a57b7ad29a376f235cb10612c5a41b20.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 1 Introduction to Human Resource Management Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -1
1 Introduction to Human Resource Management Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -1
 Learning Objectives 1. Explain what human resource management is and how it relates to the management process. 2. Show with examples why human resource management is important to all managers. 3. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line and staff (HR) managers. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -2
Learning Objectives 1. Explain what human resource management is and how it relates to the management process. 2. Show with examples why human resource management is important to all managers. 3. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line and staff (HR) managers. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -2
 Learning Objectives 4. Briefly discuss and illustrate each of the important trends influencing human resource management. 5. List and briefly describe important traits of today’s human resource managers. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -3
Learning Objectives 4. Briefly discuss and illustrate each of the important trends influencing human resource management. 5. List and briefly describe important traits of today’s human resource managers. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -3
 What is human resource (HR) management and why is it important? Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -4
What is human resource (HR) management and why is it important? Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -4
 The Management Process • Planning • Organizing (Staffing) • Leading • Controlling Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -5
The Management Process • Planning • Organizing (Staffing) • Leading • Controlling Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -5
 HRM • Conducting job analysis • Planning labor needs • Acquiring talented employees • Orienting and training new hires and existing managers and employees • Creating and administering effective performance appraisals • Managing wages (compensating employees) • Attending to concerns about labor relations, health, safety, and fairness Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -6
HRM • Conducting job analysis • Planning labor needs • Acquiring talented employees • Orienting and training new hires and existing managers and employees • Creating and administering effective performance appraisals • Managing wages (compensating employees) • Attending to concerns about labor relations, health, safety, and fairness Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -6
 Human Resource (HR) Responsibilities of Line and Staff Managers Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -7
Human Resource (HR) Responsibilities of Line and Staff Managers Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -7
 • All managers are HR managers because they all get involved in activities like recruiting, interviewing, selecting and training. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -8
• All managers are HR managers because they all get involved in activities like recruiting, interviewing, selecting and training. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -8
 You can do everything else right as a manager; o Make brilliant plans o Draw clear organization charts o Set-up world class assembly lines But still fail!!! By hiring the wrong people or by not motivating your subordinates… On the other hand, many managers have been successful even with inadequate plans, organizations or controls. They were successful because they had the right people for the right jobs and motivating, appraising and developing them. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -9
You can do everything else right as a manager; o Make brilliant plans o Draw clear organization charts o Set-up world class assembly lines But still fail!!! By hiring the wrong people or by not motivating your subordinates… On the other hand, many managers have been successful even with inadequate plans, organizations or controls. They were successful because they had the right people for the right jobs and motivating, appraising and developing them. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -9
 Line and Staff Managers • Line authority gives you the right to issue orders • Staff authority gives you the right to advise others in the organization Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -10
Line and Staff Managers • Line authority gives you the right to issue orders • Staff authority gives you the right to advise others in the organization Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -10
