47e17d7a9f7a28173294658b41b9f3c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 1
1

 The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle. 3
The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle. 3
 Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
 Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
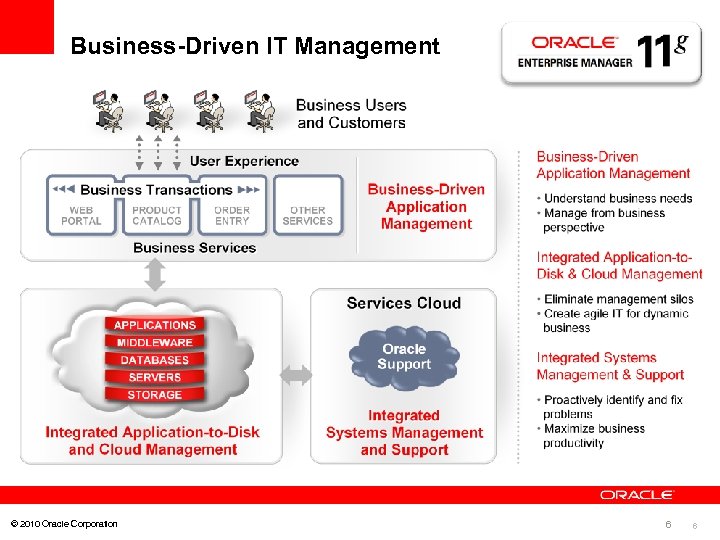 Business-Driven IT Management © 2010 Oracle Corporation 6 6
Business-Driven IT Management © 2010 Oracle Corporation 6 6
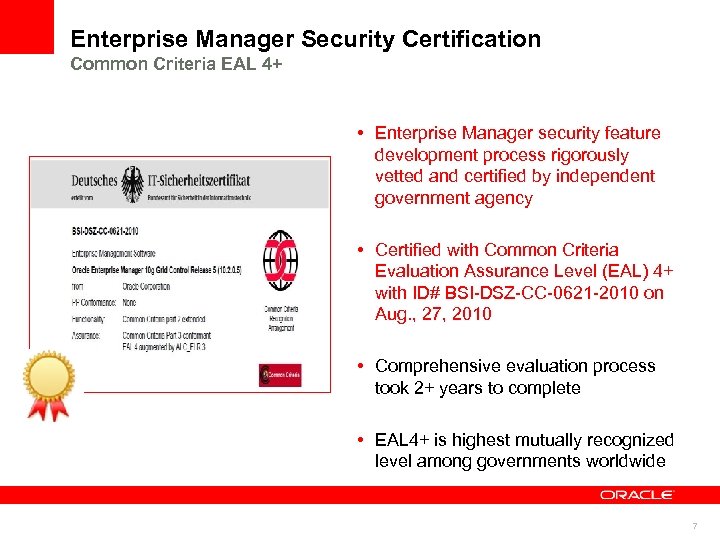 Enterprise Manager Security Certification Common Criteria EAL 4+ • Enterprise Manager security feature development process rigorously vetted and certified by independent government agency • Certified with Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) 4+ with ID# BSI-DSZ-CC-0621 -2010 on Aug. , 27, 2010 • Comprehensive evaluation process took 2+ years to complete • EAL 4+ is highest mutually recognized level among governments worldwide 7
Enterprise Manager Security Certification Common Criteria EAL 4+ • Enterprise Manager security feature development process rigorously vetted and certified by independent government agency • Certified with Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) 4+ with ID# BSI-DSZ-CC-0621 -2010 on Aug. , 27, 2010 • Comprehensive evaluation process took 2+ years to complete • EAL 4+ is highest mutually recognized level among governments worldwide 7
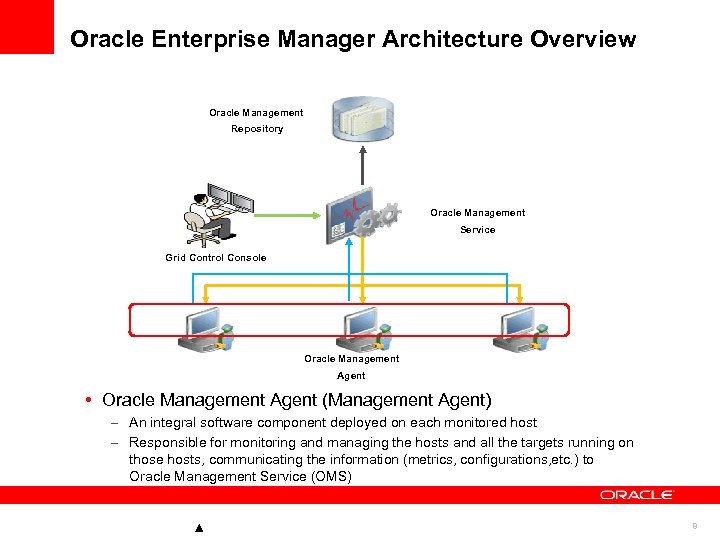 Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Oracle Management Agent (Management Agent) – An integral software component deployed on each monitored host – Responsible for monitoring and managing the hosts and all the targets running on those hosts, communicating the information (metrics, configurations, etc. ) to Oracle Management Service (OMS) 8
Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Oracle Management Agent (Management Agent) – An integral software component deployed on each monitored host – Responsible for monitoring and managing the hosts and all the targets running on those hosts, communicating the information (metrics, configurations, etc. ) to Oracle Management Service (OMS) 8
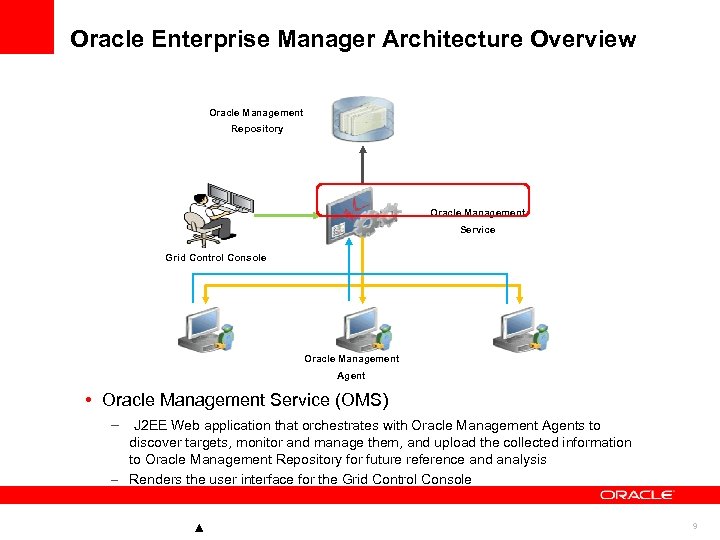 Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Oracle Management Service (OMS) – J 2 EE Web application that orchestrates with Oracle Management Agents to discover targets, monitor and manage them, and upload the collected information to Oracle Management Repository for future reference and analysis – Renders the user interface for the Grid Control Console 9
Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Oracle Management Service (OMS) – J 2 EE Web application that orchestrates with Oracle Management Agents to discover targets, monitor and manage them, and upload the collected information to Oracle Management Repository for future reference and analysis – Renders the user interface for the Grid Control Console 9
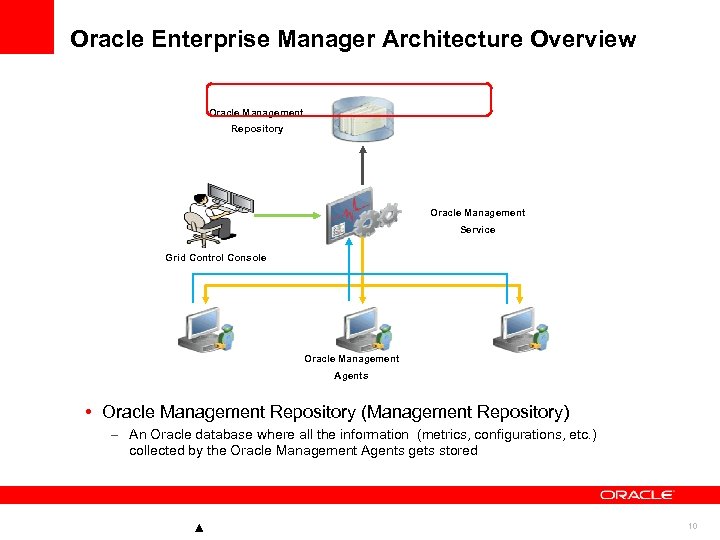 Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agents • Oracle Management Repository (Management Repository) – An Oracle database where all the information (metrics, configurations, etc. ) collected by the Oracle Management Agents gets stored 10
Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agents • Oracle Management Repository (Management Repository) – An Oracle database where all the information (metrics, configurations, etc. ) collected by the Oracle Management Agents gets stored 10
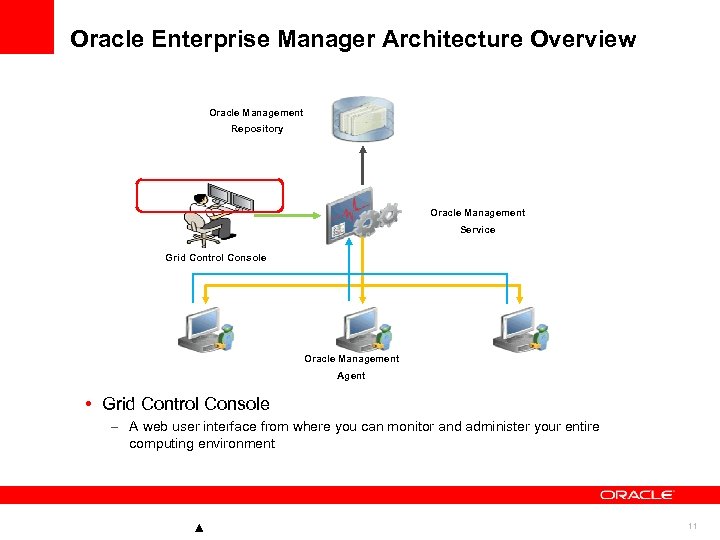 Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Grid Control Console – A web user interface from where you can monitor and administer your entire computing environment 11
Oracle Enterprise Manager Architecture Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Grid Control Console – A web user interface from where you can monitor and administer your entire computing environment 11
 Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
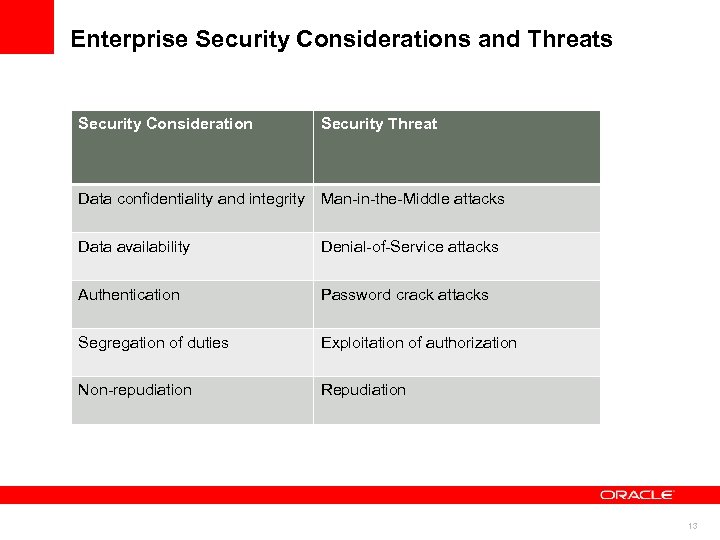 Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation 13
Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation 13
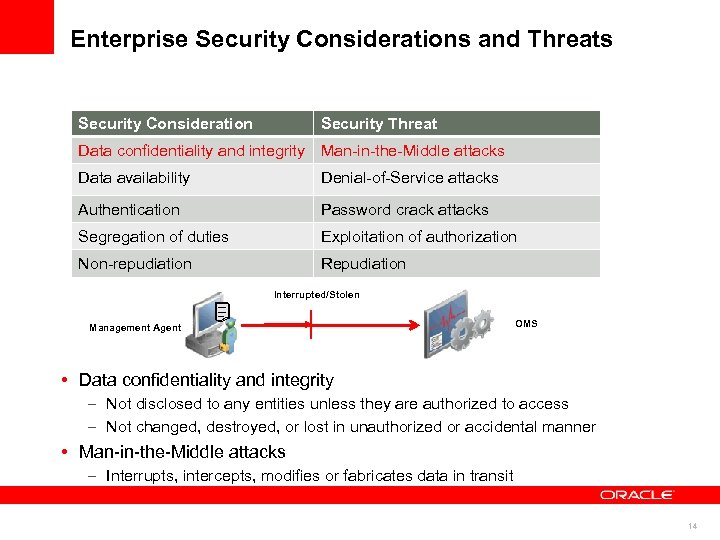 Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation Interrupted/Stolen Management Agent OMS • Data confidentiality and integrity – Not disclosed to any entities unless they are authorized to access – Not changed, destroyed, or lost in unauthorized or accidental manner • Man-in-the-Middle attacks – Interrupts, intercepts, modifies or fabricates data in transit 14
Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation Interrupted/Stolen Management Agent OMS • Data confidentiality and integrity – Not disclosed to any entities unless they are authorized to access – Not changed, destroyed, or lost in unauthorized or accidental manner • Man-in-the-Middle attacks – Interrupts, intercepts, modifies or fabricates data in transit 14
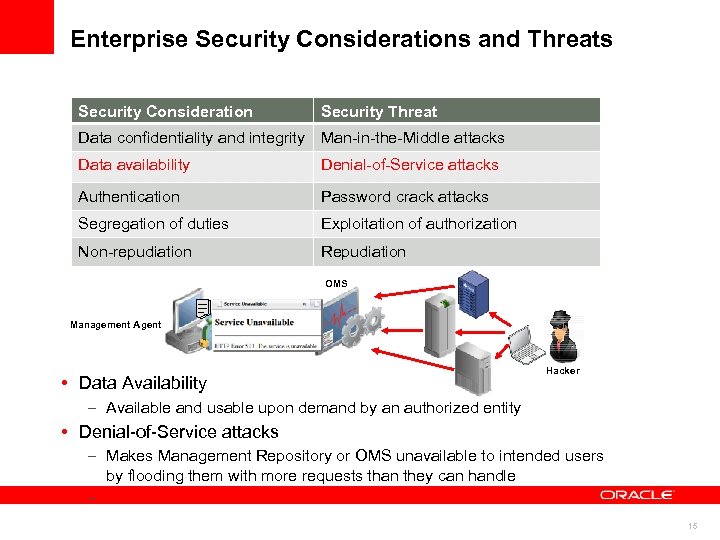 Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation OMS Management Agent • Data Availability Hacker – Available and usable upon demand by an authorized entity • Denial-of-Service attacks – Makes Management Repository or OMS unavailable to intended users by flooding them with more requests than they can handle – 15
Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation OMS Management Agent • Data Availability Hacker – Available and usable upon demand by an authorized entity • Denial-of-Service attacks – Makes Management Repository or OMS unavailable to intended users by flooding them with more requests than they can handle – 15
 Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation • Authentication – The process to verify the identity, usually username and password, claimed by a user • Password crack attacks – Obtains password from an authentication exchange, then uses the password to log on to Enterprise Manager Grid Control • For examples: guess, dictionary and brute force attacks 16
Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation • Authentication – The process to verify the identity, usually username and password, claimed by a user • Password crack attacks – Obtains password from an authentication exchange, then uses the password to log on to Enterprise Manager Grid Control • For examples: guess, dictionary and brute force attacks 16
 Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation • Segregation of duties – No person should be given responsibility for more than one related function • Exploitation of authorization – Accesses resources (targets, jobs, templates and so on) that he/she should not be authorized to 17
Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation • Segregation of duties – No person should be given responsibility for more than one related function • Exploitation of authorization – Accesses resources (targets, jobs, templates and so on) that he/she should not be authorized to 17
 Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation • Non-repudiation – Network security: Neither sender nor recipient can later deny having processed the information – Web Application security: No one can later deny the actions he/she has taken in the application • Repudiation – Refuses authoring of something that happened 18
Enterprise Security Considerations and Threats Security Consideration Security Threat Data confidentiality and integrity Man-in-the-Middle attacks Data availability Denial-of-Service attacks Authentication Password crack attacks Segregation of duties Exploitation of authorization Non-repudiation Repudiation • Non-repudiation – Network security: Neither sender nor recipient can later deny having processed the information – Web Application security: No one can later deny the actions he/she has taken in the application • Repudiation – Refuses authoring of something that happened 18
 Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview 1. Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security 2. Authentication, Authorization and Audit – The Three A’s 3. Security of target authentications 19
Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview 1. Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security 2. Authentication, Authorization and Audit – The Three A’s 3. Security of target authentications 19
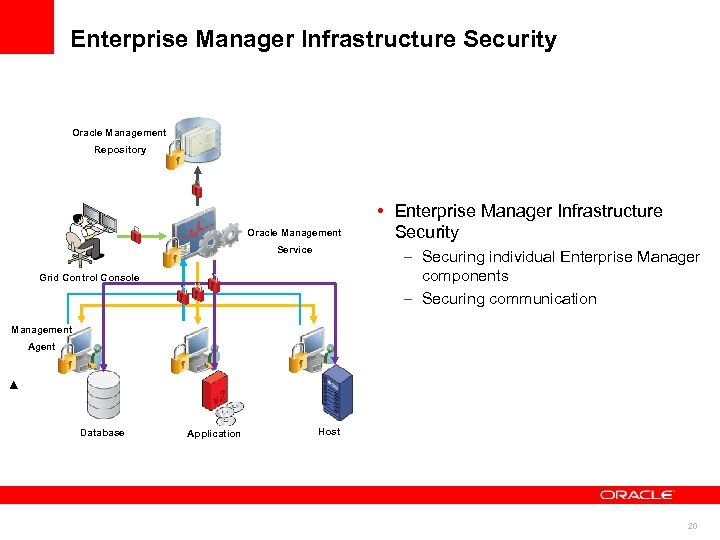 Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service • Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security – Securing individual Enterprise Manager components – Securing communication Grid Control Console Management Agent Database Application Host 20
Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service • Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security – Securing individual Enterprise Manager components – Securing communication Grid Control Console Management Agent Database Application Host 20
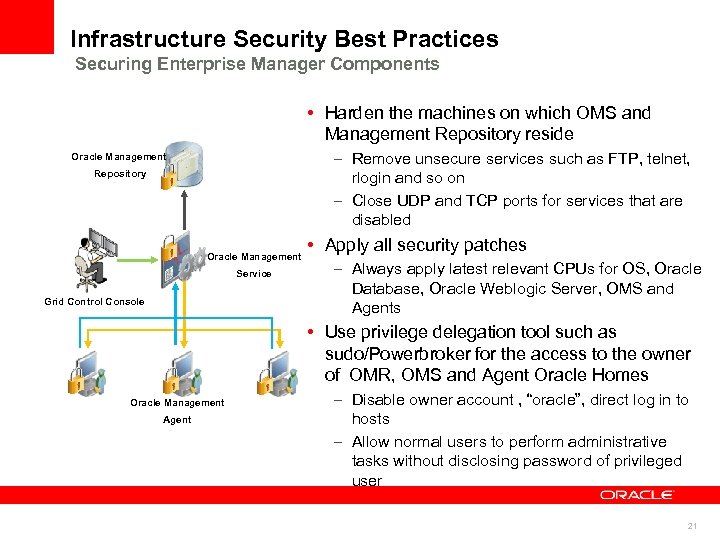 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Enterprise Manager Components • Harden the machines on which OMS and Management Repository reside – Remove unsecure services such as FTP, telnet, rlogin and so on – Close UDP and TCP ports for services that are disabled Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console • Apply all security patches – Always apply latest relevant CPUs for OS, Oracle Database, Oracle Weblogic Server, OMS and Agents • Use privilege delegation tool such as sudo/Powerbroker for the access to the owner of OMR, OMS and Agent Oracle Homes Oracle Management Agent – Disable owner account , “oracle”, direct log in to hosts – Allow normal users to perform administrative tasks without disclosing password of privileged user 21
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Enterprise Manager Components • Harden the machines on which OMS and Management Repository reside – Remove unsecure services such as FTP, telnet, rlogin and so on – Close UDP and TCP ports for services that are disabled Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console • Apply all security patches – Always apply latest relevant CPUs for OS, Oracle Database, Oracle Weblogic Server, OMS and Agents • Use privilege delegation tool such as sudo/Powerbroker for the access to the owner of OMR, OMS and Agent Oracle Homes Oracle Management Agent – Disable owner account , “oracle”, direct log in to hosts – Allow normal users to perform administrative tasks without disclosing password of privileged user 21
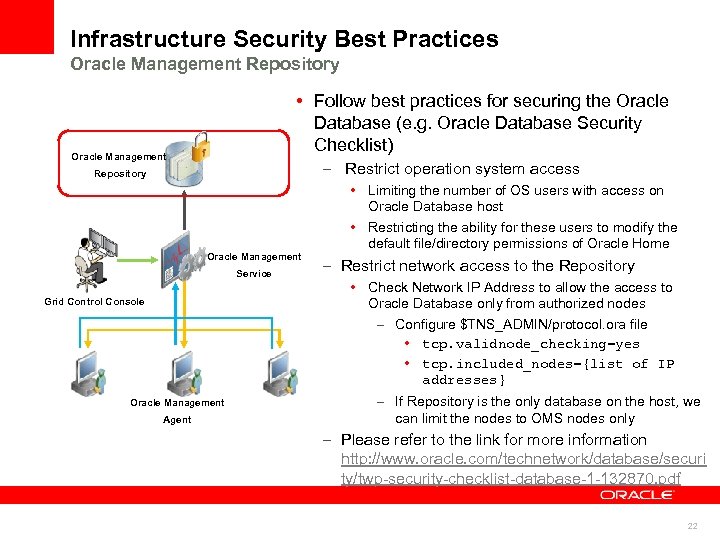 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Repository • Follow best practices for securing the Oracle Database (e. g. Oracle Database Security Checklist) Oracle Management – Restrict operation system access Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Limiting the number of OS users with access on Oracle Database host • Restricting the ability for these users to modify the default file/directory permissions of Oracle Home – Restrict network access to the Repository • Check Network IP Address to allow the access to Oracle Database only from authorized nodes – Configure $TNS_ADMIN/protocol. ora file • tcp. validnode_checking=yes • tcp. included_nodes={list of IP addresses} – If Repository is the only database on the host, we can limit the nodes to OMS nodes only – Please refer to the link for more information http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/database/securi ty/twp-security-checklist-database-1 -132870. pdf 22
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Repository • Follow best practices for securing the Oracle Database (e. g. Oracle Database Security Checklist) Oracle Management – Restrict operation system access Repository Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Limiting the number of OS users with access on Oracle Database host • Restricting the ability for these users to modify the default file/directory permissions of Oracle Home – Restrict network access to the Repository • Check Network IP Address to allow the access to Oracle Database only from authorized nodes – Configure $TNS_ADMIN/protocol. ora file • tcp. validnode_checking=yes • tcp. included_nodes={list of IP addresses} – If Repository is the only database on the host, we can limit the nodes to OMS nodes only – Please refer to the link for more information http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/database/securi ty/twp-security-checklist-database-1 -132870. pdf 22
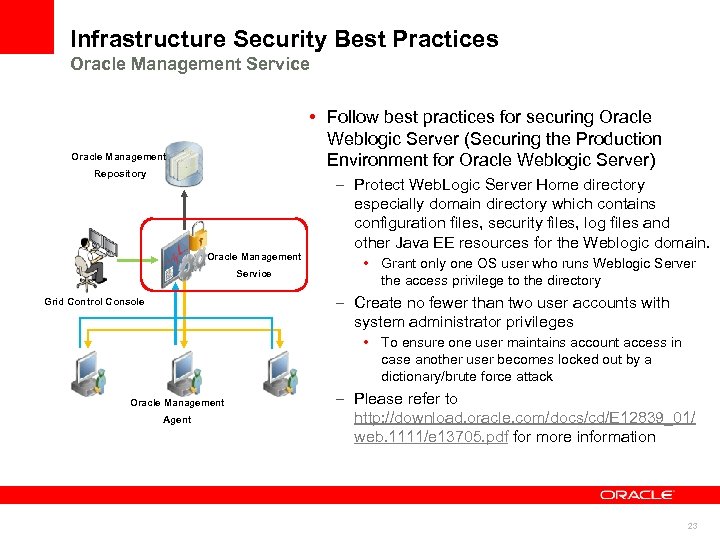 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Service • Follow best practices for securing Oracle Weblogic Server (Securing the Production Environment for Oracle Weblogic Server) Oracle Management Repository – Protect Web. Logic Server Home directory especially domain directory which contains configuration files, security files, log files and other Java EE resources for the Weblogic domain. Oracle Management Service • Grant only one OS user who runs Weblogic Server the access privilege to the directory – Create no fewer than two user accounts with system administrator privileges Grid Control Console • To ensure one user maintains account access in case another user becomes locked out by a dictionary/brute force attack Oracle Management Agent – Please refer to http: //download. oracle. com/docs/cd/E 12839_01/ web. 1111/e 13705. pdf for more information 23
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Service • Follow best practices for securing Oracle Weblogic Server (Securing the Production Environment for Oracle Weblogic Server) Oracle Management Repository – Protect Web. Logic Server Home directory especially domain directory which contains configuration files, security files, log files and other Java EE resources for the Weblogic domain. Oracle Management Service • Grant only one OS user who runs Weblogic Server the access privilege to the directory – Create no fewer than two user accounts with system administrator privileges Grid Control Console • To ensure one user maintains account access in case another user becomes locked out by a dictionary/brute force attack Oracle Management Agent – Please refer to http: //download. oracle. com/docs/cd/E 12839_01/ web. 1111/e 13705. pdf for more information 23
 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Agent • Deploy agent via pushing agents from OMS Oracle Management Repository – Secure Shell (SSH) protocol is used in this approach, which ensures the confidentiality and integrity of agent installation Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Use complex one-time registration passwords with reasonable expiry date – Registration password combined with random keys generated by OMS and agent is used to produce agent key to register and secure the agent – Protect against the possibility of unauthorized agents accessing OMS 24
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Agent • Deploy agent via pushing agents from OMS Oracle Management Repository – Secure Shell (SSH) protocol is used in this approach, which ensures the confidentiality and integrity of agent installation Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent • Use complex one-time registration passwords with reasonable expiry date – Registration password combined with random keys generated by OMS and agent is used to produce agent key to register and secure the agent – Protect against the possibility of unauthorized agents accessing OMS 24
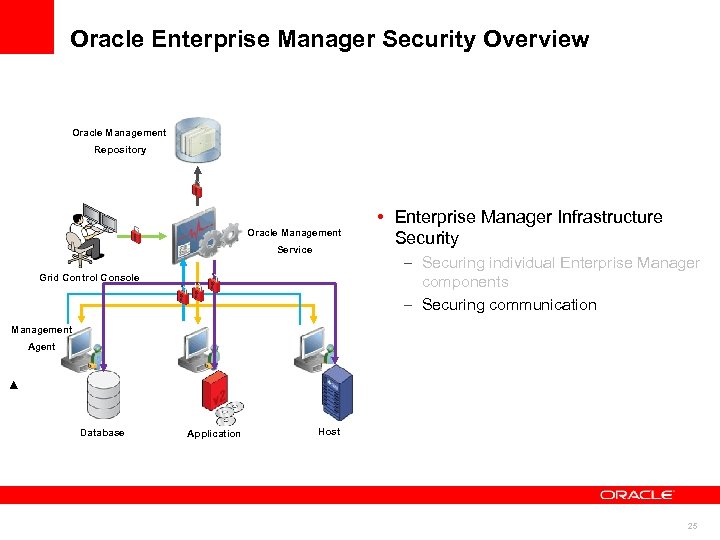 Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service • Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security – Securing individual Enterprise Manager components – Securing communication Grid Control Console Management Agent Database Application Host 25
Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview Oracle Management Repository Oracle Management Service • Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security – Securing individual Enterprise Manager components – Securing communication Grid Control Console Management Agent Database Application Host 25
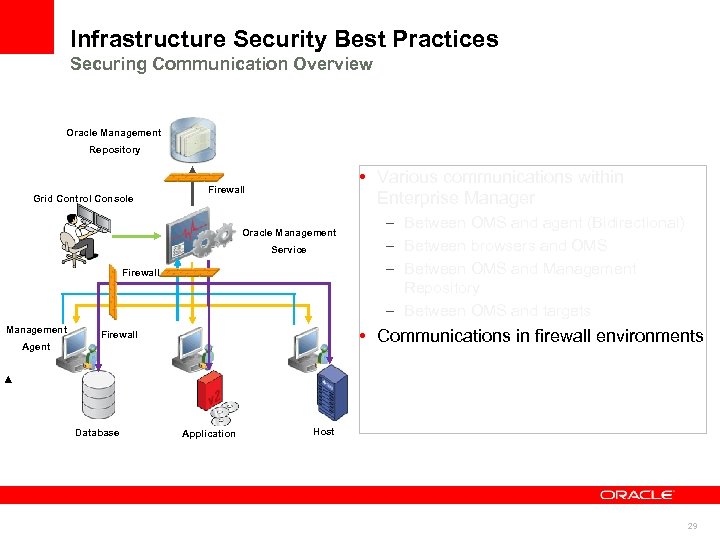
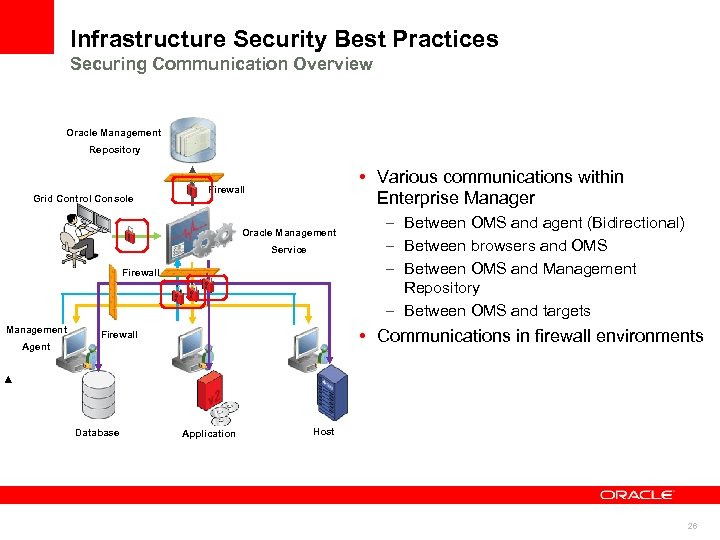 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Communication Overview Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console • Various communications within Enterprise Manager Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management • Communications in firewall environments Firewall Agent Database – Between OMS and agent (Bidirectional) – Between browsers and OMS – Between OMS and Management Repository – Between OMS and targets Application Host 26
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Communication Overview Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console • Various communications within Enterprise Manager Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management • Communications in firewall environments Firewall Agent Database – Between OMS and agent (Bidirectional) – Between browsers and OMS – Between OMS and Management Repository – Between OMS and targets Application Host 26
