Prezentatsia_Geography_of_UK.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 35

1. Geographical components and borders • The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland occupies most of the territory of the British Isles. The British Isles is the geographical name that refers to all the islands off the north-west coast of Europe: Great Britain, the whole of Ireland (Northern and Southern), the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. • Southern Island – that is the republic of Ireland (also called Eire) – is completely independent. The UK includes the Isle of Wight, Anglesey, the Isles of Scilly, the Hebrides and the island groups of Orkney and Shetland. It does not include the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. • Great Britain is the ninth largest island in the world and the largest island in Europe.
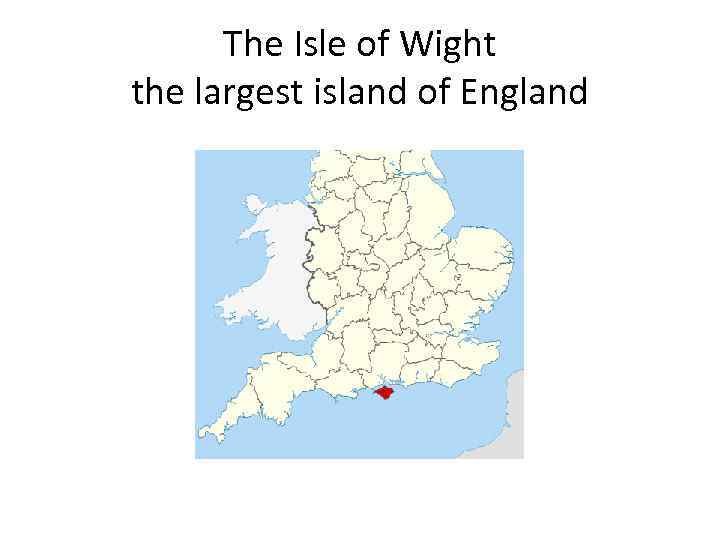
The Isle of Wight the largest island of England
Anglesey is a county off the northwest coast of Wales
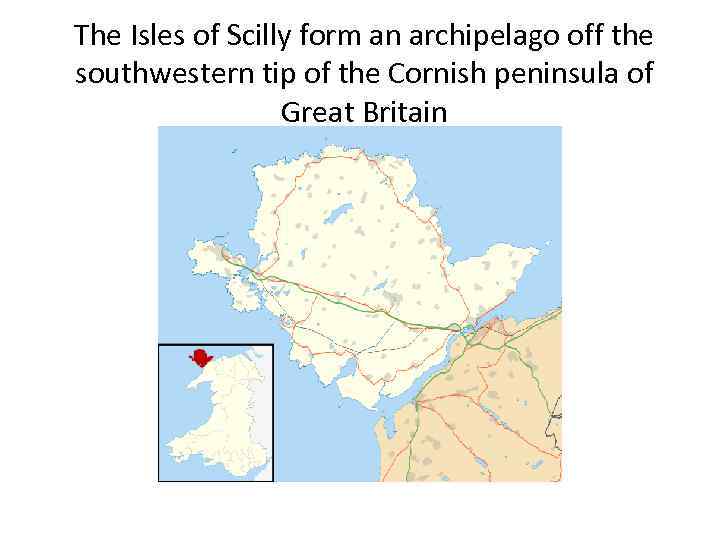
The Isles of Scilly form an archipelago off the southwestern tip of the Cornish peninsula of Great Britain
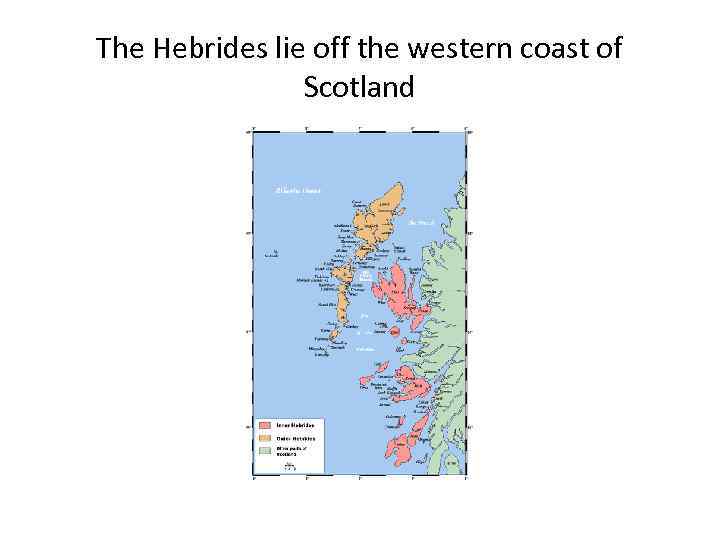
The Hebrides lie off the western coast of Scotland
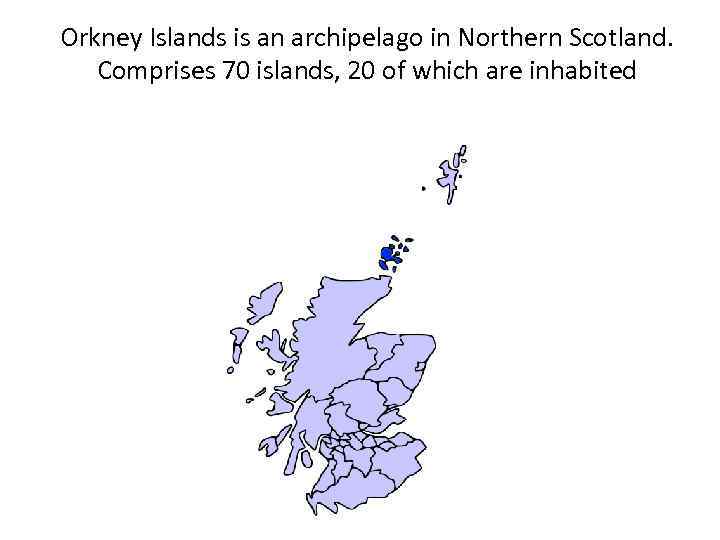
Orkney Islands is an archipelago in Northern Scotland. Comprises 70 islands, 20 of which are inhabited
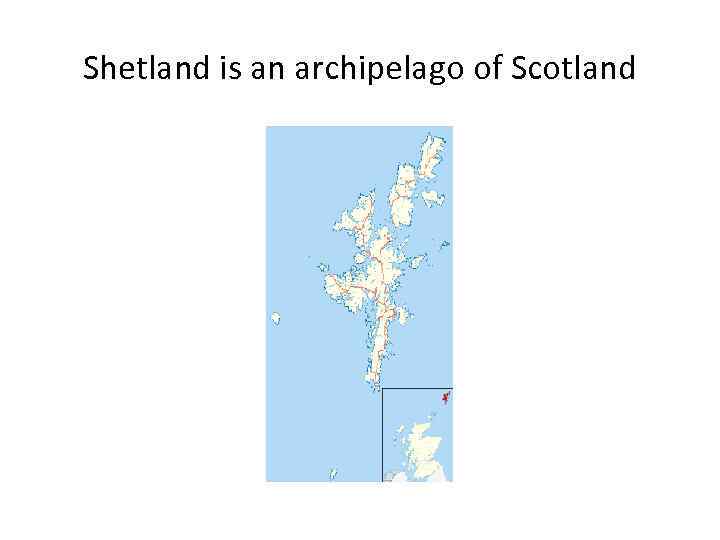
Shetland is an archipelago of Scotland

