edd08653409caf9a9a49f276e032e0a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 1. Formulating Strategy to Fill Identified Needs 2. Segmentation and Positioning MARK 430 WEEK 4
1. Formulating Strategy to Fill Identified Needs 2. Segmentation and Positioning MARK 430 WEEK 4
 What we will cover this week. . . § Now we have all that information about customer behaviour and customer needs. . what are we going to do with it? 1. Formulate a strategy to fill the needs that we have identified 2. Determine which customers to target, and how to position our product/service vis a vis the competition
What we will cover this week. . . § Now we have all that information about customer behaviour and customer needs. . what are we going to do with it? 1. Formulate a strategy to fill the needs that we have identified 2. Determine which customers to target, and how to position our product/service vis a vis the competition
 Main strategy tool: SWOT analysis § Goal is to pursue opportunities that use your company’s strengths, while avoiding threats and overcoming weaknesses (Urban p 45)
Main strategy tool: SWOT analysis § Goal is to pursue opportunities that use your company’s strengths, while avoiding threats and overcoming weaknesses (Urban p 45)
 Strategy formulation § Identify and rank strengths and weaknesses in your company / organization § Technique: § list key marketing success factors eg. § high product quality § customer loyalty § patent protection § rank your position relative to that of your competition against these factors § much worse, equal, better, much better § Objective is to recognize, then build on your strengths and overcome your weaknesses
Strategy formulation § Identify and rank strengths and weaknesses in your company / organization § Technique: § list key marketing success factors eg. § high product quality § customer loyalty § patent protection § rank your position relative to that of your competition against these factors § much worse, equal, better, much better § Objective is to recognize, then build on your strengths and overcome your weaknesses
 Strategy formulation Identify and rate opportunities and threats in the external marketing environment § Opportunities eg. § § § technological change low entry costs market growth unmet customer need weak competition customer power. . . § Threats eg. § § § technological change regulatory changes price war new competition social change customer power. . .
Strategy formulation Identify and rate opportunities and threats in the external marketing environment § Opportunities eg. § § § technological change low entry costs market growth unmet customer need weak competition customer power. . . § Threats eg. § § § technological change regulatory changes price war new competition social change customer power. . .
 Customer power: both threat and opportunity § More information, more options, simpler transactions § More knowledge, more sophistication § Threat to traditional marketing tactics - push based, one-way § marketers must “make” customers buy § Opportunity to attract the “new” customer § trust-based marketing § build mutually beneficial relationship
Customer power: both threat and opportunity § More information, more options, simpler transactions § More knowledge, more sophistication § Threat to traditional marketing tactics - push based, one-way § marketers must “make” customers buy § Opportunity to attract the “new” customer § trust-based marketing § build mutually beneficial relationship
 Which strategic approach to follow? § Which one to use: § what kind of customers do you have? § what kind of product/service are you providing? § Push-based strategy § commodities § price sensitive § deal seekers § Pull (trust-based) strategy § expensive / complex product § information seeking customers § customers that value long-term relationship § The web is fundamentally a pull medium rather than a push medium § Agree?
Which strategic approach to follow? § Which one to use: § what kind of customers do you have? § what kind of product/service are you providing? § Push-based strategy § commodities § price sensitive § deal seekers § Pull (trust-based) strategy § expensive / complex product § information seeking customers § customers that value long-term relationship § The web is fundamentally a pull medium rather than a push medium § Agree?
 Trust based marketing § The web is really good an enabling trust building (a paradox? ) § HPs Online Advisor § Acts as an online advisor, that helps people acquire products and services for their home. § How does HP benefit?
Trust based marketing § The web is really good an enabling trust building (a paradox? ) § HPs Online Advisor § Acts as an online advisor, that helps people acquire products and services for their home. § How does HP benefit?
 Benefits of trust-based marketing § Fits the nature of the web medium § Ebay - ratings of buyers and sellers without interference from EBay § Amazon - customer ratings of products (does Amazon censor? ) § Collaborative filtering § Reviews, customer ratings sites, blogs § Less churn (cheaper to keep a customer than acquire a new one) § Cheaper to serve.
