87d29d1bba702196fe20ffe68d854dc3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 1 Introduction to 1 & 2 Kings
1 Introduction to 1 & 2 Kings
 1 & 2 Kings Ø Originally one book in the Hebrew O. T. Ø Split into two books in the Greek Septuagint Ø Author: Unknown Ø Talmudic tradition says it was written by the prophet Jeremiah – except for the last two chapters 2
1 & 2 Kings Ø Originally one book in the Hebrew O. T. Ø Split into two books in the Greek Septuagint Ø Author: Unknown Ø Talmudic tradition says it was written by the prophet Jeremiah – except for the last two chapters 2
 1 & 2 Kings 3 Ø Like 1 & 2 Samuel, deals with the history of two kingdoms: § The northern kingdom of Israel § The southern kingdom of Judah Ø 1 & 2 Chronicles deals mainly with the southern kingdom of Judah
1 & 2 Kings 3 Ø Like 1 & 2 Samuel, deals with the history of two kingdoms: § The northern kingdom of Israel § The southern kingdom of Judah Ø 1 & 2 Chronicles deals mainly with the southern kingdom of Judah
 Dates of 1 & 2 Kings 4 Ø The events of 1 & 2 Kings span approximately 425 years: § From King David confirming Solomon king around 986 B. C. § To Evil-Merodach, king of Babylon, releasing Jehoiachin, king of Judah, from prison around 561 B. C. (25 years after the destruction of the temple) Ø So 45 chapters were probably written before the 586 BC fall of Jerusalem and 2 more chapters were added afterwards.
Dates of 1 & 2 Kings 4 Ø The events of 1 & 2 Kings span approximately 425 years: § From King David confirming Solomon king around 986 B. C. § To Evil-Merodach, king of Babylon, releasing Jehoiachin, king of Judah, from prison around 561 B. C. (25 years after the destruction of the temple) Ø So 45 chapters were probably written before the 586 BC fall of Jerusalem and 2 more chapters were added afterwards.
 Contribution to the Bible 1. Tells us about the rise, division, decline and fall of the kingdom of Israel 2. Synchronizes the histories of the monarchies of the kings of Israel and Judah 3. Gives evaluations of each king’s reign, using the reign of King David as the standard. 4. Describes the prophetic ministries of several of God’s prophets 5
Contribution to the Bible 1. Tells us about the rise, division, decline and fall of the kingdom of Israel 2. Synchronizes the histories of the monarchies of the kings of Israel and Judah 3. Gives evaluations of each king’s reign, using the reign of King David as the standard. 4. Describes the prophetic ministries of several of God’s prophets 5