 Line and Staff Managers • If you are a line manager, you will hold responsibilities to issue orders, provide directions and establish rules and procedures. • Staff authority gives the manager the right to advise other managers or employees. • HR manager is a staff manager and like all staff managers, is responsible for influencing and advising others. • Within the HR department you may be responsible for establishing goals and giving orders to those in your department thus serving as a line manager within HR. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -11
Line and Staff Managers • If you are a line manager, you will hold responsibilities to issue orders, provide directions and establish rules and procedures. • Staff authority gives the manager the right to advise other managers or employees. • HR manager is a staff manager and like all staff managers, is responsible for influencing and advising others. • Within the HR department you may be responsible for establishing goals and giving orders to those in your department thus serving as a line manager within HR. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -11
 HR Managers • HR managers are usually staff managers. They assist and advise line managers in areas like recruiting, hiring and compensation. • However, line managers still have human resource duties. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -12
HR Managers • HR managers are usually staff managers. They assist and advise line managers in areas like recruiting, hiring and compensation. • However, line managers still have human resource duties. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -12
 HR Managers • A line function: HR managers directs the activities of people in his or her department or in the related areas. • A coordinative function: HR manager also coordinates personnel activities with his functional authority. He ensures that line managers are implementing the firm’s HR policies and practices. • Staff function: Assisting and advising line managers. He advises the CEO so the CEO can better understand the HR aspects of the company’s strategic options. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -13
HR Managers • A line function: HR managers directs the activities of people in his or her department or in the related areas. • A coordinative function: HR manager also coordinates personnel activities with his functional authority. He ensures that line managers are implementing the firm’s HR policies and practices. • Staff function: Assisting and advising line managers. He advises the CEO so the CEO can better understand the HR aspects of the company’s strategic options. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -13
 Human Resource Duties Line Managers • • • Job placement Orientation & Training Performance Cooperation Labor costs Development Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -14
Human Resource Duties Line Managers • • • Job placement Orientation & Training Performance Cooperation Labor costs Development Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -14
 Human Resource Duties Staff Managers • Line function inside of HR department • Coordination • Assist and advise Sample HR organizational chart for a small company Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -15
Human Resource Duties Staff Managers • Line function inside of HR department • Coordination • Assist and advise Sample HR organizational chart for a small company Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -15
 Line and Staff HR Management • The line manager describes the qualifications of employees need to fill specific positions. • The the HR team takes over: o they develop sources of qualified applicants, o then conduct initial screening interviews, o administer the appropriate tests, o refer the best applicants to the line manager. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -16
Line and Staff HR Management • The line manager describes the qualifications of employees need to fill specific positions. • The the HR team takes over: o they develop sources of qualified applicants, o then conduct initial screening interviews, o administer the appropriate tests, o refer the best applicants to the line manager. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -16
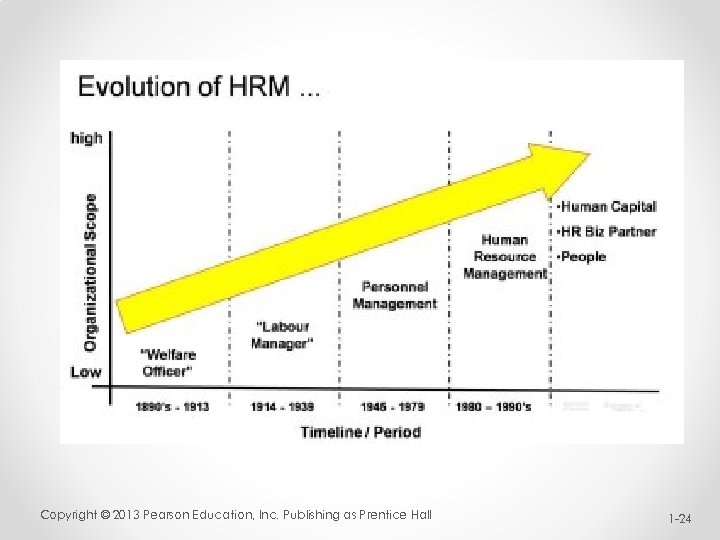
 Evolution of HRM Period before revolution industrial • The society was primarily an agriculture economy with limited production. • Number of specialized crafts was limited and was usually carried out within a village or community with apprentices assisting the master craftsmen. • Communication channel were limited. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -17
Evolution of HRM Period before revolution industrial • The society was primarily an agriculture economy with limited production. • Number of specialized crafts was limited and was usually carried out within a village or community with apprentices assisting the master craftsmen. • Communication channel were limited. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -17
