fe0c7d3c34f9f8e680b86281fb489fba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 ~1 km Development of Telescopes for Extremely Energetic Neutrinos Steven W. Barwick, UC-Irvine
~1 km Development of Telescopes for Extremely Energetic Neutrinos Steven W. Barwick, UC-Irvine
 Neutrino Telescopes: Agenda • 10 years of progress with optical Cherenkov Detectors • Extremely Energetic Neutrinos - New Technologies Radio Cherenkov: ARIANNA Teraton -Petaton
Neutrino Telescopes: Agenda • 10 years of progress with optical Cherenkov Detectors • Extremely Energetic Neutrinos - New Technologies Radio Cherenkov: ARIANNA Teraton -Petaton
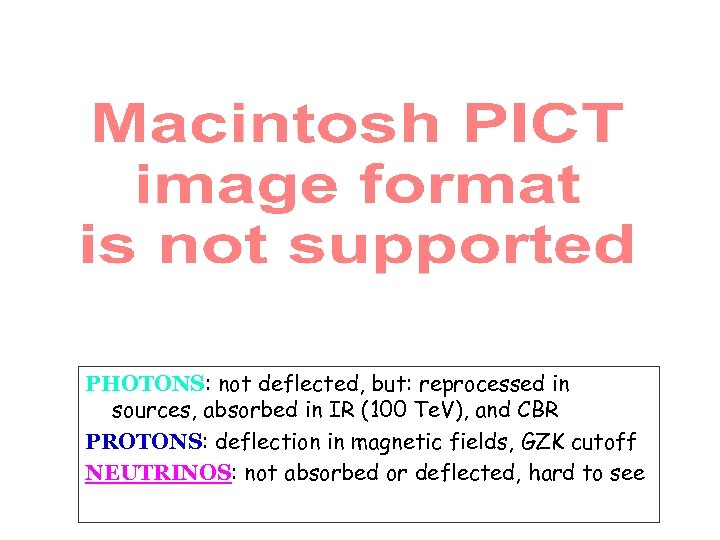 PHOTONS: not deflected, but: reprocessed in sources, absorbed in IR (100 Te. V), and CBR PROTONS: deflection in magnetic fields, GZK cutoff NEUTRINOS: not absorbed or deflected, hard to see
PHOTONS: not deflected, but: reprocessed in sources, absorbed in IR (100 Te. V), and CBR PROTONS: deflection in magnetic fields, GZK cutoff NEUTRINOS: not absorbed or deflected, hard to see
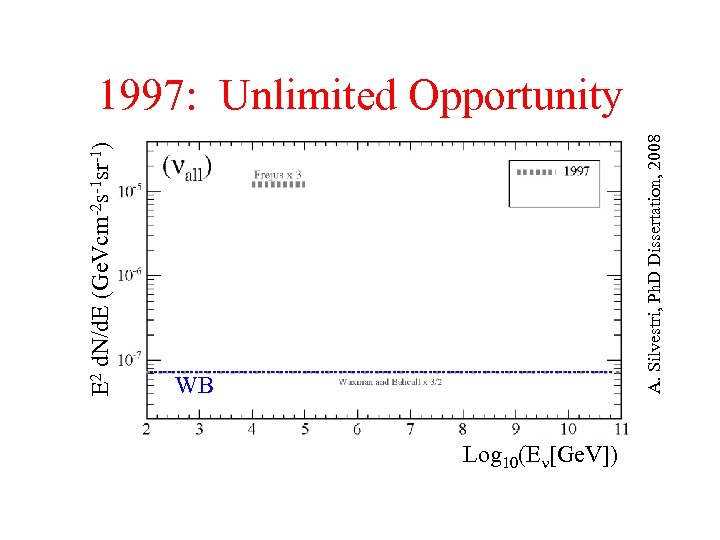 E 2 d. N/d. E (Ge. Vcm-2 s-1 sr-1) WB A. Silvestri, Ph. D Dissertation, 2008 1997: Unlimited Opportunity Log 10(E [Ge. V])
E 2 d. N/d. E (Ge. Vcm-2 s-1 sr-1) WB A. Silvestri, Ph. D Dissertation, 2008 1997: Unlimited Opportunity Log 10(E [Ge. V])
![2010 ~100 x improvement Auger x 3 ANITA AMANDA-UHE WB Log 10(E [Ge. V]) 2010 ~100 x improvement Auger x 3 ANITA AMANDA-UHE WB Log 10(E [Ge. V])](https://present5.com/presentation/fe0c7d3c34f9f8e680b86281fb489fba/image-5.jpg) 2010 ~100 x improvement Auger x 3 ANITA AMANDA-UHE WB Log 10(E [Ge. V]) A. Silvestri, Ph. D Dissertation, 2008 E 2 d. N/d. E (Ge. Vcm-2 s-1 sr-1) 13 Years of Diffuse Progress
