 1
1
 2
2
 Priority 3
Priority 3
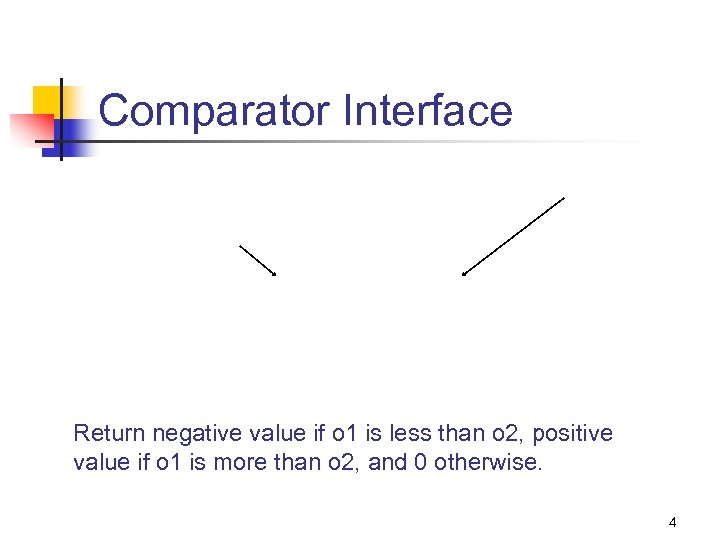 Comparator Interface Return negative value if o 1 is less than o 2, positive value if o 1 is more than o 2, and 0 otherwise. 4
Comparator Interface Return negative value if o 1 is less than o 2, positive value if o 1 is more than o 2, and 0 otherwise. 4
 5
5
 // Precondition: must not be an empty queue, otherwise it throws No. Such. Element. Exception. // Postcondition: return the most important object from this Priority. Queue. // Precondition: must not be an empty queue, otherwise