63276848bbc3cb12d96c5ad0ea3a4707.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 1 Assessing Learning Module 25
1 Assessing Learning Module 25
 2 Module 25 core objectives Be able to: 1 Demonstrate commitment to the concepts, content and policies of training within the Scout Association 2 Demonstrate acceptance of the Purpose, Principle and Method of the Scout Association 3 Undertake appropriate assessments and validations 4 Provide positive and constructive feedback 5 Identify any learning and development needs of the people you support 6 Plan to meet your own subject knowledge needs
2 Module 25 core objectives Be able to: 1 Demonstrate commitment to the concepts, content and policies of training within the Scout Association 2 Demonstrate acceptance of the Purpose, Principle and Method of the Scout Association 3 Undertake appropriate assessments and validations 4 Provide positive and constructive feedback 5 Identify any learning and development needs of the people you support 6 Plan to meet your own subject knowledge needs
 3 Training Adviser Role • Agrees Personal Learning Plan • Supports and encourages • Validates learning • Recommends Wood Badge – Subject to CTM approval Note the TA role is not about training delivery
3 Training Adviser Role • Agrees Personal Learning Plan • Supports and encourages • Validates learning • Recommends Wood Badge – Subject to CTM approval Note the TA role is not about training delivery
 4 Manager Role • Agrees and reviews role description • Ensures training is completed • Ensures appropriate permits are held • Understands process • Explain training commitment • Responsible for ongoing learning
4 Manager Role • Agrees and reviews role description • Ensures training is completed • Ensures appropriate permits are held • Understands process • Explain training commitment • Responsible for ongoing learning
 5 Nights Away Adviser Role • Supports and encourages through gaining permit • Assesses adults against 8 core skills • Assists in gaining required experience • Recommends appropriate Permit • Advises on camping and residential issues
5 Nights Away Adviser Role • Supports and encourages through gaining permit • Assesses adults against 8 core skills • Assists in gaining required experience • Recommends appropriate Permit • Advises on camping and residential issues
 6 Activity Assessor Role • Assesses technical competence • Recommends permits for specific adventurous activities
6 Activity Assessor Role • Assesses technical competence • Recommends permits for specific adventurous activities
 7 Scout Show Assessor Role • Assesses Scout Shows • Recommends national recognition
7 Scout Show Assessor Role • Assesses Scout Shows • Recommends national recognition
 8 Any Scouting assessor • Needs to understand Scouting fundamentals • Operate within Scouting’s: – – Policies Purpose Principles Methods
8 Any Scouting assessor • Needs to understand Scouting fundamentals • Operate within Scouting’s: – – Policies Purpose Principles Methods
 9 Policies Chapter 2 of POR • Equal opportunities • Safety • Anti-bullying • Child protection • Religious policy • Development
9 Policies Chapter 2 of POR • Equal opportunities • Safety • Anti-bullying • Child protection • Religious policy • Development
 10 Purpose “The purpose of Scouting is to contribute to the development of young people in achieving their full physical, intellectual, social and spiritual potentials, as individuals, as responsible citizens and as members of their local, national and international communities. ” POR
10 Purpose “The purpose of Scouting is to contribute to the development of young people in achieving their full physical, intellectual, social and spiritual potentials, as individuals, as responsible citizens and as members of their local, national and international communities. ” POR
 11 Principles Members of The Scout Association have a duty to: – their God, – other people – and themselves. Every member who makes the promise undertakes to do their best.
11 Principles Members of The Scout Association have a duty to: – their God, – other people – and themselves. Every member who makes the promise undertakes to do their best.
 12 Method People participate in Scouting by: • enjoying what they are doing; • learning by doing; • participating in varied and progressive activities; • making choices for themselves; • taking responsibility for their own actions; • working in groups; • taking increasing responsibility for others; • taking part in activities outdoors; • sharing in prayer and worship; • making and living out their Promise.
12 Method People participate in Scouting by: • enjoying what they are doing; • learning by doing; • participating in varied and progressive activities; • making choices for themselves; • taking responsibility for their own actions; • working in groups; • taking increasing responsibility for others; • taking part in activities outdoors; • sharing in prayer and worship; • making and living out their Promise.