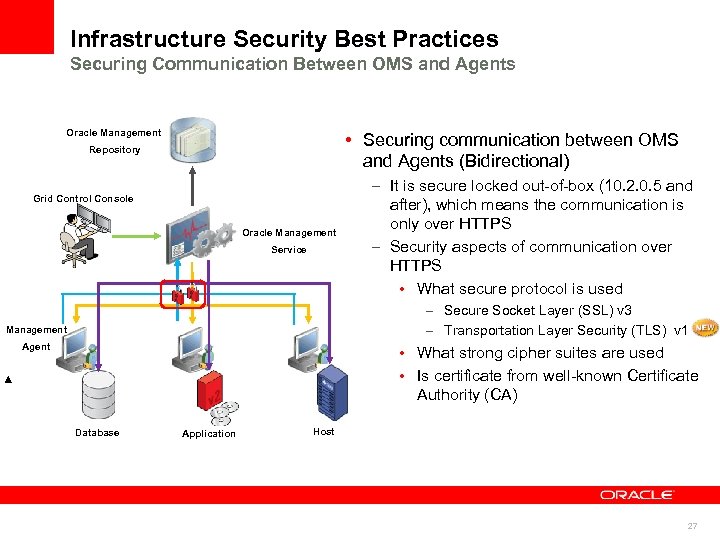 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Communication Between OMS and Agents Oracle Management • Securing communication between OMS and Agents (Bidirectional) Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service – It is secure locked out-of-box (10. 2. 0. 5 and after), which means the communication is only over HTTPS – Security aspects of communication over HTTPS • What secure protocol is used – Secure Socket Layer (SSL) v 3 – Transportation Layer Security (TLS) v 1 Management Agent • What strong cipher suites are used • Is certificate from well-known Certificate Authority (CA) Database Application Host 27
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Communication Between OMS and Agents Oracle Management • Securing communication between OMS and Agents (Bidirectional) Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service – It is secure locked out-of-box (10. 2. 0. 5 and after), which means the communication is only over HTTPS – Security aspects of communication over HTTPS • What secure protocol is used – Secure Socket Layer (SSL) v 3 – Transportation Layer Security (TLS) v 1 Management Agent • What strong cipher suites are used • Is certificate from well-known Certificate Authority (CA) Database Application Host 27
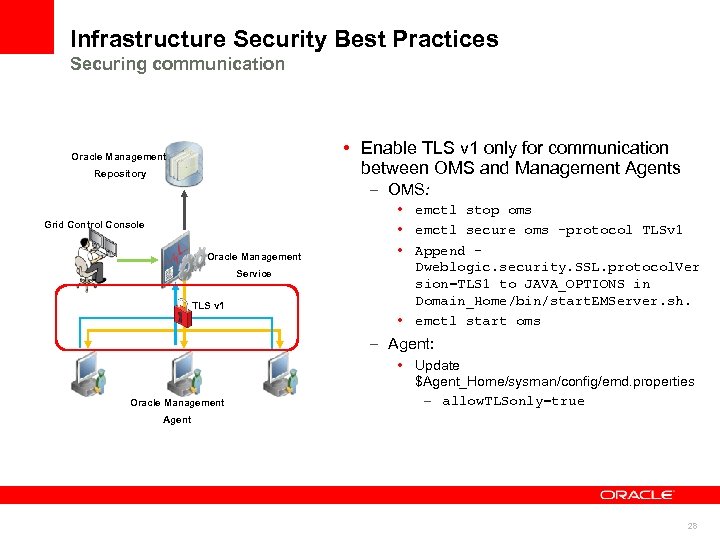 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing communication • Enable TLS v 1 only for communication between OMS and Management Agents Oracle Management Repository – OMS: Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service TLS v 1 • emctl stop oms • emctl secure oms -protocol TLSv 1 • Append Dweblogic. security. SSL. protocol. Ver sion=TLS 1 to JAVA_OPTIONS in Domain_Home/bin/start. EMServer. sh. • emctl start oms – Agent: Oracle Management • Update $Agent_Home/sysman/config/emd. properties – allow. TLSonly=true Agent 28
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing communication • Enable TLS v 1 only for communication between OMS and Management Agents Oracle Management Repository – OMS: Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service TLS v 1 • emctl stop oms • emctl secure oms -protocol TLSv 1 • Append Dweblogic. security. SSL. protocol. Ver sion=TLS 1 to JAVA_OPTIONS in Domain_Home/bin/start. EMServer. sh. • emctl start oms – Agent: Oracle Management • Update $Agent_Home/sysman/config/emd. properties – allow. TLSonly=true Agent 28
 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Communication Overview Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console • Various communications within Enterprise Manager Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management • Communications in firewall environments Firewall Agent Database – Between OMS and agent (Bidirectional) – Between browsers and OMS – Between OMS and Management Repository – Between OMS and targets Application Host 29
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Securing Communication Overview Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console • Various communications within Enterprise Manager Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management • Communications in firewall environments Firewall Agent Database – Between OMS and agent (Bidirectional) – Between browsers and OMS – Between OMS and Management Repository – Between OMS and targets Application Host 29
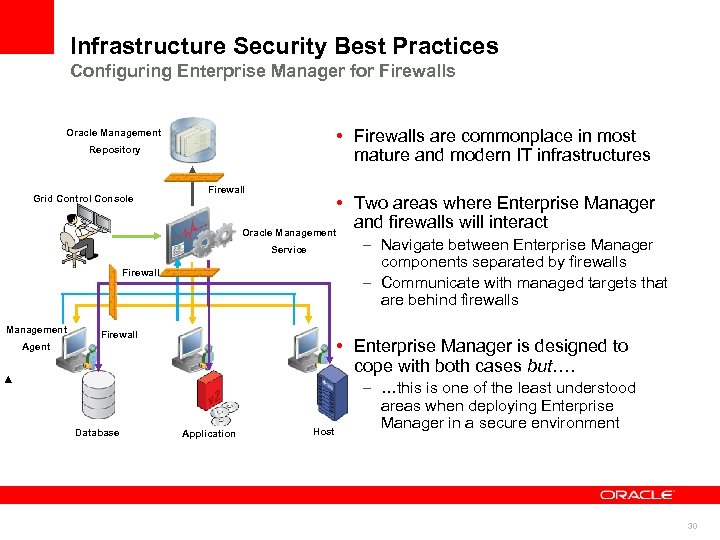 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configuring Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Firewalls are commonplace in most mature and modern IT infrastructures Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Firewall • Two areas where Enterprise Manager and firewalls will interact Oracle Management – Navigate between Enterprise Manager components separated by firewalls – Communicate with managed targets that are behind firewalls Service Firewall Management Firewall • Enterprise Manager is designed to cope with both cases but…. Agent Database Application Host – …this is one of the least understood areas when deploying Enterprise Manager in a secure environment 30
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configuring Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Firewalls are commonplace in most mature and modern IT infrastructures Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Firewall • Two areas where Enterprise Manager and firewalls will interact Oracle Management – Navigate between Enterprise Manager components separated by firewalls – Communicate with managed targets that are behind firewalls Service Firewall Management Firewall • Enterprise Manager is designed to cope with both cases but…. Agent Database Application Host – …this is one of the least understood areas when deploying Enterprise Manager in a secure environment 30
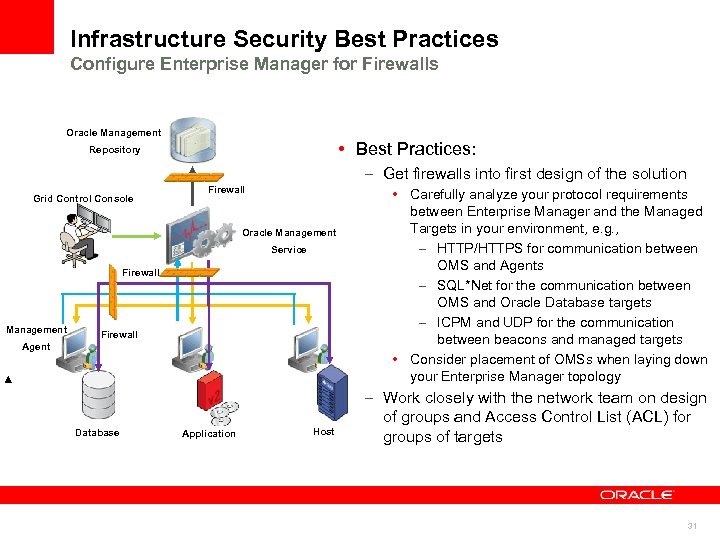 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Oracle Management • Best Practices: Repository – Get firewalls into first design of the solution Grid Control Console Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management Firewall Agent Database Application Host • Carefully analyze your protocol requirements between Enterprise Manager and the Managed Targets in your environment, e. g. , – HTTP/HTTPS for communication between OMS and Agents – SQL*Net for the communication between OMS and Oracle Database targets – ICPM and UDP for the communication between beacons and managed targets • Consider placement of OMSs when laying down your Enterprise Manager topology – Work closely with the network team on design of groups and Access Control List (ACL) for groups of targets 31
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Oracle Management • Best Practices: Repository – Get firewalls into first design of the solution Grid Control Console Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management Firewall Agent Database Application Host • Carefully analyze your protocol requirements between Enterprise Manager and the Managed Targets in your environment, e. g. , – HTTP/HTTPS for communication between OMS and Agents – SQL*Net for the communication between OMS and Oracle Database targets – ICPM and UDP for the communication between beacons and managed targets • Consider placement of OMSs when laying down your Enterprise Manager topology – Work closely with the network team on design of groups and Access Control List (ACL) for groups of targets 31
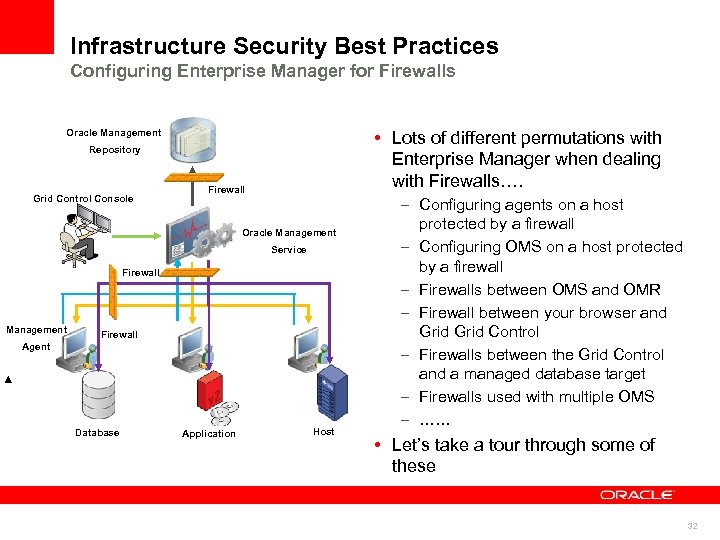 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configuring Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Oracle Management • Lots of different permutations with Enterprise Manager when dealing with Firewalls…. Repository Grid Control Console Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management Firewall Agent Database Application Host – Configuring agents on a host protected by a firewall – Configuring OMS on a host protected by a firewall – Firewalls between OMS and OMR – Firewall between your browser and Grid Control – Firewalls between the Grid Control and a managed database target – Firewalls used with multiple OMS – …… • Let’s take a tour through some of these 32
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configuring Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Oracle Management • Lots of different permutations with Enterprise Manager when dealing with Firewalls…. Repository Grid Control Console Firewall Oracle Management Service Firewall Management Firewall Agent Database Application Host – Configuring agents on a host protected by a firewall – Configuring OMS on a host protected by a firewall – Firewalls between OMS and OMR – Firewall between your browser and Grid Control – Firewalls between the Grid Control and a managed database target – Firewalls used with multiple OMS – …… • Let’s take a tour through some of these 32
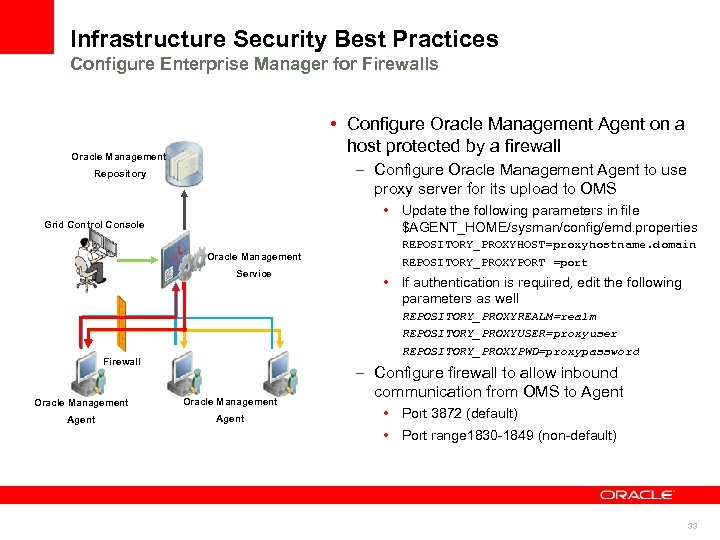 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Configure Oracle Management Agent on a host protected by a firewall Oracle Management – Configure Oracle Management Agent to use proxy server for its upload to OMS Repository • Update the following parameters in file $AGENT_HOME/sysman/config/emd. properties Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service REPOSITORY_PROXYHOST=proxyhostname. domain REPOSITORY_PROXYPORT =port • If authentication is required, edit the following parameters as well REPOSITORY_PROXYREALM=realm REPOSITORY_PROXYUSER=proxyuser REPOSITORY_PROXYPWD=proxypassword Firewall Oracle Management Agent – Configure firewall to allow inbound communication from OMS to Agent • Port 3872 (default) • Port range 1830 -1849 (non-default) 33
