1 Market Equilibrium Topic 3 Source: masterminds.
























- Размер: 933.5 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 30
Описание презентации 1 Market Equilibrium Topic 3 Source: masterminds. по слайдам
 1 Market Equilibrium Topic
1 Market Equilibrium Topic
 Source: masterminds. pl 21 acre of land on the moon
Source: masterminds. pl 21 acre of land on the moon
 Source: mariusztravel. com; gazetaprawna. pl; chip. pl; al legro. pl 3 Less sophisticated markets…
Source: mariusztravel. com; gazetaprawna. pl; chip. pl; al legro. pl 3 Less sophisticated markets…
 4 Market – definition MARKET = arrangement through which buyers and sellers meet or communicate in order to trade goods or services.
4 Market – definition MARKET = arrangement through which buyers and sellers meet or communicate in order to trade goods or services.
 5 Market Equilibrium: definition Market equilibrium prevails when quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. . There is no shortage or surplus (market is cleared). Everyone who wants to buy the good will find it available and everyone who wants to sell the good will be able to do so successfully. There is no tendency for the market price or quantity to change. .
5 Market Equilibrium: definition Market equilibrium prevails when quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. . There is no shortage or surplus (market is cleared). Everyone who wants to buy the good will find it available and everyone who wants to sell the good will be able to do so successfully. There is no tendency for the market price or quantity to change. .
 6 Equilibrium Price and Equilibrium Quantity Equilibrium price (( market-clearing price ): price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Equilibrium quantity : quantity traded at equilibrium price.
6 Equilibrium Price and Equilibrium Quantity Equilibrium price (( market-clearing price ): price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Equilibrium quantity : quantity traded at equilibrium price.
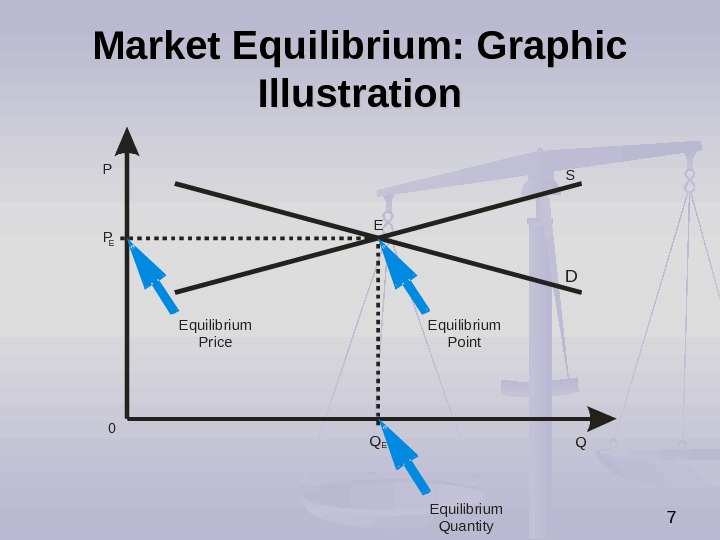
 7 Market Equilibrium: Graphic Illustration P QEquilibrium Point. Equilibrium Price Equilibrium Quantity S DP E 0 Q
7 Market Equilibrium: Graphic Illustration P QEquilibrium Point. Equilibrium Price Equilibrium Quantity S DP E 0 Q
 8 Market Disequilibrium: Surplus P QActual price is higher than PE Actual volume of sales S DPP EH 0 Q E Q HSE HDQ Surplus A A surplus exists when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. Surplus prevails when actual price of the good is higher than equilibrium price. .
8 Market Disequilibrium: Surplus P QActual price is higher than PE Actual volume of sales S DPP EH 0 Q E Q HSE HDQ Surplus A A surplus exists when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. Surplus prevails when actual price of the good is higher than equilibrium price. .