 Outline of Kings 6 1. The united kingdom (1 Kings 1– 11) • Solomon’s wisdom and temple • Jeraboam’s prophecy (1 Kings 11: 26 -40) 2. The divided kingdom (1 Kings 12 – 2 Kings 17) § From Rehoboam’s foolish and rude choice (1 Kings 12: 1 -17) § 10 tribes rebel and only Judah and Benjamin 3. The surviving kingdom of Judah (2 Kings 18– 25) § From the reign of Hezekiah § To the deportation of Judah to Babylon § To the release of Jehoiachin in Babylon
Outline of Kings 6 1. The united kingdom (1 Kings 1– 11) • Solomon’s wisdom and temple • Jeraboam’s prophecy (1 Kings 11: 26 -40) 2. The divided kingdom (1 Kings 12 – 2 Kings 17) § From Rehoboam’s foolish and rude choice (1 Kings 12: 1 -17) § 10 tribes rebel and only Judah and Benjamin 3. The surviving kingdom of Judah (2 Kings 18– 25) § From the reign of Hezekiah § To the deportation of Judah to Babylon § To the release of Jehoiachin in Babylon
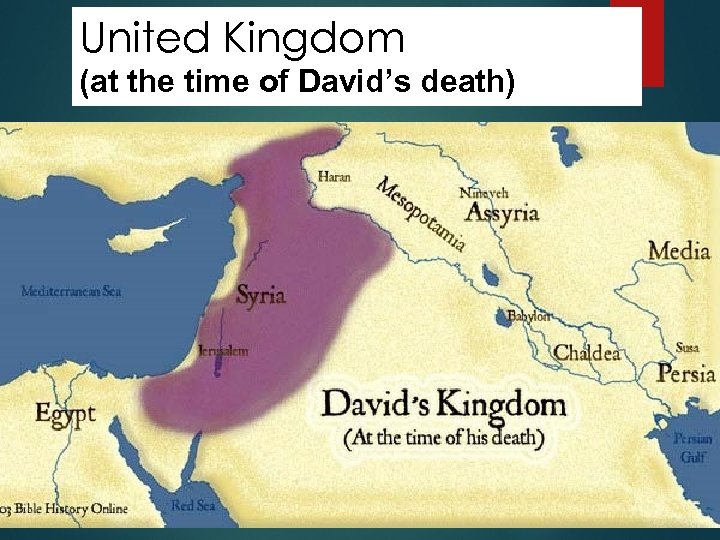 United Kingdom (at the time of David’s death) 7
United Kingdom (at the time of David’s death) 7
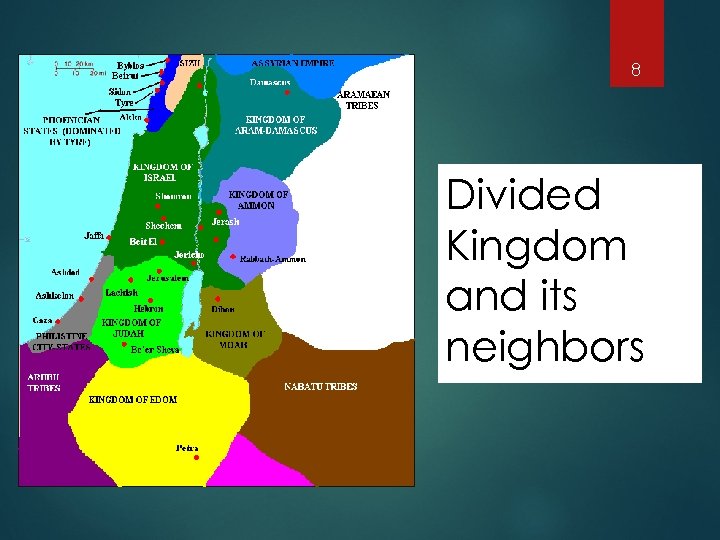 8 Divided Kingdom and its neighbors
8 Divided Kingdom and its neighbors
 9 Introduction to 1 & 2 Chronicles
9 Introduction to 1 & 2 Chronicles
 1 & 2 Chronicles 10 Ø Originally one book in the Hebrew O. T. Ø Split into two books in the Greek Septuagint Ø Organized as the last book of the Hebrew Bible Ø Talmudic tradition says it was written by the priest, Ezra Ø Perhaps it was written by one of Ezra’s contemporaries Ø It is quite similar in style to the book of Ezra Ø Chronicles and Ezra may have been one consecutive history, like Luke and Acts
1 & 2 Chronicles 10 Ø Originally one book in the Hebrew O. T. Ø Split into two books in the Greek Septuagint Ø Organized as the last book of the Hebrew Bible Ø Talmudic tradition says it was written by the priest, Ezra Ø Perhaps it was written by one of Ezra’s contemporaries Ø It is quite similar in style to the book of Ezra Ø Chronicles and Ezra may have been one consecutive history, like Luke and Acts
 Emphasis of Chronicles Ø The temple / tabernacle 11
Emphasis of Chronicles Ø The temple / tabernacle 11
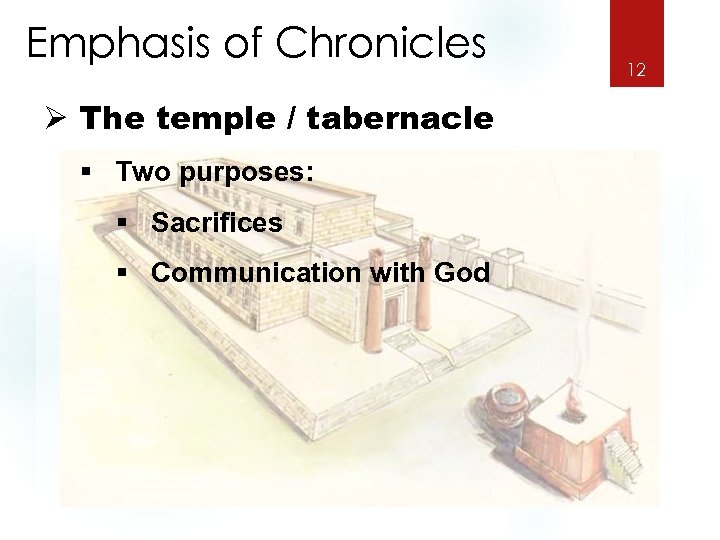 Emphasis of Chronicles Ø The temple / tabernacle § Two purposes: § Sacrifices § Communication with God 12
Emphasis of Chronicles Ø The temple / tabernacle § Two purposes: § Sacrifices § Communication with God 12