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Configure Oracle Management Agent on a host protected by a firewall Oracle Management – Configure Oracle Management Agent to use proxy server for its upload to OMS Repository • Update the following parameters in file $AGENT_HOME/sysman/config/emd. properties Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service REPOSITORY_PROXYHOST=proxyhostname. domain REPOSITORY_PROXYPORT =port • If authentication is required, edit the following parameters as well REPOSITORY_PROXYREALM=realm REPOSITORY_PROXYUSER=proxyuser REPOSITORY_PROXYPWD=proxypassword Firewall Oracle Management Agent – Configure firewall to allow inbound communication from OMS to Agent • Port 3872 (default) • Port range 1830 -1849 (non-default) 33
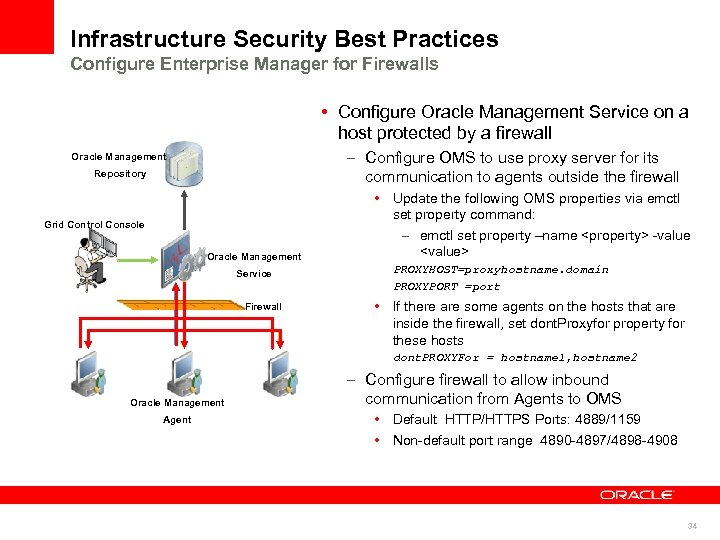 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Configure Oracle Management Service on a host protected by a firewall – Configure OMS to use proxy server for its communication to agents outside the firewall Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Firewall • Update the following OMS properties via emctl set property command: – emctl set property –name
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Configure Oracle Management Service on a host protected by a firewall – Configure OMS to use proxy server for its communication to agents outside the firewall Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Firewall • Update the following OMS properties via emctl set property command: – emctl set property –name
 Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview 1. Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security 2. Authentication, Authorization and Audit – The Three A’s 3. Security of target authentications 35
Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview 1. Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security 2. Authentication, Authorization and Audit – The Three A’s 3. Security of target authentications 35
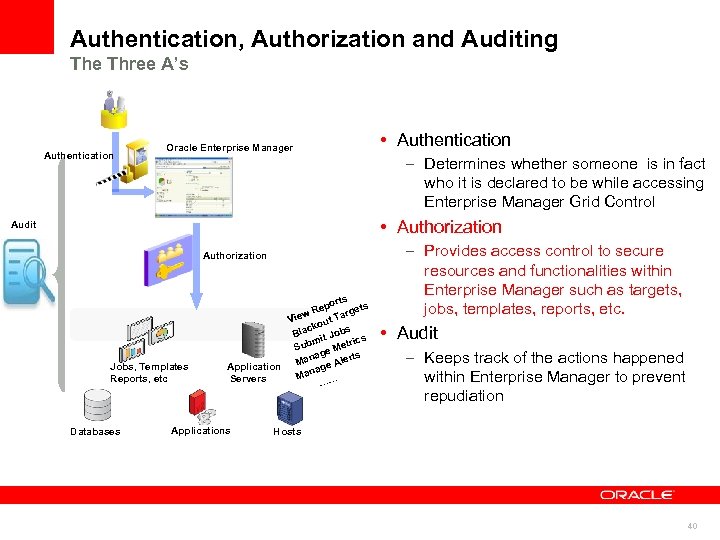
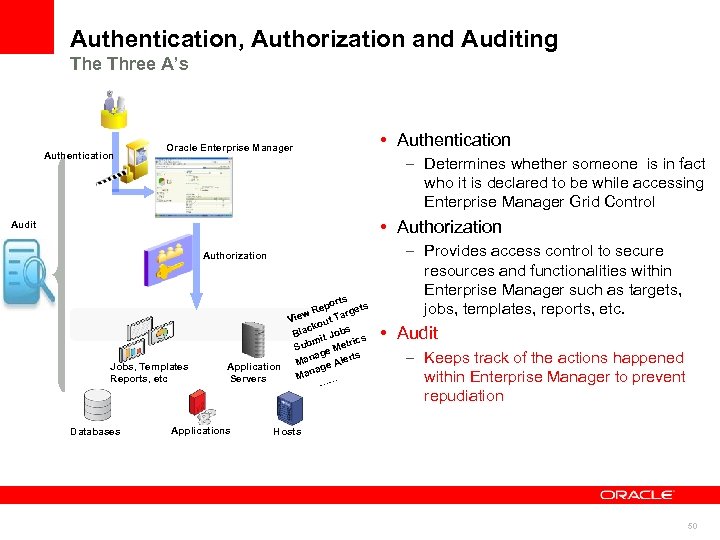
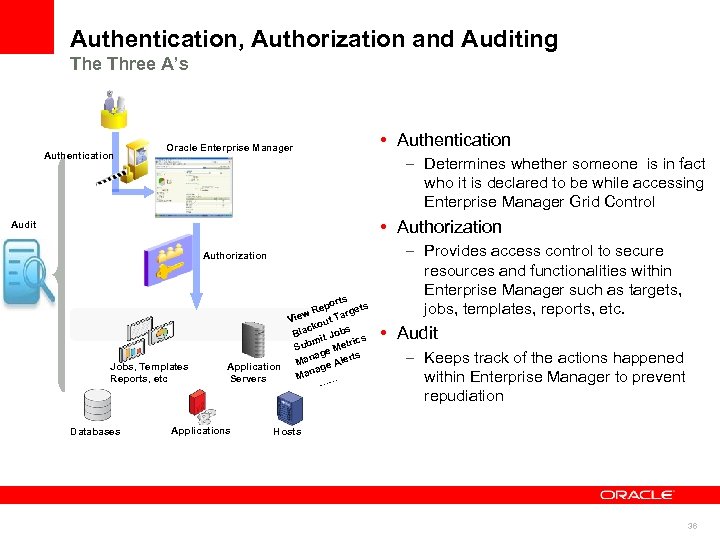 Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 36
Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 36
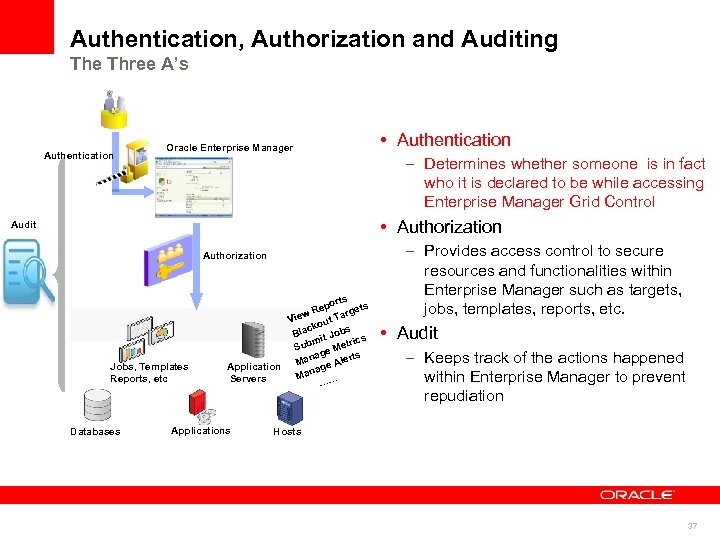 Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 37
Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 37
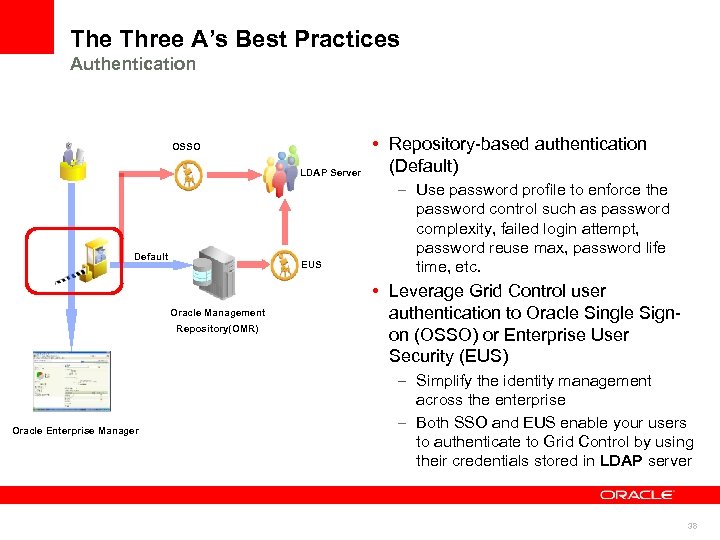 The Three A’s Best Practices Authentication OSSO LDAP Server Default EUS Oracle Management Repository(OMR) Oracle Enterprise Manager • Repository-based authentication (Default) – Use password profile to enforce the password control such as password complexity, failed login attempt, password reuse max, password life time, etc. • Leverage Grid Control user authentication to Oracle Single Signon (OSSO) or Enterprise User Security (EUS) – Simplify the identity management across the enterprise – Both SSO and EUS enable your users to authenticate to Grid Control by using their credentials stored in LDAP server 38
The Three A’s Best Practices Authentication OSSO LDAP Server Default EUS Oracle Management Repository(OMR) Oracle Enterprise Manager • Repository-based authentication (Default) – Use password profile to enforce the password control such as password complexity, failed login attempt, password reuse max, password life time, etc. • Leverage Grid Control user authentication to Oracle Single Signon (OSSO) or Enterprise User Security (EUS) – Simplify the identity management across the enterprise – Both SSO and EUS enable your users to authenticate to Grid Control by using their credentials stored in LDAP server 38
 The Three A’s Best Practices Authentication • Disable SYSMAN logging into Grid Control console by issuing the following SQL statement on Repository UPDATE MGMT_CREATED_USERS SET SYSTEM_USER=’-1’ WHERE user_name=’SYSMAN’ • If you want to enable SYSMAN logging into Grid Control Console later on: UPDATE MGMT_CREATED_USERS SET SYSTEM_USER=’ 1’ WHERE user_name=’SYSMAN’ • Change password for both SYSMAN and MGMT_VIEW on a regular basis – Prevent password crack attacks – emctl config oms -change_repos_pwd -change_in_db – emctl config oms –change_view_user_pwd 39
The Three A’s Best Practices Authentication • Disable SYSMAN logging into Grid Control console by issuing the following SQL statement on Repository UPDATE MGMT_CREATED_USERS SET SYSTEM_USER=’-1’ WHERE user_name=’SYSMAN’ • If you want to enable SYSMAN logging into Grid Control Console later on: UPDATE MGMT_CREATED_USERS SET SYSTEM_USER=’ 1’ WHERE user_name=’SYSMAN’ • Change password for both SYSMAN and MGMT_VIEW on a regular basis – Prevent password crack attacks – emctl config oms -change_repos_pwd -change_in_db – emctl config oms –change_view_user_pwd 39
 Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 40
Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 40
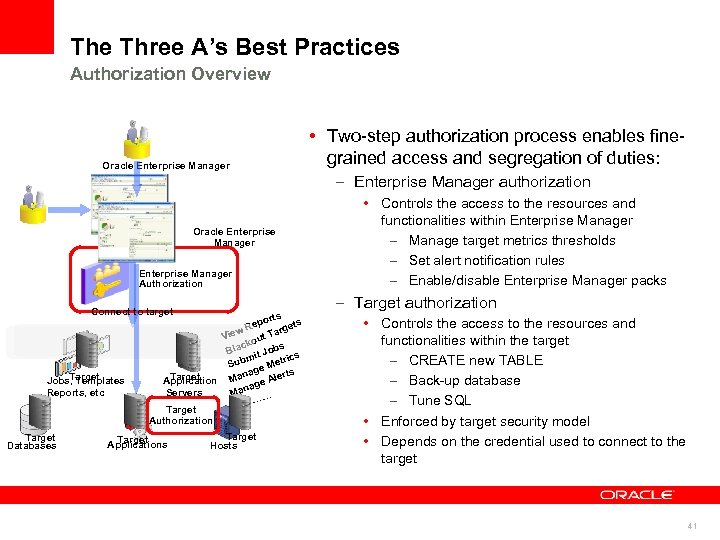 The Three A’s Best Practices Authorization Overview Oracle Enterprise Manager • Two-step authorization process enables finegrained access and segregation of duties: – Enterprise Manager authorization Oracle Enterprise Manager Authorization Connect to target Target Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Target Databases orts Rep argets w T Vie out ack Jobs Bl mit rics Sub e Met nag rts Target Application Ma ge Ale a Servers Man … … Target Authorization Target Applications Target Hosts • Controls the access to the resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager – Manage target metrics thresholds – Set alert notification rules – Enable/disable Enterprise Manager packs – Target authorization • Controls the access to the resources and functionalities within the target – CREATE new TABLE – Back-up database – Tune SQL • Enforced by target security model • Depends on the credential used to connect to the target 41
The Three A’s Best Practices Authorization Overview Oracle Enterprise Manager • Two-step authorization process enables finegrained access and segregation of duties: – Enterprise Manager authorization Oracle Enterprise Manager Authorization Connect to target Target Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Target Databases orts Rep argets w T Vie out ack Jobs Bl mit rics Sub e Met nag rts Target Application Ma ge Ale a Servers Man … … Target Authorization Target Applications Target Hosts • Controls the access to the resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager – Manage target metrics thresholds – Set alert notification rules – Enable/disable Enterprise Manager packs – Target authorization • Controls the access to the resources and functionalities within the target – CREATE new TABLE – Back-up database – Tune SQL • Enforced by target security model • Depends on the credential used to connect to the target 41
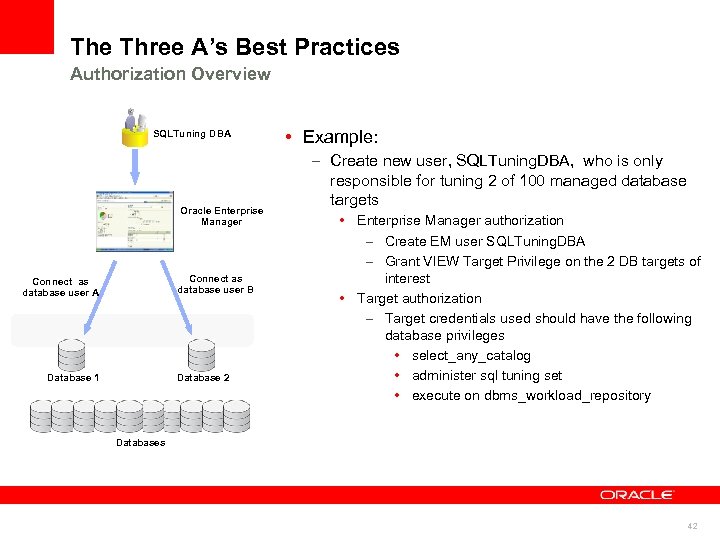 The Three A’s Best Practices Authorization Overview SQLTuning DBA Oracle Enterprise Manager Connect as database user B Connect as database user A Database 1 Database 2 • Example: – Create new user, SQLTuning. DBA, who is only responsible for tuning 2 of 100 managed database targets • Enterprise Manager authorization – Create EM user SQLTuning. DBA – Grant VIEW Target Privilege on the 2 DB targets of interest • Target authorization – Target credentials used should have the following database privileges • select_any_catalog • administer sql tuning set • execute on dbms_workload_repository Databases 42
The Three A’s Best Practices Authorization Overview SQLTuning DBA Oracle Enterprise Manager Connect as database user B Connect as database user A Database 1 Database 2 • Example: – Create new user, SQLTuning. DBA, who is only responsible for tuning 2 of 100 managed database targets • Enterprise Manager authorization – Create EM user SQLTuning. DBA – Grant VIEW Target Privilege on the 2 DB targets of interest • Target authorization – Target credentials used should have the following database privileges • select_any_catalog • administer sql tuning set • execute on dbms_workload_repository Databases 42
 The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview What type of administrator should the new user be? • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges • Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators 43
The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview What type of administrator should the new user be? • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges • Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators 43
 The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? 44
The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? 44
 The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? What target should the user be able to access? Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? 45
The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? What target should the user be able to access? Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? 45
