5fe527ac2e221b1a830a016b90163740.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

1 43 Tizen System / App Framework Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

Contents 2 43 • • Overview (System & App FW) What is Ecore? System Framework Application Framework Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

Overview 3 43 • System Framework – System managements and Device Abstractions • System condition management Low memory, Low battery, process, CPU frequency handling • Device abstraction and control display, mmc, earjack, GPS, haptic, etc. – System logging dlog – Sensor management sensor server and client library • App Framework – – Application main loop Inter-app communication and launching Application Install & Uninstall System event callback Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
What is Ecore? (Event main loop) 4 43 • Ecore: EFL core library for application – “Operating system abstraction and integration”, http: //enlightenment. org – Event-driven main loop Because GUI application is event-driven. • Many GUI Toolkit use event-driven main loop, ex) Glib – Frequently switch between IDLE / Event handling • save core resource – Can handle file descriptor and signal event • socket, pipe, vconf, IPC, etc. • Also able to use in non-GUI event driven program Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

5 43 System Framework Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
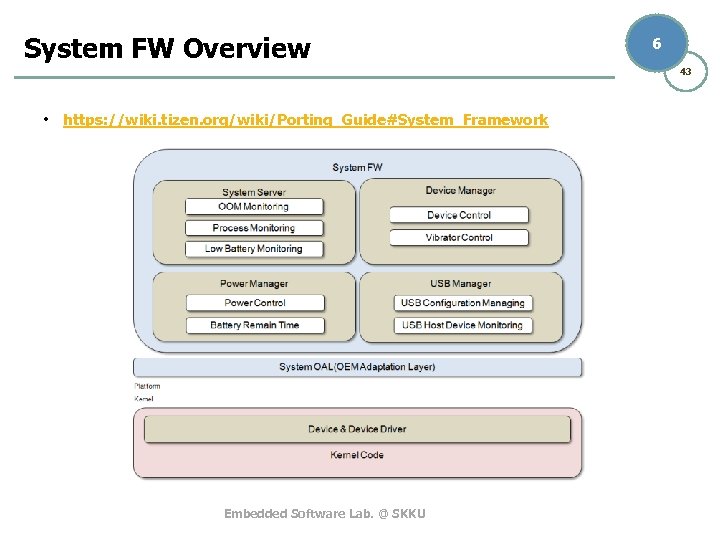
System FW Overview 6 43 • https: //wiki. tizen. org/wiki/Porting_Guide#System_Framework Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
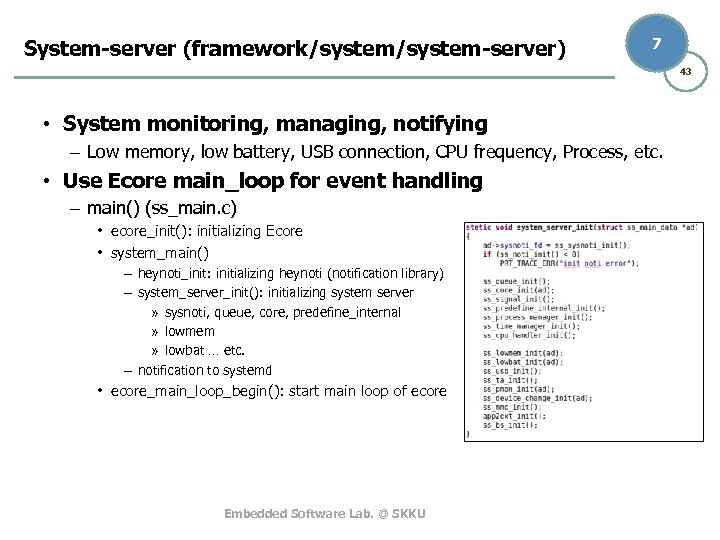
System-server (framework/system-server) 7 43 • System monitoring, managing, notifying – Low memory, low battery, USB connection, CPU frequency, Process, etc. • Use Ecore main_loop for event handling – main() (ss_main. c) • ecore_init(): initializing Ecore • system_main() – heynoti_init: initializing heynoti (notification library) – system_server_init(): initializing system server » sysnoti, queue, core, predefine_internal » lowmem » lowbat … etc. – notification to systemd • ecore_main_loop_begin(): start main loop of ecore Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
