bd5c65726be42cc51e6ab8d0e6180621.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 136
 1. General Introduction International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 1
1. General Introduction International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 1
 Introduction to International, Foreign & Comparative Law Research • • Public International Law – Treaty Search – Human Rights Search International Trade Law – WTO – CISG Regional Organizations – European Union as an example Foreign Law Research – Common Law v. Civil Law – European Countries • Comparative Law Research International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 2
Introduction to International, Foreign & Comparative Law Research • • Public International Law – Treaty Search – Human Rights Search International Trade Law – WTO – CISG Regional Organizations – European Union as an example Foreign Law Research – Common Law v. Civil Law – European Countries • Comparative Law Research International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 2
 Definitions • International Law – Public International Law – Private International Law (Conflicts of Law) • Yukos case • Foreign Law • Comparative Law Not to expect everything online. Where to start? Hornbooks, Treatises, Nutshells etc. Law review articles How to deal with abbreviations? Blue Book or Biebers International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 3
Definitions • International Law – Public International Law – Private International Law (Conflicts of Law) • Yukos case • Foreign Law • Comparative Law Not to expect everything online. Where to start? Hornbooks, Treatises, Nutshells etc. Law review articles How to deal with abbreviations? Blue Book or Biebers International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 3
 Common Law v. Civil Law • Common Law Countries U. S. , UK, Commonwealth • Civil Law Countries Continental Europe, Asian, Middle East, Latin America • Mixed Some African Counties A Great Source for overview: Foreign Law-Current Sources of Codes and Legislation in Jurisdiction of the world, by T. Reynolds & A. Flores (Call#: K 38. R 49 1988 Reference Collection) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 4
Common Law v. Civil Law • Common Law Countries U. S. , UK, Commonwealth • Civil Law Countries Continental Europe, Asian, Middle East, Latin America • Mixed Some African Counties A Great Source for overview: Foreign Law-Current Sources of Codes and Legislation in Jurisdiction of the world, by T. Reynolds & A. Flores (Call#: K 38. R 49 1988 Reference Collection) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 4
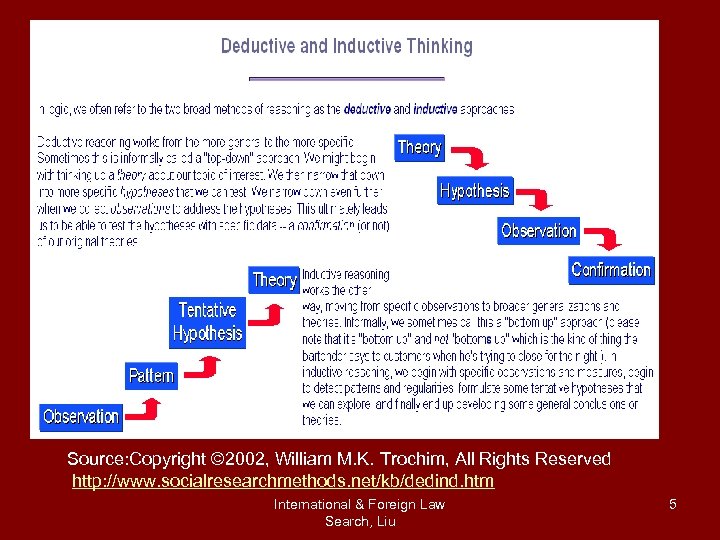 Source: Copyright © 2002, William M. K. Trochim, All Rights Reserved http: //www. socialresearchmethods. net/kb/dedind. htm International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 5
Source: Copyright © 2002, William M. K. Trochim, All Rights Reserved http: //www. socialresearchmethods. net/kb/dedind. htm International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 5
 Foreign Law Research Not as easy as finding U. S. law Useful Sources Thomas H. Reynolds & Arturo A. Flores, Foreign Law. Current Sources of Codes and Legislation in Jurisprudence of the World (K 38. R 49 1989, Reference Collection) Online Research Guide Muligan and Liu’s Foreign Primary Law on the Web LLRX. com Resource Center - Comparative and Foreign Law Foreign and International Law Sources on the Internet: Annotated Lexis. Nexis (Legal (excluding U. S. ) ) Reference Librarians International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 6
Foreign Law Research Not as easy as finding U. S. law Useful Sources Thomas H. Reynolds & Arturo A. Flores, Foreign Law. Current Sources of Codes and Legislation in Jurisprudence of the World (K 38. R 49 1989, Reference Collection) Online Research Guide Muligan and Liu’s Foreign Primary Law on the Web LLRX. com Resource Center - Comparative and Foreign Law Foreign and International Law Sources on the Internet: Annotated Lexis. Nexis (Legal (excluding U. S. ) ) Reference Librarians International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 6
 Comparative Law • For academic research, not for practice • Occasionally play a role in the U. S. Supreme Court ROPER V. SIMMONS (03633) 543 U. S. 551 (2005) 112 S. W. 3 d 397, affirmed Audio Clip: Oral Argument (MP 3/SMIL) minutes 12 --16 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 7
Comparative Law • For academic research, not for practice • Occasionally play a role in the U. S. Supreme Court ROPER V. SIMMONS (03633) 543 U. S. 551 (2005) 112 S. W. 3 d 397, affirmed Audio Clip: Oral Argument (MP 3/SMIL) minutes 12 --16 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 7
 Different Search Strategies • For common Law jurisdictions – Cases – Statutes – Secondary Sources: Leading treatises, law reviews • For civil law jurisdictions – Civil code – Occasionally cases, but don’t expect to get much from the contents – Secondary Sources: Leading Treatises, law reviews International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 8
Different Search Strategies • For common Law jurisdictions – Cases – Statutes – Secondary Sources: Leading treatises, law reviews • For civil law jurisdictions – Civil code – Occasionally cases, but don’t expect to get much from the contents – Secondary Sources: Leading Treatises, law reviews International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 8
 Sources Online Free (google. com) Subscription (westlaw, lexis etc) Books and Journals in this library UH Library Catalogue Worldcat Books from other Libraries Interlibrary Loan Service International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 9
Sources Online Free (google. com) Subscription (westlaw, lexis etc) Books and Journals in this library UH Library Catalogue Worldcat Books from other Libraries Interlibrary Loan Service International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 9
 2. European Union Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 10
2. European Union Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 10
 Economic Integration: How close can sovereign states be? Free Trade Area Custom Union Single Market Economic Union Sovereign State International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 11
Economic Integration: How close can sovereign states be? Free Trade Area Custom Union Single Market Economic Union Sovereign State International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 11
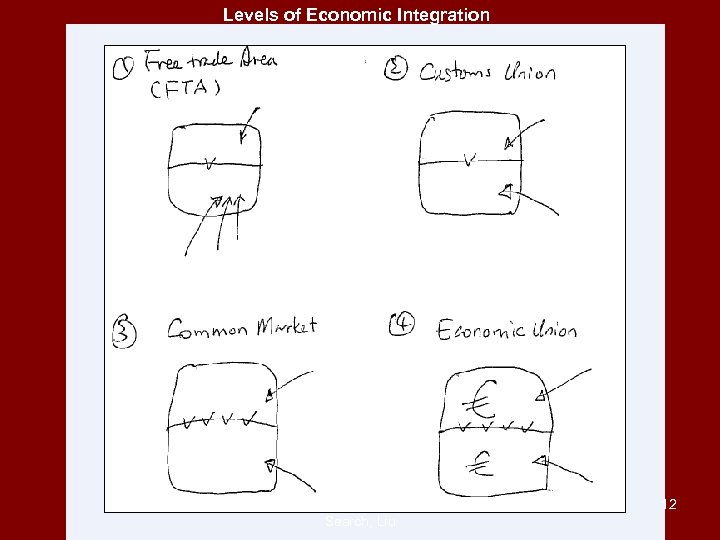 Levels of Economic Integration International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 12
Levels of Economic Integration International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 12
 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 13
International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 13
 Regional Organizations • European Union (EU) as an example – How regional TREATIES reshaped war-torn Europe International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 14
Regional Organizations • European Union (EU) as an example – How regional TREATIES reshaped war-torn Europe International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 14
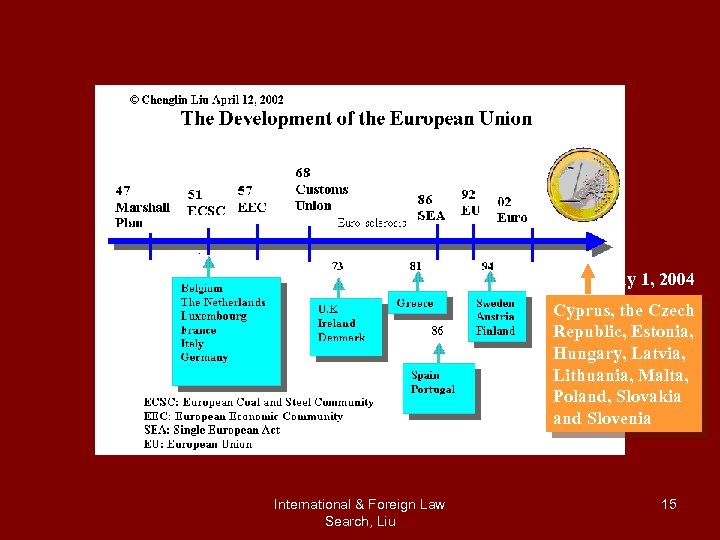 March 24, 2005 Houston 25 members, 450 million population May 1, 2004 Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 15
March 24, 2005 Houston 25 members, 450 million population May 1, 2004 Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 15
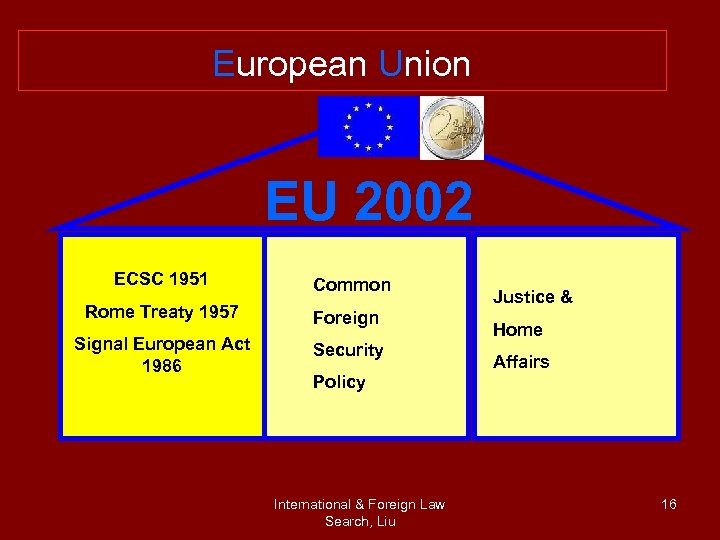 European Union EU 2002 ECSC 1951 Common Rome Treaty 1957 Foreign Signal European Act 1986 Security Justice & Home Affairs Policy International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 16
European Union EU 2002 ECSC 1951 Common Rome Treaty 1957 Foreign Signal European Act 1986 Security Justice & Home Affairs Policy International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 16
 Separation of Powers? • • Commission—executive? Council—Legislative? Parliament—Legislative? Court--Judiciary International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 17
Separation of Powers? • • Commission—executive? Council—Legislative? Parliament—Legislative? Court--Judiciary International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 17
 Eu-Lex, Lexis and West. Law • Microsoft Decision March 24, 2004 • Cases v. Decisions • Primary v. Secondary International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 18
Eu-Lex, Lexis and West. Law • Microsoft Decision March 24, 2004 • Cases v. Decisions • Primary v. Secondary International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 18
 3. Chinese Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 19
3. Chinese Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 19
 Basic Facts about China • Population – China 1. 4 billion – U. S. 290 million – EU 450 million • Size: Which country is bigger, China or the U. S. ? – CIA http: //www. cia. gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ch. html U. S. is bigger! – China. org http: //www. china. org. cn/e-changshi/index. htm China is bigger! • Nationalities: minorities 56; majority 1 (Han) • Provincial governments – – – 4 large cities: Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing 23 provinces 5 autonomous regions 2 special administrative regions (SAR): Hong Kong and Macau Taiwan • Neighboring States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 20
Basic Facts about China • Population – China 1. 4 billion – U. S. 290 million – EU 450 million • Size: Which country is bigger, China or the U. S. ? – CIA http: //www. cia. gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ch. html U. S. is bigger! – China. org http: //www. china. org. cn/e-changshi/index. htm China is bigger! • Nationalities: minorities 56; majority 1 (Han) • Provincial governments – – – 4 large cities: Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing 23 provinces 5 autonomous regions 2 special administrative regions (SAR): Hong Kong and Macau Taiwan • Neighboring States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 20
