 • • • 1. Major function of Congress – legislative powers • makes laws = bills = public policy • • 2. Great Compromise a Bicameral Congress--- • Why? • 3. Term and Sessions of Congress • – Congressional elections 4. House of Representatives Qualifications Size Representation Elections and term Congressional districts Apportionment = distributing seats – every state guaranteed 1 seat 1929, Reapportionment Act = redistributing seats – Census Bureau – Congressional districts = Single member districts – Redrawing Districts • Gerrymandering Exclusive Powers of the House 5. Senate Qualifications Size Elections and terms Exclusive Powers of the Senate • 6. Membership in Congress • 7. Responsibilities of Congressmen • Constituents • Compensation and benefits • Legislative immunity
• • • 1. Major function of Congress – legislative powers • makes laws = bills = public policy • • 2. Great Compromise a Bicameral Congress--- • Why? • 3. Term and Sessions of Congress • – Congressional elections 4. House of Representatives Qualifications Size Representation Elections and term Congressional districts Apportionment = distributing seats – every state guaranteed 1 seat 1929, Reapportionment Act = redistributing seats – Census Bureau – Congressional districts = Single member districts – Redrawing Districts • Gerrymandering Exclusive Powers of the House 5. Senate Qualifications Size Elections and terms Exclusive Powers of the Senate • 6. Membership in Congress • 7. Responsibilities of Congressmen • Constituents • Compensation and benefits • Legislative immunity
 Article One U. S. Constitution creates the Legislative Branch of our national government (that’s Congress, folks!)
Article One U. S. Constitution creates the Legislative Branch of our national government (that’s Congress, folks!)
 ARTICLE ONE Section 1 ---All legislative powers -(the power to propose laws or bills) herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
ARTICLE ONE Section 1 ---All legislative powers -(the power to propose laws or bills) herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
 Congress proposes laws. . . Other terms which mean the same • legislative powers = power to propose law • legislation = a proposed law • legislature = another name for Congress • Enact legislation = Congress passed a proposed law It becomes a law when both Houses of Congress passes the bill and it is sent to the President and he signs it or executes or enforces the law.
Congress proposes laws. . . Other terms which mean the same • legislative powers = power to propose law • legislation = a proposed law • legislature = another name for Congress • Enact legislation = Congress passed a proposed law It becomes a law when both Houses of Congress passes the bill and it is sent to the President and he signs it or executes or enforces the law.
 Congress makes laws for the nation, but it cannot. . . • make laws for the states • deny citizens legal rights • deny citizens civil rights & civil liberties guaranteed by the Bill of Rights
Congress makes laws for the nation, but it cannot. . . • make laws for the states • deny citizens legal rights • deny citizens civil rights & civil liberties guaranteed by the Bill of Rights
 Also, the legislative functions of Congress are based on the specific delegated or expressed powers. This means they are listed in the U. S. 6
Also, the legislative functions of Congress are based on the specific delegated or expressed powers. This means they are listed in the U. S. 6
