7553e16ff54589ba8d07ae3474040f2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 1 Introduction to Human Resource Management 1 -1
1 Introduction to Human Resource Management 1 -1
 LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Explain what human resource management is and how it relates to the management process. 2. Show with examples why human resource management is important to all managers. 3. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line and staff (HR) managers. 4. Briefly discuss and illustrate each of the important trends influencing human resource management. 5. List and briefly describe important trends in human resource management. 6. Define and give an example of evidence-based human resource management. 7. Outline the plan of this book. 1– 2
LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Explain what human resource management is and how it relates to the management process. 2. Show with examples why human resource management is important to all managers. 3. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line and staff (HR) managers. 4. Briefly discuss and illustrate each of the important trends influencing human resource management. 5. List and briefly describe important trends in human resource management. 6. Define and give an example of evidence-based human resource management. 7. Outline the plan of this book. 1– 2
 Human Resource Management at Work • What Is Human Resource Management (HRM)? Ø The process of acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating employees, and of attending to their labor relations, health and safety, and fairness concerns. • Organization Ø People with formally assigned roles who work together to achieve the organization’s goals. • Manager Ø The person responsible for accomplishing the organization’s goals, and who does so by managing the efforts of the organization’s people. 1– 3
Human Resource Management at Work • What Is Human Resource Management (HRM)? Ø The process of acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating employees, and of attending to their labor relations, health and safety, and fairness concerns. • Organization Ø People with formally assigned roles who work together to achieve the organization’s goals. • Manager Ø The person responsible for accomplishing the organization’s goals, and who does so by managing the efforts of the organization’s people. 1– 3
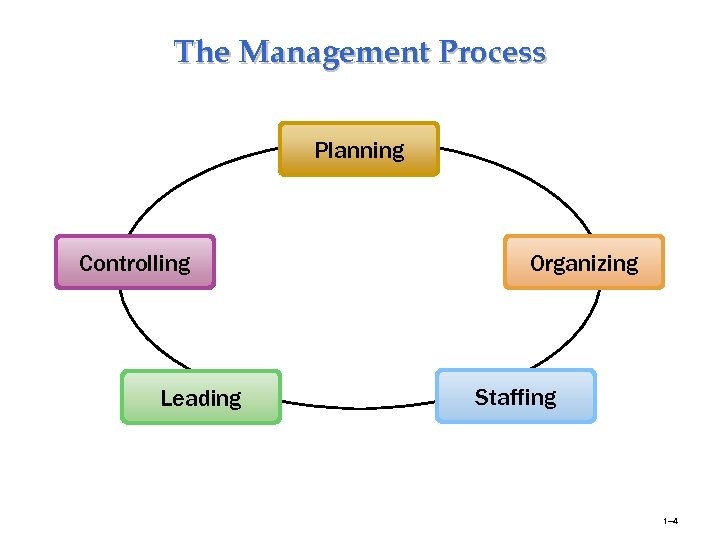 The Management Process Planning Controlling Leading Organizing Staffing 1– 4
The Management Process Planning Controlling Leading Organizing Staffing 1– 4