2010 ~100 x improvement Auger x 3 ANITA AMANDA-UHE WB Log 10(E [Ge. V]) A. Silvestri, Ph. D Dissertation, 2008 E 2 d. N/d. E (Ge. Vcm-2 s-1 sr-1) 13 Years of Diffuse Progress
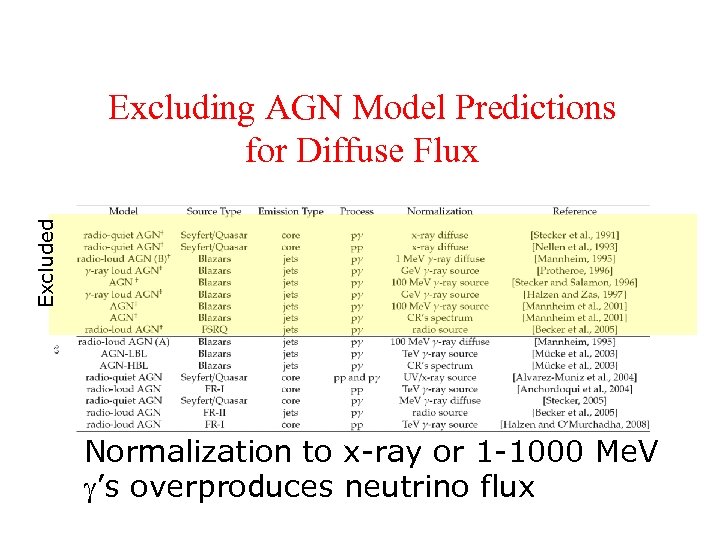 Excluded Excluding AGN Model Predictions for Diffuse Flux Normalization to x-ray or 1 -1000 Me. V ’s overproduces neutrino flux
Excluded Excluding AGN Model Predictions for Diffuse Flux Normalization to x-ray or 1 -1000 Me. V ’s overproduces neutrino flux
![GZK neutrinios [ one of the most secure predictions in the field ] New GZK neutrinios [ one of the most secure predictions in the field ] New](https://present5.com/presentation/fe0c7d3c34f9f8e680b86281fb489fba/image-7.jpg) GZK neutrinios [ one of the most secure predictions in the field ] New Technologies
GZK neutrinios [ one of the most secure predictions in the field ] New Technologies
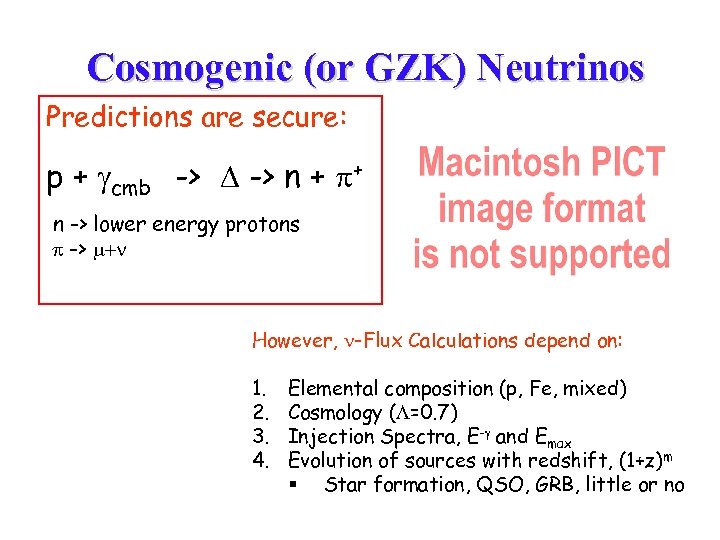 Cosmogenic (or GZK) Neutrinos Predictions are secure: p + cmb -> n + + n -> lower energy protons -> However, -Flux Calculations depend on: 1. 2. 3. 4. Elemental composition (p, Fe, mixed) Cosmology ( =0. 7) Injection Spectra, E- and Emax Evolution of sources with redshift, (1+z)m § Star formation, QSO, GRB, little or no
Cosmogenic (or GZK) Neutrinos Predictions are secure: p + cmb -> n + + n -> lower energy protons -> However, -Flux Calculations depend on: 1. 2. 3. 4. Elemental composition (p, Fe, mixed) Cosmology ( =0. 7) Injection Spectra, E- and Emax Evolution of sources with redshift, (1+z)m § Star formation, QSO, GRB, little or no
