1 3. Hot Rolling 3 Hot rolling of




















32152-v_c_1503_hr_samara.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 1 3. Hot Rolling 3 Hot rolling of strip 3.1 Technology topics 3.2 Basic methods 3.3 Layouts of HSMs 3.4 Descaling 3.5 Optimising rolling conditions 3.6 Finishing shop 3.7 Roll materials Content
1 3. Hot Rolling 3 Hot rolling of strip 3.1 Technology topics 3.2 Basic methods 3.3 Layouts of HSMs 3.4 Descaling 3.5 Optimising rolling conditions 3.6 Finishing shop 3.7 Roll materials Content
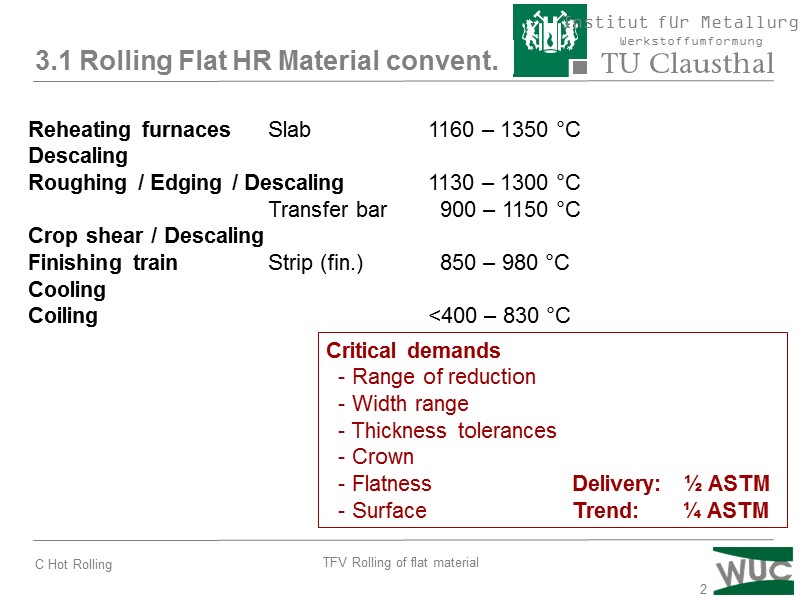
 2 3.1 Rolling Flat HR Material convent. Reheating furnaces Slab 1160 – 1350 °C Descaling Roughing / Edging / Descaling 1130 – 1300 °C Transfer bar 900 – 1150 °C Crop shear / Descaling Finishing train Strip (fin.) 850 – 980 °C Cooling Coiling <400 – 830 °C Critical demands - Range of reduction - Width range - Thickness tolerances - Crown - Flatness Delivery: ½ ASTM - Surface Trend: ¼ ASTM
2 3.1 Rolling Flat HR Material convent. Reheating furnaces Slab 1160 – 1350 °C Descaling Roughing / Edging / Descaling 1130 – 1300 °C Transfer bar 900 – 1150 °C Crop shear / Descaling Finishing train Strip (fin.) 850 – 980 °C Cooling Coiling <400 – 830 °C Critical demands - Range of reduction - Width range - Thickness tolerances - Crown - Flatness Delivery: ½ ASTM - Surface Trend: ¼ ASTM
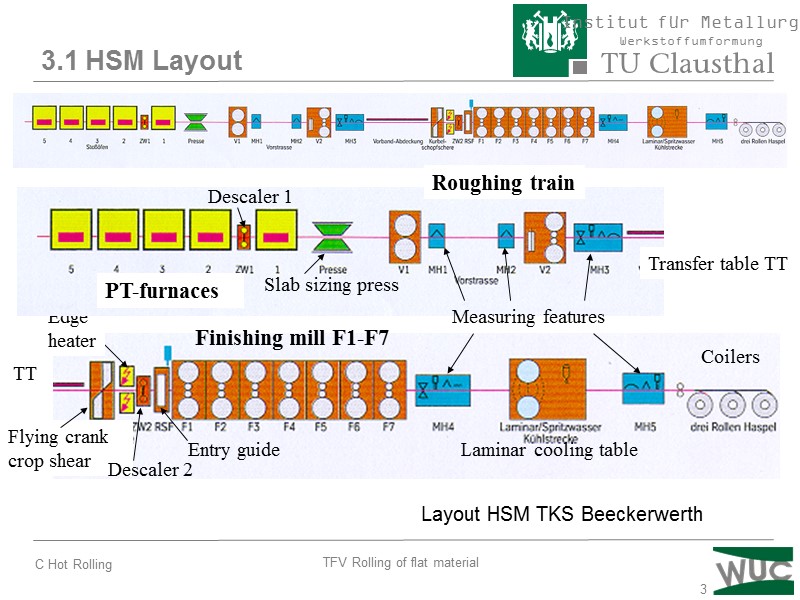
 3 Layout HSM TKS Beeckerwerth 3.1 HSM Layout
3 Layout HSM TKS Beeckerwerth 3.1 HSM Layout
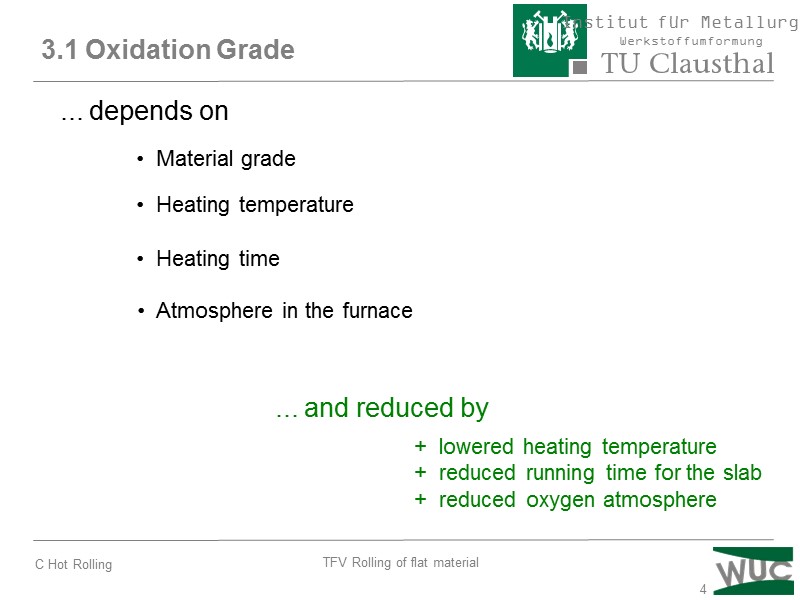
 4 3.1 Oxidation Grade ... depends on
4 3.1 Oxidation Grade ... depends on
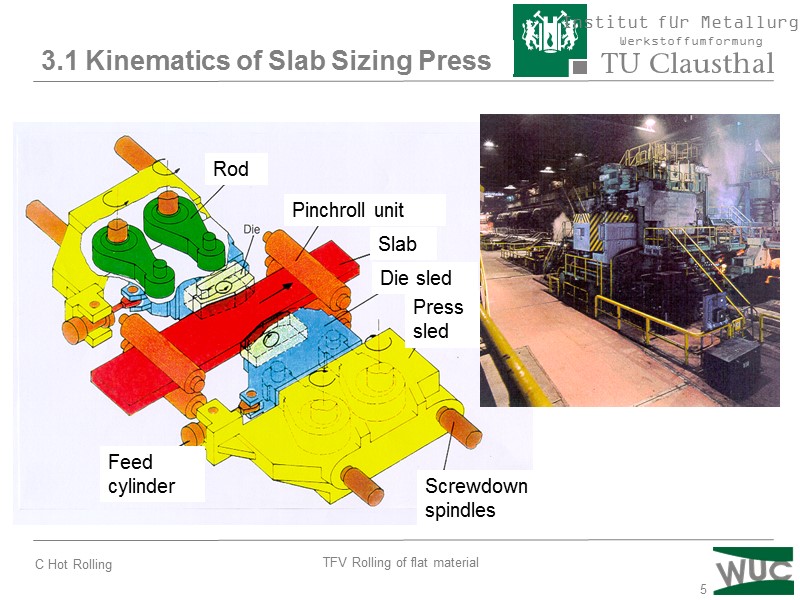
 5 3.1 Kinematics of Slab Sizing Press Press sled Die sled Slab Pinchroll unit Rod Feed cylinder Screwdown spindles
5 3.1 Kinematics of Slab Sizing Press Press sled Die sled Slab Pinchroll unit Rod Feed cylinder Screwdown spindles
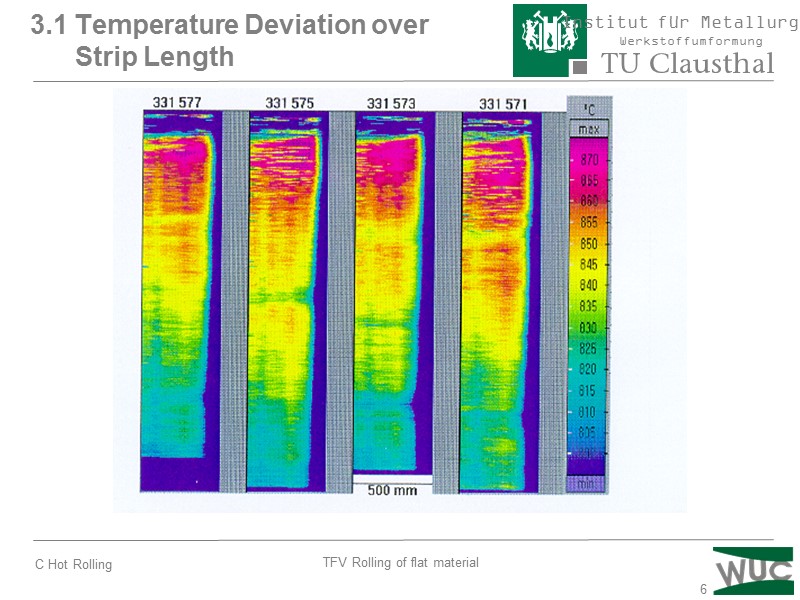
 6 3.1 Temperature Deviation over Strip Length
6 3.1 Temperature Deviation over Strip Length
 7 3.1 Heat Hoods TKS AG Beeckerwerth
7 3.1 Heat Hoods TKS AG Beeckerwerth
 8 3.1 Coilbox Coilbox furnace, TKS Bochum
8 3.1 Coilbox Coilbox furnace, TKS Bochum
 9 3.1 Surface Defects on Strip ... coming from HSM can be caused by Faults at the rollers Breakouts, cladded material Defects at descaling and cooling Worn nozzles, reduced water flow,... Defects at rolls Built-up at pinch rolls of coiler
9 3.1 Surface Defects on Strip ... coming from HSM can be caused by Faults at the rollers Breakouts, cladded material Defects at descaling and cooling Worn nozzles, reduced water flow,... Defects at rolls Built-up at pinch rolls of coiler
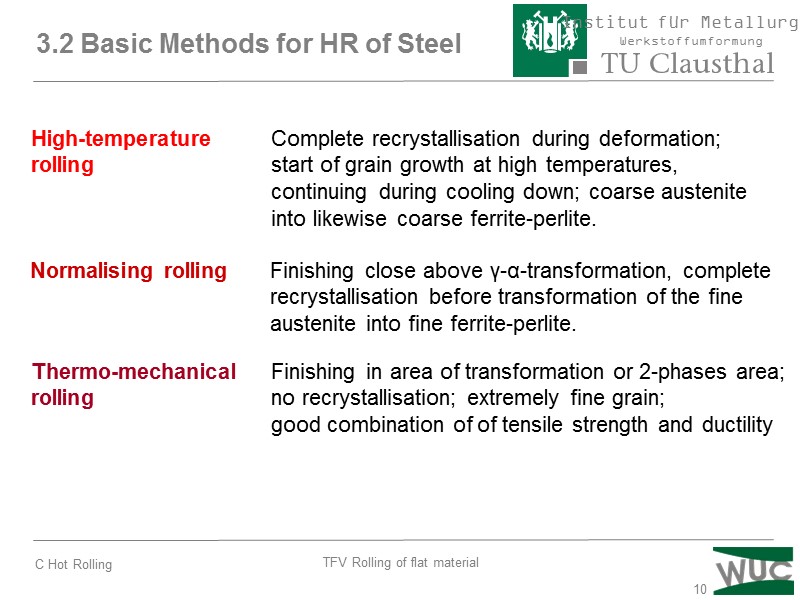
 10 3.2 Basic Methods for HR of Steel High-temperature Complete recrystallisation during deformation; rolling start of grain growth at high temperatures, continuing during cooling down; coarse austenite into likewise coarse ferrite-perlite. Normalising rolling Finishing close above γ-α-transformation, complete recrystallisation before transformation of the fine austenite into fine ferrite-perlite. Thermo-mechanical Finishing in area of transformation or 2-phases area; rolling no recrystallisation; extremely fine grain; good combination of of tensile strength and ductility
10 3.2 Basic Methods for HR of Steel High-temperature Complete recrystallisation during deformation; rolling start of grain growth at high temperatures, continuing during cooling down; coarse austenite into likewise coarse ferrite-perlite. Normalising rolling Finishing close above γ-α-transformation, complete recrystallisation before transformation of the fine austenite into fine ferrite-perlite. Thermo-mechanical Finishing in area of transformation or 2-phases area; rolling no recrystallisation; extremely fine grain; good combination of of tensile strength and ductility
