD • Sberbank – 366, 0 (477, 0 in 2014, 313, 7 in 2011) • VTB– 137, 1 (160, 0 in 2014, 96, 8 in 2011) • Gasprombank – 77, 4 (104, 8 in 2014, 64, 3 in 2011) • The # 1 in 2014 in the World • Industrial and Commercial Bank of China 3124, 0 • Total assets of Russian banking system – • less. 1000 bln USD • Assets of ING Group, (Netherlands), 26 th place in the world bank ranking – 1082, 0 bln USD 12
 13 AVK SPb. PU Banks Russian aspects • Domination of state banks ▫ (Sberbank, VTB) ≈ 50 % of total Russian banks assets ▫ Bank offices - Sberbank – 20 500, next Rosselhozbank – 1 400 • Foreign banks – app. 15 % of total Russian banks assets ▫ Scandinavian banks were active last three years (e. g. , Swedbank opened a branch of Hansabank, Sampobank bought local Profibank, SEB bought Petroenergobank) • Undeveloped System of Crediting for Individuals and Families 13
13 AVK SPb. PU Banks Russian aspects • Domination of state banks ▫ (Sberbank, VTB) ≈ 50 % of total Russian banks assets ▫ Bank offices - Sberbank – 20 500, next Rosselhozbank – 1 400 • Foreign banks – app. 15 % of total Russian banks assets ▫ Scandinavian banks were active last three years (e. g. , Swedbank opened a branch of Hansabank, Sampobank bought local Profibank, SEB bought Petroenergobank) • Undeveloped System of Crediting for Individuals and Families 13
 14 Competitors AVK SPb. PU Russian aspects • Risk of unfair competition (traditions, lack of business culture) • Competitors are enemies to be crashed, wiped out • Tendency to monopolise the market • State as a tool for pressure • Tendency to start price wars • Tendency to set up cartels 14
14 Competitors AVK SPb. PU Russian aspects • Risk of unfair competition (traditions, lack of business culture) • Competitors are enemies to be crashed, wiped out • Tendency to monopolise the market • State as a tool for pressure • Tendency to start price wars • Tendency to set up cartels 14
 15 AVK SPb. PU Customers Russian aspects • Low payment ability (lack of working capital) • Differentiation in Income through the Country Monthly income. (2016) • Russia app. 35000 Rbl • Moscow app. 70000 Rbl • St. Petersburg app. 45000 Rbl • Altaiskii krai app. 19000 • Dagestan app. 18000 • Kalmykia App. 19000 • Undeveloped Distribution Channels • Disbelief (skeptical attitude) in Advertising and trust to rumors 15
15 AVK SPb. PU Customers Russian aspects • Low payment ability (lack of working capital) • Differentiation in Income through the Country Monthly income. (2016) • Russia app. 35000 Rbl • Moscow app. 70000 Rbl • St. Petersburg app. 45000 Rbl • Altaiskii krai app. 19000 • Dagestan app. 18000 • Kalmykia App. 19000 • Undeveloped Distribution Channels • Disbelief (skeptical attitude) in Advertising and trust to rumors 15
 16 AVK SPb. PU Suppliers Russian aspects • Payment in advance • Import of materials and components (custom procedures, custom taxes, international payment transactions) • Undeveloped Information and Distribution Systems • Undeveloped Marketing System and inexperienced Marketing Staff • High tariffs for Transportation 16
16 AVK SPb. PU Suppliers Russian aspects • Payment in advance • Import of materials and components (custom procedures, custom taxes, international payment transactions) • Undeveloped Information and Distribution Systems • Undeveloped Marketing System and inexperienced Marketing Staff • High tariffs for Transportation 16
 17 AVK SPb. PU Specific features of St. Petersburg • Traditional specialisations: ▫ Machine building (shipbuilding, electro- and energy machine building, optics) ▫ Focus on Research&Development (10 % of intellectual potential of the whole Russia, 48 state universities, 250 research institutes, 170 000 scientists and researches) 17
17 AVK SPb. PU Specific features of St. Petersburg • Traditional specialisations: ▫ Machine building (shipbuilding, electro- and energy machine building, optics) ▫ Focus on Research&Development (10 % of intellectual potential of the whole Russia, 48 state universities, 250 research institutes, 170 000 scientists and researches) 17
 18 AVK SPb. PU Specific features of St. Petersburg • New clusters ▫ Cars production (Ford, Toyota, GM, Nissan Hyundai) ▫ Nanotechnologies ▫ Information Technologies 18
18 AVK SPb. PU Specific features of St. Petersburg • New clusters ▫ Cars production (Ford, Toyota, GM, Nissan Hyundai) ▫ Nanotechnologies ▫ Information Technologies 18
 19 AVK SPb. PU Modern strategic analysis PESTEL model The PESTEL framework categorises environmental influences into six main types: • Political, • Economic, • Social, • Technological, • Environmental, • Legal
19 AVK SPb. PU Modern strategic analysis PESTEL model The PESTEL framework categorises environmental influences into six main types: • Political, • Economic, • Social, • Technological, • Environmental, • Legal
 20 AVK SPb. PU Modern strategic analysis PESTEL model • Technological Factors: (new discoveries and technology developments, ICT innovations, rates of obsolescence, increased spending on R&D). • Environmental Factors: (Environmental protection regulations, energy consumption, global warming, waste disposal and re-cycling. • • Legal Factors: (competition laws, health and safety laws, employment laws, licensing laws, IPR laws)
20 AVK SPb. PU Modern strategic analysis PESTEL model • Technological Factors: (new discoveries and technology developments, ICT innovations, rates of obsolescence, increased spending on R&D). • Environmental Factors: (Environmental protection regulations, energy consumption, global warming, waste disposal and re-cycling. • • Legal Factors: (competition laws, health and safety laws, employment laws, licensing laws, IPR laws)
 21 AVK SPb. PU PESTEL model usage • Apply selectively –identify specific factors which impact on the industry, market and organisation in question. • Identify factors which are important currently but also consider which will become more important in the next few years. • Use data to support the points and analyse trends using up to date information • Identify opportunities and threats – the main point of the analysis!