 Emphasis of Chronicles 13 Ø The temple / tabernacle § Chronicles omits northern kingdom’s kings because they had no ties with the temple § Special mention is made of Jewish kings who restored the temple: § Asa § Hezekiah § Jehoshaphat § Josiah § Joash
Emphasis of Chronicles 13 Ø The temple / tabernacle § Chronicles omits northern kingdom’s kings because they had no ties with the temple § Special mention is made of Jewish kings who restored the temple: § Asa § Hezekiah § Jehoshaphat § Josiah § Joash
 First Temple 14 Ø A story of the first Jewish temple § Idea – by David (1014 B. C. ) § Preparation – by David (985 B. C. ) § Construction – by Solomon (982 -975 B. C. ) § Dedication – by Solomon (972 B. C. ) § Defiling – by bad kings § Cleansing – by good kings § Destruction – by Nebuchadnezzar (586 B. C. )
First Temple 14 Ø A story of the first Jewish temple § Idea – by David (1014 B. C. ) § Preparation – by David (985 B. C. ) § Construction – by Solomon (982 -975 B. C. ) § Dedication – by Solomon (972 B. C. ) § Defiling – by bad kings § Cleansing – by good kings § Destruction – by Nebuchadnezzar (586 B. C. )
 Second Temple 15 Ø Briefly mentioned at end of Chronicles § Idea – 1 st prophesied by Isaiah (~712 B. C. ) § Idea – proclaimed by Cyrus (539 B. C. ) § Preparation – elders & priests (539 B. C. ) § Foundation – by Zerubbabel (535 B. C. ) § Completion – by Zerubbabel (517 B. C. ) § Dedication – by priests (516 B. C. ) § Destruction – by Titus (70 A. D. )
Second Temple 15 Ø Briefly mentioned at end of Chronicles § Idea – 1 st prophesied by Isaiah (~712 B. C. ) § Idea – proclaimed by Cyrus (539 B. C. ) § Preparation – elders & priests (539 B. C. ) § Foundation – by Zerubbabel (535 B. C. ) § Completion – by Zerubbabel (517 B. C. ) § Dedication – by priests (516 B. C. ) § Destruction – by Titus (70 A. D. )
 Emphasis of Chronicles Ø Priests / the priesthood 1. They had to be men from the tribe of Levi 2. Offered gifts and sacrifices for sins 3. Compassionate with sinners 4. Interceded for sinners 5. Appointed by God 16
Emphasis of Chronicles Ø Priests / the priesthood 1. They had to be men from the tribe of Levi 2. Offered gifts and sacrifices for sins 3. Compassionate with sinners 4. Interceded for sinners 5. Appointed by God 16
 Emphasis of Chronicles 17 Ø God’s faithfulness in preserving theocratic line of Christ 1 Chronicles 1 -9 Matthew 1 Luke 3 Adam to Abraham to Jesus to Adam Zerubabbel Christ (75 generations) (56 generations) (42 generations)
