5529893c6f8a93df728210a863fffdde.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 111

1 CS 21 A • Beginning Java. Script Programming Project 2 Creating Pop-up Windows, Adding Scrolling Messages, and Validating Forms Sonny Huang

Project 2 Creating Pop-up Windows, Adding Scrolling Messages, and Validating Forms 2 Outline l Explain the four basic components of a scrolling message l Write a user-defined function to display a scrolling message in a form text box l Describe the If statement l Define conditionals and discuss the conditional operands l Define recursion l Describe the focus() method l Write a user-defined function to calculate mortgage payments l Validate data entry using a nested If…Else statement l Describe the parse. Int(), parse. Float(), and is. Na. N() built-in functions

Project 2 Creating Pop-up Windows, Adding Scrolling Messages, and Validating Forms 3 l Describe the math pow() method l Write a user-defined function to format output in currency format l Discuss For and While loops l Use the open() method to display another Web page in a pop-up window l Use the last. Modified property to display the date a Web page was last modified

4 Introduction Ø Introduction We will create a Web page that will allow Home Finders Nationwide Realty customers to calculate the amount of their monthly mortgage payment, based on the amount of mortgage, interest rate, and the number of years. We will learn 1. how to add a scrolling message, which will introduce them to the substring() method and the If statement. 2. how to use Java. Script to validate forms.

5 Introduction 3. If…Else statements, the parse. Int(), parse. Float(), and is. Na. N() built-in functions, as well as using the pow() method. 4. writing functions to calculate and display the resulting monthly payment amount using the currency format. 5. how to add a pop-up window to display information on using the mortgage payment calculator.

6 Introduction We all experienced using the Internet to purchase or searching something. Look for this web site homeadvisor. msn. com and other online lenders and realtors. Do you search for a house online? How do you feel about applying for loans online? What are the important issues?

Project Two — Home Finders Nationwide Realty We want to design a web page first loads a pop up windows to displays a message informing users of the new mortgage payment calculator. 7

Project Two — Home Finders Nationwide Realty The web page also includes a scrolling message that constantly displays to remind visitors of the current low mortgage rate. 8

Project Two — Home Finders Nationwide Realty The mortgage payment form allows users to calculate their monthly payment based on the amount of mortgage, interest rate, and years. 9

Project Two — Home Finders Nationwide Realty We will use functions to validate data, calculate monthly payment, and display the result in currency format. For the sense of up to date, we will have the last modification date displayed at the bottom of the page. 10

Project Two — Home Finders Nationwide Realty Data Validation Requirement: If the information inputted is not a number or not a valid form than we should use the alert message box to notify the user and position the insertion point in the appropriate text box. When all the entries are valid, the calculation function will be called to provide the monthly payment information. 11
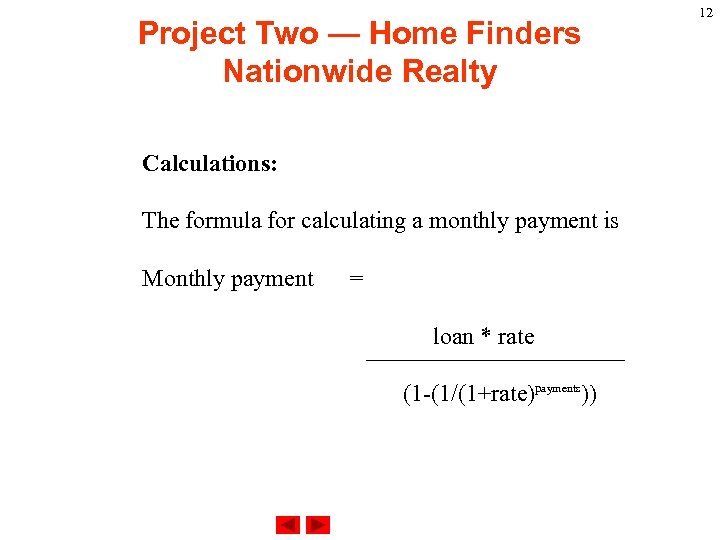
Project Two — Home Finders Nationwide Realty Calculations: The formula for calculating a monthly payment is Monthly payment = loan * rate (1 -(1/(1+rate)payments)) 12

Project Two — Home Finders Nationwide Realty Starting Notepad and opening the home. htm file 13

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page. Microsoft create marquee html tag <MARQUEE. . . > creates a scrolling display and is an MSIE extension and will probably never be supported by any other browser. The basic use of <MARQUEE. . . > is simple. Put most any kind of markup between <MARQUEE. . . > and </MARQUEE>. <MARQUEE> Hi There! <IMG SRC="graphics/idocs. gif" HEIGHT=33 WIDTH=82 ALT="Idocs Guide to HTML"> </MARQUEE> 14
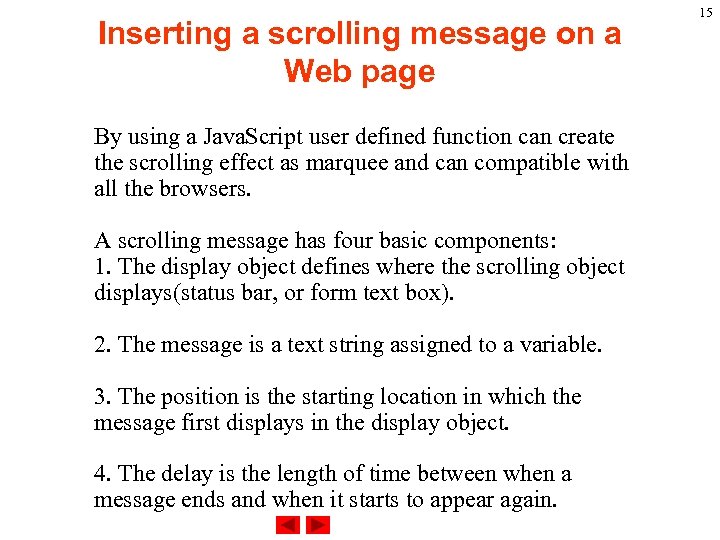
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page By using a Java. Script user defined function can create the scrolling effect as marquee and can compatible with all the browsers. A scrolling message has four basic components: 1. The display object defines where the scrolling object displays(status bar, or form text box). 2. The message is a text string assigned to a variable. 3. The position is the starting location in which the message first displays in the display object. 4. The delay is the length of time between when a message ends and when it starts to appear again. 15

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Using the form’s text box to create the scrolling effect. <FORM Name="msg. Form"> <INPUT Type="text" Name="scrolling. Msg" Size="23"> </FORM> Form: An HTML form is a section of a document containing normal content, markup, special elements called controls (checkboxes, radio buttons, menus, etc. ), and labels on those controls. Users generally "complete" a form by modifying its controls (entering text, selecting menu items, etc. ), before submitting the form to an agent for processing (e. g. , to a Web server, to a mail server, etc. ) 16

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Input(one of the form’s control types): We could create two types of controls that allow users to input text. The INPUT element creates a single-line input control and the TEXTAREA element creates a multi-line input control. Input tag’ Attribute definitions type = text This attribute specifies the type of control to create. The default value for this attribute is "text". name = name This attribute assigns the control name. 17

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page size = number This attribute tells the user agent the initial width of the control. The width is given in pixels except when type attribute has the value "text" or "password". In that case, its value refers to the (integer) number of characters. 18
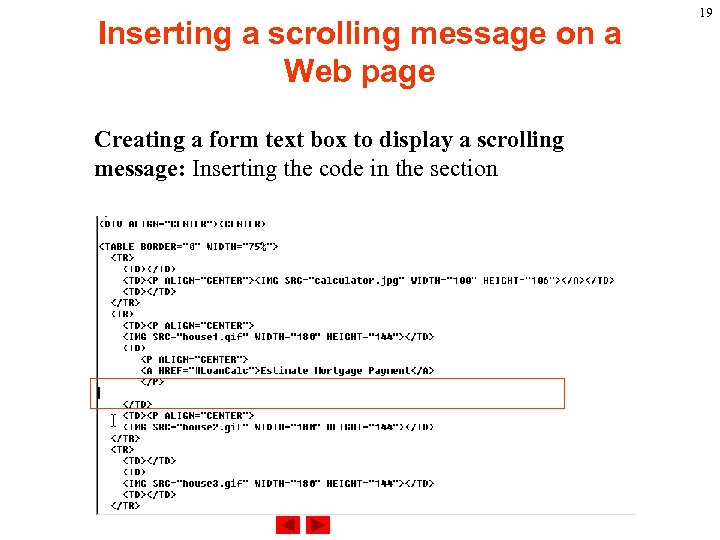
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Creating a form text box to display a scrolling message: Inserting the code in the section 19
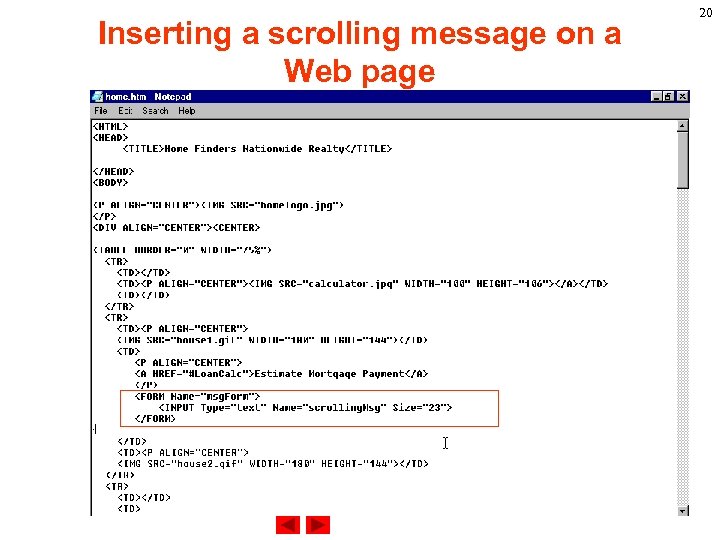
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page 20

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Creating a user-defined function for a scrolling message We will create function scrolling. Msg() to perform 1. Assign message. 2. Check the end of the message. 3. It assigns the next character in the message to the textbox. The function requires three variables: var scroll. Msg = "Mortgage rates are at their LOWEST!" var msg. Space = "--- ---" var begin. Pos = 0 21
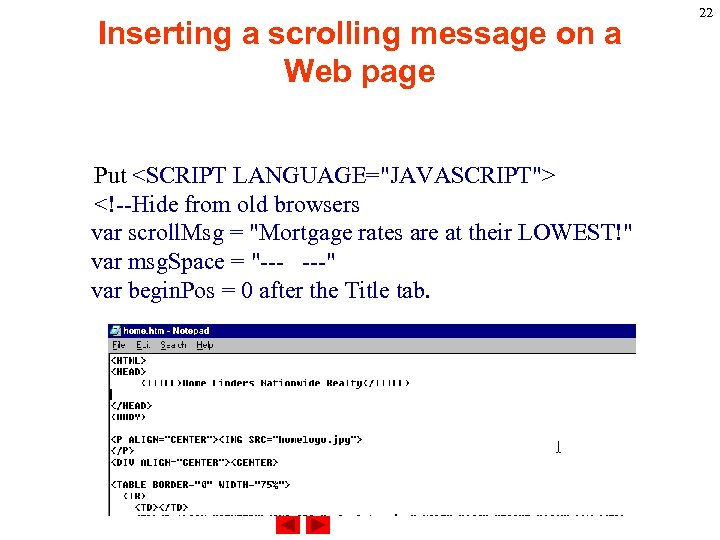
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Put <SCRIPT LANGUAGE="JAVASCRIPT"> <!--Hide from old browsers var scroll. Msg = "Mortgage rates are at their LOWEST!" var msg. Space = "--- ---" var begin. Pos = 0 after the Title tab. 22
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page 23