 US-China Trade Statistics and China's World Trade Statistics http: //www. uschina. org/statistics/tradetable. html Trade in Goods (Imports, Exports and Trade Balance) with China http: //www. census. gov/foreign-trade/balance/c 5700. html International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 21
US-China Trade Statistics and China's World Trade Statistics http: //www. uschina. org/statistics/tradetable. html Trade in Goods (Imports, Exports and Trade Balance) with China http: //www. census. gov/foreign-trade/balance/c 5700. html International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 21
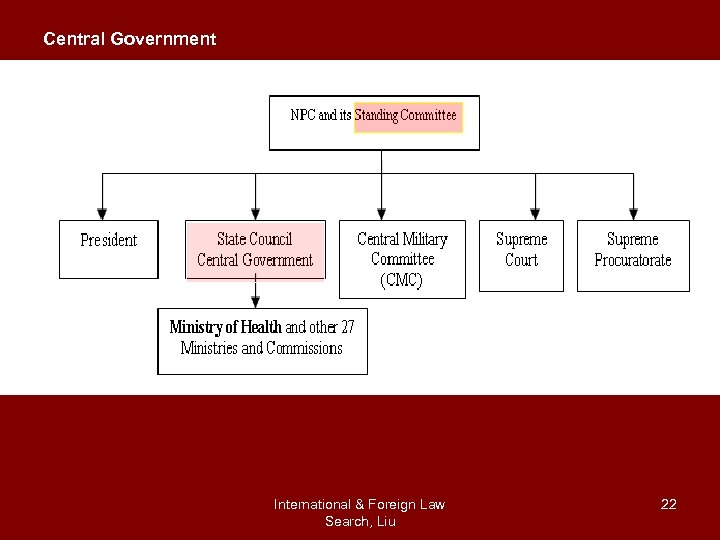 Central Government International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 22
Central Government International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 22
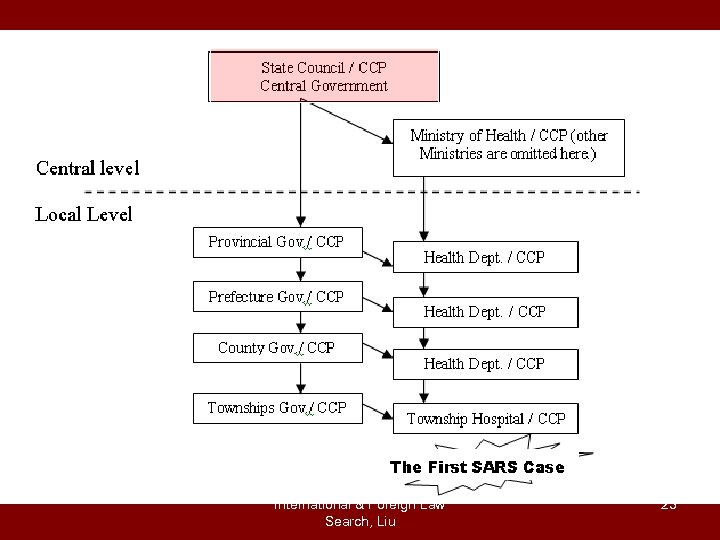 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 23
International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 23
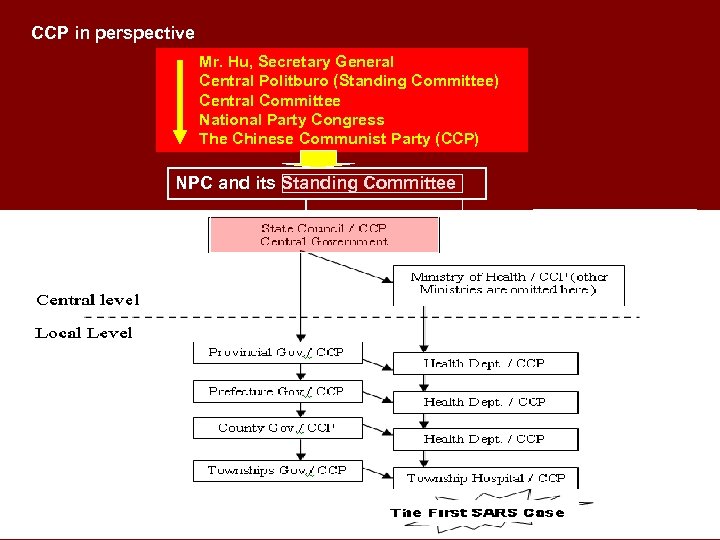 CCP in perspective Mr. Hu, Secretary General Central Politburo (Standing Committee) Central Committee National Party Congress The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) NPC and its Standing Committee Other Institutions International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 24
CCP in perspective Mr. Hu, Secretary General Central Politburo (Standing Committee) Central Committee National Party Congress The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) NPC and its Standing Committee Other Institutions International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 24
 Who is the Chief? Party Chief Military Chief President of the PRC “Political power grows out of the barrel of a gun. ” -- Mao International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 25
Who is the Chief? Party Chief Military Chief President of the PRC “Political power grows out of the barrel of a gun. ” -- Mao International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 25
 Relationships of the Central and Local Governments Principle: Democratic Centralism – The individual is subordinate to the group; – The Minority is subordinate to the majority; – The Lower is subordinate to the higher level; – The Local is subordinate to the central. Any problem with this principle? International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 26
Relationships of the Central and Local Governments Principle: Democratic Centralism – The individual is subordinate to the group; – The Minority is subordinate to the majority; – The Lower is subordinate to the higher level; – The Local is subordinate to the central. Any problem with this principle? International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 26
 Name maters • NPC ---Basic Laws • NPC (NPCSC)---Other Laws • State Council---Admin. Regulations – Ministries---Ministerial Rules • Local NPC---Local Regulations • Local Gov---Local Admin. Rules – Local Dept. ---Local Dept. Rules International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 27
Name maters • NPC ---Basic Laws • NPC (NPCSC)---Other Laws • State Council---Admin. Regulations – Ministries---Ministerial Rules • Local NPC---Local Regulations • Local Gov---Local Admin. Rules – Local Dept. ---Local Dept. Rules International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 27
 International law as Chinese law – Self Executing – None Self Executing • International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights China U. S. Signature: 10/27/1997 10/5/1977 Ratification: 3/27/2001 NO • International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights Signature: 10/5/1998 10/5/1977 Ratification: NO 6/8/1992 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 28
International law as Chinese law – Self Executing – None Self Executing • International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights China U. S. Signature: 10/27/1997 10/5/1977 Ratification: 3/27/2001 NO • International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights Signature: 10/5/1998 10/5/1977 Ratification: NO 6/8/1992 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 28
 Judgments • Limited authority • Mechanically apply the law • Cheng Kejie Case Vice NPC chairman sentenced to death on corruption charge. See handout. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 29
Judgments • Limited authority • Mechanically apply the law • Cheng Kejie Case Vice NPC chairman sentenced to death on corruption charge. See handout. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 29
 Judicial Independence Compared • Court budget http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php? st ory. Id=4598172 (Audio Clip) Supreme Court, Congress Clash on Rulings by Nina Totenberg International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 30
Judicial Independence Compared • Court budget http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php? st ory. Id=4598172 (Audio Clip) Supreme Court, Congress Clash on Rulings by Nina Totenberg International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 30
 Factors affecting Judicial Independence • Lawyers • Legal scholars • Officials, persons with connections to officials • Mediation committees • Neighborhood committees • Work Unites (Danwai) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 31
Factors affecting Judicial Independence • Lawyers • Legal scholars • Officials, persons with connections to officials • Mediation committees • Neighborhood committees • Work Unites (Danwai) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 31
 Enforcement of Judgment • Court in charge of enforcement • Low rate: 40 % • Local Protectionism – Guangdong company sought enforcement of a $900, 000 judgment against a Hainan company in 1996. Hainan court suspended the judgment with out explanation. • Judgment on Sale, jailed for seeking enforcement, etc. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 32
Enforcement of Judgment • Court in charge of enforcement • Low rate: 40 % • Local Protectionism – Guangdong company sought enforcement of a $900, 000 judgment against a Hainan company in 1996. Hainan court suspended the judgment with out explanation. • Judgment on Sale, jailed for seeking enforcement, etc. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 32
 Key Source for Chinese Law Research • Lawinfochina (library subscription) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 33
Key Source for Chinese Law Research • Lawinfochina (library subscription) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 33
 4. Essential Sources for F/I Research International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 34
4. Essential Sources for F/I Research International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 34
 Leading Treatises and Library Tour • Three Leading Treatises – Reynolds & Flores, Foreign Law—Current Sources of Codes and Legislation in Jurisdictions of the World. (looseleaf) (Hein) Reference Collection: K 38. R 49 – Germain’s Transnational Law Research (looseleaf) (Transnational Publisher) Reference Collection: K 85. G 47 – Cohen, Berring & Olson, How to Find The Law (West) Reserve: KF 240. H 6 1989 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 35
Leading Treatises and Library Tour • Three Leading Treatises – Reynolds & Flores, Foreign Law—Current Sources of Codes and Legislation in Jurisdictions of the World. (looseleaf) (Hein) Reference Collection: K 38. R 49 – Germain’s Transnational Law Research (looseleaf) (Transnational Publisher) Reference Collection: K 85. G 47 – Cohen, Berring & Olson, How to Find The Law (West) Reserve: KF 240. H 6 1989 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 35
 5. The English Legal System International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 36
5. The English Legal System International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 36
 English Legal System “It is not a faultlessly coherent and single, logically developed system. It grew piecemeal and various parts of it have been reformed and reshaped to suit the perceived needs of the time. ” “Most Civil cases are not hear in the civil courts at all but one of the major alternative forums which have proliferated in the 20 th Century. ” Reference: Darbyshire, English Legal System 6 th edition p. 1 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 37
English Legal System “It is not a faultlessly coherent and single, logically developed system. It grew piecemeal and various parts of it have been reformed and reshaped to suit the perceived needs of the time. ” “Most Civil cases are not hear in the civil courts at all but one of the major alternative forums which have proliferated in the 20 th Century. ” Reference: Darbyshire, English Legal System 6 th edition p. 1 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 37
 The Court Structure • Criminal Courts – Magistrates’ courts – The Crown Court – The Queen’s Bench Division of the High Court The Court of Appeal-Criminal Division – The House of Lords (Appellate Committee) – The Privy Council (Judicial Committee) – The European Court of Justice – The European Court of Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 38
The Court Structure • Criminal Courts – Magistrates’ courts – The Crown Court – The Queen’s Bench Division of the High Court The Court of Appeal-Criminal Division – The House of Lords (Appellate Committee) – The Privy Council (Judicial Committee) – The European Court of Justice – The European Court of Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 38
 The Court Structure • Civil Courts – Magistrates’ Court – The County Court – The High Court – The Court of Appeal-Civil Division – The House of Lords (Appellate Committee) – The Privy Council (Judicial Committee) – The European Court of Justice – The European Court of Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 39
The Court Structure • Civil Courts – Magistrates’ Court – The County Court – The High Court – The Court of Appeal-Civil Division – The House of Lords (Appellate Committee) – The Privy Council (Judicial Committee) – The European Court of Justice – The European Court of Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 39