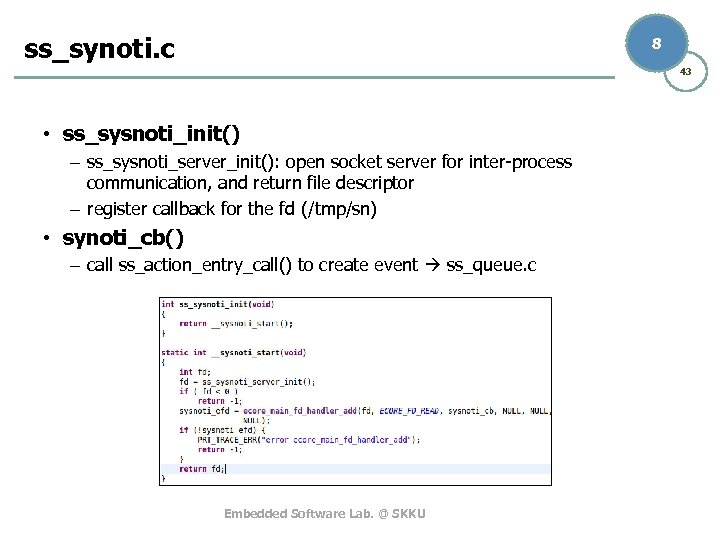
ss_synoti. c 8 43 • ss_sysnoti_init() – ss_sysnoti_server_init(): open socket server for inter-process communication, and return file descriptor – register callback for the fd (/tmp/sn) • synoti_cb() – call ss_action_entry_call() to create event ss_queue. c Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

ss_queue. c 9 43 • Task runqueue for system-server – Handle action from internal or pipe handler • ss_action_entry_add() / ss_action_entry_add_internal() – Specify action task and register to Eina list • ss_action_entry_call() / ss_action_entry_call_internal() – Insert action into run_queue (based on the msg of action_entry) – ss_core_action_run() ss_core. c • ss_run_queue_run() – run the ‘run_function’ for each action_entry • Difference between internal or not – Internal: for internal source that will execute action. – non-internal: . so library will execute action using this ss_queue interface new additional event can be served from system-server Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

ss_core. c 10 43 • Execute run queue event from pipe • ss_core_init() – Create unnamed pipe, and register call back function for the pipe as core_pipe_cb • core_pipe_cb() – Register _ss_core_action_run as ‘run_function’ for run_queue • ss_core_action_run – send msg (action run) into pipe • _ss_core_action_run – Call predefine_action of run_queue_entry Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
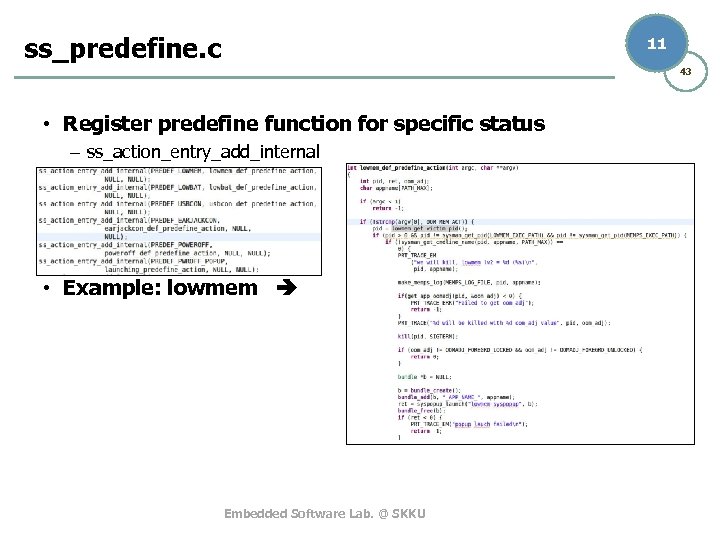
ss_predefine. c 11 43 • Register predefine function for specific status – ss_action_entry_add_internal • Example: lowmem Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
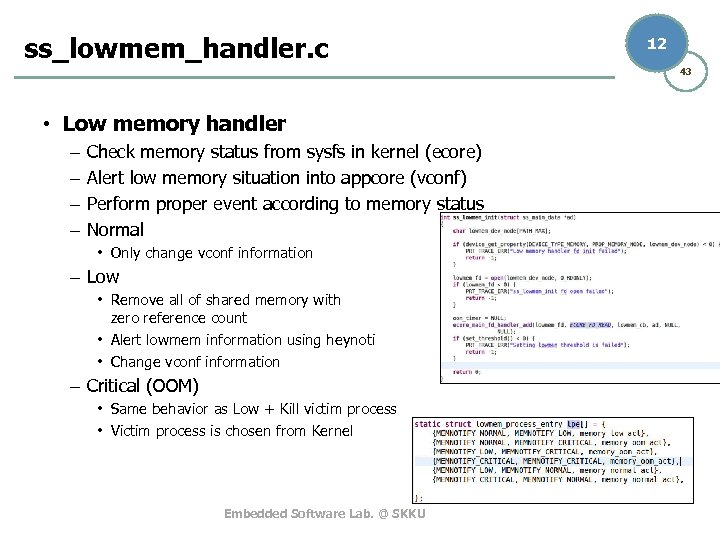