 13 Evidence • • • Demonstration Discussion Workbook Questionnaire External qualification Working documents Project Witness statement Video
13 Evidence • • • Demonstration Discussion Workbook Questionnaire External qualification Working documents Project Witness statement Video
 14 Feedback • Constructive • Positive • Consider: – – – Venue Body language Position Tone Language • Give concrete areas to work on
14 Feedback • Constructive • Positive • Consider: – – – Venue Body language Position Tone Language • Give concrete areas to work on
 15 Communication Theory Decoding Encoding Message Feedback • Communication • “The transmission of information so that the recipient understands clearly what the sender intends”
15 Communication Theory Decoding Encoding Message Feedback • Communication • “The transmission of information so that the recipient understands clearly what the sender intends”
 16 Problems in verbal communication – Not paying attention – Listening but not hearing – Thinking about what to say next – Interrupting – Hearing what one expects – Being defensive – Looking for disagreement
16 Problems in verbal communication – Not paying attention – Listening but not hearing – Thinking about what to say next – Interrupting – Hearing what one expects – Being defensive – Looking for disagreement
 17 Facts – We listen at 125 -250 wpm, we think at 10003000 wpm – 75% of the time we are distracted, preoccupied or forgetful – 20% of the time, we remember what we hear – More than 35% of businesses think listening is a top skill for success
17 Facts – We listen at 125 -250 wpm, we think at 10003000 wpm – 75% of the time we are distracted, preoccupied or forgetful – 20% of the time, we remember what we hear – More than 35% of businesses think listening is a top skill for success
 18 Active listening § Avoid distractions § Don’t pre-conceive § Pay attention to the speaker § Don’t interrupt Show your interest to the speaker § Concentrate on what is being said
18 Active listening § Avoid distractions § Don’t pre-conceive § Pay attention to the speaker § Don’t interrupt Show your interest to the speaker § Concentrate on what is being said
 19 Active listening § Listen for the whole message § Hear message before evaluating § Ask open questions to check understanding Check understanding § Repeat back in your own words to convey understanding
19 Active listening § Listen for the whole message § Hear message before evaluating § Ask open questions to check understanding Check understanding § Repeat back in your own words to convey understanding
 20 Questioning Open questions Focus Closed questions Understanding
20 Questioning Open questions Focus Closed questions Understanding
 21 Active listening Do I understand what they think they said ?
21 Active listening Do I understand what they think they said ?
 22 Communication Do we get the ratio right? One mouth Two ears
22 Communication Do we get the ratio right? One mouth Two ears
 23 Active listening • Allows you to make sure you hear the words • and … • understand the meaning behind the words
23 Active listening • Allows you to make sure you hear the words • and … • understand the meaning behind the words
 24 Questioning & Listening Process • Open ended questions: – What, how, who, where, why, when Listen for vagueness or significant remarks Probing questions Summary to check understanding Silence is a useful technique
24 Questioning & Listening Process • Open ended questions: – What, how, who, where, why, when Listen for vagueness or significant remarks Probing questions Summary to check understanding Silence is a useful technique
 25 Questioning Avoid if possible – Interruptions – Multiple questions – Leading questions – Biased questions – Ambiguous questions
25 Questioning Avoid if possible – Interruptions – Multiple questions – Leading questions – Biased questions – Ambiguous questions