it throws No. Such. Element. Exception. // Postcondition: remove and return the most important object from this Priority. Queue. 6
// Precondition: must not be an empty queue, otherwise it throws No. Such. Element. Exception. // Postcondition: return the most important object from this Priority. Queue. // Precondition: must not be an empty queue, otherwise it throws No. Such. Element. Exception. // Postcondition: remove and return the most important object from this Priority. Queue. 6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
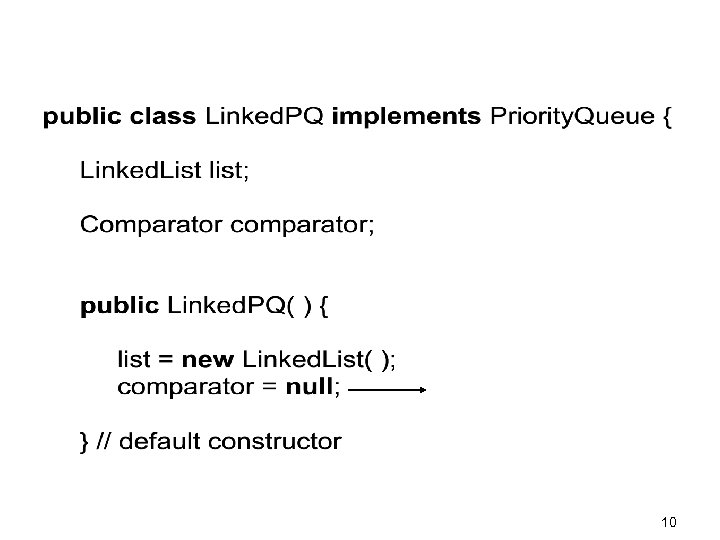 10
10
 List methods in this chapter comes from Linked. List class in Java. 11
List methods in this chapter comes from Linked. List class in Java. 11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
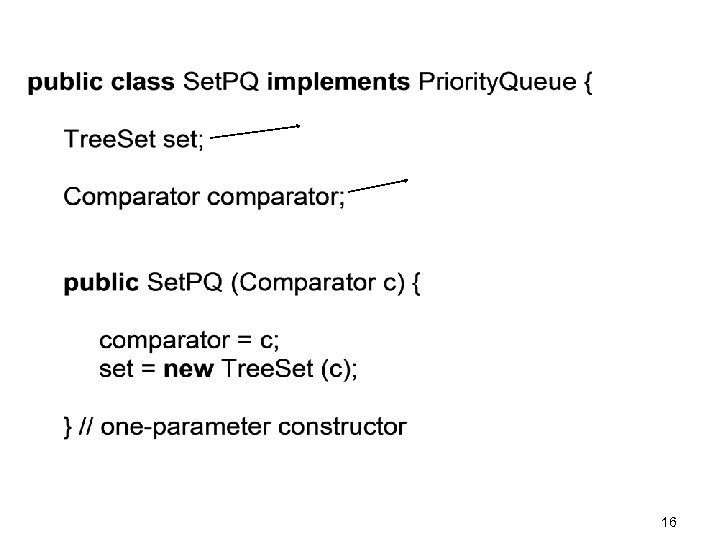 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
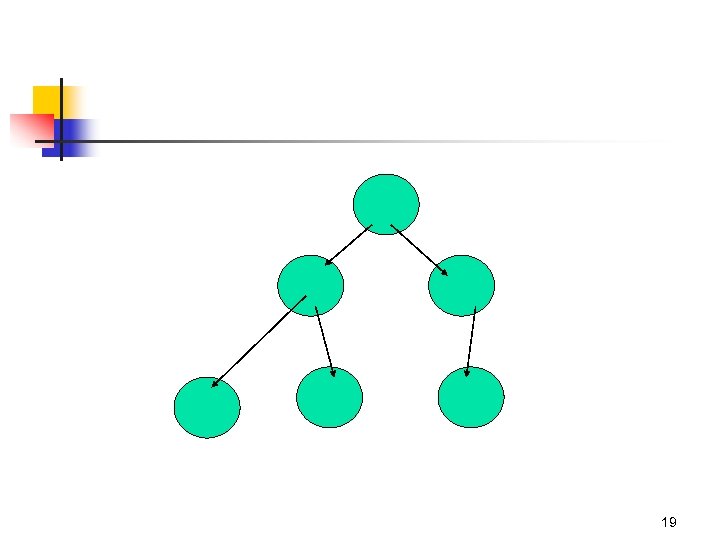 19
19
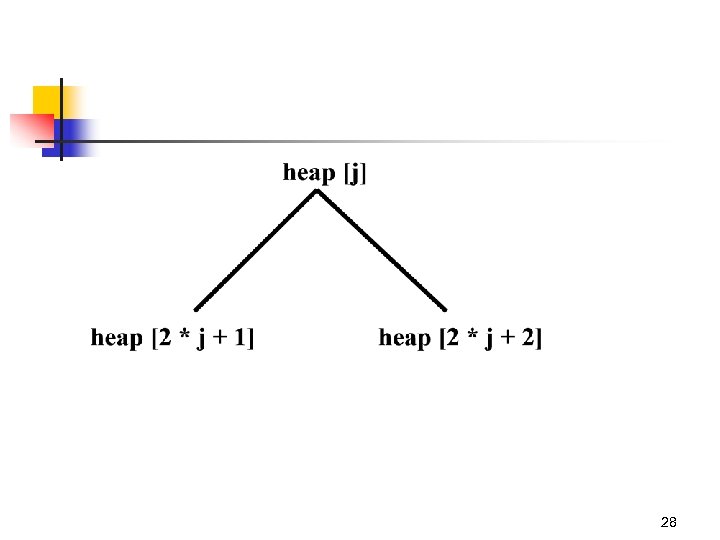
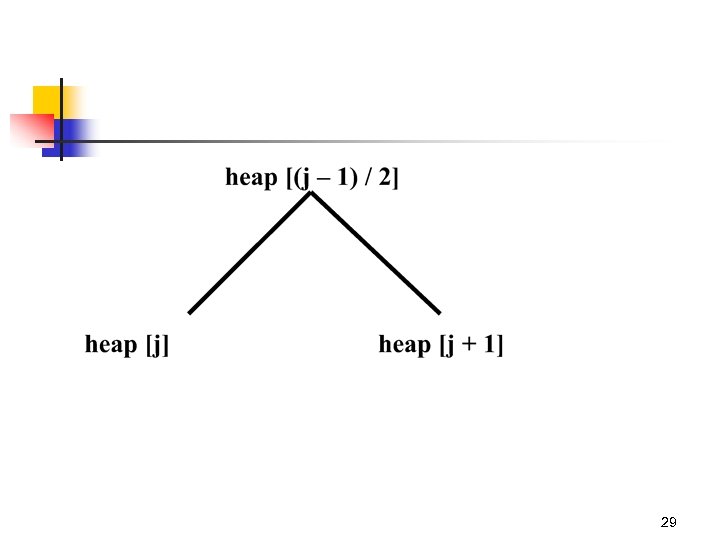
 Heap is a complete binary tree 20
Heap is a complete binary tree 20
