41fdf0b1c6d831422a149fe94f64ccda.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

1 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet CHAPTER 7 THE INTERNET AND INTRANETS

2 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet Learning Objectives Describe what the Internet is, how it works, and how users connect to it Describe the capabilities that the Internet offers to users Describe the World Wide Web and differentiate it from the Internet Identify and describe the tools that allow users to view and search the Web Identify and briefly describe the management challenges caused by the Internet Define the term intranet and discuss how intranets are used by business

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 3 Chapter Overview The Evolution of the Internet • The Internet today • The infrastructure • Internet 2 The World Wide Web • Browsers • Offline Browsers • Search Engines • Push Technology • Information Filters • Clipping Services • Personalized Web Services • Collaborative Filtering • Web Authoring The Operation of the Internet • Addresses on the Internet • Accessing the Internet Services Provided by the Internet • Communications Services • Information Retrieval Services Internet Challenges • New Technologies • Internet Regulation • Internet Expansion • Internet Privacy Intranets • Teamware • Security

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 4 Case : Schwab’s New Internet Business Model The Business Problem î give top-notch advice and service but not to push products or recommend which stocks to buy; keen competition from both deep-discount Internet brokers and full-service investment firms The Solution î coach people on investing through the Internet î allow customers access to their own Web pages and initial public offerings; online interviews with top executives The Results î the more they go online for routine business, the less the staff needs at Schwab’s service centers and branches î earns its highest ratings on “customer confidence, ” but not initially rated well in “ease-to-use”

5 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet Case (continued…) What have we learned from this case? ? î Internet strategy is no longer just a source of competitive advantage; it is necessary for survival î An innovative use of the Internet can bring competitive advantage but it may not be sustainable î The Internet in its various incarnations is a powerful medium whose understanding is essential for the modern business competitor

6 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet What is the Internet? The Largest computer network in the world (a network of networks) Exchanges information seamlessly by using the same open, non-proprietary standards and protocols, within interconnected networks Forms a massive electronic communications network Provides a true democratic communications forum and has produced a democratization of information
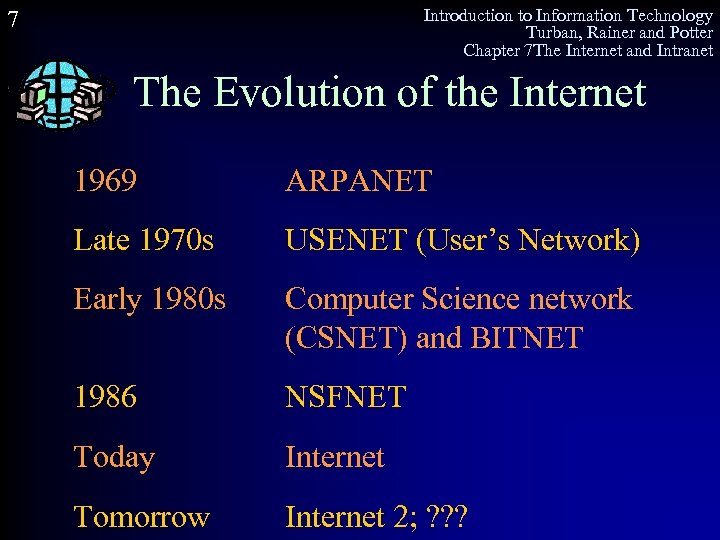
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 7 The Evolution of the Internet 1969 ARPANET Late 1970 s USENET (User’s Network) Early 1980 s Computer Science network (CSNET) and BITNET 1986 NSFNET Today Internet Tomorrow Internet 2; ? ? ?

8 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet The Internet Today The Internet is international, with users on all continents The cost of personal computers and Internet connections are prohibitively high for most of the population Political, cultural, and regulatory barriers have slowed the rate of Internet adoption The vast majority of sites are in English The vast majority of content is generated in the United States

9 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet The Infrastructure of the Internet Commercial communications companies now largely provide the physical network backbone of the Internet The U. S. government continues to contribute some funds to essential administrative processes The National Science Foundation (NSF), in the USA, pays for certain high-performance portions of the network backbone The Internet infrastructure is supplied by network service provider

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 10 Internet 2 In 1996 a consortium of universities began establishing a faster network, Internet 2, with limited access devoted exclusively to research purposes Internet 2 grew from 34 to more than 110 U. S. research universities in one year Internet 2 is capable of transmitting gigabits of information per second

11 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet The Operation of the Internet Addresses on the Internet î IP address - uniquely identifies one from the other computers î Domain name system (DNS) - derives the names of the computers î Domain name - consists of multiple parts, separated by dots, and are translated from right to left; upper names are most important (the dot com; wiley. com)

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 12 The Operation of the Internet (continued …) Accessing the Internet î Connect via LAN Server î Connect via Serial Line Internet Protocol/Point Protocol (SLIP/PPP) î Connect via an Online Service

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 13 Services Provided by the Internet Communication Services Electronic Mail (e-mail) USENET Newsgroups (Forums) LISTSERV Telnet Streaming Audio and Video Internet Fax Chatting Internet Telephony Real-Time Audio and Video