 26 Active listening Do I understand what they think they said ?
26 Active listening Do I understand what they think they said ?
 27 Active listening – Avoid distractions – Don’t pre-conceive – Pay attention to the speaker – Concentrate on what is being said – Don’t interrupt – Listen for the whole message Show your interest to the speaker – Hear message before evaluating – Ask open questions to check understanding – Repeat back in your own words to convey understanding
27 Active listening – Avoid distractions – Don’t pre-conceive – Pay attention to the speaker – Concentrate on what is being said – Don’t interrupt – Listen for the whole message Show your interest to the speaker – Hear message before evaluating – Ask open questions to check understanding – Repeat back in your own words to convey understanding
 28 Module 25 core objectives Be able to: 1 Demonstrate commitment to the concepts, content and policies of training within the Scout Association 2 Demonstrate acceptance of the Purpose, Principle and Method of the Scout Association 3 Undertake appropriate assessments and validations 4 Provide positive and constructive feedback 5 Identify any learning and development needs of the people you support 6 Plan to meet your own subject knowledge needs
28 Module 25 core objectives Be able to: 1 Demonstrate commitment to the concepts, content and policies of training within the Scout Association 2 Demonstrate acceptance of the Purpose, Principle and Method of the Scout Association 3 Undertake appropriate assessments and validations 4 Provide positive and constructive feedback 5 Identify any learning and development needs of the people you support 6 Plan to meet your own subject knowledge needs
 29 Training Advisers / Managers
29 Training Advisers / Managers
 30 Training scheme principles • Considers needs of learner • Modular • Flexibility • Accessible • Recognises prior learning • LOVE • Uses Scout methods • National scheme • OCN and ILM recognition
30 Training scheme principles • Considers needs of learner • Modular • Flexibility • Accessible • Recognises prior learning • LOVE • Uses Scout methods • National scheme • OCN and ILM recognition
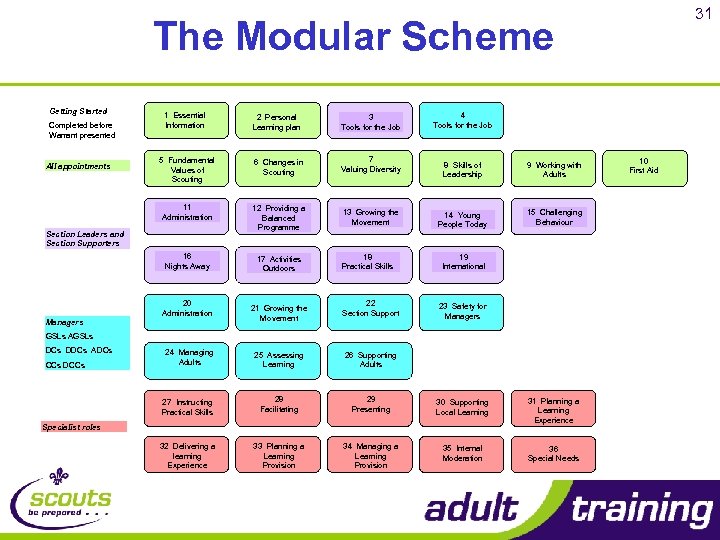 31 The Modular Scheme Getting Started 2 Personal Learning plan 3 Tools for the Job 5 Fundamental Values of Scouting 6 Changes in Scouting 7 Valuing Diversity 12 Providing a Balanced Programme 13 Growing the Movement 16 Nights Away All appointments 1 Essential Information 11 Administration Completed before Warrant presented 17 Activities Outdoors Section Leaders and Section Supporters Managers 20 Administration 21 Growing the Movement 18 Practical Skills 22 Section Support 4 Tools for the Job 8 Skills of Leadership 9 Working with Adults 14 Young People Today 15 Challenging Behaviour 19 International 23 Safety for Managers GSLs AGSLs DCs DDCs ADCs 24 Managing Adults 25 Assessing Learning 26 Supporting Adults 27 Instructing Practical Skills CCs DCCs 28 Facilitating 29 Presenting 30 Supporting Local Learning 31 Planning a Learning Experience 32 Delivering a learning Experience 33 Planning a Learning Provision 34 Managing a Learning Provision 35 Internal Moderation 36 Special Needs Specialist roles 10 First Aid