 Alternative to the Courts • Tribunals • Arbitration – by contract – by reference from the court – By statute • Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) – Mediation – Conciliation – Arbitration International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 40
Alternative to the Courts • Tribunals • Arbitration – by contract – by reference from the court – By statute • Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) – Mediation – Conciliation – Arbitration International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 40
 Sources • Acts of Parliament – “Parliamentary sovereignty precludes the courts’ questioning Acts of Parliament where there is no conflict with EC Law. ” • EC legislation • The European Convention of Human Rights • Precedent – – State of law Ratio decidendi (reasoning) In a court whose decisions are binding Obiter dictum is not binding International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 41
Sources • Acts of Parliament – “Parliamentary sovereignty precludes the courts’ questioning Acts of Parliament where there is no conflict with EC Law. ” • EC legislation • The European Convention of Human Rights • Precedent – – State of law Ratio decidendi (reasoning) In a court whose decisions are binding Obiter dictum is not binding International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 41
 Interpretation of Statutes • Need for interpretation – – – Ellipsis Broad Terms Politic uncertainty Unforeseeable developments Miscellaneous drafting errors • Rules of interpretation – The Literal Rule – The Golden Rule (permitting to depart from giving their ordinary natural meaning) – The Mischief Rule (much wider approach) – Contextual approach International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 42
Interpretation of Statutes • Need for interpretation – – – Ellipsis Broad Terms Politic uncertainty Unforeseeable developments Miscellaneous drafting errors • Rules of interpretation – The Literal Rule – The Golden Rule (permitting to depart from giving their ordinary natural meaning) – The Mischief Rule (much wider approach) – Contextual approach International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 42
 6. NAFTA International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 43
6. NAFTA International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 43
 Early Development • Free trade as an alternative of annexation. • Elgin-Marcy Treaty of 1854—free trade agreement between U. S. and Canada. Not implemented because of civil war. • In 1911, U. S. proposed trade agreement, but rejected by the Canadian Parliament. • Protectionism in the 1920 s-1930 s. Trade negotiations after WWII was not successful. • GATT (1947) provided alternative that discouraged trade talks between U. S. and Canada. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 44
Early Development • Free trade as an alternative of annexation. • Elgin-Marcy Treaty of 1854—free trade agreement between U. S. and Canada. Not implemented because of civil war. • In 1911, U. S. proposed trade agreement, but rejected by the Canadian Parliament. • Protectionism in the 1920 s-1930 s. Trade negotiations after WWII was not successful. • GATT (1947) provided alternative that discouraged trade talks between U. S. and Canada. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 44
 From CFTA to NAFTA • In 1986, Uruguay Round was initiated, but seemed endless. Frustrated with the progress, the two countries began to engage bilateral trade negotiation. • CFTA took effect January 1, 1989. • After CFTA, Mexican Government looked for alternatives, but without success. Finally decided to negotiate with the U. S. Negotiation – 1 n 1991, the negotiations to create NAFTA began. – In 1992, President Bush (lame-duck) signed the NAFTA agreement. – Clinton added two supplemental agreements: Labor and Environment. Ratification – U. S. : In 1993, the Senate ratified the agreement over fierce opposition: Public Law No. 103 -182 The NAFTA Implementation Act expressly provides that the NAFTA agreement does not modify U. S. law except as provided for the by the Act. – Canada: Mulroney Government approved the NAFTA agreement before it lost election. – Mexican: No difficulty at all. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 45
From CFTA to NAFTA • In 1986, Uruguay Round was initiated, but seemed endless. Frustrated with the progress, the two countries began to engage bilateral trade negotiation. • CFTA took effect January 1, 1989. • After CFTA, Mexican Government looked for alternatives, but without success. Finally decided to negotiate with the U. S. Negotiation – 1 n 1991, the negotiations to create NAFTA began. – In 1992, President Bush (lame-duck) signed the NAFTA agreement. – Clinton added two supplemental agreements: Labor and Environment. Ratification – U. S. : In 1993, the Senate ratified the agreement over fierce opposition: Public Law No. 103 -182 The NAFTA Implementation Act expressly provides that the NAFTA agreement does not modify U. S. law except as provided for the by the Act. – Canada: Mulroney Government approved the NAFTA agreement before it lost election. – Mexican: No difficulty at all. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 45
 Impact of NAFTA • Canada: unemployment • U. S. : Labor and Environment • Mexico: Maquiladoras – Rules of Origin International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 46
Impact of NAFTA • Canada: unemployment • U. S. : Labor and Environment • Mexico: Maquiladoras – Rules of Origin International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 46
 NAFTA • Goods – Deadlines for elimination of tariffs on goods: • U. S. and Canada, 1998 • Mexican, 2003 • By 2008, all North American trade in goods is duty free. • Services – CFTA— “Positive List”; NAFTA –- “Negative List” (broader) – Foreign Legal Consultants – NAFTA Business Visas: preferential treatment for citizens in three countries. • Investment – Article 11 • Minimum Standard of treatment • Prohibition of expropriation – Metalclad Corp. v. United Mexican States • IP – Copyright, patent, trademarks International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 47
NAFTA • Goods – Deadlines for elimination of tariffs on goods: • U. S. and Canada, 1998 • Mexican, 2003 • By 2008, all North American trade in goods is duty free. • Services – CFTA— “Positive List”; NAFTA –- “Negative List” (broader) – Foreign Legal Consultants – NAFTA Business Visas: preferential treatment for citizens in three countries. • Investment – Article 11 • Minimum Standard of treatment • Prohibition of expropriation – Metalclad Corp. v. United Mexican States • IP – Copyright, patent, trademarks International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 47
 Dispute Settlement • Chapter 19—antidumping and countervailing duty disputes • Chapter 20 general dispute settlement procedures • Chapter 11 investor-state arbitration procedures • Chapters 6, 9, 10 Environmental and labor cooperation disputes International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 48
Dispute Settlement • Chapter 19—antidumping and countervailing duty disputes • Chapter 20 general dispute settlement procedures • Chapter 11 investor-state arbitration procedures • Chapters 6, 9, 10 Environmental and labor cooperation disputes International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 48
 Panels • Binational panels • Each party to the dispute chooses two panelists; the fifth is chosen either by agreement or by lot if no agreement. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 49
Panels • Binational panels • Each party to the dispute chooses two panelists; the fifth is chosen either by agreement or by lot if no agreement. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 49
 Research • • NAFTA Agreement Panel Decisions Domestic Cases Arbitration Rule and Cases International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 50
Research • • NAFTA Agreement Panel Decisions Domestic Cases Arbitration Rule and Cases International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 50
 7. Public International Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 51
7. Public International Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 51
 Public International Law Sources Primary and Secondary Sources • International Treaties • International Customary Laws • The general principles of law recognized by civilized nations • Judicial decisions, teachings of most highly qualified scholars (persuasive) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 52
Public International Law Sources Primary and Secondary Sources • International Treaties • International Customary Laws • The general principles of law recognized by civilized nations • Judicial decisions, teachings of most highly qualified scholars (persuasive) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 52
 Treaty Search • Treaties are agreements between or among sovereign States. • Treaties have other names: agreements, covenants, conventions, charters, protocols, declarations, memoranda of understanding, modus vivendi and exchange of notes. • Bilateral and Multilateral Treaties • Self executing v. Non-self executing – Trade treaties (self executing) – Human Rights (non-self executing) • Executive agreements (U. S. ). International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 53
Treaty Search • Treaties are agreements between or among sovereign States. • Treaties have other names: agreements, covenants, conventions, charters, protocols, declarations, memoranda of understanding, modus vivendi and exchange of notes. • Bilateral and Multilateral Treaties • Self executing v. Non-self executing – Trade treaties (self executing) – Human Rights (non-self executing) • Executive agreements (U. S. ). International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 53