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Put the user define function, scrolling. Msg(), after the variable declaration. function scrolling. Msg() { document. msg. Form. scrolling. Msg. value = scroll. Msg. substring(begin. Pos, scroll. Msg. length)+msg. Spa ce+scroll. Msg. substring(0, begin. Pos) 24

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page The scroll. Msg and msg. Space are concatenated and assigned to the scrolling. Msg text box through the following statement document. msg. Form. scrolling. Msg. value = scroll. Msg. substring(begin. Pos, scroll. Msg. length)+msg. Spa ce+scroll. Msg. substring(0, begin. Pos) Mortgage rates are at their LOWEST! --- 25
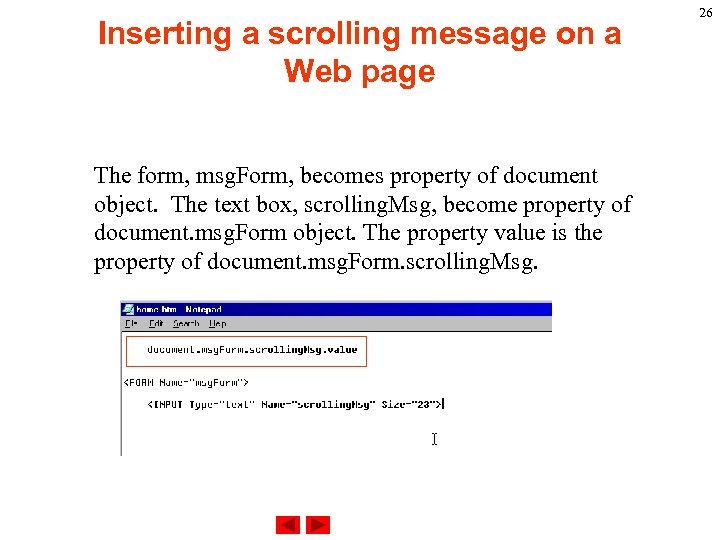
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page The form, msg. Form, becomes property of document object. The text box, scrolling. Msg, become property of document. msg. Form object. The property value is the property of document. msg. Form. scrolling. Msg. 26
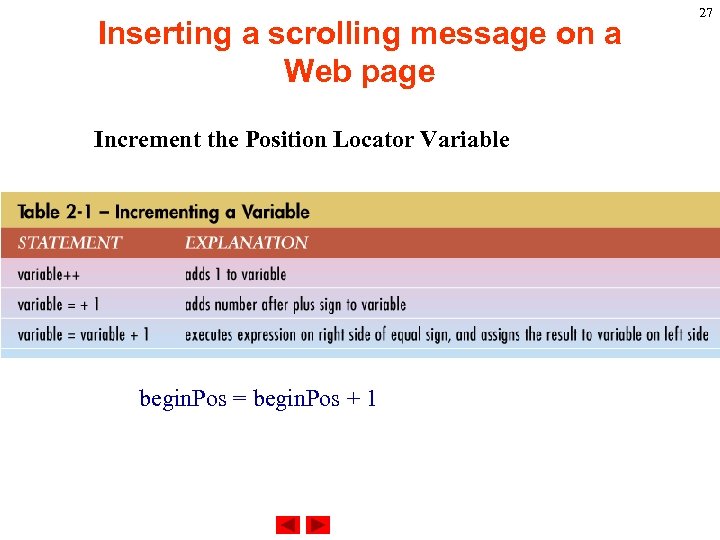
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Increment the Position Locator Variable begin. Pos = begin. Pos + 1 27

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Entering an If Statement 28

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page if (condition) { statements 1 } else { statements 2 } The condition can be any Java. Script expression that evaluates to true or false. The statements to be executed can be any Java. Script statements, including further nested if statements. If you want to use more than one statement after an if or else statement, you must enclose the statements in curly braces, {}. 29

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page 30
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page 31

Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page Example. In the following example, the function check. Data returns true if the number of characters in a Text object is three; otherwise, it displays an alert and returns false. function check. Data () { if (document. form 1. three. Char. value. length == 3) { return true } else { alert("Enter exactly three characters. “ + document. form 1. three. Char. value + " is not valid. ") return false } } 32

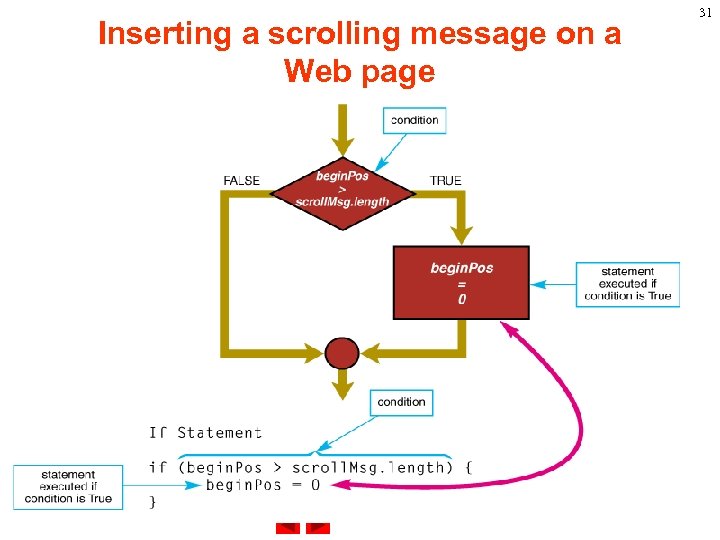
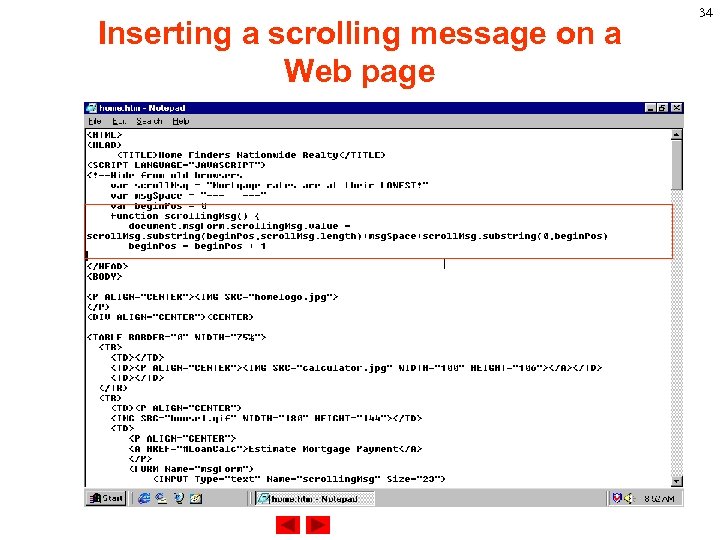
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page If the beginning position is greater than the message length then set the beginning position to zero. begin. Pos = begin. Pos + 1 if (begin. Pos > scroll. Msg. length) { begin. Pos = 0 } 33
Inserting a scrolling message on a Web page If the beginning position is greater than the message length then set the beginning position to zero. begin. Pos = begin. Pos + 1 if (begin. Pos > scroll. Msg. length) { begin. Pos = 0 } 34

Using the set. Timeout() Method to create a Recursive Function Call Recursion A programming method in which a routine calls itself. Recursion is an extremely powerful concept, but it can strain a computer's memory resources Using the set. Timeout function to call itself to create Scrolling Effect. window. set. Timeout("scrolling. Msg()", 200) 35

Using the set. Timeout() Method to create a Recursive Function Call 36

Using the set. Timeout() Method to create a Recursive Function Call Adding an Event Handler We will place an onload() even handler in the <Body> tag to create the scrolling message when the web page is load. 37

Using the set. Timeout() Method to create a Recursive Function Call 38

Using the set. Timeout() Method to create a Recursive Function Call Insert the following statement <BODY onload="scrolling. Msg()"> 39
Saving the HTML file and Testing the page 40
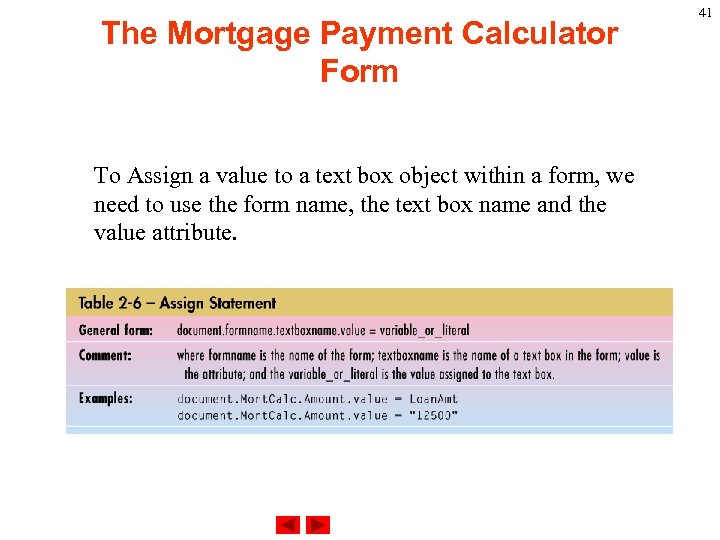
The Mortgage Payment Calculator Form To Assign a value to a text box object within a form, we need to use the form name, the text box name and the value attribute. 41

The Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Inserting an Event Handler in an Anchor Tag A link is a connection from one Web resource to another. Although a simple concept, the link has been one of the primary forces driving the success of the Web. A link has two ends -- called anchors -- and a direction. The link starts at the "source" anchor and points to the "destination" anchor, which may be any Web resource (e. g. , an image, a video clip, a sound bite, a program, an HTML document, an element within an HTML document, etc. ). 42

The Mortgage Payment Calculator Form An anchor name is the value of either the name or id attribute when used in the context of anchors. Anchor names must observe the following rules: Ø Uniqueness: Anchor names must be unique within a document. Anchor names that differ only in case may not appear in the same document. Ø String matching: Comparisons between fragment identifiers and anchor names must be done by exact (case -sensitive) match. 43

The Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Thus, the following example is correct with respect to string matching and must be considered a match by user agents: <P><A href="#xxx">. . . </A>. . . more document. . . <P> <A name="xxx">. . . </A> 44