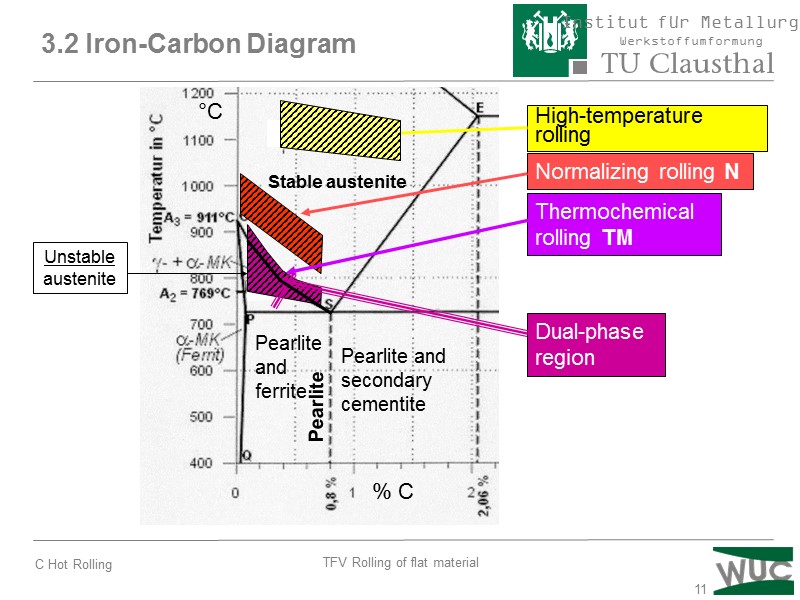
 11 3.2 Iron-Carbon Diagram °C High-temperature rolling Normalizing rolling N Thermochemical rolling TM Stable austenite Unstable austenite Pearlite and ferrite Pearlite and secondary cementite Dual-phase region % C Pearlite
11 3.2 Iron-Carbon Diagram °C High-temperature rolling Normalizing rolling N Thermochemical rolling TM Stable austenite Unstable austenite Pearlite and ferrite Pearlite and secondary cementite Dual-phase region % C Pearlite
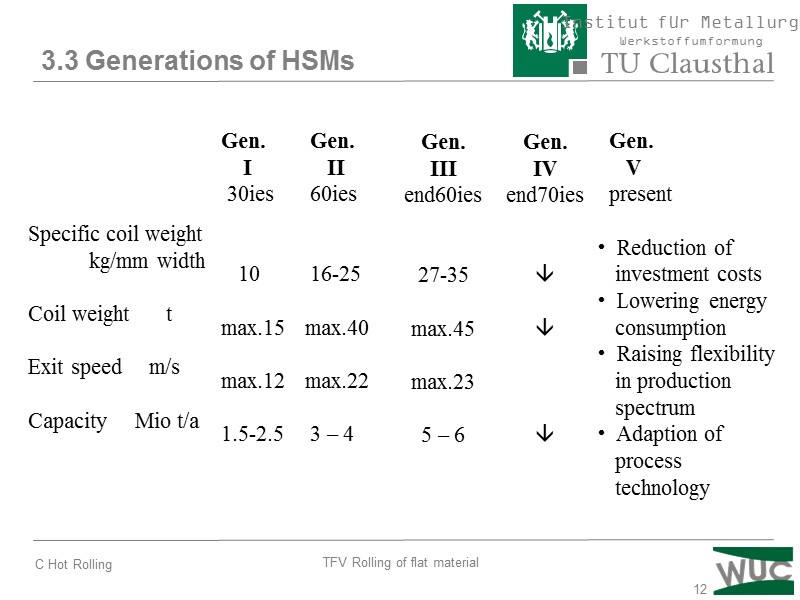
 12 (Quelle: Hoesch Archiv. Zeitschrift „Werk und Wir“. Ausgabe 10/1958) 3.3 Generations of HSMs Gen. II 60ies 16-25 max.40 max.22 3 – 4 Specific coil weight kg/mm width Coil weight t Exit speed m/s Capacity Mio t/a Gen. I 30ies 10 max.15 max.12 1.5-2.5 Gen. III end60ies 27-35 max.45 max.23 5 – 6 Gen. IV end70ies Gen. V present Reduction of investment costs Lowering energy consumption Raising flexibility in production spectrum Adaption of process technology
12 (Quelle: Hoesch Archiv. Zeitschrift „Werk und Wir“. Ausgabe 10/1958) 3.3 Generations of HSMs Gen. II 60ies 16-25 max.40 max.22 3 – 4 Specific coil weight kg/mm width Coil weight t Exit speed m/s Capacity Mio t/a Gen. I 30ies 10 max.15 max.12 1.5-2.5 Gen. III end60ies 27-35 max.45 max.23 5 – 6 Gen. IV end70ies Gen. V present Reduction of investment costs Lowering energy consumption Raising flexibility in production spectrum Adaption of process technology
 13 · · 3.3 Designing HSMs Capacity Type and concept of plant Product spectrum Plant type Mechanical and electrical dimensioning Product quality Plant type Mechanical and electrical dimensioning Configuration of adaptive systems Automatization and models
13 · · 3.3 Designing HSMs Capacity Type and concept of plant Product spectrum Plant type Mechanical and electrical dimensioning Product quality Plant type Mechanical and electrical dimensioning Configuration of adaptive systems Automatization and models
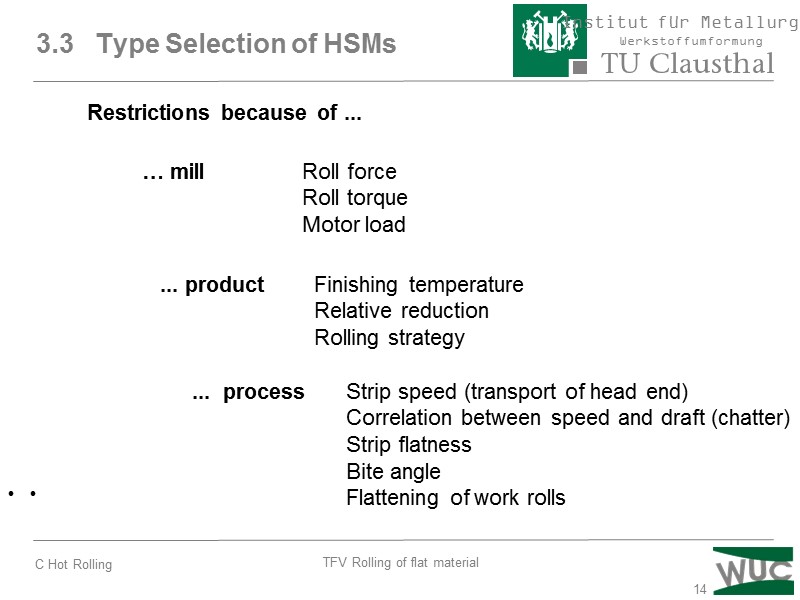
 14 · · 3.3 Type Selection of HSMs … mill Roll force Roll torque Motor load Restrictions because of ... ... product Finishing temperature Relative reduction Rolling strategy ... process Strip speed (transport of head end) Correlation between speed and draft (chatter) Strip flatness Bite angle Flattening of work rolls
14 · · 3.3 Type Selection of HSMs … mill Roll force Roll torque Motor load Restrictions because of ... ... product Finishing temperature Relative reduction Rolling strategy ... process Strip speed (transport of head end) Correlation between speed and draft (chatter) Strip flatness Bite angle Flattening of work rolls
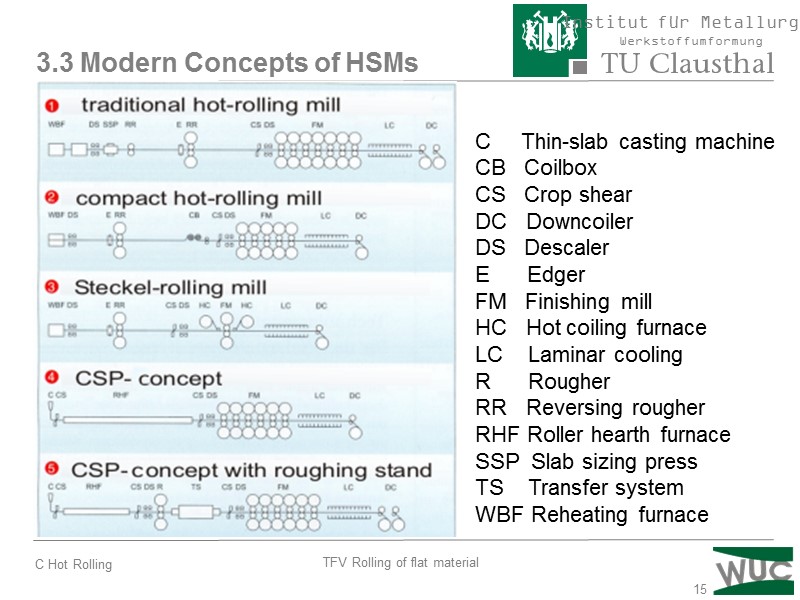
 15 3.3 Modern Concepts of HSMs C Thin-slab casting machine CB Coilbox CS Crop shear DC Downcoiler DS Descaler E Edger FM Finishing mill HC Hot coiling furnace LC Laminar cooling R Rougher RR Reversing rougher RHF Roller hearth furnace SSP Slab sizing press TS Transfer system WBF Reheating furnace
15 3.3 Modern Concepts of HSMs C Thin-slab casting machine CB Coilbox CS Crop shear DC Downcoiler DS Descaler E Edger FM Finishing mill HC Hot coiling furnace LC Laminar cooling R Rougher RR Reversing rougher RHF Roller hearth furnace SSP Slab sizing press TS Transfer system WBF Reheating furnace