 The Management Process • Planning: Establishing goals and standards; developing rules and procedures; developing plans and forecasting. • Organizing: Giving each subordinate a specific task; establishing departments; delegating authority to subordinates; establishing channels of authority and communication; coordinating the work of subordinates. 1– 5
The Management Process • Planning: Establishing goals and standards; developing rules and procedures; developing plans and forecasting. • Organizing: Giving each subordinate a specific task; establishing departments; delegating authority to subordinates; establishing channels of authority and communication; coordinating the work of subordinates. 1– 5
 The Management Process • Staffing: Determining what type of people should be hired Recruiting prospective employees Selecting employees Setting performance standards Compensating employees Evaluating performance Counseling employees Training and developing employees 1– 6
The Management Process • Staffing: Determining what type of people should be hired Recruiting prospective employees Selecting employees Setting performance standards Compensating employees Evaluating performance Counseling employees Training and developing employees 1– 6
 The Management Process • Leading: Getting others to get the job done; maintaining morale; motivating subordinates. • Controlling: - Setting standards such as sales quotas, quality standards, or production levels - Checking to see how actual performance compares with this standards - Taking corrective action as needed. 1– 7
The Management Process • Leading: Getting others to get the job done; maintaining morale; motivating subordinates. • Controlling: - Setting standards such as sales quotas, quality standards, or production levels - Checking to see how actual performance compares with this standards - Taking corrective action as needed. 1– 7
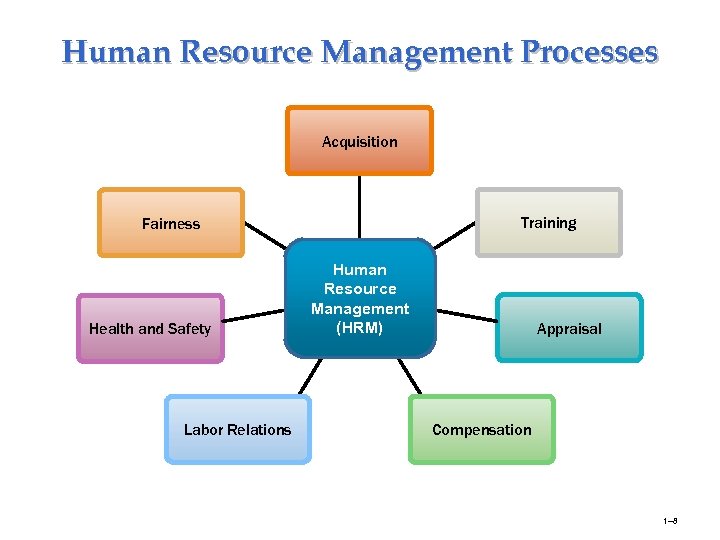 Human Resource Management Processes Acquisition Training Fairness Health and Safety Labor Relations Human Resource Management (HRM) Appraisal Compensation 1– 8
Human Resource Management Processes Acquisition Training Fairness Health and Safety Labor Relations Human Resource Management (HRM) Appraisal Compensation 1– 8
 Personnel Aspects of a Manager’s Job • Conducting job analyses • Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates • Selecting job candidates • Orienting and training new employees • Managing wages and salaries • Providing incentives and benefits • Appraising performance • Communicating • Training and developing managers • Building employee commitment 1– 9