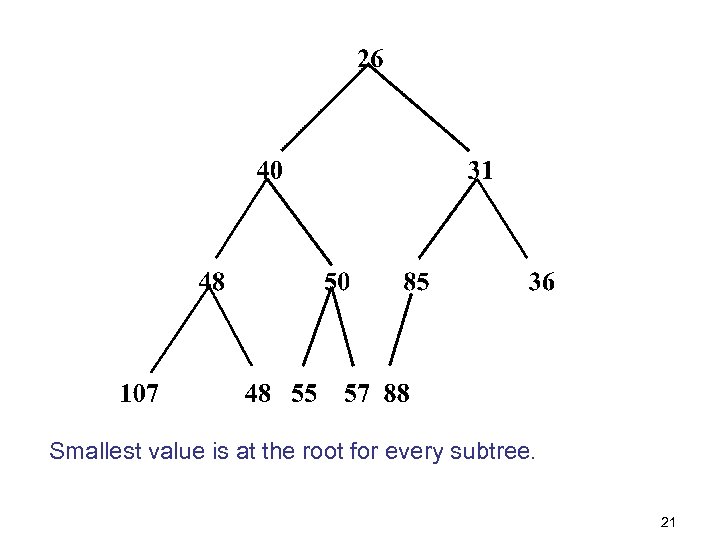 Smallest value is at the root for every subtree. 21
Smallest value is at the root for every subtree. 21
 22
22
 23
23
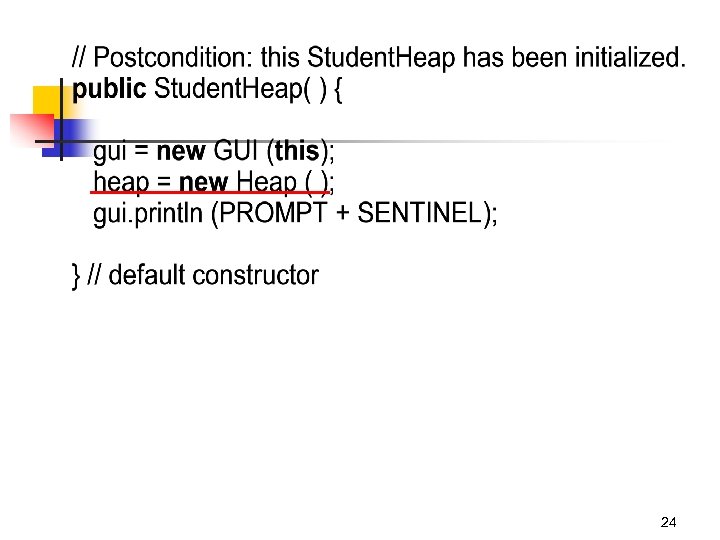 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
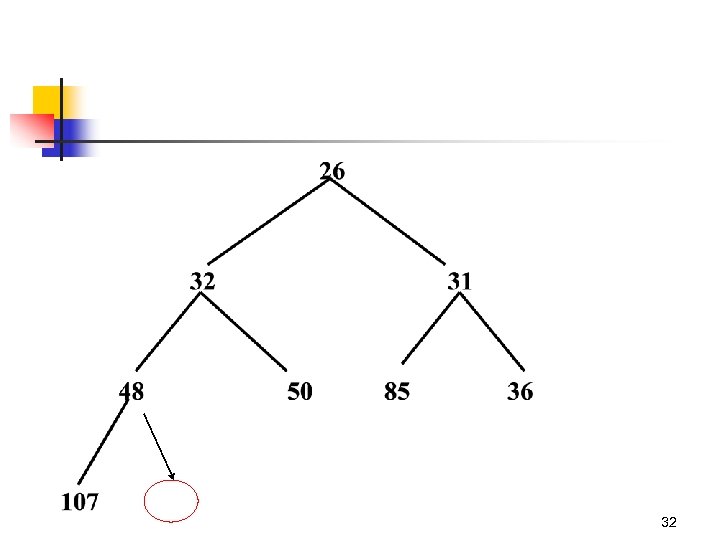
 Depends on avarage time of percolate. Up Resize array, this is O(n) The real operation. 31
Depends on avarage time of percolate. Up Resize array, this is O(n) The real operation. 31
 32
32
 33
33
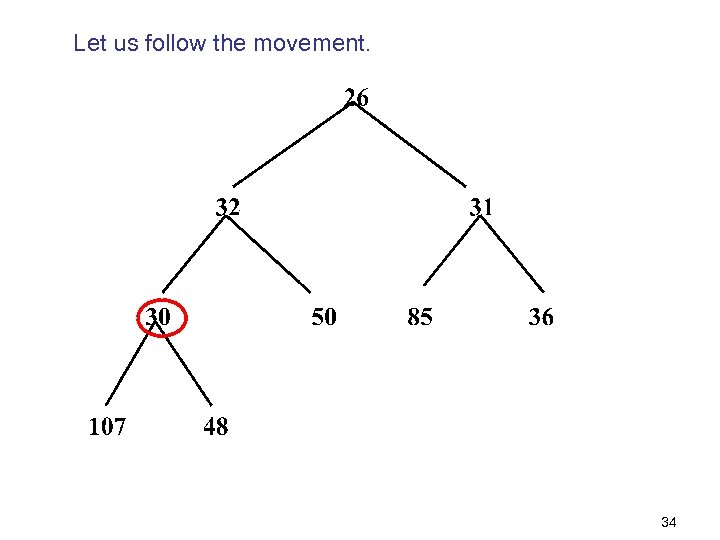 Let us follow the movement. 34
Let us follow the movement. 34