Emphasis of Chronicles 17 Ø God’s faithfulness in preserving theocratic line of Christ 1 Chronicles 1 -9 Matthew 1 Luke 3 Adam to Abraham to Jesus to Adam Zerubabbel Christ (75 generations) (56 generations) (42 generations)
 Contribution to the Bible 18 1. Provides the most comprehensive genealogical tables in the Bible 2. Shows the work of God in preserving a people for Himself from the beginning of human history to the period after the Babylonian exile – more than other books 3. Demonstrates God’s keeping His covenant promises in maintaining the Davidic line through the centuries
Contribution to the Bible 18 1. Provides the most comprehensive genealogical tables in the Bible 2. Shows the work of God in preserving a people for Himself from the beginning of human history to the period after the Babylonian exile – more than other books 3. Demonstrates God’s keeping His covenant promises in maintaining the Davidic line through the centuries
 Outline of Chronicles 1. The royal line of David (1 Chr. 1 -9) § Genealogy; around 3500 years 2. The reign of David (1 Chr. 10 -29) § History; 33 years 3. The reign of Solomon (2 Chr. 1 -9) § 40 years 4. Reigns of the kings of Judah (2 Chr. 1036) § 393 years 19
Outline of Chronicles 1. The royal line of David (1 Chr. 1 -9) § Genealogy; around 3500 years 2. The reign of David (1 Chr. 10 -29) § History; 33 years 3. The reign of Solomon (2 Chr. 1 -9) § 40 years 4. Reigns of the kings of Judah (2 Chr. 1036) § 393 years 19
 Israelite Dynasties Year B. C. Kings of Judah 20 Kings of Israel 933 1 Rehoboam (bad) 1 Jeroboam I 915 2 Abijah (bad) 912 3 Asa (good) 911 910 887 2 Nadab 3 Baasha 4 Elah
Israelite Dynasties Year B. C. Kings of Judah 20 Kings of Israel 933 1 Rehoboam (bad) 1 Jeroboam I 915 2 Abijah (bad) 912 3 Asa (good) 911 910 887 2 Nadab 3 Baasha 4 Elah
 Israelite Dynasties 886 875 874 855 854 4 Jehoshaphat (good) 21 5 Zimri 6 Omri 7 Ahab 8 Ahaziah 9 Joram
Israelite Dynasties 886 875 874 855 854 4 Jehoshaphat (good) 21 5 Zimri 6 Omri 7 Ahab 8 Ahaziah 9 Joram
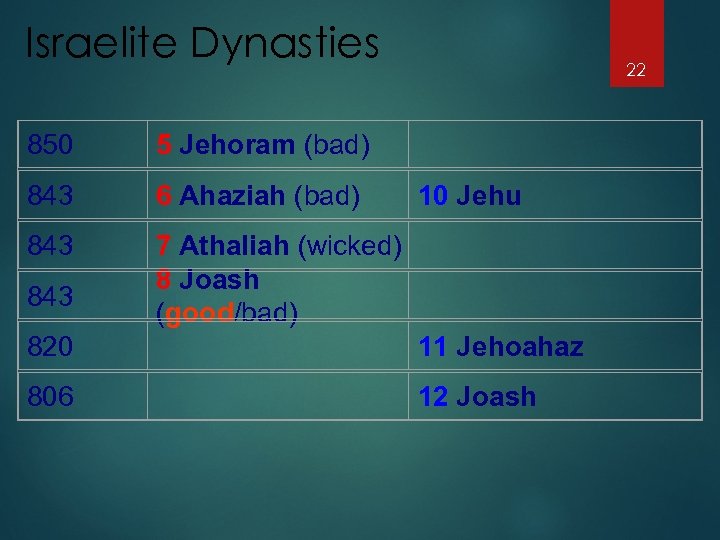 Israelite Dynasties 22 850 5 Jehoram (bad) 843 6 Ahaziah (bad) 843 7 Athaliah (wicked) 8 Joash (good/bad) 11 Jehoahaz 12 Joash 843 820 806 10 Jehu
Israelite Dynasties 22 850 5 Jehoram (bad) 843 6 Ahaziah (bad) 843 7 Athaliah (wicked) 8 Joash (good/bad) 11 Jehoahaz 12 Joash 843 820 806 10 Jehu