• The UK consists of 4 main parts which are England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Island. Their capitals are London, Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast. • The Area of the UK is some 244, 100 sq km. • It is bordered on the South, that is it is separated from Europe by the English Channel (or La Manche) and the Strait of Dover (Pas de Calais), on the east by the North Sea and on the west by the Irish Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.

England is the largest, most populous and wealthiest division of the UK. England is separated from Scotland by the Cheviot Hills, a range of hills running from east to west.

England • England is divided into the North West, The North East, the Midlands (центральные графства), East Anglia, the Home Counties (around London) and the West Country.

• England is mostly a lowland country. The Lake District in Northern England with its lakes, mountains and valleys is a popular holiday area. The chief cities are London, Birmingham (metal goods), Leeds and Bradford where the wool industry is centred, Manchester where the cotton industry is centred, Newcastleupon-Tyne. • In Southern England there is the Stonehenge.

Stonehenge, an ancient building on the Salisbury Plain in England, the most famous prehistoric place in Europe

Scotland • Scotland is not densely populated although it takes up one third of the territory of the British Isles. • The Cheviot Hills mark the boundary between England Scotland. Apart from this land link with England, Scotland is surrounded by the sea. Scotland includes the Hebrides, the Orkney and Shetland Islands. • The Highlands of Scotland are among the oldest mountains in the world. They reach the highest point in Ben Nevis (1343 m). • Many valleys between the hills are filled with lakes, called lochs. The best known is Loch Ness.

• The most important city is Aberdeen which is the oil centre. Most population is concentrated in and around Glasgow in the Lowlands, Scotland’s biggest city. Glasgow stands on the river Clyde. • One of the things that people associate with Scotland is a kilt. The kilt is a relic of the time when the clan system existed in the Highlands. Everybody in the clan had the same family name, like Mac. Donald or Mac. Gregor (Mac means son of). Each clan had its own tartan (традиционный шотландский рисунок из перекрещивающихся полос). • Ediburgh is the cultural centre. It is associated with George Gordon Byron, Walter Scott, Robert Louis Stevenson, Robert Burns and Arthur Conan Doyle. It is also well-known for its world-famous Festival of Music and Drama.
Wales • Wales. The Welsh call their country Cymru and they call themselves Cymry (the word which has the same root as comrader). • Cardiff (the capital) is situated near the mouth of the river Taff. The second largest city is Swansea. • Wales is bordered by England to the east and by sea in all other directions. • The pride of Wales in scenery is Snowdonia, a region of high mountains. Snowdon is the highest mountain in England Wales (1, 085 m).

The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia. The highest is Snowdon.

Northern Ireland • Northern Island contains six of the 9 of the historic province of Ulster and that’s why the name Ulster is sometimes used as equivalent to northern Island. • The capital is Belfast. • The largest river is Shannon.
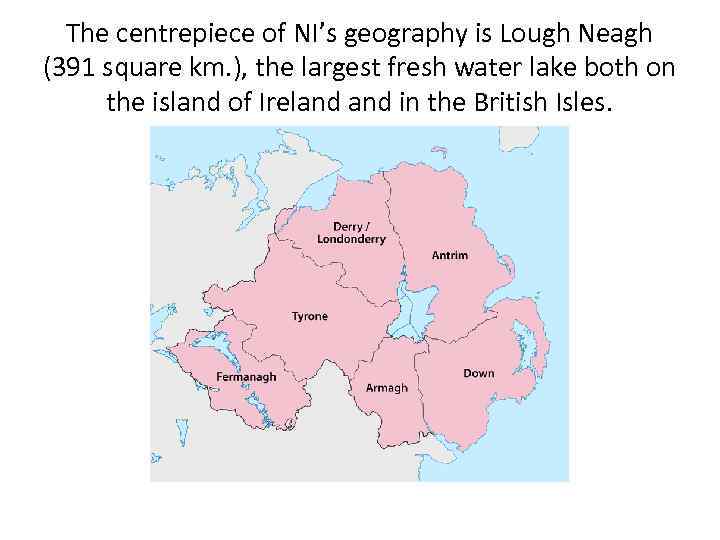
The centrepiece of NI’s geography is Lough Neagh (391 square km. ), the largest fresh water lake both on the island of Ireland in the British Isles.
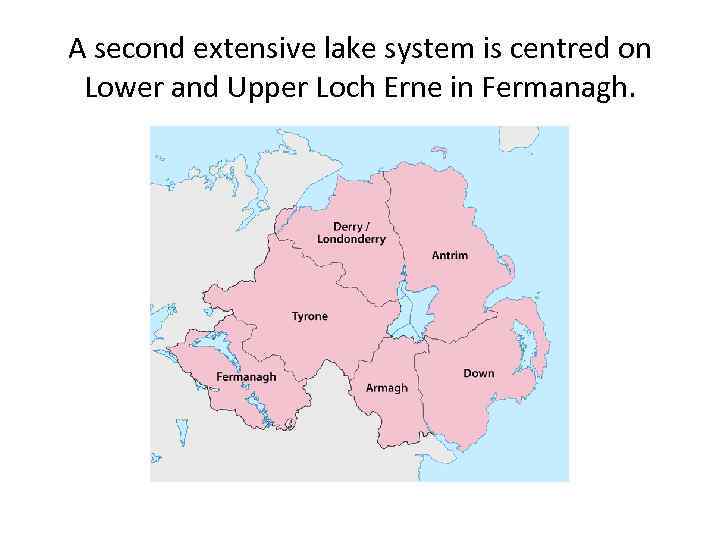
A second extensive lake system is centred on Lower and Upper Loch Erne in Fermanagh.