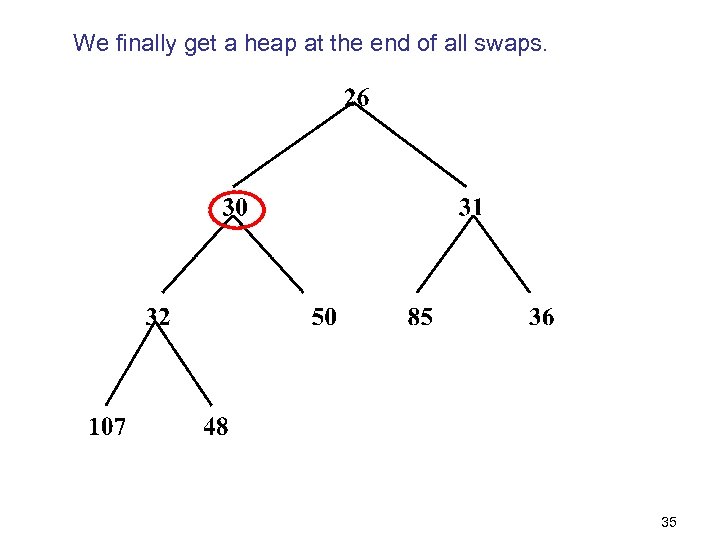 We finally get a heap at the end of all swaps. 35
We finally get a heap at the end of all swaps. 35
 // Postcondition: move the last element up the tree. The worst Depend on the height of the tree. Worst case happens when we need to swap up to the root. 36
// Postcondition: move the last element up the tree. The worst Depend on the height of the tree. Worst case happens when we need to swap up to the root. 36
 Average time -percolate. Up 37
Average time -percolate. Up 37
 38
38