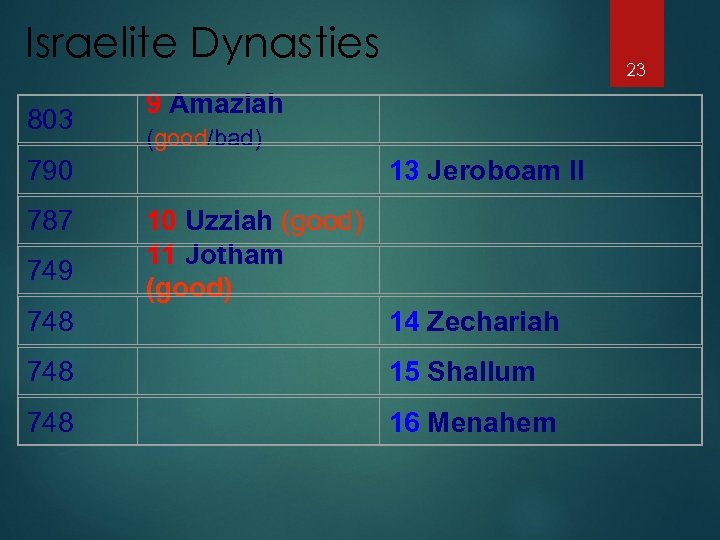 Israelite Dynasties 803 790 787 749 748 748 9 Amaziah (good/bad) 23 13 Jeroboam II 10 Uzziah (good) 11 Jotham (good) 14 Zechariah 15 Shallum 16 Menahem
Israelite Dynasties 803 790 787 749 748 748 9 Amaziah (good/bad) 23 13 Jeroboam II 10 Uzziah (good) 11 Jotham (good) 14 Zechariah 15 Shallum 16 Menahem
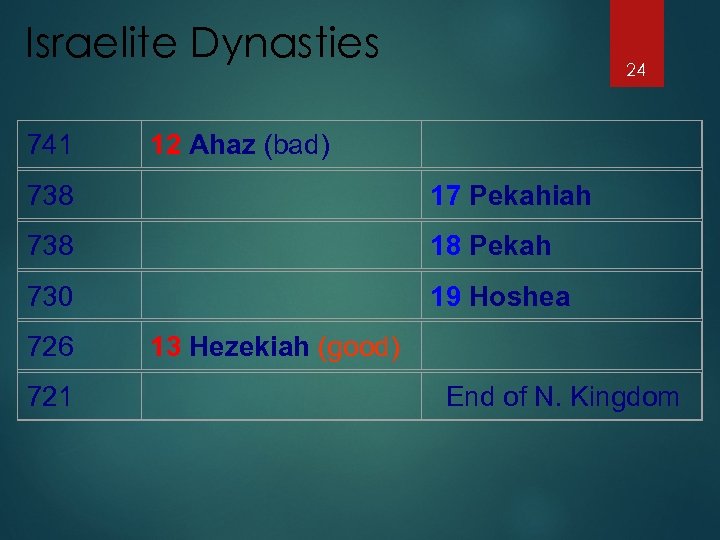 Israelite Dynasties 741 738 730 726 721 12 Ahaz (bad) 13 Hezekiah (good) 24 17 Pekahiah 18 Pekah 19 Hoshea End of N. Kingdom
Israelite Dynasties 741 738 730 726 721 12 Ahaz (bad) 13 Hezekiah (good) 24 17 Pekahiah 18 Pekah 19 Hoshea End of N. Kingdom
 Israelite Dynasties 697 641 639 608 597 586 14 Manasseh (evil, but repented) 15 Amon (bad) 16 Josiah (good) 17 Jehoahaz (bad) 18 Jehoiakim (bad) 19 Jehoiachin (bad) 20 Zedekiah (bad) End of Southern Kingdom 25
Israelite Dynasties 697 641 639 608 597 586 14 Manasseh (evil, but repented) 15 Amon (bad) 16 Josiah (good) 17 Jehoahaz (bad) 18 Jehoiakim (bad) 19 Jehoiachin (bad) 20 Zedekiah (bad) End of Southern Kingdom 25
 Comparison of 2 Histories Samuel and Kings Israel’s history from the united kingdom to the two captivities Political history Prophetic emphasis on moral concerns Written soon after the events 26 Chronicles Southern kingdom’s history, especially the Davidic line Religious history Priestly emphasis on spiritual concerns Written many years after the events
Comparison of 2 Histories Samuel and Kings Israel’s history from the united kingdom to the two captivities Political history Prophetic emphasis on moral concerns Written soon after the events 26 Chronicles Southern kingdom’s history, especially the Davidic line Religious history Priestly emphasis on spiritual concerns Written many years after the events
 Comparison of 2 Histories Samuel and Kings More negative – about rebellion and tragedy Message of judgment Man’s failings Emphasizes kings and prophets 27 Chronicles More positive – tells of apostacy, but offers hope in spite of tragedy Message of hope God’s faithfulness Emphasizes the temple and the priests
Comparison of 2 Histories Samuel and Kings More negative – about rebellion and tragedy Message of judgment Man’s failings Emphasizes kings and prophets 27 Chronicles More positive – tells of apostacy, but offers hope in spite of tragedy Message of hope God’s faithfulness Emphasizes the temple and the priests


