 1 DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS An Example
1 DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS An Example
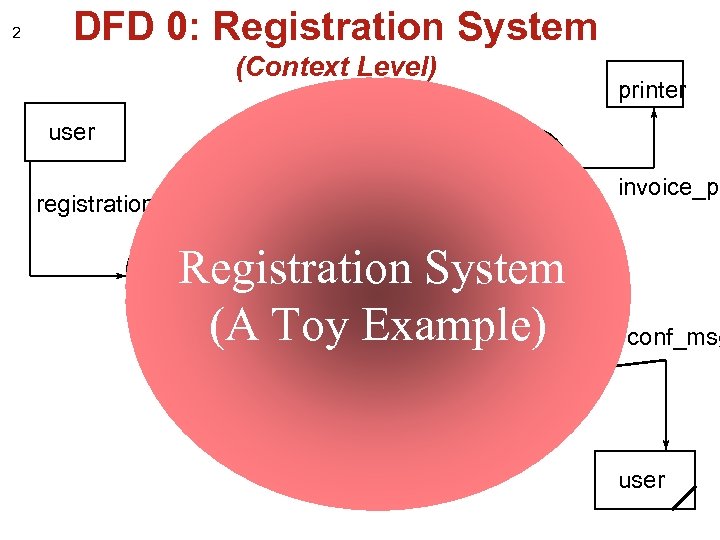 2 DFD 0: Registration System (Context Level) user P 2 invoice Prepare registration reg+ invoice reg. P 1 prices Read profile & check registration db printer P 4 Print invoice_pr Registration System (A Toy reg_info Example) conf_msg reg+ P 3 Accept reg. conf. P 5 Write conf. user
2 DFD 0: Registration System (Context Level) user P 2 invoice Prepare registration reg+ invoice reg. P 1 prices Read profile & check registration db printer P 4 Print invoice_pr Registration System (A Toy reg_info Example) conf_msg reg+ P 3 Accept reg. conf. P 5 Write conf. user
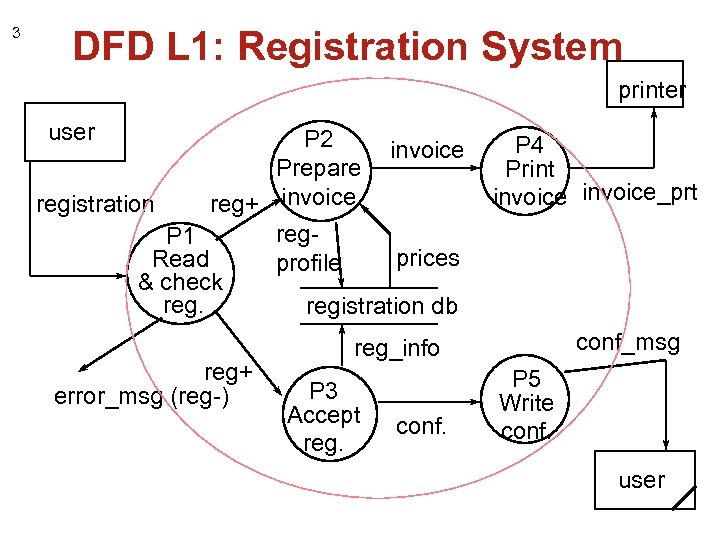 3 DFD L 1: Registration System printer user P 2 invoice Prepare registration reg+ invoice reg. P 1 prices Read profile & check registration db reg+ error_msg (reg-) P 4 Print invoice_prt conf_msg reg_info P 3 Accept reg. conf. P 5 Write conf. user
3 DFD L 1: Registration System printer user P 2 invoice Prepare registration reg+ invoice reg. P 1 prices Read profile & check registration db reg+ error_msg (reg-) P 4 Print invoice_prt conf_msg reg_info P 3 Accept reg. conf. P 5 Write conf. user
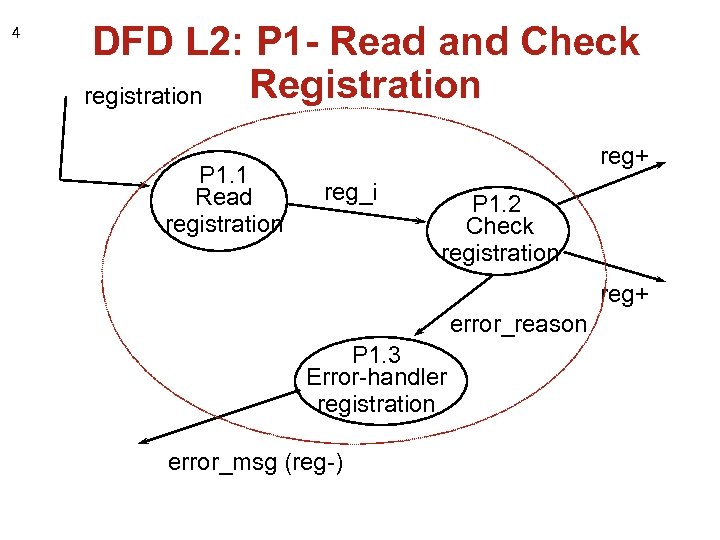 4 DFD L 2: P 1 - Read and Check Registration registration P 1. 1 Read registration reg+ reg_i P 1. 2 Check registration reg+ error_reason P 1. 3 Error-handler registration error_msg (reg-)
