0b61439e1c8017024d44d0e1e919ea1b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 1. Election of 1800: The rise of political parties caused a problem in the electoral college Federalists Adams--Pres---65 Hamilton---VP Democratic Republicans Jefferson---Pres. ---73 Burr---VP----73 2. There was a tie in electors between Jefferson and Burr. Federalist House of Representatives (headed by Hamilton) e-v-e-n-t-u-a-l-l-y chooses Jefferson. 3. To eliminate future problems § 12 th Amendment: Electors specify which person for President and VP on separate ballots. No more VP is the runner up (Otherwise we’d have president Obama and VP Romney). 1
1. Election of 1800: The rise of political parties caused a problem in the electoral college Federalists Adams--Pres---65 Hamilton---VP Democratic Republicans Jefferson---Pres. ---73 Burr---VP----73 2. There was a tie in electors between Jefferson and Burr. Federalist House of Representatives (headed by Hamilton) e-v-e-n-t-u-a-l-l-y chooses Jefferson. 3. To eliminate future problems § 12 th Amendment: Electors specify which person for President and VP on separate ballots. No more VP is the runner up (Otherwise we’d have president Obama and VP Romney). 1
 • Secretary of State under Washington, Informal- used charm to sway congress Contradictory presidency (life): Anti-War /Anti-Navy (Pacifist) • Went to war with Barbary Pirates • Built the “mosquito fleet” of naval ships Anti-British /Pro-French • Almost allied with England went to war with France (for New Orleans). Believed in limited Gov’t • Embargo Act- of the biggest gov’t intrusions in US history 2 Strict Construction of Constitution • Used loose construction to purchase Louisiana territory
• Secretary of State under Washington, Informal- used charm to sway congress Contradictory presidency (life): Anti-War /Anti-Navy (Pacifist) • Went to war with Barbary Pirates • Built the “mosquito fleet” of naval ships Anti-British /Pro-French • Almost allied with England went to war with France (for New Orleans). Believed in limited Gov’t • Embargo Act- of the biggest gov’t intrusions in US history 2 Strict Construction of Constitution • Used loose construction to purchase Louisiana territory
 John Adams Federalist Democratic/Republican Thomas Jefferson Significance: • peaceful transfer of power between political parties • Helped 2 -party system by showing that defeat (for Federalists) didn’t mean disaster • Jefferson kept most of Federalist policies including the bank and tariff • Dismissed few Federalist office holders 3
John Adams Federalist Democratic/Republican Thomas Jefferson Significance: • peaceful transfer of power between political parties • Helped 2 -party system by showing that defeat (for Federalists) didn’t mean disaster • Jefferson kept most of Federalist policies including the bank and tariff • Dismissed few Federalist office holders 3
 • This period is a transition in US Democracy. • Saw the Government as too powerful- Tried to reduce it’s power (but expanded it) • Laissez faire--govt. stays out of people’s lives • Jeffersonian Democracy: common man (white, educated) should vote • Believed education prepared them for democracy. • Visualized an agrarian society • Republican Motherhood : woman’s 4 responsibility was to educate children to be KING GEORGE FEDERALISTS JEFFERSON good Republican citizens
• This period is a transition in US Democracy. • Saw the Government as too powerful- Tried to reduce it’s power (but expanded it) • Laissez faire--govt. stays out of people’s lives • Jeffersonian Democracy: common man (white, educated) should vote • Believed education prepared them for democracy. • Visualized an agrarian society • Republican Motherhood : woman’s 4 responsibility was to educate children to be KING GEORGE FEDERALISTS JEFFERSON good Republican citizens
 Notes 2 Louisiana Purchase 5
Notes 2 Louisiana Purchase 5
 Haitian rev • New Orleans was a key to future expansion as there were few good ports in the South. • A slave rebellion in Haiti led by Toussaint L’Ouverture forced Napoleon to abandon his dream 6 of a French America.
Haitian rev • New Orleans was a key to future expansion as there were few good ports in the South. • A slave rebellion in Haiti led by Toussaint L’Ouverture forced Napoleon to abandon his dream 6 of a French America.