 Treaty Search Process • Information on signatories, ratifications, and reservations – Example: Kyoto Treaty – International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) Article 6 (5) • 5. Sentence of death shall not be imposed for crimes committed by persons below eighteen years of age and shall not be carried out on pregnant women. • Legislative History • Judicial Interpretations • Effective Date, Validity International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 54
Treaty Search Process • Information on signatories, ratifications, and reservations – Example: Kyoto Treaty – International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) Article 6 (5) • 5. Sentence of death shall not be imposed for crimes committed by persons below eighteen years of age and shall not be carried out on pregnant women. • Legislative History • Judicial Interpretations • Effective Date, Validity International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 54
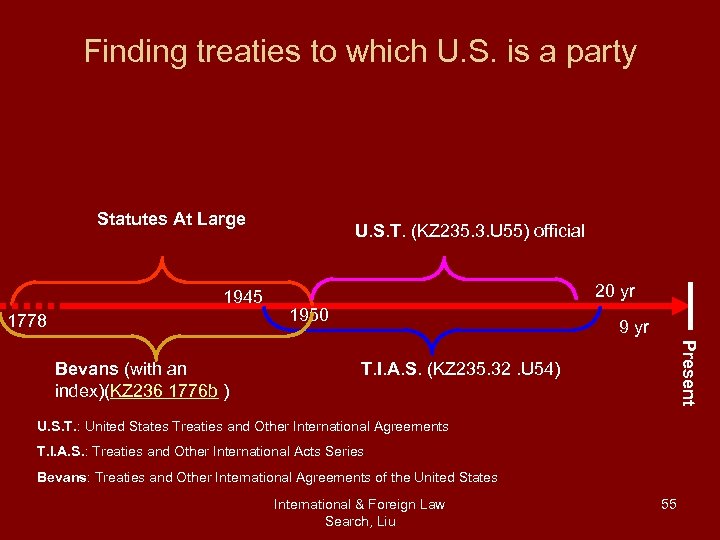 Finding treaties to which U. S. is a party Statutes At Large 1945 1778 20 yr 1950 9 yr Present Bevans (with an index)(KZ 236 1776 b ) U. S. T. (KZ 235. 3. U 55) official T. I. A. S. (KZ 235. 32. U 54) U. S. T. : United States Treaties and Other International Agreements T. I. A. S. : Treaties and Other International Acts Series Bevans: Treaties and Other International Agreements of the United States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 55
Finding treaties to which U. S. is a party Statutes At Large 1945 1778 20 yr 1950 9 yr Present Bevans (with an index)(KZ 236 1776 b ) U. S. T. (KZ 235. 3. U 55) official T. I. A. S. (KZ 235. 32. U 54) U. S. T. : United States Treaties and Other International Agreements T. I. A. S. : Treaties and Other International Acts Series Bevans: Treaties and Other International Agreements of the United States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 55
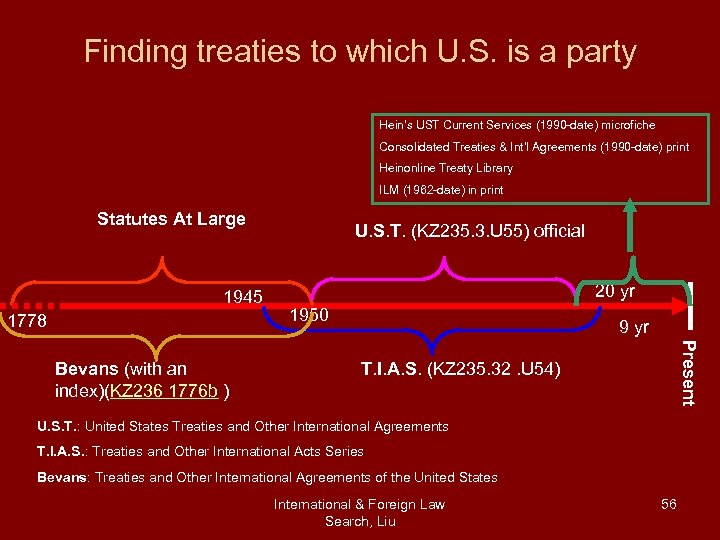 Finding treaties to which U. S. is a party Hein’s UST Current Services (1990 -date) microfiche Consolidated Treaties & Int’l Agreements (1990 -date) print Heinonline Treaty Library ILM (1962 -date) in print Statutes At Large 1945 1778 20 yr 1950 9 yr Present Bevans (with an index)(KZ 236 1776 b ) U. S. T. (KZ 235. 3. U 55) official T. I. A. S. (KZ 235. 32. U 54) U. S. T. : United States Treaties and Other International Agreements T. I. A. S. : Treaties and Other International Acts Series Bevans: Treaties and Other International Agreements of the United States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 56
Finding treaties to which U. S. is a party Hein’s UST Current Services (1990 -date) microfiche Consolidated Treaties & Int’l Agreements (1990 -date) print Heinonline Treaty Library ILM (1962 -date) in print Statutes At Large 1945 1778 20 yr 1950 9 yr Present Bevans (with an index)(KZ 236 1776 b ) U. S. T. (KZ 235. 3. U 55) official T. I. A. S. (KZ 235. 32. U 54) U. S. T. : United States Treaties and Other International Agreements T. I. A. S. : Treaties and Other International Acts Series Bevans: Treaties and Other International Agreements of the United States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 56
 Sources for Treaty Search • • • UST, TIAS, Bevans, Statutes At Large Westlaw (USTREATIES) Lexis. Nexis (USTRTY) International Law Materials (ILM) (Selected Treaties) USCA and USCS (a few important treaties) Bevans: Treaties and Other International Agreement of the U. S. of America, 1776 -1949 • Websites – – UN Texts of Recently Deposited Multilateral Treaties UN Treaty Collection (Law Library Subscription) State Dept. Treaty in Force Thomas (Treaties Section) • Hein online (Law Library Subscription) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 57
Sources for Treaty Search • • • UST, TIAS, Bevans, Statutes At Large Westlaw (USTREATIES) Lexis. Nexis (USTRTY) International Law Materials (ILM) (Selected Treaties) USCA and USCS (a few important treaties) Bevans: Treaties and Other International Agreement of the U. S. of America, 1776 -1949 • Websites – – UN Texts of Recently Deposited Multilateral Treaties UN Treaty Collection (Law Library Subscription) State Dept. Treaty in Force Thomas (Treaties Section) • Hein online (Law Library Subscription) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 57
 Indexes • State Dept. Treaty in Force (Annually) – Also in Print (Reference) – Hein on Line • Commercial indexes: – Kavass: Guide to the United States Treaties in Force (Hein on Line) – In print: Kavass, Current Treaty Index-United States Treaty Index Consolidation (KZ 235. U 54 C. 2) • UN Treaty Series Database • Westlaw and Lexis (Boolean Search) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 58
Indexes • State Dept. Treaty in Force (Annually) – Also in Print (Reference) – Hein on Line • Commercial indexes: – Kavass: Guide to the United States Treaties in Force (Hein on Line) – In print: Kavass, Current Treaty Index-United States Treaty Index Consolidation (KZ 235. U 54 C. 2) • UN Treaty Series Database • Westlaw and Lexis (Boolean Search) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 58
 Verification and Updating State Dept. Treaty in Force State Dept. Treaty Actions UN Treaty Collection (Status Search, signatory, ratification, reservation etc. ) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 59
Verification and Updating State Dept. Treaty in Force State Dept. Treaty Actions UN Treaty Collection (Status Search, signatory, ratification, reservation etc. ) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 59
 8. The United Nations International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 60
8. The United Nations International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 60
 Historical Milestones • Peace of Westphalia 1648 – The principle of the sovereignty of nation-states and the fundamental right of political self determination – The principle of (legal) equality between nation-states – The principle of pacta sunt servanda (treaties are to be observed) – The principle of non-intervention of one state in the internal affairs of another state • Final Act of the Congress of Vienna 1815 – Established diplomatic protocol – Condemned the slave state – Established the principle of free and unimpeded navigation on international rivers • League of Nations 1920 International & Foreign Law 61 • United Nations 1945 Search, Liu
Historical Milestones • Peace of Westphalia 1648 – The principle of the sovereignty of nation-states and the fundamental right of political self determination – The principle of (legal) equality between nation-states – The principle of pacta sunt servanda (treaties are to be observed) – The principle of non-intervention of one state in the internal affairs of another state • Final Act of the Congress of Vienna 1815 – Established diplomatic protocol – Condemned the slave state – Established the principle of free and unimpeded navigation on international rivers • League of Nations 1920 International & Foreign Law 61 • United Nations 1945 Search, Liu
 United Nations Main Bodies • • UN Charter, October 24, 1945 http: //www. un. org/aboutun/charter/index. html 191 members • • Organization Chart: http: //www. un. org/aboutun/chart. html General Assembly – Subsidiary Organs Committee on Information Human Rights Council • Security Council – – Peacebuilding Commission Counter-terrorism Committee Al-Qaida and Taliban Sanctions Committee 1540 Committee • Economic and Social Council • Trusteeship Council • Secretariat • International & Foreign Law International Court of Justice Search, Liu 62
United Nations Main Bodies • • UN Charter, October 24, 1945 http: //www. un. org/aboutun/charter/index. html 191 members • • Organization Chart: http: //www. un. org/aboutun/chart. html General Assembly – Subsidiary Organs Committee on Information Human Rights Council • Security Council – – Peacebuilding Commission Counter-terrorism Committee Al-Qaida and Taliban Sanctions Committee 1540 Committee • Economic and Social Council • Trusteeship Council • Secretariat • International & Foreign Law International Court of Justice Search, Liu 62
 Binding Character of UN resolution • GA resolutions: Not binding • Security Council Resolutions: Binding International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 63
Binding Character of UN resolution • GA resolutions: Not binding • Security Council Resolutions: Binding International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 63
 UN Security Council • Five Permanent Members • “A conviction has grown, among nations large and small, that an opportunity has been regained to achieve the great objectives of the Charter…” UN Secretary Boutros. Ghali, 1992 • “There has been a regrettable tendency for the Security Council not to be involved in the efforts to maintain international peace and security. ” UN Secretary Kofi Annan, 1999 • “Will the United Nations serve the purpose of its founding, or will it be irrelevant? ” George W. Bush, 2002 • In a 1994 speech at the liberal World Federalist Association, John Robert Bolton declared that “There is no such thing as the United Nations. ” To underscore his point, Bolton said: “If the UN secretary building in New York lost ten stories, it wouldn't make a bit of difference. ” --Bolton, the U. S. Permanent Representative to the United 64 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu Nations.
UN Security Council • Five Permanent Members • “A conviction has grown, among nations large and small, that an opportunity has been regained to achieve the great objectives of the Charter…” UN Secretary Boutros. Ghali, 1992 • “There has been a regrettable tendency for the Security Council not to be involved in the efforts to maintain international peace and security. ” UN Secretary Kofi Annan, 1999 • “Will the United Nations serve the purpose of its founding, or will it be irrelevant? ” George W. Bush, 2002 • In a 1994 speech at the liberal World Federalist Association, John Robert Bolton declared that “There is no such thing as the United Nations. ” To underscore his point, Bolton said: “If the UN secretary building in New York lost ten stories, it wouldn't make a bit of difference. ” --Bolton, the U. S. Permanent Representative to the United 64 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu Nations.
