a313fcd44d3088b959ff1e647434ddee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 1
1
 2 nd ICT Med Workshop Informatics in Medical Imaging New Advences & Horizons Alireza Shakibafard MD Shiraz University of Medical Sciences(SUMS)
2 nd ICT Med Workshop Informatics in Medical Imaging New Advences & Horizons Alireza Shakibafard MD Shiraz University of Medical Sciences(SUMS)
 Medical Imaging
Medical Imaging
 Digital Imaging
Digital Imaging
 Digital Imaging Image or Magic ? ? ?
Digital Imaging Image or Magic ? ? ?
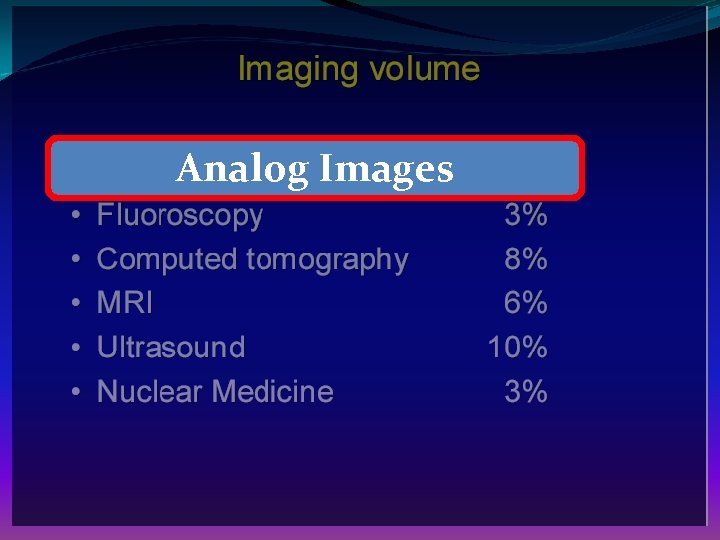 Analog Images
Analog Images
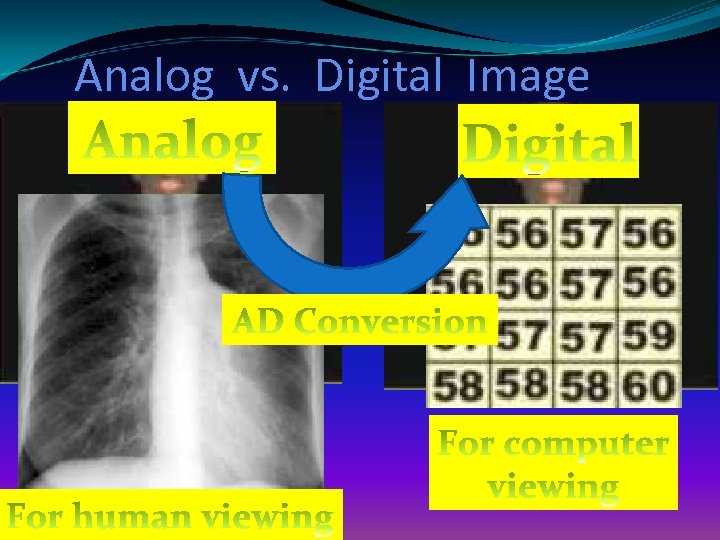 Analog vs. Digital Image
Analog vs. Digital Image
 Digital Image is ready for any 1. Change 2. Storage 3. Transfer
Digital Image is ready for any 1. Change 2. Storage 3. Transfer
 New Paradigm Moving from traditional film-screen(analog) toward electronic media In electronic imaging the functional parts of conventional radiology have been separated: Image Capture , Storage & Display
New Paradigm Moving from traditional film-screen(analog) toward electronic media In electronic imaging the functional parts of conventional radiology have been separated: Image Capture , Storage & Display