 Evolution of HRM Period of industrial revolution (1750 to 1850) • Industrial revolution marked the conversion of economy from agriculture based to industry based. • Modernization and increased means if communication gave way to industrial setup. • A department was set up to look into workers wages, welfare and other related issues. This led to emergence of personnel management with the major task as o Worker’s wages and salaries o Worker’s record maintenance o Worker’s housing facilities and health care Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -18
Evolution of HRM Period of industrial revolution (1750 to 1850) • Industrial revolution marked the conversion of economy from agriculture based to industry based. • Modernization and increased means if communication gave way to industrial setup. • A department was set up to look into workers wages, welfare and other related issues. This led to emergence of personnel management with the major task as o Worker’s wages and salaries o Worker’s record maintenance o Worker’s housing facilities and health care Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -18
 Evolution of HRM An important event in industrial revolution was growth of Labour Union (1790) • The works working in the industries or factories were subjected to long working hours and very less wages. • With growing unrest, workers across the world started protest and this led to the establishment of labour unions. • To deal with labour issues at one end and management at the other Personnel Management department had to be capable of politics and diplomacy, thus the industrial relation department emerged. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -19
Evolution of HRM An important event in industrial revolution was growth of Labour Union (1790) • The works working in the industries or factories were subjected to long working hours and very less wages. • With growing unrest, workers across the world started protest and this led to the establishment of labour unions. • To deal with labour issues at one end and management at the other Personnel Management department had to be capable of politics and diplomacy, thus the industrial relation department emerged. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -19
 Evolution of HRM Post Industrial revolution • The term Human resource Management saw a major evolution after 1850. Various studies were released and many experiments were conducted during this period which gave HRM altogether a new meaning and importance. • A brief overview of major theories release during this period is presented below: • Frederick W. Taylor gave principles of scientific management (1857 - 1911) led to the evolution of scientific human resource management approach which was involved in o Worker’s training o Maintaining wage uniformity o Focus on attaining better productivity Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -20
Evolution of HRM Post Industrial revolution • The term Human resource Management saw a major evolution after 1850. Various studies were released and many experiments were conducted during this period which gave HRM altogether a new meaning and importance. • A brief overview of major theories release during this period is presented below: • Frederick W. Taylor gave principles of scientific management (1857 - 1911) led to the evolution of scientific human resource management approach which was involved in o Worker’s training o Maintaining wage uniformity o Focus on attaining better productivity Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -20
 Evolution of HRM Hawthorne studies, conducted by Elton Mayo & Fritz Roethlisberger (1927 to 1940). • Observations and findings of Hawthorne experiment shifted the focus of human resource from increasing worker’s productivity to increasing worker’s efficiency through greater work satisfaction. Douglas Mc. Gregor Theory X and Theory Y (1960) and Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs ( 1954) • These studies and observations led to the transition from the administrative and passive Personnel Management approach to a more dynamic Human Resource Management approach which considered workers as a valuable resource. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -21
Evolution of HRM Hawthorne studies, conducted by Elton Mayo & Fritz Roethlisberger (1927 to 1940). • Observations and findings of Hawthorne experiment shifted the focus of human resource from increasing worker’s productivity to increasing worker’s efficiency through greater work satisfaction. Douglas Mc. Gregor Theory X and Theory Y (1960) and Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs ( 1954) • These studies and observations led to the transition from the administrative and passive Personnel Management approach to a more dynamic Human Resource Management approach which considered workers as a valuable resource. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -21