Benefits of trust-based marketing § Fits the nature of the web medium § Ebay - ratings of buyers and sellers without interference from EBay § Amazon - customer ratings of products (does Amazon censor? ) § Collaborative filtering § Reviews, customer ratings sites, blogs § Less churn (cheaper to keep a customer than acquire a new one) § Cheaper to serve.
 What we will cover this week. . . § Now we have all that information about customer behaviour and customer needs. . what are we going to do with it? 1. Formulate a strategy to fill the needs that we have identified 2. Determine which customers to target, and how to position our product/service vis a vis the competition
What we will cover this week. . . § Now we have all that information about customer behaviour and customer needs. . what are we going to do with it? 1. Formulate a strategy to fill the needs that we have identified 2. Determine which customers to target, and how to position our product/service vis a vis the competition
 Which customers will you serve? Segmentation and Targeting § Marketing segmentation § the process of aggregating individuals or businesses with similar characteristics § that relate to the use, consumption, or benefits of a product or service. § Targeting § the process of selecting the market segments that are most attractive to the firm
Which customers will you serve? Segmentation and Targeting § Marketing segmentation § the process of aggregating individuals or businesses with similar characteristics § that relate to the use, consumption, or benefits of a product or service. § Targeting § the process of selecting the market segments that are most attractive to the firm
 Why segment? § Customers prefer “custom” products § § The market of one? Cost How many segments should we deliver? What characteristics do we use to group people into market segments § How do we know we are reaching those segments?
Why segment? § Customers prefer “custom” products § § The market of one? Cost How many segments should we deliver? What characteristics do we use to group people into market segments § How do we know we are reaching those segments?
 Traditional marketing complaint § I know I am wasting 50% of my advertising budget, but I don’t know which 50% § Did the right segment see the ad? § Internet technologies can answer that question much more effectively than traditional advertising media
Traditional marketing complaint § I know I am wasting 50% of my advertising budget, but I don’t know which 50% § Did the right segment see the ad? § Internet technologies can answer that question much more effectively than traditional advertising media
 The Internet advantage § The Internet is the marketer’s dream § Ad server companies (eg. Double. Click) compile and serve much narrower consumer segments than mass media § Cost to deliver an ad is much smaller § User registration info and cookies provide specific user data § including what they did after they saw the ad § immediately § later
The Internet advantage § The Internet is the marketer’s dream § Ad server companies (eg. Double. Click) compile and serve much narrower consumer segments than mass media § Cost to deliver an ad is much smaller § User registration info and cookies provide specific user data § including what they did after they saw the ad § immediately § later