 Art 1 ARTICLE ONE • Section 2 & 3 ---Qualifications for Congress • Section 4 ---Elections and Meetings • Section 5 ---Rules of Order • Section 6 ---Pay Privileges • Section 7 ---How Bills Become Laws • Section 8 ---Powers of Congress Clauses 1 - 17 • Section 9 ---Powers Denied to
Art 1 ARTICLE ONE • Section 2 & 3 ---Qualifications for Congress • Section 4 ---Elections and Meetings • Section 5 ---Rules of Order • Section 6 ---Pay Privileges • Section 7 ---How Bills Become Laws • Section 8 ---Powers of Congress Clauses 1 - 17 • Section 9 ---Powers Denied to
 Taxation Education Health care Environment Working conditions National Security Commerce/Trade Military Crime Transportation Civil rights General welfare Economics Regulate industry
Taxation Education Health care Environment Working conditions National Security Commerce/Trade Military Crime Transportation Civil rights General welfare Economics Regulate industry
 A Bicameral Congress At the Constitutional Convention in 1787, the Founding Fathers created a bicameral (2 houses) legislature for 3 reasons Historical: The British Parliament consisted of Historical two houses since the 1300 s, and many colonial assemblies were similar in form. Practical: A bicameral legislature was necessary to compromise the Virginia and New Jersey plans of representation. Theoretical: The Framers favored a bicameral Congress in order that one house might act as
A Bicameral Congress At the Constitutional Convention in 1787, the Founding Fathers created a bicameral (2 houses) legislature for 3 reasons Historical: The British Parliament consisted of Historical two houses since the 1300 s, and many colonial assemblies were similar in form. Practical: A bicameral legislature was necessary to compromise the Virginia and New Jersey plans of representation. Theoretical: The Framers favored a bicameral Congress in order that one house might act as
 • Great Compromise created a bicameral Congress. • Representative Democracy • Check and Balance CONGRESS HOUSE OF REPESENTATIVES • Elected by the people • Representatives based on population per state…. . • More population the more representatives you have • 2 year term • Satisfied larger states SENATE • Elected by each state’s congress • Equal representatives • 2 representatives per state • 6 year term • Satisfied smaller states
• Great Compromise created a bicameral Congress. • Representative Democracy • Check and Balance CONGRESS HOUSE OF REPESENTATIVES • Elected by the people • Representatives based on population per state…. . • More population the more representatives you have • 2 year term • Satisfied larger states SENATE • Elected by each state’s congress • Equal representatives • 2 representatives per state • 6 year term • Satisfied smaller states
 HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • 25 years of age SENATE • 30 years of age • U. S. Citizen at least 7 years • U. S. Citizen at least 9 years • Resident of state and district elected from. • Resident of state elected from. • Informal? ? ? CONSTITUTIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • 25 years of age SENATE • 30 years of age • U. S. Citizen at least 7 years • U. S. Citizen at least 9 years • Resident of state and district elected from. • Resident of state elected from. • Informal? ? ? CONSTITUTIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