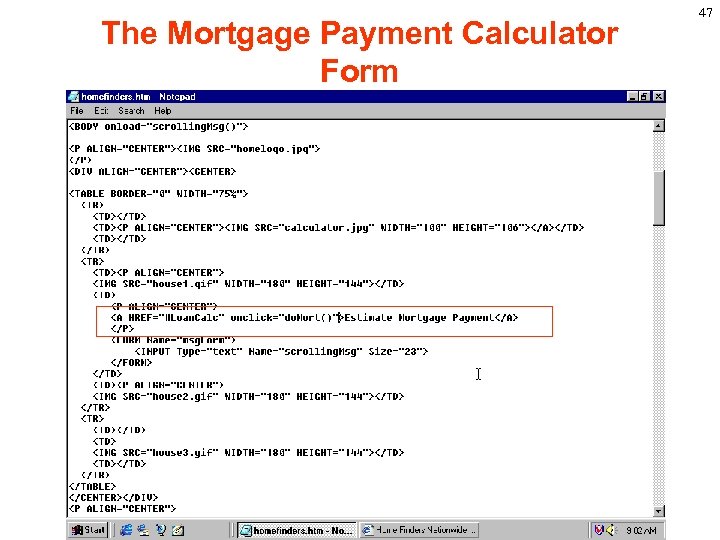
The Mortgage Payment Calculator Form We will use the onclick event handler within the <A> tag to triger a user defined function, do. Mort(). The do. Mort() function will clear the text box and place the insertion point in the Amount Mortgage box. In an Html file the following statement should match with each other. <A HREF="#Loan. Calc" onclick="do. Mort()">Estimate Mortgage Payment</A> <A NAME="Loan. Calc"></P> 45
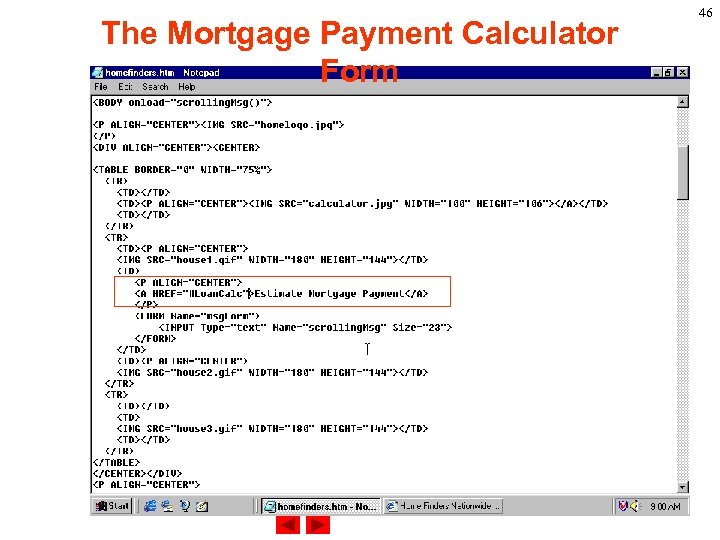
The Mortgage Payment Calculator Form 46
The Mortgage Payment Calculator Form 47

Writing the do. Mort() User-Defined Function We will use the onclick event handler within the <A> tag to triger a user defined function, do. Mort(). The do. Mort() function will clear the text box and place the insertion point in the Amount Mortgage box. In an Html file the following statement should match with each other. <A HREF="#Loan. Calc" onclick="do. Mort()">Estimate Mortgage Payment</A> <A NAME="Loan. Calc"></P> 48

Writing the do. Mort() User-Defined Function focus Method. Gives focus to the specified object. Syntax 1. file. Upload. Name. focus() 2. password. Name. focus() 3. select. Name. focus() 4. text. Name. focus() 5. textarea. Name. focus() 6. frame. Reference. focus() 7. window. Reference. focus() 49
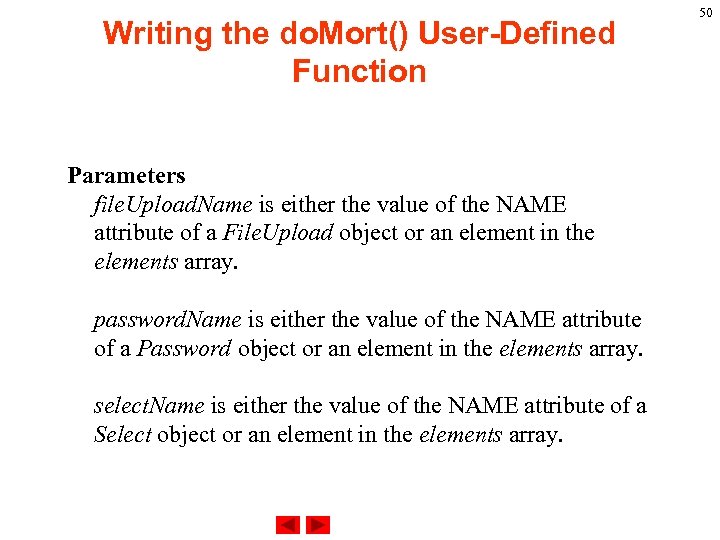
Writing the do. Mort() User-Defined Function Parameters file. Upload. Name is either the value of the NAME attribute of a File. Upload object or an element in the elements array. password. Name is either the value of the NAME attribute of a Password object or an element in the elements array. select. Name is either the value of the NAME attribute of a Select object or an element in the elements array. 50
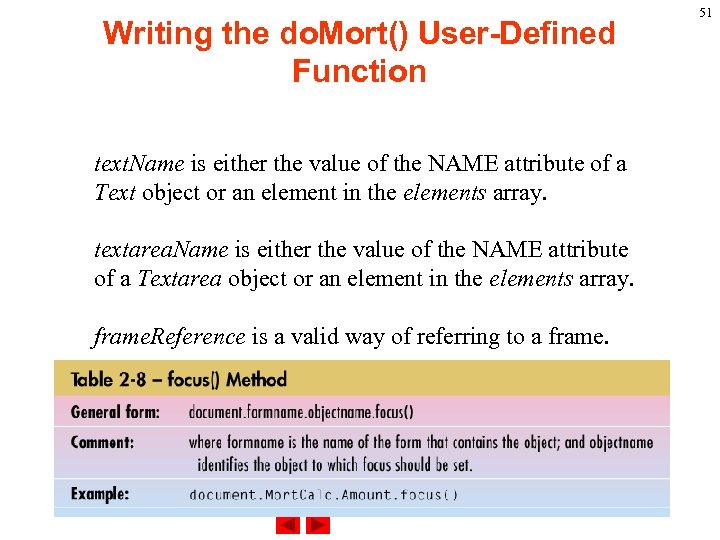
Writing the do. Mort() User-Defined Function text. Name is either the value of the NAME attribute of a Text object or an element in the elements array. textarea. Name is either the value of the NAME attribute of a Textarea object or an element in the elements array. frame. Reference is a valid way of referring to a frame. 51
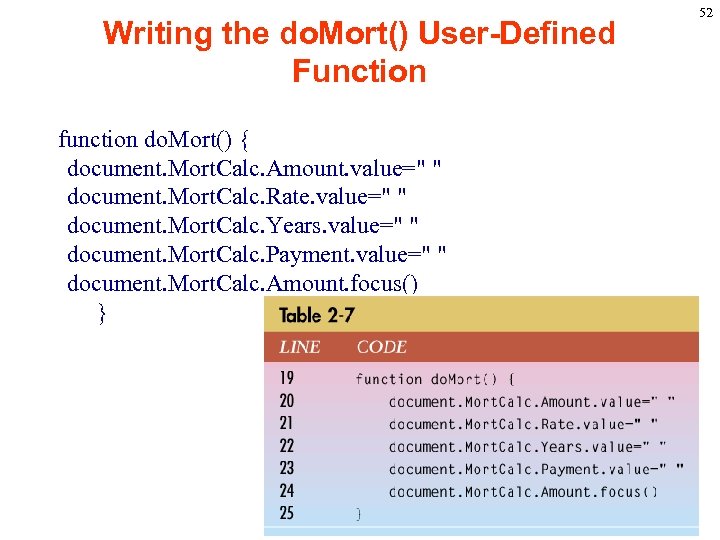
Writing the do. Mort() User-Defined Function function do. Mort() { document. Mort. Calc. Amount. value=" " document. Mort. Calc. Rate. value=" " document. Mort. Calc. Years. value=" " document. Mort. Calc. Payment. value=" " document. Mort. Calc. Amount. focus() } 52
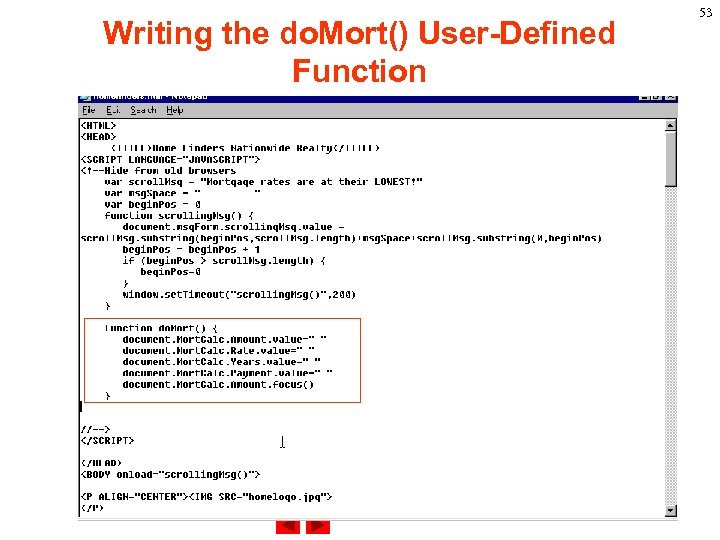
Writing the do. Mort() User-Defined Function 53
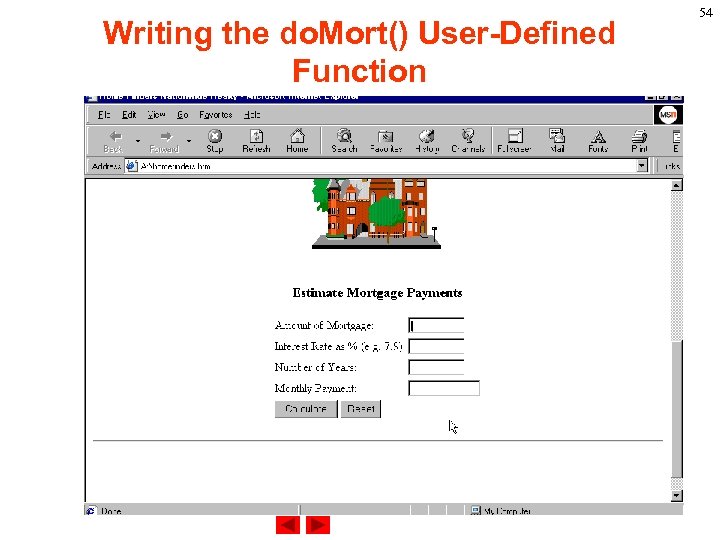
Writing the do. Mort() User-Defined Function 54
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form 55
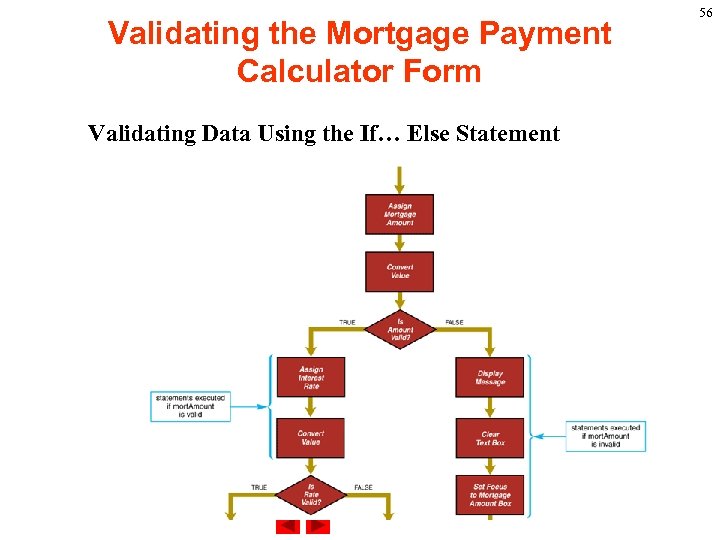
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Validating Data Using the If… Else Statement 56
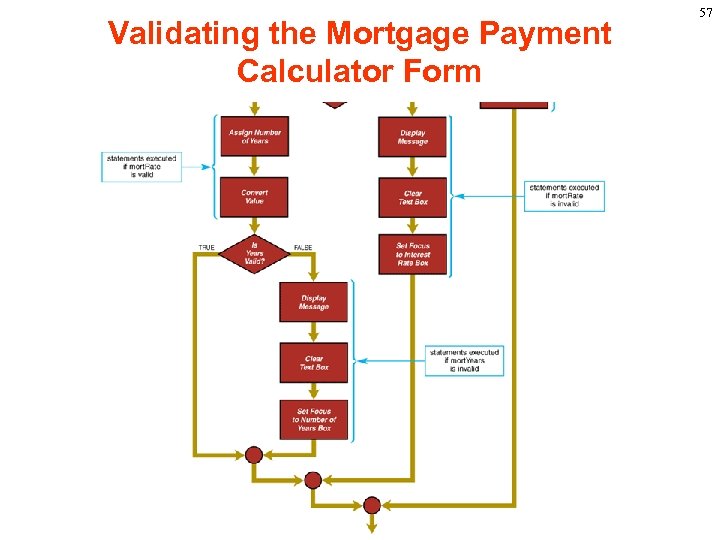
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form 57
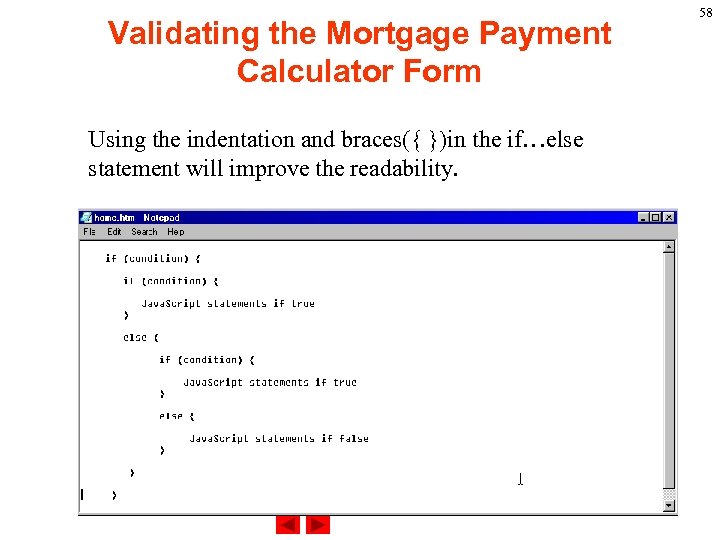
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Using the indentation and braces({ })in the if…else statement will improve the readability. 58
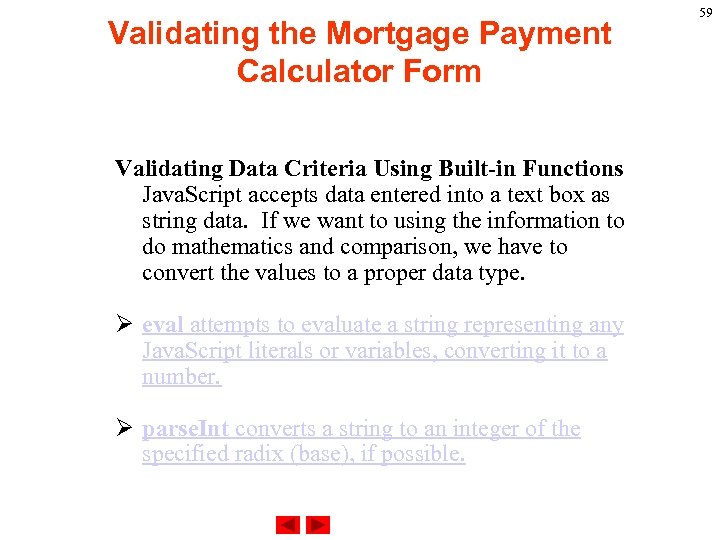
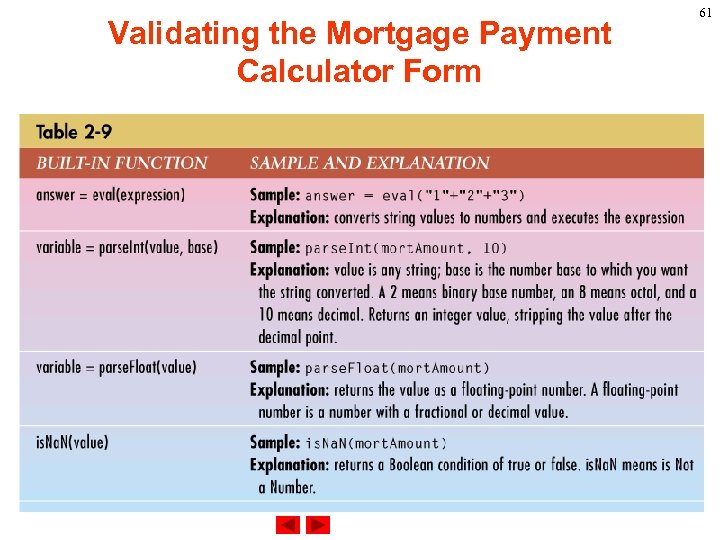
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Validating Data Criteria Using Built-in Functions Java. Script accepts data entered into a text box as string data. If we want to using the information to do mathematics and comparison, we have to convert the values to a proper data type. Ø eval attempts to evaluate a string representing any Java. Script literals or variables, converting it to a number. Ø parse. Int converts a string to an integer of the specified radix (base), if possible. 59

Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Ø parse. Float converts a string to a floating-point number, if possible. Ø The is. Na. N function evaluates an argument to determine if it is "Na. N" (not a number). 60
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form 61
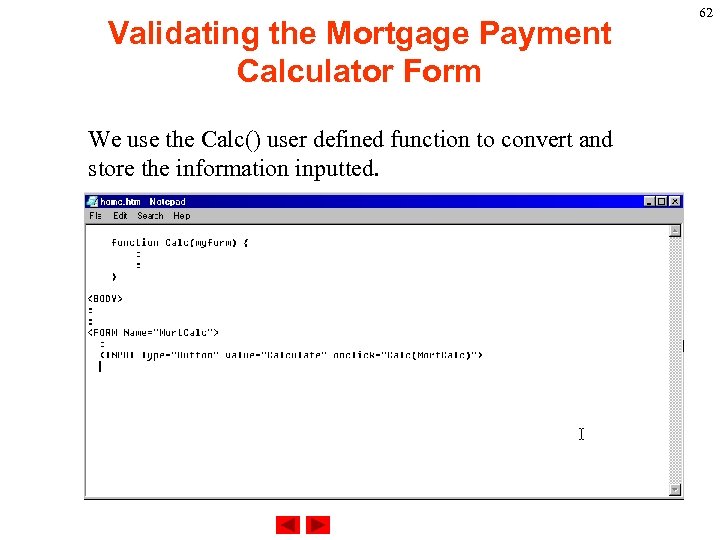
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form We use the Calc() user defined function to convert and store the information inputted. 62
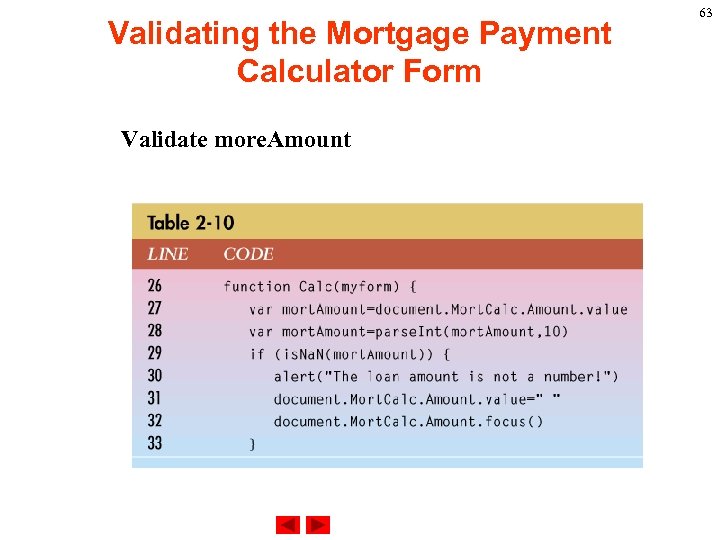
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Validate more. Amount 63
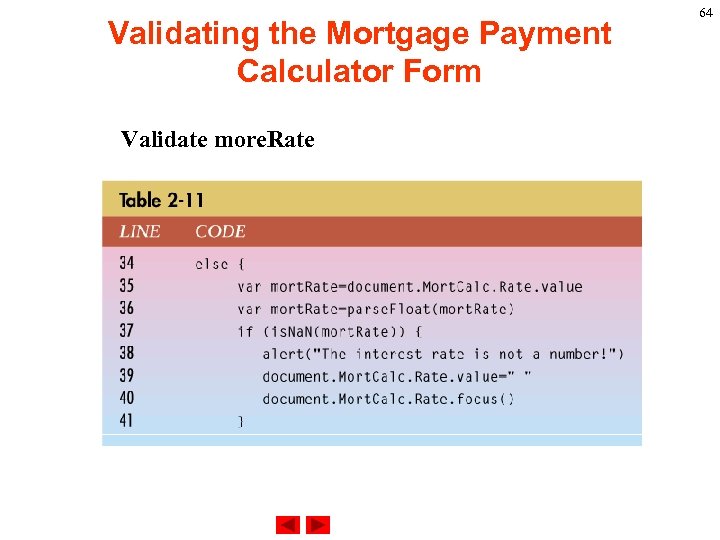
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Validate more. Rate 64
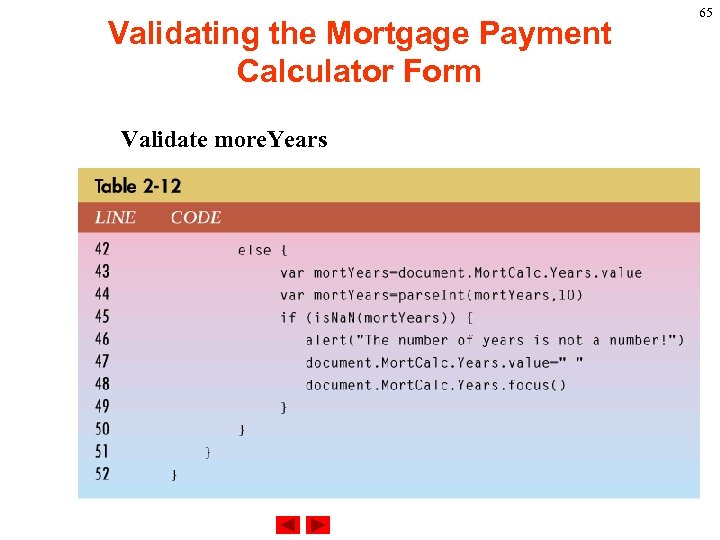
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Validate more. Years 65
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form 66
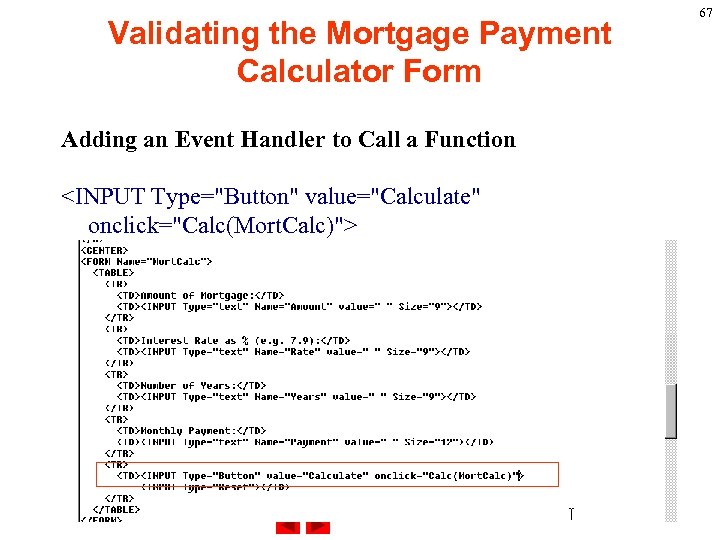
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Adding an Event Handler to Call a Function <INPUT Type="Button" value="Calculate" onclick="Calc(Mort. Calc)"> 67
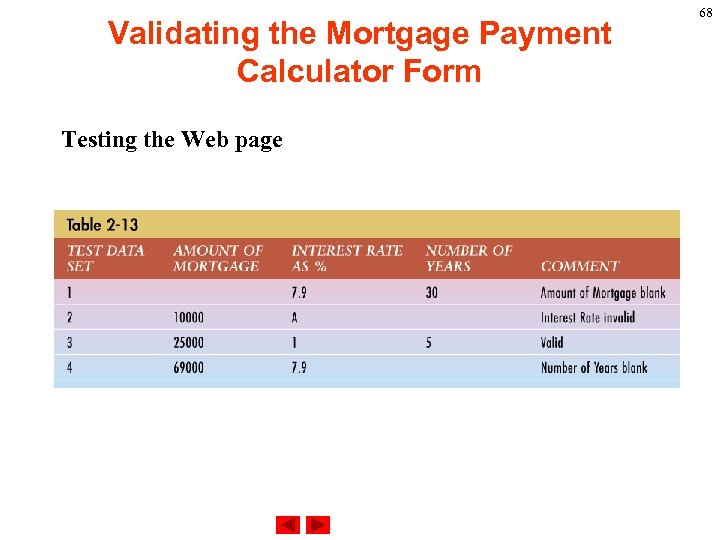
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form Testing the Web page 68
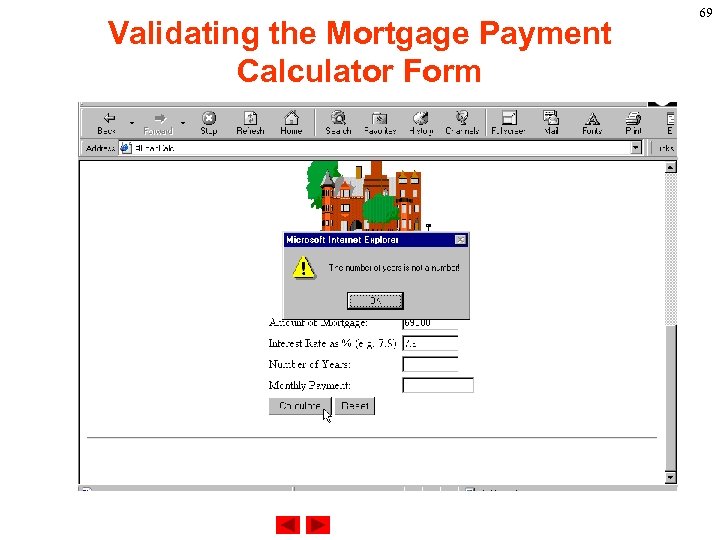
Validating the Mortgage Payment Calculator Form 69