 Evolution of HRM • As a result of these principles and studies, Human resource management became increasingly line management function, linked to core business operations. • Some of the major activities of HR department are listed as; o Recruitment and selection of skilled workforce. o Motivation and employee benefits o Training and development of workforce o Performance related salaries and appraisals. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -22
Evolution of HRM • As a result of these principles and studies, Human resource management became increasingly line management function, linked to core business operations. • Some of the major activities of HR department are listed as; o Recruitment and selection of skilled workforce. o Motivation and employee benefits o Training and development of workforce o Performance related salaries and appraisals. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -22
 Evolution of HRM Strategic Human Resource Management Approach • With increase in technology and knowledge base industries and as a result of global competition, Human Resource Management is assuming more critical role today. • Its major accomplishment is aligning individual goals and objectives with corporate goals and objectives. • Strategic HRM focuses on actions that differentiate the organization from its competitors and aims to make long term impact on the success of organization. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -23
Evolution of HRM Strategic Human Resource Management Approach • With increase in technology and knowledge base industries and as a result of global competition, Human Resource Management is assuming more critical role today. • Its major accomplishment is aligning individual goals and objectives with corporate goals and objectives. • Strategic HRM focuses on actions that differentiate the organization from its competitors and aims to make long term impact on the success of organization. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -23
 Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -24
Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -24
 Important Trends in Human Resource Management Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -25
Important Trends in Human Resource Management Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -25
 Trends in Human Resource Management • • • Globalization Competition Technological innovation More high-tech & service jobs More knowledge work Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -26
Trends in Human Resource Management • • • Globalization Competition Technological innovation More high-tech & service jobs More knowledge work Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -26
 Globalization • Globalization refers to the tendency of firms to extend their sales, ownership and manufacturing to new markets abroad. • Sales expansion • Lower labor costs • Forming partnerships • Becoming more competitive Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -27
Globalization • Globalization refers to the tendency of firms to extend their sales, ownership and manufacturing to new markets abroad. • Sales expansion • Lower labor costs • Forming partnerships • Becoming more competitive Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -27
 Globalization • Dell, for example, is planning to supply PCs to China is expected to become the largest market for computers in the world. • Companies such as Toyota, Ford, Hyundai build and sell some of their vehicles here in different countries and even ship them to other countries. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -28
Globalization • Dell, for example, is planning to supply PCs to China is expected to become the largest market for computers in the world. • Companies such as Toyota, Ford, Hyundai build and sell some of their vehicles here in different countries and even ship them to other countries. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -28
 Globalization Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -29
Globalization Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -29
 Globalization • Companies expand for several reasons; o Sales expansion o Cut labor costs o New foreign products o Forming partnerships Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -30
Globalization • Companies expand for several reasons; o Sales expansion o Cut labor costs o New foreign products o Forming partnerships Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -30
 Technological Trends • • Smart phones Tablet computers Facebook Job seeking Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -31
Technological Trends • • Smart phones Tablet computers Facebook Job seeking Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -31