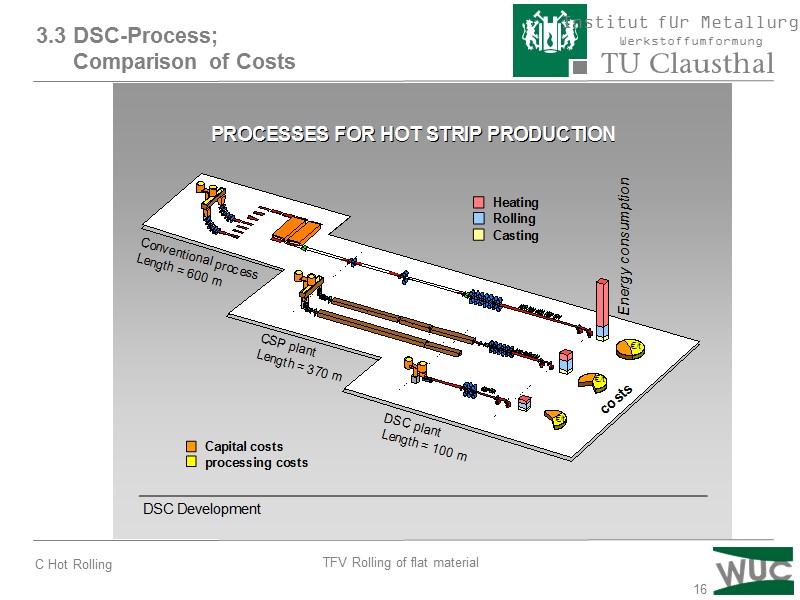
 16 3.3 DSC-Process; Comparison of Costs
16 3.3 DSC-Process; Comparison of Costs
 17 Operator‘s business at HSM HSM 1st generation HSM 5th generation 3.3 Operating HSM of 1st and 5th Generation (Source: Hoesch Archiv. Zeitschrift „Werk und Wir“. Ausgabe 10/1958) Source: SMS DEMAG
17 Operator‘s business at HSM HSM 1st generation HSM 5th generation 3.3 Operating HSM of 1st and 5th Generation (Source: Hoesch Archiv. Zeitschrift „Werk und Wir“. Ausgabe 10/1958) Source: SMS DEMAG
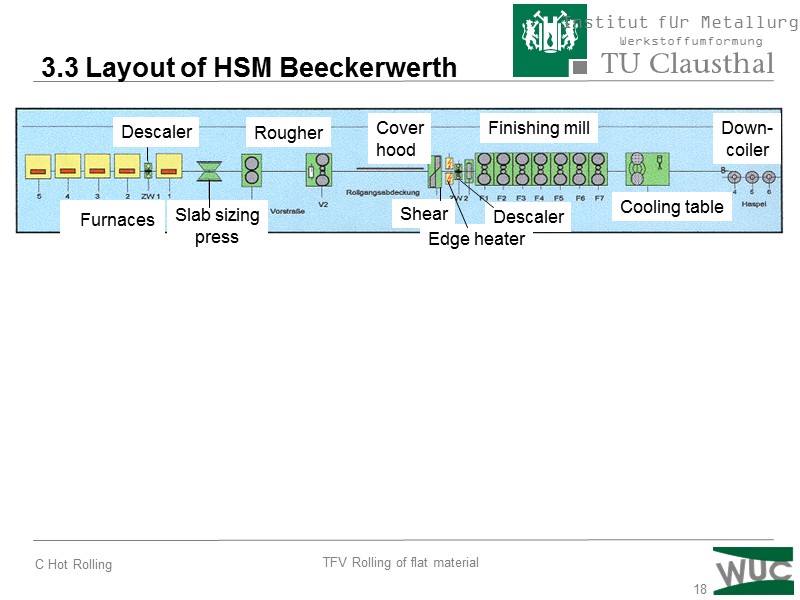
 18 3.3 Layout of HSM Beeckerwerth Furnaces Descaler Rougher Slab sizing press Cover hood Shear Descaler Finishing mill Edge heater Cooling table Down- coiler
18 3.3 Layout of HSM Beeckerwerth Furnaces Descaler Rougher Slab sizing press Cover hood Shear Descaler Finishing mill Edge heater Cooling table Down- coiler
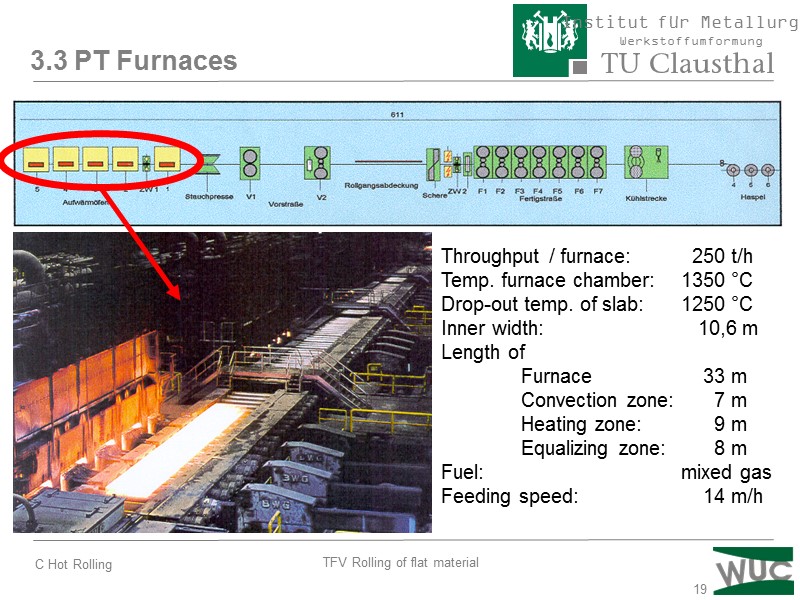
 19 3.3 PT Furnaces TKS Beeckerwerth Throughput / furnace: 250 t/h Temp. furnace chamber: 1350 °C Drop-out temp. of slab: 1250 °C Inner width: 10,6 m Length of Furnace 33 m Convection zone: 7 m Heating zone: 9 m Equalizing zone: 8 m Fuel: mixed gas Feeding speed: 14 m/h
19 3.3 PT Furnaces TKS Beeckerwerth Throughput / furnace: 250 t/h Temp. furnace chamber: 1350 °C Drop-out temp. of slab: 1250 °C Inner width: 10,6 m Length of Furnace 33 m Convection zone: 7 m Heating zone: 9 m Equalizing zone: 8 m Fuel: mixed gas Feeding speed: 14 m/h
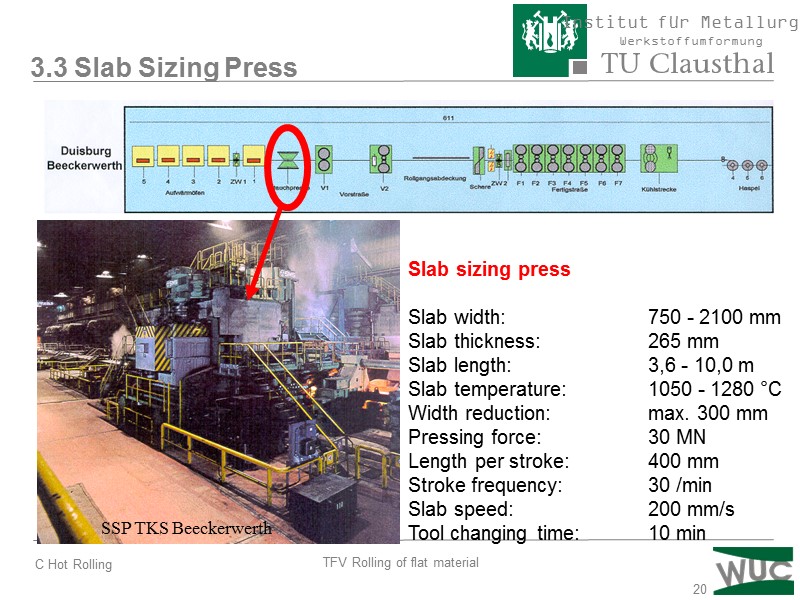
 20 Slab sizing press Slab width: 750 - 2100 mm Slab thickness: 265 mm Slab length: 3,6 - 10,0 m Slab temperature: 1050 - 1280 °C Width reduction: max. 300 mm Pressing force: 30 MN Length per stroke: 400 mm Stroke frequency: 30 /min Slab speed: 200 mm/s Tool changing time: 10 min 3.3 Slab Sizing Press SSP TKS Beeckerwerth
20 Slab sizing press Slab width: 750 - 2100 mm Slab thickness: 265 mm Slab length: 3,6 - 10,0 m Slab temperature: 1050 - 1280 °C Width reduction: max. 300 mm Pressing force: 30 MN Length per stroke: 400 mm Stroke frequency: 30 /min Slab speed: 200 mm/s Tool changing time: 10 min 3.3 Slab Sizing Press SSP TKS Beeckerwerth
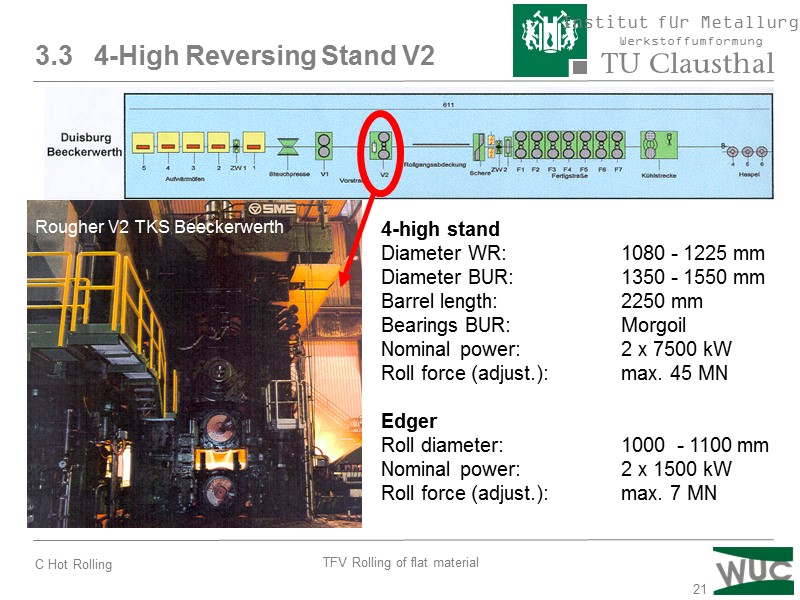
 21 4-high stand Diameter WR: 1080 - 1225 mm Diameter BUR: 1350 - 1550 mm Barrel length: 2250 mm Bearings BUR: Morgoil Nominal power: 2 x 7500 kW Roll force (adjust.): max. 45 MN Edger Roll diameter: 1000 - 1100 mm Nominal power: 2 x 1500 kW Roll force (adjust.): max. 7 MN 3.3 4-High Reversing Stand V2 Rougher V2 TKS Beeckerwerth
21 4-high stand Diameter WR: 1080 - 1225 mm Diameter BUR: 1350 - 1550 mm Barrel length: 2250 mm Bearings BUR: Morgoil Nominal power: 2 x 7500 kW Roll force (adjust.): max. 45 MN Edger Roll diameter: 1000 - 1100 mm Nominal power: 2 x 1500 kW Roll force (adjust.): max. 7 MN 3.3 4-High Reversing Stand V2 Rougher V2 TKS Beeckerwerth
 22 3.3 Roller Covers
22 3.3 Roller Covers
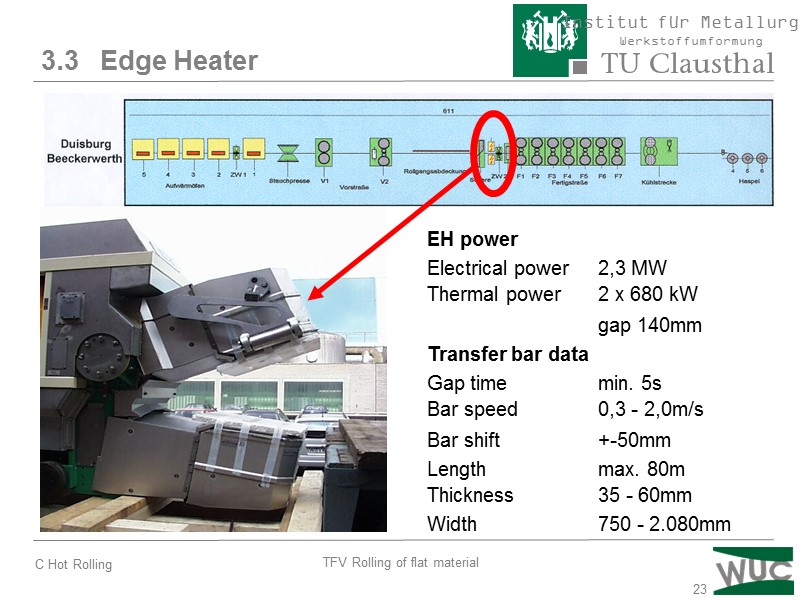
 23 EH power Electrical power 2,3 MW Thermal power 2 x 680 kW gap 140mm Transfer bar data Gap time min. 5s Bar speed 0,3 - 2,0m/s Bar shift +-50mm Length max. 80m Thickness 35 - 60mm Width 750 - 2.080mm 3.3 Edge Heater
23 EH power Electrical power 2,3 MW Thermal power 2 x 680 kW gap 140mm Transfer bar data Gap time min. 5s Bar speed 0,3 - 2,0m/s Bar shift +-50mm Length max. 80m Thickness 35 - 60mm Width 750 - 2.080mm 3.3 Edge Heater
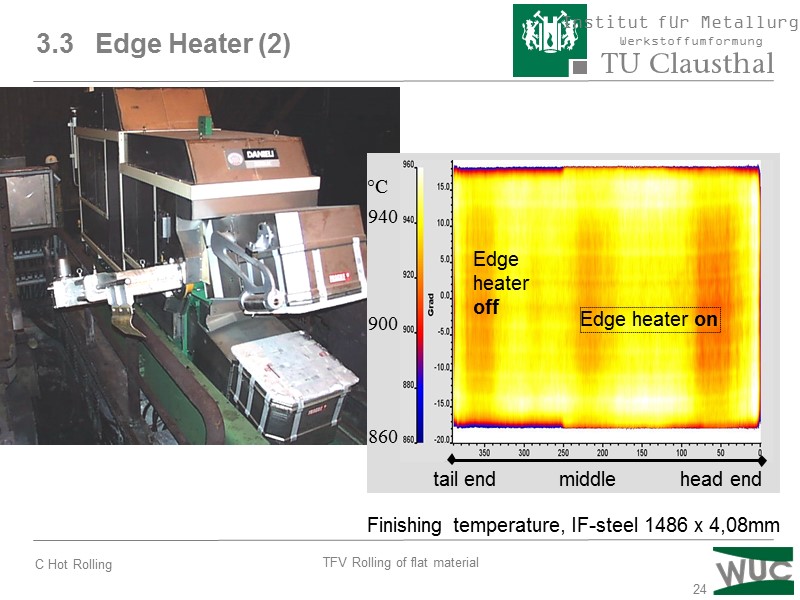
 24 3.3 Edge Heater (2)
24 3.3 Edge Heater (2)
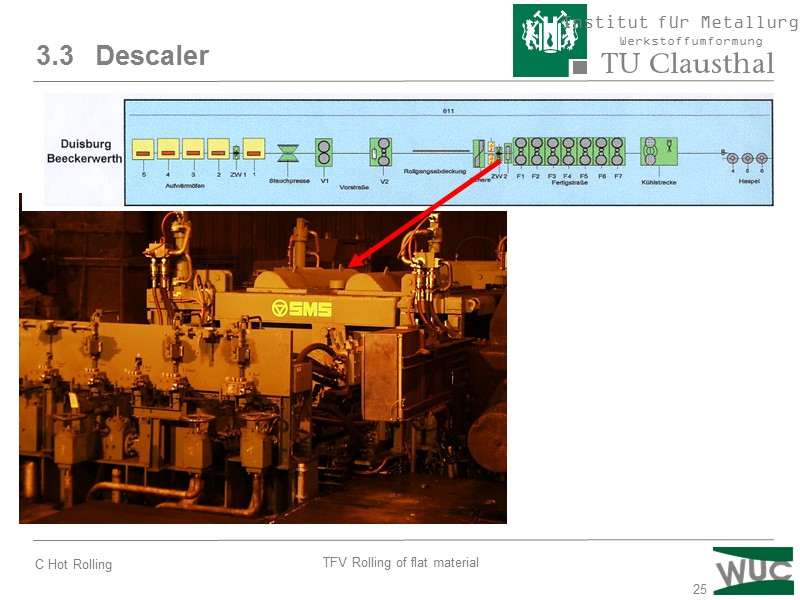
 25 3.3 Descaler
25 3.3 Descaler
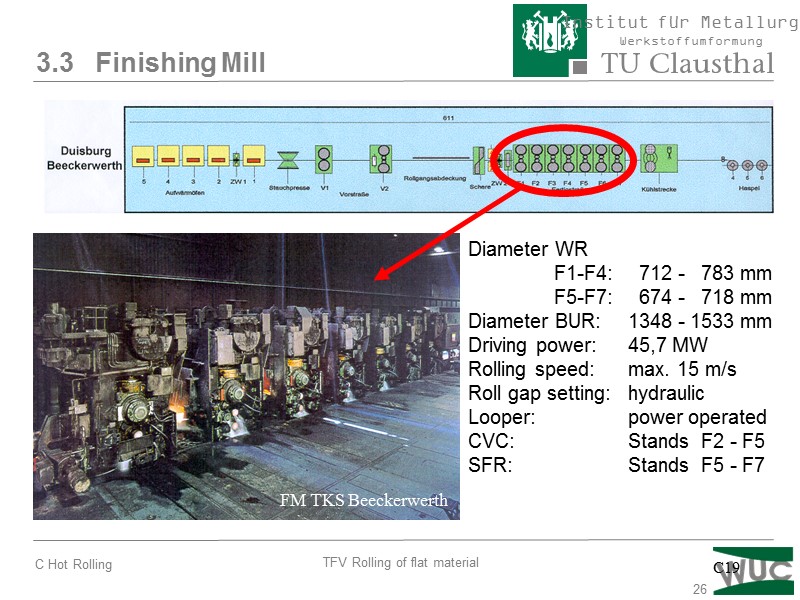