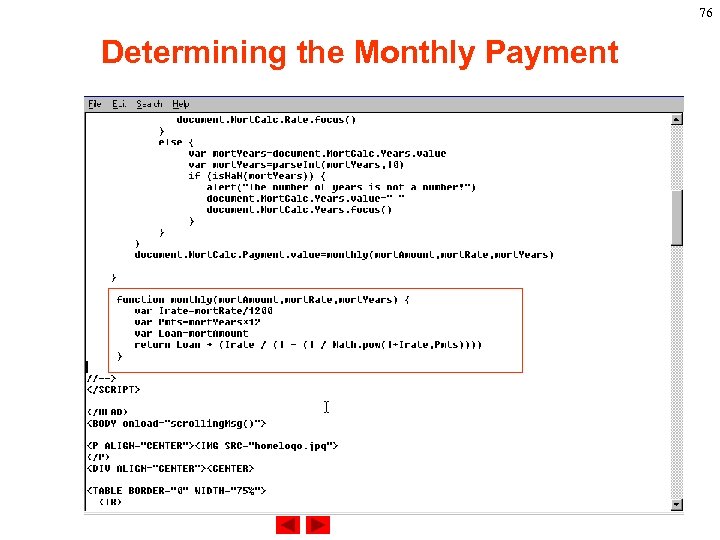
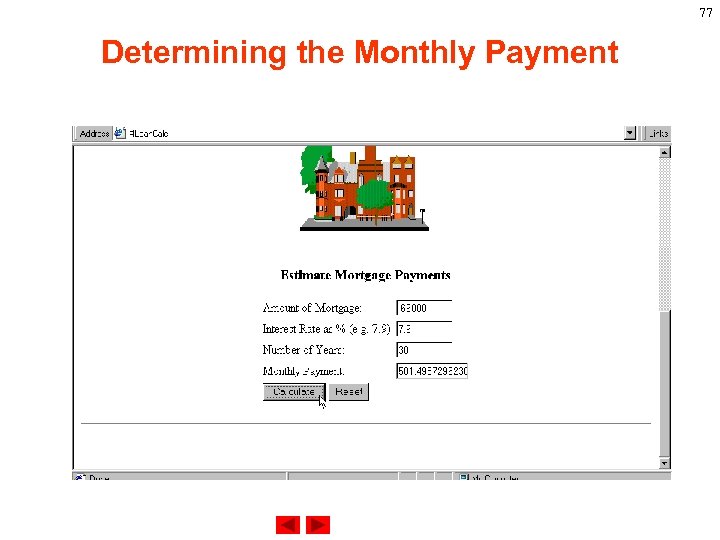
70 Determining the Monthly Payment After validating all the inputted information, we want to use the information to generate the monthly payment. We will define a function monthly() which pass in mort. Amount, mort. Rate, and mort. Years to the function and return a monthly payment. The return information will assignment to document. Mort. Calc. Payment. value. So, we will insert the following statement in the Calc() function. document. Mort. Calc. Payment. value=monthly(mort. Amou nt, mort. Rate, mort. Years)
71 Determining the Monthly Payment
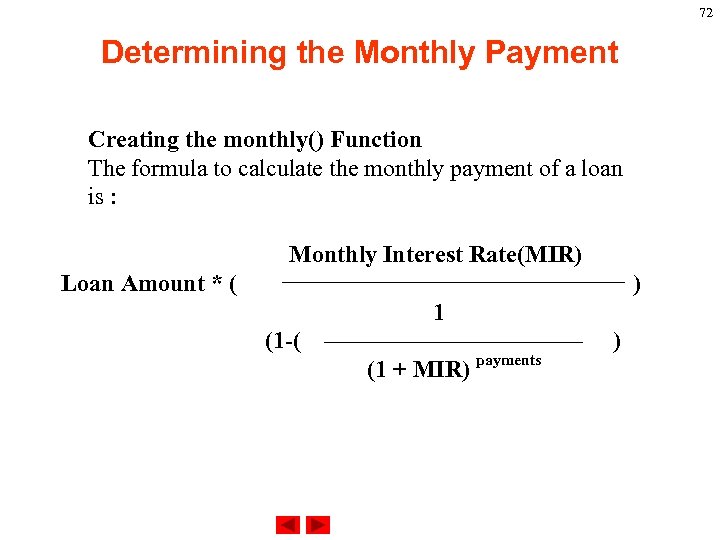
72 Determining the Monthly Payment Creating the monthly() Function The formula to calculate the monthly payment of a loan is : Monthly Interest Rate(MIR) Loan Amount * ( ) 1 (1 -( (1 + MIR) payments )
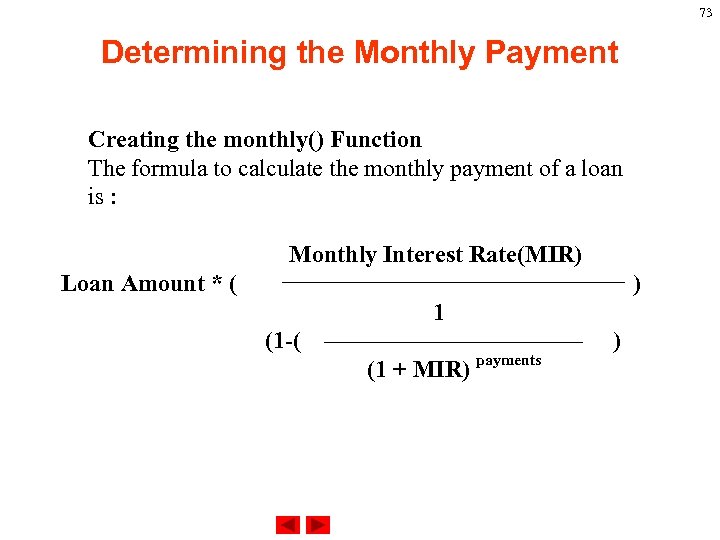
73 Determining the Monthly Payment Creating the monthly() Function The formula to calculate the monthly payment of a loan is : Monthly Interest Rate(MIR) Loan Amount * ( ) 1 (1 -( (1 + MIR) payments )
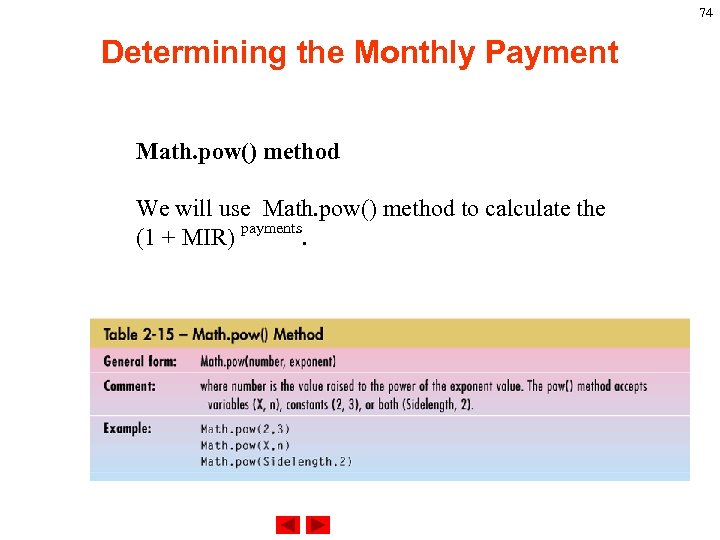
74 Determining the Monthly Payment Math. pow() method We will use Math. pow() method to calculate the payments (1 + MIR) .
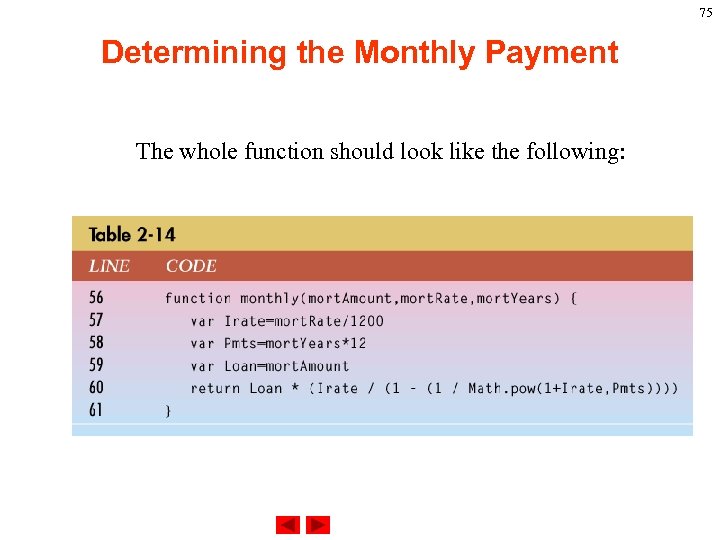
75 Determining the Monthly Payment The whole function should look like the following:
76 Determining the Monthly Payment
77 Determining the Monthly Payment