Personnel Aspects of a Manager’s Job • Conducting job analyses • Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates • Selecting job candidates • Orienting and training new employees • Managing wages and salaries • Providing incentives and benefits • Appraising performance • Communicating • Training and developing managers • Building employee commitment 1– 9
 Personnel Mistakes • Hire the wrong person for the job • Experience high turnover • Have your people not doing their best • Waste time with useless interviews • Have your firm in court because of discriminatory actions • Have some employees think their salaries are unfair and inequitable relative to others in the organization • Allow a lack of training to undermine your department’s effectiveness • Commit any unfair labor practices 1– 10
Personnel Mistakes • Hire the wrong person for the job • Experience high turnover • Have your people not doing their best • Waste time with useless interviews • Have your firm in court because of discriminatory actions • Have some employees think their salaries are unfair and inequitable relative to others in the organization • Allow a lack of training to undermine your department’s effectiveness • Commit any unfair labor practices 1– 10
 Line and Staff Aspects of HRM Authority is the right to make decisions, to direct the work of others, and to give orders • Line Manager Ø Is authorized (has line authority) to direct the work of subordinates and is responsible for accomplishing the organization’s tasks. • Staff Manager Ø Assists and advises line managers. Ø Has functional authority to coordinate personnel activities and enforce organization policies. 1– 11
Line and Staff Aspects of HRM Authority is the right to make decisions, to direct the work of others, and to give orders • Line Manager Ø Is authorized (has line authority) to direct the work of subordinates and is responsible for accomplishing the organization’s tasks. • Staff Manager Ø Assists and advises line managers. Ø Has functional authority to coordinate personnel activities and enforce organization policies. 1– 11
 Line Managers’ HRM Responsibilities 1. Placing the right person on the right job 2. Starting new employees in the organization (orientation) 3. Training employees for jobs that are new to them 4. Improving the job performance of each person 5. Gaining creative cooperation and developing smooth working relationships 6. Interpreting the firm’s policies and procedures 7. Controlling labor costs 8. Developing the abilities of each person 9. Creating and maintaining department morale 10. Protecting employees’ health and physical condition 1– 12