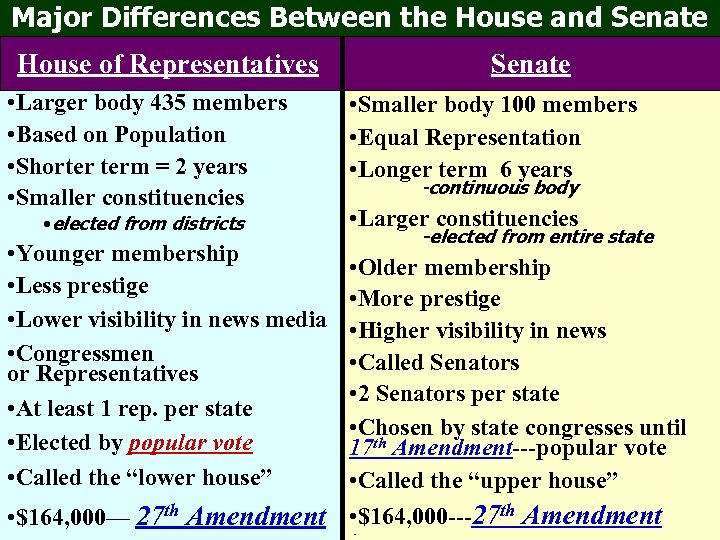 Major Differences Between the House and Senate House of Representatives • Larger body 435 members • Based on Population • Shorter term = 2 years • Smaller constituencies • elected from districts Senate • Smaller body 100 members • Equal Representation • Longer term 6 years -continuous body • Larger constituencies -elected from entire state • Younger membership • Less prestige • Lower visibility in news media • Congressmen or Representatives • At least 1 rep. per state • Elected by popular vote • Called the “lower house” • Older membership • More prestige • Higher visibility in news • Called Senators • 2 Senators per state • Chosen by state congresses until 17 th Amendment---popular vote • Called the “upper house” • $164, 000— 27 th Amendment • $164, 000 ---27 th Amendment differences
Major Differences Between the House and Senate House of Representatives • Larger body 435 members • Based on Population • Shorter term = 2 years • Smaller constituencies • elected from districts Senate • Smaller body 100 members • Equal Representation • Longer term 6 years -continuous body • Larger constituencies -elected from entire state • Younger membership • Less prestige • Lower visibility in news media • Congressmen or Representatives • At least 1 rep. per state • Elected by popular vote • Called the “lower house” • Older membership • More prestige • Higher visibility in news • Called Senators • 2 Senators per state • Chosen by state congresses until 17 th Amendment---popular vote • Called the “upper house” • $164, 000— 27 th Amendment • $164, 000 ---27 th Amendment differences
 The realities of politics require some informal qualifications to become a Congressmen vparty identification vname familiarity v. Gender vethnic characteristics vpolitical experience v. Education v. Family life v. Morality
The realities of politics require some informal qualifications to become a Congressmen vparty identification vname familiarity v. Gender vethnic characteristics vpolitical experience v. Education v. Family life v. Morality
 Profile of the U. $. Congre$$ college grad$ lawyer$ White Male Prote$tant in their fiftie$ $ub$tantially wealthier
Profile of the U. $. Congre$$ college grad$ lawyer$ White Male Prote$tant in their fiftie$ $ub$tantially wealthier
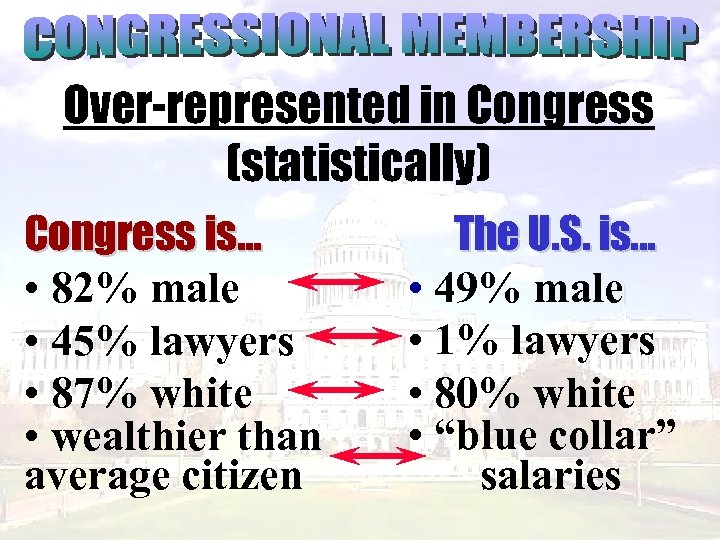 Over-represented in Congress (statistically) Congress is. . . • 82% male • 45% lawyers • 87% white • wealthier than average citizen The U. S. is. . . • 49% male • 1% lawyers • 80% white • “blue collar” salaries
Over-represented in Congress (statistically) Congress is. . . • 82% male • 45% lawyers • 87% white • wealthier than average citizen The U. S. is. . . • 49% male • 1% lawyers • 80% white • “blue collar” salaries
 Ø A term of Congress lasts for 2 years which includes 2 sessions. Currently, sessions Congress just began the 1 st Session of the 113 th term Ø The first term of Congress began on th, 1789 and ended two years March 4 later on March 4 th, 1791
Ø A term of Congress lasts for 2 years which includes 2 sessions. Currently, sessions Congress just began the 1 st Session of the 113 th term Ø The first term of Congress began on th, 1789 and ended two years March 4 later on March 4 th, 1791
 th Amendment 20 Changed the date Congress convenes after elections, from March 4 th to January 3 rd, in oddnumbered years I’m was just a lame duck!
th Amendment 20 Changed the date Congress convenes after elections, from March 4 th to January 3 rd, in oddnumbered years I’m was just a lame duck!
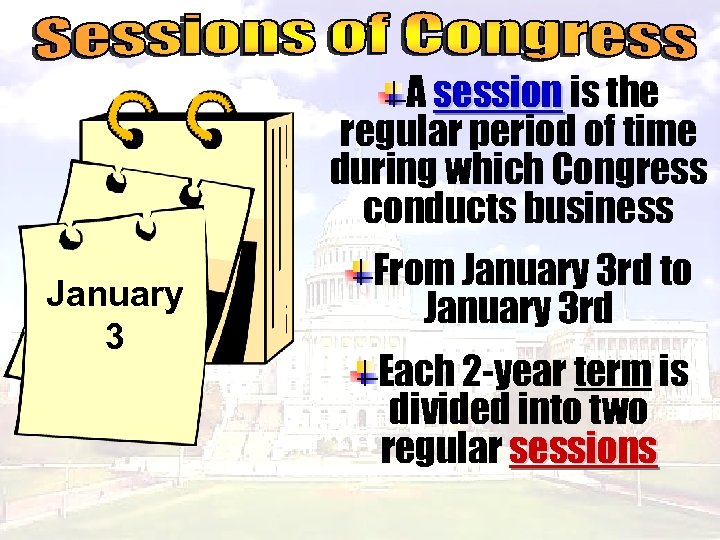 A session is the regular period of time during which Congress conducts business January 3 From January 3 rd to January 3 rd Each 2 -year term is divided into two regular sessions