Lower Lough Erne
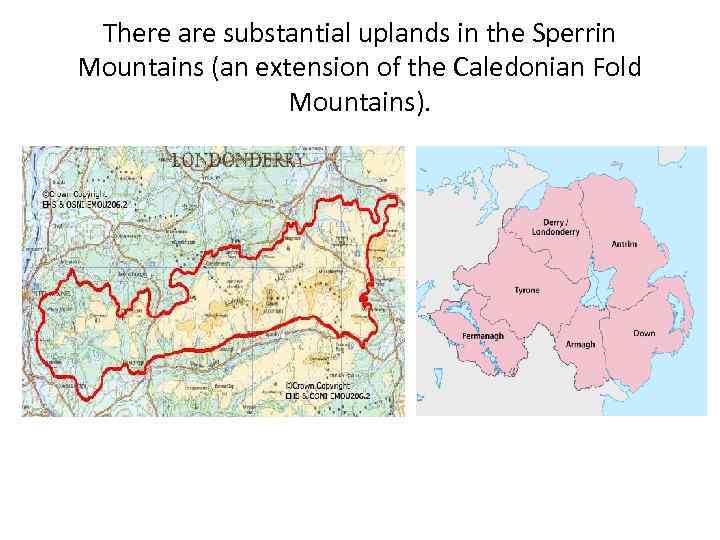
There are substantial uplands in the Sperrin Mountains (an extension of the Caledonian Fold Mountains).

2. Natural regions • Geographically, the island of Great Britain is subdivided into main regions – the highland zone in the north and west and the lowland zone in the south and east. • The Highland Britain consists of Scotland, most of Wales, the Pennines (the backbone of England), and the Lake District.
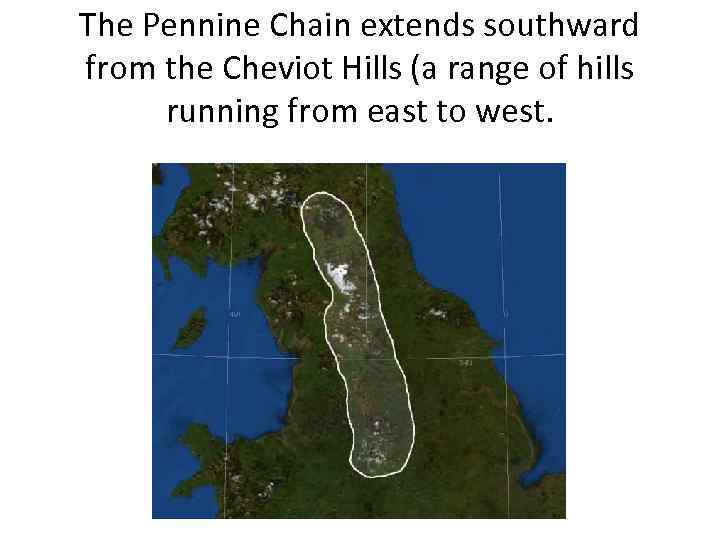
The Pennine Chain extends southward from the Cheviot Hills (a range of hills running from east to west.