21 AVK SPb. PU PESTEL model usage • Apply selectively –identify specific factors which impact on the industry, market and organisation in question. • Identify factors which are important currently but also consider which will become more important in the next few years. • Use data to support the points and analyse trends using up to date information • Identify opportunities and threats – the main point of the analysis!
 22 AVK SPb. PU PESTEL model usage (Scenarios) • Scenarios are detailed and plausible views of how the environment of an organisation might develop in the future based on key drivers of change about which there is a high level of uncertainty. • Build on PESTEL analysis • Do not offer a single forecast of how the environment will change. • An organisation should develop a few alternative scenarios (2– 4) to analyse future strategic options.
22 AVK SPb. PU PESTEL model usage (Scenarios) • Scenarios are detailed and plausible views of how the environment of an organisation might develop in the future based on key drivers of change about which there is a high level of uncertainty. • Build on PESTEL analysis • Do not offer a single forecast of how the environment will change. • An organisation should develop a few alternative scenarios (2– 4) to analyse future strategic options.
 23 AVK SPb. PU PESTEL model usage (Scenarios) • Develop scenario ‘stories’ - That is, coherent and plausible descriptions of the environment that result from opposing outcomes • Identify the impact of each scenario on the organisation and evaluate future strategies in the light of the anticipated scenarios. • Scenario analysis is used in industries with long planning horizons for example, the oil industry or airlines. • .
23 AVK SPb. PU PESTEL model usage (Scenarios) • Develop scenario ‘stories’ - That is, coherent and plausible descriptions of the environment that result from opposing outcomes • Identify the impact of each scenario on the organisation and evaluate future strategies in the light of the anticipated scenarios. • Scenario analysis is used in industries with long planning horizons for example, the oil industry or airlines. • .
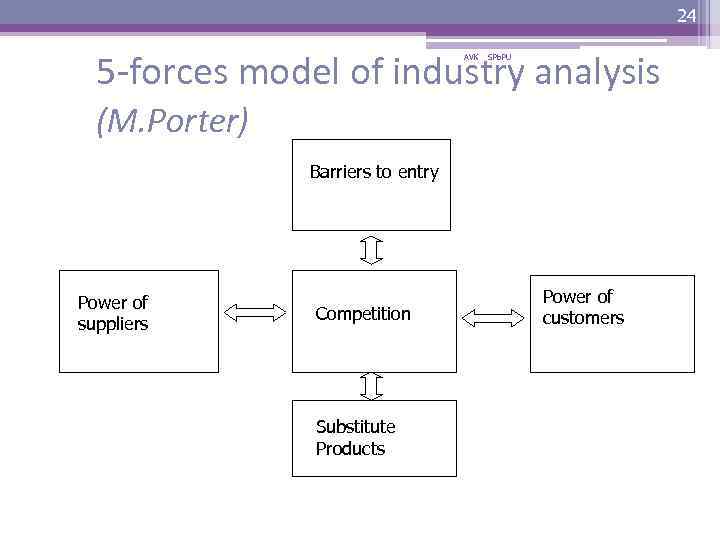 24 5 -forces model of industry analysis AVK SPb. PU (M. Porter) Barriers to entry Power of suppliers Competition Substitute Products Power of customers
24 5 -forces model of industry analysis AVK SPb. PU (M. Porter) Barriers to entry Power of suppliers Competition Substitute Products Power of customers
 25 Industries, markets and sectors AVK SPb. PU • An industry is a group of firms producing products and services that are essentially the same. For example, automobile industry and airline industry. • A market is a group of customers for specific products or services that are essentially the same (e. g. the market for luxury cars in Germany). • A sector is a broad industry group (or a group of markets) especially in the public sector (e. g. the health sector)
25 Industries, markets and sectors AVK SPb. PU • An industry is a group of firms producing products and services that are essentially the same. For example, automobile industry and airline industry. • A market is a group of customers for specific products or services that are essentially the same (e. g. the market for luxury cars in Germany). • A sector is a broad industry group (or a group of markets) especially in the public sector (e. g. the health sector)
 26 AVK SPb. PU The bargaining power of customers Customers are powerful if Purchase large proportion of company sales Company products are standard/ undifferentiated Earn low profits Have low switching costs Have full market information (costs, profits, . . . ) Company product unimportant to quality of customers product • Have a capability to backward integration • • •