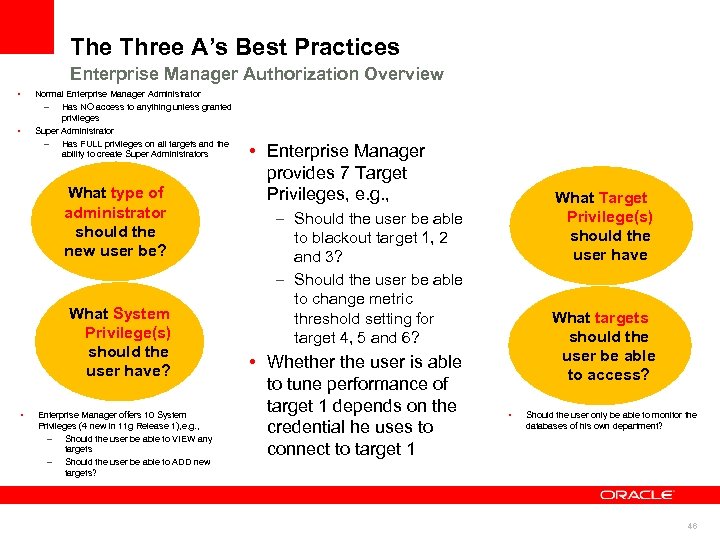 The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? • Enterprise Manager provides 7 Target Privileges, e. g. , What Target Privilege(s) should the user have – Should the user be able to blackout target 1, 2 and 3? – Should the user be able to change metric threshold setting for target 4, 5 and 6? • Whether the user is able to tune performance of target 1 depends on the credential he uses to connect to target 1 What targets should the user be able to access? • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? 46
The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? • Enterprise Manager provides 7 Target Privileges, e. g. , What Target Privilege(s) should the user have – Should the user be able to blackout target 1, 2 and 3? – Should the user be able to change metric threshold setting for target 4, 5 and 6? • Whether the user is able to tune performance of target 1 depends on the credential he uses to connect to target 1 What targets should the user be able to access? • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? 46
 The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? • If groups of targets are always monitored and managed in the same way, do we have to grant the privileges on these individual targets to the user? • Privilege Propagating Group – Privileges granted on the group automatically granted on its members Privilege Propagating Group • Enterprise Manager provides 7 Target Privileges, e. g. , – Should the user be able to blackout target 1, 2 and 3? – Should the user be able to change metric threshold setting for target 4, 5 and 6? • Whether the user is able to tune performance of target 1 depends on the credential he uses to connect to target 1 What Target Privilege(s) should the user have What targets should the user be able to access? • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? 47
The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? • If groups of targets are always monitored and managed in the same way, do we have to grant the privileges on these individual targets to the user? • Privilege Propagating Group – Privileges granted on the group automatically granted on its members Privilege Propagating Group • Enterprise Manager provides 7 Target Privileges, e. g. , – Should the user be able to blackout target 1, 2 and 3? – Should the user be able to change metric threshold setting for target 4, 5 and 6? • Whether the user is able to tune performance of target 1 depends on the credential he uses to connect to target 1 What Target Privilege(s) should the user have What targets should the user be able to access? • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? 47
 The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? Role • If there a set of users sharing the same responsibilities, do we have to grant all the individual privileges one by one to these users? • Role -- Set of privileges • • • Enterprise Manager provides 7 Target Privileges, e. g. , – Should the user be able to blackout target 1, 2 and 3? – Should the user be able to change metric threshold setting for target 4, 5 and 6? • Whether the user is able to tune performance of target 1 depends on the credential he uses to connect to target 1 What Target Privilege(s) should the user have What targets should the user be able to access? If groups of targets are always monitored and managed in the same way, do we have to grant the privileges on these individual targets to the user? Privilege Propagating Group – Privileges granted on the group automatically granted on its members Privilege Propagating Group • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? 48
The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization Overview • • Normal Enterprise Manager Administrator – Has NO access to anything unless granted privileges Super Administrator – Has FULL privileges on all targets and the ability to create Super Administrators What type of administrator should the new user be? What System Privilege(s) should the user have? • Enterprise Manager offers 10 System Privileges (4 new in 11 g Release 1), e. g. , – Should the user be able to VIEW any targets – Should the user be able to ADD new targets? Role • If there a set of users sharing the same responsibilities, do we have to grant all the individual privileges one by one to these users? • Role -- Set of privileges • • • Enterprise Manager provides 7 Target Privileges, e. g. , – Should the user be able to blackout target 1, 2 and 3? – Should the user be able to change metric threshold setting for target 4, 5 and 6? • Whether the user is able to tune performance of target 1 depends on the credential he uses to connect to target 1 What Target Privilege(s) should the user have What targets should the user be able to access? If groups of targets are always monitored and managed in the same way, do we have to grant the privileges on these individual targets to the user? Privilege Propagating Group – Privileges granted on the group automatically granted on its members Privilege Propagating Group • Should the user only be able to monitor the databases of his own department? 48
 The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization • Reduce the number of Super Administrators Oracle Enterprise Manager – Super Administrators have FULL privilege on all targets and could create additional Super Administrators • Grant only the minimum set of privileges – Follow the principle of least privilege to grant only the minimum set of privileges to the users to fulfill his responsibility Authorization • Achieve segregation of duties and simplify authorization management – Grant roles instead of individual privileges to users – Use roles along with Privilege Propagating groups Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases Application Servers Applications • Monitor privilege/role operations through Enterprise Manager Auditing Hosts 49
The Three A’s Best Practices Enterprise Manager Authorization • Reduce the number of Super Administrators Oracle Enterprise Manager – Super Administrators have FULL privilege on all targets and could create additional Super Administrators • Grant only the minimum set of privileges – Follow the principle of least privilege to grant only the minimum set of privileges to the users to fulfill his responsibility Authorization • Achieve segregation of duties and simplify authorization management – Grant roles instead of individual privileges to users – Use roles along with Privilege Propagating groups Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases Application Servers Applications • Monitor privilege/role operations through Enterprise Manager Auditing Hosts 49
 Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 50
Authentication, Authorization and Auditing The Three A’s Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • Authentication – Determines whether someone is in fact who it is declared to be while accessing Enterprise Manager Grid Control • Authorization Audit Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases orts Rep argets w t. T Vie kou bs lac B Jo mit rics Sub e Met ag ts Man e Aler Application g a Man … Servers … Applications – Provides access control to secure resources and functionalities within Enterprise Manager such as targets, jobs, templates, reports, etc. • Audit – Keeps track of the actions happened within Enterprise Manager to prevent repudiation Hosts 50
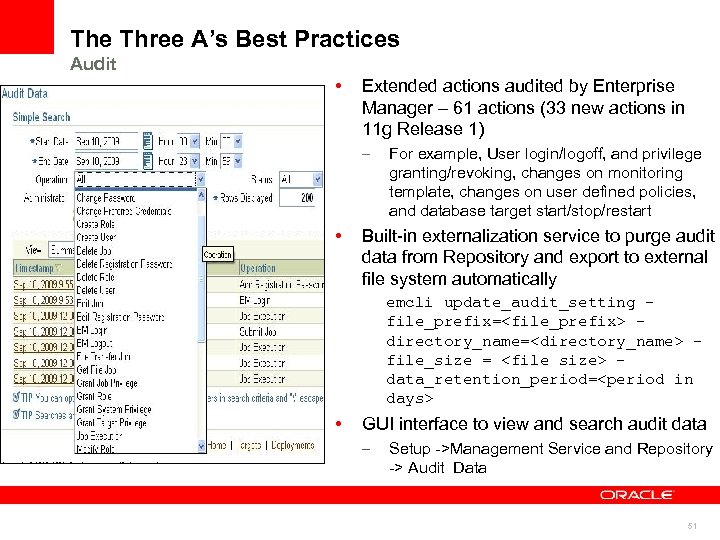 The Three A’s Best Practices Audit • Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager Audit – • Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases Extended actions audited by Enterprise Manager – 61 actions (33 new actions in 11 g Release 1) Built-in externalization service to purge audit data from Repository and export to external file system automatically emcli update_audit_setting file_prefix=
The Three A’s Best Practices Audit • Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager Audit – • Authorization Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Databases Extended actions audited by Enterprise Manager – 61 actions (33 new actions in 11 g Release 1) Built-in externalization service to purge audit data from Repository and export to external file system automatically emcli update_audit_setting file_prefix=