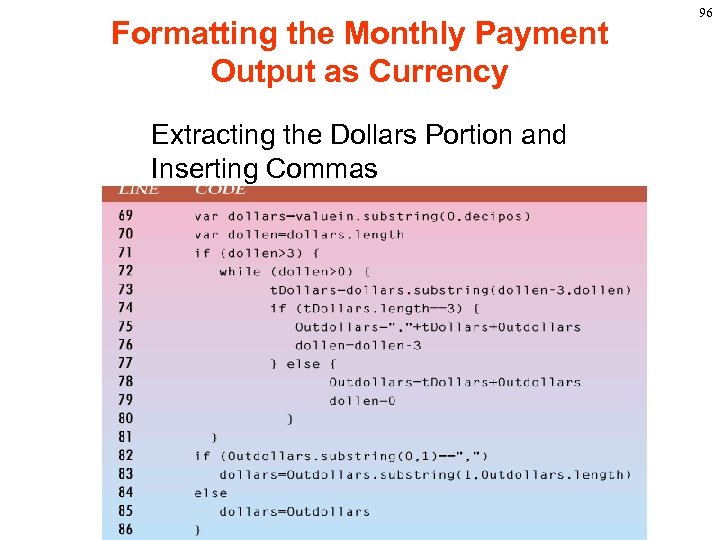
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency There are five steps we need to go through to format the currency: 1). Take the monthly payment dollar string value and separate the dollars from the cents based on the position of the decimal point. 2). Using the index. Of() method to determine the decimal point location. 3). Separate the value to dollar amount and cents amount by using the decimal point. 78

Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 4). Insert commas to the dollar amount for every three position. 5). Insert a dollar sign at the beginning of the string and concatenate it with the dollar amount, a decimal point and two digits of cents information and return the value. 79

Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency We put these steps into a function called dollar. Format(). This function need to pass in an argument, monthly payment amount, and will return a structured currency format. function dollar. Format(valuein) 80
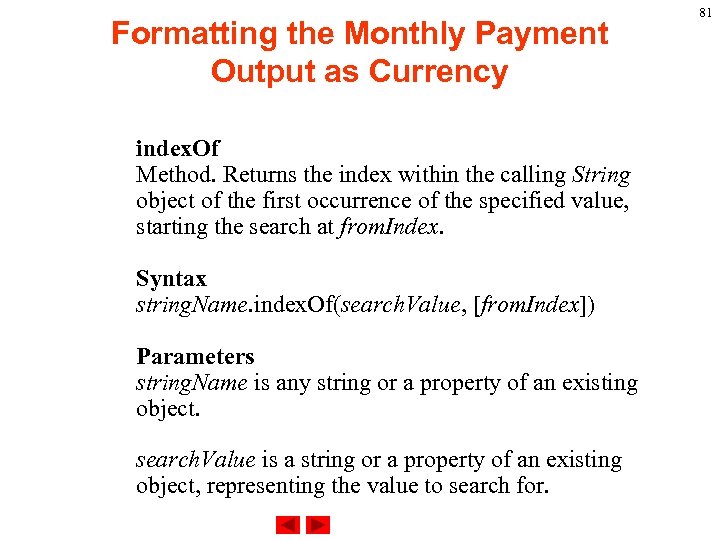
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency index. Of Method. Returns the index within the calling String object of the first occurrence of the specified value, starting the search at from. Index. Syntax string. Name. index. Of(search. Value, [from. Index]) Parameters string. Name is any string or a property of an existing object. search. Value is a string or a property of an existing object, representing the value to search for. 81
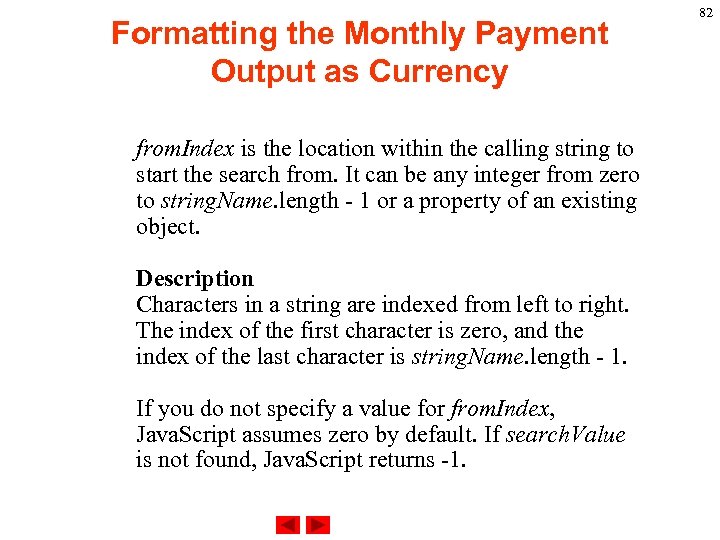
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency from. Index is the location within the calling string to start the search from. It can be any integer from zero to string. Name. length - 1 or a property of an existing object. Description Characters in a string are indexed from left to right. The index of the first character is zero, and the index of the last character is string. Name. length - 1. If you do not specify a value for from. Index, Java. Script assumes zero by default. If search. Value is not found, Java. Script returns -1. 82
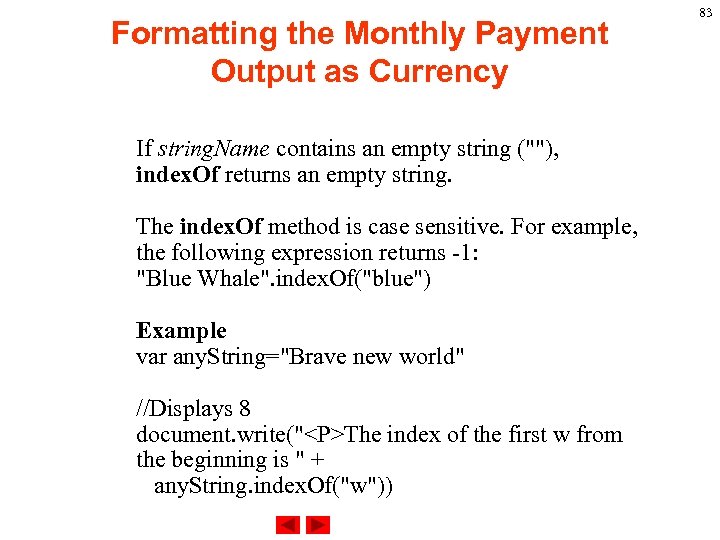
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency If string. Name contains an empty string (""), index. Of returns an empty string. The index. Of method is case sensitive. For example, the following expression returns -1: "Blue Whale". index. Of("blue") Example var any. String="Brave new world" //Displays 8 document. write("<P>The index of the first w from the beginning is " + any. String. index. Of("w")) 83
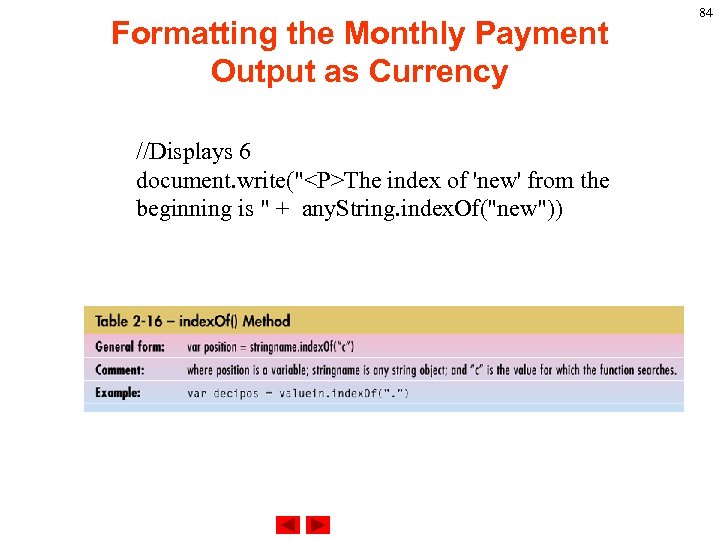
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency //Displays 6 document. write("<P>The index of 'new' from the beginning is " + any. String. index. Of("new")) 84
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 85
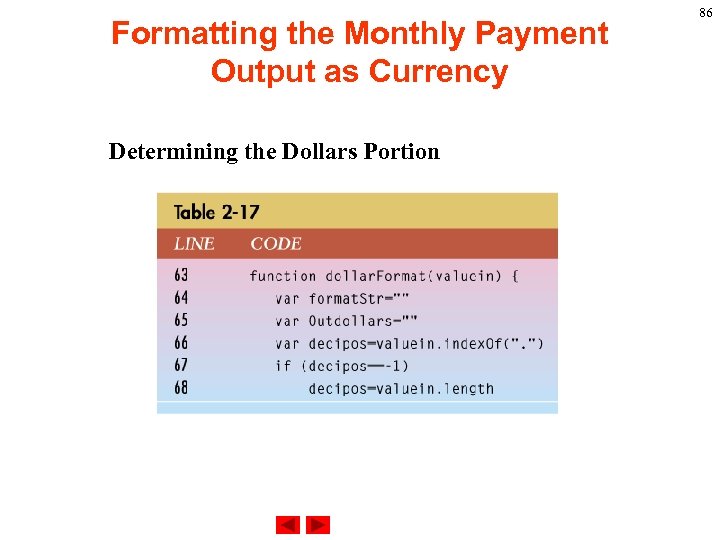
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Determining the Dollars Portion 86
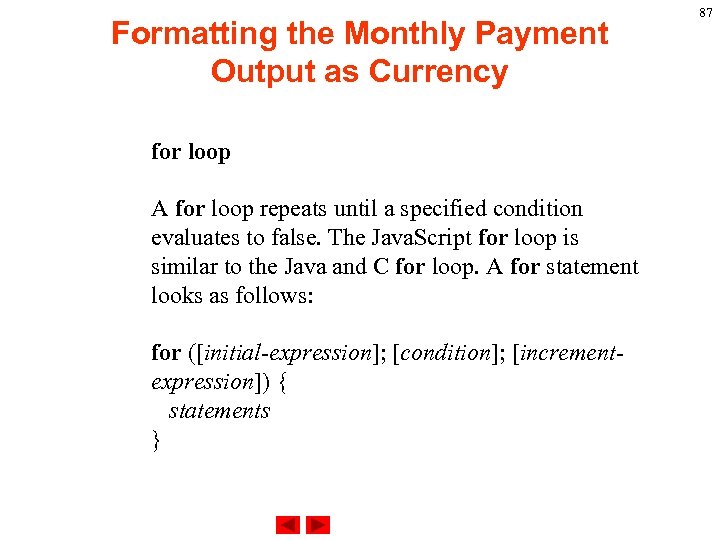
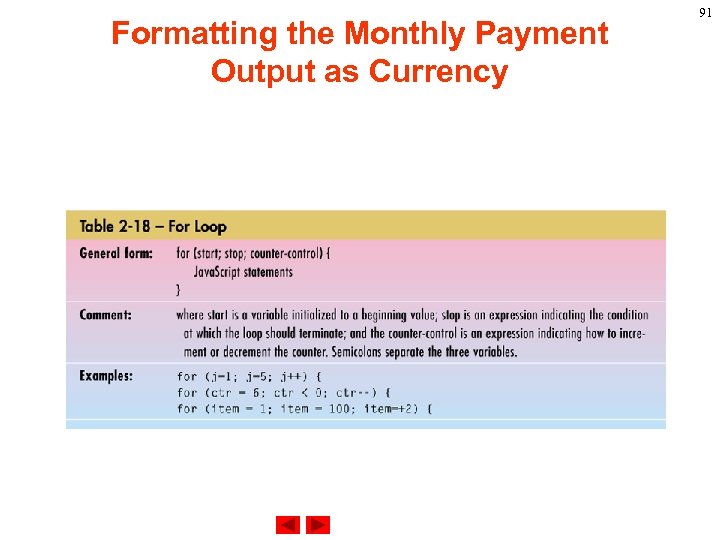
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency for loop A for loop repeats until a specified condition evaluates to false. The Java. Script for loop is similar to the Java and C for loop. A for statement looks as follows: for ([initial-expression]; [condition]; [incrementexpression]) { statements } 87

Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency When a for loop executes, the following occurs: 1. The initializing expression initial-expression, if any, is executed. This expression usually initializes one or more loop counters, but the syntax allows an expression of any degree of complexity. 2. The condition expression is evaluated. If the value of condition is true, the loop statements execute. If the value of condition is false, the for loop terminates. 88

Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 3. The update expression increment-expression executes. 4. The statements execute, and control returns to step 2. Example. The following function contains a for statement that counts the number of selected options in a scrolling list (a Select object that allows multiple selections). The for statement declares the variable i and initializes it to zero. 89
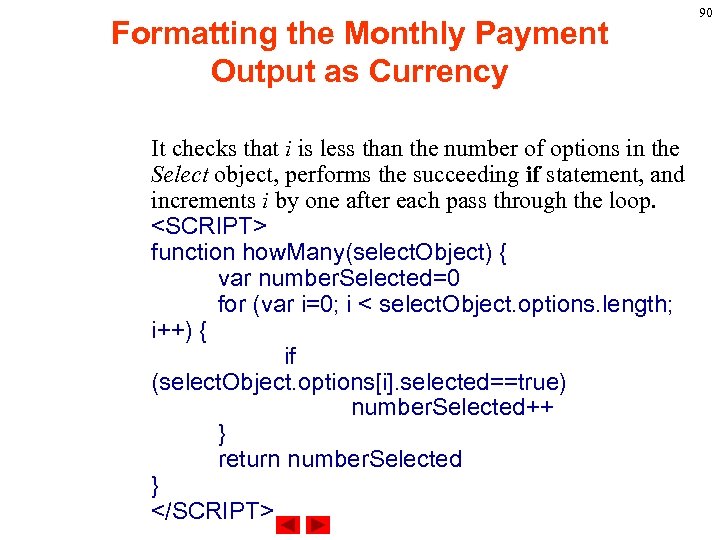
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency It checks that i is less than the number of options in the Select object, performs the succeeding if statement, and increments i by one after each pass through the loop. <SCRIPT> function how. Many(select. Object) { var number. Selected=0 for (var i=0; i < select. Object. options. length; i++) { if (select. Object. options[i]. selected==true) number. Selected++ } return number. Selected } </SCRIPT> 90
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 91
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 92
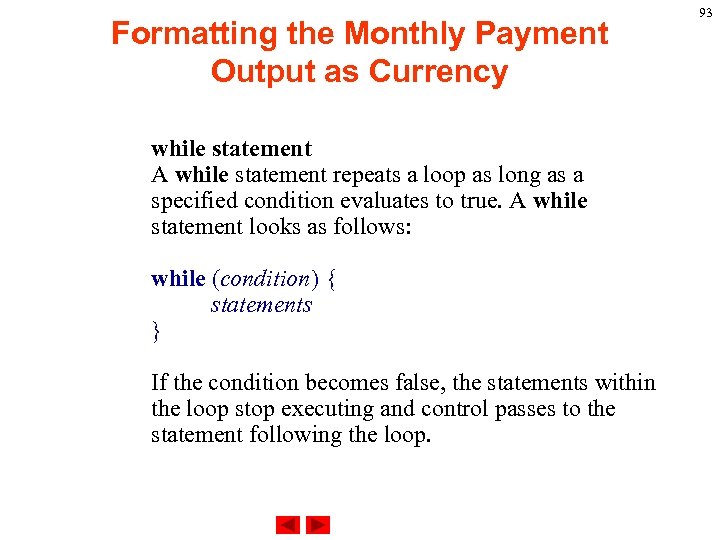
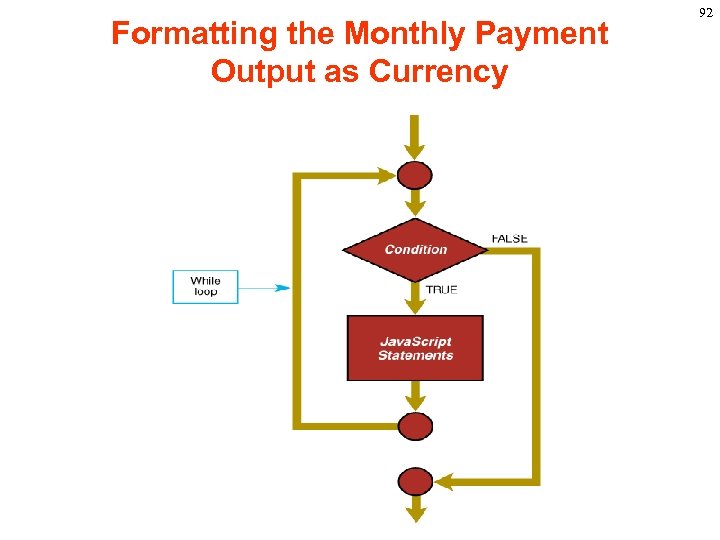
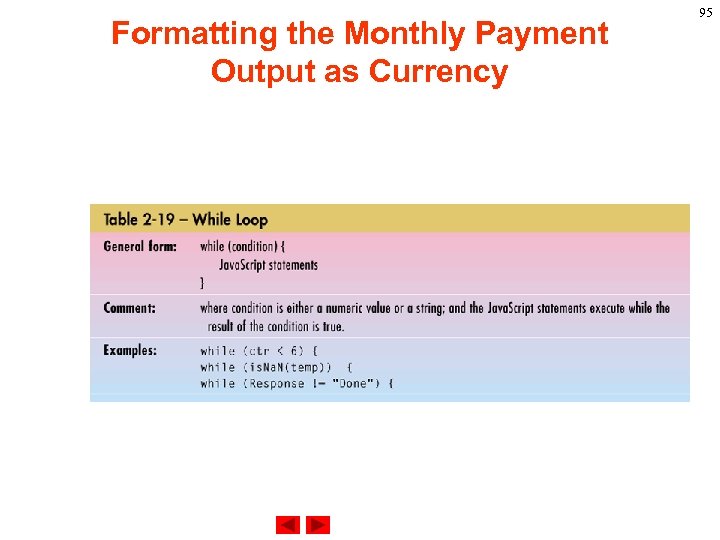
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency while statement A while statement repeats a loop as long as a specified condition evaluates to true. A while statement looks as follows: while (condition) { statements } If the condition becomes false, the statements within the loop stop executing and control passes to the statement following the loop. 93
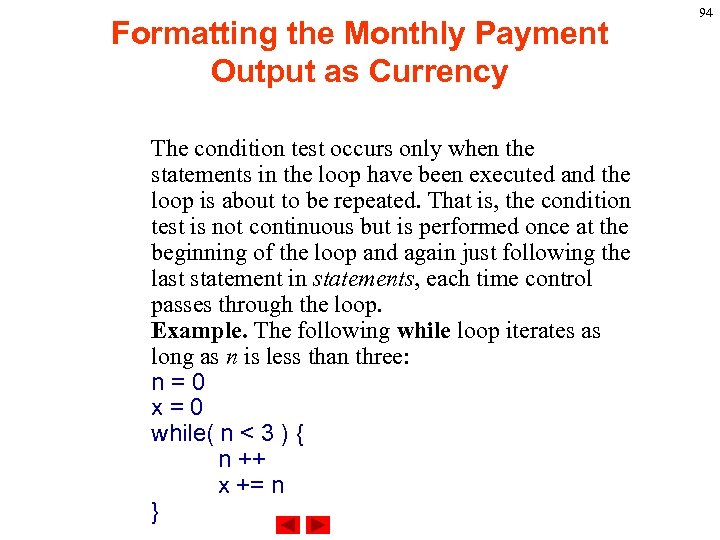
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency The condition test occurs only when the statements in the loop have been executed and the loop is about to be repeated. That is, the condition test is not continuous but is performed once at the beginning of the loop and again just following the last statement in statements, each time control passes through the loop. Example. The following while loop iterates as long as n is less than three: n=0 x=0 while( n < 3 ) { n ++ x += n } 94
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 95
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Extracting the Dollars Portion and Inserting Commas 96
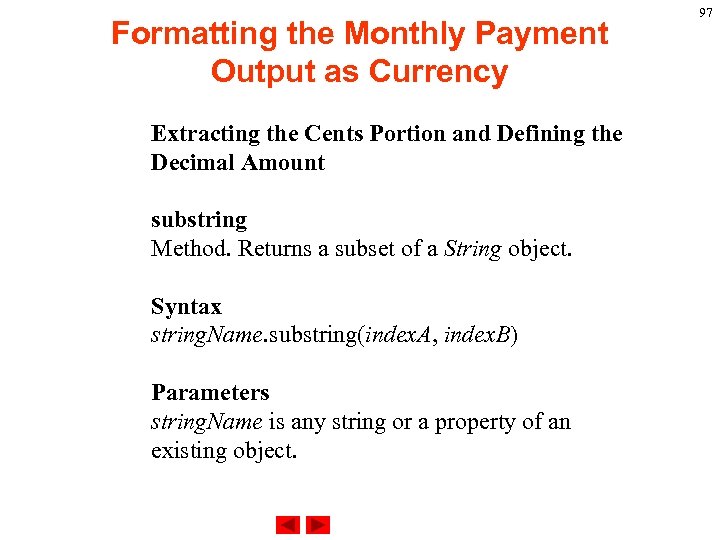