A session is the regular period of time during which Congress conducts business January 3 From January 3 rd to January 3 rd Each 2 -year term is divided into two regular sessions
 Congress adjourns, or suspends adjourns until the next session, each regular session as it sees fit. If necessary, the President has the power to prorogue, or adjourn, a adjourn session, but only when the two houses cannot agree on a date for adjournment. Only the President may call Congress into a special session —a meeting to deal with some
Congress adjourns, or suspends adjourns until the next session, each regular session as it sees fit. If necessary, the President has the power to prorogue, or adjourn, a adjourn session, but only when the two houses cannot agree on a date for adjournment. Only the President may call Congress into a special session —a meeting to deal with some
 v. Congress is an elected assembly. November in 2008 v. Congressional elections are held on the Tuesday following the first Monday in November of each evennumbered year
v. Congress is an elected assembly. November in 2008 v. Congressional elections are held on the Tuesday following the first Monday in November of each evennumbered year
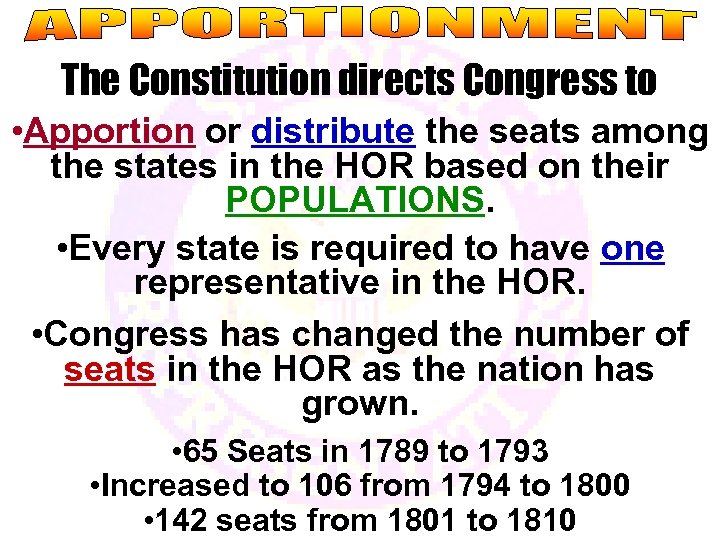 The Constitution directs Congress to • Apportion or distribute the seats among the states in the HOR based on their POPULATIONS. • Every state is required to have one representative in the HOR. • Congress has changed the number of seats in the HOR as the nation has grown. • 65 Seats in 1789 to 1793 • Increased to 106 from 1794 to 1800 • 142 seats from 1801 to 1810
The Constitution directs Congress to • Apportion or distribute the seats among the states in the HOR based on their POPULATIONS. • Every state is required to have one representative in the HOR. • Congress has changed the number of seats in the HOR as the nation has grown. • 65 Seats in 1789 to 1793 • Increased to 106 from 1794 to 1800 • 142 seats from 1801 to 1810
 Article 1 of the Constitution directs Congress to Reapportion or redistribute the seats in the HOR after each decennial census…. Reapportionment Act of 1929 Permanent size of the House is 435 members Census Bureau conducts a decennial census and reapportions the seats each state should have. Submitted to the President, sends it to Congress
Article 1 of the Constitution directs Congress to Reapportion or redistribute the seats in the HOR after each decennial census…. Reapportionment Act of 1929 Permanent size of the House is 435 members Census Bureau conducts a decennial census and reapportions the seats each state should have. Submitted to the President, sends it to Congress
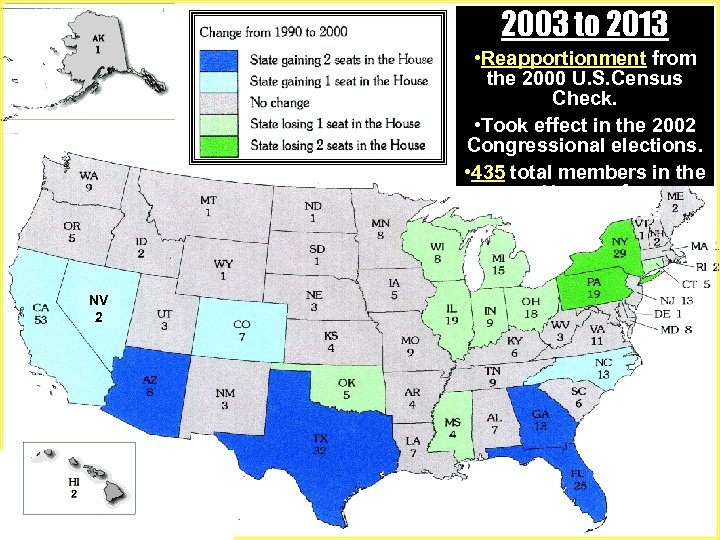 2003 to 2013 1993 to 2003 • Reapportionment from 2000 the 1990 U. S. Census Check. 2002 • Took effect in the 1992 Congressional elections. • 435 total members in the House of Representatives NV 2
2003 to 2013 1993 to 2003 • Reapportionment from 2000 the 1990 U. S. Census Check. 2002 • Took effect in the 1992 Congressional elections. • 435 total members in the House of Representatives NV 2
 Powers only given to the House of Representatives. v Bring charges of impeachment. v Elects President if there is no majority in the Electoral College. v Elects its own officers. v Judges the qualifications and disciplines its membership. v Expel or censure members of the House.
Powers only given to the House of Representatives. v Bring charges of impeachment. v Elects President if there is no majority in the Electoral College. v Elects its own officers. v Judges the qualifications and disciplines its membership. v Expel or censure members of the House.