ss_lowmem_handler. c 12 43 • Low memory handler – – Check memory status from sysfs in kernel (ecore) Alert low memory situation into appcore (vconf) Perform proper event according to memory status Normal • Only change vconf information – Low • Remove all of shared memory with zero reference count • Alert lowmem information using heynoti • Change vconf information – Critical (OOM) • Same behavior as Low + Kill victim process • Victim process is chosen from Kernel Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
Others 13 43 • Other system events (Low battery, USB connection, Device change, MMC device) are also similar as low memory handler. – Handle system-level event for device • e. g. – mount, and unmount, format event will be handled from system-server – Storage I/O will not be handled from system-server Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

Inter-process communication 14 43 • Various Inter-process communication – – – heynoti ss_synoti socket pipe vconf dbus Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
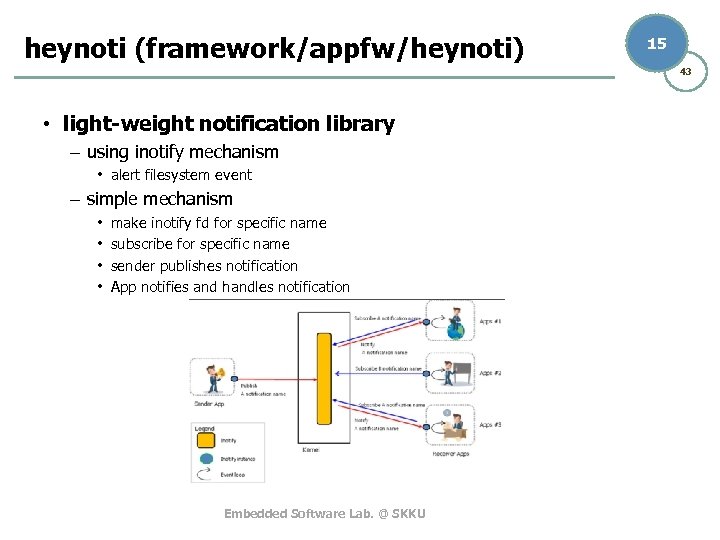
heynoti (framework/appfw/heynoti) 15 43 • light-weight notification library – using inotify mechanism • alert filesystem event – simple mechanism • • make inotify fd for specific name subscribe for specific name sender publishes notification App notifies and handles notification Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
ss_sysnoti 16 43 • Send event into system-server – Enable run_queue (in system-server) to handle the event from proper handler – Using socket communication • libslp_sysman – Helper library to notify the message to system-server – sysnoti. c • synoti_send(msg): send socket msg into /tmp/sn • sysman_call_predef_action(): request into system-server to run predefined function for the event Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
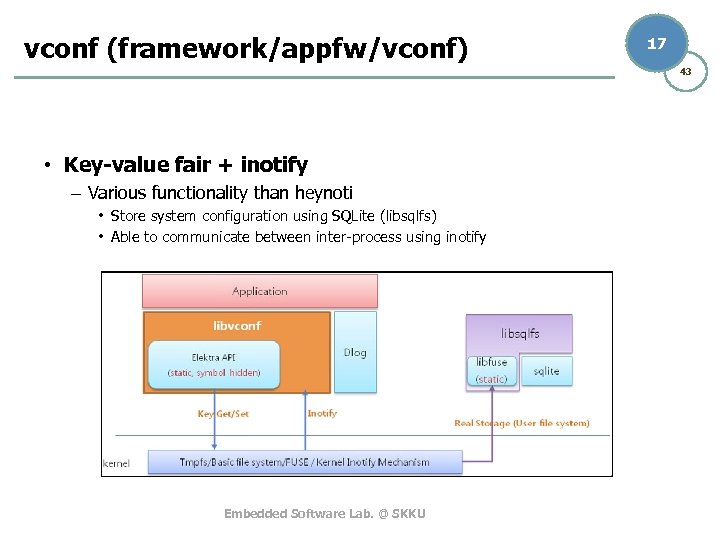