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 14 Services Provided by the Internet (continued …) Information Retrieval Services File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Gophers Archie Wide Area Information Servers (WAIS) Veronica (Very Easy Rodent-Oriented Netwide Index to Computer Archives)

15 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet The World Wide Web The Internet - functions as the transport mechanism The World Wide Web - an application that uses the Internet transport functions, a system with universally accepted standards for storing, retrieving, formatting, and displaying information via a client/server architecture Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) - standard hypertext language used in Web Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML) text-based language for describing the content and structure of digital documents Hyperlinks - from one Web page to another

16 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet The World Wide Web (continued …) Home Page - a text and graphical screen display; first, introductory page in a web site Web Site - all the pages of a company or individual Webmaster - the person in charge of a Web site Uniform Resource Locator (URL) - points to the address of a specific resource on the Web Hypertext transport Protocol (HTTP) communications standard used to transfer pages across the WWW portion of the Internet

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 17 The World Wide Web (continued …) Browser (software application that is used to access and navigate the Web) î Netscape Communicator ê a multipurpose suite that handles news, e-mail, audio- and video conferencing, and more î Microsoft Internet Explorer ê Internet Explorer’s tight integration with Windows offers users the advantage of “one-stop computing” Offline Browser î enables a user to retrieve pages automatically from Web sites at predetermined times, often during the night

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 18 The World Wide Web (continued …) Search Engines î programs that return a list of Web sites or pages that match some user-selected criteria î ways to select pages for inclusion in the database : Web Crawlers and Registration î metasearch engines ê automatically enter search queries into a number of other search engines and return the results

19 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet The World Wide Web (continued …) Push Technology automatically supplies desirable information to users by means of a process running on either the user’s desktop or a network server î provides timely, prioritized distribution of information over a corporate network in the workplace î enhances traditional Web advertising in the consumer market î used for software delivery and updates

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 20 The World Wide Web (continued …) Information Filters î automated methods of sorting relevant from irrelevant information Clipping Services î track news topics and retrieve articles from database of publications î personalized Web Services î offer the ability to generate Web content that is personalized for individual Web site visitors Collaborative Filtering î a form of personalization services exemplified by Personalogic

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 21 The World Wide Web (continued …) Web Authoring (for page and site design) î Standard HTML is the common denominator î Compu. Serve Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) and Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) is the common format of graphics files î Enhancements to HTML ê ê ê cascading style sheets (CSSs) Dynamic HTML (DHYML) Extensible markup language (XML) Voice markup language (Vox. ML) Virtual reality modeling language (VRML)

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 22 Internet Challenges New Technologies î Vendors are adopting new technologies more rapidly than many users and customers can implement them Internet Regulation î Some technical organizations are not formally charged in any legal or operational sense with responsibility for the Internet Expansion î The massive growth of Internet traffic has strained some elements of the network

23 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet Internet Challenges (continued …) Internet Privacy (Web sites collect information with and without consumers’ knowledge) î Cookie - small data file placed on users’ hard drives when they first visit a site î three potential bills are in USA Congress ê the government should let groups develop voluntary privacy standards but not take any action now unless real problems arise ê the government should recommend privacy standards for the Internet but not pass laws at this time ê the government should pass laws now for how personal information can be collected and used on the Internet

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 24 Intranets A private network that uses Internet software and TCP/IP protocols Teamware (intranet software) î used for team building, sharing ideas and documents, brainstorming, scheduling, and archiving decision to facilitate productivity Security î public key security, encryption, digital certificates, firewall and assured pipelines

25 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet Examples of Intranet Nations. Bank’s Intranet improves relations with big business customers î sales associates can get a global customer overview Philips Electronics cuts delivery time î the intranet and the CAD eliminated the mislabelling of products, inaccurate manufacturing fulfilment, and correct areas of customer dissatisfaction How BD manages knowledge î anyone at the company can find an in-house expert on the firm’s core competencies

Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet 26 What’s in IT for Me? For Accounting î Accounting personnel use corporate intranets to consolidate transaction data to provide an overall view of internal projects î Internet keeps accounting personnel informed on legal and other changes affecting their profession For Finance î Corporate intranets can provide a risk-evaluation model so that financial analysts can evaluate the risk of a project or an investment î The Web can be a marketing and service provision channel

27 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet What’s in IT for Me? (continued …) For Marketing î Marketing managers use corporate intranets to coordinate the activities of the sales force î The Internet opens a completely new marketing channel For Production/Operations Management î Intranet provides three-dimensional models and animation to speed product development î The Internet is a great source of cutting-edge information for POM pros.

28 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter Chapter 7 The Internet and Intranet What’s in IT for Me? (continued …) For Human Resource Management î On intranets, you publish corporate policy manuals, job postings, company telephone directories, and you conduct training classes î Companies deliver online training obtained from the Internet to employees through their intranets î the Internet supports worldwide recruiting efforts
41fdf0b1c6d831422a149fe94f64ccda.ppt