 9 Market Disequilibrium: Shortage A A shortage exists when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. Shortage prevails when actual price of the good is lower than equilibrium price. . P QActual price is lower than PE Actual volume of sales S DP P E L 0 Q E Q LDE LSQ Shortage
9 Market Disequilibrium: Shortage A A shortage exists when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. Shortage prevails when actual price of the good is lower than equilibrium price. . P QActual price is lower than PE Actual volume of sales S DP P E L 0 Q E Q LDE LSQ Shortage
 10 Self-Equilibrating Markets: Invisible Hand When there is disequilibrium in a market, competition among buyers for goods, and among sellers for sales, will set up forces that cause the price to change and reach equilibrium. There is no need to regulate the market. Market is a self-regulating mechanism. The force behind the mechanism is called „„ invisible hand of the market ””. .
10 Self-Equilibrating Markets: Invisible Hand When there is disequilibrium in a market, competition among buyers for goods, and among sellers for sales, will set up forces that cause the price to change and reach equilibrium. There is no need to regulate the market. Market is a self-regulating mechanism. The force behind the mechanism is called „„ invisible hand of the market ””. .
 11 Invisible Hand under Surplus Conditions P QS DPP EH 0 Q E Q HSE HDQ Surplus Down ward pressure on price Surplus means that some goods brought to the market will go unsold. Sellers will accept lower prices rather than allow their supply to spoil („sell it or smell it”). They will also strive to avoid the costs of maintaining inventory or transporting goods back to the point of production. A surplus results in downward pressure on market price. .
11 Invisible Hand under Surplus Conditions P QS DPP EH 0 Q E Q HSE HDQ Surplus Down ward pressure on price Surplus means that some goods brought to the market will go unsold. Sellers will accept lower prices rather than allow their supply to spoil („sell it or smell it”). They will also strive to avoid the costs of maintaining inventory or transporting goods back to the point of production. A surplus results in downward pressure on market price. .
 12 Invisible Hand under Shortage Conditions P QS DP P E L 0 Q E Q LDE LSQ Shortage Upward pressure on price Shortage means that some buyers willing and able to pay the market price of a good will find it unavailable. Some consumers will be willing to pay more than actual price rather than go without the good. Shortage results in upward pressure on market price. .
12 Invisible Hand under Shortage Conditions P QS DP P E L 0 Q E Q LDE LSQ Shortage Upward pressure on price Shortage means that some buyers willing and able to pay the market price of a good will find it unavailable. Some consumers will be willing to pay more than actual price rather than go without the good. Shortage results in upward pressure on market price. .
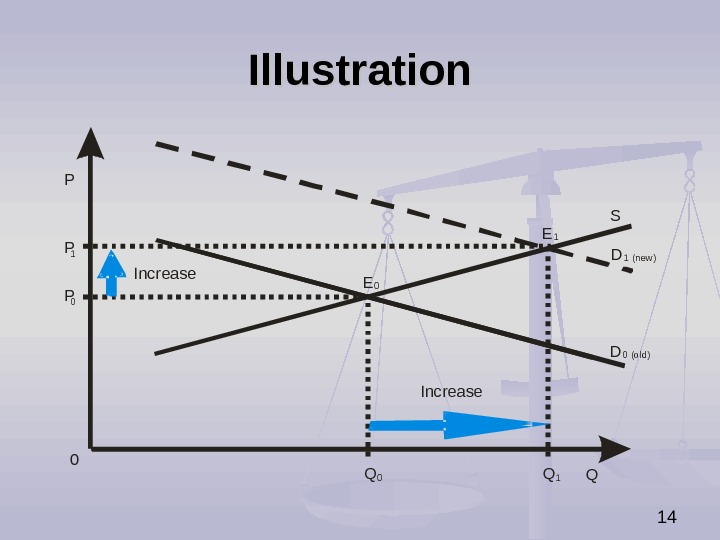
 13 The Impact of Increase in Demand on Market Equilibrium Increase in demand causes (ceteris paribus): increase in equilibrium price, increase in equilibrium quantity.
13 The Impact of Increase in Demand on Market Equilibrium Increase in demand causes (ceteris paribus): increase in equilibrium price, increase in equilibrium quantity.
