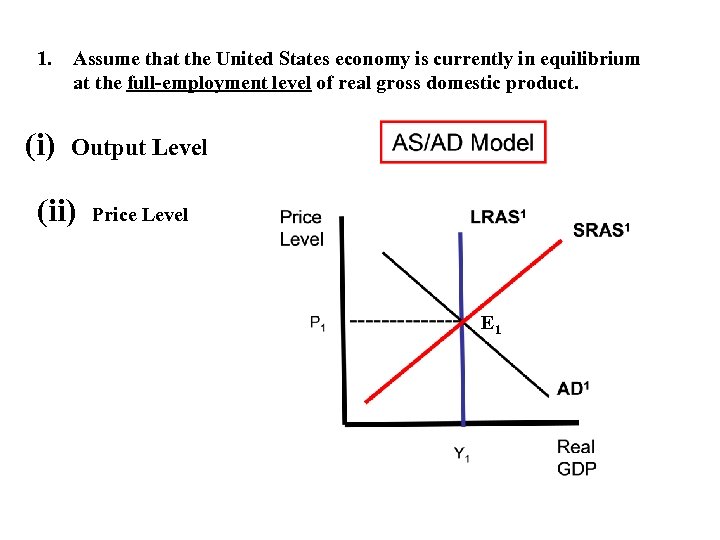
 1. (i) Assume that the United States economy is currently in equilibrium at the full-employment level of real gross domestic product. Output Level (ii) Price Level E 1
1. (i) Assume that the United States economy is currently in equilibrium at the full-employment level of real gross domestic product. Output Level (ii) Price Level E 1
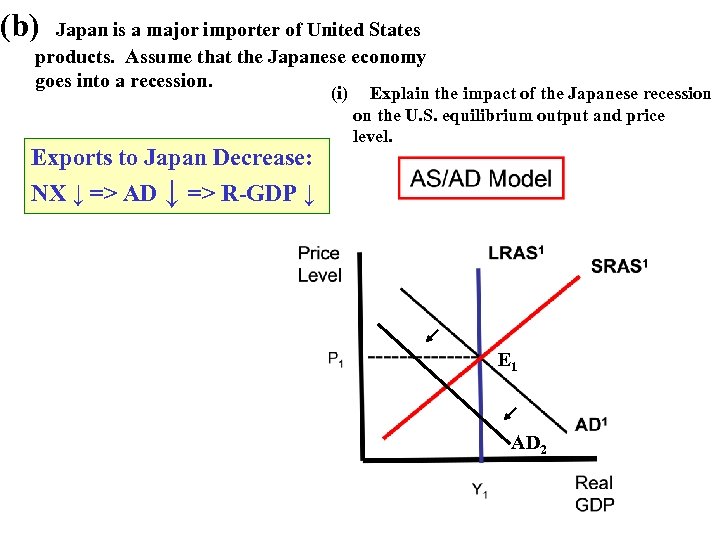 (b) Japan is a major importer of United States products. Assume that the Japanese economy goes into a recession. (i) Exports to Japan Decrease: Explain the impact of the Japanese recession on the U. S. equilibrium output and price level. NX ↓ => AD ↓ => R-GDP ↓ E 1 AD 2
(b) Japan is a major importer of United States products. Assume that the Japanese economy goes into a recession. (i) Exports to Japan Decrease: Explain the impact of the Japanese recession on the U. S. equilibrium output and price level. NX ↓ => AD ↓ => R-GDP ↓ E 1 AD 2
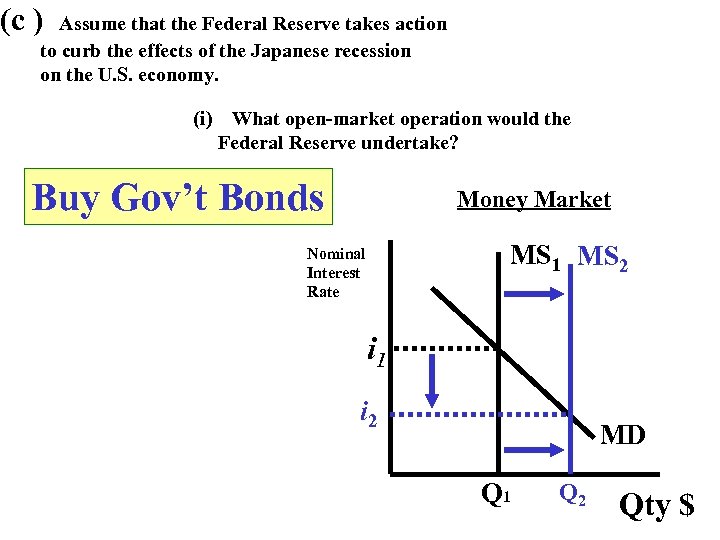 (c ) Assume that the Federal Reserve takes action to curb the effects of the Japanese recession on the U. S. economy. (i) What open-market operation would the Federal Reserve undertake? Buy Gov’t Bonds Money Market MS 1 MS 2 Nominal Interest Rate i 1 i 2 MD Q 1 Q 2 Qty $
(c ) Assume that the Federal Reserve takes action to curb the effects of the Japanese recession on the U. S. economy. (i) What open-market operation would the Federal Reserve undertake? Buy Gov’t Bonds Money Market MS 1 MS 2 Nominal Interest Rate i 1 i 2 MD Q 1 Q 2 Qty $
 (iii) Explain how the change in the nominal interest rate in part (c ) (ii) will affect aggregate demand price level, and real output in the U. S. When nominal interest rates drop => Investment ↑ (I) & Consumption ↑ (C) => Therefore AD ↑
(iii) Explain how the change in the nominal interest rate in part (c ) (ii) will affect aggregate demand price level, and real output in the U. S. When nominal interest rates drop => Investment ↑ (I) & Consumption ↑ (C) => Therefore AD ↑
 (d) Define the real interest rate. real rate = nominal rate – expected inflation
(d) Define the real interest rate. real rate = nominal rate – expected inflation
 (e) Indicate the effect of the open-market operation you identified in part (c ) (i) on the real interest rate in the United States. When the nominal rate is going down and the inflation rate is going up (AD shift), then the real rate must go down. Formula: real rate = nominal – expected inflation
(e) Indicate the effect of the open-market operation you identified in part (c ) (i) on the real interest rate in the United States. When the nominal rate is going down and the inflation rate is going up (AD shift), then the real rate must go down. Formula: real rate = nominal – expected inflation