26 AVK SPb. PU The bargaining power of customers Customers are powerful if Purchase large proportion of company sales Company products are standard/ undifferentiated Earn low profits Have low switching costs Have full market information (costs, profits, . . . ) Company product unimportant to quality of customers product • Have a capability to backward integration • • •
 27 AVK SPb. PU The bargaining power of suppliers Suppliers are powerful if • Dominated by a few companies and concentrated than industry selling to • No available substitutes • Switching costs are high (it is disruptive or expensive to change suppliers) • Company is not important customer of supplier • Suppliers products are important of buyers business • Company product unimportant to quality of customers product • Suppliers have a capability to forward integration
27 AVK SPb. PU The bargaining power of suppliers Suppliers are powerful if • Dominated by a few companies and concentrated than industry selling to • No available substitutes • Switching costs are high (it is disruptive or expensive to change suppliers) • Company is not important customer of supplier • Suppliers products are important of buyers business • Company product unimportant to quality of customers product • Suppliers have a capability to forward integration
 28 AVK SPb. PU The extent of rivalry between competitors • Many competitors are of roughly equal size • Competitors are aggressive in seeking leadership • Slow growth (The market is mature or declining) • High fixed costs • Weak differentiation • High barriers to exit
28 AVK SPb. PU The extent of rivalry between competitors • Many competitors are of roughly equal size • Competitors are aggressive in seeking leadership • Slow growth (The market is mature or declining) • High fixed costs • Weak differentiation • High barriers to exit
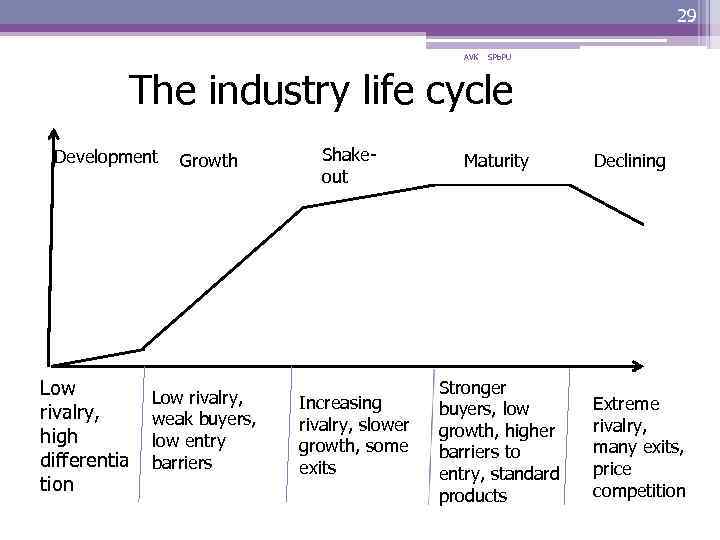 29 AVK SPb. PU The industry life cycle Development Low rivalry, high differentia tion Growth Low rivalry, weak buyers, low entry barriers Shakeout Increasing rivalry, slower growth, some exits Maturity Stronger buyers, low growth, higher barriers to entry, standard products Declining Extreme rivalry, many exits, price competition
29 AVK SPb. PU The industry life cycle Development Low rivalry, high differentia tion Growth Low rivalry, weak buyers, low entry barriers Shakeout Increasing rivalry, slower growth, some exits Maturity Stronger buyers, low growth, higher barriers to entry, standard products Declining Extreme rivalry, many exits, price competition
 30 AVK SPb. PU The Threat of Entry & Barriers to Entry The threat of entry is low when the barriers to entry are high and vice versa. • The main barriers to entry are: ▫ Economies of scale/high fixed costs ▫ Experience and learning ▫ Access to supply and distribution channels ▫ Differentiation and market penetration costs ▫ Government restrictions (e. g. licensing) ▫ Entrants must also consider the expected reaction from organisations already in the market
30 AVK SPb. PU The Threat of Entry & Barriers to Entry The threat of entry is low when the barriers to entry are high and vice versa. • The main barriers to entry are: ▫ Economies of scale/high fixed costs ▫ Experience and learning ▫ Access to supply and distribution channels ▫ Differentiation and market penetration costs ▫ Government restrictions (e. g. licensing) ▫ Entrants must also consider the expected reaction from organisations already in the market
 31 Threat of substitute products AVK SPb. PU • Substitutes limit upper profitability levels of industry • Substitutes may be difficult to identify and hence keep out • Substitutes are most likely to succeed when ▫ Industry prices are going up ▫ Industry is making high profit
31 Threat of substitute products AVK SPb. PU • Substitutes limit upper profitability levels of industry • Substitutes may be difficult to identify and hence keep out • Substitutes are most likely to succeed when ▫ Industry prices are going up ▫ Industry is making high profit