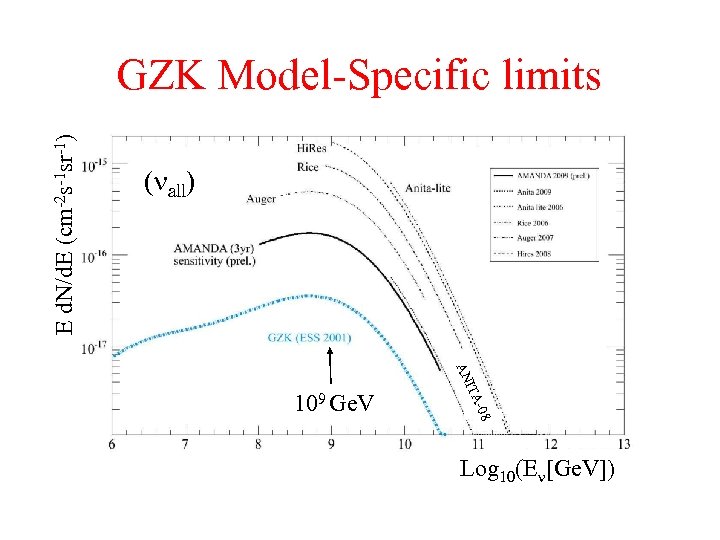 E d. N/d. E (cm-2 s-1 sr-1) GZK Model-Specific limits all) ITA AN -08 109 Ge. V Log 10(E [Ge. V])
E d. N/d. E (cm-2 s-1 sr-1) GZK Model-Specific limits all) ITA AN -08 109 Ge. V Log 10(E [Ge. V])
 Why Big Detectors? • • GZK Flux, (E~1018 e. V): 100 /km 2/yr Interaction Length, : 500 km Event Rate/km 3/yr = [ ] ~ 0. 2 Efficiency, livetime, nice if more than one So GZK detection requires > 10 km 3 (aperture > 60 km 3 sr) Note: ARIANNA has ~ 2400 km 3 sr
Why Big Detectors? • • GZK Flux, (E~1018 e. V): 100 /km 2/yr Interaction Length, : 500 km Event Rate/km 3/yr = [ ] ~ 0. 2 Efficiency, livetime, nice if more than one So GZK detection requires > 10 km 3 (aperture > 60 km 3 sr) Note: ARIANNA has ~ 2400 km 3 sr
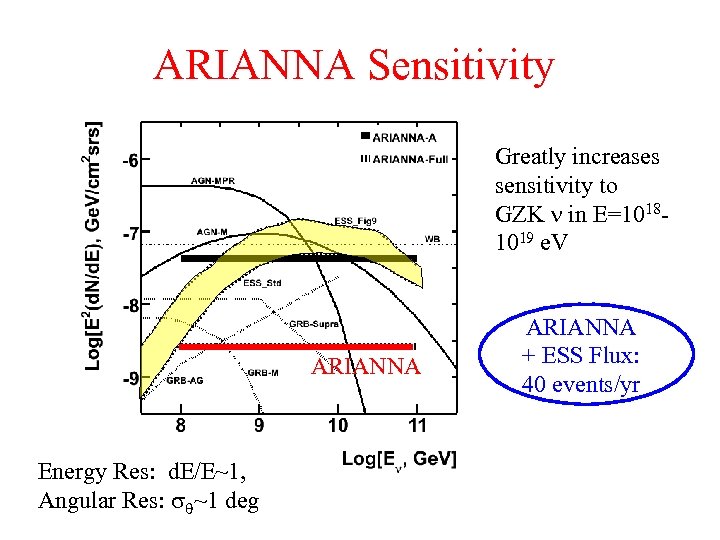 ARIANNA Sensitivity Greatly increases sensitivity to GZK in E=10181019 e. V ARIANNA Energy Res: d. E/E~1, Angular Res: ~1 deg ARIANNA + ESS Flux: 40 events/yr
ARIANNA Sensitivity Greatly increases sensitivity to GZK in E=10181019 e. V ARIANNA Energy Res: d. E/E~1, Angular Res: ~1 deg ARIANNA + ESS Flux: 40 events/yr
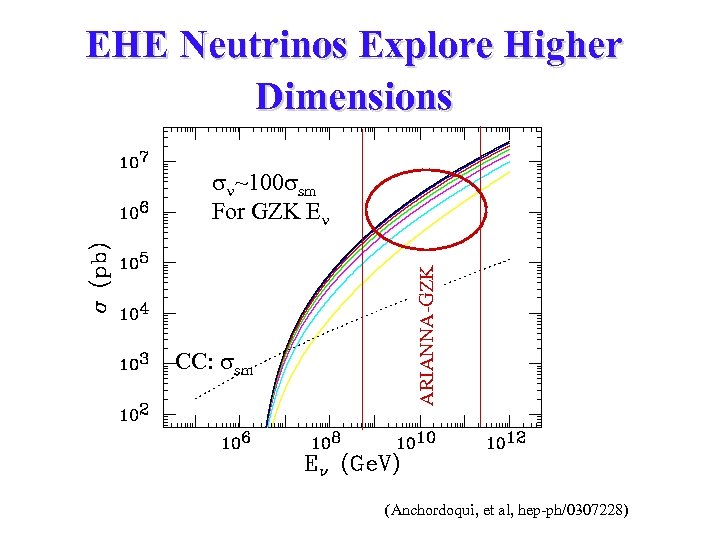 EHE Neutrinos Explore Higher Dimensions CC: sm ARIANNA-GZK ~100 sm For GZK E (Anchordoqui, et al, hep-ph/0307228)
EHE Neutrinos Explore Higher Dimensions CC: sm ARIANNA-GZK ~100 sm For GZK E (Anchordoqui, et al, hep-ph/0307228)
