d7d6492bde39b160ca478acfa863f98b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

1. AGRICULTURAL PUBLIC POLICY & HOW IT WORKS IN U. S. Larry D. Sanders Fall 2005 Dept. of Ag Economics Oklahoma State University

Introduction Purpose: gain an awareness of ag public policy & the process of policy development ® Content Learning Objectives: 1. Define agricultural public policy 2. Understand the process of policy development & implementation 3. Understand the underlying philosophies of policy formation ® 2

Introduction--continued ® Process Learning Objectives; develop skills of: 1. Critical Thinking 2. Written & Verbal Communication 3. Problem Solving 4. Teamwork 3

Lecture The process by which an idea is transcribed from the notes of the teacher to the notes of the student without going through the mind of either 4

“Anxiety Test” ® “The ultimate test of a set of economic ideas. . . is whether it illuminates the anxieties of the time. Does it explain problems that people find urgent? Does it bear on the current criticism of economic performance? . . . Does it bear upon the issues of political debate? For these, though many have always preferred to believe otherwise, do not ignite spontaneously or emerge maliciously from the mouths of agitators to afflict the comfortable. ” --John Kenneth Galbraith, Economics & the Public Purpose, 1973 [bold italics added by instructor] 5

What is agricultural public policy? ® Policy Definition ® Determinants of Policy Position ® Agricultural Policy Objectives ® Policy Process 6

Policy Definition Class ® Knutson: ® Policy: guiding principle leading to a course of action or specific program that is pursued by the government ® Ag/food policy: embody principles that guide govt. programs in production, resources utilized in production, domestic & int’l markets for commodities & food products, food consumption, & rural America conditions. ® Working definition: ® “Whatever government chooses to do or not do” ® 7

Policy Determinants ® Facts: what is ® Beliefs: what people think ® Values: what should be ® Myths: widely shared “stories” about how society ought to be organized ® Goals: desired results ® Examples 8

TWO WORMS OO v 9

US Agricultural Policy Objectives ® Protect farmers from market instability ® Maintain adequate food supply at reasonable prices ® Encourage agricultural exports to pay for US growth in productivity: ® Industrialization ® Imports ® Economic Growth 10

Policy Process ® Kings & Kingmakers ® Power Clusters ® Hahn’s Model ® How a bill becomes law ® Role of Government ® Iron Triangle 11
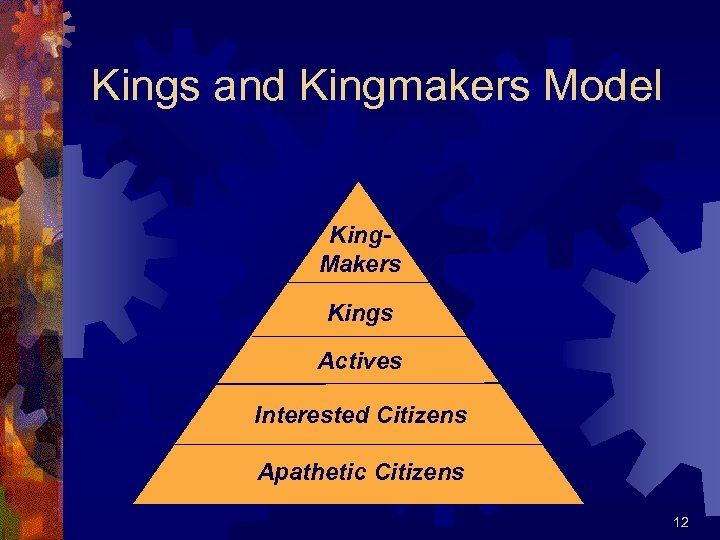
Kings and Kingmakers Model King. Makers Kings Actives Interested Citizens Apathetic Citizens 12

Role of Government (Evolving Process) 1. Economy: Purpose is provisioning of society 2. 1930 s: Economic poor health 3. Keynes: More govt. necessary to counter “shortrun” market problems “In the long run, market will stabilize. But in the long run, we’ll all be dead. ” 13