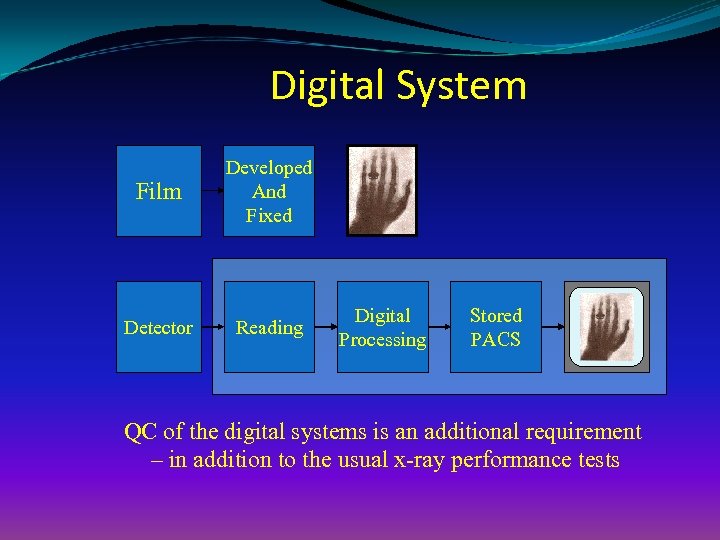 Digital System Film Developed And Fixed Detector Reading Digital Processing Stored PACS Viewed Display QC of the digital systems is an additional requirement – in addition to the usual x-ray performance tests
Digital System Film Developed And Fixed Detector Reading Digital Processing Stored PACS Viewed Display QC of the digital systems is an additional requirement – in addition to the usual x-ray performance tests
 11
11
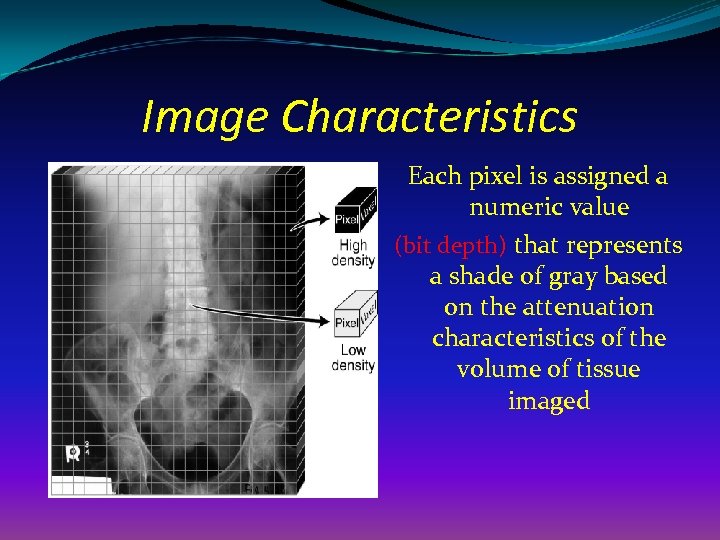 Image Characteristics Each pixel is assigned a numeric value (bit depth) that represents a shade of gray based on the attenuation characteristics of the volume of tissue imaged
Image Characteristics Each pixel is assigned a numeric value (bit depth) that represents a shade of gray based on the attenuation characteristics of the volume of tissue imaged
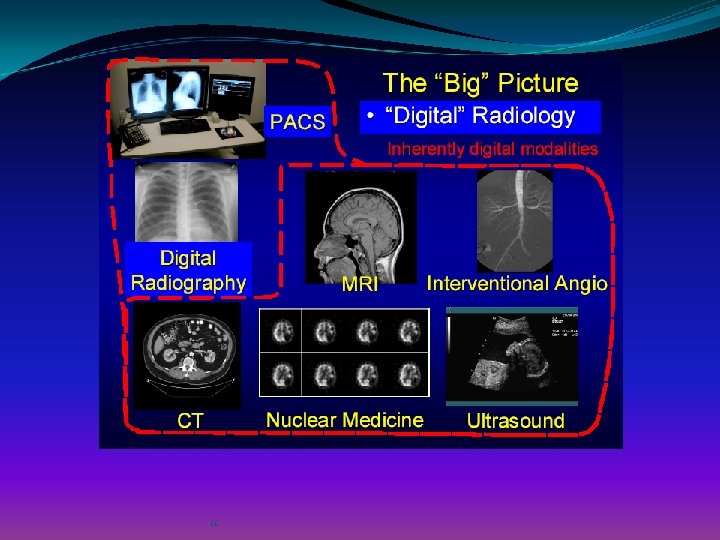
 Medical Imaging Advanced Applications
Medical Imaging Advanced Applications
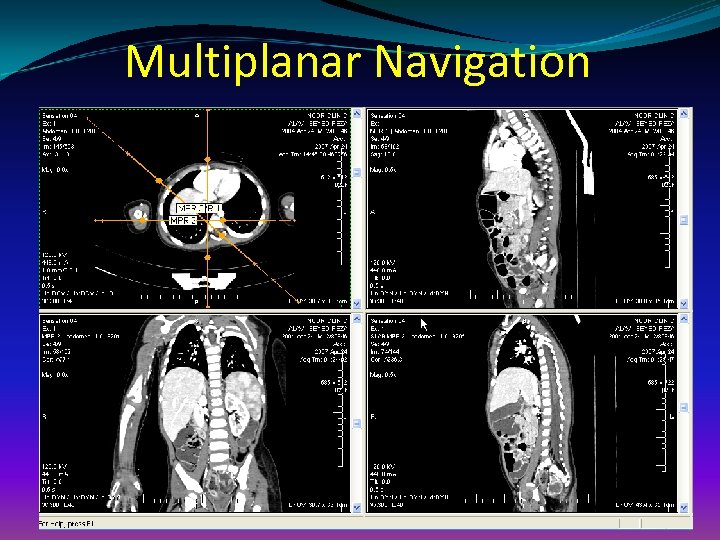 Multiplanar Navigation