4 DFD L 2: P 1 - Read and Check Registration registration P 1. 1 Read registration reg+ reg_i P 1. 2 Check registration reg+ error_reason P 1. 3 Error-handler registration error_msg (reg-)
 5 Remember during Composition • a process should not have identical inputs and outputs • all data flows must be labelled • sources / sinks are not processes (=active) • data stores should not be connected directly to sources / sinks
5 Remember during Composition • a process should not have identical inputs and outputs • all data flows must be labelled • sources / sinks are not processes (=active) • data stores should not be connected directly to sources / sinks
 6 Suggestions for a Good Style • organise diagram from left to right or top to bottom • provide input and output “filters” for each major data flow • keep sources / sinks on the left or right boundary of your diagram
6 Suggestions for a Good Style • organise diagram from left to right or top to bottom • provide input and output “filters” for each major data flow • keep sources / sinks on the left or right boundary of your diagram
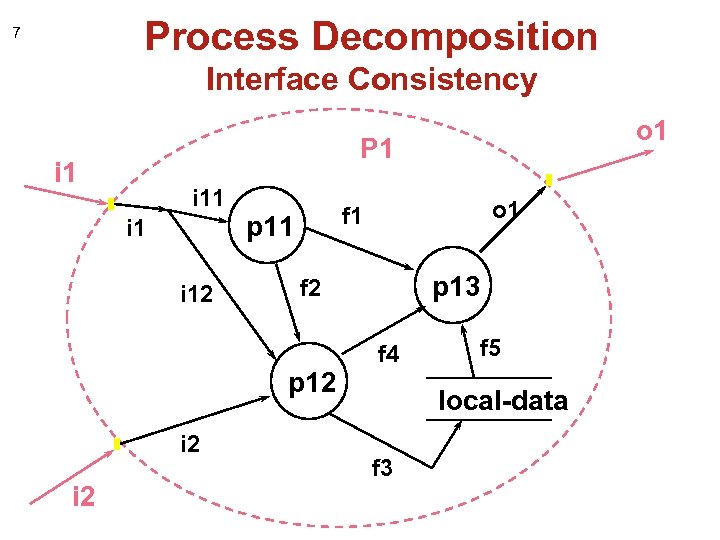 Process Decomposition 7 Interface Consistency P 1 i 11 i 12 i 2 o 1 f 1 p 13 f 2 p 12 i 2 o 1 f 4 f 5 local-data f 3