 14 Illustration. P Q S D D P P 01 0 Q 0 Q 1 E E Increase 1 0 0 (old) 1 (new )
14 Illustration. P Q S D D P P 01 0 Q 0 Q 1 E E Increase 1 0 0 (old) 1 (new )
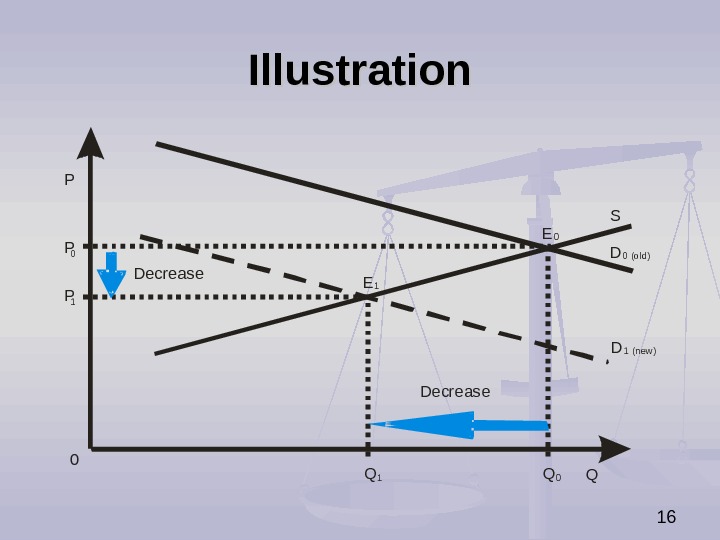
 15 The Impact of Decrease in Demand on Market Equilibrium Decrease in demand causes (ceteris paribus): decrease in equilibrium price, decrease in equilibrium quantity.
15 The Impact of Decrease in Demand on Market Equilibrium Decrease in demand causes (ceteris paribus): decrease in equilibrium price, decrease in equilibrium quantity.
 16 Illustration. P Q S D D P P 10 0 Q 1 Q 0 E E Decrease 0 1 0 (old) 1 (new )
16 Illustration. P Q S D D P P 10 0 Q 1 Q 0 E E Decrease 0 1 0 (old) 1 (new )
 17 The Impact of Increase in Supply on Market Equilibrium Increase in supply causes (ceteris paribus): decrease in equilibrium price, increase in equilibrium quantity.
17 The Impact of Increase in Supply on Market Equilibrium Increase in supply causes (ceteris paribus): decrease in equilibrium price, increase in equilibrium quantity.
 18 Illustration P Q SS DPP 10 0 Q 1 Q 0 EE Decrease Increase 0 1 1 (new )0 (old)
18 Illustration P Q SS DPP 10 0 Q 1 Q 0 EE Decrease Increase 0 1 1 (new )0 (old)