 26 3.3 Finishing Mill FM TKS Beeckerwerth Diameter WR F1-F4: 712 - 783 mm F5-F7: 674 - 718 mm Diameter BUR: 1348 - 1533 mm Driving power: 45,7 MW Rolling speed: max. 15 m/s Roll gap setting: hydraulic Looper: power operated CVC: Stands F2 - F5 SFR: Stands F5 - F7 C19
26 3.3 Finishing Mill FM TKS Beeckerwerth Diameter WR F1-F4: 712 - 783 mm F5-F7: 674 - 718 mm Diameter BUR: 1348 - 1533 mm Driving power: 45,7 MW Rolling speed: max. 15 m/s Roll gap setting: hydraulic Looper: power operated CVC: Stands F2 - F5 SFR: Stands F5 - F7 C19
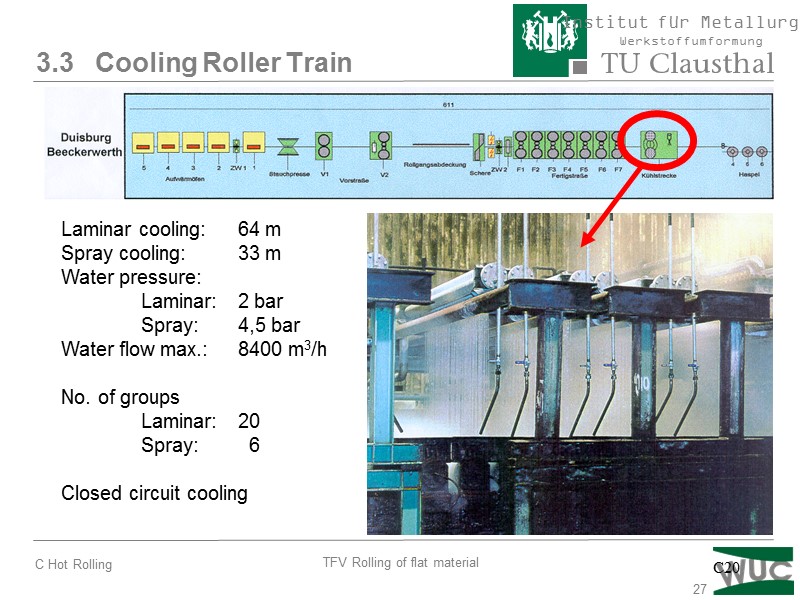
 27 3.3 Cooling Roller Train Laminar cooling: 64 m Spray cooling: 33 m Water pressure: Laminar: 2 bar Spray: 4,5 bar Water flow max.: 8400 m3/h No. of groups Laminar: 20 Spray: 6 Closed circuit cooling C20
27 3.3 Cooling Roller Train Laminar cooling: 64 m Spray cooling: 33 m Water pressure: Laminar: 2 bar Spray: 4,5 bar Water flow max.: 8400 m3/h No. of groups Laminar: 20 Spray: 6 Closed circuit cooling C20
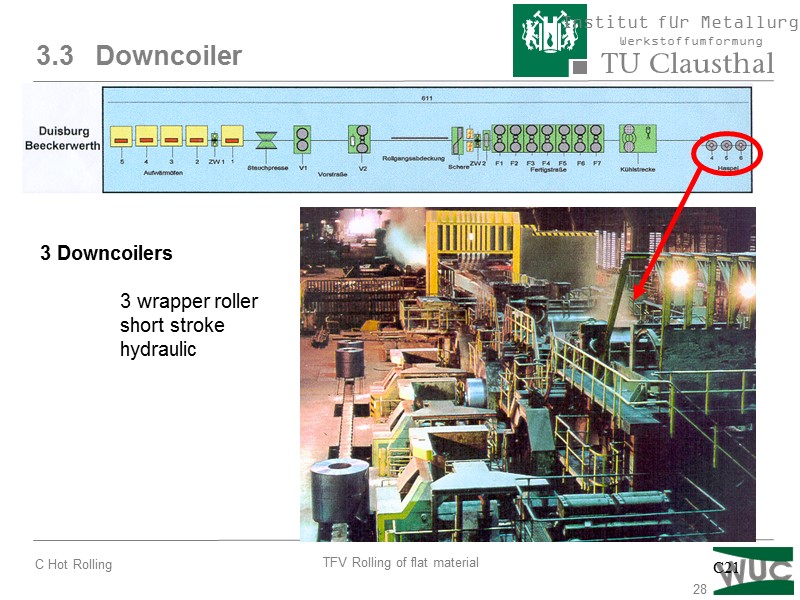
 28 3.3 Downcoiler 3 Downcoilers 3 wrapper roller short stroke hydraulic C21
28 3.3 Downcoiler 3 Downcoilers 3 wrapper roller short stroke hydraulic C21
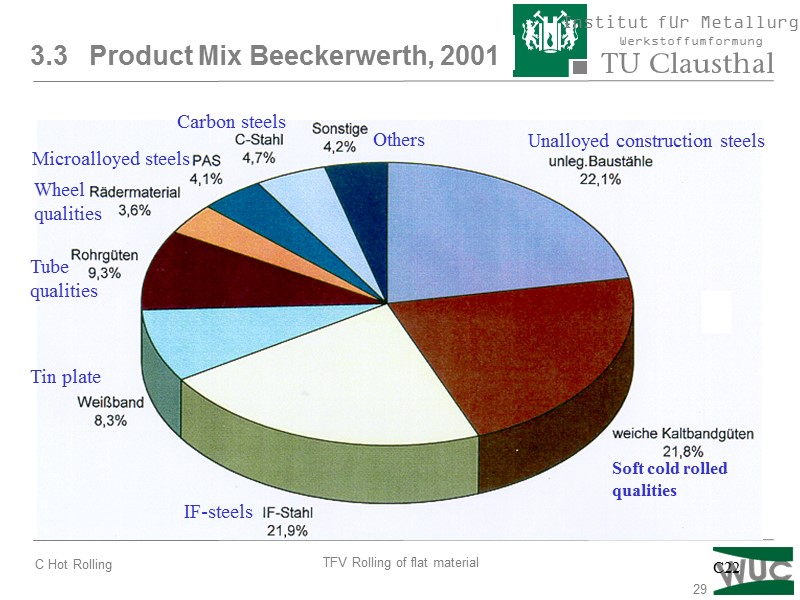
 29 3.3 Product Mix Beeckerwerth, 2001 Soft cold rolled qualities Unalloyed construction steels IF-steels Tin plate Tube qualities Wheel qualities Microalloyed steels Carbon steels Others C22
29 3.3 Product Mix Beeckerwerth, 2001 Soft cold rolled qualities Unalloyed construction steels IF-steels Tin plate Tube qualities Wheel qualities Microalloyed steels Carbon steels Others C22
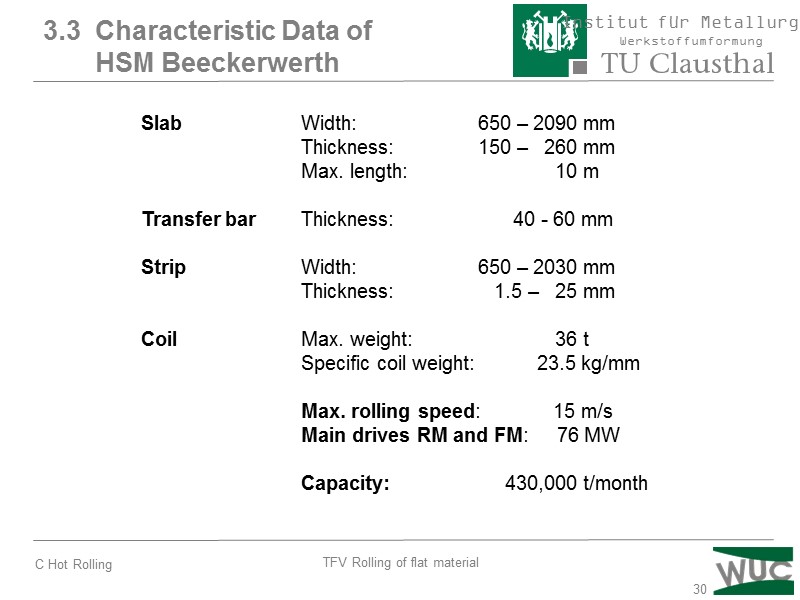
 30 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Beeckerwerth Slab Width: 650 – 2090 mm Thickness: 150 – 260 mm Max. length: 10 m Transfer bar Thickness: 40 - 60 mm Strip Width: 650 – 2030 mm Thickness: 1.5 – 25 mm Coil Max. weight: 36 t Specific coil weight: 23.5 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 15 m/s Main drives RM and FM: 76 MW Capacity: 430,000 t/month
30 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Beeckerwerth Slab Width: 650 – 2090 mm Thickness: 150 – 260 mm Max. length: 10 m Transfer bar Thickness: 40 - 60 mm Strip Width: 650 – 2030 mm Thickness: 1.5 – 25 mm Coil Max. weight: 36 t Specific coil weight: 23.5 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 15 m/s Main drives RM and FM: 76 MW Capacity: 430,000 t/month
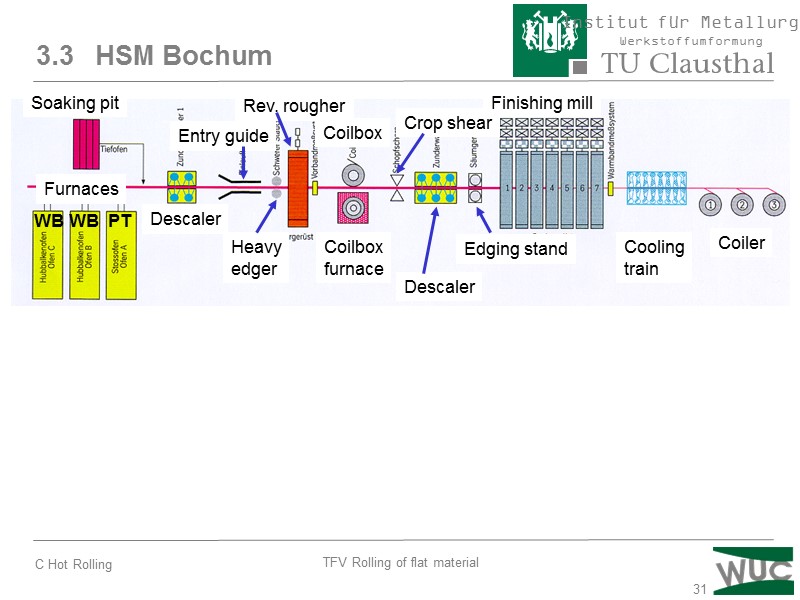
 31 3.3 HSM Bochum
31 3.3 HSM Bochum
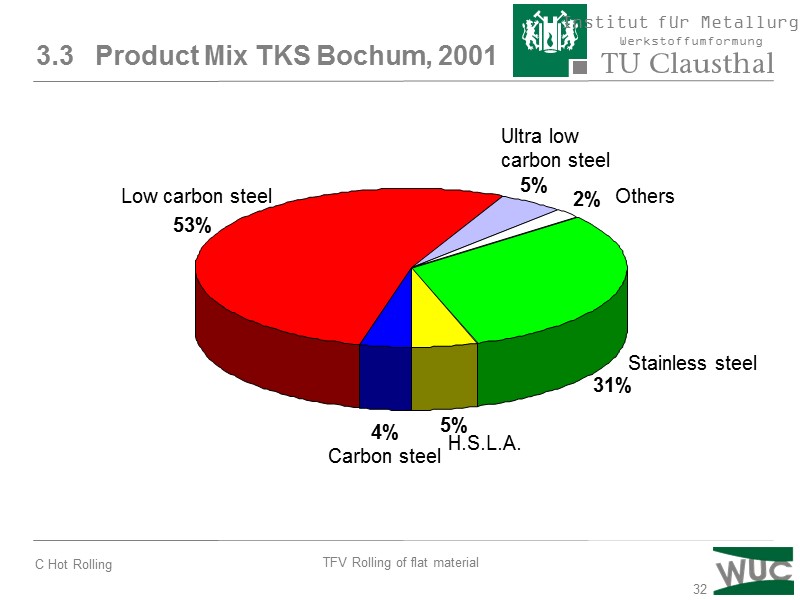
 32 4% 5% 31% 5% 2% 53% 3.3 Product Mix TKS Bochum, 2001 Low carbon steel Ultra low carbon steel Others Stainless steel H.S.L.A. Carbon steel
32 4% 5% 31% 5% 2% 53% 3.3 Product Mix TKS Bochum, 2001 Low carbon steel Ultra low carbon steel Others Stainless steel H.S.L.A. Carbon steel
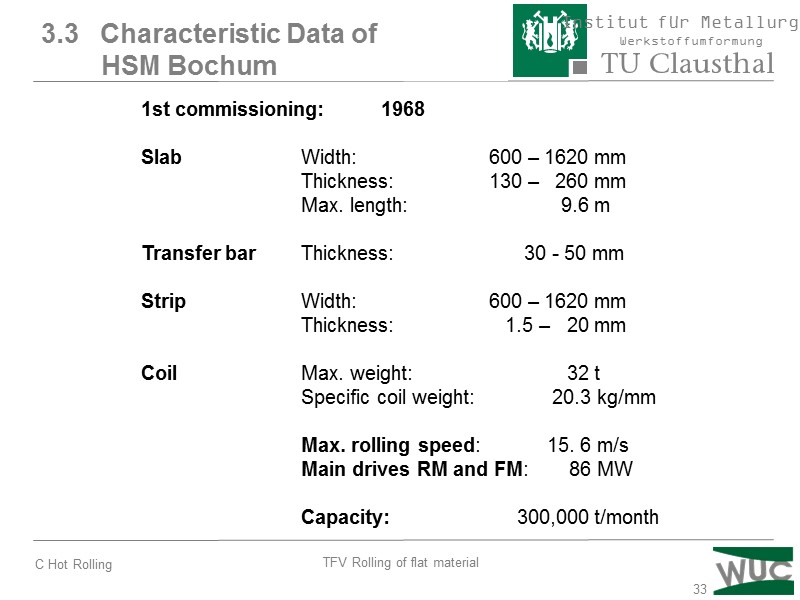
 33 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Bochum 1st commissioning: 1968 Slab Width: 600 – 1620 mm Thickness: 130 – 260 mm Max. length: 9.6 m Transfer bar Thickness: 30 - 50 mm Strip Width: 600 – 1620 mm Thickness: 1.5 – 20 mm Coil Max. weight: 32 t Specific coil weight: 20.3 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 15. 6 m/s Main drives RM and FM: 86 MW Capacity: 300,000 t/month
33 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Bochum 1st commissioning: 1968 Slab Width: 600 – 1620 mm Thickness: 130 – 260 mm Max. length: 9.6 m Transfer bar Thickness: 30 - 50 mm Strip Width: 600 – 1620 mm Thickness: 1.5 – 20 mm Coil Max. weight: 32 t Specific coil weight: 20.3 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 15. 6 m/s Main drives RM and FM: 86 MW Capacity: 300,000 t/month