![Neutrino Cross-Section A. Connolly, 2006 ARIANNA - 10 years GQRS [ ] = 0. Neutrino Cross-Section A. Connolly, 2006 ARIANNA - 10 years GQRS [ ] = 0.](https://present5.com/presentation/fe0c7d3c34f9f8e680b86281fb489fba/image-13.jpg) Neutrino Cross-Section A. Connolly, 2006 ARIANNA - 10 years GQRS [ ] = 0. 24 If Nev = 400 If =0. 5 o If =2 GQRS 2 parameter fit: Normalization cross-section
Neutrino Cross-Section A. Connolly, 2006 ARIANNA - 10 years GQRS [ ] = 0. 24 If Nev = 400 If =0. 5 o If =2 GQRS 2 parameter fit: Normalization cross-section
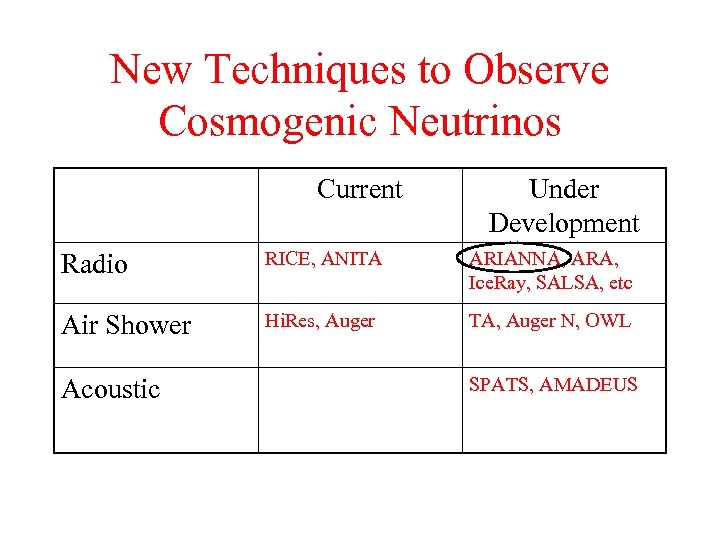 New Techniques to Observe Cosmogenic Neutrinos Current Under Development Radio RICE, ANITA ARIANNA, ARA, Ice. Ray, SALSA, etc Air Shower Hi. Res, Auger TA, Auger N, OWL Acoustic SPATS, AMADEUS
New Techniques to Observe Cosmogenic Neutrinos Current Under Development Radio RICE, ANITA ARIANNA, ARA, Ice. Ray, SALSA, etc Air Shower Hi. Res, Auger TA, Auger N, OWL Acoustic SPATS, AMADEUS
 Askaryan Radio Emission from SLAC beam in Ice Gorham, Barwick, et al. , astro-ph/0611008 Absolute RF power and frequency dependence confirmed Width of cherenkov cone and frequency dependence confirmed
Askaryan Radio Emission from SLAC beam in Ice Gorham, Barwick, et al. , astro-ph/0611008 Absolute RF power and frequency dependence confirmed Width of cherenkov cone and frequency dependence confirmed
![31 x 31 array [30 km x 30 km] ARIANNA UCI, LBL, OSU, Wash. 31 x 31 array [30 km x 30 km] ARIANNA UCI, LBL, OSU, Wash.](https://present5.com/presentation/fe0c7d3c34f9f8e680b86281fb489fba/image-16.jpg) 31 x 31 array [30 km x 30 km] ARIANNA UCI, LBL, OSU, Wash. U, KU, UC-London, S. Korea Barwick, astro-ph/0610631 600 m 1 km