Line Managers’ HRM Responsibilities 1. Placing the right person on the right job 2. Starting new employees in the organization (orientation) 3. Training employees for jobs that are new to them 4. Improving the job performance of each person 5. Gaining creative cooperation and developing smooth working relationships 6. Interpreting the firm’s policies and procedures 7. Controlling labor costs 8. Developing the abilities of each person 9. Creating and maintaining department morale 10. Protecting employees’ health and physical condition 1– 12
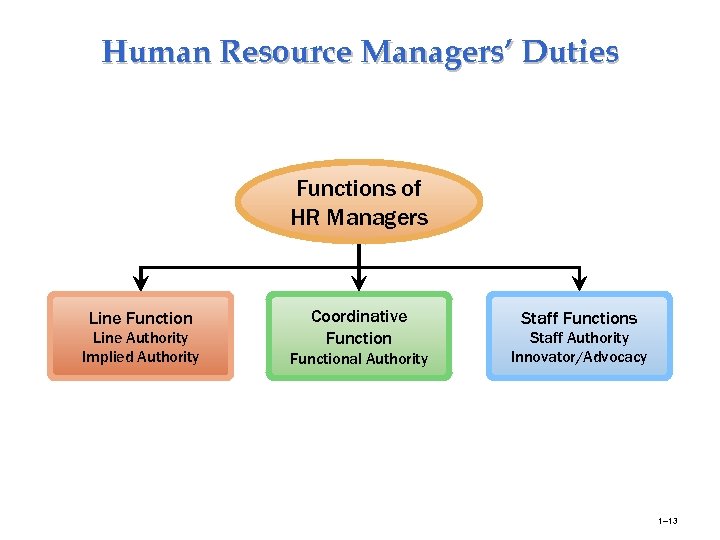 Human Resource Managers’ Duties Functions of HR Managers Line Function Line Authority Implied Authority Coordinative Functional Authority Staff Functions Staff Authority Innovator/Advocacy 1– 13
Human Resource Managers’ Duties Functions of HR Managers Line Function Line Authority Implied Authority Coordinative Functional Authority Staff Functions Staff Authority Innovator/Advocacy 1– 13
 FIGURE 1– 1 Human Resources Organization Chart for a Large Organization 1– 14
FIGURE 1– 1 Human Resources Organization Chart for a Large Organization 1– 14
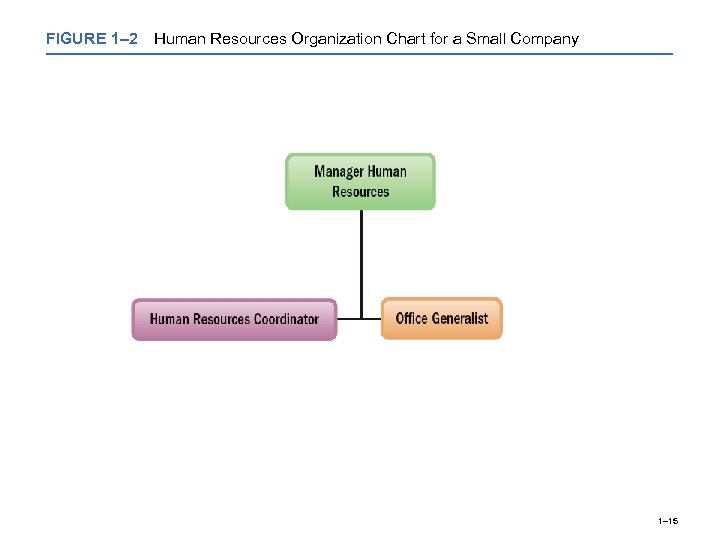 FIGURE 1– 2 Human Resources Organization Chart for a Small Company 1– 15
FIGURE 1– 2 Human Resources Organization Chart for a Small Company 1– 15
 Human Resource Specialties Recruiter Labor relations specialist EEO coordinator Human Resource Specialties Job analyst Training specialist Compensation manager 1– 16
Human Resource Specialties Recruiter Labor relations specialist EEO coordinator Human Resource Specialties Job analyst Training specialist Compensation manager 1– 16
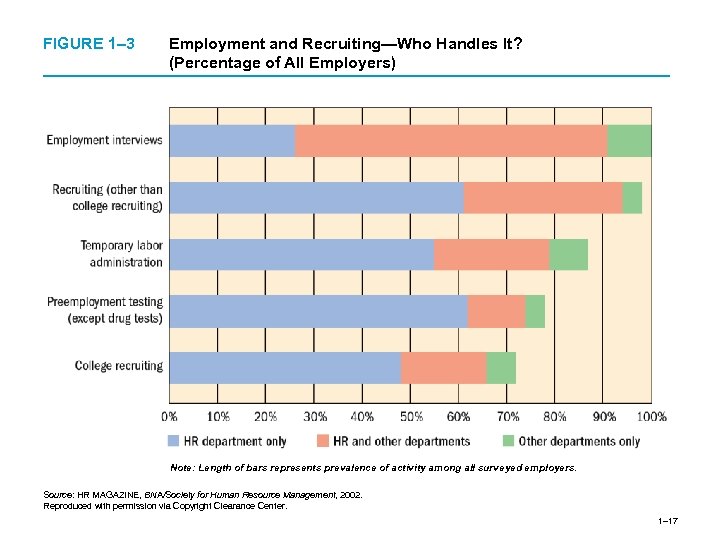 FIGURE 1– 3 Employment and Recruiting—Who Handles It? (Percentage of All Employers) Note: Length of bars represents prevalence of activity among all surveyed employers. Source: HR MAGAZINE, BNA/Society for Human Resource Management, 2002. Reproduced with permission via Copyright Clearance Center. 1– 17
FIGURE 1– 3 Employment and Recruiting—Who Handles It? (Percentage of All Employers) Note: Length of bars represents prevalence of activity among all surveyed employers. Source: HR MAGAZINE, BNA/Society for Human Resource Management, 2002. Reproduced with permission via Copyright Clearance Center. 1– 17
 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Globalization and Competition Trends Indebtedness (“Leverage”) and Deregulation Technological Trends in HR Management Workforce and Demographic Trends in the Nature of Work Economic Challenges and Trends 1– 18
Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Globalization and Competition Trends Indebtedness (“Leverage”) and Deregulation Technological Trends in HR Management Workforce and Demographic Trends in the Nature of Work Economic Challenges and Trends 1– 18
