1 Minor Syntax.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 1. 2. 3. Definition of the phrase. Classifications of phrases. Connections (bonds) between the phrase constituents Minor Syntax: Syntax of the Phrase Lecture 1
1. 2. 3. Definition of the phrase. Classifications of phrases. Connections (bonds) between the phrase constituents Minor Syntax: Syntax of the Phrase Lecture 1
 Two types of syntax Major syntax sentence Minor syntax phrase Словосочетание ~ сочетание слов? Phrase ~ word group / cluster ~ word combination ~ collocation ~ chunk
Two types of syntax Major syntax sentence Minor syntax phrase Словосочетание ~ сочетание слов? Phrase ~ word group / cluster ~ word combination ~ collocation ~ chunk
 Chunk(ing) (оборот речи, словесный / фразеологический оборот) (comp. ) A chunk is a fragment of information which is used in many multimedia format. (psych. ) the (individually differing) segmentation and bundling of information units in one’s memory; the remembered piece of information. (ling. ) several words that are customarily used together in a fixed expression, such as “How are you? “, "to make a long story short, ““you know, “or “sort of”. They make speech fluent.
Chunk(ing) (оборот речи, словесный / фразеологический оборот) (comp. ) A chunk is a fragment of information which is used in many multimedia format. (psych. ) the (individually differing) segmentation and bundling of information units in one’s memory; the remembered piece of information. (ling. ) several words that are customarily used together in a fixed expression, such as “How are you? “, "to make a long story short, ““you know, “or “sort of”. They make speech fluent.
 collocation Characteristic word combinations which have developed an idiomatic semantic relation based on their frequent cooccurrence. Primarily semantically (not grammatically) based: dog : bark; dark : night What kind of berry is it? – Black currents. – And why is it red? – Because it is green.
collocation Characteristic word combinations which have developed an idiomatic semantic relation based on their frequent cooccurrence. Primarily semantically (not grammatically) based: dog : bark; dark : night What kind of berry is it? – Black currents. – And why is it red? – Because it is green.
 Word group / cluster Any group of words with or with no grammatical or semantic relation Corpus data: and doing it if you see benefit in that. So hold the side in you see? Yeah. I mean but be added to it you see. Mm and just his ‘s all it is you see, there’s no mention
Word group / cluster Any group of words with or with no grammatical or semantic relation Corpus data: and doing it if you see benefit in that. So hold the side in you see? Yeah. I mean but be added to it you see. Mm and just his ‘s all it is you see, there’s no mention
 Are these phrases? read a book an interesting book his own sells well at school a book and a notebook a book sells in the
Are these phrases? read a book an interesting book his own sells well at school a book and a notebook a book sells in the
 Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; consisting of notional parts of speech; chracterised by subordinate relations. V. V. Vinogradov
Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; consisting of notional parts of speech; chracterised by subordinate relations. V. V. Vinogradov
 Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; in the consisting of notional parts of speech; chracterised by subordinate relations. V. V. Vinogradov
Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; in the consisting of notional parts of speech; chracterised by subordinate relations. V. V. Vinogradov
 Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; in the consisting of notional parts of speech; at school chracterised by subordinate relations. V. V. Vinogradov
Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; in the consisting of notional parts of speech; at school chracterised by subordinate relations. V. V. Vinogradov
 Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination (V. V. Vinogradov) the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; in the consisting of notional parts of speech; at school chracterised by subordinate relations. a book and a notebook a book sells
Phrase: the narrow approach Word combination (V. V. Vinogradov) the syntactic unit used as a notional part of a sentence; in the consisting of notional parts of speech; at school chracterised by subordinate relations. a book and a notebook a book sells
 Phrase: a broader approach Leonard Bloomfield, V. V. Burlakova, M. Ya. Blokh, V. M. Zhirmunsky, B. Ilyish : any syntactically organized group of syntagmatically connected words, including combinations of functional and notional words, and predicative and coordinative combinations of words
Phrase: a broader approach Leonard Bloomfield, V. V. Burlakova, M. Ya. Blokh, V. M. Zhirmunsky, B. Ilyish : any syntactically organized group of syntagmatically connected words, including combinations of functional and notional words, and predicative and coordinative combinations of words
 Phrase Narrow approach Broad approach beautiful girl + + go home + + Mother and Father - + at home - + He slept - +
Phrase Narrow approach Broad approach beautiful girl + + go home + + Mother and Father - + at home - + He slept - +
 WORD vs. PHRASE WORD Simple nomination: a girl a decision A ready-made unit PHRASE Complex / polynomination a beautiful girl his unexpected decision Freely formed in speech (but for idioms)
WORD vs. PHRASE WORD Simple nomination: a girl a decision A ready-made unit PHRASE Complex / polynomination a beautiful girl his unexpected decision Freely formed in speech (but for idioms)
 PHRASE vs. SENTENCE The phrase cannot express full predication, it denotes a fragment of a situation: They considered the problem. = S their consideration of the problem; for them to consider the problem; their considering of the problem. Ph The phrase enters speech only as a constituent of a sentence, as “a denoteme” (M. Blokh), or “a polydenoteme” as contrasted with the word, which enters a sentence as “a monodenoteme”
PHRASE vs. SENTENCE The phrase cannot express full predication, it denotes a fragment of a situation: They considered the problem. = S their consideration of the problem; for them to consider the problem; their considering of the problem. Ph The phrase enters speech only as a constituent of a sentence, as “a denoteme” (M. Blokh), or “a polydenoteme” as contrasted with the word, which enters a sentence as “a monodenoteme”
 Classes of phrases(Y. Blokh) (nominative criterion) notional phrases • semantically independent (“autosemantic”) combinations of notional words • Peter’s desk; brown desk; stay home formative phrases • a combination of a notional word with a functional word, which is contextually dependent (“synsemantic”) and functionally similar to a notional word • of Peter (= Peter’s); in a moment functional phrases • combinations of functional words similar to regular functional words • apart from, as soon as, with reference to, must be able
Classes of phrases(Y. Blokh) (nominative criterion) notional phrases • semantically independent (“autosemantic”) combinations of notional words • Peter’s desk; brown desk; stay home formative phrases • a combination of a notional word with a functional word, which is contextually dependent (“synsemantic”) and functionally similar to a notional word • of Peter (= Peter’s); in a moment functional phrases • combinations of functional words similar to regular functional words • apart from, as soon as, with reference to, must be able
 Based on the constituent rank Subordinative / dominational /dependent Coordinative / equipotent / hypotactic paratactic one word modifies another read a book read to me VERY beautiful equal syntactic rank poor but honest; mad, bad, and dangerous; mine, not yours