31 x 31 array [30 km x 30 km] ARIANNA UCI, LBL, OSU, Wash. U, KU, UC-London, S. Korea Barwick, astro-ph/0610631 600 m 1 km
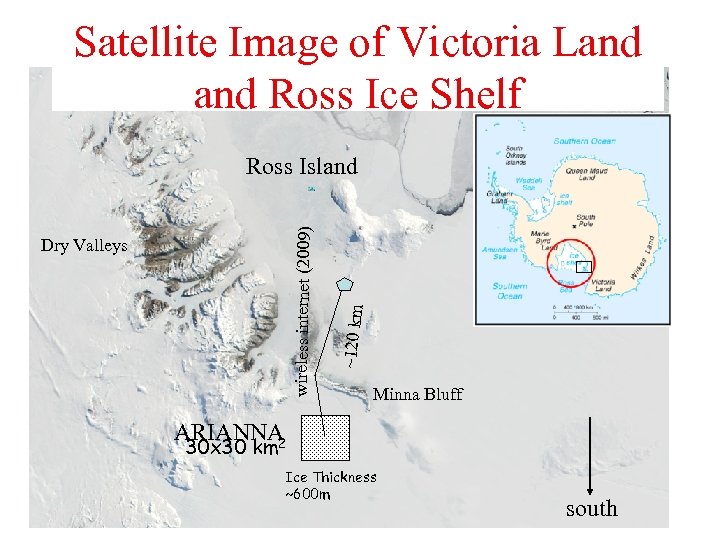 Satellite Image of Victoria Land Ross Ice Shelf Dry Valleys ~120 km wireless internet (2009) Ross Island Minna Bluff ARIANNA 2 30 x 30 km Ice Thickness ~600 m south
Satellite Image of Victoria Land Ross Ice Shelf Dry Valleys ~120 km wireless internet (2009) Ross Island Minna Bluff ARIANNA 2 30 x 30 km Ice Thickness ~600 m south
 ARIANNA Advantages • Straightforward logistics – not far (~120 km) from main US science station – surface deployment (no drilling) • Excellent site properties – Protected from man-made noise – Remarkable attenuation length and reflectivity from bottom • Lightweight, robust technologies (so low $$) • Internet access 24/7 • Array is reconfigurable to follow science
ARIANNA Advantages • Straightforward logistics – not far (~120 km) from main US science station – surface deployment (no drilling) • Excellent site properties – Protected from man-made noise – Remarkable attenuation length and reflectivity from bottom • Lightweight, robust technologies (so low $$) • Internet access 24/7 • Array is reconfigurable to follow science
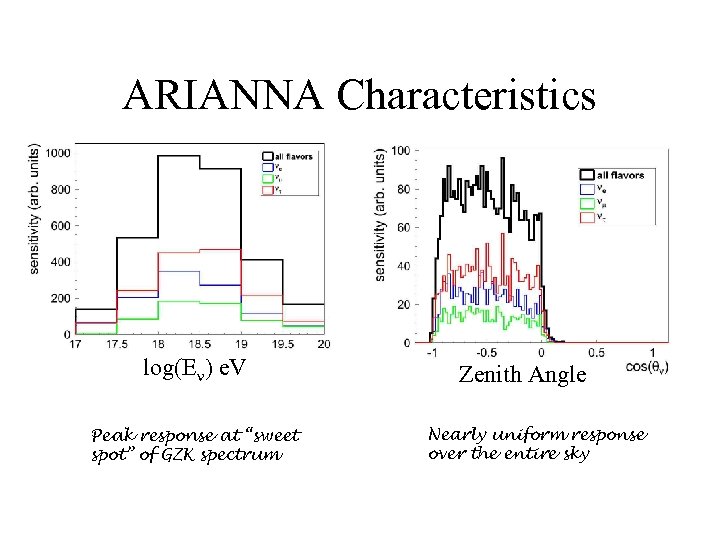 ARIANNA Characteristics log(E ) e. V Peak response at “sweet spot” of GZK spectrum Zenith Angle Nearly uniform response over the entire sky
ARIANNA Characteristics log(E ) e. V Peak response at “sweet spot” of GZK spectrum Zenith Angle Nearly uniform response over the entire sky