• The highland zone contains what is known rough country, consisting to a large extent of hills, mountains and eroded areas frequently broken by valleys and plains, where farming is impossible. ) • The highland zone is cooler than the lowland zone, and receives more rainfall and less sunlight. The lowland zone comprises southern and eastern England. Unlike lowlands, it receives less rain and more sunshine, it has a milder climate and better soils for farming.

3. Rivers and lakes • The Severn (290 km) flows along the border between England Wales. Its tributaries (притоки) are the Avon, famed by Shakespeare, and the Thames, which flows eastward to the port of London. • The swiftest flowing river in the British Isles is the Spey. • Part of the border between Scotland England is along the lower reaches of the Tweed. Near this river they make the woollen fabric that bears its name. • Rivers in central and eastern Britain tend to flow slowly and steadily because they are fed by the frequent rain. Rivers and streams moving westward down from the Highlands tend to be swift and turbulent.

Lakes • On the northwest side of the Pennine system (гряда Пенинских гор) lies the Lake District. This district is widely known for its association with the history of English Literature and especially with the name of William Wordsworth (1770 1859), the founder of the Lake School of poets. • The largest lakes are Windermere, Coniston water, Derwent water and Ullswater. • Much of the land is high and thinly peopled. These high parts are used as rough pastures for sheep. (пастбище на неровной местности). The whole region is well-known for its natural beauty.

• Since the Lake District is a national park, there is special control over building, to make sure that the beauty of the countryside is not spoiled. • Nearly one quarter of the Lake District National Park is owned by the National Trust. • The National Trust is a charity, which means it is financed by ordinary people who pay to become members. It is not financed or run by the government. The Trust was set up in 1895 by three people who thought that industrialization could spoil the countryside and ancient buildings of England Wales.

4. Natural resources • In northern areas the soils are thin, lying right above rock formations, while the south possesses areas of rich loam and heavy clay soils. • While 77 percent of the land in Britain is used for agriculture, only 25 percent of this land is used to grow crops. • Almost all of the rest is used as grazing land. Today only 9. 9 percent of the UK is forested, roughly 2 million hectares. In contrast, 25 percent of Europe is forested. • Britain’s forests produce about 15 percent of the total wood the country consumes, and Britain imports substantial amounts of wood and wood products.

Extensive forests remain in eastern and northern Scotland in southeastern and western areas. The Highlands with thin soil are largely moorland (вересковая пустошь) with heather and grasses

• . Britain's mineral resources were historically important, but today most of these resources are either exhausted or produced in small quantities. • Britain currently relies upon imports from larger, cheaper foreign supplies. • Nearly every tin mine in Britain has been exhausted and shut down. Today Britain imports iron, along with most other minerals used for industrial production, although small amounts of iron, zinc, and copper are still produced.

• Today Britain is the world's eighth largest producer of crude oil and natural gas liquids. But more than half of North Sea oil reserves have been extracted. • Coal nowadays is far less important to the British economy, so Britain imports much more coal than it exports. • It also meets 28 percent of its energy needs through nuclear energy.

5. Climate of the UK • The climate of the UK is generally mild and temperate due to the influence of the Gulf Stream. The southwestern winds carry warmth and moisture into Britain. • Rainfall is more or less even throughout the year. In the mountains there is heavier rainfall than in the plains of the south and east. The driest period is from March to June and the wettest months are from October to January.

• The average range of temperature is from 5 to 23 degrees above zero. Winter temperatures below 10 degrees are rare. It seldom snows heavily in winter. January and February are usually the coldest months, July and August are the warmest. So, we may say that the British climate has three main features: it is mild, humid and changeable.

• This humid and mild climate is good for plants. They begin to blossom early in spring. Some of them have become symbols in the UK. • The poppy is the symbol of peace, the red rose is the national emblem of England. • The thistle is the national emblem of Scotland. • The daffodil (жёлтый нарцисс, 2 ая эмблема Уэльса) and the leek (лук порей) are the emblems of Wales. • The shamrock (трилистник) (a kind of clover клевер) is the emblem of Ireland.
Prezentatsia_Geography_of_UK.pptx