Based on the constituent rank Subordinative / dominational /dependent Coordinative / equipotent / hypotactic paratactic one word modifies another read a book read to me VERY beautiful equal syntactic rank poor but honest; mad, bad, and dangerous; mine, not yours
 Coordinative connection for homogeneous notional parts of the sentence a coordinative conjunction: poor but honest syndetic connection mad, bad, and dangerous syndetic connection mine, not yours asyndetic connection mad, bad asyndetic connection
Coordinative connection for homogeneous notional parts of the sentence a coordinative conjunction: poor but honest syndetic connection mad, bad, and dangerous syndetic connection mine, not yours asyndetic connection mad, bad asyndetic connection
 Coordinat(iv)e connection: word order cold and rainy 1: 2 men and women 1: 2 ladies and gentlemen 2: 3 Oxford and Cambridge my mother and I
Coordinat(iv)e connection: word order cold and rainy 1: 2 men and women 1: 2 ladies and gentlemen 2: 3 Oxford and Cambridge my mother and I
 Intermediary case: cumulative connection (аккумулятивная связь) formally equipotent phrases of a non-consecutive type (to find the car gone) sequential elements are unequal in the character of nomination (heavy oak door) a coordinative conjunction came, but late; agreed, or nearly so
Intermediary case: cumulative connection (аккумулятивная связь) formally equipotent phrases of a non-consecutive type (to find the car gone) sequential elements are unequal in the character of nomination (heavy oak door) a coordinative conjunction came, but late; agreed, or nearly so
 Cumulation = (ак)кумуляция / скопление outer cumulation of sentences inner cumulation of words his own (invitation) *his and own *own his (to give) her a present (to see) a man for three minutes
Cumulation = (ак)кумуляция / скопление outer cumulation of sentences inner cumulation of words his own (invitation) *his and own *own his (to give) her a present (to see) a man for three minutes
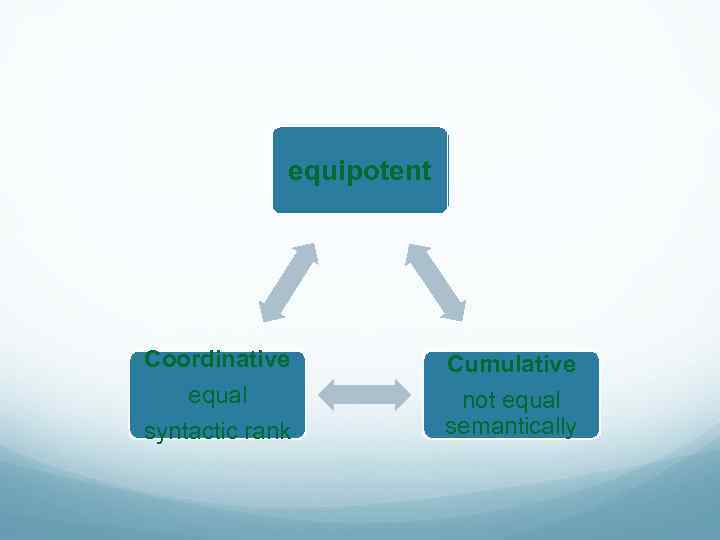 equipotent Coordinative Cumulative equal syntactic rank not equal semantically
equipotent Coordinative Cumulative equal syntactic rank not equal semantically
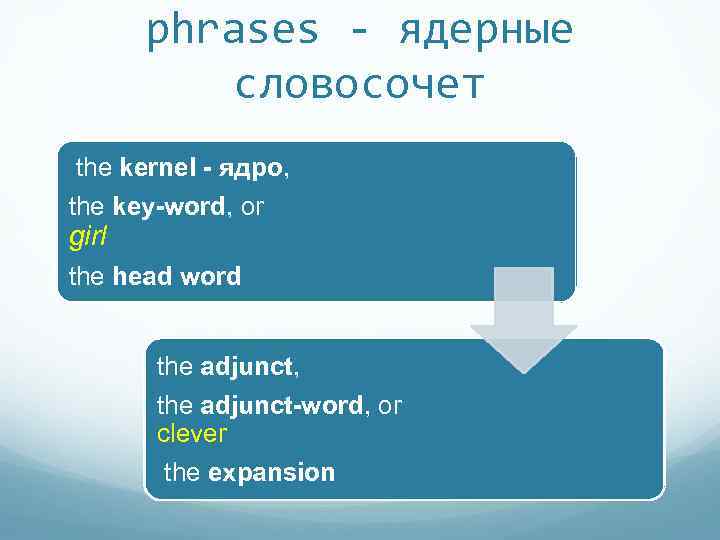 phrases - ядерные словосочет the kernel - ядро, the key-word, or girl the head word the adjunct, the adjunct-word, or clever the expansion
phrases - ядерные словосочет the kernel - ядро, the key-word, or girl the head word the adjunct, the adjunct-word, or clever the expansion
 Subordinative (dominational) phrases consecutive / subordinative cumulative definitely off the point, definitely
Subordinative (dominational) phrases consecutive / subordinative cumulative definitely off the point, definitely
 Subordinate connection is achieved by different forms of the word categorial agreement (concord) government connective words prepositional government категориальное согласование управление предложное управление word order adjoining enclosure примыкание замыкание
Subordinate connection is achieved by different forms of the word categorial agreement (concord) government connective words prepositional government категориальное согласование управление предложное управление word order adjoining enclosure примыкание замыкание
 Agreement (concord) the subordinate word assumes a form similar to the form of the kernel: this boy – these boys; the child plays – the children play Agreement only in number
Agreement (concord) the subordinate word assumes a form similar to the form of the kernel: this boy – these boys; the child plays – the children play Agreement only in number
 English: agreement Formal • Our family was big. • Bread and butter are food products. Semantic • The family were at dinner table. • Bread and butter is eaten for breakfast.