 House of Representatives http: //www. house. gov/ Tim Bishop Steve Israel Representative District #1 Representative District #2
House of Representatives http: //www. house. gov/ Tim Bishop Steve Israel Representative District #1 Representative District #2
 Senate http: //www. house. gov/ Charles Schumer U. S. Senator Kirstin Gillibrand
Senate http: //www. house. gov/ Charles Schumer U. S. Senator Kirstin Gillibrand
 SITS AS JURY DURING IMPEACHMENT ELECTS V. P. IF NO MAJORITY IN ELECTORAL COLLEGE RATIFIES TREATIES AND APPOINTMENTS ELECTS OWN OFFICERS JUDGES THE QUALIFICATIONS AND DISCIPLINES ITS MEMBERSHIP
SITS AS JURY DURING IMPEACHMENT ELECTS V. P. IF NO MAJORITY IN ELECTORAL COLLEGE RATIFIES TREATIES AND APPOINTMENTS ELECTS OWN OFFICERS JUDGES THE QUALIFICATIONS AND DISCIPLINES ITS MEMBERSHIP
 Delegates • Delegates see themselves as agents of the people who elected them. They vote how their constituents want them to vote Trustees • Vote for what is best for the country, even if it is counter to what the constituents want. Believe that each question they face must be decided on its merits. Partisans • Lawmakers who owe their first allegiance to their political party are partisans. Politicos • Attempts to combine the basic elements of the trustee, delegate, and partisan roles.
Delegates • Delegates see themselves as agents of the people who elected them. They vote how their constituents want them to vote Trustees • Vote for what is best for the country, even if it is counter to what the constituents want. Believe that each question they face must be decided on its merits. Partisans • Lawmakers who owe their first allegiance to their political party are partisans. Politicos • Attempts to combine the basic elements of the trustee, delegate, and partisan roles.
 Single Member District: State Congresses create Congressional Districts. . . Under the single-member district arrangement, the voter’s in each district elect one of the State’s representatives. At-Large: Elected from the State as a whole, rather than from a particular district. • At Large was considered unfair……. • Area within the state with the most population could control all the seats in the House of Representatives.
Single Member District: State Congresses create Congressional Districts. . . Under the single-member district arrangement, the voter’s in each district elect one of the State’s representatives. At-Large: Elected from the State as a whole, rather than from a particular district. • At Large was considered unfair……. • Area within the state with the most population could control all the seats in the House of Representatives.
 Drawing Congressional District After Congress has approved the Census Bureau’s Reapportionment of the 435 seats in the House, the Congressional Districts must be redrawn. This is the responsibility of each state’s legislature. Re-districting: to re. Re-districting draw boundaries of
Drawing Congressional District After Congress has approved the Census Bureau’s Reapportionment of the 435 seats in the House, the Congressional Districts must be redrawn. This is the responsibility of each state’s legislature. Re-districting: to re. Re-districting draw boundaries of
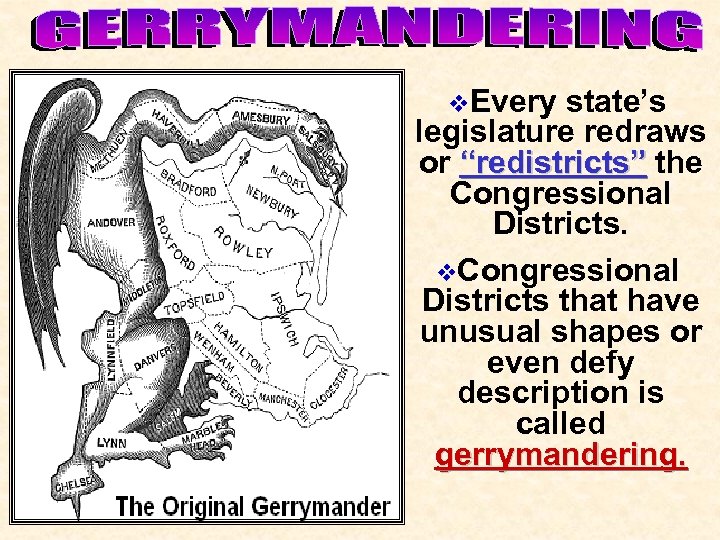 v. Every state’s legislature redraws or “redistricts” the Congressional Districts. v. Congressional Districts that have unusual shapes or even defy description is called gerrymandering.
v. Every state’s legislature redraws or “redistricts” the Congressional Districts. v. Congressional Districts that have unusual shapes or even defy description is called gerrymandering.
 v. Practice of establishing district lines that favor one party or group over another v. Both parties engage in gerrymandering.
v. Practice of establishing district lines that favor one party or group over another v. Both parties engage in gerrymandering.