Multiplanar Navigation
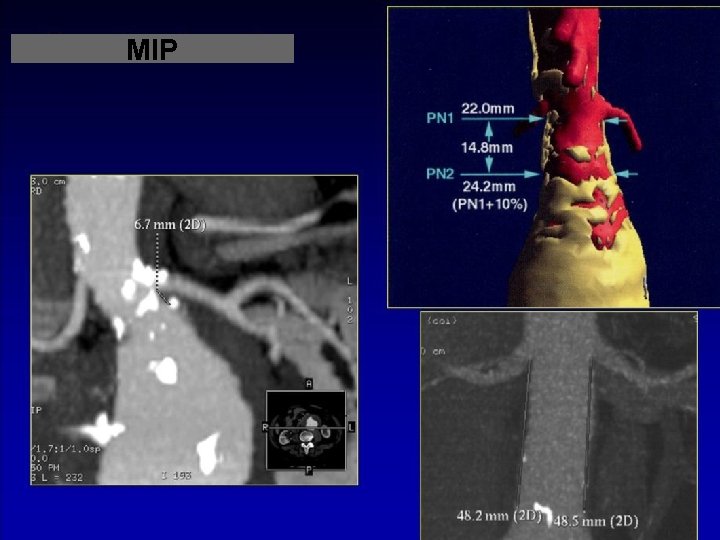 MIP
MIP

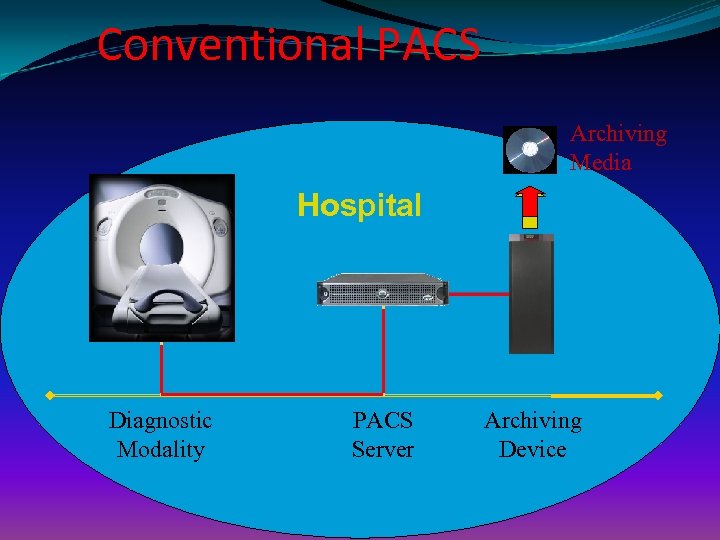 Conventional PACS Archiving Media Hospital Diagnostic Modality PACS Server Archiving Device
Conventional PACS Archiving Media Hospital Diagnostic Modality PACS Server Archiving Device
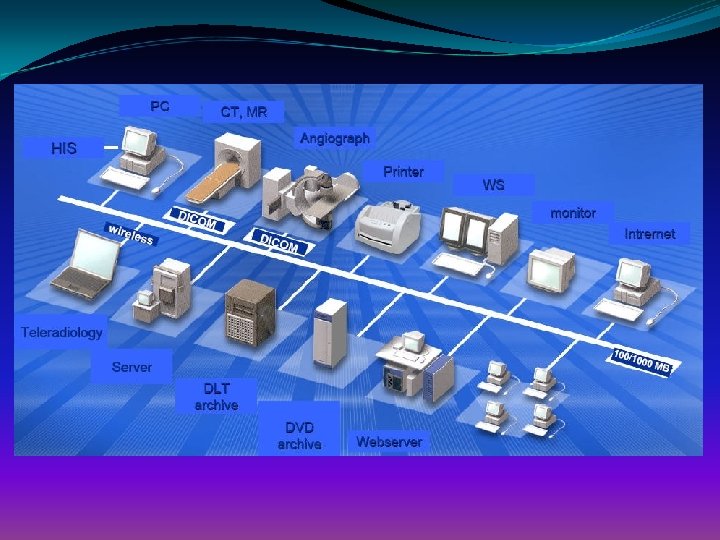
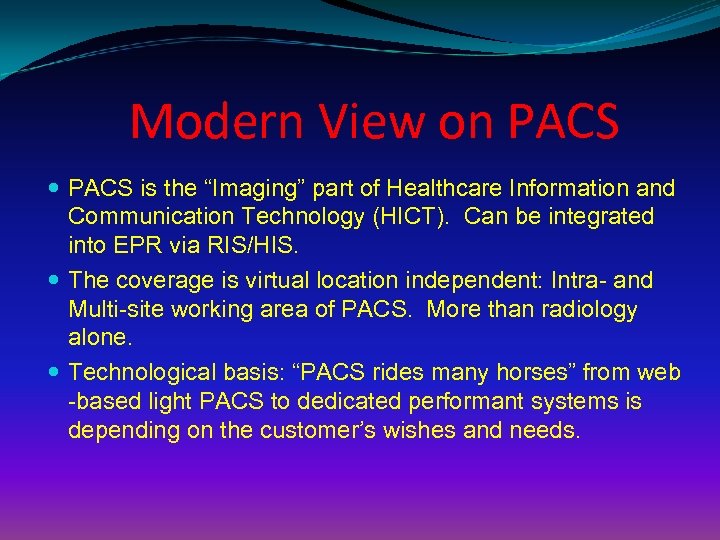 Modern View on PACS is the “Imaging” part of Healthcare Information and Communication Technology (HICT). Can be integrated into EPR via RIS/HIS. The coverage is virtual location independent: Intra- and Multi-site working area of PACS. More than radiology alone. Technological basis: “PACS rides many horses” from web -based light PACS to dedicated performant systems is depending on the customer’s wishes and needs.
Modern View on PACS is the “Imaging” part of Healthcare Information and Communication Technology (HICT). Can be integrated into EPR via RIS/HIS. The coverage is virtual location independent: Intra- and Multi-site working area of PACS. More than radiology alone. Technological basis: “PACS rides many horses” from web -based light PACS to dedicated performant systems is depending on the customer’s wishes and needs.
 Historical Evolution 80 -ties: MODALITY PACS = CT & MRI 80 -ties radiologists, advanced 3 D systems. 90 ties: departmental PACS + RIS = film-less radiology and organ-based radiology specialties, film still used documents in clinics. Cost-effective? ? >2000: Enterprise-PACS+RIS+PACS = film-less >2000 hospitals. >2007: Newest achievements: Multi-site PACS using >2007 MPI (Master Patient Index) to allow the patient’s access on all sites Hospitals will skip historical steps and adopt to state of the art PACS and HIS.
Historical Evolution 80 -ties: MODALITY PACS = CT & MRI 80 -ties radiologists, advanced 3 D systems. 90 ties: departmental PACS + RIS = film-less radiology and organ-based radiology specialties, film still used documents in clinics. Cost-effective? ? >2000: Enterprise-PACS+RIS+PACS = film-less >2000 hospitals. >2007: Newest achievements: Multi-site PACS using >2007 MPI (Master Patient Index) to allow the patient’s access on all sites Hospitals will skip historical steps and adopt to state of the art PACS and HIS.