English: agreement Formal • Our family was big. • Bread and butter are food products. Semantic • The family were at dinner table. • Bread and butter is eaten for breakfast.
 Government a certain form of adjunct is required by its head-word, but it does not coincide with the form of the head word to see him to talk to him
Government a certain form of adjunct is required by its head-word, but it does not coincide with the form of the head word to see him to talk to him
 Adjoining no special formal mark of dependence between constituents; words are combined by sheer contact: go home beautiful girl behaves bravely
Adjoining no special formal mark of dependence between constituents; words are combined by sheer contact: go home beautiful girl behaves bravely
 Enclosure a subordinate word is placed between two parts of an analytical head-word form: to thoroughly think over then government an interesting question
Enclosure a subordinate word is placed between two parts of an analytical head-word form: to thoroughly think over then government an interesting question
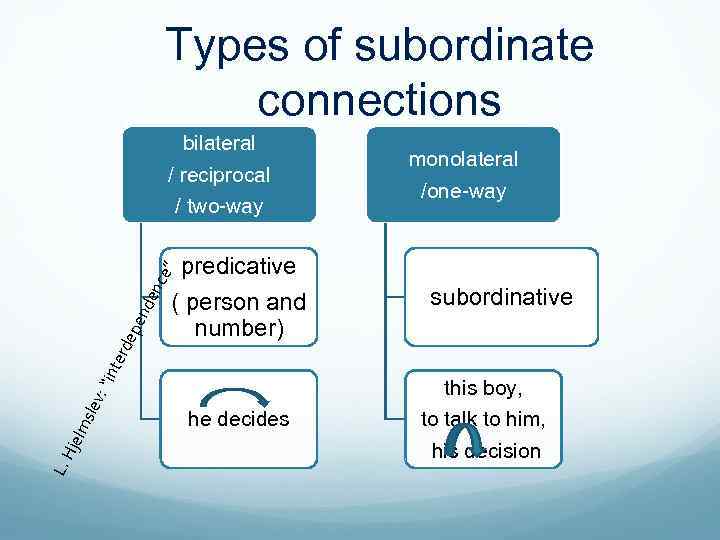 Types of subordinate connections ( person and number) : “i sle v L. H jelm monolateral /one-way predicative nte rde pen den c e” bilateral / reciprocal / two-way he decides subordinative this boy, to talk to him, his decision
Types of subordinate connections ( person and number) : “i sle v L. H jelm monolateral /one-way predicative nte rde pen den c e” bilateral / reciprocal / two-way he decides subordinative this boy, to talk to him, his decision
 4 basic types of syntagmatic connections of words: coordination consecutive equipotent connection subordination consecutive subordinate connection predication, or interdependence bilateral subordinate connection cumulation inner cumulation
4 basic types of syntagmatic connections of words: coordination consecutive equipotent connection subordination consecutive subordinate connection predication, or interdependence bilateral subordinate connection cumulation inner cumulation
 Traditional classification of phrases based on the part-of -speech of the kernel NP - noun phrases : a beautiful girl; men, women and children; VP - verbal phrases : went home; came and went; AP - adjective phrases : quite unexpected; nice and quiet; DP - adverbial phrases: quite unexpectedly
Traditional classification of phrases based on the part-of -speech of the kernel NP - noun phrases : a beautiful girl; men, women and children; VP - verbal phrases : went home; came and went; AP - adjective phrases : quite unexpected; nice and quiet; DP - adverbial phrases: quite unexpectedly
 Based on kernel-adjunct relations objective connections: direct objective indirect objective to see a child; give (to) him put on the table qualifying connections attributive adverbial beautiful girl came soon