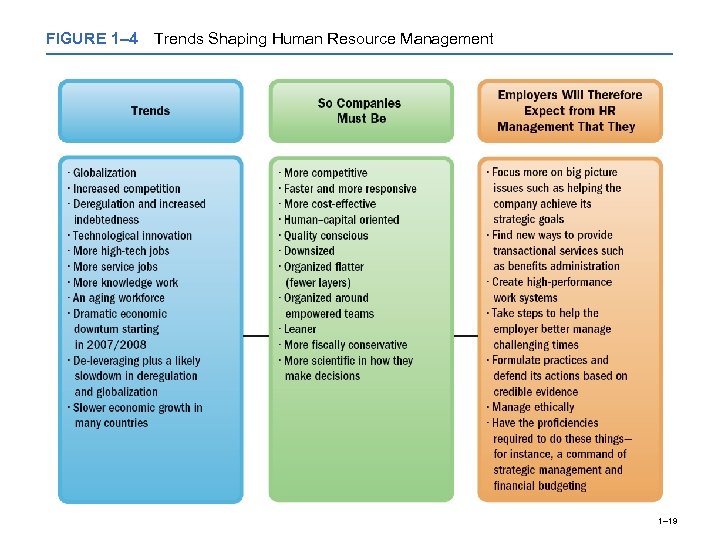 FIGURE 1– 4 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management 1– 19
FIGURE 1– 4 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management 1– 19
 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Globalization Trends: • Firms extend sales, ownership and • • manufacturing to other countries Sales expansion Lower labor costs Forming partnerships Offshoring 1– 20
Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Globalization Trends: • Firms extend sales, ownership and • • manufacturing to other countries Sales expansion Lower labor costs Forming partnerships Offshoring 1– 20
 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Indebtedness (“Leverage”) and Deregulation: • • • Stock brokering by banks Lending practices Spending > Income Balance of payments Treasury bonds 1– 21
Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Indebtedness (“Leverage”) and Deregulation: • • • Stock brokering by banks Lending practices Spending > Income Balance of payments Treasury bonds 1– 21
 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Technological Trends: • Virtual online communities, • Virtual design environments • Internet-based distribution systems have enabled firms to become more competitive. HR faces the challenge of quickly applying technology to the task of improving its own operations. 1– 22
Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Technological Trends: • Virtual online communities, • Virtual design environments • Internet-based distribution systems have enabled firms to become more competitive. HR faces the challenge of quickly applying technology to the task of improving its own operations. 1– 22
 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Trends in the Nature of Work: Jobs are changing due to new technological demands. Nontraditional workers, such as those who hold multiple jobs, “contingent” or part-time workers, or people working in alternative work arrangements, enable employers to keep costs down. - High-Tech Jobs - Service Jobs - Human Capital 1– 23
Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Trends in the Nature of Work: Jobs are changing due to new technological demands. Nontraditional workers, such as those who hold multiple jobs, “contingent” or part-time workers, or people working in alternative work arrangements, enable employers to keep costs down. - High-Tech Jobs - Service Jobs - Human Capital 1– 23
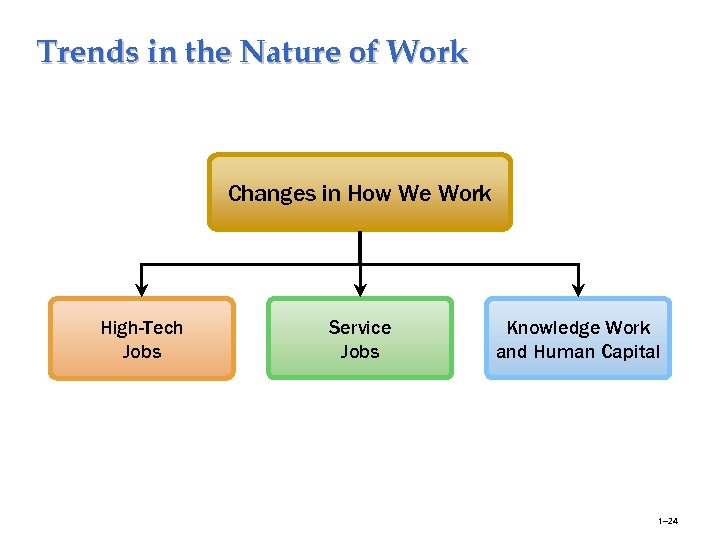 Trends in the Nature of Work Changes in How We Work High-Tech Jobs Service Jobs Knowledge Work and Human Capital 1– 24
Trends in the Nature of Work Changes in How We Work High-Tech Jobs Service Jobs Knowledge Work and Human Capital 1– 24