vconf (framework/appfw/vconf) 17 43 • Key-value fair + inotify – Various functionality than heynoti • Store system configuration using SQLite (libsqlfs) • Able to communicate between inter-process using inotify Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
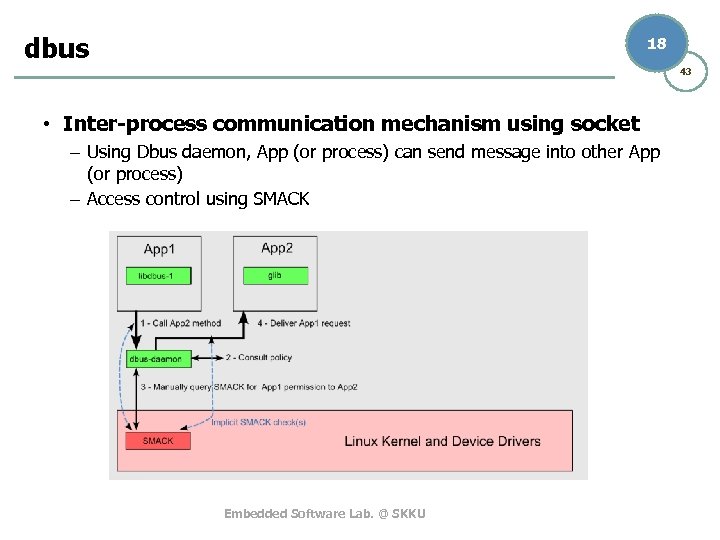
dbus 18 43 • Inter-process communication mechanism using socket – Using Dbus daemon, App (or process) can send message into other App (or process) – Access control using SMACK Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
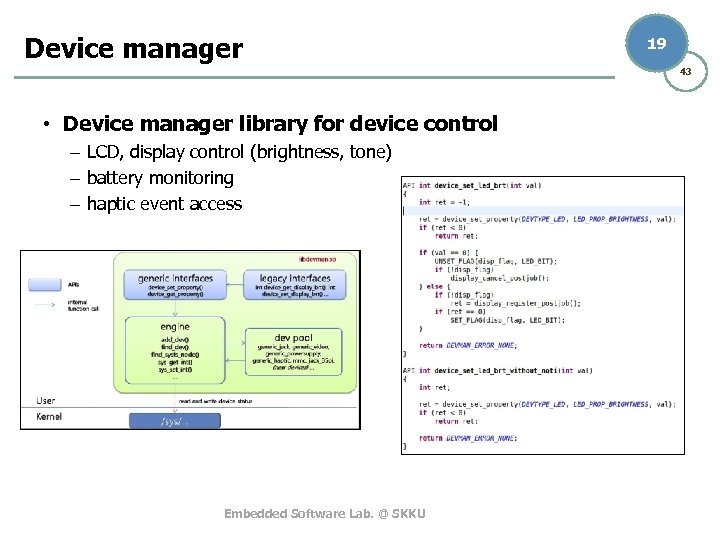
Device manager 19 43 • Device manager library for device control – LCD, display control (brightness, tone) – battery monitoring – haptic event access Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
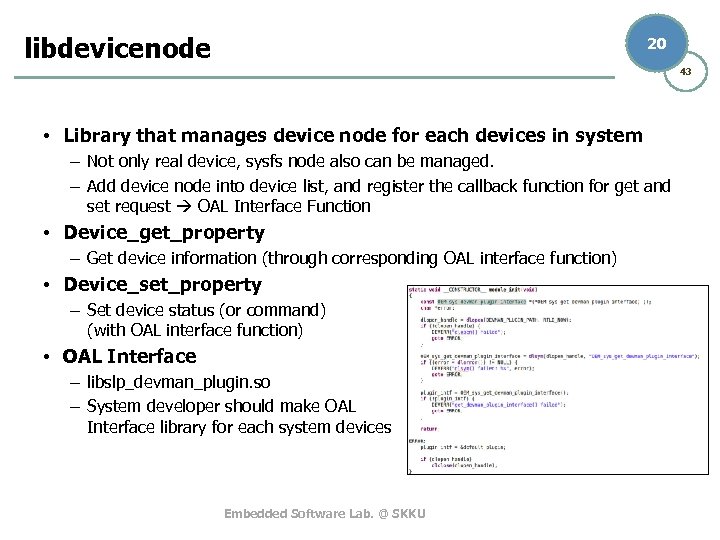
libdevicenode 20 43 • Library that manages device node for each devices in system – Not only real device, sysfs node also can be managed. – Add device node into device list, and register the callback function for get and set request OAL Interface Function • Device_get_property – Get device information (through corresponding OAL interface function) • Device_set_property – Set device status (or command) (with OAL interface function) • OAL Interface – libslp_devman_plugin. so – System developer should make OAL Interface library for each system devices Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
Sensor Framework 21 43 • Types of Sensors – Tizen supports individual plugin frameworks for these sensors: • • • Accelerometer sensor Gyroscope sensor Proximity sensor Motion sensor Geomagnetic sensor Light sensor Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

Sensor details 22 43 • Accelerometer sensor – The accelerometer sensor is used to measure the acceleration of the device. The three dimensional coordinate system is used to illustrate the direction of the acceleration. When a phone is moving along an axis, the acceleration is positive if it moves in a positive direction. • Gyroscope sensor – A gyroscope is a device used primarily for navigation and measurement