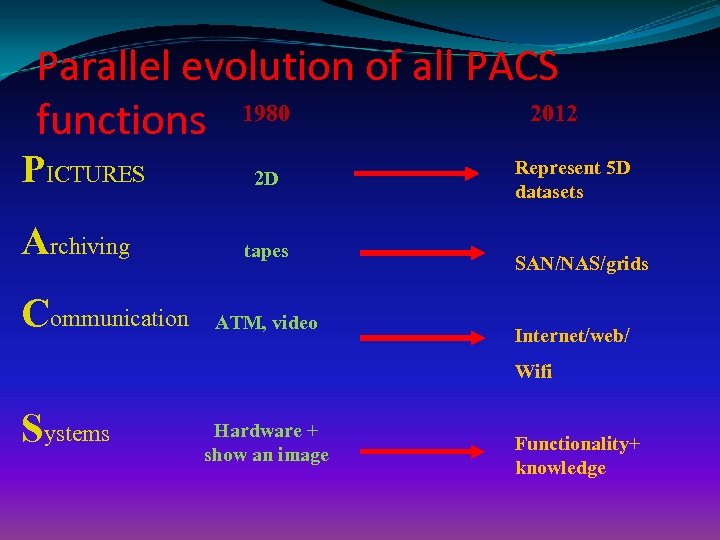 Parallel evolution of all PACS 2012 functions 1980 PICTURES Archiving Communication 2 D tapes ATM, video Represent 5 D datasets SAN/NAS/grids Internet/web/ Wifi Systems Hardware + show an image Functionality+ knowledge
Parallel evolution of all PACS 2012 functions 1980 PICTURES Archiving Communication 2 D tapes ATM, video Represent 5 D datasets SAN/NAS/grids Internet/web/ Wifi Systems Hardware + show an image Functionality+ knowledge
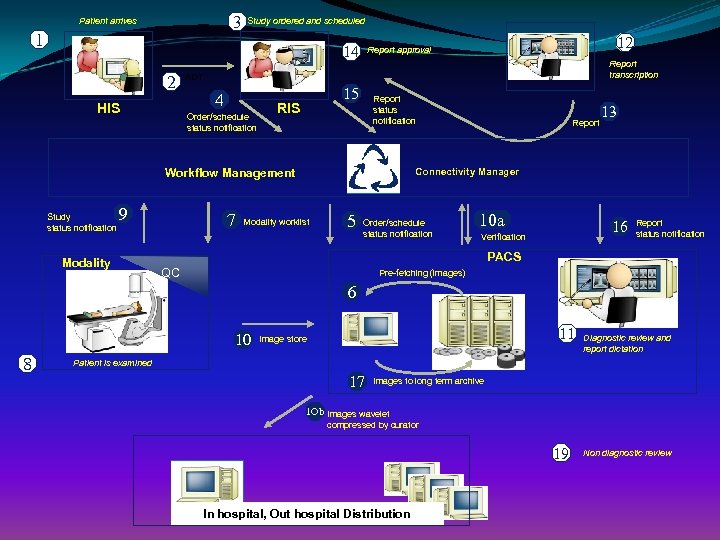 3 Patient arrives 1 Study ordered and scheduled 14 2 HIS Report transcription ADT 4 Order/schedule status notification 15 RIS Report status notification 9 Modality 7 Report 13 Connectivity Manager Workflow Management Study status notification 12 Report approval Modality worklist 5 Order/schedule status notification 10 a 16 Verification Report status notification PACS QC Pre-fetching (images) 6 10 8 11 Image store Diagnostic review and report dictation Patient is examined 17 Images to long term archive 1 Ob Images wavelet compressed by curator 19 In hospital, Out hospital Distribution Non diagnostic review
3 Patient arrives 1 Study ordered and scheduled 14 2 HIS Report transcription ADT 4 Order/schedule status notification 15 RIS Report status notification 9 Modality 7 Report 13 Connectivity Manager Workflow Management Study status notification 12 Report approval Modality worklist 5 Order/schedule status notification 10 a 16 Verification Report status notification PACS QC Pre-fetching (images) 6 10 8 11 Image store Diagnostic review and report dictation Patient is examined 17 Images to long term archive 1 Ob Images wavelet compressed by curator 19 In hospital, Out hospital Distribution Non diagnostic review
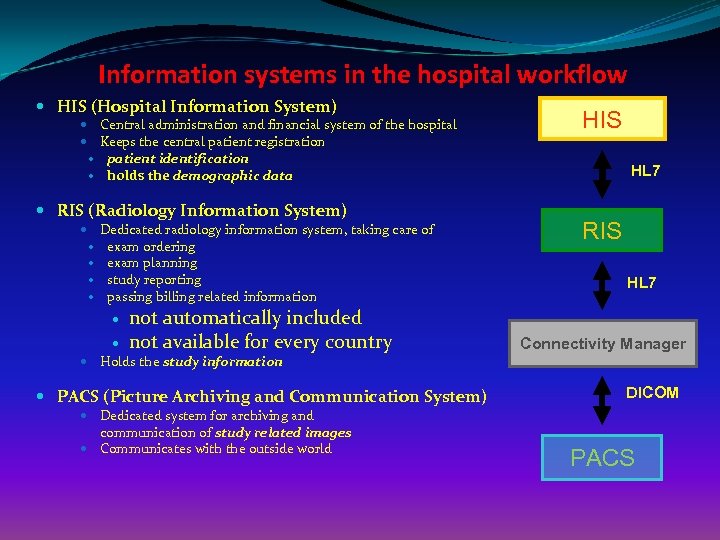 Information systems in the hospital workflow HIS (Hospital Information System) Central administration and financial system of the hospital Keeps the central patient registration patient identification holds the demographic data RIS (Radiology Information System) Dedicated radiology information system, taking care of exam ordering exam planning study reporting passing billing related information not automatically included not available for every country Holds the study information PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) Dedicated system for archiving and communication of study related images Communicates with the outside world HIS HL 7 RIS HL 7 Connectivity Manager DICOM PACS