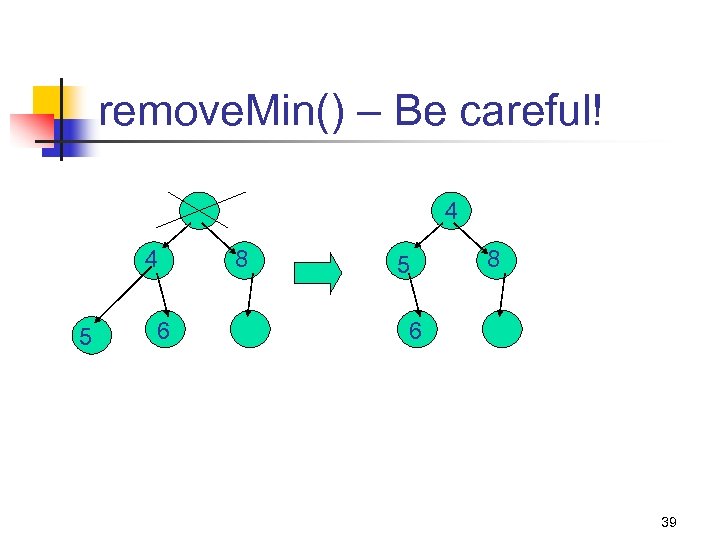 remove. Min() – Be careful! 4 4 5 6 8 5 8 6 39
remove. Min() – Be careful! 4 4 5 6 8 5 8 6 39
 40
40
 41
41
 Percolate. Down is 42
Percolate. Down is 42
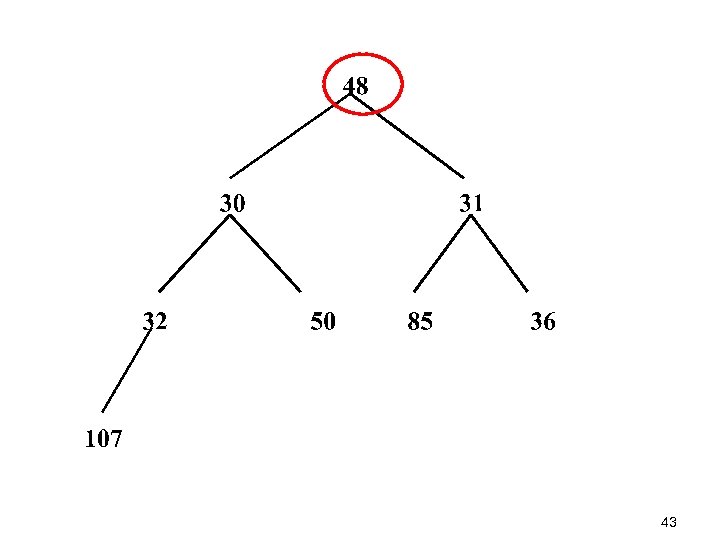 43
43
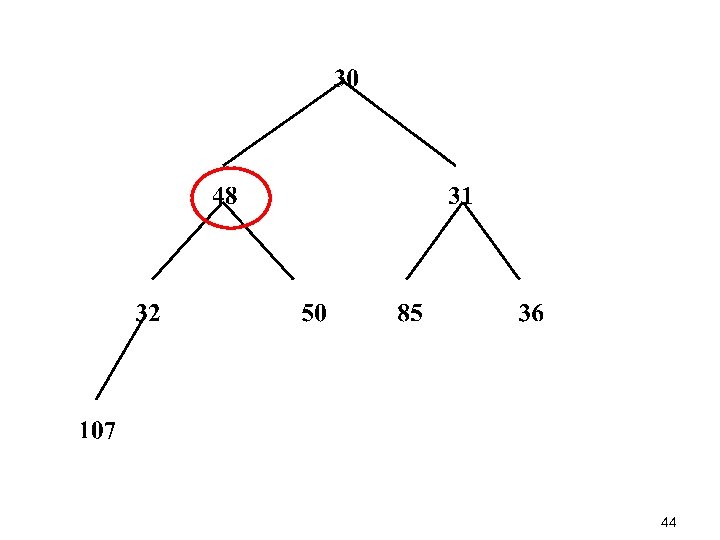 44
44
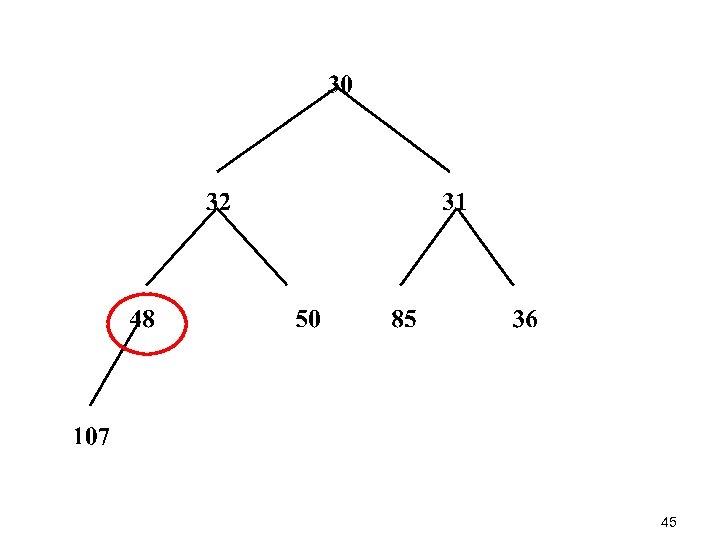 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
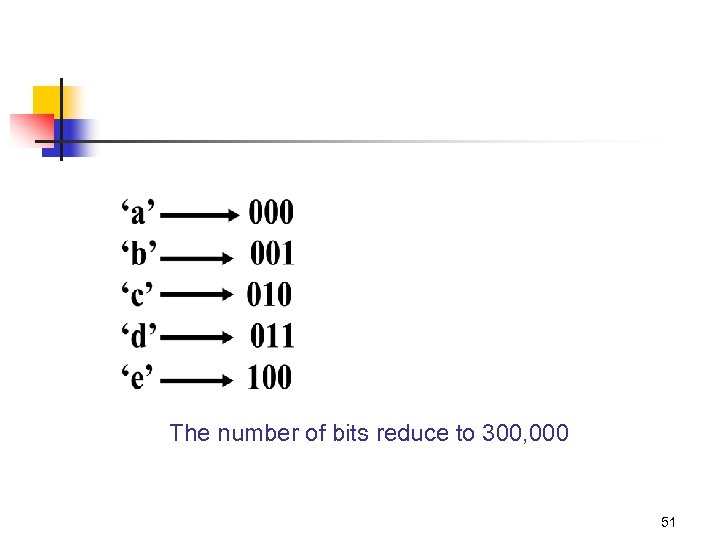 The number of bits reduce to 300, 000 51
The number of bits reduce to 300, 000 51
 Can it be reduced even more? 52
Can it be reduced even more? 52
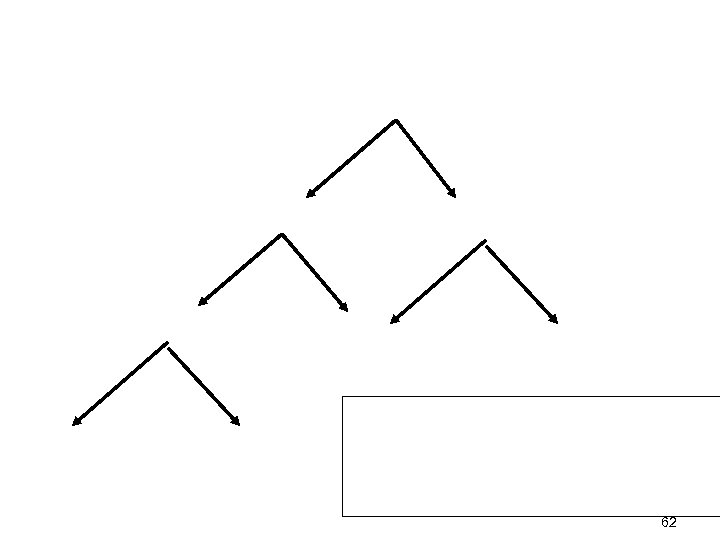