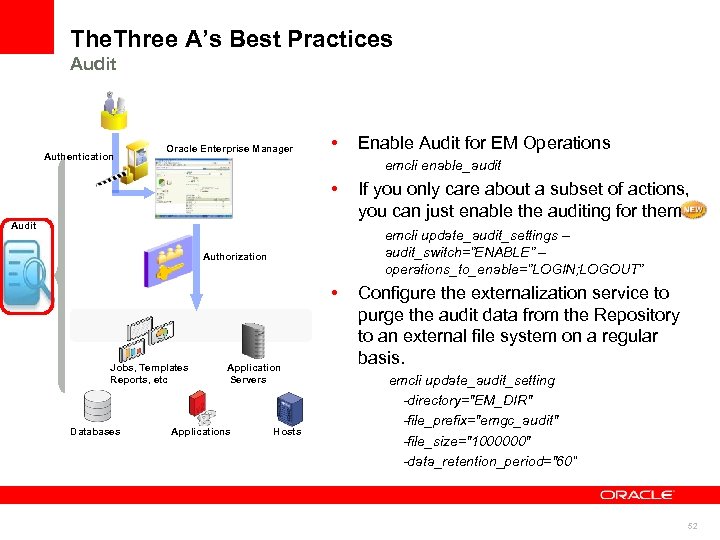 The. Three A’s Best Practices Audit Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • emcli enable_audit • Audit • Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Application Servers Applications If you only care about a subset of actions, you can just enable the auditing for them emcli update_audit_settings – audit_switch=”ENABLE” – operations_to_enable=”LOGIN; LOGOUT” Authorization Databases Enable Audit for EM Operations Hosts Configure the externalization service to purge the audit data from the Repository to an external file system on a regular basis. emcli update_audit_setting -directory="EM_DIR" -file_prefix="emgc_audit" -file_size="1000000" -data_retention_period="60“ 52
The. Three A’s Best Practices Audit Authentication Oracle Enterprise Manager • emcli enable_audit • Audit • Jobs, Templates Reports, etc Application Servers Applications If you only care about a subset of actions, you can just enable the auditing for them emcli update_audit_settings – audit_switch=”ENABLE” – operations_to_enable=”LOGIN; LOGOUT” Authorization Databases Enable Audit for EM Operations Hosts Configure the externalization service to purge the audit data from the Repository to an external file system on a regular basis. emcli update_audit_setting -directory="EM_DIR" -file_prefix="emgc_audit" -file_size="1000000" -data_retention_period="60“ 52
 Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview 1. Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security 2. Authentication, Authorization and Audit – The Three A’s 3. Security of target authentications 53
Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Overview 1. Enterprise Manager Infrastructure Security 2. Authentication, Authorization and Audit – The Three A’s 3. Security of target authentications 53
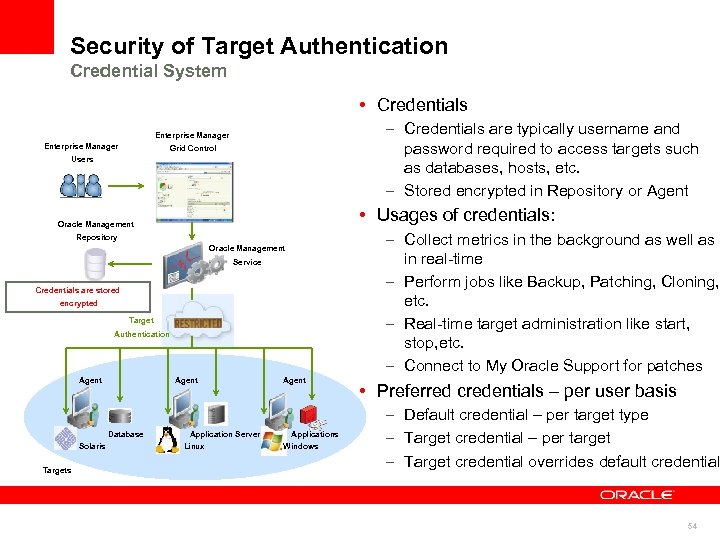 Security of Target Authentication Credential System • Credentials – Credentials are typically username and password required to access targets such as databases, hosts, etc. – Stored encrypted in Repository or Agent Enterprise Manager Grid Control Users • Usages of credentials: Oracle Management – Collect metrics in the background as well as in real-time – Perform jobs like Backup, Patching, Cloning, etc. – Real-time target administration like start, stop, etc. – Connect to My Oracle Support for patches Repository Oracle Management Service Credentials are stored encrypted Target Authentication Agent Database Solaris Targets Application Server Linux Agent Applications Windows • Preferred credentials – per user basis – Default credential – per target type – Target credential – per target – Target credential overrides default credential 54
Security of Target Authentication Credential System • Credentials – Credentials are typically username and password required to access targets such as databases, hosts, etc. – Stored encrypted in Repository or Agent Enterprise Manager Grid Control Users • Usages of credentials: Oracle Management – Collect metrics in the background as well as in real-time – Perform jobs like Backup, Patching, Cloning, etc. – Real-time target administration like start, stop, etc. – Connect to My Oracle Support for patches Repository Oracle Management Service Credentials are stored encrypted Target Authentication Agent Database Solaris Targets Application Server Linux Agent Applications Windows • Preferred credentials – per user basis – Default credential – per target type – Target credential – per target – Target credential overrides default credential 54
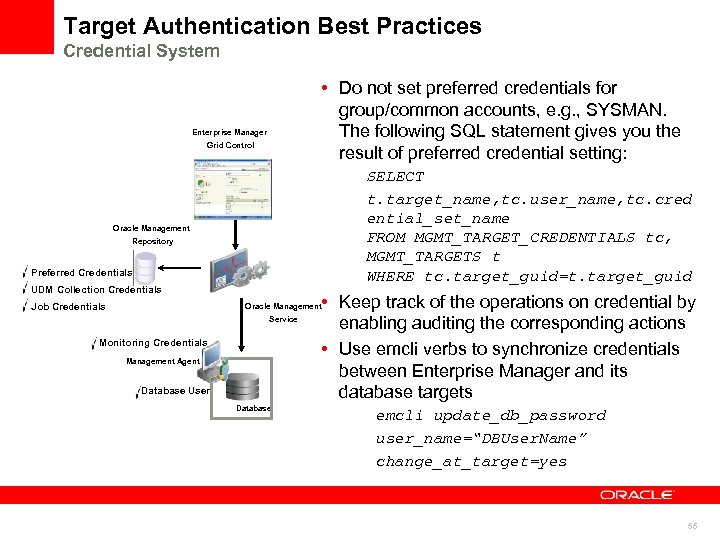 Target Authentication Best Practices Credential System • Do not set preferred credentials for group/common accounts, e. g. , SYSMAN. The following SQL statement gives you the result of preferred credential setting: Enterprise Manager Grid Control SELECT t. target_name, tc. user_name, tc. cred ential_set_name FROM MGMT_TARGET_CREDENTIALS tc, MGMT_TARGETS t WHERE tc. target_guid=t. target_guid Oracle Management Repository Preferred Credentials UDM Collection Credentials Job Credentials • Keep track of the operations on credential by enabling auditing the corresponding actions • Use emcli verbs to synchronize credentials between Enterprise Manager and its database targets Oracle Management Service Monitoring Credentials Management Agent Database User Database emcli update_db_password user_name=“DBUser. Name” change_at_target=yes 55
Target Authentication Best Practices Credential System • Do not set preferred credentials for group/common accounts, e. g. , SYSMAN. The following SQL statement gives you the result of preferred credential setting: Enterprise Manager Grid Control SELECT t. target_name, tc. user_name, tc. cred ential_set_name FROM MGMT_TARGET_CREDENTIALS tc, MGMT_TARGETS t WHERE tc. target_guid=t. target_guid Oracle Management Repository Preferred Credentials UDM Collection Credentials Job Credentials • Keep track of the operations on credential by enabling auditing the corresponding actions • Use emcli verbs to synchronize credentials between Enterprise Manager and its database targets Oracle Management Service Monitoring Credentials Management Agent Database User Database emcli update_db_password user_name=“DBUser. Name” change_at_target=yes 55
 Target Authentication Best Practices Host Target Authentication • Configure Pluggable Authentication Module(PAM) to take advantage of rich authentication approaches to Host access – Kerberos, RADIUS and LDAP supported to take advantage of the centralized identity storage and management – Web. IV 422073. 1: How to configure Agent with PAM to support LDAP authentication • Privilege Delegation (sudo/Power. Broker) supported across Enterprise Manager – Enable users to perform administrative tasks without providing credentials for functional accounts 56
Target Authentication Best Practices Host Target Authentication • Configure Pluggable Authentication Module(PAM) to take advantage of rich authentication approaches to Host access – Kerberos, RADIUS and LDAP supported to take advantage of the centralized identity storage and management – Web. IV 422073. 1: How to configure Agent with PAM to support LDAP authentication • Privilege Delegation (sudo/Power. Broker) supported across Enterprise Manager – Enable users to perform administrative tasks without providing credentials for functional accounts 56
 Threats vs. Best Practices Security Threats Best Practices Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Securing the communication Enable TLS v 1 protocol Configure firewalls …… Denial-of-Service Attacks Secure individual Enterprise Manager components …… Exploitation of Authorization Principle of least privileges Auditing the authorization actions …… Password crack Attacks Change password on a regular basis Enable password profile to enforce password control …… Repudiation Enable auditing for Grid Control actions 57
Threats vs. Best Practices Security Threats Best Practices Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Securing the communication Enable TLS v 1 protocol Configure firewalls …… Denial-of-Service Attacks Secure individual Enterprise Manager components …… Exploitation of Authorization Principle of least privileges Auditing the authorization actions …… Password crack Attacks Change password on a regular basis Enable password profile to enforce password control …… Repudiation Enable auditing for Grid Control actions 57
 Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
Agenda • Oracle Enterprise Manager Overview • Security Best Practices • Managing Enterprise Manager Security using Enterprise Manager • Q & A • Appendix
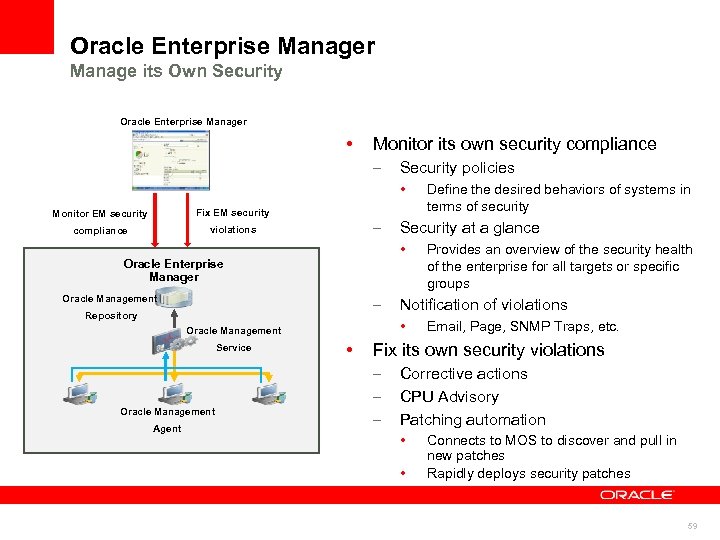 Oracle Enterprise Manager Manage its Own Security Oracle Enterprise Manager • Monitor its own security compliance – Security policies • Monitor EM security Fix EM security compliance violations – Oracle Management – Repository Oracle Management Agent • Provides an overview of the security health of the enterprise for all targets or specific groups Notification of violations • Oracle Management Service Security at a glance • Oracle Enterprise Manager Define the desired behaviors of systems in terms of security Email, Page, SNMP Traps, etc. Fix its own security violations – – – Corrective actions CPU Advisory Patching automation • • Connects to MOS to discover and pull in new patches Rapidly deploys security patches 59
Oracle Enterprise Manager Manage its Own Security Oracle Enterprise Manager • Monitor its own security compliance – Security policies • Monitor EM security Fix EM security compliance violations – Oracle Management – Repository Oracle Management Agent • Provides an overview of the security health of the enterprise for all targets or specific groups Notification of violations • Oracle Management Service Security at a glance • Oracle Enterprise Manager Define the desired behaviors of systems in terms of security Email, Page, SNMP Traps, etc. Fix its own security violations – – – Corrective actions CPU Advisory Patching automation • • Connects to MOS to discover and pull in new patches Rapidly deploys security patches 59