 Human Rights Council • U. S. refuse to run for the UN Human Rights Council • Bolton: “I believe rather strongly that our leverage in terms of the performance of the new council is greater by the U. S. not running and sending the signal ‘this is not business as usual’ this year than if we were to run. ” International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 65
Human Rights Council • U. S. refuse to run for the UN Human Rights Council • Bolton: “I believe rather strongly that our leverage in terms of the performance of the new council is greater by the U. S. not running and sending the signal ‘this is not business as usual’ this year than if we were to run. ” International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 65
 9. The International Court of Justice International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 66
9. The International Court of Justice International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 66
 International Court of Justice (ICJ) • International Court of Justice Peace Palace 2517 KJ The Hague The Netherlands • 15 Judges International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 67
International Court of Justice (ICJ) • International Court of Justice Peace Palace 2517 KJ The Hague The Netherlands • 15 Judges International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 67
 ICJ Jurisdiction The Parties Only States may apply to and appear before the Court. The Member States of the United Nations (at present numbering 191) are so entitled. Jurisdiction The Court is competent to entertain a dispute only if the States concerned have accepted its jurisdiction in one or more of the following ways: 1. by the conclusion between them of a special agreement to submit the dispute to the Court; 2. by virtue of a jurisdictional clause, i. e. , typically, when they are parties to a treaty containing a provision whereby, in the event of a disagreement over its interpretation or application, one of them may refer the dispute to the Court. Over three hundred treaties or conventions contain a clause to such effect; 3. through the reciprocal effect of declarations made by them under the Statute whereby each has accepted the jurisdiction of the Court as compulsory in the event of a dispute with another State having made a similar declaration. The declarations of 67 States are at present in force, a number of them having been made subject to the exclusion of certain categories of dispute. In cases of doubt as to whether the Court has jurisdiction, it is the Court itself which decides. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 68
ICJ Jurisdiction The Parties Only States may apply to and appear before the Court. The Member States of the United Nations (at present numbering 191) are so entitled. Jurisdiction The Court is competent to entertain a dispute only if the States concerned have accepted its jurisdiction in one or more of the following ways: 1. by the conclusion between them of a special agreement to submit the dispute to the Court; 2. by virtue of a jurisdictional clause, i. e. , typically, when they are parties to a treaty containing a provision whereby, in the event of a disagreement over its interpretation or application, one of them may refer the dispute to the Court. Over three hundred treaties or conventions contain a clause to such effect; 3. through the reciprocal effect of declarations made by them under the Statute whereby each has accepted the jurisdiction of the Court as compulsory in the event of a dispute with another State having made a similar declaration. The declarations of 67 States are at present in force, a number of them having been made subject to the exclusion of certain categories of dispute. In cases of doubt as to whether the Court has jurisdiction, it is the Court itself which decides. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 68
 ICJ Procedure The procedure of the ICJ followed by the Court in contentious cases is defined in the ICJ Statute: http: //www. icj-cij. org/icjwww/ibasicdocuments. htm Official Languages: English and French • After the oral proceedings the Court deliberates in camera and then delivers its judgment at a public sitting. T • The judgment is final and without appeal. Should one of the States involved fail to comply with it, the other party may have recourse to the Security Council of the United Nations. • The Court discharges its duties as a full court but, at the request of the parties, it may also establish a special chamber. within its jurisdiction. • Since 1946 the Court has delivered 92 Judgments on disputes concerning inter alia land frontiers and maritime boundaries, territorial sovereignty, the non-use of force, non-interference in the internal affairs of States, diplomatic relations, hostage-taking, the right of asylum, nationality, guardianship, rights of passage and economic rights. International & Foreign Law 69 Search, Liu
ICJ Procedure The procedure of the ICJ followed by the Court in contentious cases is defined in the ICJ Statute: http: //www. icj-cij. org/icjwww/ibasicdocuments. htm Official Languages: English and French • After the oral proceedings the Court deliberates in camera and then delivers its judgment at a public sitting. T • The judgment is final and without appeal. Should one of the States involved fail to comply with it, the other party may have recourse to the Security Council of the United Nations. • The Court discharges its duties as a full court but, at the request of the parties, it may also establish a special chamber. within its jurisdiction. • Since 1946 the Court has delivered 92 Judgments on disputes concerning inter alia land frontiers and maritime boundaries, territorial sovereignty, the non-use of force, non-interference in the internal affairs of States, diplomatic relations, hostage-taking, the right of asylum, nationality, guardianship, rights of passage and economic rights. International & Foreign Law 69 Search, Liu
 ICJ Decisions • http: //www. icj-cij. org/icjwww/idecisions. htm • Avena Case Avena and other Mexican Nationals (Mexico v. United States of America) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 70
ICJ Decisions • http: //www. icj-cij. org/icjwww/idecisions. htm • Avena Case Avena and other Mexican Nationals (Mexico v. United States of America) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 70
 10. Special Session on North Korea International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 71
10. Special Session on North Korea International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 71
 Special Session on North Korea • 1. Whether has NK breached international law? If yes, what law? Why is NK obligated not to develop nuclear bombs, while some other nations have already had such weapons? • 2. What could have been done to prevent the "provocative test"? • 3. What recourses can the concerned parties (U. S. , China, Russia, Japan and South Korea) take to punish NK? • 4. Why is it difficult for China to cut off food and energy aid to NK even after the test? • 5. What options does the U. S. have to deal with this issue? • 6. How would Republicans and Democrats react to the test in next few weeks? Is any impact of the provocative test on the upcoming election in November? International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 72
Special Session on North Korea • 1. Whether has NK breached international law? If yes, what law? Why is NK obligated not to develop nuclear bombs, while some other nations have already had such weapons? • 2. What could have been done to prevent the "provocative test"? • 3. What recourses can the concerned parties (U. S. , China, Russia, Japan and South Korea) take to punish NK? • 4. Why is it difficult for China to cut off food and energy aid to NK even after the test? • 5. What options does the U. S. have to deal with this issue? • 6. How would Republicans and Democrats react to the test in next few weeks? Is any impact of the provocative test on the upcoming election in November? International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 72
 Research Method • Where to start? – Primary Sources? – Secondary Sources? • The value of news analysis – Accurate? – In-depth? – Comprehensive? • The value of scholarly writings International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 73
Research Method • Where to start? – Primary Sources? – Secondary Sources? • The value of news analysis – Accurate? – In-depth? – Comprehensive? • The value of scholarly writings International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 73
 UN Charter Chapter 7 and the Power of the Security Council • • Article 39 The Security Council shall determine the existence of any threat to the peace, breach of the peace, or act of aggression and shall make recommendations, or decide what measures shall be taken in accordance with Articles 41 and 42, to maintain or restore international peace and security. Article 40 In order to prevent an aggravation of the situation, the Security Council may, before making the recommendations or deciding upon the measures provided for in Article 39, call upon the parties concerned to comply with such provisional measures as it deems necessary or desirable. Such provisional measures shall be without prejudice to the rights, claims, or position of the parties concerned. The Security Council shall duly take account of failure to comply with such provisional measures. • Article 41 The Security Council may decide what measures not involving the use of armed force are to be employed to give effect to its decisions, and it may call upon the Members of the United Nations to apply such measures. These may include complete or partial interruption of economic relations and of rail, sea, air, postal, telegraphic, radio, and other means of communication, and the severance of diplomatic relations. • Article 42 Should the Security Council consider that measures provided for in Article 41 would be inadequate or have proved to be inadequate, it may take such action by air, sea, or land forces as may be necessary to maintain or restore international peace and security. Such action may include demonstrations, blockade, and other operations by air, sea, or land forces of Members of the United Nations. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 74
UN Charter Chapter 7 and the Power of the Security Council • • Article 39 The Security Council shall determine the existence of any threat to the peace, breach of the peace, or act of aggression and shall make recommendations, or decide what measures shall be taken in accordance with Articles 41 and 42, to maintain or restore international peace and security. Article 40 In order to prevent an aggravation of the situation, the Security Council may, before making the recommendations or deciding upon the measures provided for in Article 39, call upon the parties concerned to comply with such provisional measures as it deems necessary or desirable. Such provisional measures shall be without prejudice to the rights, claims, or position of the parties concerned. The Security Council shall duly take account of failure to comply with such provisional measures. • Article 41 The Security Council may decide what measures not involving the use of armed force are to be employed to give effect to its decisions, and it may call upon the Members of the United Nations to apply such measures. These may include complete or partial interruption of economic relations and of rail, sea, air, postal, telegraphic, radio, and other means of communication, and the severance of diplomatic relations. • Article 42 Should the Security Council consider that measures provided for in Article 41 would be inadequate or have proved to be inadequate, it may take such action by air, sea, or land forces as may be necessary to maintain or restore international peace and security. Such action may include demonstrations, blockade, and other operations by air, sea, or land forces of Members of the United Nations. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 74
 The Security Council (1) • Membership in 2006 The Council is composed of five permanent members — China, France, Russian Federation, the United Kingdom and the United States — and ten non-permament members (with year of term's end): • Argentina (2006)Greece (2006)Qatar (2007)Congo (Republic of the) (2007)Japan (2006)Slovakia (2007)Denmark (2006)Peru (2007)United Republic of Tanzania (2006)Ghana (2007) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 75
The Security Council (1) • Membership in 2006 The Council is composed of five permanent members — China, France, Russian Federation, the United Kingdom and the United States — and ten non-permament members (with year of term's end): • Argentina (2006)Greece (2006)Qatar (2007)Congo (Republic of the) (2007)Japan (2006)Slovakia (2007)Denmark (2006)Peru (2007)United Republic of Tanzania (2006)Ghana (2007) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 75
 The Security Council 2 • The Presidency of the Security Council is held in turn by the members of the Security Council in the English alphabetical order of their names. Each President holds office for one calendar month. • Ten non-permament members, elected by the General Assembly for two-year terms and not eligible for immediate re-election. The number of non-permanent members was increased from six to ten by an amendment of the Charter which came into force in 1965. • Each Council member has one vote. Decisions on procedural matters are made by an affirmative vote of at least nine of the 15 members. Decisions on substantive matters require nine votes, including the concurring votes of all five permanent members. This is the rule of "great Power unanimity", often referred to as the "veto" power. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 76
The Security Council 2 • The Presidency of the Security Council is held in turn by the members of the Security Council in the English alphabetical order of their names. Each President holds office for one calendar month. • Ten non-permament members, elected by the General Assembly for two-year terms and not eligible for immediate re-election. The number of non-permanent members was increased from six to ten by an amendment of the Charter which came into force in 1965. • Each Council member has one vote. Decisions on procedural matters are made by an affirmative vote of at least nine of the 15 members. Decisions on substantive matters require nine votes, including the concurring votes of all five permanent members. This is the rule of "great Power unanimity", often referred to as the "veto" power. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 76
 Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty • Opened for signature in 1968, the Treaty entered into force in 1970. A total of 187 parties have joined the Treaty, including the five nuclearweapon States. • The Treaty establishes a safeguards system under the responsibility of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). • Article VIII, paragraph 3, provides a review of the operation of the Treaty every five years. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 77
Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty • Opened for signature in 1968, the Treaty entered into force in 1970. A total of 187 parties have joined the Treaty, including the five nuclearweapon States. • The Treaty establishes a safeguards system under the responsibility of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). • Article VIII, paragraph 3, provides a review of the operation of the Treaty every five years. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 77
 Non Proliferation Treaty • First pillar: non-proliferation • Second pillar: disarmament • Third pillar: the right to peacefully use nuclear technology International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 78
Non Proliferation Treaty • First pillar: non-proliferation • Second pillar: disarmament • Third pillar: the right to peacefully use nuclear technology International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 78
 The comprehensive Nuclear Test -Ban Treaty • The Treaty was opened for signature on 24 September 1996 and it will remain open for signature until its entry into force, in accordance with article XI. • International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 79
The comprehensive Nuclear Test -Ban Treaty • The Treaty was opened for signature on 24 September 1996 and it will remain open for signature until its entry into force, in accordance with article XI. • International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 79
 China’s Options • Major provider of food and fuel • Loss of face • Delicate relations with the U. S. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 80
China’s Options • Major provider of food and fuel • Loss of face • Delicate relations with the U. S. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 80
 10. The International Criminal Court International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 81
10. The International Criminal Court International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 81
 International Criminal Court (ICC) • The International Criminal Court was established by the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, on 17 July 1998 by the United Nations Diplomatic Conference of Plenipotentiaries on the Establishment of an International Criminal Court (Rome Statute). • Binding only on those States which formally express their consent to be bound by its provisions. These States then become “Parties” to the Statute. • Entered into force on 1 July 2002 • Members: 100 States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 82
International Criminal Court (ICC) • The International Criminal Court was established by the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, on 17 July 1998 by the United Nations Diplomatic Conference of Plenipotentiaries on the Establishment of an International Criminal Court (Rome Statute). • Binding only on those States which formally express their consent to be bound by its provisions. These States then become “Parties” to the Statute. • Entered into force on 1 July 2002 • Members: 100 States International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 82
 ICC and Rome Treaty • The ICC is a court of last resort. It will not act if a case is investigated or prosecuted by a national judicial system unless the national proceedings are not genuine. – for example if formal proceedings were undertaken solely to shield a person from criminal responsibility. • Unable or unwilling • The ICC only tries those accused of the gravest crimes. • The jurisdiction and functioning of the ICC are governed by the Rome Statute. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 83
ICC and Rome Treaty • The ICC is a court of last resort. It will not act if a case is investigated or prosecuted by a national judicial system unless the national proceedings are not genuine. – for example if formal proceedings were undertaken solely to shield a person from criminal responsibility. • Unable or unwilling • The ICC only tries those accused of the gravest crimes. • The jurisdiction and functioning of the ICC are governed by the Rome Statute. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 83
 ICC Jurisdictions and Admissibility • Jurisdiction – Temporal v. Retroactive Jurisdiction • does a court has the power to try crimes committed before the court was established? – Personal Jurisdiction • Minors – Subject matters • Genocide • Crimes again humanity • War crimes Drug related crimes and terrorism were excluded from the jurisdiction • Admissibility – The principle of complementaity: article 10—the ICC shall be complementary to national criminal jurisdictions – Article 17: ICC is required to rule a case inadmissible when it is being appropriately dealt with by a national justice system. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 84
ICC Jurisdictions and Admissibility • Jurisdiction – Temporal v. Retroactive Jurisdiction • does a court has the power to try crimes committed before the court was established? – Personal Jurisdiction • Minors – Subject matters • Genocide • Crimes again humanity • War crimes Drug related crimes and terrorism were excluded from the jurisdiction • Admissibility – The principle of complementaity: article 10—the ICC shall be complementary to national criminal jurisdictions – Article 17: ICC is required to rule a case inadmissible when it is being appropriately dealt with by a national justice system. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 84
 ICC Structure • Judges – Elected by the Assembly of States Parties for a term of nine years. One judge of any given nationality at any one time. • Prosecutor – Elected by secret ballot of absolute majority of the Assembly of States Parties. • Ethical matters – Removal of a judge first requires a recommendation by 2/3 majority of other judges. Then 2/3 majority of the States parties must agree – Removal of the Prosecutor requires a majority vote. • • Assembly of States Parties Funding – UN does not provide funding. – Based on assessed contributions upon States Parties, following the basic scale already in use in the UN, a calculation that considers population and relative wealth. – Voluntary donations • Working languages: English and French International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 85
ICC Structure • Judges – Elected by the Assembly of States Parties for a term of nine years. One judge of any given nationality at any one time. • Prosecutor – Elected by secret ballot of absolute majority of the Assembly of States Parties. • Ethical matters – Removal of a judge first requires a recommendation by 2/3 majority of other judges. Then 2/3 majority of the States parties must agree – Removal of the Prosecutor requires a majority vote. • • Assembly of States Parties Funding – UN does not provide funding. – Based on assessed contributions upon States Parties, following the basic scale already in use in the UN, a calculation that considers population and relative wealth. – Voluntary donations • Working languages: English and French International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 85
 ICC: Common Law v. Civil Law • Adversarial trial • Article 63 (6) (d): “trial chamber has the power to order the production of evidence in addition to that already collected prior to the trial or presented during the trial by the parties” International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 86
ICC: Common Law v. Civil Law • Adversarial trial • Article 63 (6) (d): “trial chamber has the power to order the production of evidence in addition to that already collected prior to the trial or presented during the trial by the parties” International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 86
 U. S. and the ICC • Article 98 Cooperation with respect to waiver of immunity and consent to surrender 1. The Court may not proceed with a request for surrender or assistance which would require the requested State to act inconsistently with its obligations under international law with respect to the State or diplomatic immunity of a person or property of a third State, unless the Court can first obtain the cooperation of that third State for the waiver of the immunity. 2. The Court may not proceed with a request for surrender which would require the requested State to act inconsistently with its obligations under international agreements pursuant to which the consent of a sending State is required to surrender a person of that State to the Court, unless the Court can first obtain the cooperation of the sending State for the giving of consent for the surrender. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 87
U. S. and the ICC • Article 98 Cooperation with respect to waiver of immunity and consent to surrender 1. The Court may not proceed with a request for surrender or assistance which would require the requested State to act inconsistently with its obligations under international law with respect to the State or diplomatic immunity of a person or property of a third State, unless the Court can first obtain the cooperation of that third State for the waiver of the immunity. 2. The Court may not proceed with a request for surrender which would require the requested State to act inconsistently with its obligations under international agreements pursuant to which the consent of a sending State is required to surrender a person of that State to the Court, unless the Court can first obtain the cooperation of the sending State for the giving of consent for the surrender. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 87
 U. S. and ICC • Bolton’s Speech – Two flaws: substantive and structural • • Broad power to interpretation Crimes can be added Crimes vaguely defined, such as “aggression” Judges and the prosecutor: lack of accountability and checks and balances • Interference with the Security Council’s work • No deterrence • Alternatives – Truth and Reconciliation Commission model – Domestic trial model International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 88
U. S. and ICC • Bolton’s Speech – Two flaws: substantive and structural • • Broad power to interpretation Crimes can be added Crimes vaguely defined, such as “aggression” Judges and the prosecutor: lack of accountability and checks and balances • Interference with the Security Council’s work • No deterrence • Alternatives – Truth and Reconciliation Commission model – Domestic trial model International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 88
 11. Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 89
11. Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 89
 Human Rights Search: Basic Documents • United Nations Charter 1945 Article 55 • Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 • International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights 1966 • International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights 1966 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 90
Human Rights Search: Basic Documents • United Nations Charter 1945 Article 55 • Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 • International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights 1966 • International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights 1966 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 90
 Human Rights Search: Recommended Sources • University of Minnesota Law Library HR Website • United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 91
Human Rights Search: Recommended Sources • University of Minnesota Law Library HR Website • United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 91
 The Humanitarian Law of Armed Conflict: Sources of law • The Hague Conventions and Declarations of 1907 • The Nuremberg Charter of 1945 • The Geneva Conventions of 1949 • Protocol Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 1949 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 92
The Humanitarian Law of Armed Conflict: Sources of law • The Hague Conventions and Declarations of 1907 • The Nuremberg Charter of 1945 • The Geneva Conventions of 1949 • Protocol Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 1949 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 92
 Geneva and Hague Conventions • Protection of Individual – – Combatants Wounded , Sick and Shipwrecked Combatants POW Civilians • Protection of Property – Military Installations – Civilian Populace – Areas with Special Protection Lawyer Discusses Implications of New Detainee Law NPR audio Yoo Defends Detainee Measures as 'Rules of War‘NPR audio Letters: Strong Response to John Yoo Interview NPR audio International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 93
Geneva and Hague Conventions • Protection of Individual – – Combatants Wounded , Sick and Shipwrecked Combatants POW Civilians • Protection of Property – Military Installations – Civilian Populace – Areas with Special Protection Lawyer Discusses Implications of New Detainee Law NPR audio Yoo Defends Detainee Measures as 'Rules of War‘NPR audio Letters: Strong Response to John Yoo Interview NPR audio International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 93
 Regional Human Rights Law and Institutions • European System – The European Convention on Human Rights – European Commission of Human Rights – European Court of Human Rights (not to be confused with ECJ, they are difference court!) – Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe • Inter-American System – The OAS Charter of 1948 – The American Declaration of the Rights and Duties of Man of 1960 • African Regional System – African Charter of Human and People’s Rights of 1986 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 94
Regional Human Rights Law and Institutions • European System – The European Convention on Human Rights – European Commission of Human Rights – European Court of Human Rights (not to be confused with ECJ, they are difference court!) – Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe • Inter-American System – The OAS Charter of 1948 – The American Declaration of the Rights and Duties of Man of 1960 • African Regional System – African Charter of Human and People’s Rights of 1986 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 94
 European Convention of Human Rights • Don’t mistake it for EU. ECHR and EU are related, but difference organizations. – The Council of European Union • ECHR International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 95
European Convention of Human Rights • Don’t mistake it for EU. ECHR and EU are related, but difference organizations. – The Council of European Union • ECHR International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 95
 Peck v. United Kingdom European Convention of Human Rights ARTICLE 8 • Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home and his correspondence. • There shall be no interference by a public authority with the exercise of this right except such as is in accordance with the law and is necessary in a democratic society in the interests of national security, public safety or the economic well-being of the country, for the prevention of disorder or crime, for the protection of health or morals, or for the protection of the rights and freedoms of others. ARTICLE 13 • Everyone whose rights and freedoms as set forth in this Convention are violated shall have an effective remedy before a national authority notwithstanding that the violation has been committed by persons acting in an official capacity. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 96