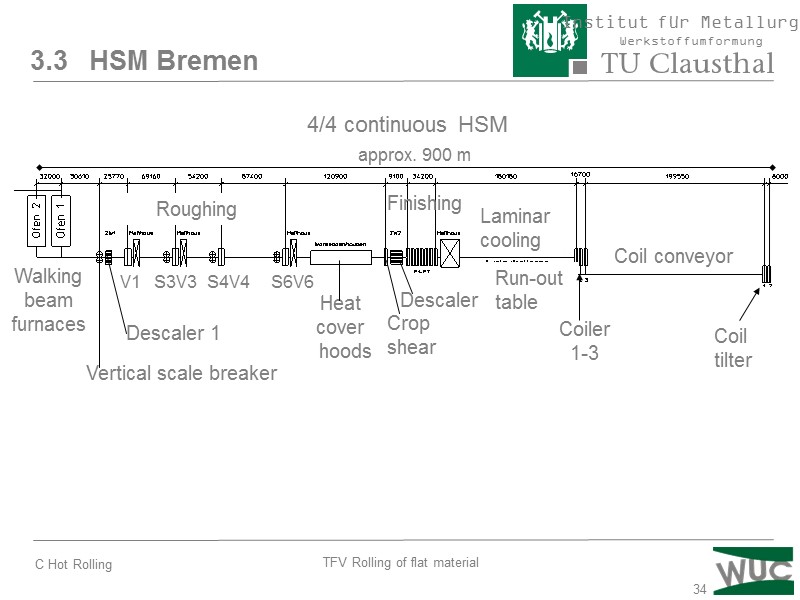
 34 3.3 HSM Bremen
34 3.3 HSM Bremen
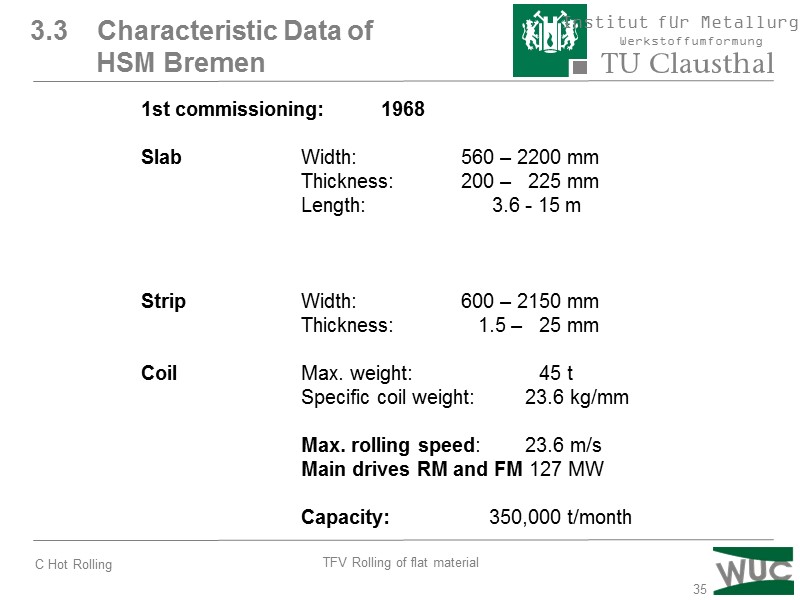
 35 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Bremen 1st commissioning: 1968 Slab Width: 560 – 2200 mm Thickness: 200 – 225 mm Length: 3.6 - 15 m Strip Width: 600 – 2150 mm Thickness: 1.5 – 25 mm Coil Max. weight: 45 t Specific coil weight: 23.6 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 23.6 m/s Main drives RM and FM 127 MW Capacity: 350,000 t/month
35 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Bremen 1st commissioning: 1968 Slab Width: 560 – 2200 mm Thickness: 200 – 225 mm Length: 3.6 - 15 m Strip Width: 600 – 2150 mm Thickness: 1.5 – 25 mm Coil Max. weight: 45 t Specific coil weight: 23.6 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 23.6 m/s Main drives RM and FM 127 MW Capacity: 350,000 t/month
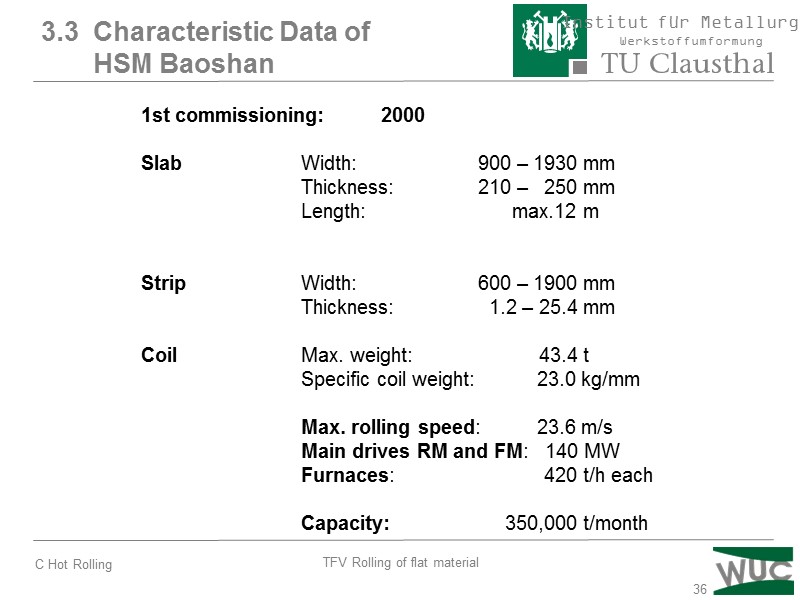
 36 1st commissioning: 2000 Slab Width: 900 – 1930 mm Thickness: 210 – 250 mm Length: max.12 m Strip Width: 600 – 1900 mm Thickness: 1.2 – 25.4 mm Coil Max. weight: 43.4 t Specific coil weight: 23.0 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 23.6 m/s Main drives RM and FM: 140 MW Furnaces: 420 t/h each Capacity: 350,000 t/month 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Baoshan
36 1st commissioning: 2000 Slab Width: 900 – 1930 mm Thickness: 210 – 250 mm Length: max.12 m Strip Width: 600 – 1900 mm Thickness: 1.2 – 25.4 mm Coil Max. weight: 43.4 t Specific coil weight: 23.0 kg/mm Max. rolling speed: 23.6 m/s Main drives RM and FM: 140 MW Furnaces: 420 t/h each Capacity: 350,000 t/month 3.3 Characteristic Data of HSM Baoshan
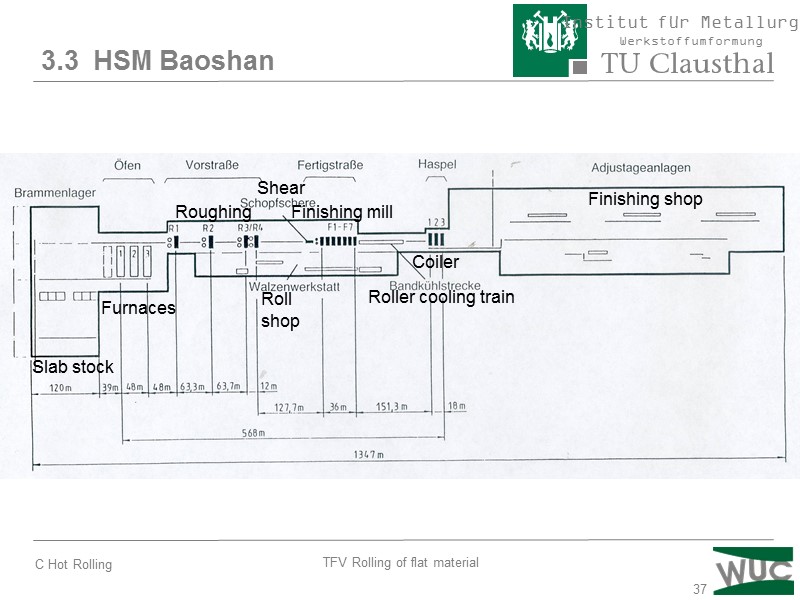
 37 3.3 HSM Baoshan
37 3.3 HSM Baoshan
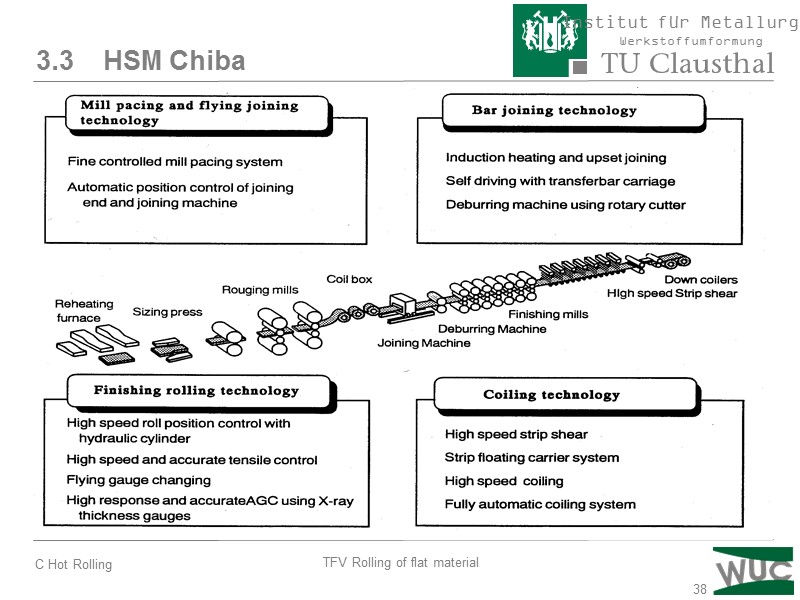
 38 3.3 HSM Chiba
38 3.3 HSM Chiba
 39 3.3 Welding Unit in HSM Chiba 3
39 3.3 Welding Unit in HSM Chiba 3
 40 3.3 CSP Technology Basic Principle
40 3.3 CSP Technology Basic Principle
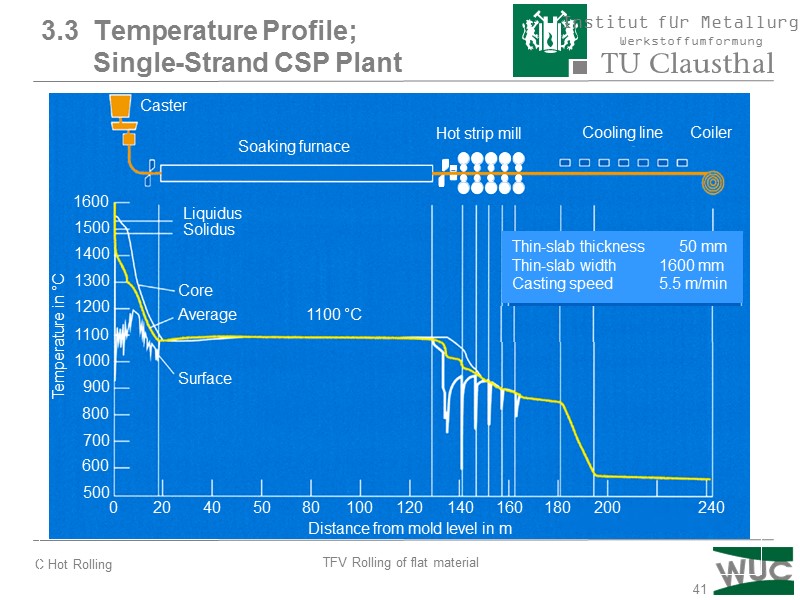
 41 220 Caster Soaking furnace Hot strip mill Cooling line Coiler Liquidus Solidus Core Average 1100 °C Surface 1600 1500 1400 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 600 500 Thin-slab thickness 50 mm Thin-slab width 1600 mm Casting speed 5.5 m/min 0 20 40 50 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 240 Distance from mold level in m Temperature in °C 3.3 Temperature Profile; Single-Strand CSP Plant
41 220 Caster Soaking furnace Hot strip mill Cooling line Coiler Liquidus Solidus Core Average 1100 °C Surface 1600 1500 1400 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 600 500 Thin-slab thickness 50 mm Thin-slab width 1600 mm Casting speed 5.5 m/min 0 20 40 50 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 240 Distance from mold level in m Temperature in °C 3.3 Temperature Profile; Single-Strand CSP Plant
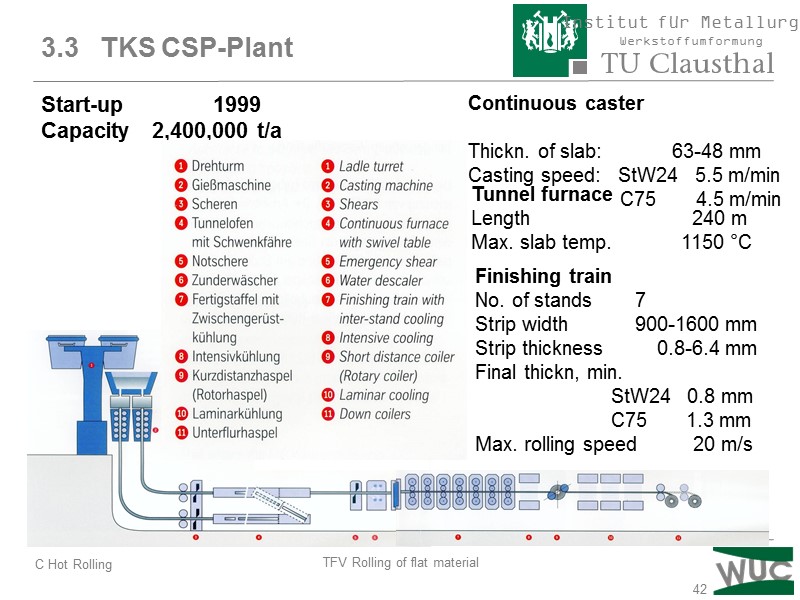
 42 Start-up 1999 Capacity 2,400,000 t/a 3.3 TKS CSP-Plant
42 Start-up 1999 Capacity 2,400,000 t/a 3.3 TKS CSP-Plant
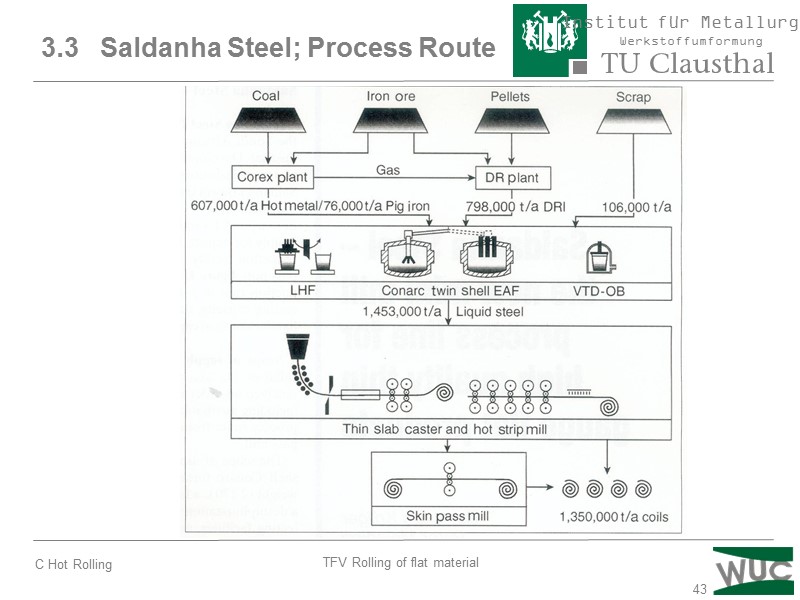
 43 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Process Route
43 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Process Route
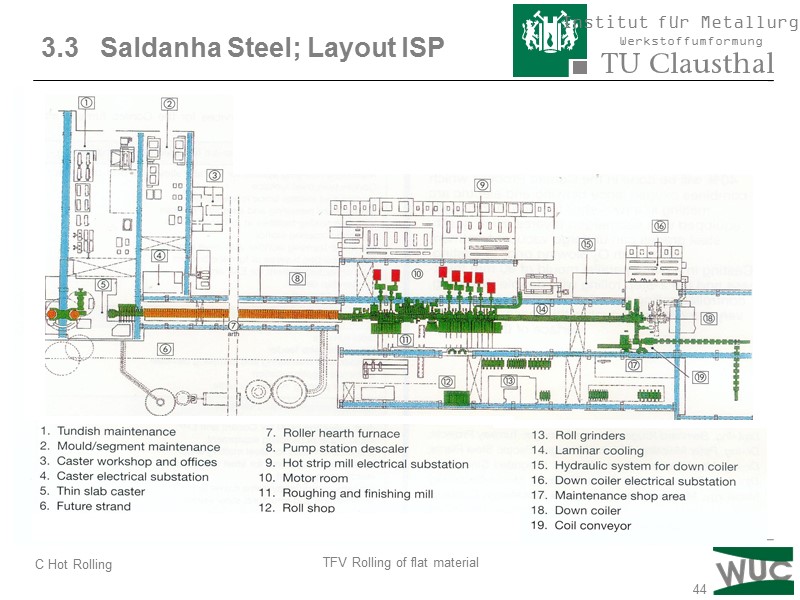
 44 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Layout ISP
44 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Layout ISP
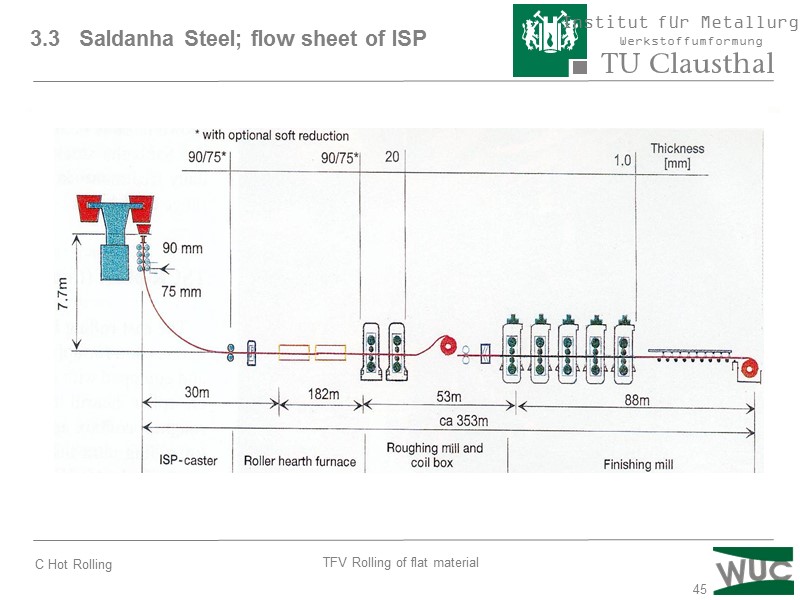