31 The Modular Scheme Getting Started 2 Personal Learning plan 3 Tools for the Job 5 Fundamental Values of Scouting 6 Changes in Scouting 7 Valuing Diversity 12 Providing a Balanced Programme 13 Growing the Movement 16 Nights Away All appointments 1 Essential Information 11 Administration Completed before Warrant presented 17 Activities Outdoors Section Leaders and Section Supporters Managers 20 Administration 21 Growing the Movement 18 Practical Skills 22 Section Support 4 Tools for the Job 8 Skills of Leadership 9 Working with Adults 14 Young People Today 15 Challenging Behaviour 19 International 23 Safety for Managers GSLs AGSLs DCs DDCs ADCs 24 Managing Adults 25 Assessing Learning 26 Supporting Adults 27 Instructing Practical Skills CCs DCCs 28 Facilitating 29 Presenting 30 Supporting Local Learning 31 Planning a Learning Experience 32 Delivering a learning Experience 33 Planning a Learning Provision 34 Managing a Learning Provision 35 Internal Moderation 36 Special Needs Specialist roles 10 First Aid
 32 Appointment process Before warrant: • Agree job spec • Complete getting started – Tools for the job – Essential information • Produce agreed Personal Learning Plan • Meet Appointment sub-Committee
32 Appointment process Before warrant: • Agree job spec • Complete getting started – Tools for the job – Essential information • Produce agreed Personal Learning Plan • Meet Appointment sub-Committee
 33 Stage 1 AA & CRB Adult GSL AA Segment B & CRB Appts Sec HQ
33 Stage 1 AA & CRB Adult GSL AA Segment B & CRB Appts Sec HQ
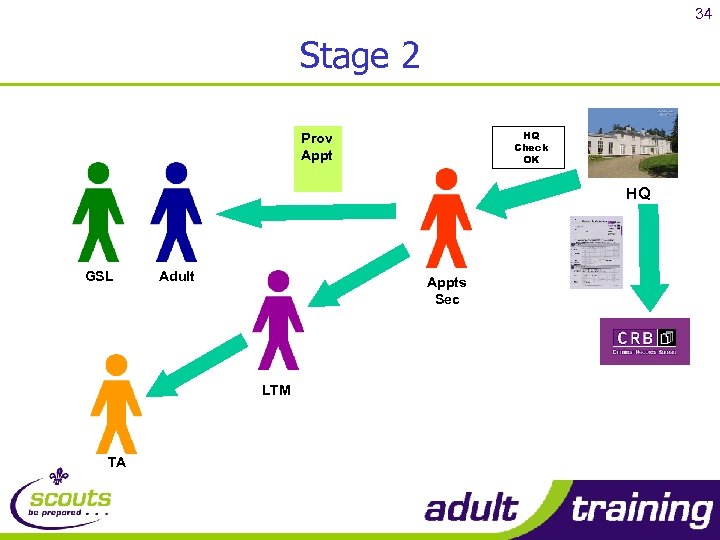 34 Stage 2 HQ Check OK Prov Appt HQ GSL Adult Appts Sec LTM TA
34 Stage 2 HQ Check OK Prov Appt HQ GSL Adult Appts Sec LTM TA
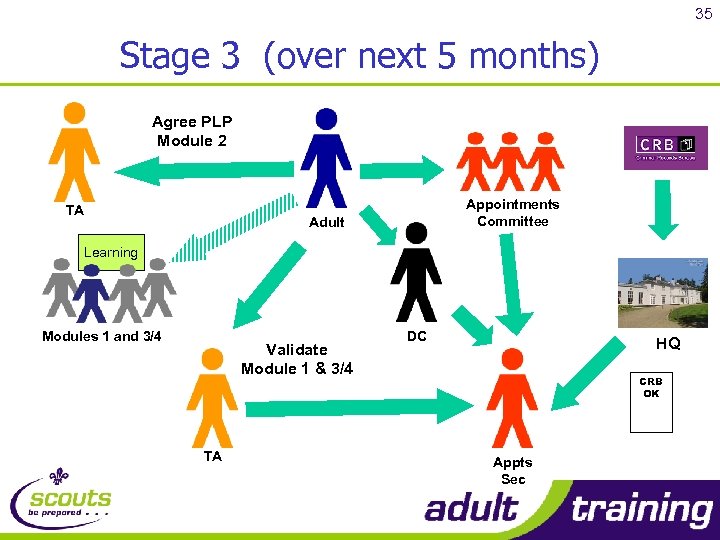 35 Stage 3 (over next 5 months) Agree PLP Module 2 TA Appointments Committee Adult Learning Modules 1 and 3/4 Validate Module 1 & 3/4 TA DC HQ CRB OK Appts Sec
35 Stage 3 (over next 5 months) Agree PLP Module 2 TA Appointments Committee Adult Learning Modules 1 and 3/4 Validate Module 1 & 3/4 TA DC HQ CRB OK Appts Sec
 36 Stage 4 When ALL stage 3 completed AA Segment C Appts Sec Full Appt DC Adult HQ
36 Stage 4 When ALL stage 3 completed AA Segment C Appts Sec Full Appt DC Adult HQ
 37 The Seven Steps 1 Identify learning and development needs 2 Agree and record a Personal Learning Plan 3 Monitor progress at regular intervals 4 Provide constructive feedback 5 Support and encourage 6 Validate the learning 7 Identify new needs and repeat the process
37 The Seven Steps 1 Identify learning and development needs 2 Agree and record a Personal Learning Plan 3 Monitor progress at regular intervals 4 Provide constructive feedback 5 Support and encourage 6 Validate the learning 7 Identify new needs and repeat the process
 38 Role of TA in PLP • Identify appropriate modules for the role • Familiar with content of modules • Establish which parts learner can already do • Establish what learning the learner will need to complete • Establish which methods will be best for learners • Complete Personal Learning Plan
38 Role of TA in PLP • Identify appropriate modules for the role • Familiar with content of modules • Establish which parts learner can already do • Establish what learning the learner will need to complete • Establish which methods will be best for learners • Complete Personal Learning Plan
 39 Personal Learning Plan
39 Personal Learning Plan
 40 Personal Learning Plan
40 Personal Learning Plan