Peck v. United Kingdom European Convention of Human Rights ARTICLE 8 • Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home and his correspondence. • There shall be no interference by a public authority with the exercise of this right except such as is in accordance with the law and is necessary in a democratic society in the interests of national security, public safety or the economic well-being of the country, for the prevention of disorder or crime, for the protection of health or morals, or for the protection of the rights and freedoms of others. ARTICLE 13 • Everyone whose rights and freedoms as set forth in this Convention are violated shall have an effective remedy before a national authority notwithstanding that the violation has been committed by persons acting in an official capacity. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 96
 ENFORCEMENT OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAW IN THE U. S. AND OTHER DOMESTIC COURTS • Because the United States has failed to ratify so many human rights treaties, enforcement of human rights largely depends on the incorporation of custom into U. S. law by the courts. (Ref. Linda A. Malone, International Human Rights) • Hand out (excerpt from Malone’s book: International Human Rights, 2002) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 97
ENFORCEMENT OF HUMAN RIGHTS LAW IN THE U. S. AND OTHER DOMESTIC COURTS • Because the United States has failed to ratify so many human rights treaties, enforcement of human rights largely depends on the incorporation of custom into U. S. law by the courts. (Ref. Linda A. Malone, International Human Rights) • Hand out (excerpt from Malone’s book: International Human Rights, 2002) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 97
 12. The World Trade Organization International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 98
12. The World Trade Organization International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 98
 From GATT to WTO • GATT 1947 – ITO failed • WTO 1995 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 99
From GATT to WTO • GATT 1947 – ITO failed • WTO 1995 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 99
 Most Favored Nation Treatment • Article I • General Most-Favoured-Nation Treatment 1. With respect to customs duties and charges of any kind imposed on or in connection with importation or exportation or imposed on the international transfer of payments for imports or exports, and with respect to the method of levying such duties and charges, and with respect to all rules and formalities in connection with importation and exportation, and with respect to all matters referred to in paragraphs 2 and 4 of Article III, any advantage, favour, privilege or immunity granted by any contracting party to any product originating in or destined for any other country shall be accorded immediately and unconditionally to the like product originating in or destined for the territories of all other contracting parties. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 100
Most Favored Nation Treatment • Article I • General Most-Favoured-Nation Treatment 1. With respect to customs duties and charges of any kind imposed on or in connection with importation or exportation or imposed on the international transfer of payments for imports or exports, and with respect to the method of levying such duties and charges, and with respect to all rules and formalities in connection with importation and exportation, and with respect to all matters referred to in paragraphs 2 and 4 of Article III, any advantage, favour, privilege or immunity granted by any contracting party to any product originating in or destined for any other country shall be accorded immediately and unconditionally to the like product originating in or destined for the territories of all other contracting parties. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 100
 Coverage • http: //www. wto. org/english/info_e/site_e. ht m • GATS • TRIPS International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 101
Coverage • http: //www. wto. org/english/info_e/site_e. ht m • GATS • TRIPS International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 101
 Trade Barriers • Tariffs and Customs • Non-tariff Trade Barriers International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 102
Trade Barriers • Tariffs and Customs • Non-tariff Trade Barriers International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 102
 WTO and China • • 1948 GATT goes into effect (China is a contracting party) 1950 China withdraws from GATT 1982 Observer Status 1986 China intents to join GATT 1989 Application suspended 1994 Uruguay round (China is a signatory. ) 1999 U. S. –China agreement on China’s accession 2001 Membership (Reference: Karen Kalverson, China’s WTO Accession: Economic, Legal and Political Implications) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 103
WTO and China • • 1948 GATT goes into effect (China is a contracting party) 1950 China withdraws from GATT 1982 Observer Status 1986 China intents to join GATT 1989 Application suspended 1994 Uruguay round (China is a signatory. ) 1999 U. S. –China agreement on China’s accession 2001 Membership (Reference: Karen Kalverson, China’s WTO Accession: Economic, Legal and Political Implications) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 103
 Concession and Accession • • Market access in goods Market access in services Agriculture Subsidies Transparency-related commitments Non-market economy treatment in anti-dumping cases Discriminatory safeguard rule (Reference: Karen Kalverson, China’s WTO Accession: Economic, Legal and Political Implications) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 104
Concession and Accession • • Market access in goods Market access in services Agriculture Subsidies Transparency-related commitments Non-market economy treatment in anti-dumping cases Discriminatory safeguard rule (Reference: Karen Kalverson, China’s WTO Accession: Economic, Legal and Political Implications) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 104
 Antidumping • Luoyang case 347 F. Supp. 2 d 1326 – Chevron test – Statutory background – Normal Value • Surrogate values • Whether welfare and labor costs should be included in the valuation International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 105
Antidumping • Luoyang case 347 F. Supp. 2 d 1326 – Chevron test – Statutory background – Normal Value • Surrogate values • Whether welfare and labor costs should be included in the valuation International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 105
 Luoyang Case • Tapered Roller Bearings International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 106
Luoyang Case • Tapered Roller Bearings International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 106
 13. International Environmental Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 107
13. International Environmental Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 107
 International Environmental Law Issues • Global Climate Change – Ozone Depletion – Antarctica – Global Health • Toxic and Hazardous Substances – Legal and Illegal Dumping • Pollution – Land Based Pollution – Vessel Based Pollution – Trans-boundary Water/Air Pollution • Desertification • Nuclear Damage • Population • Biodiversity • Conservation of Marine Living Resources Reference: Guruswamy, International Environmental Law (West, 2003) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 108
International Environmental Law Issues • Global Climate Change – Ozone Depletion – Antarctica – Global Health • Toxic and Hazardous Substances – Legal and Illegal Dumping • Pollution – Land Based Pollution – Vessel Based Pollution – Trans-boundary Water/Air Pollution • Desertification • Nuclear Damage • Population • Biodiversity • Conservation of Marine Living Resources Reference: Guruswamy, International Environmental Law (West, 2003) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 108
 Implementation • International Organizations – – – • Regional Organizations – – • UN Environment Development (UNED) World Bank International Court of Justice International Law Commission IAEA EU OECD (Economic Cooperation and Development) OAS (Organizations of American States) South Pacific Regional Organizations Specific Treaty Organizations – Conferences of parties • Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) – World Conservation Union – The World Wildlife Fund – Green Peace International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 109
Implementation • International Organizations – – – • Regional Organizations – – • UN Environment Development (UNED) World Bank International Court of Justice International Law Commission IAEA EU OECD (Economic Cooperation and Development) OAS (Organizations of American States) South Pacific Regional Organizations Specific Treaty Organizations – Conferences of parties • Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) – World Conservation Union – The World Wildlife Fund – Green Peace International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 109
 Compliance Mechanisms • Judicial Remedies • Diplomatic Avenues International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 110
Compliance Mechanisms • Judicial Remedies • Diplomatic Avenues International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 110
 From UN Convention to Kyoto Protocol • The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (FCCC), The Conference of Parties (COP-1, Rio de Janeiro, 1992) • COP-2, Geneva, 1996 • COP-3, Kyoto, 1997 • … • COP-12, Nairobi, 2006 UNFCCC website http: //unfccc. int/2860. php International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 111
From UN Convention to Kyoto Protocol • The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (FCCC), The Conference of Parties (COP-1, Rio de Janeiro, 1992) • COP-2, Geneva, 1996 • COP-3, Kyoto, 1997 • … • COP-12, Nairobi, 2006 UNFCCC website http: //unfccc. int/2860. php International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 111
 Kyoto Protocol The provisions of the Kyoto Protocol and its rulebook The 1997 Kyoto Protocol shares the Convention’s objective, principles and institutions, but significantly strengthens the Convention by committing Annex I Parties to individual, legallybinding targets to limit or reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Only Parties to the Convention that have also become Parties to the Protocol (i. e by ratifying, accepting, approving, or acceding to it) will be bound by the Protocol’s commitments. 165 countries have ratified the Protocol to date. Of these, 35 countries and the EEC are required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions below levels specified for each of them in the treaty. The individual targets for Annex I Parties are listed in the Kyoto Protocol’s Annex B. These add up to a total cut in greenhouse-gas emissions of at least 5% from 1990 levels in the commitment period 2008 -2012. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 112
Kyoto Protocol The provisions of the Kyoto Protocol and its rulebook The 1997 Kyoto Protocol shares the Convention’s objective, principles and institutions, but significantly strengthens the Convention by committing Annex I Parties to individual, legallybinding targets to limit or reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Only Parties to the Convention that have also become Parties to the Protocol (i. e by ratifying, accepting, approving, or acceding to it) will be bound by the Protocol’s commitments. 165 countries have ratified the Protocol to date. Of these, 35 countries and the EEC are required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions below levels specified for each of them in the treaty. The individual targets for Annex I Parties are listed in the Kyoto Protocol’s Annex B. These add up to a total cut in greenhouse-gas emissions of at least 5% from 1990 levels in the commitment period 2008 -2012. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 112
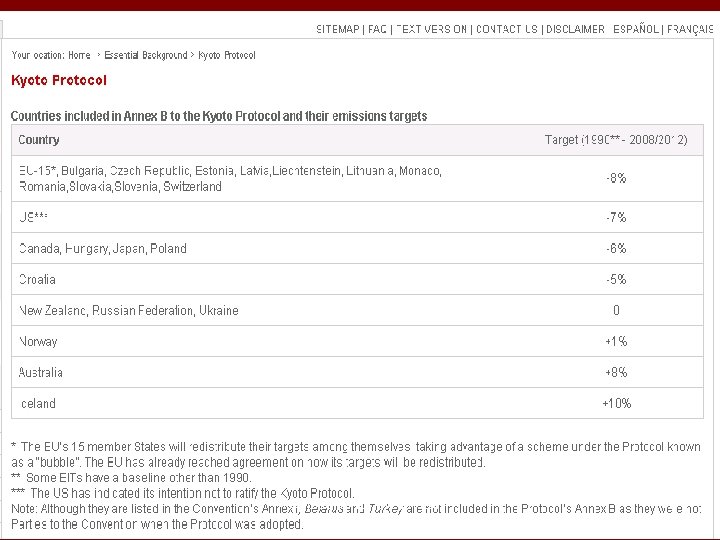 International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 113
International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 113
 Emission Trading System Two sources for the explanation of ET system • UK http: //www. defra. gov. uk/Environment/climatecha nge/trading/index. htm • EU http: //europa. eu/rapid/press. Releases. Action. do? r eference=MEMO/05/84&format=HTML&aged=1 &language=EN&gui. Language=en International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 114
Emission Trading System Two sources for the explanation of ET system • UK http: //www. defra. gov. uk/Environment/climatecha nge/trading/index. htm • EU http: //europa. eu/rapid/press. Releases. Action. do? r eference=MEMO/05/84&format=HTML&aged=1 &language=EN&gui. Language=en International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 114
 Waste Dumping Ivory Coast Tragedy Exposes Toxic Flow to Poor International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 115
Waste Dumping Ivory Coast Tragedy Exposes Toxic Flow to Poor International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 115
 Environmental Degradation in China International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 116
Environmental Degradation in China International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 116
 Songhua Spill • China's Government Cracks Down After Toxic Spill International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 117
Songhua Spill • China's Government Cracks Down After Toxic Spill International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 117
 14. United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 118
14. United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 118
 CISG Zapata Case • CISG: Pace University Law School Website, the best source of CISG research http: //www. cisg. law. pace. edu/ • Article 74 CISG Damages for breach of contract by one party consist of a sum equal to the loss, including loss of profit, suffered by the other party as a consequence of the breach. Such damages may not exceed the loss which the party in breach foresaw or ought to have foreseen at the time of the conclusion of the contract, in the light of the facts and matters of which he then knew or ought to have known, as a possible consequence International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 119
CISG Zapata Case • CISG: Pace University Law School Website, the best source of CISG research http: //www. cisg. law. pace. edu/ • Article 74 CISG Damages for breach of contract by one party consist of a sum equal to the loss, including loss of profit, suffered by the other party as a consequence of the breach. Such damages may not exceed the loss which the party in breach foresaw or ought to have foreseen at the time of the conclusion of the contract, in the light of the facts and matters of which he then knew or ought to have known, as a possible consequence International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 119