 45 3.3 Saldanha Steel; flow sheet of ISP
45 3.3 Saldanha Steel; flow sheet of ISP
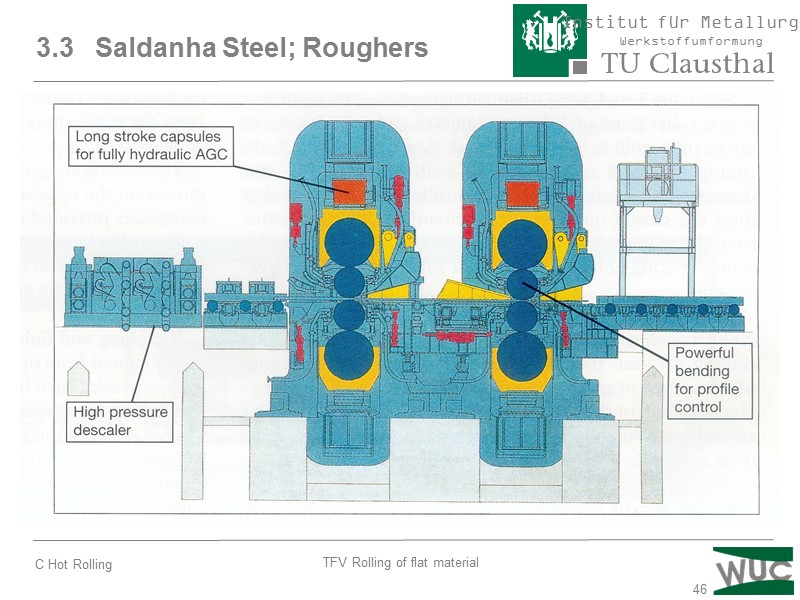
 46 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Roughers
46 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Roughers
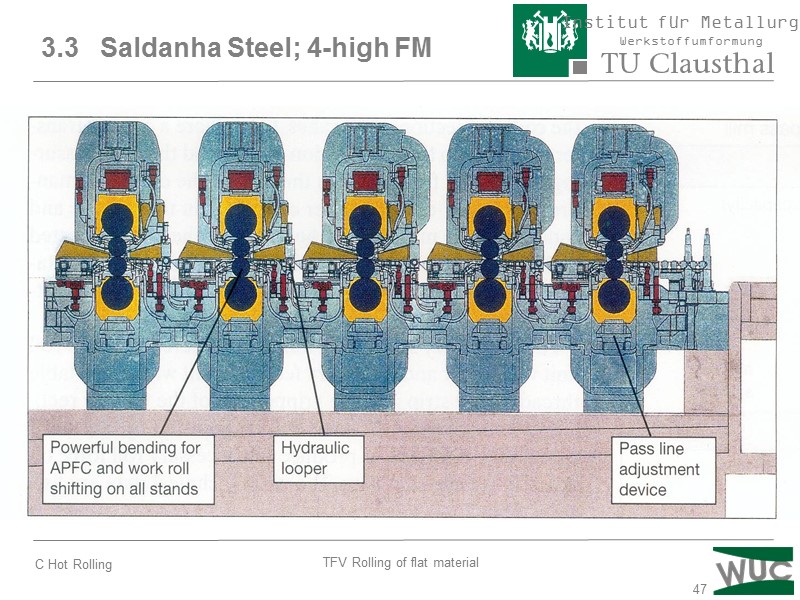
 47 3.3 Saldanha Steel; 4-high FM
47 3.3 Saldanha Steel; 4-high FM
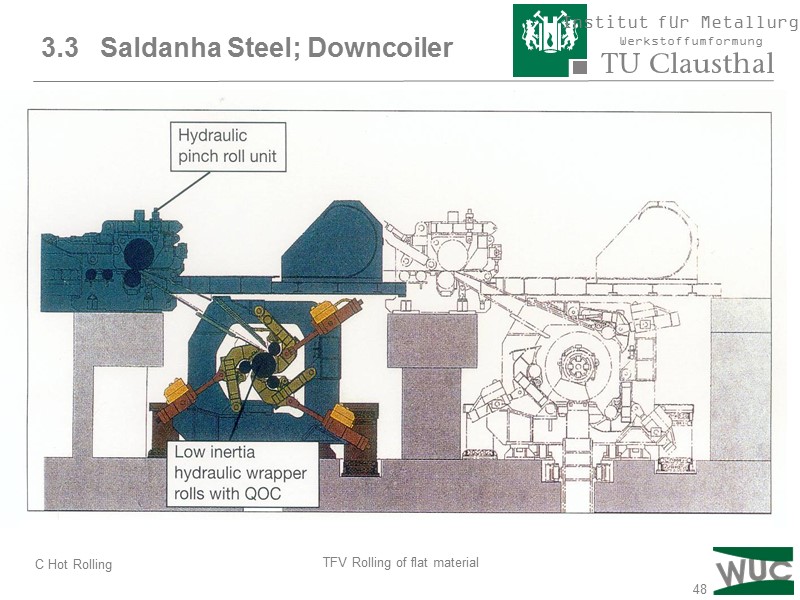
 48 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Downcoiler
48 3.3 Saldanha Steel; Downcoiler
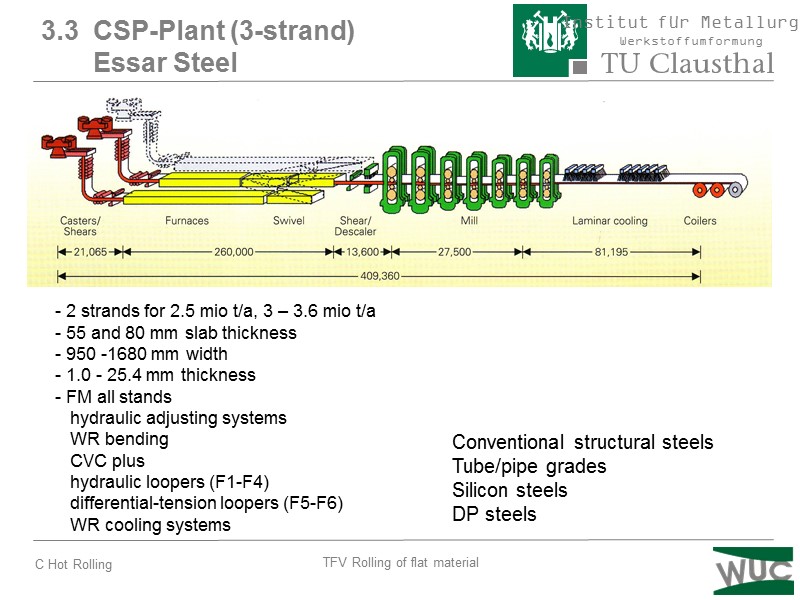
 3.3 CSP-Plant (3-strand) Essar Steel 2 strands for 2.5 mio t/a, 3 – 3.6 mio t/a 55 and 80 mm slab thickness 950 -1680 mm width 1.0 - 25.4 mm thickness FM all stands hydraulic adjusting systems WR bending CVC plus hydraulic loopers (F1-F4) differential-tension loopers (F5-F6) WR cooling systems Conventional structural steels Tube/pipe grades Silicon steels DP steels
3.3 CSP-Plant (3-strand) Essar Steel 2 strands for 2.5 mio t/a, 3 – 3.6 mio t/a 55 and 80 mm slab thickness 950 -1680 mm width 1.0 - 25.4 mm thickness FM all stands hydraulic adjusting systems WR bending CVC plus hydraulic loopers (F1-F4) differential-tension loopers (F5-F6) WR cooling systems Conventional structural steels Tube/pipe grades Silicon steels DP steels
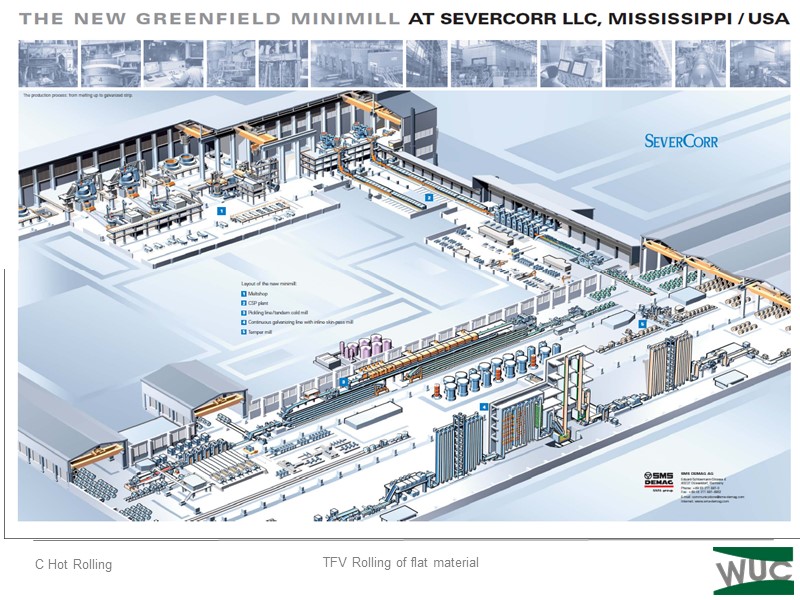
 3.3 Greenfield Minimill Severcorr LLC, Mississippi, USA
3.3 Greenfield Minimill Severcorr LLC, Mississippi, USA
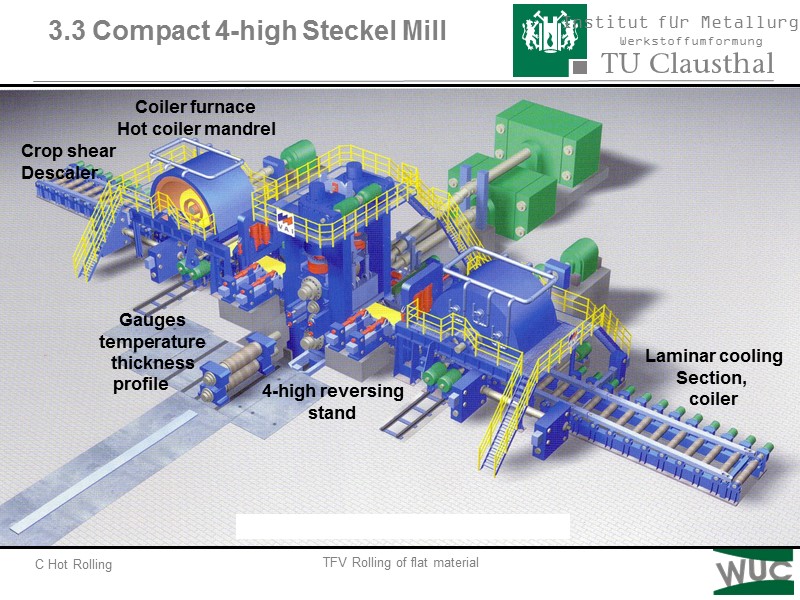
 3.3 Compact 4-high Steckel Mill
3.3 Compact 4-high Steckel Mill
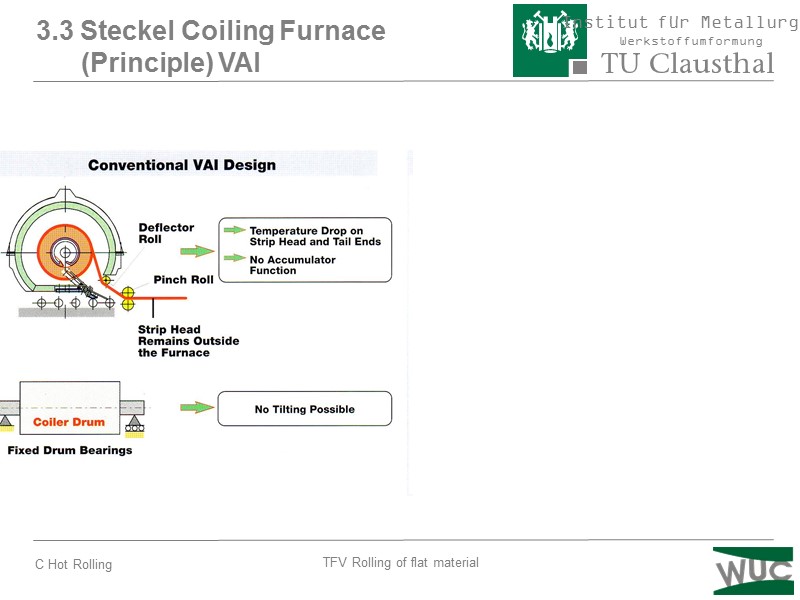
 3.3 Steckel Coiling Furnace (Principle) VAI
3.3 Steckel Coiling Furnace (Principle) VAI
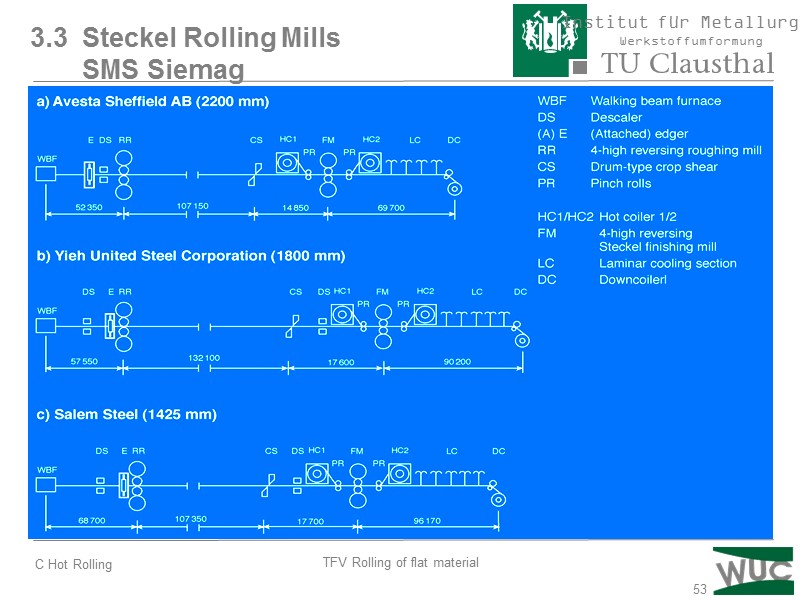
 53 3.3 Steckel Rolling Mills SMS Siemag
53 3.3 Steckel Rolling Mills SMS Siemag
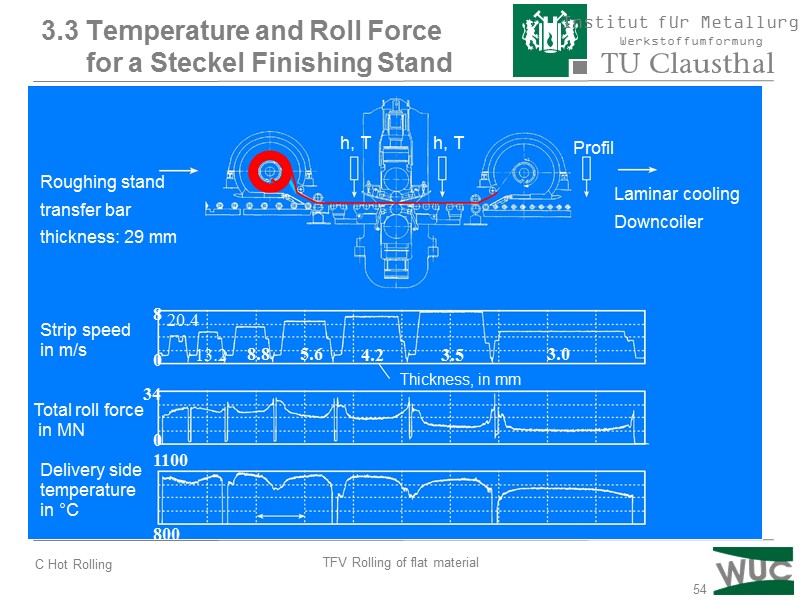
 54 Roughing stand transfer bar thickness: 29 mm h, T h, T Profil Laminar cooling Downcoiler Strip speed in m/s Total roll force in MN Delivery side temperature in °C Thickness, in mm 3.0 3.5 4.2 5.6 8.8 13.2 20.4 8 0 34 0 1100 800 3.3 Temperature and Roll Force for a Steckel Finishing Stand
54 Roughing stand transfer bar thickness: 29 mm h, T h, T Profil Laminar cooling Downcoiler Strip speed in m/s Total roll force in MN Delivery side temperature in °C Thickness, in mm 3.0 3.5 4.2 5.6 8.8 13.2 20.4 8 0 34 0 1100 800 3.3 Temperature and Roll Force for a Steckel Finishing Stand
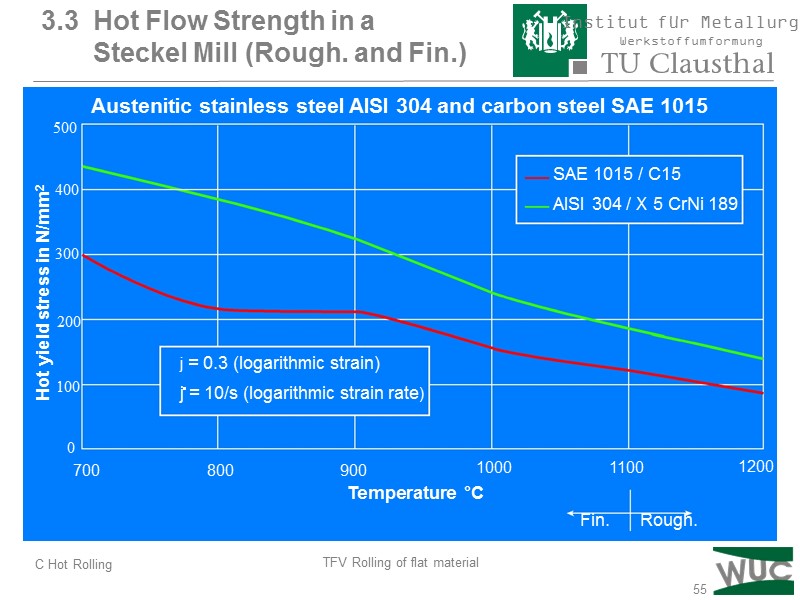
 55 Hot yield stress in N/mm2 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 SAE 1015 / C15 AISI 304 / X 5 CrNi 189 Temperature °C Fin. Rough. Austenitic stainless steel AISI 304 and carbon steel SAE 1015 3.3 Hot Flow Strength in a Steckel Mill (Rough. and Fin.) 0 100 200 300 400 500
55 Hot yield stress in N/mm2 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 SAE 1015 / C15 AISI 304 / X 5 CrNi 189 Temperature °C Fin. Rough. Austenitic stainless steel AISI 304 and carbon steel SAE 1015 3.3 Hot Flow Strength in a Steckel Mill (Rough. and Fin.) 0 100 200 300 400 500
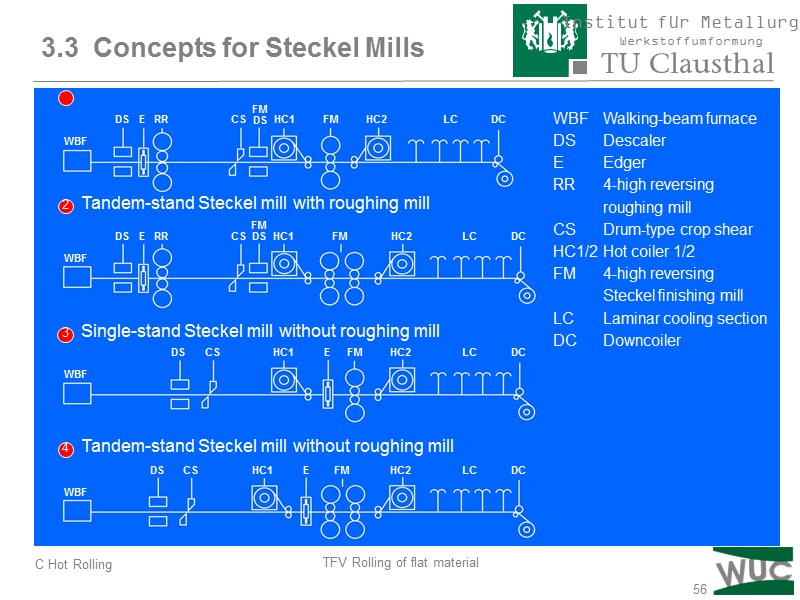
 56 WBF DS E RR CS HC1 FM HC2 LC DC WBF DS CS HC1 FM HC2 LC DC E WBF DS CS HC1 FM HC2 LC DC E FMDS 1 Single-stand Steckel mill with roughing mill 2 Tandem-stand Steckel mill with roughing mill 3 Single-stand Steckel mill without roughing mill 4 Tandem-stand Steckel mill without roughing mill WBF Walking-beam furnace DS Descaler E Edger RR 4-high reversing roughing mill CS Drum-type crop shear HC1/2 Hot coiler 1/2 FM 4-high reversing Steckel finishing mill LC Laminar cooling section DC Downcoiler 3.3 Concepts for Steckel Mills