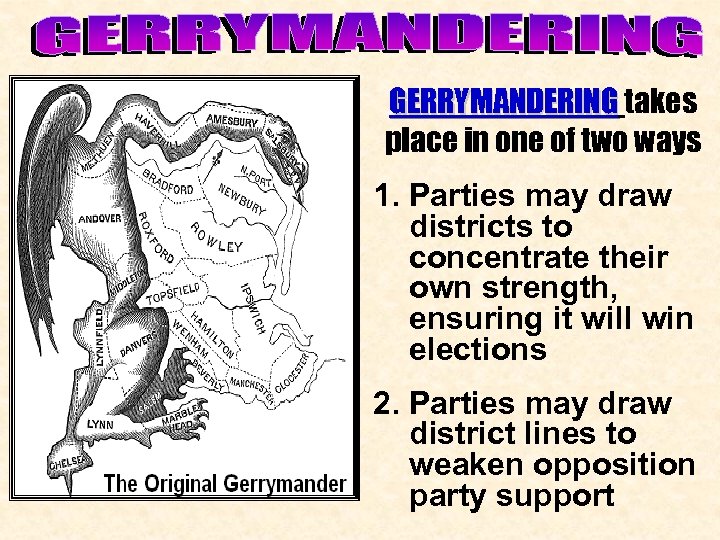 GERRYMANDERING takes place in one of two ways 1. Parties may draw districts to concentrate their own strength, ensuring it will win elections 2. Parties may draw district lines to weaken opposition party support
GERRYMANDERING takes place in one of two ways 1. Parties may draw districts to concentrate their own strength, ensuring it will win elections 2. Parties may draw district lines to weaken opposition party support
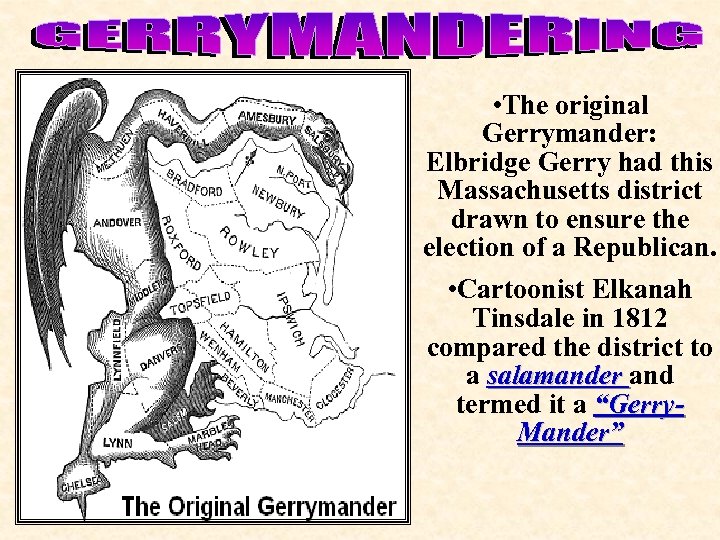 • The original Gerrymander: Elbridge Gerry had this Massachusetts district drawn to ensure the election of a Republican. • Cartoonist Elkanah Tinsdale in 1812 compared the district to a salamander and termed it a “Gerry. Mander”
• The original Gerrymander: Elbridge Gerry had this Massachusetts district drawn to ensure the election of a Republican. • Cartoonist Elkanah Tinsdale in 1812 compared the district to a salamander and termed it a “Gerry. Mander”
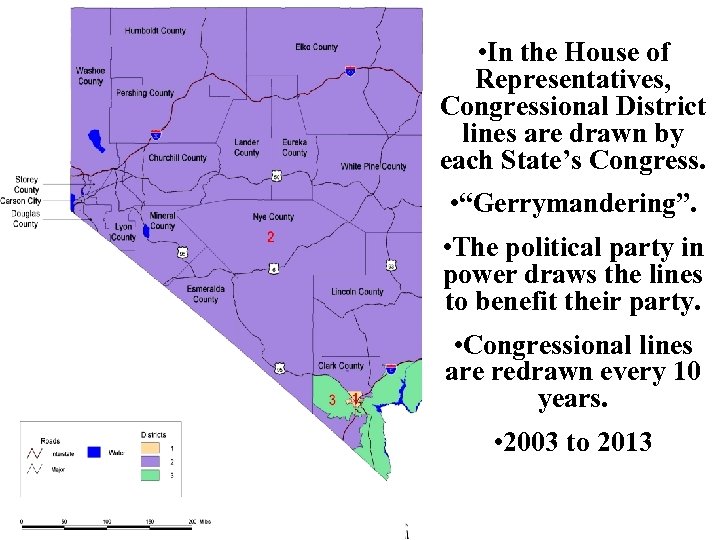 • In the House of Representatives, Congressional District lines are drawn by each State’s Congress. • “Gerrymandering”. • The political party in power draws the lines to benefit their party. • Congressional lines are redrawn every 10 years. • 2003 to 2013