 How do we prevent ambiguity 53
How do we prevent ambiguity 53
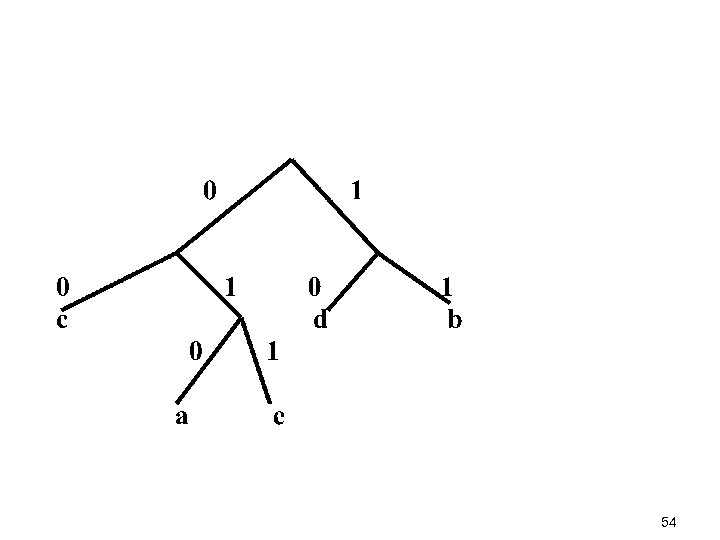 54
54
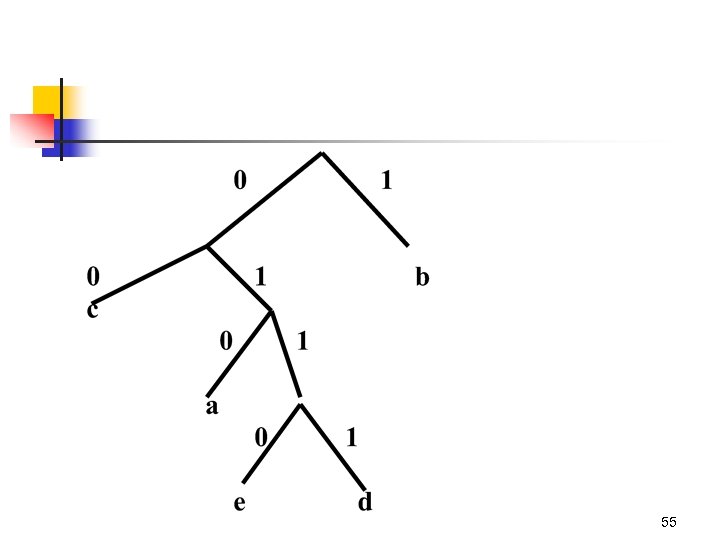 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
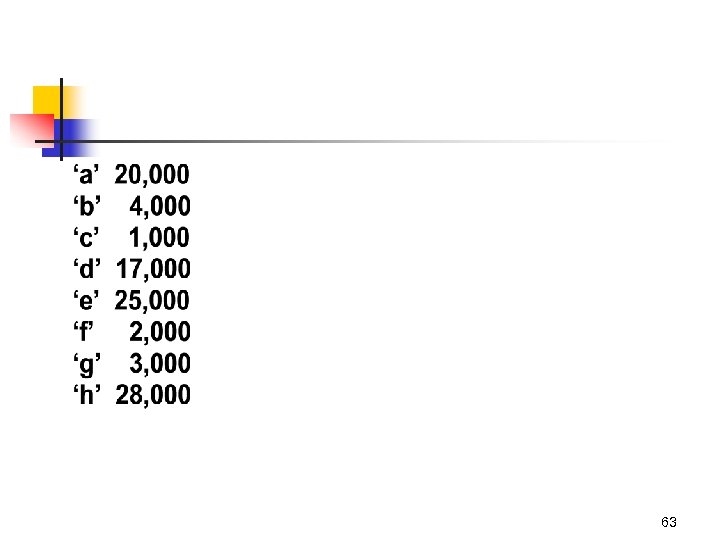
 Put pair )character, frequency) into Priority Q 58
Put pair )character, frequency) into Priority Q 58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 Huffman class example 64
Huffman class example 64
 65
65
 66
66
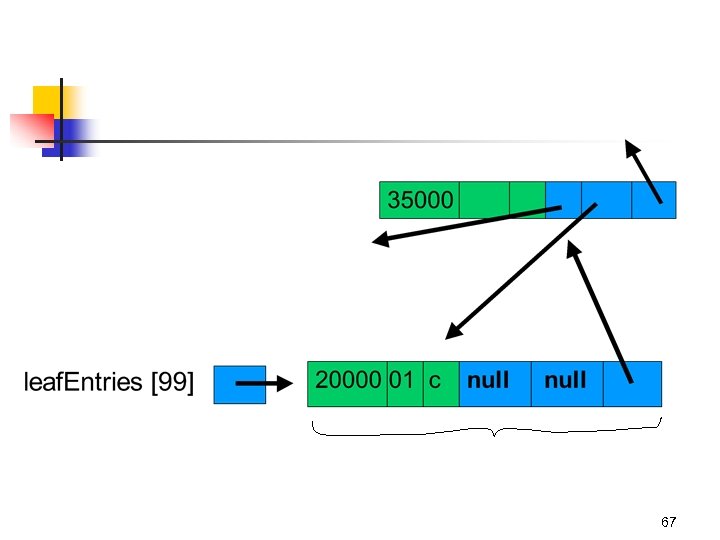 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