56 WBF DS E RR CS HC1 FM HC2 LC DC WBF DS CS HC1 FM HC2 LC DC E WBF DS CS HC1 FM HC2 LC DC E FMDS 1 Single-stand Steckel mill with roughing mill 2 Tandem-stand Steckel mill with roughing mill 3 Single-stand Steckel mill without roughing mill 4 Tandem-stand Steckel mill without roughing mill WBF Walking-beam furnace DS Descaler E Edger RR 4-high reversing roughing mill CS Drum-type crop shear HC1/2 Hot coiler 1/2 FM 4-high reversing Steckel finishing mill LC Laminar cooling section DC Downcoiler 3.3 Concepts for Steckel Mills
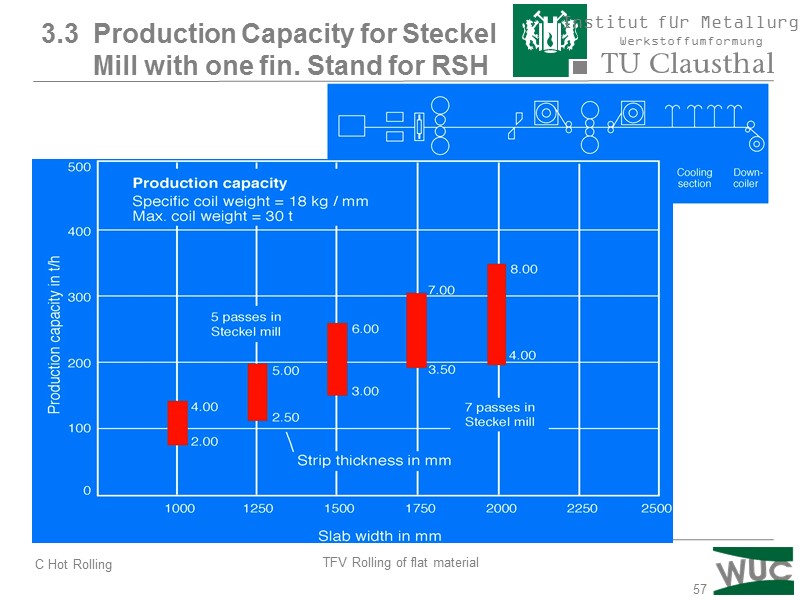
 57 3.3 Production Capacity for Steckel Mill with one fin. Stand for RSH
57 3.3 Production Capacity for Steckel Mill with one fin. Stand for RSH
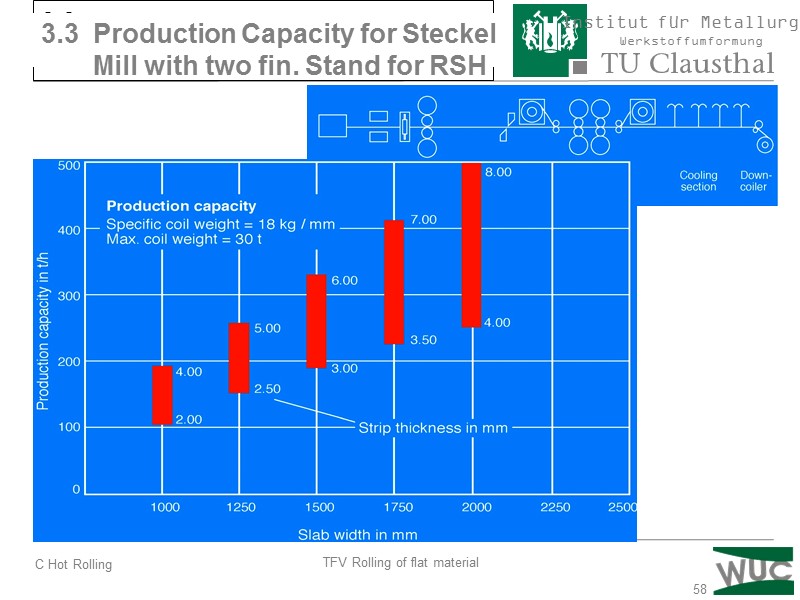
 58 3.3 Production capacity of a Steckel mill with 2 finishing stands for stainless steel 3.3 Production Capacity for Steckel Mill with two fin. Stand for RSH
58 3.3 Production capacity of a Steckel mill with 2 finishing stands for stainless steel 3.3 Production Capacity for Steckel Mill with two fin. Stand for RSH
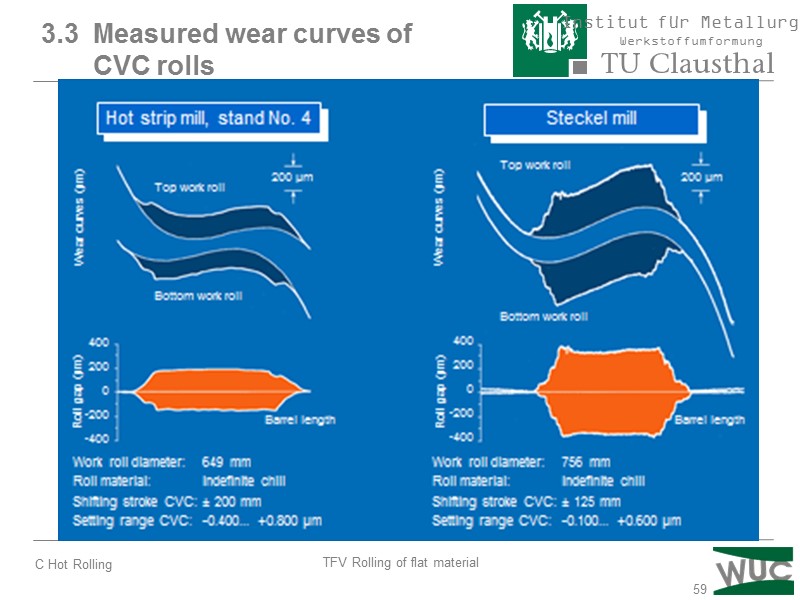
 59 3.3 Measured wear curves of CVC rolls
59 3.3 Measured wear curves of CVC rolls
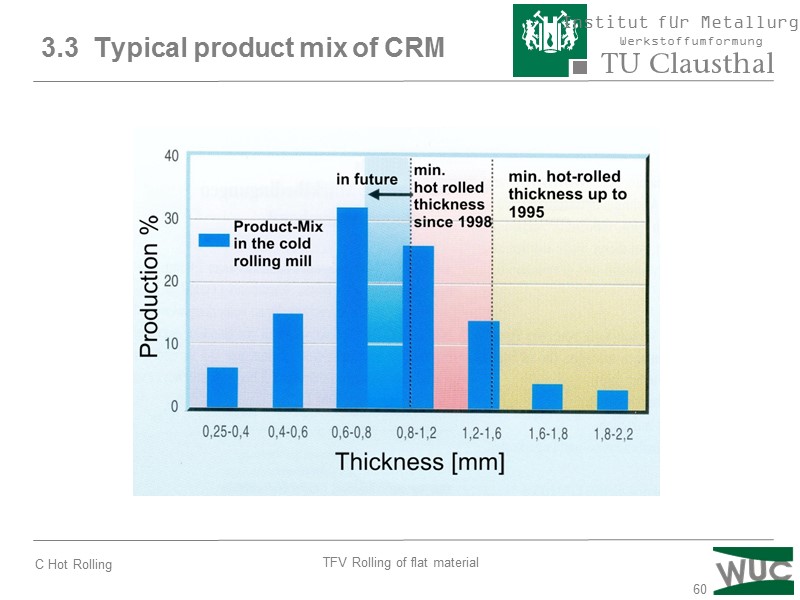
 60 3.3 Typical product mix of CRM
60 3.3 Typical product mix of CRM
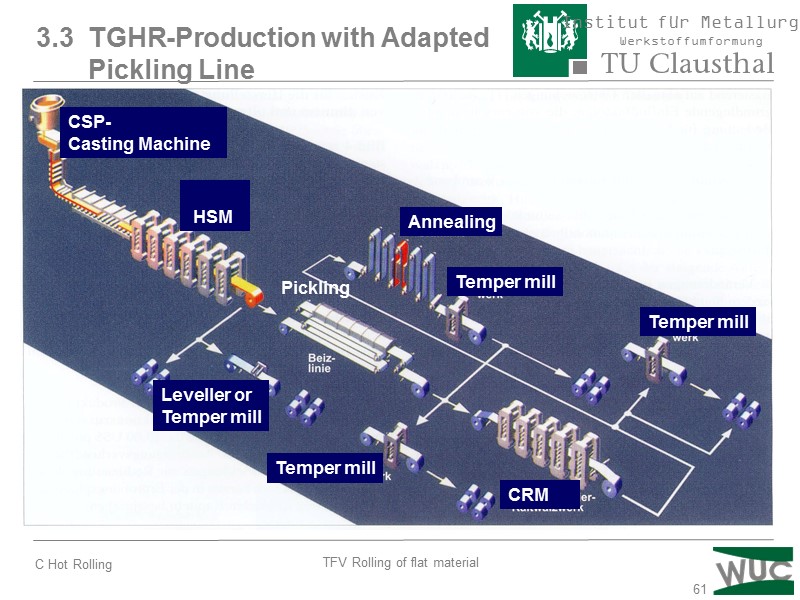
 61 3.3 TGHR-Production with Adapted Pickling Line Pickling
61 3.3 TGHR-Production with Adapted Pickling Line Pickling
 62 3.3 Technology packages for TGHR Automatic level control ALC Dynamic actions, esp. during feeding and tailing out; FFC (feed-forward-control) Improved flatness control AFC extended to front stands; improved process model for flatness and profile; shifting startegies for CVC High-speed thickness control Hydraulic AGC system (high dynamics) - resistance to mistakes in set-up - constant mass flow - high precision of stand modelling Mass flow and tension control Fast correction of differences: hydraulic looper systems, feedback control circuits tension: mechanics with low-inertia Roll gap lubrication Surface quality, roll wear and roll forces
62 3.3 Technology packages for TGHR Automatic level control ALC Dynamic actions, esp. during feeding and tailing out; FFC (feed-forward-control) Improved flatness control AFC extended to front stands; improved process model for flatness and profile; shifting startegies for CVC High-speed thickness control Hydraulic AGC system (high dynamics) - resistance to mistakes in set-up - constant mass flow - high precision of stand modelling Mass flow and tension control Fast correction of differences: hydraulic looper systems, feedback control circuits tension: mechanics with low-inertia Roll gap lubrication Surface quality, roll wear and roll forces
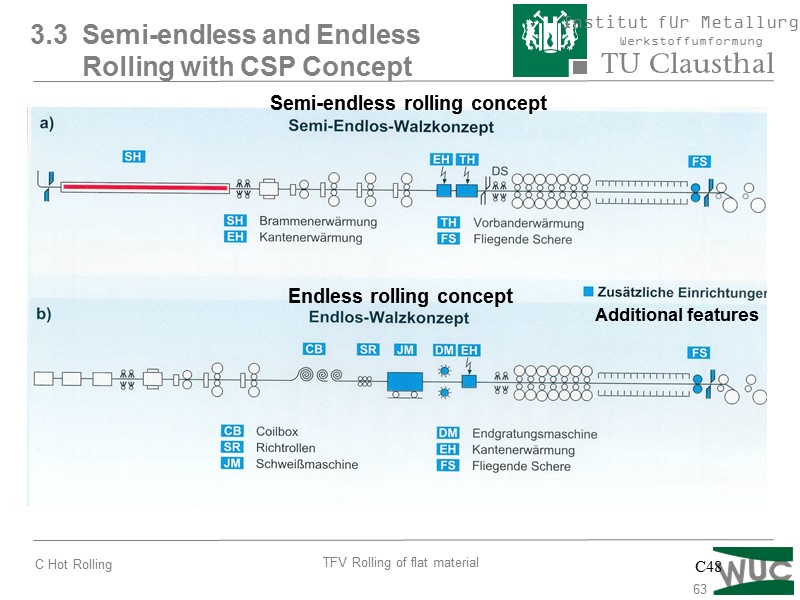
 63 C48 3.3 Semi-endless and Endless Rolling with CSP Concept Semi-endless rolling concept Endless rolling concept Additional features
63 C48 3.3 Semi-endless and Endless Rolling with CSP Concept Semi-endless rolling concept Endless rolling concept Additional features
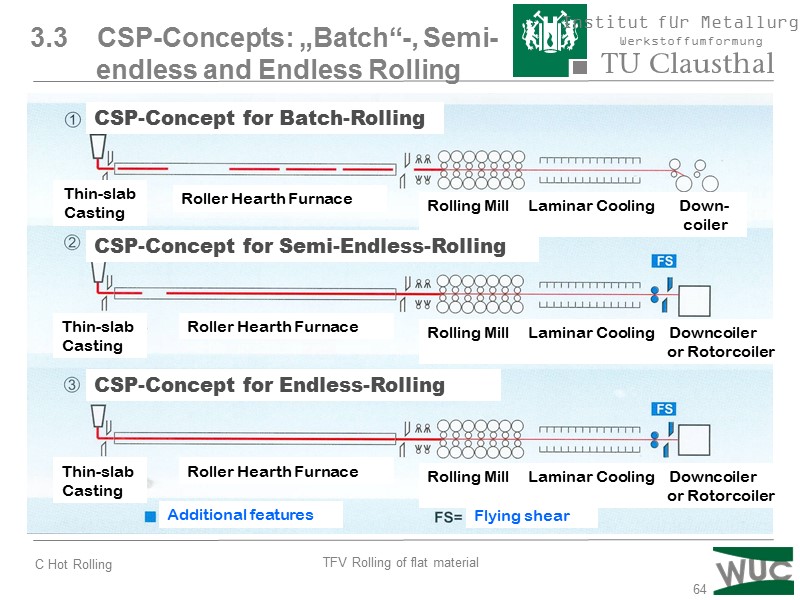
 64 3.3 CSP-Concepts: „Batch“-, Semi- endless and Endless Rolling
64 3.3 CSP-Concepts: „Batch“-, Semi- endless and Endless Rolling
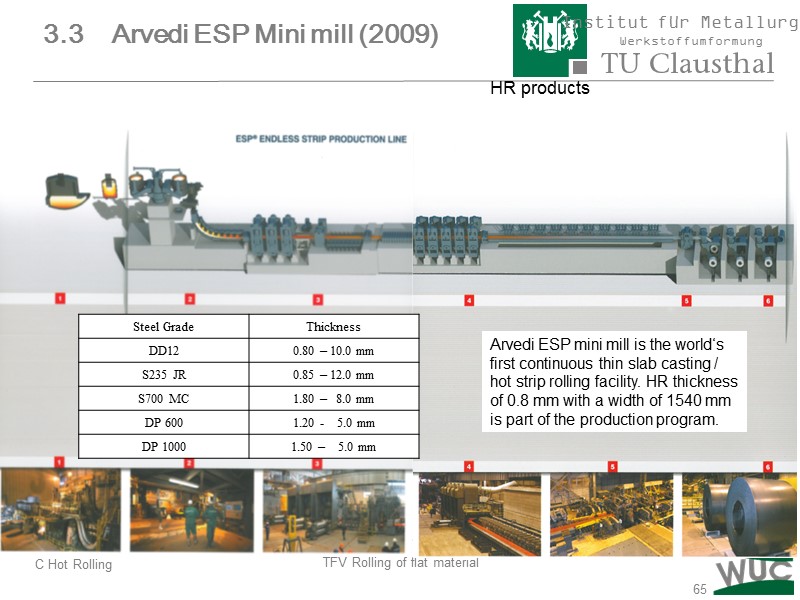
 65 HR products Arvedi ESP mini mill is the world‘s first continuous thin slab casting / hot strip rolling facility. HR thickness of 0.8 mm with a width of 1540 mm is part of the production program. 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