of angular velocity. Gyroscopes measure how quickly an object rotates. This rate of rotation can be measured along any of the three axes X, Y, and Z. • Proximity sensor – A proximity sensor can detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact. That is, it indicates if the device is close or not close to the user. • Motion sensor – A motion sensor is a virtual sensor that uses the accelerometer and gyroscope sensors. Motion sensor detects snap, panning, tilt, shake, overturn, and double tap event. • Geomagnetic sensor – A geomagnetic sensor indicates the strength of the geomagnetic flux density in the X, Y, and Z axes. This sensor is used to find the orientation of a body, which is a description of how it is aligned to the space it is in. • Light sensor – A light sensor measures the amount of light that it receives or the surrounding light conditions. The ambient light state is measured as a step value, where 0 is very dark and 10 is bright sunlight. Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

Sensor Framework details 23 43 • Components of Sensor Framework – The Sensor framework provides a sensor server for creating plugins and a medium through which the client applications are connected to the sensor hardware to exchange data. The sensor plugins retrieve data from sensor hardware and enable the client applications to use the data for specific requirements. – Sensor Library • The application that wants to access the sensor service should communicate with the daemon through the sensor API library. An API library allows the application to access the sensor service. As shown in the below diagram, applications/middleware frameworks can have the sensor-framework client library in the process context. – Sensor Server • The sensor server is a daemon which communicates uniquely to sensor drivers in the system and dispatches sensor data to the application. The sensor server takes care of interacting with the sensor driver in hardware initialization, driver