 Key Source for CISG Search • Pace University School of Law CISG Site International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 120
Key Source for CISG Search • Pace University School of Law CISG Site International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 120
 15. International Arbitration International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 121
15. International Arbitration International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 121
 Two basic types of international commercial arbitrations • Ad hoc – Goodwill, flexibility, speedy, cheap • Institutional – Supervisory services, a stable of experienced arbitrators and a fixed fee schedule (higher) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 122
Two basic types of international commercial arbitrations • Ad hoc – Goodwill, flexibility, speedy, cheap • Institutional – Supervisory services, a stable of experienced arbitrators and a fixed fee schedule (higher) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 122
 Institutions • WTO: Dispute settlement • WTO Archive list of panel and Appellate Body reports • World Bank: International Center for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) was created in 1966 to facilitate the settlement of investment disputes between governments and foreign investors. – List of Contracting States ICSID Basic documents ICSID cases List of bilateral investment treaties • ICC (International Chamber of Commerce) • Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) PCA was founded in The Hague in 1899 during the first Hague Peace Conference. The 1899 Convention, which provided the legal basis for the PCA, was revised at the second Hague Peace Conference in 1907. There are currently 97 States which are parties to one or both of the Conventions. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 123
Institutions • WTO: Dispute settlement • WTO Archive list of panel and Appellate Body reports • World Bank: International Center for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) was created in 1966 to facilitate the settlement of investment disputes between governments and foreign investors. – List of Contracting States ICSID Basic documents ICSID cases List of bilateral investment treaties • ICC (International Chamber of Commerce) • Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) PCA was founded in The Hague in 1899 during the first Hague Peace Conference. The 1899 Convention, which provided the legal basis for the PCA, was revised at the second Hague Peace Conference in 1907. There are currently 97 States which are parties to one or both of the Conventions. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 123
 Model Arbitration Clauses • London Court of Arbitration as an example: – The validity, construction and performance of this contract shall be governed by the laws of England any dispute that may arise out of or in connection with this contract, including its validity, construction and performance, shall be determined by arbitration under the Rules of the London Court of Arbitration at the date hereof, which Rules with respect to matters not regulated by them, incorporate the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules, the parties agree that service of any notices in reference to such arbitration at their addresses as given in this contract shall be valid and sufficient. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 124
Model Arbitration Clauses • London Court of Arbitration as an example: – The validity, construction and performance of this contract shall be governed by the laws of England any dispute that may arise out of or in connection with this contract, including its validity, construction and performance, shall be determined by arbitration under the Rules of the London Court of Arbitration at the date hereof, which Rules with respect to matters not regulated by them, incorporate the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules, the parties agree that service of any notices in reference to such arbitration at their addresses as given in this contract shall be valid and sufficient. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 124
 International Arbitration Rules 1. UNCITRAL • • http: //www. uncitral. org/uncitral/en/index. html The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) was established by the General Assembly in 1966 ( Resolution 2205(XXI) of 17 December 1966). In establishing the Commission, the General Assembly recognized that disparities in national laws governing international trade created obstacles to the flow of trade, and it regarded the Commission as the vehicle by which the United Nations could play a more active role in reducing or removing these obstacles. 2. ICSID International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 125
International Arbitration Rules 1. UNCITRAL • • http: //www. uncitral. org/uncitral/en/index. html The United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) was established by the General Assembly in 1966 ( Resolution 2205(XXI) of 17 December 1966). In establishing the Commission, the General Assembly recognized that disparities in national laws governing international trade created obstacles to the flow of trade, and it regarded the Commission as the vehicle by which the United Nations could play a more active role in reducing or removing these obstacles. 2. ICSID International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 125
 1985 - UNCITRAL Model Law on International Commercial Arbitration • Adopted by UNCITRAL on 21 June 1985, the Model Law is designed to assist States in reforming and modernizing their laws on arbitral procedure so as to take into account the particular features and needs of international commercial arbitration. It covers all stages of the arbitral process from the arbitration agreement, the composition and jurisdiction of the arbitral tribunal and the extent of court intervention through to the recognition and enforcement of the arbitral award. It reflects worldwide consensus on key aspects of international arbitration practice having been accepted by States of all regions and the different legal or economic systems of the world. • This Model Law has also been enacted as state law by California, Connecticut, Georgia, Oregon, Texas and other states. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 126
1985 - UNCITRAL Model Law on International Commercial Arbitration • Adopted by UNCITRAL on 21 June 1985, the Model Law is designed to assist States in reforming and modernizing their laws on arbitral procedure so as to take into account the particular features and needs of international commercial arbitration. It covers all stages of the arbitral process from the arbitration agreement, the composition and jurisdiction of the arbitral tribunal and the extent of court intervention through to the recognition and enforcement of the arbitral award. It reflects worldwide consensus on key aspects of international arbitration practice having been accepted by States of all regions and the different legal or economic systems of the world. • This Model Law has also been enacted as state law by California, Connecticut, Georgia, Oregon, Texas and other states. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 126
 Enforcement of Arbitration: The New York Convention • Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards (The New York Convention, 1958) • In the United States, the NY Convention is implemented in conjunction with the Federal Arbitration Act. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 127
Enforcement of Arbitration: The New York Convention • Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards (The New York Convention, 1958) • In the United States, the NY Convention is implemented in conjunction with the Federal Arbitration Act. International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 127
 Research Sources • Sources on Int'l Arbitration (Born, International Commercial Arbitration. Transnational Publishers, 2001) • Kluwer International Arbitration (fee based) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 128
Research Sources • Sources on Int'l Arbitration (Born, International Commercial Arbitration. Transnational Publishers, 2001) • Kluwer International Arbitration (fee based) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 128
 16. International Health Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 129
16. International Health Law International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 129
 Development of Global Health Issues • “The microbe that felled one child in a distant continent yesterday can reach yours today and seed a global pandemic tomorrow” – Joshua Lederberg, Nobel Laureate • “Globalization has resulted in, no only free movements of goods, capital, services and persons, but free movements of diseases” – Chenglin Liu • Infectious diseases—a long history – Example, 63 major epidemics of plague between 900 to 1500 – 14 -15 million Europeans fell victim to plague during the 14 th Century. – Hernando Cortez brought smallpox to Mexico which killed 3 million in Mexico – 1918 Influenza took about 20 million lives Other influenza outbreaks Reference: Allyn L. Taylor, Controlling the global spread of infectious diseases: toward a reinforced role for the international health regulations 33 Houston Law Review 1327 (1997) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 130
Development of Global Health Issues • “The microbe that felled one child in a distant continent yesterday can reach yours today and seed a global pandemic tomorrow” – Joshua Lederberg, Nobel Laureate • “Globalization has resulted in, no only free movements of goods, capital, services and persons, but free movements of diseases” – Chenglin Liu • Infectious diseases—a long history – Example, 63 major epidemics of plague between 900 to 1500 – 14 -15 million Europeans fell victim to plague during the 14 th Century. – Hernando Cortez brought smallpox to Mexico which killed 3 million in Mexico – 1918 Influenza took about 20 million lives Other influenza outbreaks Reference: Allyn L. Taylor, Controlling the global spread of infectious diseases: toward a reinforced role for the international health regulations 33 Houston Law Review 1327 (1997) International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 130
 From Medical Success to Complacency • Development of therapeutic and preventive interventions in the 20 th Century – Eradication of smallpox in 1977 • Attitude Change and new approaches: Control the border, stay complacency and enjoy life International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 131
From Medical Success to Complacency • Development of therapeutic and preventive interventions in the 20 th Century – Eradication of smallpox in 1977 • Attitude Change and new approaches: Control the border, stay complacency and enjoy life International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 131
 Emerging and Re-emerging Diseases (ERD) • ERD: AIDS, Legionnaires’ disease, Lyme disease, toxic shock syndrome, hepatitis C, virulent new strains of E. coli, SARS etc. • Causes – – – Social, political and environmental changes Poverty War Population growth International travel International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 132
Emerging and Re-emerging Diseases (ERD) • ERD: AIDS, Legionnaires’ disease, Lyme disease, toxic shock syndrome, hepatitis C, virulent new strains of E. coli, SARS etc. • Causes – – – Social, political and environmental changes Poverty War Population growth International travel International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 132
 Interrelated World • http: //tinet. ita. doc. gov/view/f-2004 -101 -001/index. html outbound U. S. travelers: 27 million (2004) • http: //tinet. ita. doc. gov/view/f-2004 -07 -001/index. html inbound travelers to the U. S. 20 million (2004), used to be 50 million according to some articles. Probably because of the tight visa control. • http: //english. people. com. cn/english/200101/16/eng 2 0010116_60652. html Travelers in and out of China (2000): 187 million. • http: //quickfacts. census. gov/qfd/ TX (2004): 22 million International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 133
Interrelated World • http: //tinet. ita. doc. gov/view/f-2004 -101 -001/index. html outbound U. S. travelers: 27 million (2004) • http: //tinet. ita. doc. gov/view/f-2004 -07 -001/index. html inbound travelers to the U. S. 20 million (2004), used to be 50 million according to some articles. Probably because of the tight visa control. • http: //english. people. com. cn/english/200101/16/eng 2 0010116_60652. html Travelers in and out of China (2000): 187 million. • http: //quickfacts. census. gov/qfd/ TX (2004): 22 million International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 133
 International Health Regulations (IHR) • Cholera epidemics that overran Europe between 1830 and 1847 – International Sanitary Conference in Paris in 1851 • IHR 1969 – No changes until 2005 – Safeguard borders – Narrow scope: cholera, plague, yellow fever – Weak enforcement • Excessive measures • Lack of cooperation International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 134
International Health Regulations (IHR) • Cholera epidemics that overran Europe between 1830 and 1847 – International Sanitary Conference in Paris in 1851 • IHR 1969 – No changes until 2005 – Safeguard borders – Narrow scope: cholera, plague, yellow fever – Weak enforcement • Excessive measures • Lack of cooperation International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 134
 IHR 2005 • IHR 2005 – Proactive approach – Larger scope – Monitoring system to promote compliance • Focal points in member states and vertical reporting • Horizontal reporting • Third party reporting – Assistance International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 135
IHR 2005 • IHR 2005 – Proactive approach – Larger scope – Monitoring system to promote compliance • Focal points in member states and vertical reporting • Horizontal reporting • Third party reporting – Assistance International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 135
 Global Health • WHO – – – Established in 1948 Headquarters in Geneva 6 regional offices Director-General Office NPR report on the new DG nomination audio • WHO Constitution – Attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health • Enabling law – UN Charter 55: to promote solutions of international economic, social, health, and related problems… International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 136
Global Health • WHO – – – Established in 1948 Headquarters in Geneva 6 regional offices Director-General Office NPR report on the new DG nomination audio • WHO Constitution – Attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health • Enabling law – UN Charter 55: to promote solutions of international economic, social, health, and related problems… International & Foreign Law Search, Liu 136