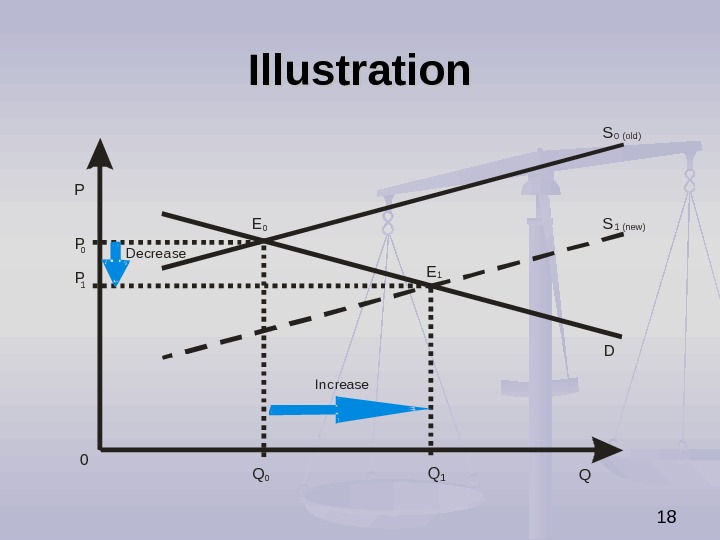
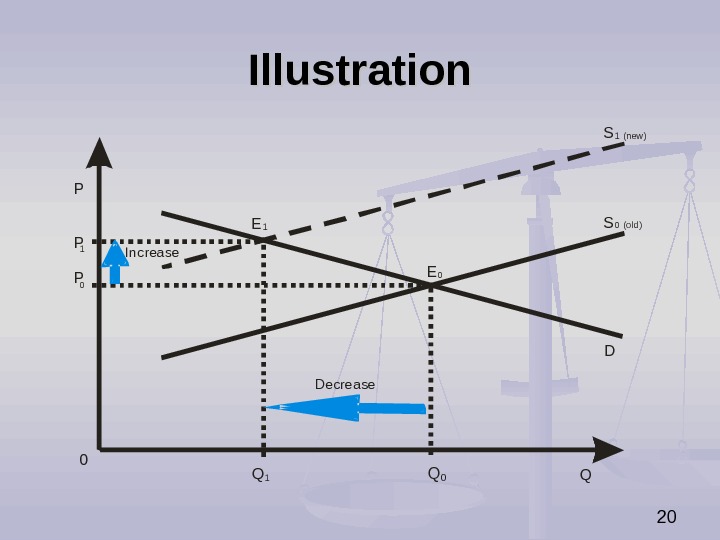
 19 The Impact of Decrease in Supply on Market Equilibrium Decrease in supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase in equilibrium price, decrease in equilibrium quantity.
19 The Impact of Decrease in Supply on Market Equilibrium Decrease in supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase in equilibrium price, decrease in equilibrium quantity.
 20 Illustration P Q S DPP 01 0 Q 0 Q 1 EE Increase Decrease 1 0 1 (new ) S 0 (old)
20 Illustration P Q S DPP 01 0 Q 0 Q 1 EE Increase Decrease 1 0 1 (new ) S 0 (old)
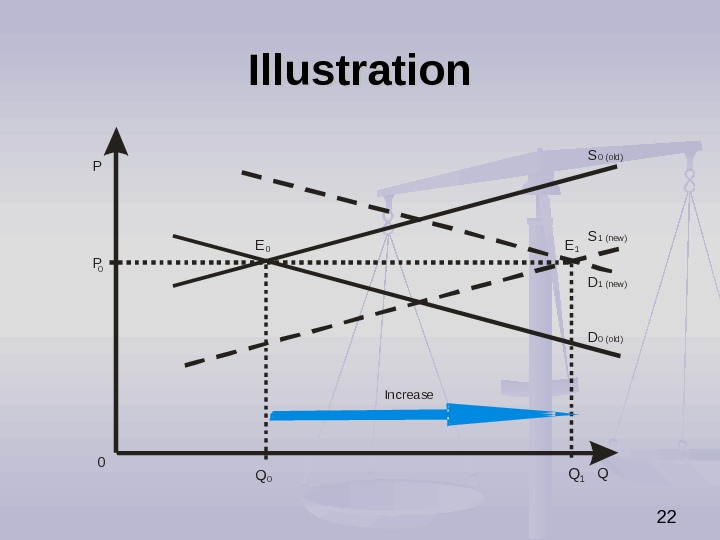
 21 The Impact of Simultaneous Increase in Demand Supply Simultaneous increase in demand and supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase or decrease in equilibrium price (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors), increase in equilibrium quantity.
21 The Impact of Simultaneous Increase in Demand Supply Simultaneous increase in demand and supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase or decrease in equilibrium price (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors), increase in equilibrium quantity.