 • Through emissaries, Jefferson offered $10 million for New Orleans. If the sale failed, they were instructed to seek alliance with England • Napoleon Wanted to sell ALL of Louisiana for $15 m • He did so without Congressional approval. Doubling the size of America 7
• Through emissaries, Jefferson offered $10 million for New Orleans. If the sale failed, they were instructed to seek alliance with England • Napoleon Wanted to sell ALL of Louisiana for $15 m • He did so without Congressional approval. Doubling the size of America 7
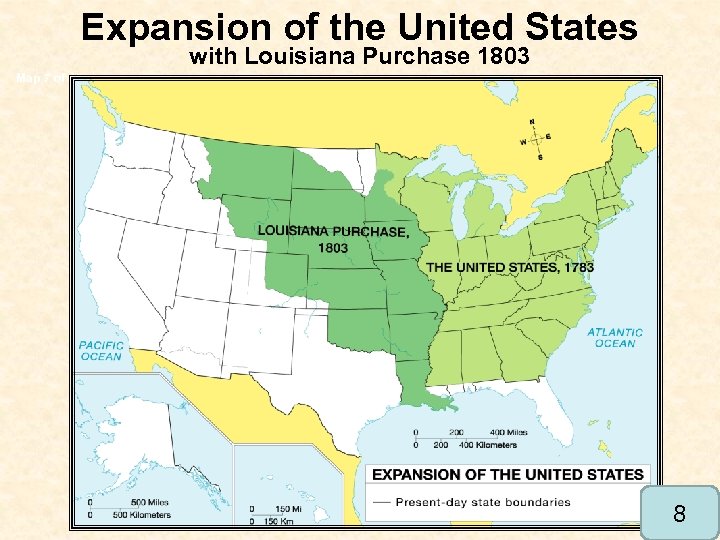 Expansion of the United States with Louisiana Purchase 1803 Map 7 of 45 8
Expansion of the United States with Louisiana Purchase 1803 Map 7 of 45 8
 Jefferson’s greatest accomplishment but… Does the President have the right to purchase land if it is not expressed in the US Constitution? • Hamilton and Federalists were against this purchase • Why? Population shift take Federalist power away in Congress • Feared Jefferson’s vision of an “agrarian society” • Jefferson referred to this as his “valley of democracy” 9
Jefferson’s greatest accomplishment but… Does the President have the right to purchase land if it is not expressed in the US Constitution? • Hamilton and Federalists were against this purchase • Why? Population shift take Federalist power away in Congress • Feared Jefferson’s vision of an “agrarian society” • Jefferson referred to this as his “valley of democracy” 9
 • 1804: Jefferson sends 28 men led by Meriwether Lewis and William Clark to explore north Louisiana Purpose: • Indian Alliances • Establish land claims • Northwest Passage 10
• 1804: Jefferson sends 28 men led by Meriwether Lewis and William Clark to explore north Louisiana Purpose: • Indian Alliances • Establish land claims • Northwest Passage 10
 • Interpreter and guide for Lewis and Clark • Her knowledge of trails and mountain passes helped with the success of the expedition. • She was also a “diplomat” for Lewis and Clark. Many tribes had never seen white men before. • Her presence with a baby was looked upon as 11
• Interpreter and guide for Lewis and Clark • Her knowledge of trails and mountain passes helped with the success of the expedition. • She was also a “diplomat” for Lewis and Clark. Many tribes had never seen white men before. • Her presence with a baby was looked upon as 11
 Zebulon Pike- 1805 • Explored the Southern Portion of the Louisiana Purchase • Captured in Mexico but was released • This capture gave the US insight about the nature of Mexican politics • Pike’s Peak named after him 12
Zebulon Pike- 1805 • Explored the Southern Portion of the Louisiana Purchase • Captured in Mexico but was released • This capture gave the US insight about the nature of Mexican politics • Pike’s Peak named after him 12
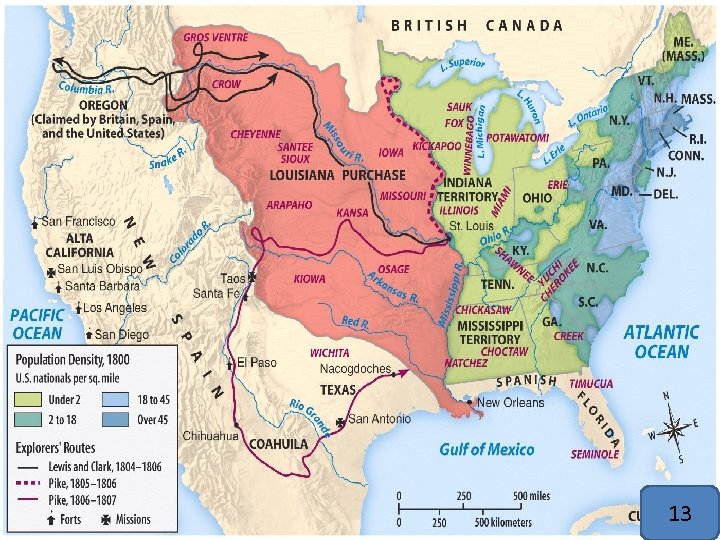 Map LP/3 13
Map LP/3 13
 14
14