Role of Government (cont. ) 4. FDR: Relief, Reform, Recovery --Dramatic increase in government intervention 5. 1940 s: WWII supported Keynes’ claim --Employment Act of 1946 6. 1960 s: Heller--”Ability to fine-tune economy within sight. ” --BUT fighting 2 wars (Poverty & Vietnam) 14

Role of Government (cont. ) 7. 1970 s: The “bill” comes due --Inflation & Recession --Stagflation 8. 1980 s: Reaganomics--intended to reduce govt. in marketplace, enhancing free market & national security (in fact greatly increased federal spending) 9. 1992: Clintonomics I--”new liberalism” to reduce govt. with social concern (mixed success) 15

Role of Government (cont. ) 10. 1994: Conservative “revolution” --”contract” to reduce federal govt. & let state or private sector decide (mixed success) 11. 1997: Clintonomics II--”new liberalism” constrained by Conservative Congress 12. 2001: “Compassionate Conservatism”? ? ? 16

Role of Government (cont. ) 13. 2002+: b b b Global Terrorism Wartime Economy; Desire to downsize domestic govt. conflicts with entrenched interest groups “W” legacy still evolving 17

The Role of the Federal Government? “. . . Getting government off the back of business simply means putting business on the back of government. . Historically it is the national government that has served as the protector of the powerless. “. . . Democratic capitalism has triumphed because of the long campaign of reformers. . . To use the national government to humanize the industrial order, to cushion the operations of the economic system, to strengthen the bargaining position of workers and farmers and consumers, to regulate wages and hours, the quality of products and the sale of securities, to insure against recurrent depression by built-in economic stabilizers, . . . To combine individual opportunity with social responsibility. . . ” --Arthur Schlesinger, Jr. 18 (1995)

Legislative Key Committees Senate Ag Committee (20 members; 11 R; 9 D) Chair: Chambliss (GA) Subcommittees (4) Production/Price Competitiveness (Mc. Connell. KY) Marketing, Inspection & Product Promotion (Talent-MO) Forestry, Conservation & Rural Revitalization (Crapo-ID) Research, Nutrition & General Legislation (Santorum-PA) http: //www. senate. gov/ http: //www. house. gov/ 19

Legislative Committees (cont. ) ® House Ag Committee (45 members; 24 R; 21 D) ® Chair: Goodlatte (VA); Subcommittees (4) ® General Farm Commodities & Risk Management (Moran-KS) l Lucas (OK) ® Livestock & Horticulture (Hayes-NC) ® Conservation, Credit, Rural Development & Research (Lucas-OK) ® Specialty Crops & Foreign Ag Programs (Jenkins. TN) ® Dept. Operations, Oversight, Nutrition & Forestry (Gutknecht-MN) 20

Legislative Committees (cont. ) ® Senate Appropriations ® Chair: (Cochran-MS) ® Ag Subcommittee (Bennett-UT) ® House Appropriations ® Chair: J. Lewis (CA) ® Ag Subcommittee (Bonilla-TX) ® Senate Budget (Gregg-NH) ® House Budget (Nussle-IA) ® Senate Foreign Relations (Lugar-IN) ® House International Relations (Hyde-IL) 21

Legislative (cont. ) ® Senate-OK reps’ committee memberships ® Inhofe (R-OK) ® Armed Services ® Environment & Public Works (Chair) ® Coburn (R-OK) ® Indian Affairs ® Judiciary (subcommittee chair) ® Homeland Security & Govt Affairs (subcommittee chair) 22

Legislative (cont. ) ® House—OK Representatives’ memberships District 1– Sullivan (R-OK) l Energy & Commerce ® District 2 --Boren (D-OK) l Armed Services l Resources ® District 3 --Lucas (R-OK) l Agriculture l Financial Services l Science ® 23

