1 Chapter-I Macroeconomics 2 DefinitionofEconomics Lord









- Размер: 164 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 9
Описание презентации 1 Chapter-I Macroeconomics 2 DefinitionofEconomics Lord по слайдам
 1 Chapter-I Macroeconomics
1 Chapter-I Macroeconomics
 2 Definitionof. Economics Lord J. M Keynes, the defines economics as the “study of the administration of scarce resources and of the determinatio nof incomeandemployment. ” Benham defines economics as “a study of the factors affecting the size, distribution and stability of a country’s nationalincome. ” Divisionof. Economics Themoderneconomistsdividedeconomicsinto: Microeconomics, and Macroeconomics. 1. Microeconomics considers economy as units of smaller parts
2 Definitionof. Economics Lord J. M Keynes, the defines economics as the “study of the administration of scarce resources and of the determinatio nof incomeandemployment. ” Benham defines economics as “a study of the factors affecting the size, distribution and stability of a country’s nationalincome. ” Divisionof. Economics Themoderneconomistsdividedeconomicsinto: Microeconomics, and Macroeconomics. 1. Microeconomics considers economy as units of smaller parts
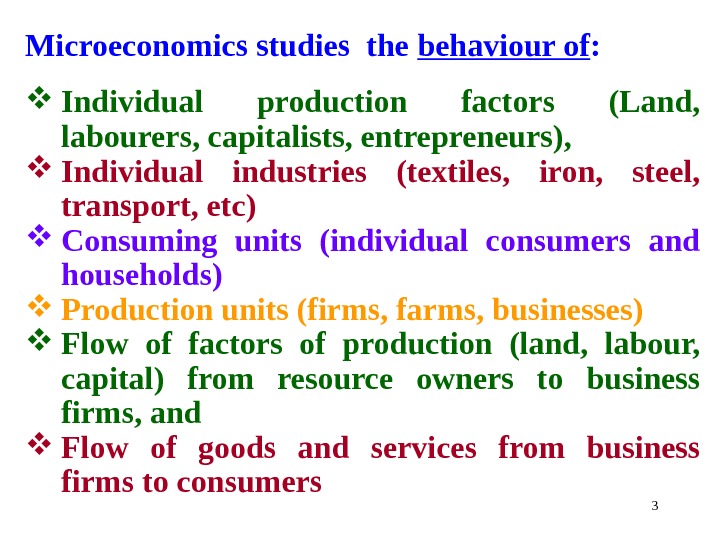
 3 Microeconomicsstudiesthe behaviourof : Individual production factors (Land, labourers, capitalists, entrepreneurs), Individual industries (textiles, iron, steel, transport, etc) Consuming units (individual consumers and households) Productionunits(firms, farms, businesses) Flow of factors of production (land, labour, capital) from resource owners to business firms, and Flow of goods and services from business firmstoconsumers
3 Microeconomicsstudiesthe behaviourof : Individual production factors (Land, labourers, capitalists, entrepreneurs), Individual industries (textiles, iron, steel, transport, etc) Consuming units (individual consumers and households) Productionunits(firms, farms, businesses) Flow of factors of production (land, labour, capital) from resource owners to business firms, and Flow of goods and services from business firmstoconsumers
 4 Macroeconomicsstudies : How NI , GDP , employment , demandandsupply , generallevelofprice , etc aredetermined Whatcauses fluctuation inthe. NI, GDP, employment, pricelevel How economiesgrow , and Howmaximum employment and income couldbe achieved? Developmentof. Macroeconomicstheorieshavebeendeveloped mainlyinthe Post-Keynesianperiod Itisfurtherdevelopedinthe last 70 yearsafterthe World. War. II
4 Macroeconomicsstudies : How NI , GDP , employment , demandandsupply , generallevelofprice , etc aredetermined Whatcauses fluctuation inthe. NI, GDP, employment, pricelevel How economiesgrow , and Howmaximum employment and income couldbe achieved? Developmentof. Macroeconomicstheorieshavebeendeveloped mainlyinthe Post-Keynesianperiod Itisfurtherdevelopedinthe last 70 yearsafterthe World. War. II
 52. 1 Functionof. Macroeconomics Followingsarethefunctionsmacroeconomics: It helps understanding the fluctuation of economic development Itprovidesa bird’seyeview ofthenationaleconomyand economicworld Microeconomicshelps formulatepolicies for growth and stability oftheeconomy It is helps to regulate aggregate employment and nationalincome Ithelps plan nationaleconomicgrowthrate Itisusefultoplan nationalwagepolicy Ithelpsunderstanding economyinitsdynamicaspect
52. 1 Functionof. Macroeconomics Followingsarethefunctionsmacroeconomics: It helps understanding the fluctuation of economic development Itprovidesa bird’seyeview ofthenationaleconomyand economicworld Microeconomicshelps formulatepolicies for growth and stability oftheeconomy It is helps to regulate aggregate employment and nationalincome Ithelps plan nationaleconomicgrowthrate Itisusefultoplan nationalwagepolicy Ithelpsunderstanding economyinitsdynamicaspect
 62. 2 Limitationof. Macroeconomics ignores the individual actors of the economy, however , individual welfare is themainaimofeconomics So, increasingnationalsavings atthe costof the individualwelfare cannotbewise Macroeconomics overlooks individual differences For example, the general price level may be stable, but price of food grains can ruin the poor
62. 2 Limitationof. Macroeconomics ignores the individual actors of the economy, however , individual welfare is themainaimofeconomics So, increasingnationalsavings atthe costof the individualwelfare cannotbewise Macroeconomics overlooks individual differences For example, the general price level may be stable, but price of food grains can ruin the poor
 74. Major. Economic. Challengesand. Problems Challenges Majoreconomicproblemsand bestpossibleuseofresources Ensure maximumsatisfactionforconsumers Maximumprofit forproducers
74. Major. Economic. Challengesand. Problems Challenges Majoreconomicproblemsand bestpossibleuseofresources Ensure maximumsatisfactionforconsumers Maximumprofit forproducers
 8 Problems Followingsaremajorproblemsare: Whatistoproduce? Howtoproduce? Forwhomtoproduce? Aretheresourceseconomicallyused? Howfullemploymentistoensure? How satisfactory efficiency of national economy could be achieved? Howsatisfactorygrowthcouldbeachieved?
8 Problems Followingsaremajorproblemsare: Whatistoproduce? Howtoproduce? Forwhomtoproduce? Aretheresourceseconomicallyused? Howfullemploymentistoensure? How satisfactory efficiency of national economy could be achieved? Howsatisfactorygrowthcouldbeachieved?
 9 Model Questions: Define macroeconomics. What are the objectives of macroeconomics? Describe the principal issues of economic analysis or what are problems and challenges of economic management? Do you support that state should intervene in the economic activities. Why?
9 Model Questions: Define macroeconomics. What are the objectives of macroeconomics? Describe the principal issues of economic analysis or what are problems and challenges of economic management? Do you support that state should intervene in the economic activities. Why?