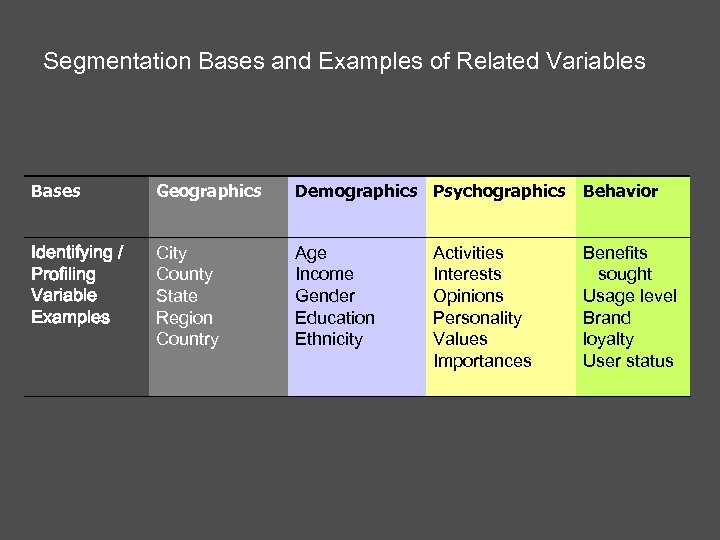 Segmentation Bases and Examples of Related Variables Bases Geographics Demographics Psychographics Behavior Identifying / Profiling Variable Examples City County State Region Country Age Income Gender Education Ethnicity Benefits sought Usage level Brand loyalty User status Activities Interests Opinions Personality Values Importances
Segmentation Bases and Examples of Related Variables Bases Geographics Demographics Psychographics Behavior Identifying / Profiling Variable Examples City County State Region Country Age Income Gender Education Ethnicity Benefits sought Usage level Brand loyalty User status Activities Interests Opinions Personality Values Importances
 VALS § An example of a Marketing strategy tool (VALS stands for values and lifestyle, but now focuses on personality) § segments the market on the basis of personality traits § traits assumed to drive consumer behaviour § uses a survey instrument § The VALS personality types § Primary and secondary types
VALS § An example of a Marketing strategy tool (VALS stands for values and lifestyle, but now focuses on personality) § segments the market on the basis of personality traits § traits assumed to drive consumer behaviour § uses a survey instrument § The VALS personality types § Primary and secondary types
 After Segmentation > Positioning § Product positioning takes place within a target market segment § Position is based on consumer perception § What we need to know: § What product dimensions/attributes do consumers use to evaluate? § How important are these when decisions are made? § How do we and our competitors sit relative to these dimensions § One tool we can use is a Perceptual Map
After Segmentation > Positioning § Product positioning takes place within a target market segment § Position is based on consumer perception § What we need to know: § What product dimensions/attributes do consumers use to evaluate? § How important are these when decisions are made? § How do we and our competitors sit relative to these dimensions § One tool we can use is a Perceptual Map
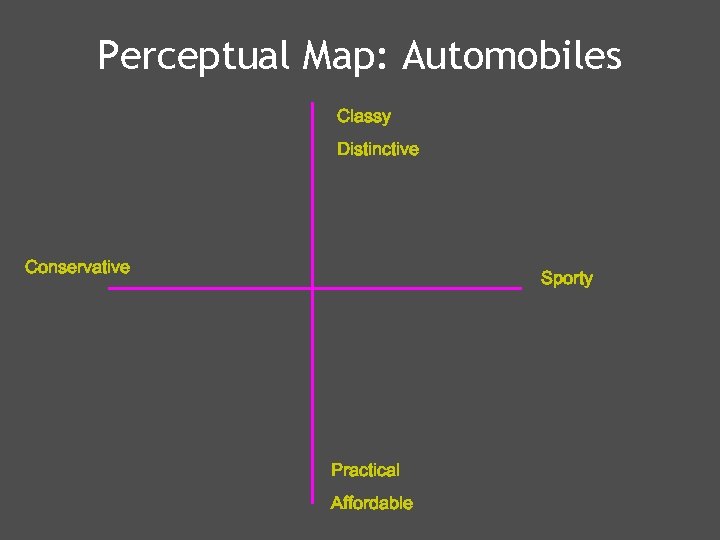 Perceptual Map: Automobiles Classy Distinctive Conservative Sporty Practical Affordable
Perceptual Map: Automobiles Classy Distinctive Conservative Sporty Practical Affordable
 2 uses for a perceptual map Identify areas without competitors § § § § Mercedes Honda Ford Nissan Porsche BMW Chrysler VW § § § § Hyundai Toyota Cadillac Dodge Jeep Saturn Kia Lexus Display consumer’s ideal points § These points reflect ideal combinations of the two dimensions as seen by a consumer. § Use them to identify potential market segments
2 uses for a perceptual map Identify areas without competitors § § § § Mercedes Honda Ford Nissan Porsche BMW Chrysler VW § § § § Hyundai Toyota Cadillac Dodge Jeep Saturn Kia Lexus Display consumer’s ideal points § These points reflect ideal combinations of the two dimensions as seen by a consumer. § Use them to identify potential market segments
 § The Internet’s big promise is individualized targeting giving individual consumers exactly what they want at the right time and place.
§ The Internet’s big promise is individualized targeting giving individual consumers exactly what they want at the right time and place.