 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Workforce Demographic Trends: The labor force is getting older and more multiethnic. The aging labor force presents significant changes in terms of potential labor shortages, and many firms are instituting new policies aimed at encouraging employees to stay, or at attracting previously retired employees. 1– 25
Trends Shaping Human Resource Management Workforce Demographic Trends: The labor force is getting older and more multiethnic. The aging labor force presents significant changes in terms of potential labor shortages, and many firms are instituting new policies aimed at encouraging employees to stay, or at attracting previously retired employees. 1– 25
 Demographic Trends 1 -26
Demographic Trends 1 -26
 “Generation Y” Workers • Considered to be high-performance and high-maintenance • Fair and direct supervisors • Creative challenges • Day 1 impact • Small goals • Faster and better workers 1 -27
“Generation Y” Workers • Considered to be high-performance and high-maintenance • Fair and direct supervisors • Creative challenges • Day 1 impact • Small goals • Faster and better workers 1 -27
 Retirees, Nontraditional Workers, Workers from Abroad • Bringing retirees back • Multiple jobs • Contingent workers • Alternative work arrangements • Workers from abroad 1 -28
Retirees, Nontraditional Workers, Workers from Abroad • Bringing retirees back • Multiple jobs • Contingent workers • Alternative work arrangements • Workers from abroad 1 -28
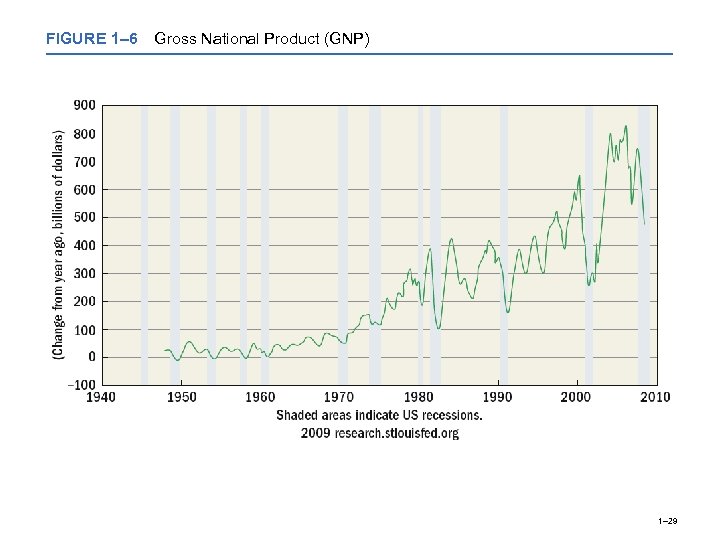 FIGURE 1– 6 Gross National Product (GNP) 1– 29
FIGURE 1– 6 Gross National Product (GNP) 1– 29
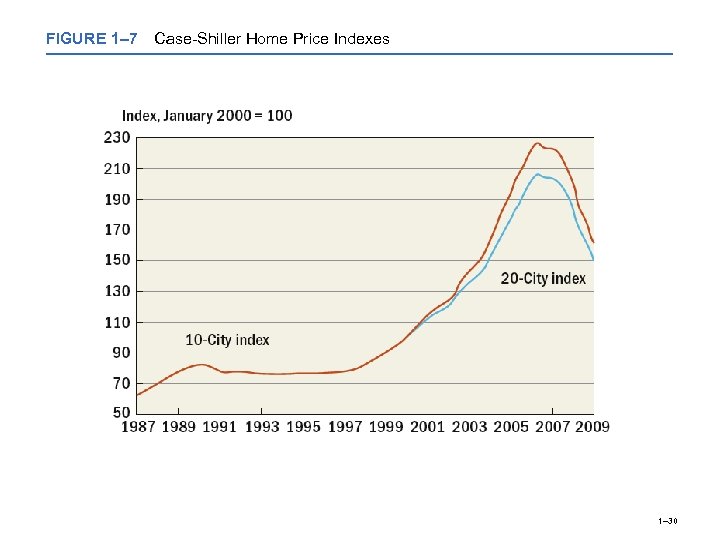 FIGURE 1– 7 Case-Shiller Home Price Indexes 1– 30
FIGURE 1– 7 Case-Shiller Home Price Indexes 1– 30
 Important Trends in HRM Add value Competencies Performance, results, evidencebased practice Big picture Transactional Services The New Human Resource Managers Employee Engagement Talent Management Ethics 1– 31
Important Trends in HRM Add value Competencies Performance, results, evidencebased practice Big picture Transactional Services The New Human Resource Managers Employee Engagement Talent Management Ethics 1– 31
 Managing Ethics • Ethics Ø Standards that someone uses to decide what his or her conduct should be • HRM-related Ethical Issues Ø Workplace safety Ø Security of employee records Ø Employee theft Ø Affirmative action Ø Comparable work Ø Employee privacy rights 1– 32
Managing Ethics • Ethics Ø Standards that someone uses to decide what his or her conduct should be • HRM-related Ethical Issues Ø Workplace safety Ø Security of employee records Ø Employee theft Ø Affirmative action Ø Comparable work Ø Employee privacy rights 1– 32