65 HR products Arvedi ESP mini mill is the world‘s first continuous thin slab casting / hot strip rolling facility. HR thickness of 0.8 mm with a width of 1540 mm is part of the production program. 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
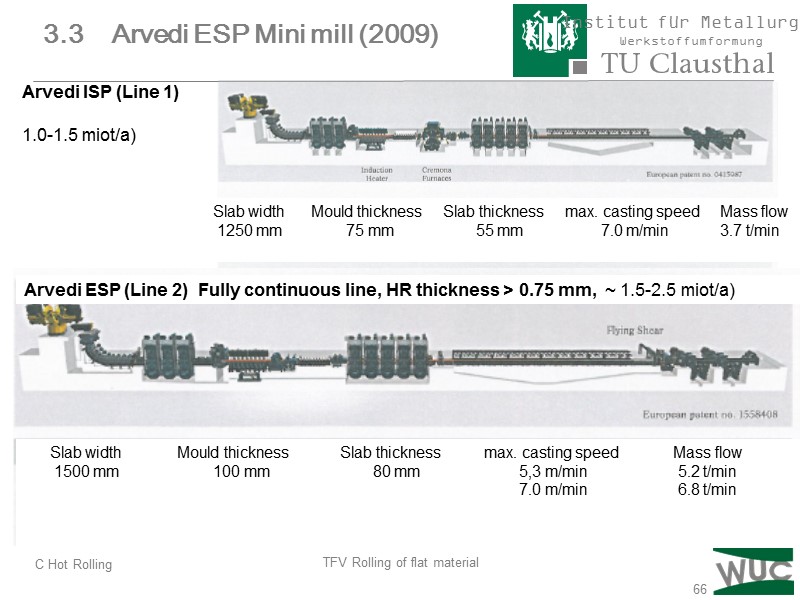
 66 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
66 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
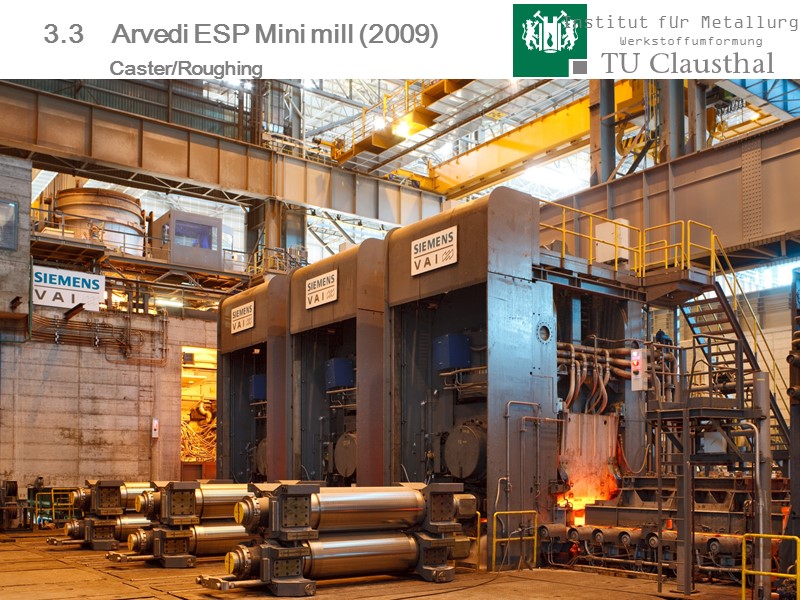
 67 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009) Caster/Roughing
67 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009) Caster/Roughing
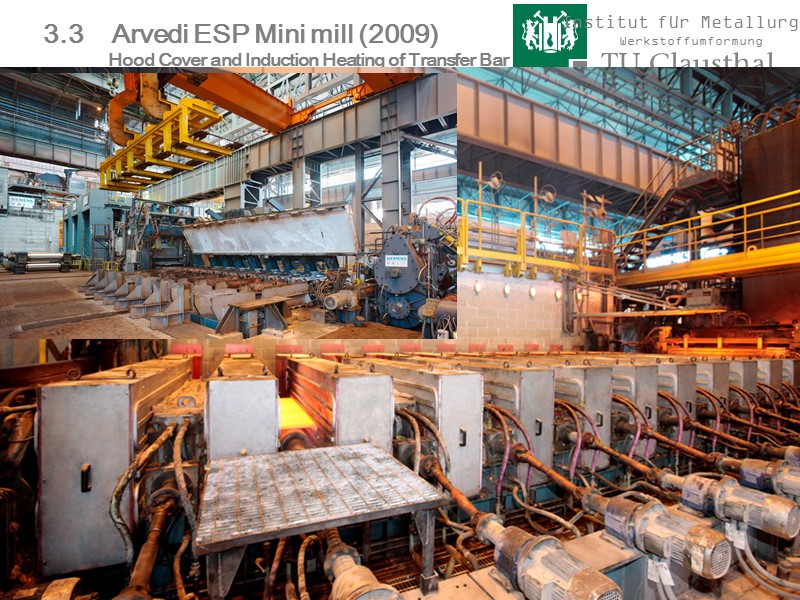
 68 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009) Hood Cover and Induction Heating of Transfer Bar
68 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009) Hood Cover and Induction Heating of Transfer Bar
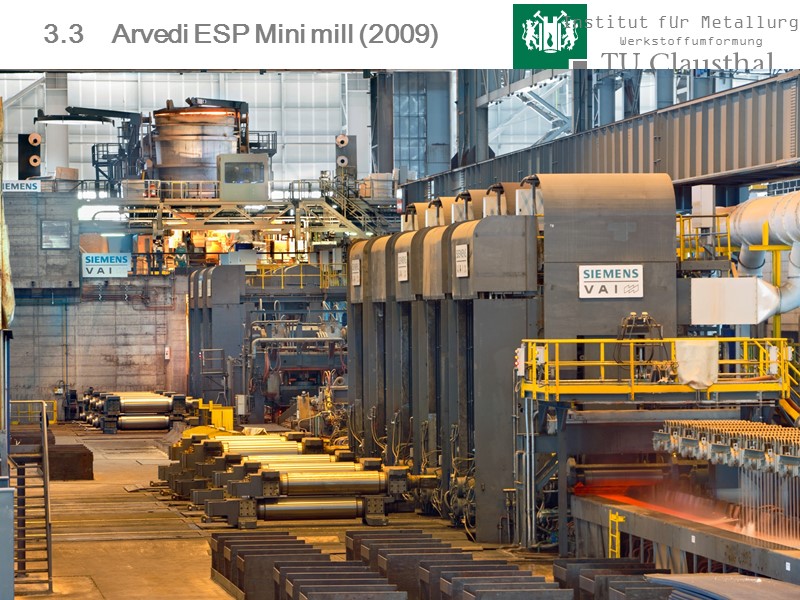
 69 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
69 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
 70 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
70 3.3 Arvedi ESP Mini mill (2009)
 71 3.3 Endless Rolling Essential steps Rolling speed about 20 m/s (austenite region even for ultra thin strip possible) Advantages - No acceleration / deceleration effects - Improved homogenity over length - Maximisation of mill working ratio Crucial - Efficient and affordable joining techniques Kawasaki: inductive welding NSC: laser welding - Coiling techniques - WR cooling
71 3.3 Endless Rolling Essential steps Rolling speed about 20 m/s (austenite region even for ultra thin strip possible) Advantages - No acceleration / deceleration effects - Improved homogenity over length - Maximisation of mill working ratio Crucial - Efficient and affordable joining techniques Kawasaki: inductive welding NSC: laser welding - Coiling techniques - WR cooling
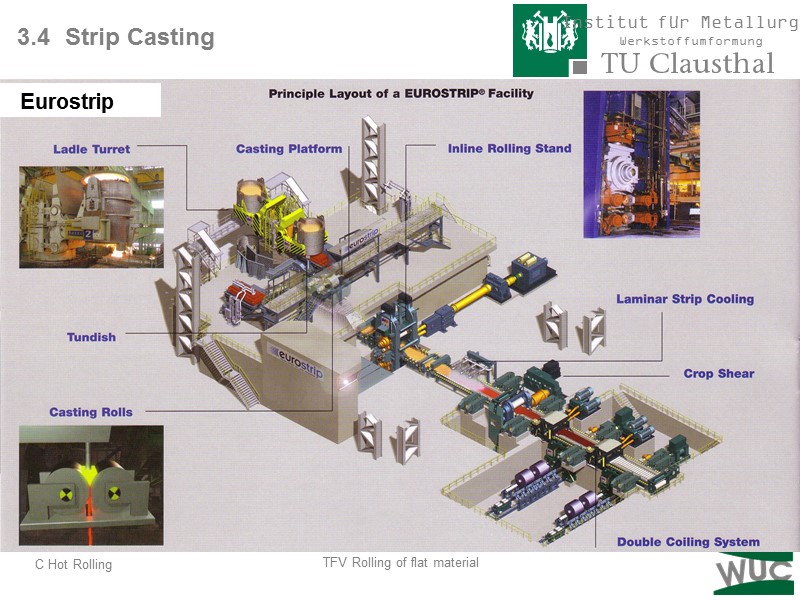
 3.4 Strip Casting Eurostrip
3.4 Strip Casting Eurostrip
 73 3.4 Strip Casting (BCT) Model of the pilot system in Peine
73 3.4 Strip Casting (BCT) Model of the pilot system in Peine
 74 3.4 Strip casting (BCT) HSD-steel-interior (seat) Fe-Mn-Al-Si-steel Exeptional properties TS 1000 – 1350 MPa YS 600 – 1100 MPa ER 50 – 17 % Adaptable for applications for crash-relevant components: Part: Side member of module seat Material: HSD 600 Weight reduction: 30 % (0.6 kg/car) Crash demands as a component and test drive fulfilled!
74 3.4 Strip casting (BCT) HSD-steel-interior (seat) Fe-Mn-Al-Si-steel Exeptional properties TS 1000 – 1350 MPa YS 600 – 1100 MPa ER 50 – 17 % Adaptable for applications for crash-relevant components: Part: Side member of module seat Material: HSD 600 Weight reduction: 30 % (0.6 kg/car) Crash demands as a component and test drive fulfilled!
 75 3.4 Strip casting (BCT) HCT780XD 1.25 mm HSD1100 1.05 mm HSD-Stahl Seitenaufprallträger Potential analysis (Audi AG) Serial part: HCT780XD, 1.25 mm Test: Pile set test, comparison of force-way Crash performance: improved using HSD1100, 1.05 mm adaption of geometry Weight reduction: 17 % (230 g/part)
75 3.4 Strip casting (BCT) HCT780XD 1.25 mm HSD1100 1.05 mm HSD-Stahl Seitenaufprallträger Potential analysis (Audi AG) Serial part: HCT780XD, 1.25 mm Test: Pile set test, comparison of force-way Crash performance: improved using HSD1100, 1.05 mm adaption of geometry Weight reduction: 17 % (230 g/part)
 76 3.4 Cobble in HSM
76 3.4 Cobble in HSM
 77 3.4 Cobble on ROT or Coiler
77 3.4 Cobble on ROT or Coiler
 78 3.4 Art in Processing
78 3.4 Art in Processing