 § France or England used to protect our ships. § Barbary pirates under Yusuf Karamanli were hijacking US ships for ransom. § Jefferson disagreed with paying, but had almost no navy so he agreed to paying a tribute. § Karamanji wanted more money and declared war as a bluff…fail. § “Mosquito fleet” of 200 small gunboats constructed. § War of 1812: these boats would prove to be ineffective. § 8 marines (and 300 mercenaries) defeated the pirates at the battle of Derna (mercenaries still awaiting payment…) 15
§ France or England used to protect our ships. § Barbary pirates under Yusuf Karamanli were hijacking US ships for ransom. § Jefferson disagreed with paying, but had almost no navy so he agreed to paying a tribute. § Karamanji wanted more money and declared war as a bluff…fail. § “Mosquito fleet” of 200 small gunboats constructed. § War of 1812: these boats would prove to be ineffective. § 8 marines (and 300 mercenaries) defeated the pirates at the battle of Derna (mercenaries still awaiting payment…) 15
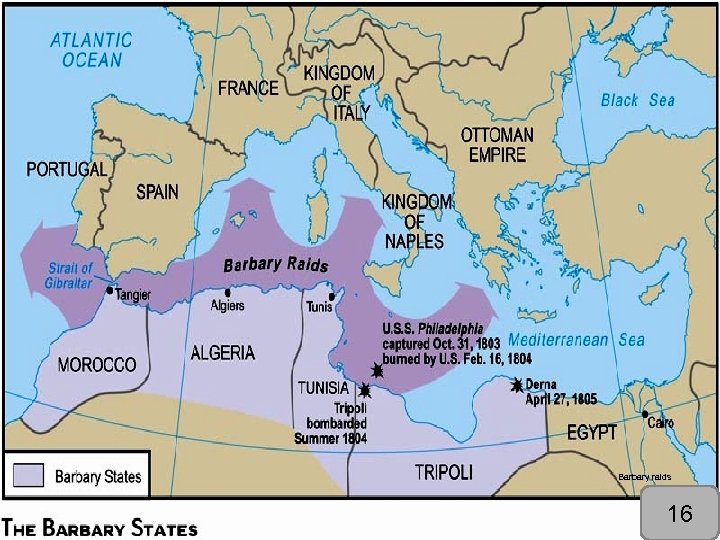 Barbary raids 16
Barbary raids 16
 Berlin Decree (1806), Milan Decree (1807): issued by Napoleon (he controlled mainland Europe) ships that docked in Britain could not land on mainland continent and they would seize any ships trying to trade at British ports. Orders-in-council British laws which permitted impressing neutral sailors (hijacking). Neutral ships had to go to British ports before going to French ones. America couldn’t trade anywhere in Europe without risking seizure by England or France… Where could they trade? 17
Berlin Decree (1806), Milan Decree (1807): issued by Napoleon (he controlled mainland Europe) ships that docked in Britain could not land on mainland continent and they would seize any ships trying to trade at British ports. Orders-in-council British laws which permitted impressing neutral sailors (hijacking). Neutral ships had to go to British ports before going to French ones. America couldn’t trade anywhere in Europe without risking seizure by England or France… Where could they trade? 17
 Chesapeake affair • 1806, Chesapeake was a US merchant ship 10 miles off the coast of Virginia. A British ship (The Leopard) ordered it to stop. • 3 Americans were killed, 18 wounded and 4 sailors impressed • Public opinion after this favored war 18
Chesapeake affair • 1806, Chesapeake was a US merchant ship 10 miles off the coast of Virginia. A British ship (The Leopard) ordered it to stop. • 3 Americans were killed, 18 wounded and 4 sailors impressed • Public opinion after this favored war 18
 • Jefferson’s response to the Chesapeake Affair was the Embargo Act of 1807…. • Jefferson attempted to defend our neutrality by stopping all American exports to the world. 19
• Jefferson’s response to the Chesapeake Affair was the Embargo Act of 1807…. • Jefferson attempted to defend our neutrality by stopping all American exports to the world. 19