 HR Certification • HR is becoming more professionalized. • Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) Ø SHRM’s Human Resource Certification Institute (HRCI) v PHR (Professional in HR) certificate v GPHR (Global Professional in HR) certificate v SPHR (Senior Professional in HR) certificate 1– 33
HR Certification • HR is becoming more professionalized. • Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) Ø SHRM’s Human Resource Certification Institute (HRCI) v PHR (Professional in HR) certificate v GPHR (Global Professional in HR) certificate v SPHR (Senior Professional in HR) certificate 1– 33
 The Plan of This Book: Basic Themes • HRM is the responsibility of every manager. • The workforce is becoming increasingly diverse. • Current economic challenges require that HR managers develop new and better skills to effectively and efficiently deliver and manage HR services. • The intensely competitive nature of business today means human resource managers must defend their plans and contributions in measurable terms. 1– 34
The Plan of This Book: Basic Themes • HRM is the responsibility of every manager. • The workforce is becoming increasingly diverse. • Current economic challenges require that HR managers develop new and better skills to effectively and efficiently deliver and manage HR services. • The intensely competitive nature of business today means human resource managers must defend their plans and contributions in measurable terms. 1– 34
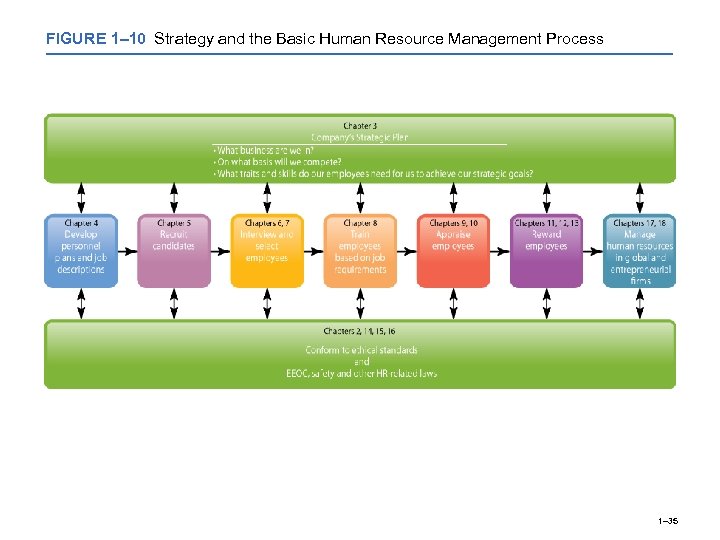 FIGURE 1– 10 Strategy and the Basic Human Resource Management Process 1– 35
FIGURE 1– 10 Strategy and the Basic Human Resource Management Process 1– 35
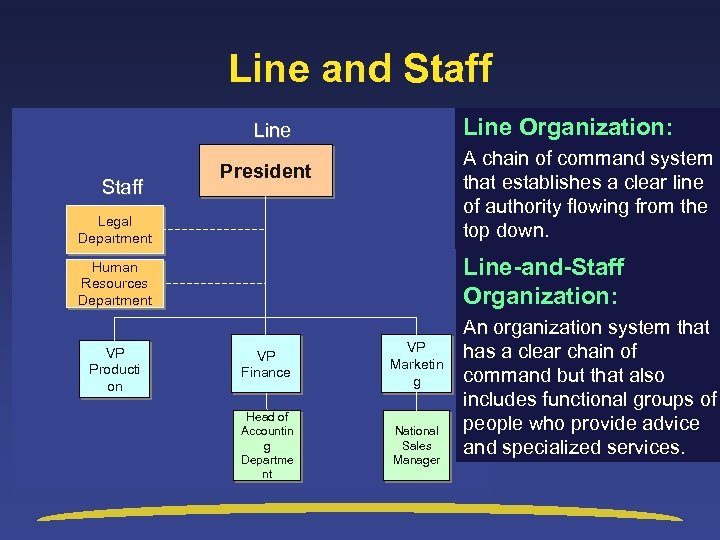 Line and Staff Line Organization: Line Legal Department A chain of command system that establishes a clear line of authority flowing from the top down. Human Resources Department Line-and-Staff Organization: Staff VP Producti on President VP Finance VP Marketin g Head of Accountin g Departme nt National Sales Manager An organization system that has a clear chain of command but that also includes functional groups of people who provide advice and specialized services.
Line and Staff Line Organization: Line Legal Department A chain of command system that establishes a clear line of authority flowing from the top down. Human Resources Department Line-and-Staff Organization: Staff VP Producti on President VP Finance VP Marketin g Head of Accountin g Departme nt National Sales Manager An organization system that has a clear chain of command but that also includes functional groups of people who provide advice and specialized services.