 Useful Whitepapers • Oracle Database Security Best Practices – http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/database/security/twpsecurity-checklist-database-1 -132870. pdf • Oracle Weblogic Server Security Best Practices – http: //download. oracle. com/docs/cd/E 12839_01/web. 1111/e 13705. pdf • Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Deployment Best Practices – http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/oem/grid-control/twpsecurity-best-practices-133704. pdf 60
Useful Whitepapers • Oracle Database Security Best Practices – http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/database/security/twpsecurity-checklist-database-1 -132870. pdf • Oracle Weblogic Server Security Best Practices – http: //download. oracle. com/docs/cd/E 12839_01/web. 1111/e 13705. pdf • Oracle Enterprise Manager Security Deployment Best Practices – http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/oem/grid-control/twpsecurity-best-practices-133704. pdf 60
 Additional Oracle Enterprise Manager Sessions Thursday, Sept. 23 Location • 3: 00 p. m - The X-Files: Managing the Oracle Exadata and Highly Available Oracle Databases • Moscone S. Room 102 • 3: 00 p. m. - Monitoring and Diagnosing Oracle RAC Performance with Oracle Enterprise Manager • Moscone S. Room 310
Additional Oracle Enterprise Manager Sessions Thursday, Sept. 23 Location • 3: 00 p. m - The X-Files: Managing the Oracle Exadata and Highly Available Oracle Databases • Moscone S. Room 102 • 3: 00 p. m. - Monitoring and Diagnosing Oracle RAC Performance with Oracle Enterprise Manager • Moscone S. Room 310
 Oracle Enterprise Manager 11 g Resource Center Access Videos, Webcasts, White Papers, and More Oracle. com/enterprisemanager 11 g
Oracle Enterprise Manager 11 g Resource Center Access Videos, Webcasts, White Papers, and More Oracle. com/enterprisemanager 11 g
 63
63
 64
64

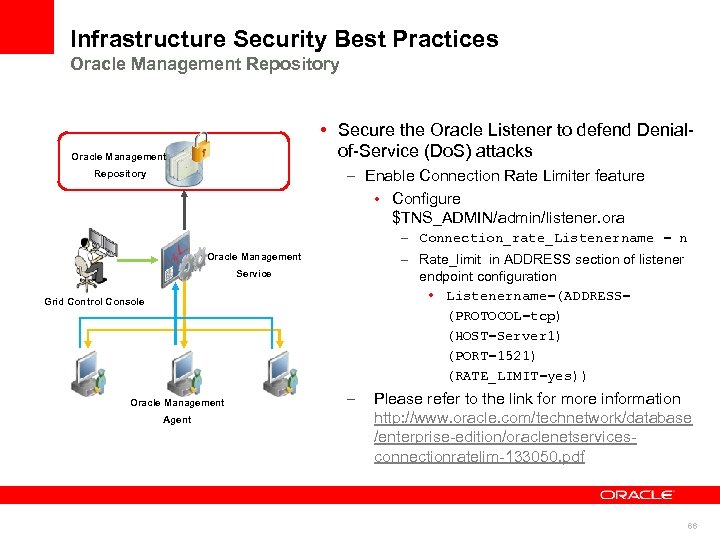 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Repository • Secure the Oracle Listener to defend Denialof-Service (Do. S) attacks Oracle Management – Enable Connection Rate Limiter feature • Configure $TNS_ADMIN/admin/listener. ora Repository – Connection_rate_Listenername = n – Rate_limit in ADDRESS section of listener endpoint configuration • Listenername=(ADDRESS= (PROTOCOL=tcp) (HOST=Server 1) (PORT=1521) (RATE_LIMIT=yes)) Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent – Please refer to the link for more information http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/database /enterprise-edition/oraclenetservicesconnectionratelim-133050. pdf 66
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Oracle Management Repository • Secure the Oracle Listener to defend Denialof-Service (Do. S) attacks Oracle Management – Enable Connection Rate Limiter feature • Configure $TNS_ADMIN/admin/listener. ora Repository – Connection_rate_Listenername = n – Rate_limit in ADDRESS section of listener endpoint configuration • Listenername=(ADDRESS= (PROTOCOL=tcp) (HOST=Server 1) (PORT=1521) (RATE_LIMIT=yes)) Oracle Management Service Grid Control Console Oracle Management Agent – Please refer to the link for more information http: //www. oracle. com/technetwork/database /enterprise-edition/oraclenetservicesconnectionratelim-133050. pdf 66
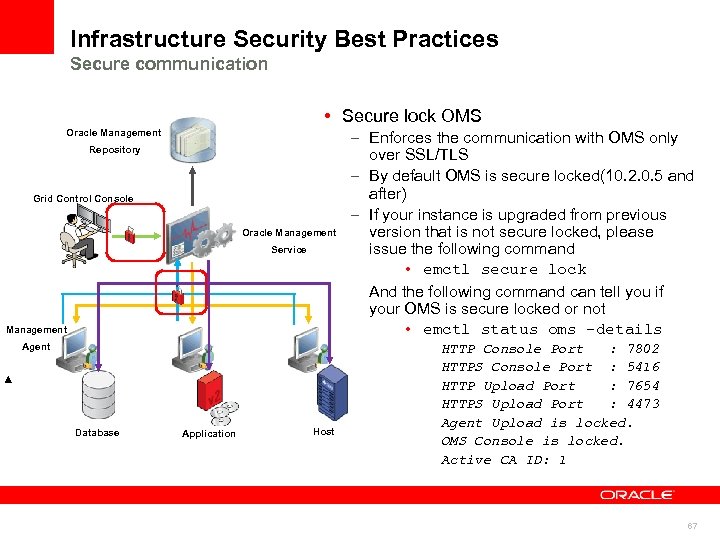 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Secure lock OMS Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application Host – Enforces the communication with OMS only over SSL/TLS – By default OMS is secure locked(10. 2. 0. 5 and after) – If your instance is upgraded from previous version that is not secure locked, please issue the following command • emctl secure lock And the following command can tell you if your OMS is secure locked or not • emctl status oms –details HTTP Console Port : 7802 HTTPS Console Port : 5416 HTTP Upload Port : 7654 HTTPS Upload Port : 4473 Agent Upload is locked. OMS Console is locked. Active CA ID: 1 67
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Secure lock OMS Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application Host – Enforces the communication with OMS only over SSL/TLS – By default OMS is secure locked(10. 2. 0. 5 and after) – If your instance is upgraded from previous version that is not secure locked, please issue the following command • emctl secure lock And the following command can tell you if your OMS is secure locked or not • emctl status oms –details HTTP Console Port : 7802 HTTPS Console Port : 5416 HTTP Upload Port : 7654 HTTPS Upload Port : 4473 Agent Upload is locked. OMS Console is locked. Active CA ID: 1 67
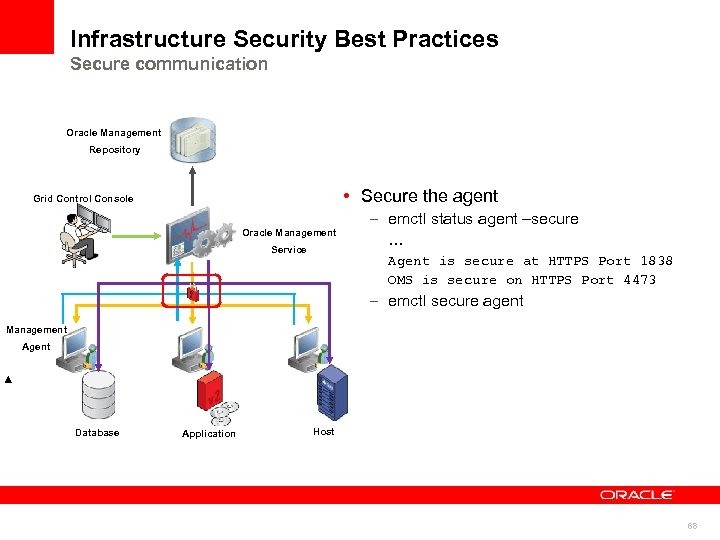 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication Oracle Management Repository • Secure the agent Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service – emctl status agent –secure … Agent is secure at HTTPS Port 1838 OMS is secure on HTTPS Port 4473 – emctl secure agent Management Agent Database Application Host 68
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication Oracle Management Repository • Secure the agent Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service – emctl status agent –secure … Agent is secure at HTTPS Port 1838 OMS is secure on HTTPS Port 4473 – emctl secure agent Management Agent Database Application Host 68
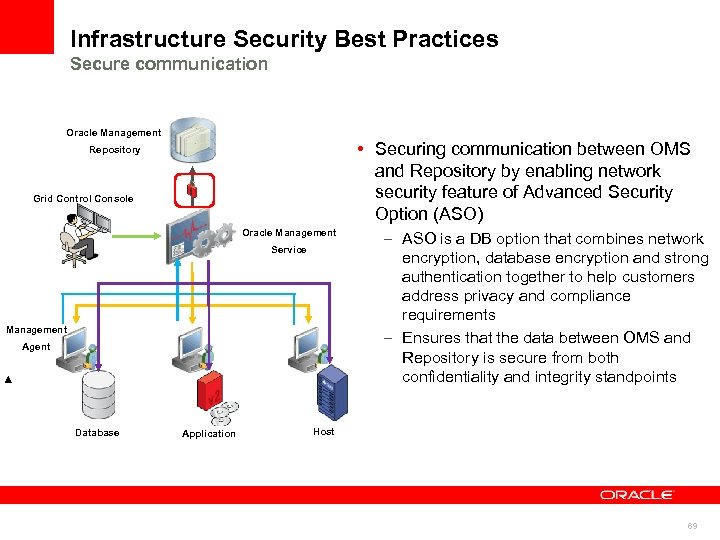 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication Oracle Management • Securing communication between OMS and Repository by enabling network security feature of Advanced Security Option (ASO) Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application – ASO is a DB option that combines network encryption, database encryption and strong authentication together to help customers address privacy and compliance requirements – Ensures that the data between OMS and Repository is secure from both confidentiality and integrity standpoints Host 69
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication Oracle Management • Securing communication between OMS and Repository by enabling network security feature of Advanced Security Option (ASO) Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application – ASO is a DB option that combines network encryption, database encryption and strong authentication together to help customers address privacy and compliance requirements – Ensures that the data between OMS and Repository is secure from both confidentiality and integrity standpoints Host 69
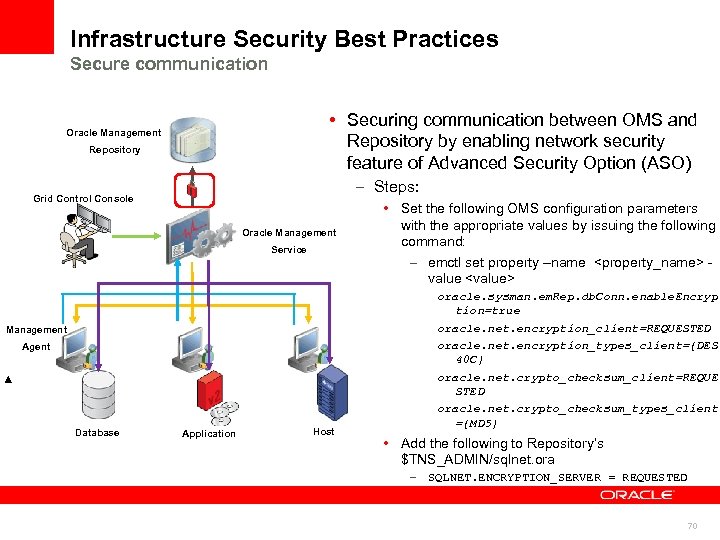 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Securing communication between OMS and Repository by enabling network security feature of Advanced Security Option (ASO) Oracle Management Repository – Steps: Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application Host • Set the following OMS configuration parameters with the appropriate values by issuing the following command: – emctl set property –name
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Securing communication between OMS and Repository by enabling network security feature of Advanced Security Option (ASO) Oracle Management Repository – Steps: Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application Host • Set the following OMS configuration parameters with the appropriate values by issuing the following command: – emctl set property –name
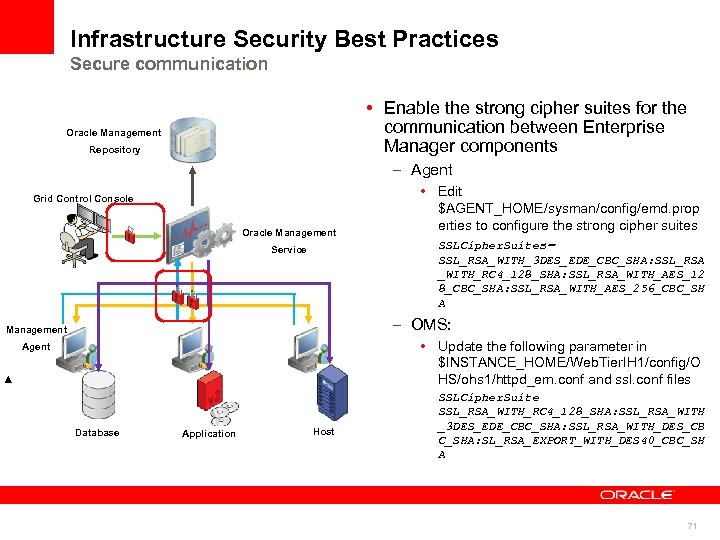 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Enable the strong cipher suites for the communication between Enterprise Manager components Oracle Management Repository – Agent Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service • Edit $AGENT_HOME/sysman/config/emd. prop erties to configure the strong cipher suites SSLCipher. Suites = SSL_RSA_WITH_3 DES_EDE_CBC_SHA: SSL_RSA _WITH_RC 4_128_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH_AES_12 8_CBC_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SH A – OMS: Management • Update the following parameter in $INSTANCE_HOME/Web. Tier. IH 1/config/O HS/ohs 1/httpd_em. conf and ssl. conf files Agent Database Application Host SSLCipher. Suite SSL_RSA_WITH_RC 4_128_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH _3 DES_EDE_CBC_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH_DES_CB C_SHA: SL_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_DES 40_CBC_SH A 71