Process Decomposition 7 Interface Consistency P 1 i 11 i 12 i 2 o 1 f 1 p 13 f 2 p 12 i 2 o 1 f 4 f 5 local-data f 3
 8 Process Decomposition • processes can be decomposed / refined • one process ===> complete DFD • interface flows must remain consistent • lower level processes, data flows and data stores can be added on • sources sinks remain on level-1
8 Process Decomposition • processes can be decomposed / refined • one process ===> complete DFD • interface flows must remain consistent • lower level processes, data flows and data stores can be added on • sources sinks remain on level-1
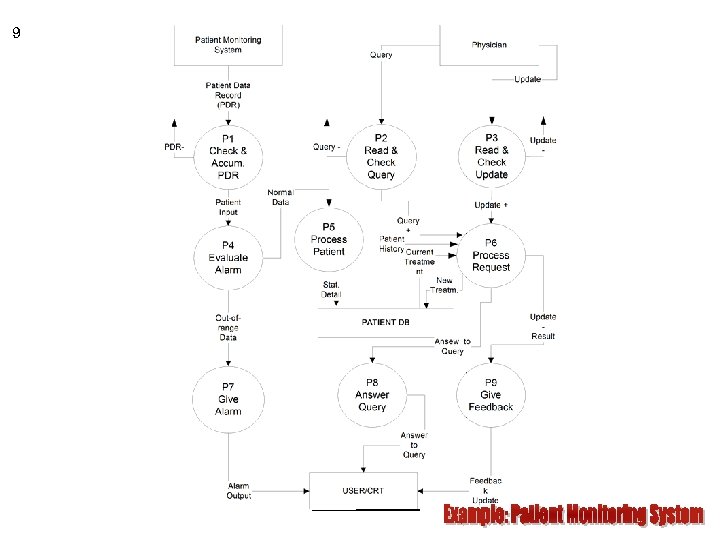 9
9
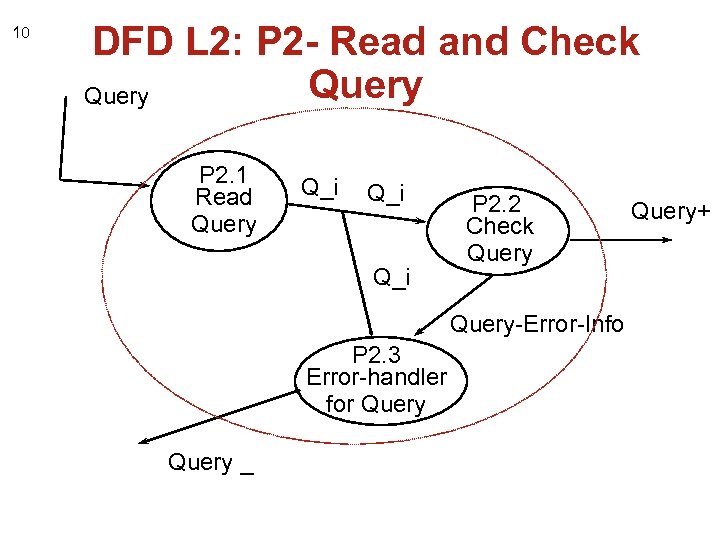 10 DFD L 2: P 2 - Read and Check Query P 2. 1 Read Query Q_i Q_i P 2. 2 Check Query-Error-Info P 2. 3 Error-handler for Query _ Query+
10 DFD L 2: P 2 - Read and Check Query P 2. 1 Read Query Q_i Q_i P 2. 2 Check Query-Error-Info P 2. 3 Error-handler for Query _ Query+
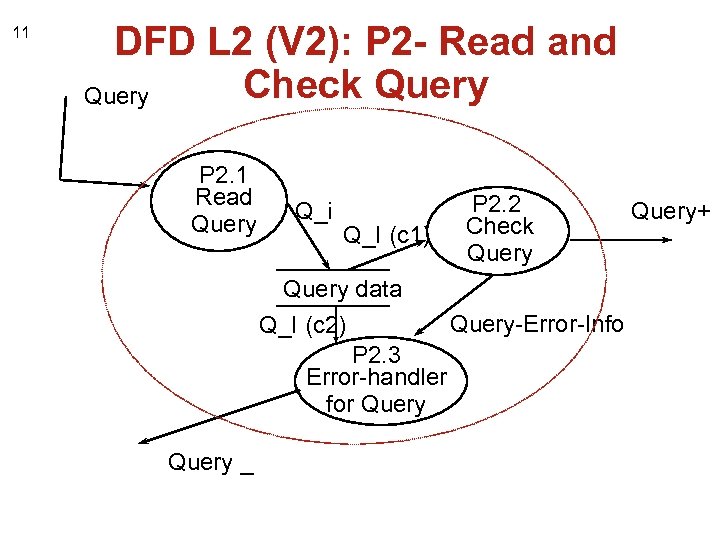 11 DFD L 2 (V 2): P 2 - Read and Check Query P 2. 1 Read Query Q_i Q_I (c 1) P 2. 2 Check Query data Query-Error-Info Q_I (c 2) P 2. 3 Error-handler for Query _ Query+
11 DFD L 2 (V 2): P 2 - Read and Check Query P 2. 1 Read Query Q_i Q_I (c 1) P 2. 2 Check Query data Query-Error-Info Q_I (c 2) P 2. 3 Error-handler for Query _ Query+
 12 End of Section 2 c coming up: data dictionaries
12 End of Section 2 c coming up: data dictionaries