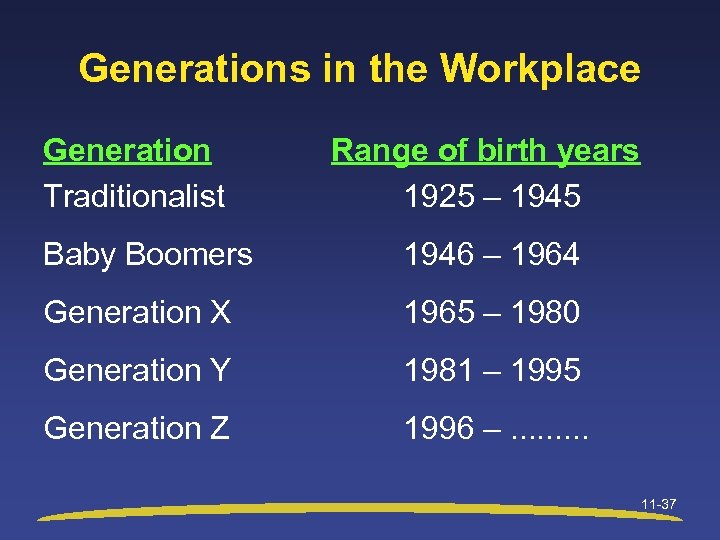 Generations in the Workplace Generation Traditionalist Range of birth years 1925 – 1945 Baby Boomers 1946 – 1964 Generation X 1965 – 1980 Generation Y 1981 – 1995 Generation Z 1996 –. . 11 -37
Generations in the Workplace Generation Traditionalist Range of birth years 1925 – 1945 Baby Boomers 1946 – 1964 Generation X 1965 – 1980 Generation Y 1981 – 1995 Generation Z 1996 –. . 11 -37
 Characteristics of Generation Y • They want fair and direct supervisors who are highly engaged in their professional development • They seek out creative challenges and view colleagues as vast resources from whom to gain knowledge • They want to make important impact on Day 1. • They want small goals with tight deadlines so they can build up ownership of task • They aim to work faster and better than other workers 11 -38
Characteristics of Generation Y • They want fair and direct supervisors who are highly engaged in their professional development • They seek out creative challenges and view colleagues as vast resources from whom to gain knowledge • They want to make important impact on Day 1. • They want small goals with tight deadlines so they can build up ownership of task • They aim to work faster and better than other workers 11 -38
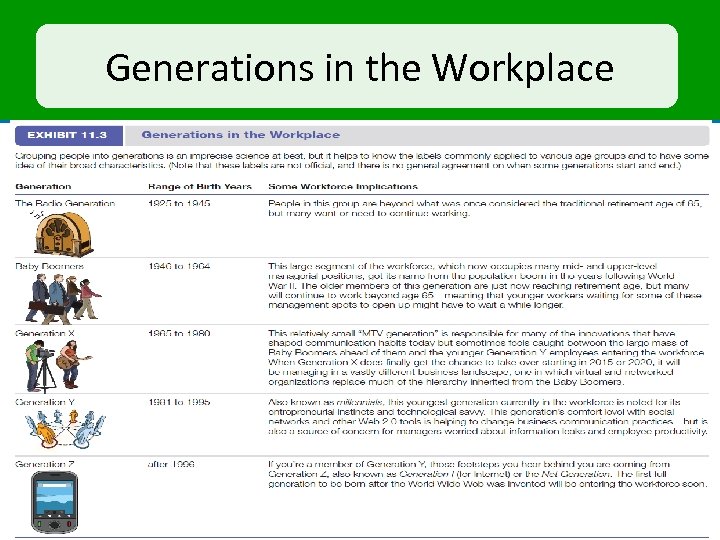 Generations in the Workplace 11 -39
Generations in the Workplace 11 -39
 KEY TERMS organization manager management process human resource management (HRM) authority line authority staff authority line manager staff manager functional authority globalization human capital 1– 40
KEY TERMS organization manager management process human resource management (HRM) authority line authority staff authority line manager staff manager functional authority globalization human capital 1– 40
 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. 1– 41
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. 1– 41