 41 The Seven Steps 1 Identify learning and development needs 2 Agree and record a Personal Learning Plan 3 Monitor progress at regular intervals 4 Provide constructive feedback 5 Support and encourage 6 Validate the learning 7 Identify new needs and repeat the process
41 The Seven Steps 1 Identify learning and development needs 2 Agree and record a Personal Learning Plan 3 Monitor progress at regular intervals 4 Provide constructive feedback 5 Support and encourage 6 Validate the learning 7 Identify new needs and repeat the process
 42 Monitor and support • • Monitor progress regularly Provide constructive feedback Support and encourage the learner Be flexible to changing conditions
42 Monitor and support • • Monitor progress regularly Provide constructive feedback Support and encourage the learner Be flexible to changing conditions
 43 The Seven Steps 1 Identify learning and development needs 2 Agree and record a Personal Learning Plan 3 Monitor progress at regular intervals 4 Provide constructive feedback 5 Support and encourage 6 Validate the learning 7 Identify new needs and repeat the process
43 The Seven Steps 1 Identify learning and development needs 2 Agree and record a Personal Learning Plan 3 Monitor progress at regular intervals 4 Provide constructive feedback 5 Support and encourage 6 Validate the learning 7 Identify new needs and repeat the process
 44 Validation is about confirming that someone is able to do what they are supposed to be able to do “That they are fit for purpose” It is about confirming that the required learning has taken place by checking what the learner has done with it in practice.
44 Validation is about confirming that someone is able to do what they are supposed to be able to do “That they are fit for purpose” It is about confirming that the required learning has taken place by checking what the learner has done with it in practice.
 45 Validation - Do’s • Encourage learner to take responsibility • Compare evidence against the validation guidelines • Sign off validation if evidence demonstrates understanding of required learning • Value the learners effort and work • Suggest positive ways forward
45 Validation - Do’s • Encourage learner to take responsibility • Compare evidence against the validation guidelines • Sign off validation if evidence demonstrates understanding of required learning • Value the learners effort and work • Suggest positive ways forward
 46 Validation - Do’s • • Use open questions to probe Ask another TA or LTM if unsure Keep a written record Keep the learner aware
46 Validation - Do’s • • Use open questions to probe Ask another TA or LTM if unsure Keep a written record Keep the learner aware
 47 Validation - Don’ts • Sign off validation if – not convinced – evidence is not current – not happy criteria met • Be afraid to ask for further evidence / training • Be afraid to say “no”
47 Validation - Don’ts • Sign off validation if – not convinced – evidence is not current – not happy criteria met • Be afraid to ask for further evidence / training • Be afraid to say “no”
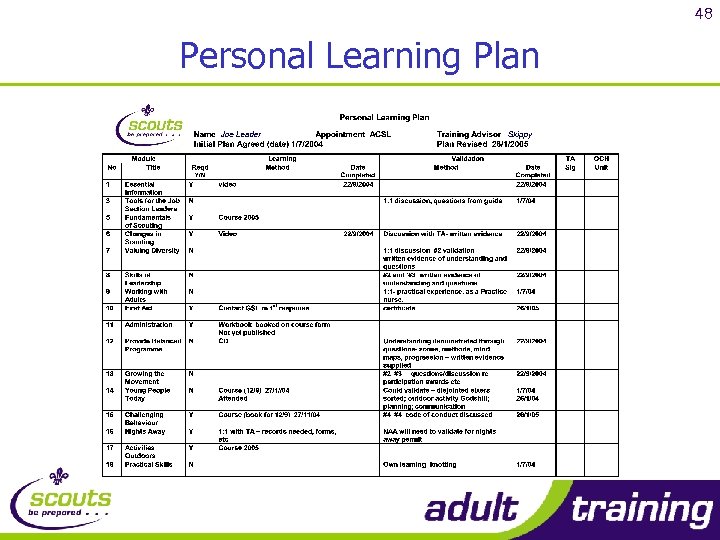 48 Personal Learning Plan
48 Personal Learning Plan
 49 Grievances Two possible areas: • Learner and TA unable to agree on which modules are required. • Participant disagrees with a validation decision
49 Grievances Two possible areas: • Learner and TA unable to agree on which modules are required. • Participant disagrees with a validation decision