Legislative (cont. ) ® House OK Reps (cont. ) District 4 -- Cole(R-OK) l Rules l Ethics l Armed Services l Deputy Majority Whip ® District 5 --Istook (R-OK) l Appropriations ® 24

Policy Philosophies ® Free Market ® Let market work; market signals must be allowed to work ® Govt. action ineffective/part of problem ® Humanitarian ® Feed expanding world population ® Govt. obligated to expand production (distribution is important) ® Right-to-food 25

Political Philosophies (cont. ) ® Agricultural Fundamentalist ® All real wealth in land/agriculture (Physiocrats) ® Govt. must preserve agriculture to preserve culture & society (parity concept) ® Stabilizer ® Instability is the real problem ® Govt. must stabilize prices 26

Political Philosophies (cont. ) ® Regulator ® Free market is unreliable, unstable (chronic problems) ® Govt. must plan entire process for “rational” coordination to control production, educate key players & consumers 27

USDA ® Farm & Foreign Ag Service ® Marketing & Regulatory Programs ® Food Safety ® Rural Development ® Natural Resources & Environment ® Food, Nutrition & Consumer Services ® Research, Education & Economics http: //www. usda. gov/services. html 28

Forces of Policy Change ® Instability ® Globalization ® Technology ® Food Safety ® Environment ® Industrialization ® Politics ® Unforseen Events 29
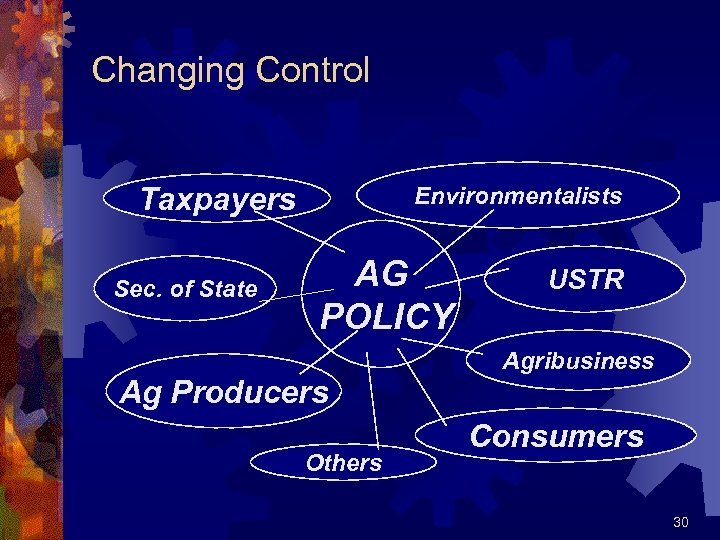
Changing Control Taxpayers Sec. of State Environmentalists AG POLICY Ag Producers Others USTR Agribusiness Consumers 30

Fact or Myth or Belief? 1. Agrarian values are simple & basic to American values. 2. Farming is the primary rural business, occurring only in rural areas. 3. Most farms are “average”. 4. Production = productivity in ag. 31

Fact or Myth or Belief? 5. Farm prices alone describe the farm financial situation. 6. US ag does not need global trade. 7. “Good” farming means a healthy environment. 8. Farm programs are effective food programs. 32

Fact or Myth or Belief? 9. Govt. programs are successful in achieving their stated goals. 10. The trend toward fewer, larger farms is escalating. 11. Large corporations have taken over farming. 12. Most farm family incomes from farm income. 33

Assignment ® 25 Aug: Read Knutson Ch. 1, 3 ® Identify OK US Senators & Representatives; list their committee assignments (CLUE: Check these web sites ® http: //www. house. gov; http: //www. senate. gov) ® 1 Sep: Read K ch. 2; determine which statements are facts, myths or beliefs on slides 30 -32 & briefly explain. 34

Fall 2005: Class-defined Issues (not prioritized) 35
d7d6492bde39b160ca478acfa863f98b.ppt