configuration, and data fetching, to manage all sensors on the platform. • Type of plugins in sensor framework – Sensor Plugin • Sensor plugins takes care of interacting with the sensor driver. Plug-ins process data from sensor drivers and communicate it to the sensor server. – Processor • Active component (it has a thread) that processes data or makes events from a filter or from sensor data. – Filter • Passive component that converts sensor raw data to other types of data – Sensor • Passive component that gets raw data from the kernel node Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

24 43 App Framework Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
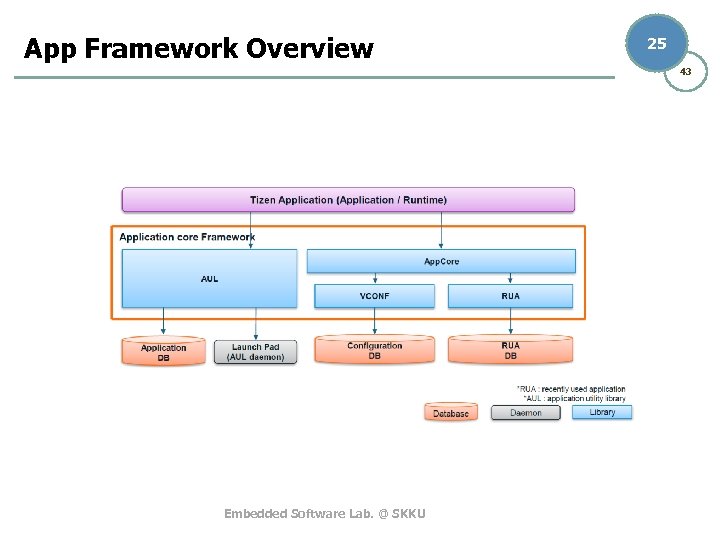
App Framework Overview 25 43 Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
Tizen Core Application Types 26 43 • Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
Appcore 27 43 • Appcore is the application core handling various important events each of which application should be ware of. • Using appcore, developers can – Manage application life-cycle • Create, Reset, Pause, Resume, Terminate – Handle System Events • • Low Memory Low Battery Screen orientation Change Language & Region Change Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
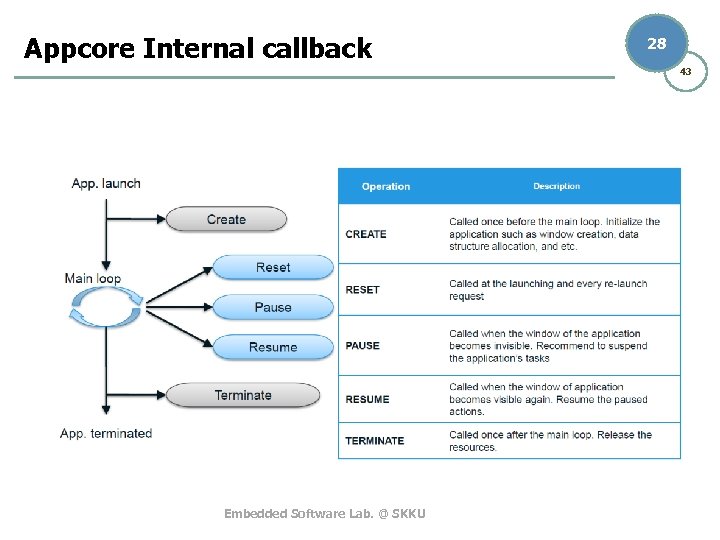
Appcore Internal callback 28 43 Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

Using appcore 29 43 • Include appcore_common. h or appcore_efl. h • fill appcore_ops for proper function pointers • call appcore_efl_main when using EFL Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
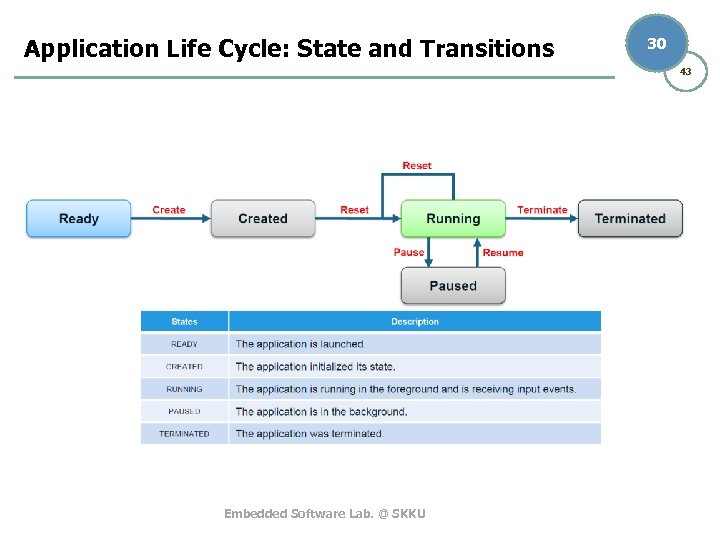
Application Life Cycle: State and Transitions 30 43 Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
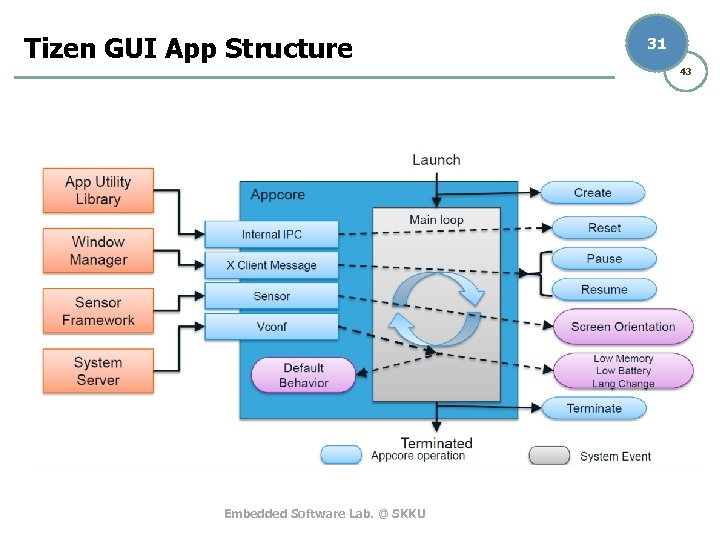
Tizen GUI App Structure 31 43 Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