 50 Validating Module 25 Training Advisers – Work as a Training Adviser for at least 2 new adults over at least 3 months – Determine their learning needs – Help them prepare Personal Learning Plans – Support them through at least 3 modules – Keep a record of meetings with them, discussions held, and how agreements were reached
50 Validating Module 25 Training Advisers – Work as a Training Adviser for at least 2 new adults over at least 3 months – Determine their learning needs – Help them prepare Personal Learning Plans – Support them through at least 3 modules – Keep a record of meetings with them, discussions held, and how agreements were reached
 51 www. scouts-hants. org. uk/Adult-Training
51 www. scouts-hants. org. uk/Adult-Training
 52 Training Adviser Page
52 Training Adviser Page
 53 scouts. org. uk/learnerresources
53 scouts. org. uk/learnerresources
 54 scouts. org. uk/learnerresources
54 scouts. org. uk/learnerresources
 55 Nights Away Adviser
55 Nights Away Adviser
 56 Role • Assessing people for Nights Away Permits • Recommending people for Nights Away permits • Providing advice and support on gaining Nights Away Permit • Advise on camping and residential issues • Promoting nights away
56 Role • Assessing people for Nights Away Permits • Recommending people for Nights Away permits • Providing advice and support on gaining Nights Away Permit • Advise on camping and residential issues • Promoting nights away
 57 Nights Away core skills 1. Planning a nights away event 2. Ensuring effective administration of an event 3. Preparing and coordinating a programme if activities 4. Choosing and preparing the event team 5. Choosing, organising and maintaining the right equipment 6. Ensuring the health, happiness and safety of self and others 7. Organising good catering 8. Making best use of venue
57 Nights Away core skills 1. Planning a nights away event 2. Ensuring effective administration of an event 3. Preparing and coordinating a programme if activities 4. Choosing and preparing the event team 5. Choosing, organising and maintaining the right equipment 6. Ensuring the health, happiness and safety of self and others 7. Organising good catering 8. Making best use of venue
 58 Validating Module 25 Night Away Advisers – Work as NAA for at least 2 adults over at least 3 months – Offer support and advice to adults working towards a Nights Away Permit – Keep a record of meetings with them, discussions held, and how agreements were reached
58 Validating Module 25 Night Away Advisers – Work as NAA for at least 2 adults over at least 3 months – Offer support and advice to adults working towards a Nights Away Permit – Keep a record of meetings with them, discussions held, and how agreements were reached
 59 Validating Module 25 Managers / Supporters – Prepare a briefing to a new adult to Scouting on the Adult Training Scheme and how it works – As part of a review meeting with someone you support, review training progress. – Record and action any support required
59 Validating Module 25 Managers / Supporters – Prepare a briefing to a new adult to Scouting on the Adult Training Scheme and how it works – As part of a review meeting with someone you support, review training progress. – Record and action any support required
 60 Finally • Good luck
60 Finally • Good luck