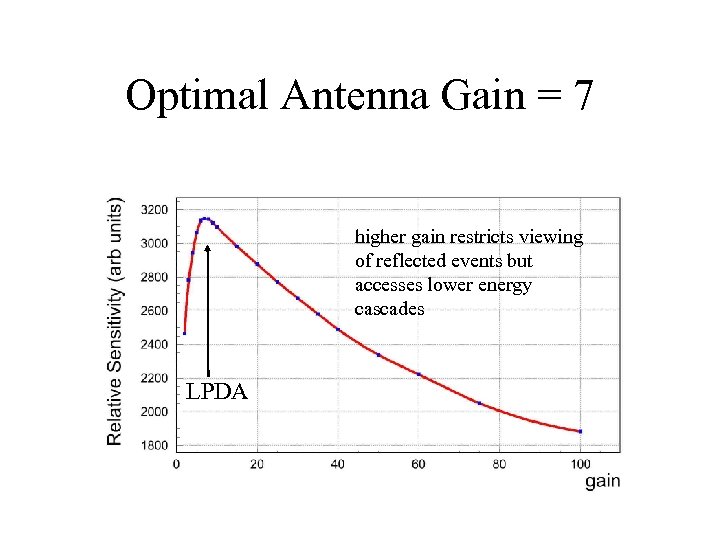 Optimal Antenna Gain = 7 higher gain restricts viewing of reflected events but accesses lower energy cascades LPDA
Optimal Antenna Gain = 7 higher gain restricts viewing of reflected events but accesses lower energy cascades LPDA
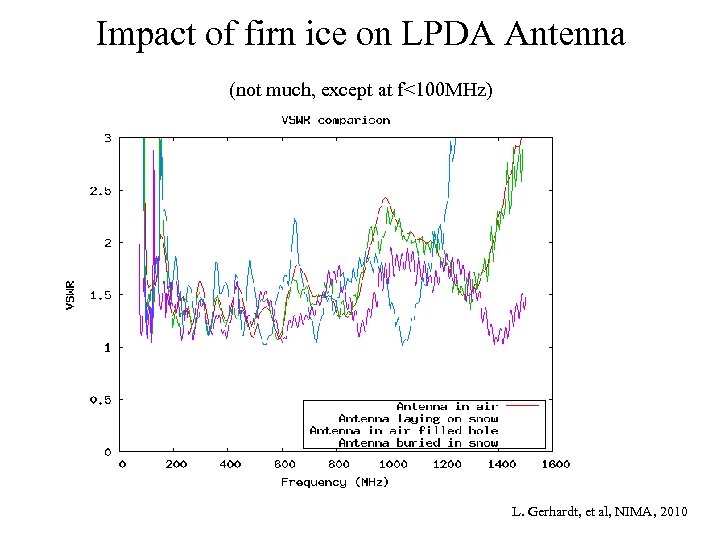 Impact of firn ice on LPDA Antenna (not much, except at f<100 MHz) L. Gerhardt, et al, NIMA, 2010
Impact of firn ice on LPDA Antenna (not much, except at f<100 MHz) L. Gerhardt, et al, NIMA, 2010
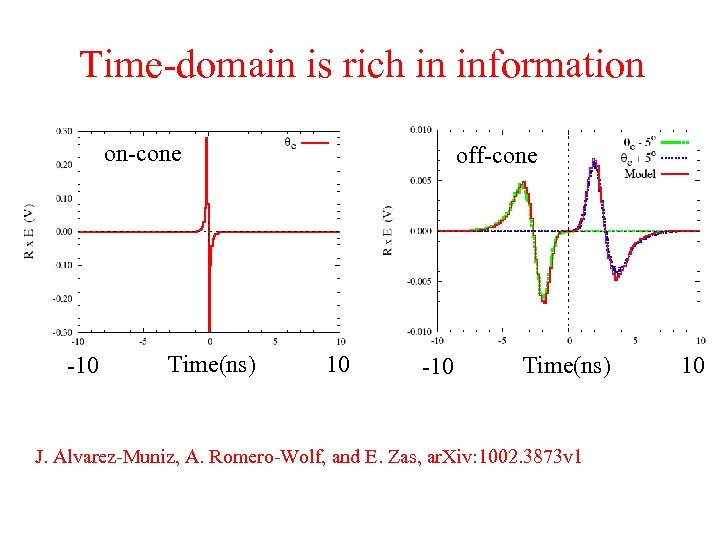 Time-domain is rich in information on-cone -10 Time(ns) off-cone 10 -10 Time(ns) J. Alvarez-Muniz, A. Romero-Wolf, and E. Zas, ar. Xiv: 1002. 3873 v 1 10
Time-domain is rich in information on-cone -10 Time(ns) off-cone 10 -10 Time(ns) J. Alvarez-Muniz, A. Romero-Wolf, and E. Zas, ar. Xiv: 1002. 3873 v 1 10
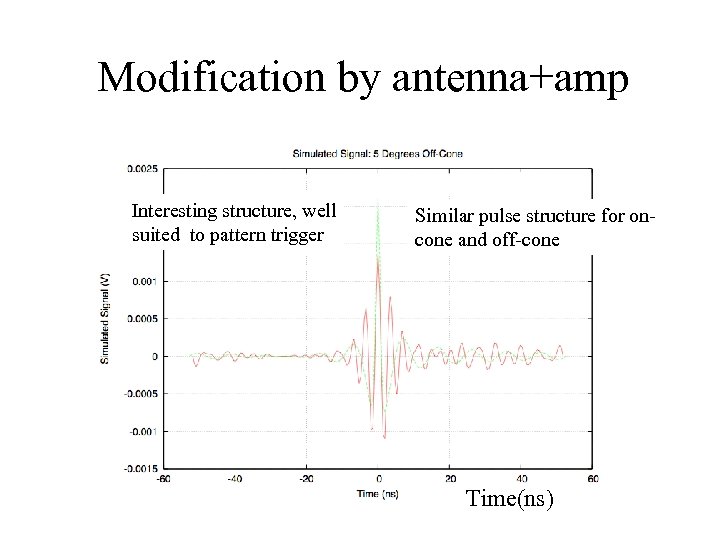 Modification by antenna+amp Interesting structure, well suited to pattern trigger Similar pulse structure for oncone and off-cone Time(ns)
Modification by antenna+amp Interesting structure, well suited to pattern trigger Similar pulse structure for oncone and off-cone Time(ns)

 Camping at Moore’s Bay Site David Saltzberg
Camping at Moore’s Bay Site David Saltzberg
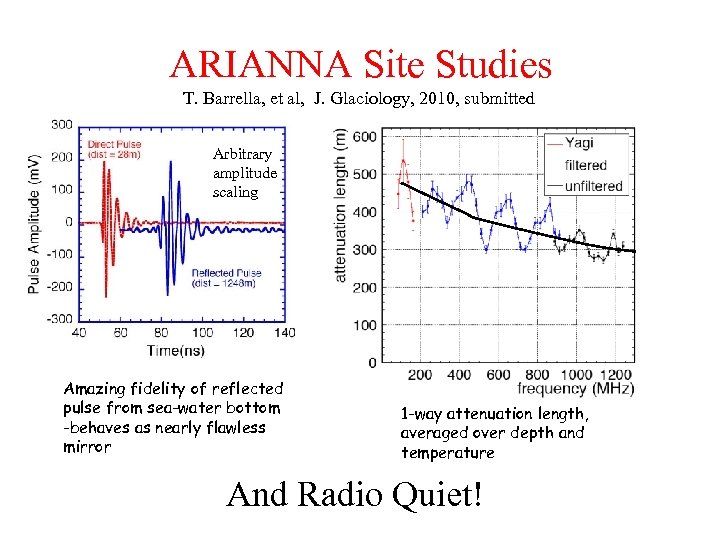 ARIANNA Site Studies T. Barrella, et al, J. Glaciology, 2010, submitted Arbitrary amplitude scaling Preliminary Value assumed prior to this work Amazing fidelity of reflected pulse from sea-water bottom -behaves as nearly flawless mirror 1 -way attenuation length, averaged over depth and temperature And Radio Quiet!