Application Utility Library: AUL 32 43 • Application Utility Library (AUL) provides the following features – Launching/terminating applications – Providing running application information • AUL consists of the following sub-components: – AUL library: Sending/receiving requests for launching and terminating – AUL daemon (a. k. a. launch pad): Handling the requests Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
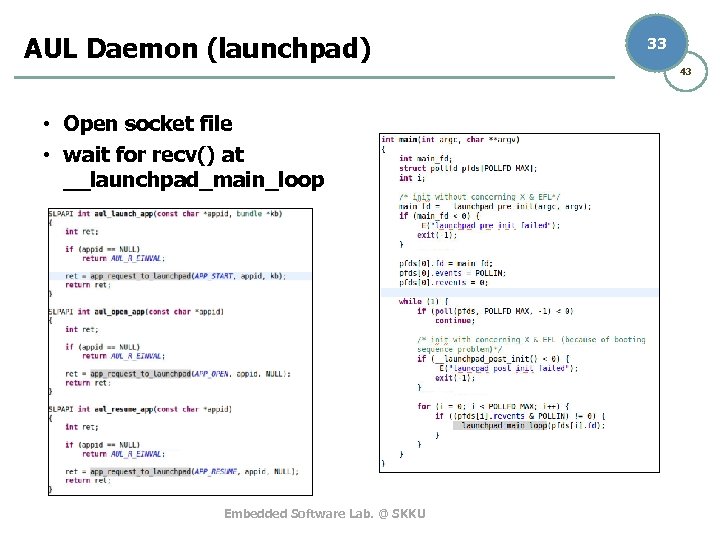
AUL Daemon (launchpad) 33 43 • Open socket file • wait for recv() at __launchpad_main_loop Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
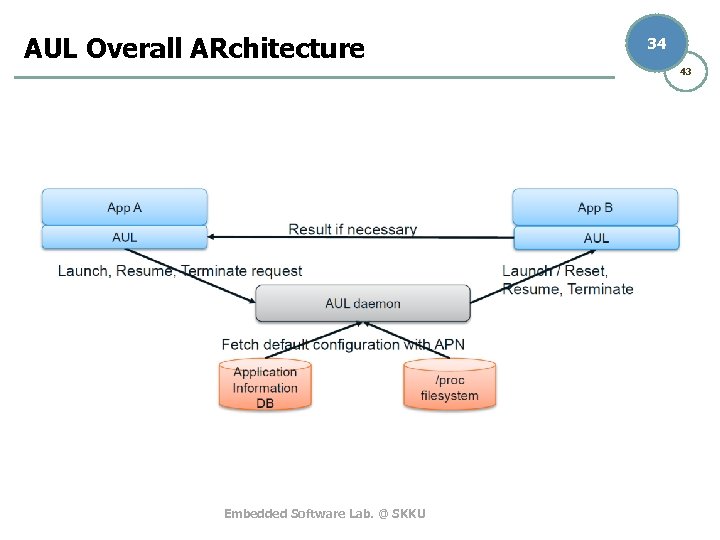
AUL Overall ARchitecture 34 43 Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
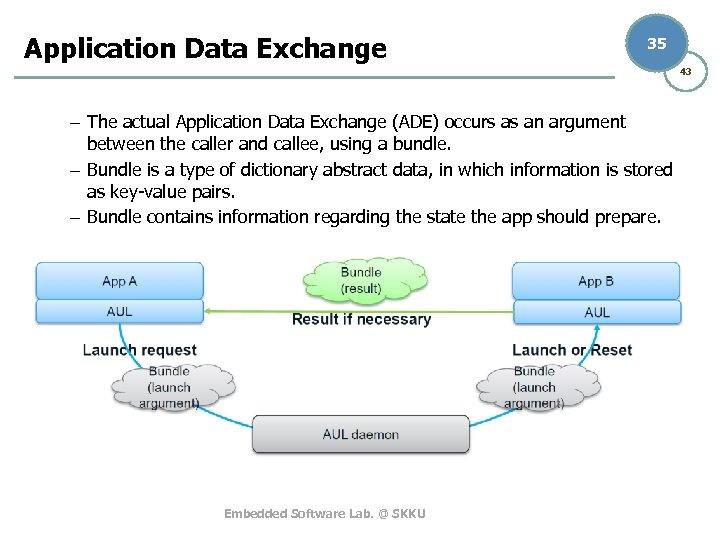
Application Data Exchange 35 43 – The actual Application Data Exchange (ADE) occurs as an argument between the caller and callee, using a bundle. – Bundle is a type of dictionary abstract data, in which information is stored as key-value pairs. – Bundle contains information regarding the state the app should prepare. Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
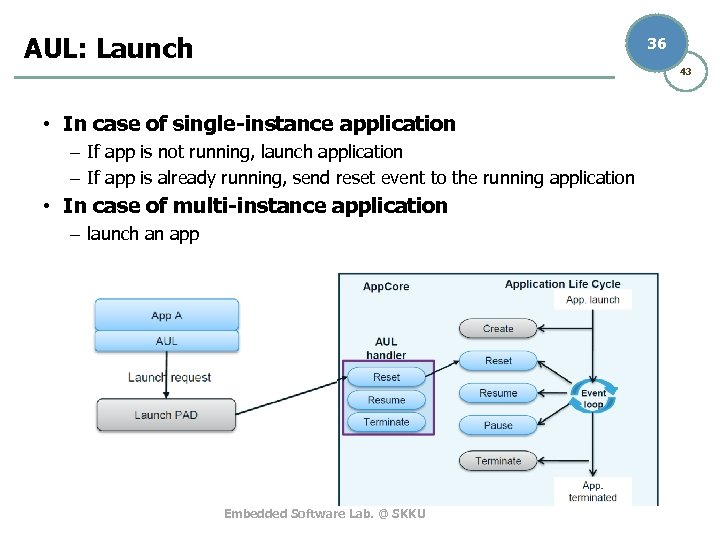
AUL: Launch 36 43 • In case of single-instance application – If app is not running, launch application – If app is already running, send reset event to the running application • In case of multi-instance application – launch an app Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
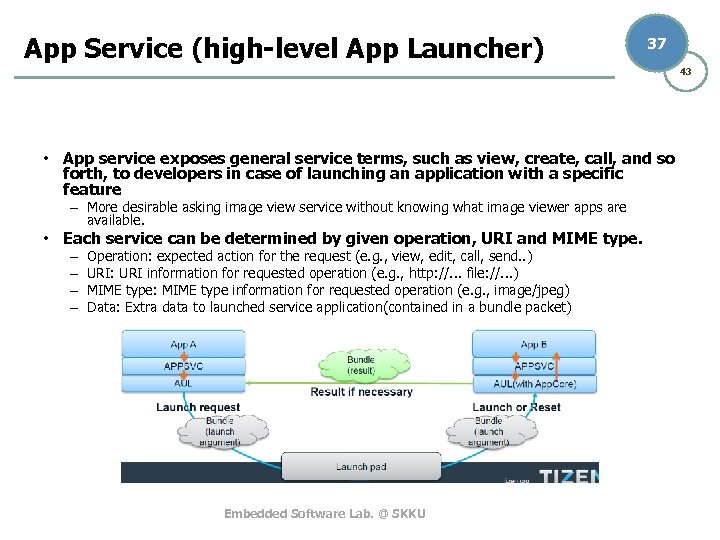
App Service (high-level App Launcher) 37 43 • App service exposes general service terms, such as view, create, call, and so forth, to developers in case of launching an application with a specific feature – More desirable asking image view service without knowing what image viewer apps are available. • Each service can be determined by given operation, URI and MIME type. – – Operation: expected action for the request (e. g. , view, edit, call, send. . ) URI: URI information for requested operation (e. g. , http: //. . . file: //. . . ) MIME type: MIME type information for requested operation (e. g. , image/jpeg) Data: Extra data to launched service application(contained in a bundle packet) Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