Information systems in the hospital workflow HIS (Hospital Information System) Central administration and financial system of the hospital Keeps the central patient registration patient identification holds the demographic data RIS (Radiology Information System) Dedicated radiology information system, taking care of exam ordering exam planning study reporting passing billing related information not automatically included not available for every country Holds the study information PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) Dedicated system for archiving and communication of study related images Communicates with the outside world HIS HL 7 RIS HL 7 Connectivity Manager DICOM PACS
 Information exchange standards HL 7 (Health Level 7) Provides standards for the exchange, management and integration of data that support clinical patient care and for the management, delivery and evaluation of healthcare services. E. g. patient demographics, appointment schedules, insurance policies, financial transactions, clinical data, clinical treatment plans, observation reports, … DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine) DICOM is a standard, to enable efficient and flexible integration and communication of image data between components (modalities, printers, storage, databases, …) in a medical network However: DICOM does not guarantee the interoperability of systems that claim to be DICOM conformant
Information exchange standards HL 7 (Health Level 7) Provides standards for the exchange, management and integration of data that support clinical patient care and for the management, delivery and evaluation of healthcare services. E. g. patient demographics, appointment schedules, insurance policies, financial transactions, clinical data, clinical treatment plans, observation reports, … DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine) DICOM is a standard, to enable efficient and flexible integration and communication of image data between components (modalities, printers, storage, databases, …) in a medical network However: DICOM does not guarantee the interoperability of systems that claim to be DICOM conformant
 Translate HIS/RIS messages (e. g. HL 7) to DICOM PACS Connectivity Services (Connectivity Manager) PV 1||E|TRAUMA|A||||^DOE ^JOHN^W. ^DR. ^|||WAITING ROOM RIS ? ? ? CM Do you speak DICOM ?
Translate HIS/RIS messages (e. g. HL 7) to DICOM PACS Connectivity Services (Connectivity Manager) PV 1||E|TRAUMA|A||||^DOE ^JOHN^W. ^DR. ^|||WAITING ROOM RIS ? ? ? CM Do you speak DICOM ?