 • Reasoning: England France traded for most of their natural resources with us. By cutting off exports to them, it would forces them to respect our neutrality or: economic coercion. • It has the reverse effect…… • The Embargo Act killed our economy. Many Americans defied the law and began to smuggle goods. • New England begins shifting from trade to industry and they were furious! • Lasted 15 months, repealed in March of 1809 • Like Washington & Adams, Jefferson finishes his presidency on a sour note. 20
• Reasoning: England France traded for most of their natural resources with us. By cutting off exports to them, it would forces them to respect our neutrality or: economic coercion. • It has the reverse effect…… • The Embargo Act killed our economy. Many Americans defied the law and began to smuggle goods. • New England begins shifting from trade to industry and they were furious! • Lasted 15 months, repealed in March of 1809 • Like Washington & Adams, Jefferson finishes his presidency on a sour note. 20
 Hamilton and Burr 21
Hamilton and Burr 21
 • Aaron Burr (1756 -1836) • Born in Newark N. J. • Fought in the Revolutionary war. • A practicing lawyer in New York City • Vice President of the United States (1801 -1805). • Kills Hamilton in a duel • Involved in Conspiracy 22
• Aaron Burr (1756 -1836) • Born in Newark N. J. • Fought in the Revolutionary war. • A practicing lawyer in New York City • Vice President of the United States (1801 -1805). • Kills Hamilton in a duel • Involved in Conspiracy 22
 §Angered by an insulting remark made by Hamilton, §Burr challenged the Federalist leader to a duel and fatally shot him §Hamilton’s death in 1804 deprived the Federalists of their last great leader and earned Burr the hostility of many 23
§Angered by an insulting remark made by Hamilton, §Burr challenged the Federalist leader to a duel and fatally shot him §Hamilton’s death in 1804 deprived the Federalists of their last great leader and earned Burr the hostility of many 23
 §Burr may have been mentally unbalanced and made many promises to many people. §In 1806, Burr planned to take Mexico from Spain and possibly unite it with Louisiana under his rule §Jefferson learned of the conspiracy and ordered Burr’s arrest and trial for treason. §A jury acquitted Burr, basing its decision on Marshall’s narrow definition of treason and the lack of 24 witnesses to any “overt act” by Burr
§Burr may have been mentally unbalanced and made many promises to many people. §In 1806, Burr planned to take Mexico from Spain and possibly unite it with Louisiana under his rule §Jefferson learned of the conspiracy and ordered Burr’s arrest and trial for treason. §A jury acquitted Burr, basing its decision on Marshall’s narrow definition of treason and the lack of 24 witnesses to any “overt act” by Burr