 22 Illustration P QS DP 0 0 Q 1 Q 0 E E Increase 0 1 1 (new )S D 0 (old)
22 Illustration P QS DP 0 0 Q 1 Q 0 E E Increase 0 1 1 (new )S D 0 (old)
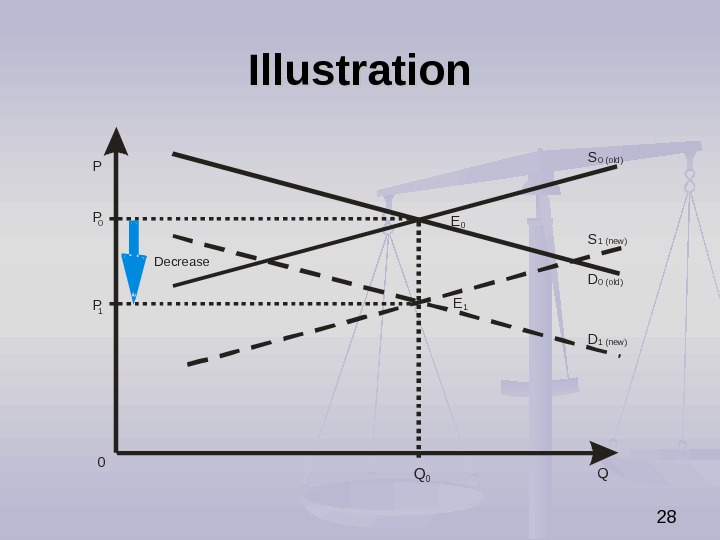
 23 The Impact of Simultaneous Decrease in Demand Supply Simultaneous decrease in demand and supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase or decrease in equilibrium price (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors), decrease in equilibrium quantity.
23 The Impact of Simultaneous Decrease in Demand Supply Simultaneous decrease in demand and supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase or decrease in equilibrium price (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors), decrease in equilibrium quantity.
 24 Illustration P QS DP 0 0 Q 0 Q 1 E E De crea se 1 0 0 (old) 1 (new )S D 1 (new ) 0 (old)
24 Illustration P QS DP 0 0 Q 0 Q 1 E E De crea se 1 0 0 (old) 1 (new )S D 1 (new ) 0 (old)
 25 The Impact of Simultaneous Increase in Demand Decrease in Supply Simultaneous increase in demand and decrease in supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase in equilibrium price, increase or decrease in equilibrium quantity (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors).
25 The Impact of Simultaneous Increase in Demand Decrease in Supply Simultaneous increase in demand and decrease in supply causes (ceteris paribus): increase in equilibrium price, increase or decrease in equilibrium quantity (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors).
 26 Illustration P QS D PP 01 0 Q 0 E E Increa se 1 0 0 (old) 1 (new )S D 1 (new ) 0 (old)
26 Illustration P QS D PP 01 0 Q 0 E E Increa se 1 0 0 (old) 1 (new )S D 1 (new ) 0 (old)
 27 The Impact of Simultaneous Decrease in Demand Increase in Supply Simultaneous decrease in demand and increase in supply causes (ceteris paribus): decrease in equilibrium price, increase or decrease in equilibrium quantity (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors).
27 The Impact of Simultaneous Decrease in Demand Increase in Supply Simultaneous decrease in demand and increase in supply causes (ceteris paribus): decrease in equilibrium price, increase or decrease in equilibrium quantity (it depends on relative strenghts of these two factors).
 28 Illustration P QS DPP 10 0 Q 0 E E Decre ase 0 1 0 (old) 1 (new )S D 1 (new ) 0 (old)
28 Illustration P QS DPP 10 0 Q 0 E E Decre ase 0 1 0 (old) 1 (new )S D 1 (new ) 0 (old)
 29 Government Regulations in the Market: Floor Prices. P Q S D P PEFLO OR 0 Q EP S ED P Su rplus Floor price : a minimum price established by law. Floor prices are introduced to protect sellers’ interest. Floor price is higher than equilibrium price.
29 Government Regulations in the Market: Floor Prices. P Q S D P PEFLO OR 0 Q EP S ED P Su rplus Floor price : a minimum price established by law. Floor prices are introduced to protect sellers’ interest. Floor price is higher than equilibrium price.
 30 Government Regulations in the Market: Ceiling Prices P QS DP E P CEILING 0 Q E Q DE SQ Shortage Ceiling price : : a maximum price established by law. Floor prices are introduced to protect buyers’ interest. Floor price is lower than equilibrium price.
30 Government Regulations in the Market: Ceiling Prices P QS DP E P CEILING 0 Q E Q DE SQ Shortage Ceiling price : : a maximum price established by law. Floor prices are introduced to protect buyers’ interest. Floor price is lower than equilibrium price.