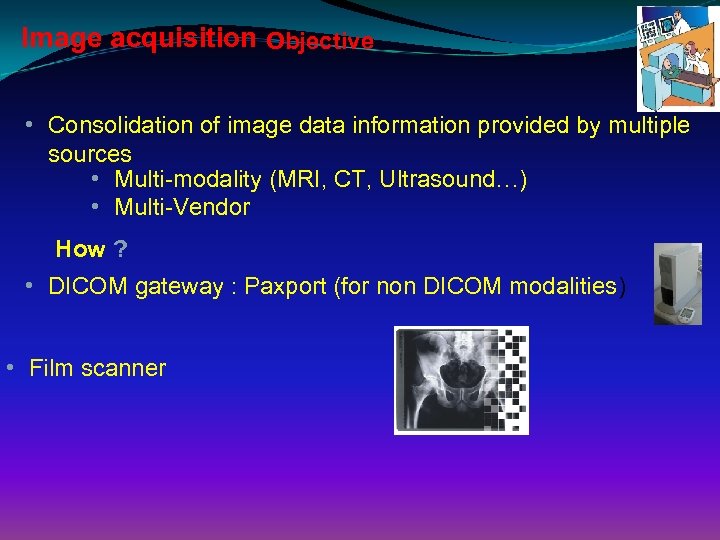 Image acquisition Objective • Consolidation of image data information provided by multiple sources • Multi-modality (MRI, CT, Ultrasound…) • Multi-Vendor How ? • DICOM gateway : Paxport (for non DICOM modalities) • Film scanner
Image acquisition Objective • Consolidation of image data information provided by multiple sources • Multi-modality (MRI, CT, Ultrasound…) • Multi-Vendor How ? • DICOM gateway : Paxport (for non DICOM modalities) • Film scanner
 Image data storage and archiving • Storage (. dcm files) • Type of media (disks, UDO, LTO) • Everything on line solutions, nearline, off-line • Data compression • Data availability
Image data storage and archiving • Storage (. dcm files) • Type of media (disks, UDO, LTO) • Everything on line solutions, nearline, off-line • Data compression • Data availability
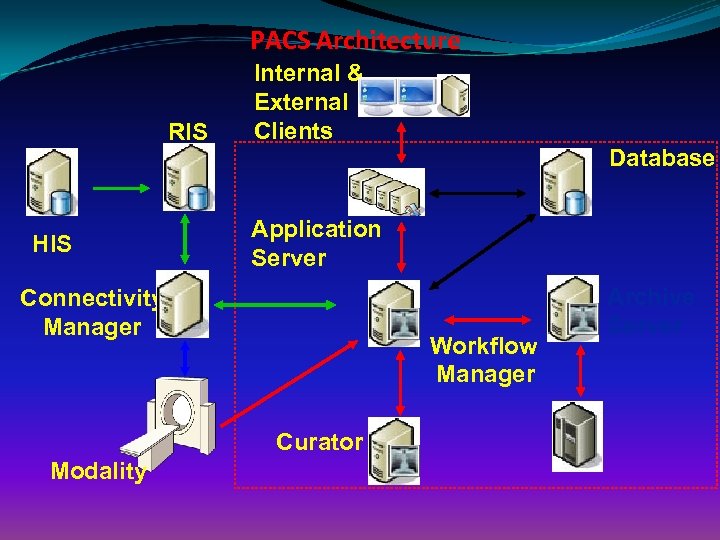 PACS Architecture RIS HIS Internal & External Clients Application Server Connectivity Manager Workflow Manager Curator Modality Database Archive Server
PACS Architecture RIS HIS Internal & External Clients Application Server Connectivity Manager Workflow Manager Curator Modality Database Archive Server
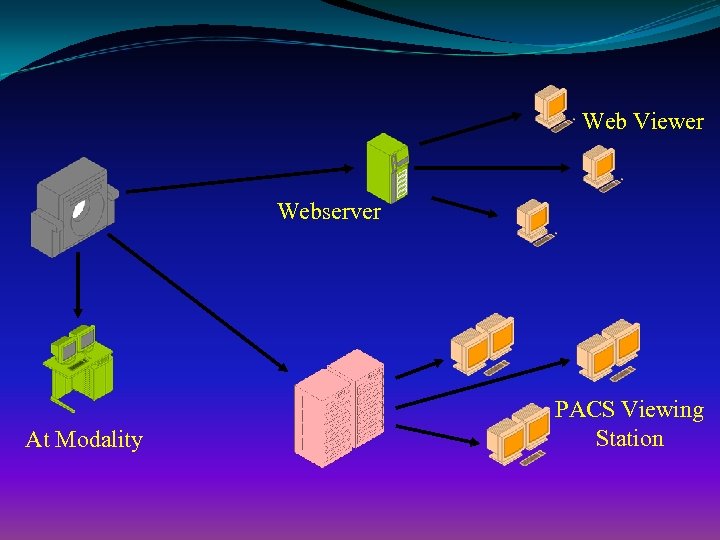 Web Viewer Webserver At Modality PACS Viewing Station
Web Viewer Webserver At Modality PACS Viewing Station
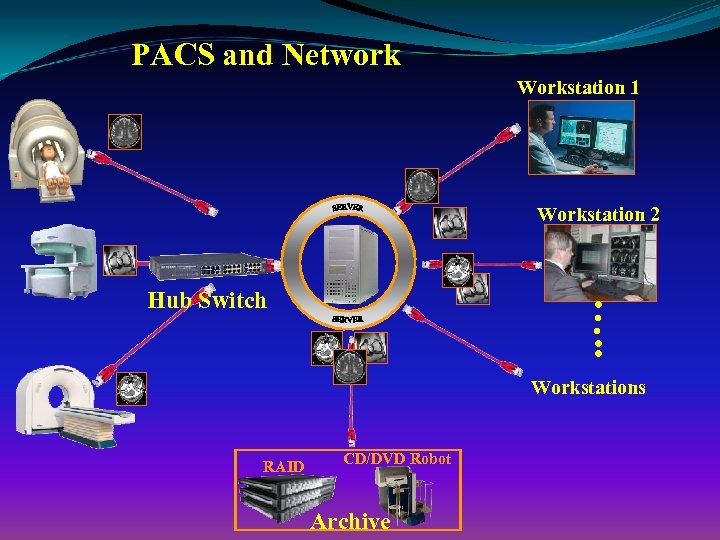 PACS and Network Workstation 1 Workstation 2 …. . Hub Switch Workstations RAID CD/DVD Robot Archive
PACS and Network Workstation 1 Workstation 2 …. . Hub Switch Workstations RAID CD/DVD Robot Archive