ARIANNA Site Studies T. Barrella, et al, J. Glaciology, 2010, submitted Arbitrary amplitude scaling Preliminary Value assumed prior to this work Amazing fidelity of reflected pulse from sea-water bottom -behaves as nearly flawless mirror 1 -way attenuation length, averaged over depth and temperature And Radio Quiet!
 L. Gerhardt, et al, NIMA, 2010 ARIANNA Prototype Station (deployed Dec. 2009) “lab” Power Tower Wireless
L. Gerhardt, et al, NIMA, 2010 ARIANNA Prototype Station (deployed Dec. 2009) “lab” Power Tower Wireless
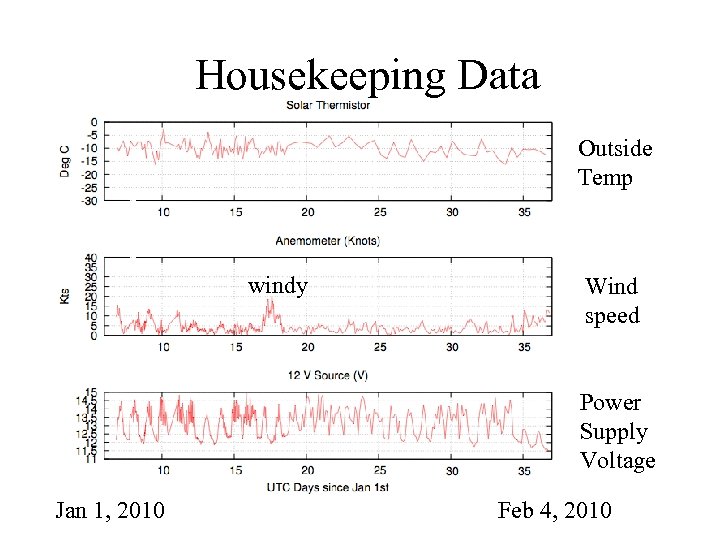 Housekeeping Data Outside Temp windy Wind speed Power Supply Voltage Jan 1, 2010 Feb 4, 2010
Housekeeping Data Outside Temp windy Wind speed Power Supply Voltage Jan 1, 2010 Feb 4, 2010
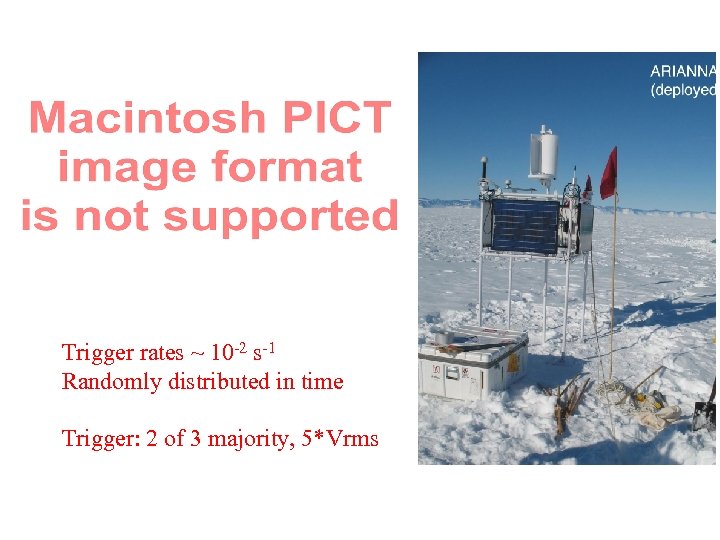 Trigger rates ~ 10 -2 s-1 Randomly distributed in time Trigger: 2 of 3 majority, 5*Vrms
Trigger rates ~ 10 -2 s-1 Randomly distributed in time Trigger: 2 of 3 majority, 5*Vrms
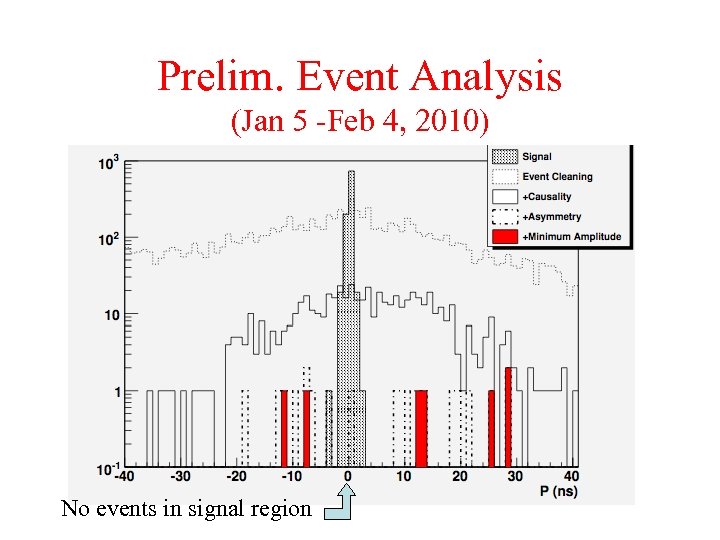 Prelim. Event Analysis (Jan 5 -Feb 4, 2010) No events in signal region
Prelim. Event Analysis (Jan 5 -Feb 4, 2010) No events in signal region
 ARIANNA Visualization
ARIANNA Visualization