• In the House of Representatives, Congressional District lines are drawn by each State’s Congress. • “Gerrymandering”. • The political party in power draws the lines to benefit their party. • Congressional lines are redrawn every 10 years. • 2003 to 2013
 Shelly Berkley
Shelly Berkley
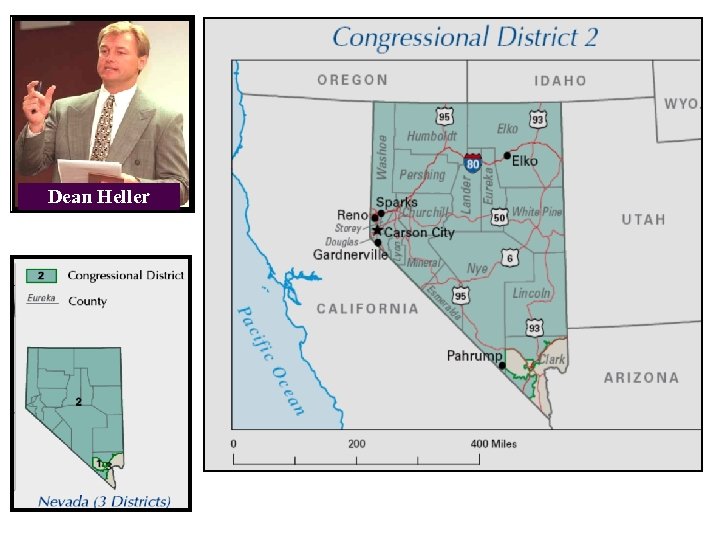 Dean Heller
Dean Heller
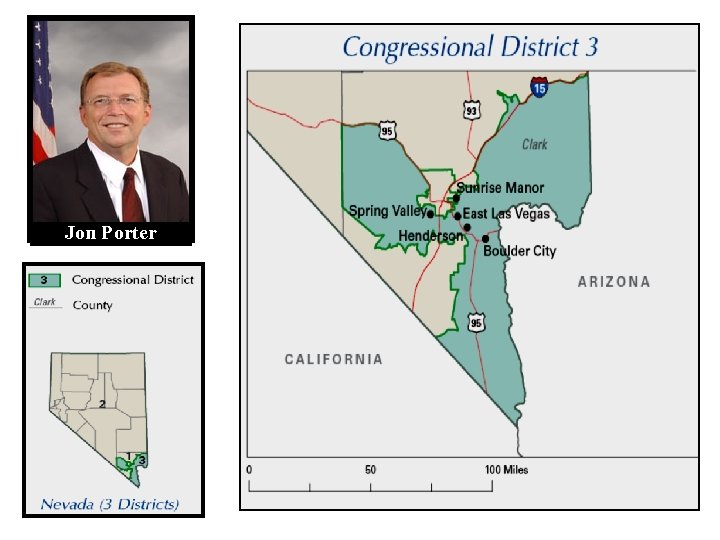 Jon Porter
Jon Porter
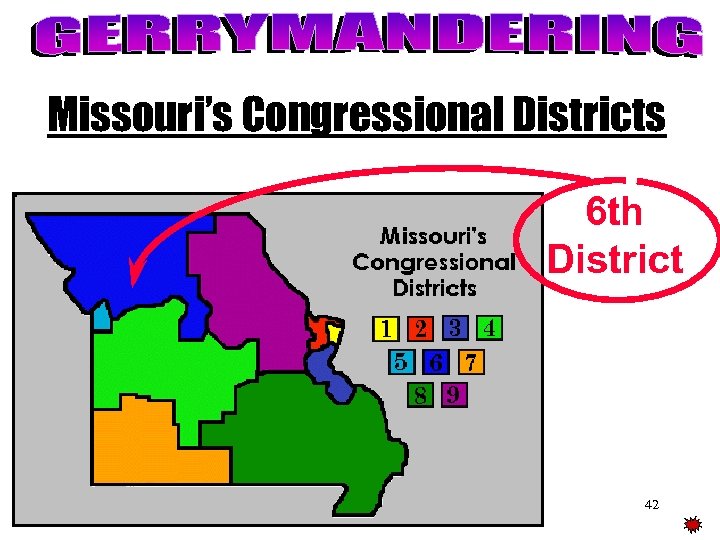 Missouri’s Congressional Districts 6 th District 42
Missouri’s Congressional Districts 6 th District 42
 THE US SENATE IS REFERRED TO AS A CONTINUOUS BODY 1 3 2010 1 3 NY Senator Charles Schumer was re-elected 2012 NY Senator Kirstin Gillibrand is up for re-election 1 = 3 2014 No NY Senators are up for re-election 100 US Senators who serve 6 year terms…. . Every terms 2 years during elections, there are 66 or 67 not up for re-election. ·Every 2 yrs. , one third are up for reelection. ·Provides stability in the US Senate unlike the House ·Reduces pressure for campaigning and re-election.