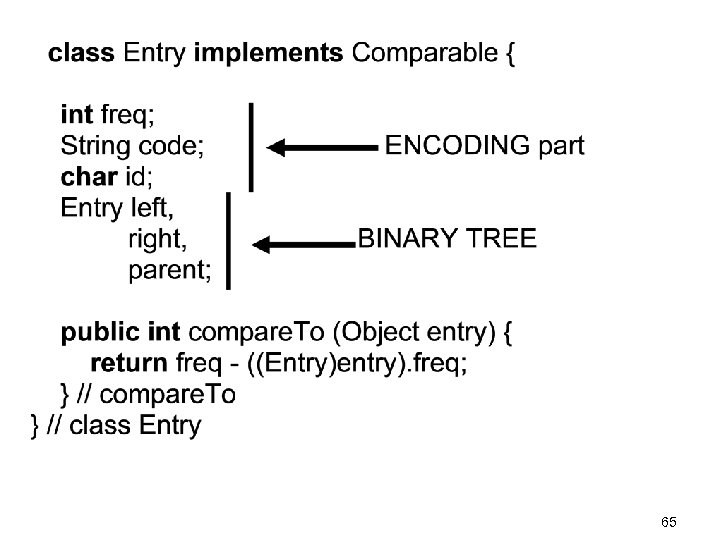
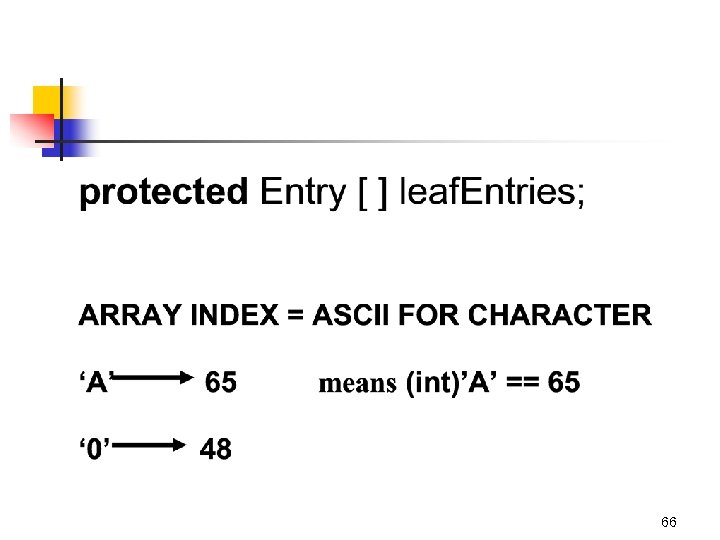
 Fields in the Huffman class 70
Fields in the Huffman class 70
 71
71
 Method process. Input 72
Method process. Input 72
 Method create. PQ 73
Method create. PQ 73
 Method create. Huffman. Tree 74
Method create. Huffman. Tree 74
 Method calculate. Huffman. Codes 75
Method calculate. Huffman. Codes 75
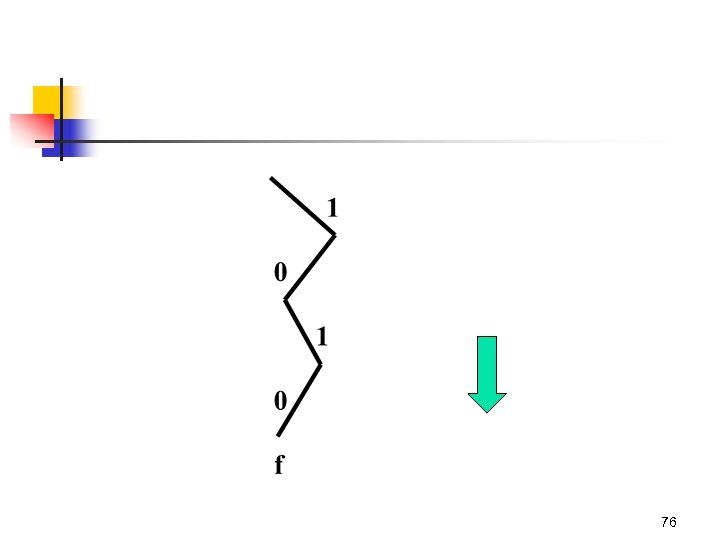 76
76
 77
77
 Method save. To. File 78
Method save. To. File 78
 79
79
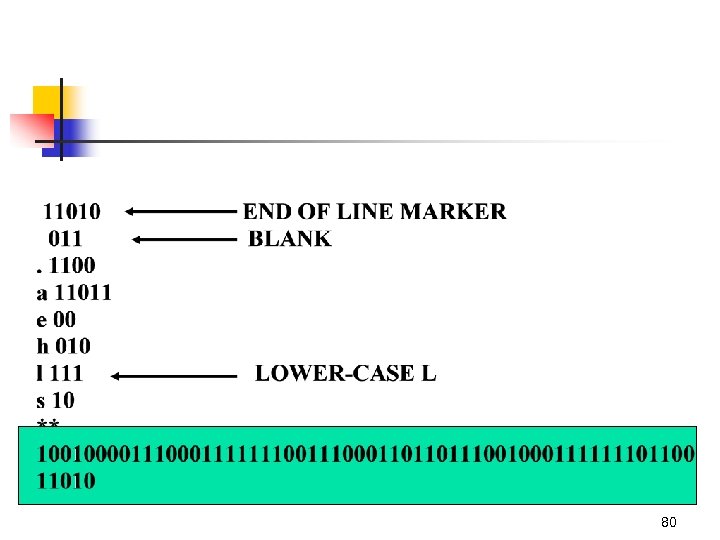 80
80