 Outlook • To probe the GZK neutrino fluxes and particle physics at highest energies, new techniques are being developed based on radio cherenkov , air shower and acoustic detection. • ARIANNA has the right combination of size and simplicity of deployment to keep costs down – Ice studies in Nov’ 06 astonishingly good – Recent protostation studies show low Anthropogenic noise over 1 month periods • 7 -station engineering array approved by NSF in April 2010
Outlook • To probe the GZK neutrino fluxes and particle physics at highest energies, new techniques are being developed based on radio cherenkov , air shower and acoustic detection. • ARIANNA has the right combination of size and simplicity of deployment to keep costs down – Ice studies in Nov’ 06 astonishingly good – Recent protostation studies show low Anthropogenic noise over 1 month periods • 7 -station engineering array approved by NSF in April 2010

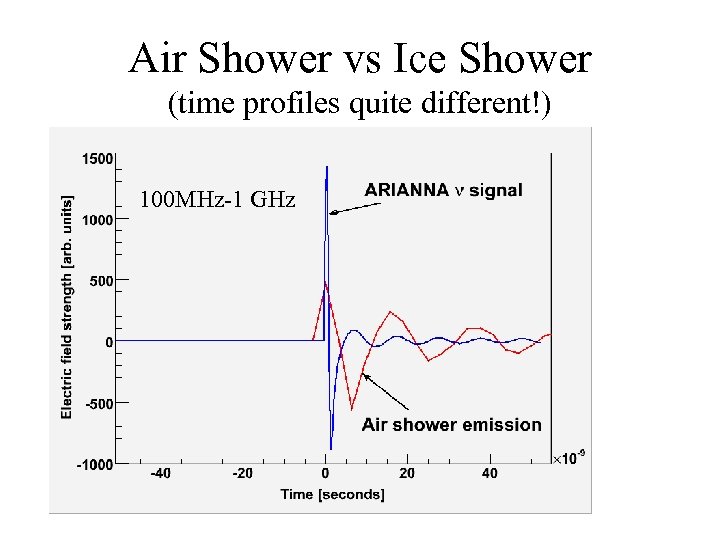 Air Shower vs Ice Shower (time profiles quite different!) 100 MHz-1 GHz
Air Shower vs Ice Shower (time profiles quite different!) 100 MHz-1 GHz
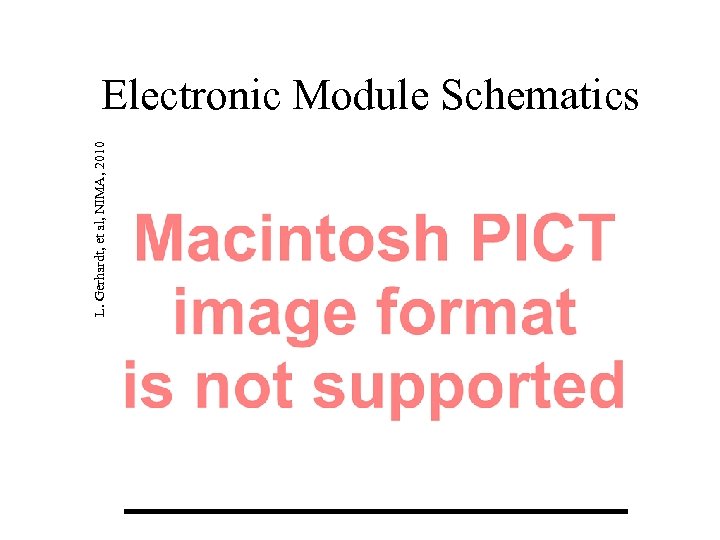 L. Gerhardt, et al, NIMA, 2010 Electronic Module Schematics
L. Gerhardt, et al, NIMA, 2010 Electronic Module Schematics
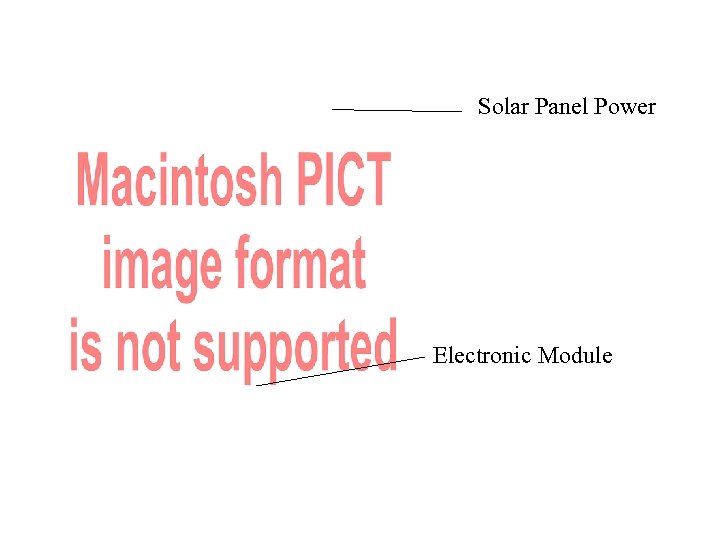 Solar Panel Power Electronic Module
Solar Panel Power Electronic Module