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Extracting the Cents Portion and Defining the Decimal Amount substring Method. Returns a subset of a String object. Syntax string. Name. substring(index. A, index. B) Parameters string. Name is any string or a property of an existing object. 97
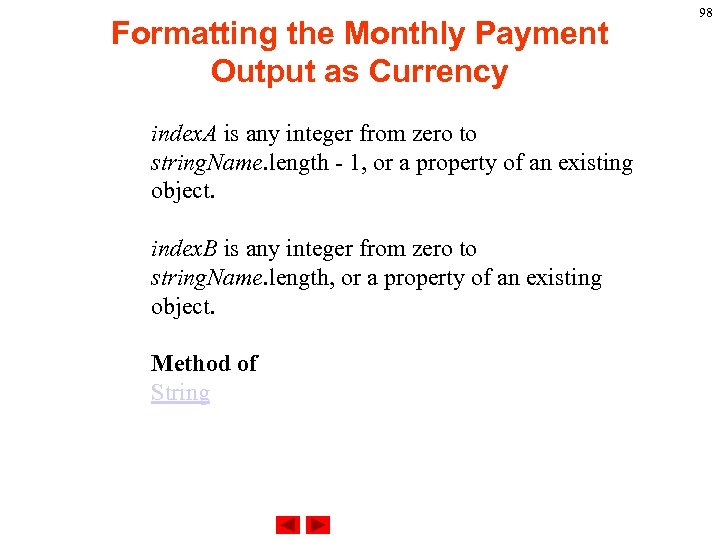
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency index. A is any integer from zero to string. Name. length - 1, or a property of an existing object. index. B is any integer from zero to string. Name. length, or a property of an existing object. Method of String 98
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Description Characters in a string are indexed from left to right. The index of the first character is zero, and the index of the last character is string. Name. length - 1. Ø If index. A is less than index. B, the substring method returns the subset starting with the character at index. A and ending with the character before index. B. Ø If index. A is greater than index. B, the substring method returns the subset starting with the character before index. B and ending with the character at index. A. Ø If index. A is equal to index. B, the substring method returns the empty string. 99
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Examples The following examples use substring to display characters from the string "Netscape": var any. String="Netscape" //Displays "Net" document. write(any. String. substring(0, 3)) document. write(any. String. substring(3, 0)) //Displays "cap" document. write(any. String. substring(4, 7)) document. write(any. String. substring(7, 4)) 100
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency //Displays "Netscap" document. write(any. String. substring(0, 7)) //Displays "Netscape" document. write(any. String. substring(0, 8)) document. write(any. String. substring(0, 10)) 101
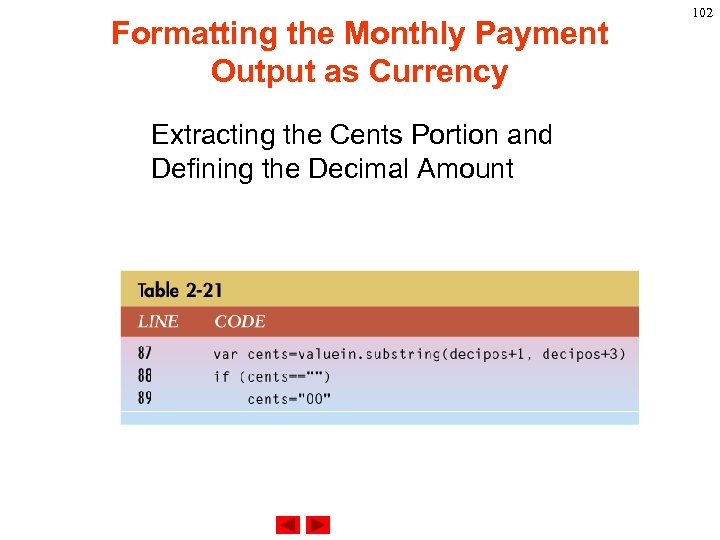
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Extracting the Cents Portion and Defining the Decimal Amount 102
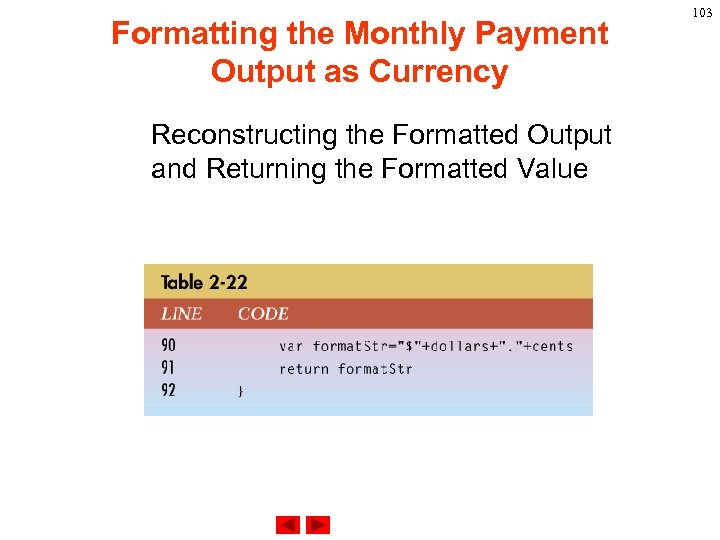
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Reconstructing the Formatted Output and Returning the Formatted Value 103
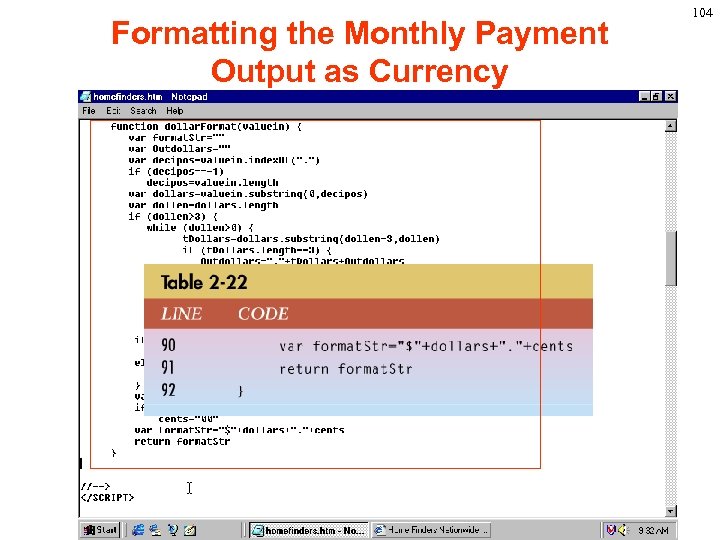
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 104
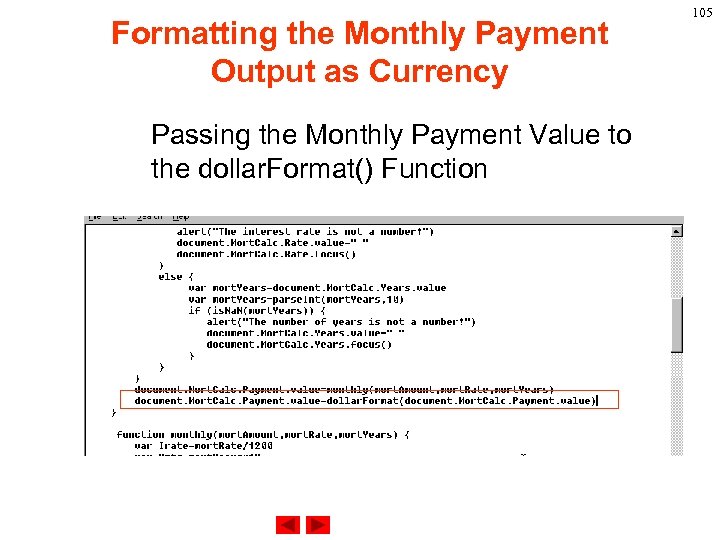
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency Passing the Monthly Payment Value to the dollar. Format() Function 105
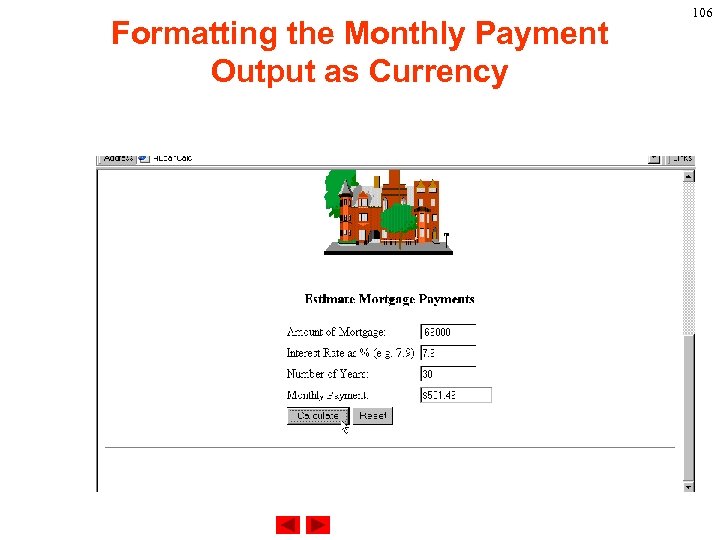
Formatting the Monthly Payment Output as Currency 106

107 Adding a Pop-up Window Except alert and confirm message boxes, we can use Java. Script (window object ‘s open())to open another HTML file to create a pop-up window.

108 Adding a Pop-up Window open()’s attributes.

109 Adding a Pop-up Window
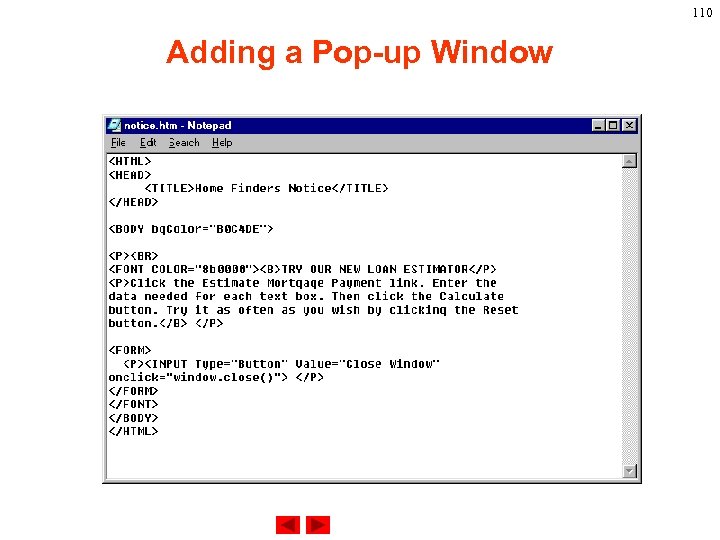
110 Adding a Pop-up Window

111 Adding a Pop-up Window Adding the Date Last Modified
5529893c6f8a93df728210a863fffdde.ppt