 PACS Beyond Radiology Other Types of Images: Vascular Angiography Cardiac Angiography Echocardiography Obstetric Ultrasound Medical Photography Retinal Imaging Colposcopy / Cytology…. . May be more of a RIS Issue than PACS
PACS Beyond Radiology Other Types of Images: Vascular Angiography Cardiac Angiography Echocardiography Obstetric Ultrasound Medical Photography Retinal Imaging Colposcopy / Cytology…. . May be more of a RIS Issue than PACS
 Imaging Informatics New Advances
Imaging Informatics New Advances
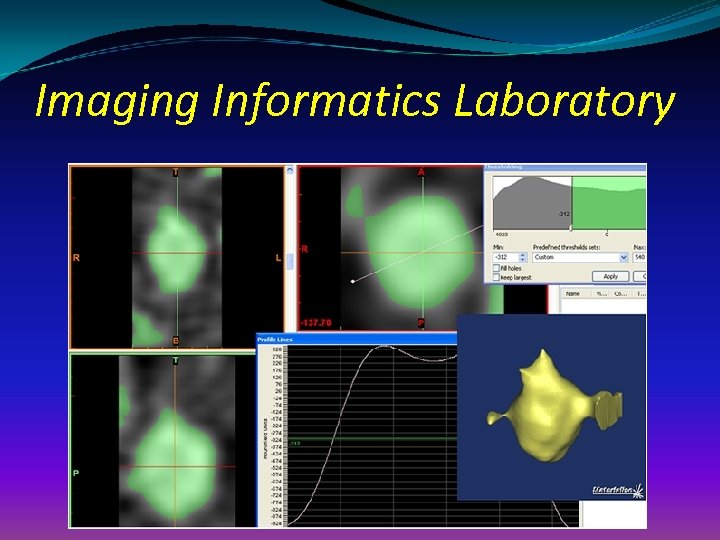 Imaging Informatics Laboratory
Imaging Informatics Laboratory
 The Bottom Line • • Modern Image Processing Automated CAD with interpretation and reporting Portable medical records – perhaps imbedded in patient Integrated RIS-PACS-HIS through I. T. Robotic imaging Molecular Imaging Image guided chemotherapy and gene therapy ………….
The Bottom Line • • Modern Image Processing Automated CAD with interpretation and reporting Portable medical records – perhaps imbedded in patient Integrated RIS-PACS-HIS through I. T. Robotic imaging Molecular Imaging Image guided chemotherapy and gene therapy ………….
 Take Home Point: Beyond Bytes & Bits : Healthcare IT ; When needed , Where needed Integrated & Enterprise
Take Home Point: Beyond Bytes & Bits : Healthcare IT ; When needed , Where needed Integrated & Enterprise
 Take Home Point: Healthcare IT ; Beyond one person , one department , one …. . , it is across … It needs collaboration , communication & decision making
Take Home Point: Healthcare IT ; Beyond one person , one department , one …. . , it is across … It needs collaboration , communication & decision making
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR NICE ATTENTION
THANK YOU FOR YOUR NICE ATTENTION