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Enable the strong cipher suites for the communication between Enterprise Manager components Oracle Management Repository – Agent Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service • Edit $AGENT_HOME/sysman/config/emd. prop erties to configure the strong cipher suites SSLCipher. Suites = SSL_RSA_WITH_3 DES_EDE_CBC_SHA: SSL_RSA _WITH_RC 4_128_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH_AES_12 8_CBC_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SH A – OMS: Management • Update the following parameter in $INSTANCE_HOME/Web. Tier. IH 1/config/O HS/ohs 1/httpd_em. conf and ssl. conf files Agent Database Application Host SSLCipher. Suite SSL_RSA_WITH_RC 4_128_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH _3 DES_EDE_CBC_SHA: SSL_RSA_WITH_DES_CB C_SHA: SL_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_DES 40_CBC_SH A 71
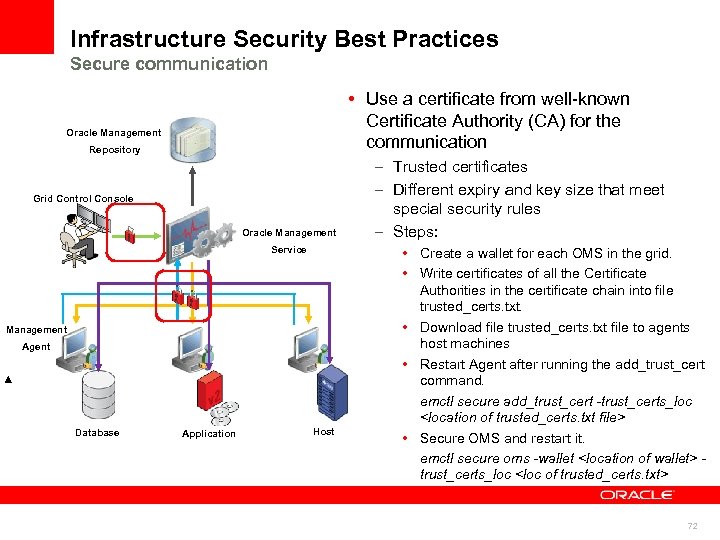 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Use a certificate from well-known Certificate Authority (CA) for the communication Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application Host – Trusted certificates – Different expiry and key size that meet special security rules – Steps: • Create a wallet for each OMS in the grid. • Write certificates of all the Certificate Authorities in the certificate chain into file trusted_certs. txt. • Download file trusted_certs. txt file to agents host machines • Restart Agent after running the add_trust_cert command. emctl secure add_trust_cert -trust_certs_loc
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Secure communication • Use a certificate from well-known Certificate Authority (CA) for the communication Oracle Management Repository Grid Control Console Oracle Management Service Management Agent Database Application Host – Trusted certificates – Different expiry and key size that meet special security rules – Steps: • Create a wallet for each OMS in the grid. • Write certificates of all the Certificate Authorities in the certificate chain into file trusted_certs. txt. • Download file trusted_certs. txt file to agents host machines • Restart Agent after running the add_trust_cert command. emctl secure add_trust_cert -trust_certs_loc
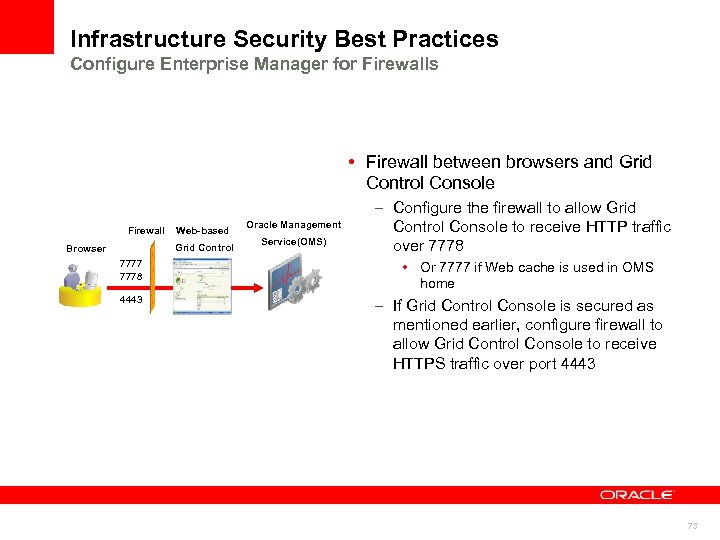 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Firewall between browsers and Grid Control Console Firewall Web-based Grid Control Browser 7777 7778 4443 Oracle Management Service(OMS) – Configure the firewall to allow Grid Control Console to receive HTTP traffic over 7778 • Or 7777 if Web cache is used in OMS home – If Grid Control Console is secured as mentioned earlier, configure firewall to allow Grid Control Console to receive HTTPS traffic over port 4443 73
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls • Firewall between browsers and Grid Control Console Firewall Web-based Grid Control Browser 7777 7778 4443 Oracle Management Service(OMS) – Configure the firewall to allow Grid Control Console to receive HTTP traffic over 7778 • Or 7777 if Web cache is used in OMS home – If Grid Control Console is secured as mentioned earlier, configure firewall to allow Grid Control Console to receive HTTPS traffic over port 4443 73
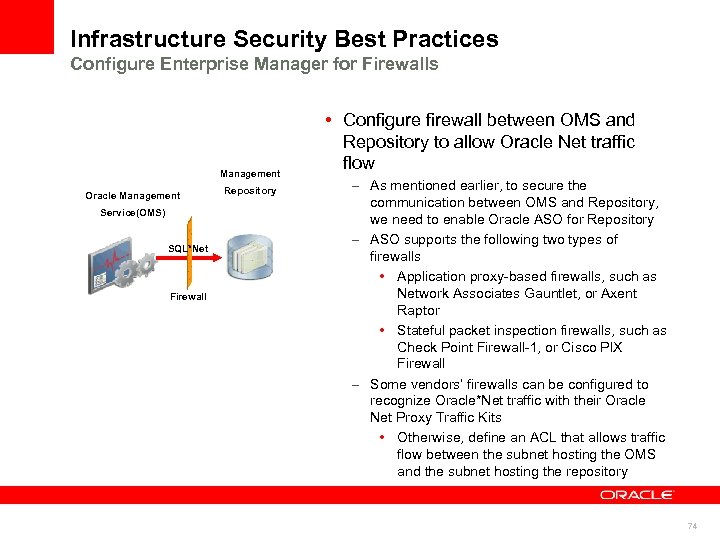 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Management Oracle Management Service(OMS) SQL*Net Firewall Repository • Configure firewall between OMS and Repository to allow Oracle Net traffic flow – As mentioned earlier, to secure the communication between OMS and Repository, we need to enable Oracle ASO for Repository – ASO supports the following two types of firewalls • Application proxy-based firewalls, such as Network Associates Gauntlet, or Axent Raptor • Stateful packet inspection firewalls, such as Check Point Firewall-1, or Cisco PIX Firewall – Some vendors’ firewalls can be configured to recognize Oracle*Net traffic with their Oracle Net Proxy Traffic Kits • Otherwise, define an ACL that allows traffic flow between the subnet hosting the OMS and the subnet hosting the repository 74
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Management Oracle Management Service(OMS) SQL*Net Firewall Repository • Configure firewall between OMS and Repository to allow Oracle Net traffic flow – As mentioned earlier, to secure the communication between OMS and Repository, we need to enable Oracle ASO for Repository – ASO supports the following two types of firewalls • Application proxy-based firewalls, such as Network Associates Gauntlet, or Axent Raptor • Stateful packet inspection firewalls, such as Check Point Firewall-1, or Cisco PIX Firewall – Some vendors’ firewalls can be configured to recognize Oracle*Net traffic with their Oracle Net Proxy Traffic Kits • Otherwise, define an ACL that allows traffic flow between the subnet hosting the OMS and the subnet hosting the repository 74
 Privilege Propagating Group • Privilege Propagating Group – A special group that the privileges granted on will be propagated to its nested and direct members • For a normal group, no matter what privileges (FULL, OPERATOR or VIEW) on the group is granted to you, you’ll only get VIEW privileges on the group members – System privilege “Create Privilege Propagating Group” is required to create this type of group – “Full privilege” on the target is required to add the target as a member of a group – emcli verb to convert the normal group and privilege propagating group • emcli modify_group –privilege_propagating =true/false • Privilege Propagating System, Redundancy Group, Aggregate Services 75
Privilege Propagating Group • Privilege Propagating Group – A special group that the privileges granted on will be propagated to its nested and direct members • For a normal group, no matter what privileges (FULL, OPERATOR or VIEW) on the group is granted to you, you’ll only get VIEW privileges on the group members – System privilege “Create Privilege Propagating Group” is required to create this type of group – “Full privilege” on the target is required to add the target as a member of a group – emcli verb to convert the normal group and privilege propagating group • emcli modify_group –privilege_propagating =true/false • Privilege Propagating System, Redundancy Group, Aggregate Services 75
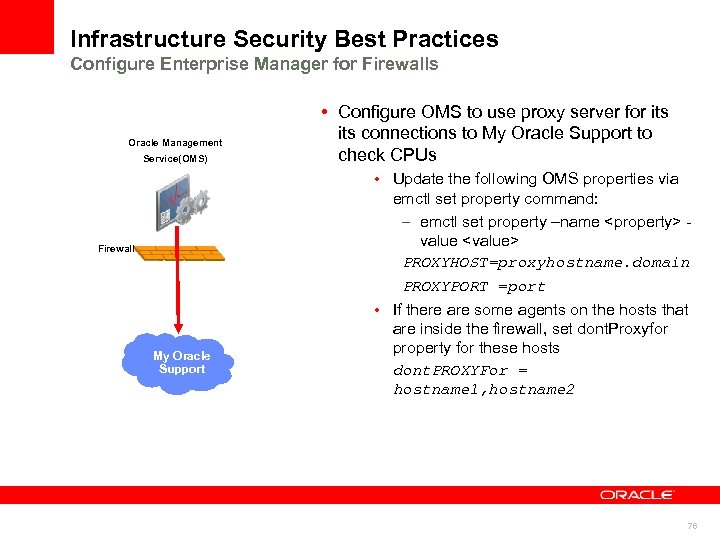 Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Oracle Management Service(OMS) Firewall My Oracle Support • Configure OMS to use proxy server for its connections to My Oracle Support to check CPUs • Update the following OMS properties via emctl set property command: – emctl set property –name
Infrastructure Security Best Practices Configure Enterprise Manager for Firewalls Oracle Management Service(OMS) Firewall My Oracle Support • Configure OMS to use proxy server for its connections to My Oracle Support to check CPUs • Update the following OMS properties via emctl set property command: – emctl set property –name
 Manage Enterprise Manager Security Monitor its own Security • Security Policies – – – Oracle Enterprise Manager • Security at a glance – Security Violations • Help you quickly identify systems that are not in compliance Out-of-box policies adopted from industry best practices Customize policies to meet specific security need in your organization Helps you to quickly focus on security issues by showing statistics about security policy violations and noting the critical security patches that have not been applied • Compliance scores and Violation flux Notification of violations – E-mail, Page, SNMP Traps, etc. 77
Manage Enterprise Manager Security Monitor its own Security • Security Policies – – – Oracle Enterprise Manager • Security at a glance – Security Violations • Help you quickly identify systems that are not in compliance Out-of-box policies adopted from industry best practices Customize policies to meet specific security need in your organization Helps you to quickly focus on security issues by showing statistics about security policy violations and noting the critical security patches that have not been applied • Compliance scores and Violation flux Notification of violations – E-mail, Page, SNMP Traps, etc. 77
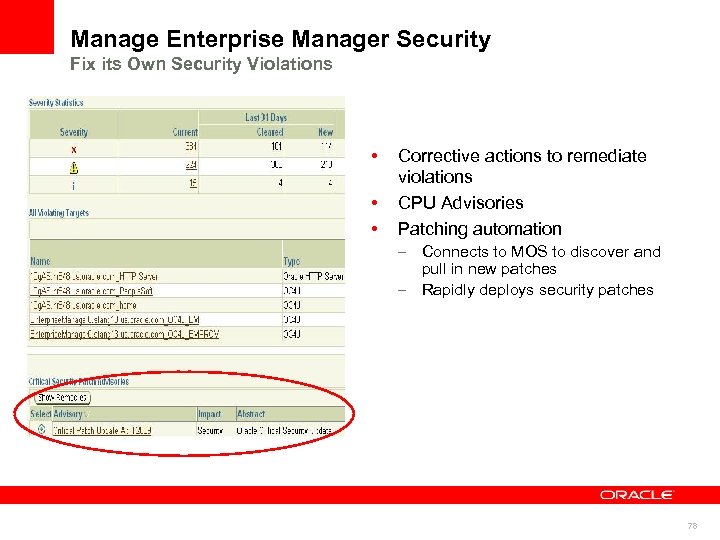 Manage Enterprise Manager Security Fix its Own Security Violations • • • Oracle Enterprise Manager Corrective actions to remediate violations CPU Advisories Patching automation – Connects to MOS to discover and pull in new patches – Rapidly deploys security patches Corrective Actions Security Violations 78
Manage Enterprise Manager Security Fix its Own Security Violations • • • Oracle Enterprise Manager Corrective actions to remediate violations CPU Advisories Patching automation – Connects to MOS to discover and pull in new patches – Rapidly deploys security patches Corrective Actions Security Violations 78