 Technological Trends • The impact and growth in the use of smart phones and tablet computers, such as the i. Pad, have opened doors to people and the workplace in a way that previously has never occurred. • The speed of information exchange has contributed to the growth of social networking sites such as Facebook and Linked. In. • Facebook, for example, offers Facebookrecruiting which provides a rapid conduit between employers and job-seekers. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -32
Technological Trends • The impact and growth in the use of smart phones and tablet computers, such as the i. Pad, have opened doors to people and the workplace in a way that previously has never occurred. • The speed of information exchange has contributed to the growth of social networking sites such as Facebook and Linked. In. • Facebook, for example, offers Facebookrecruiting which provides a rapid conduit between employers and job-seekers. Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -32
 Technological Trends • Dell and thousands of other employees established call-center jobs to India. • Zara does not need expensive inventories. Zara operates its own internet based worldwide distribution network Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -33
Technological Trends • Dell and thousands of other employees established call-center jobs to India. • Zara does not need expensive inventories. Zara operates its own internet based worldwide distribution network Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -33
 Trends in the Nature of Work • Technology has also had a huge impact on how people work and on the skills and training today’s workers need. • High-tech jobs • Service jobs • Knowledge work and human capital Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -34
Trends in the Nature of Work • Technology has also had a huge impact on how people work and on the skills and training today’s workers need. • High-tech jobs • Service jobs • Knowledge work and human capital Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -34
 Trends in the Nature of Work • Another trend, human capital, refers to the knowledge, education, training, skills, and expertise of a firm’s workers. • Today’s (and tomorrow’s) best jobs will go to the individuals with the best reading, math, and communication skills. In other words, the best knowledge workers will be hired first Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -35
Trends in the Nature of Work • Another trend, human capital, refers to the knowledge, education, training, skills, and expertise of a firm’s workers. • Today’s (and tomorrow’s) best jobs will go to the individuals with the best reading, math, and communication skills. In other words, the best knowledge workers will be hired first Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -35
 Workforce and Demographic Trends Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -36
Workforce and Demographic Trends Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -36
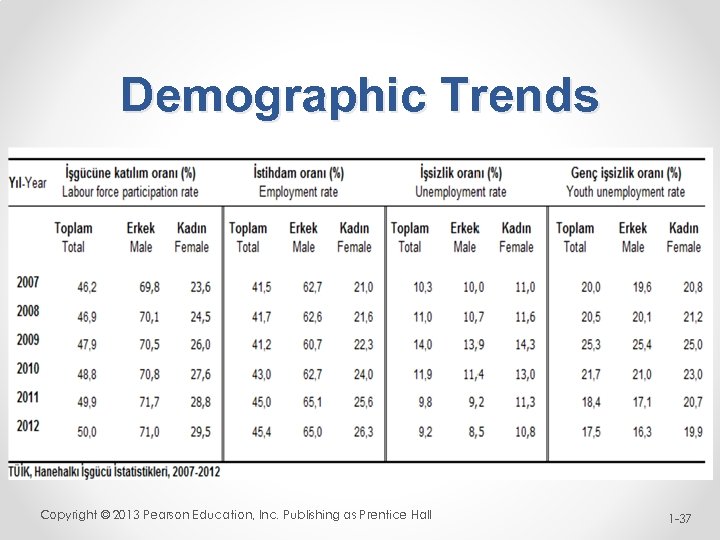 Demographic Trends Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -37
Demographic Trends Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -37
 “Generation Y” Workers • Many younger workers may have different work values than their parents. • Older employees were more work-centric but younger workers tend to be more family-centric or dual-centric. • Considered to be high-performance and high-maintenance • Fair and direct supervisors • Creative challenges • Faster and better workers Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -38
“Generation Y” Workers • Many younger workers may have different work values than their parents. • Older employees were more work-centric but younger workers tend to be more family-centric or dual-centric. • Considered to be high-performance and high-maintenance • Fair and direct supervisors • Creative challenges • Faster and better workers Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -38
 Economic Challenges and Trends • • • Inflation rates Interest rates Gross National Income Economic crisis Recessions Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -39
Economic Challenges and Trends • • • Inflation rates Interest rates Gross National Income Economic crisis Recessions Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 -39
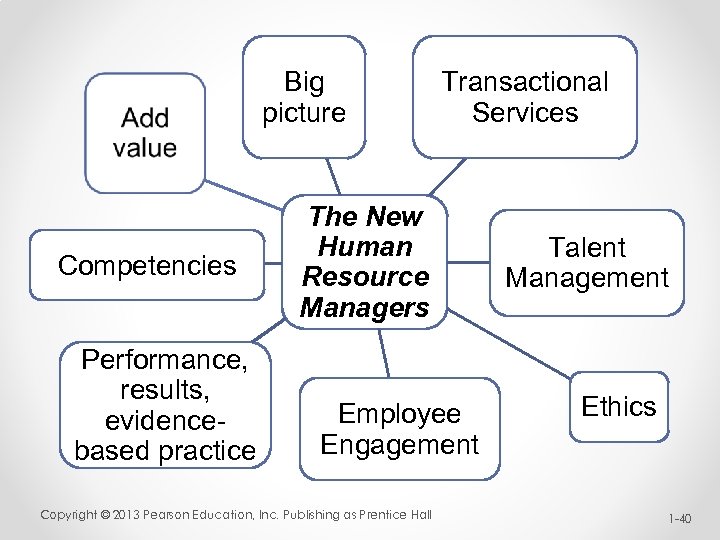 Big picture Competencies Performance, results, evidencebased practice Transactional Services The New Human Resource Managers Employee Engagement Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Talent Management Ethics 1 -40
Big picture Competencies Performance, results, evidencebased practice Transactional Services The New Human Resource Managers Employee Engagement Copyright © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Talent Management Ethics 1 -40