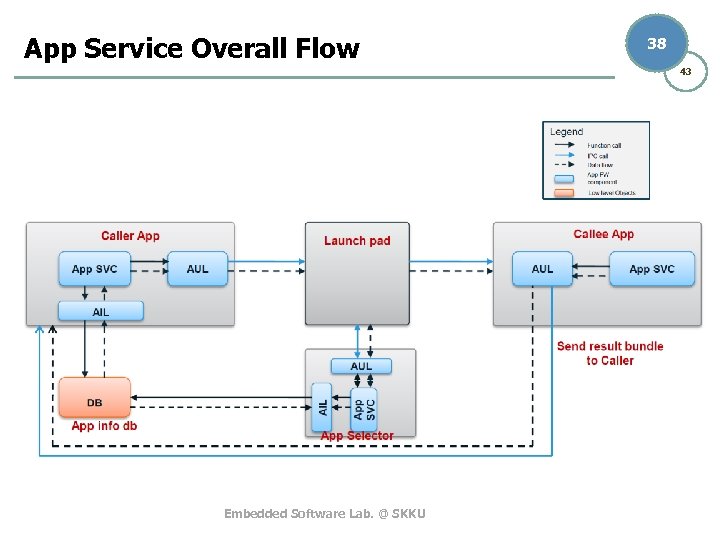
App Service Overall Flow 38 43 Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
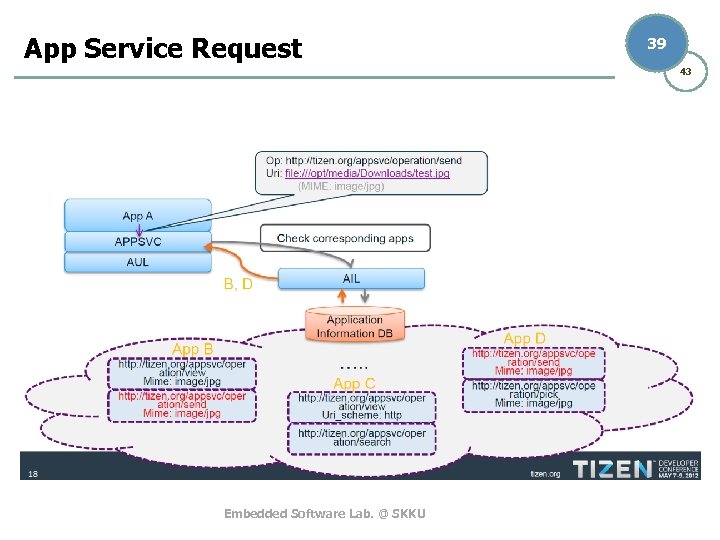
App Service Request 39 43 Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
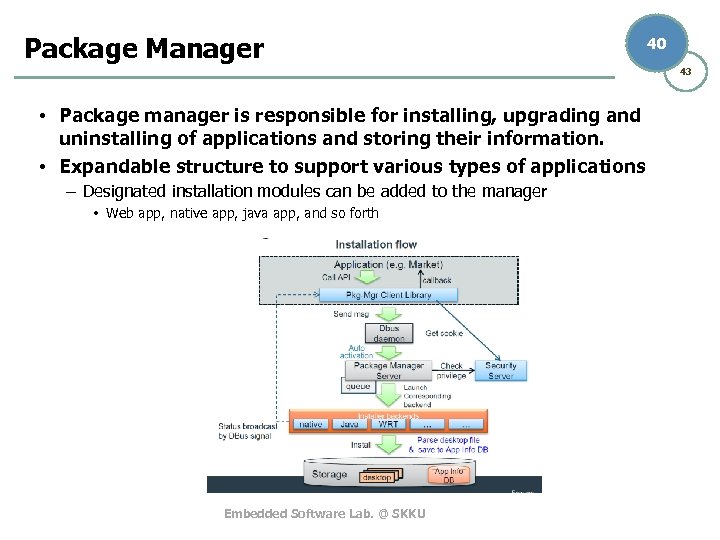
Package Manager 40 43 • Package manager is responsible for installing, upgrading and uninstalling of applications and storing their information. • Expandable structure to support various types of applications – Designated installation modules can be added to the manager • Web app, native app, java app, and so forth Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
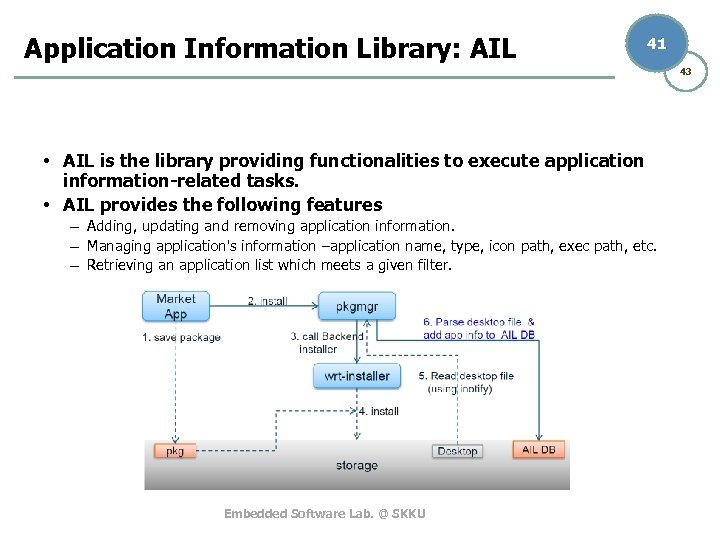
Application Information Library: AIL 41 43 • AIL is the library providing functionalities to execute application information-related tasks. • AIL provides the following features – Adding, updating and removing application information. – Managing application's information –application name, type, icon path, exec path, etc. – Retrieving an application list which meets a given filter. Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

App Use History: RUA 42 43 • Recently Used Application (RUA) logs application use history. – When an application is launched, launch pad updates the history and task manager can either get or clear the history. • RUA also provides below information regarding launching: – – package name launch time application path application launch argument Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU

References 43 43 • “An Overview of Tizen Application Core Framework”, TDC 2012 • “Tizen Core APIs: A Core Framework Layer to Build In. House Applications”, TDC 2014 • Tizen wiki, https: //wiki. tizen. org • http: //seoz. egloos. com Embedded Software Lab. @ SKKU
5fe527ac2e221b1a830a016b90163740.ppt