Based on kernel-adjunct relations objective connections: direct objective indirect objective to see a child; give (to) him put on the table qualifying connections attributive adverbial beautiful girl came soon
 Based of the position of the adjunct in relation to the kernel regressive : the adjunct precedes the kernel a beautiful girl progressive phrases: the adjunct follows the kernel came home
Based of the position of the adjunct in relation to the kernel regressive : the adjunct precedes the kernel a beautiful girl progressive phrases: the adjunct follows the kernel came home
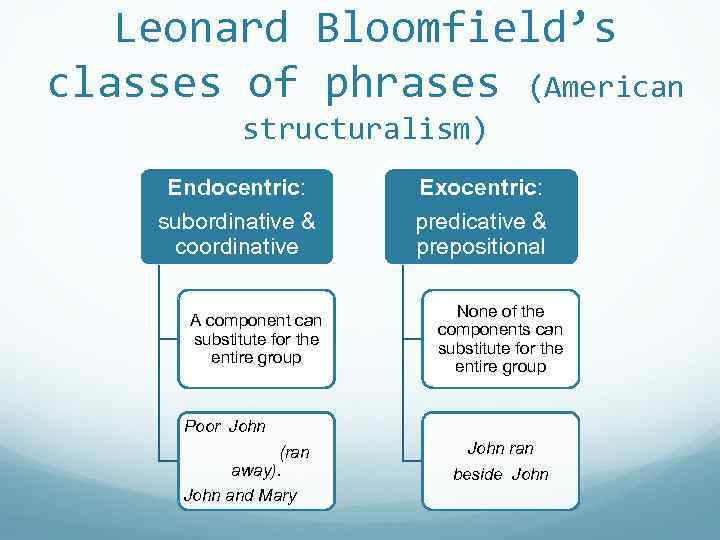 Leonard Bloomfield’s classes of phrases (American structuralism) Endocentric: subordinative & coordinative A component can substitute for the entire group Exocentric: predicative & prepositional None of the components can substitute for the entire group Poor John (ran away). John and Mary John ran beside John
Leonard Bloomfield’s classes of phrases (American structuralism) Endocentric: subordinative & coordinative A component can substitute for the entire group Exocentric: predicative & prepositional None of the components can substitute for the entire group Poor John (ran away). John and Mary John ran beside John
 Glossary Большой синтаксис Подчинительная связь Малый синтаксис Сочинительная связь Словосочетание Синтагматическая связь Сочетание / группа слов Аккумулятивная связь Оборот речи Полная предикация Коллокация Конституэнт Знаменательная часть речи Гипотаксис Функциональное слово Паратаксис Формативная группа слов Эквипотентный однородный зависимый
Glossary Большой синтаксис Подчинительная связь Малый синтаксис Сочинительная связь Словосочетание Синтагматическая связь Сочетание / группа слов Аккумулятивная связь Оборот речи Полная предикация Коллокация Конституэнт Знаменательная часть речи Гипотаксис Функциональное слово Паратаксис Формативная группа слов Эквипотентный однородный зависимый
 Союзная связь Формальное согласование Бессоюзная связь Смысловое согласование Ядро Односторпнняя связь Главное слово Двусторонняя связь зависимое слово Взаимозависимость Расширение Квалификативная связь Согласование Атрибутивная связь Управление Адвербиальная связь Примыкание Объектная связь замыкание
Союзная связь Формальное согласование Бессоюзная связь Смысловое согласование Ядро Односторпнняя связь Главное слово Двусторонняя связь зависимое слово Взаимозависимость Расширение Квалификативная связь Согласование Атрибутивная связь Управление Адвербиальная связь Примыкание Объектная связь замыкание
 Именное словосочетание Глагольное словосочетание Регрессивное словосочетание Прогрессивное словосочетание Эндоцентрическое словосочетание Экзоцентрическое словосочетание
Именное словосочетание Глагольное словосочетание Регрессивное словосочетание Прогрессивное словосочетание Эндоцентрическое словосочетание Экзоцентрическое словосочетание