THE US SENATE IS REFERRED TO AS A CONTINUOUS BODY 1 3 2010 1 3 NY Senator Charles Schumer was re-elected 2012 NY Senator Kirstin Gillibrand is up for re-election 1 = 3 2014 No NY Senators are up for re-election 100 US Senators who serve 6 year terms…. . Every terms 2 years during elections, there are 66 or 67 not up for re-election. ·Every 2 yrs. , one third are up for reelection. ·Provides stability in the US Senate unlike the House ·Reduces pressure for campaigning and re-election.
 Constituents are voters who elect their representatives. Members of the House and the Senate act as servants of their constituents Requests from voters vary widely, and members of Congress take heed to many of them. Ignoring their 3 4 constituencies would 1 2 Go To Section:
Constituents are voters who elect their representatives. Members of the House and the Senate act as servants of their constituents Requests from voters vary widely, and members of Congress take heed to many of them. Ignoring their 3 4 constituencies would 1 2 Go To Section:
 Senators and representatives are paid a salary of $174, 000 a year. Certain members, Speaker of the House and the Senate’s president pro tem, are paid more. Constitution says that Congress fixes its own “compensation. ” Check and balance: President’s veto and fear of voter backlash against a pay increase. 27 th Amendment: Congress can give itself
Senators and representatives are paid a salary of $174, 000 a year. Certain members, Speaker of the House and the Senate’s president pro tem, are paid more. Constitution says that Congress fixes its own “compensation. ” Check and balance: President’s veto and fear of voter backlash against a pay increase. 27 th Amendment: Congress can give itself
 Question: Do you think Congressmen should be paid a high salary? • Base salary for members of Congress is $174, 000. 00 • Median income (U. S. Census Bureau, 2010) for all households in the U. S. was $49, 000. 00
Question: Do you think Congressmen should be paid a high salary? • Base salary for members of Congress is $174, 000. 00 • Median income (U. S. Census Bureau, 2010) for all households in the U. S. was $49, 000. 00
 Fringe Benefits “Perks” a benefit awarded to Congressmen because of their public service. suite of offices expense accounts money to set up office in home district phone & computer & broadcast
Fringe Benefits “Perks” a benefit awarded to Congressmen because of their public service. suite of offices expense accounts money to set up office in home district phone & computer & broadcast
 Fringe benefits -- money for travel for members of Congress and their staff to home state or district Franking privilege -- free postal service on mail to constituents
Fringe benefits -- money for travel for members of Congress and their staff to home state or district Franking privilege -- free postal service on mail to constituents
 Fringe Benefits Low-cost health care Low-cost life insurance Generous pension plan Free research service at Library of Congress Low-cost meals at special dining rooms
Fringe Benefits Low-cost health care Low-cost life insurance Generous pension plan Free research service at Library of Congress Low-cost meals at special dining rooms
 Staying In Office Incumbents -- those already in office -- are usually able to be re-elected again and again, and “perks” give them advantages at time of election
Staying In Office Incumbents -- those already in office -- are usually able to be re-elected again and again, and “perks” give them advantages at time of election
 Advantages to Incumbents Pork barrel projects -- projects or grants of money that chiefly benefit the home district or state, such as… a new dam a federal office building highway funding Go To Section: 1 2 3 4
Advantages to Incumbents Pork barrel projects -- projects or grants of money that chiefly benefit the home district or state, such as… a new dam a federal office building highway funding Go To Section: 1 2 3 4
 Advantages to Incumbents greater name recognition free TV coverage paid trips to home state easier to raise campaign money ability to secure pork-barrel 1 2 3 4 programs pleases constituents Go To Section:
Advantages to Incumbents greater name recognition free TV coverage paid trips to home state easier to raise campaign money ability to secure pork-barrel 1 2 3 4 programs pleases constituents Go To Section:
 Advantages to Incumbents Casework that is done to help constituents, by congressional staff in D. C. and offices “back home” Personal favors such as finding Grandma’s “lost” Social Security check, helping people to receive govt 4 1 2 3 benefits. Go To Section:
Advantages to Incumbents Casework that is done to help constituents, by congressional staff in D. C. and offices “back home” Personal favors such as finding Grandma’s “lost” Social Security check, helping people to receive govt 4 1 2 3 benefits. Go To Section:
 Members of Congress are immune (protected) from arrest for noncriminal offenses while engaged in congressional business. More importantly, the Speech and Debate Clause (Article I, Section 6, Clause 1) protects representatives and senators from suits arising from their official conduct.
Members of Congress are immune (protected) from arrest for noncriminal offenses while engaged in congressional business. More importantly, the Speech and Debate Clause (Article I, Section 6, Clause 1) protects representatives and senators from suits arising from their official conduct.


