General Psychology lecture 5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. General Psychology Human Memory Lecture 5 Definition of Memory Processes Stages of memory storage Forgetting Improvement of memory
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. General Psychology Human Memory Lecture 5 Definition of Memory Processes Stages of memory storage Forgetting Improvement of memory
 In order to remember smth learn it! To test learning measure what is remembered! Memory involves storing information that is learned, so that it can be retrieved and used at a later time.
In order to remember smth learn it! To test learning measure what is remembered! Memory involves storing information that is learned, so that it can be retrieved and used at a later time.
 Retention level the amount of info stored after learning has taken place. Retention is measured by asking a person to retrieve previously learned info. Retention loss = forgetting a part of original learning that can’t be retrieved.
Retention level the amount of info stored after learning has taken place. Retention is measured by asking a person to retrieve previously learned info. Retention loss = forgetting a part of original learning that can’t be retrieved.
 Ebbinghaus Research H. Ebbinghaus demonstrated that a greater memory loss occurs in the first 20 min after learning than in the remaining 31 days. Savings score Time/Days App 100%- 80% App 60%- 50% 40% 35% 30% 25% 1 st/ immediate recall 1 st/ after 20 min 1 st/ after an hour 1 st/ after 9 hours 2 nd – 4 th 6 th- 31 st
Ebbinghaus Research H. Ebbinghaus demonstrated that a greater memory loss occurs in the first 20 min after learning than in the remaining 31 days. Savings score Time/Days App 100%- 80% App 60%- 50% 40% 35% 30% 25% 1 st/ immediate recall 1 st/ after 20 min 1 st/ after an hour 1 st/ after 9 hours 2 nd – 4 th 6 th- 31 st
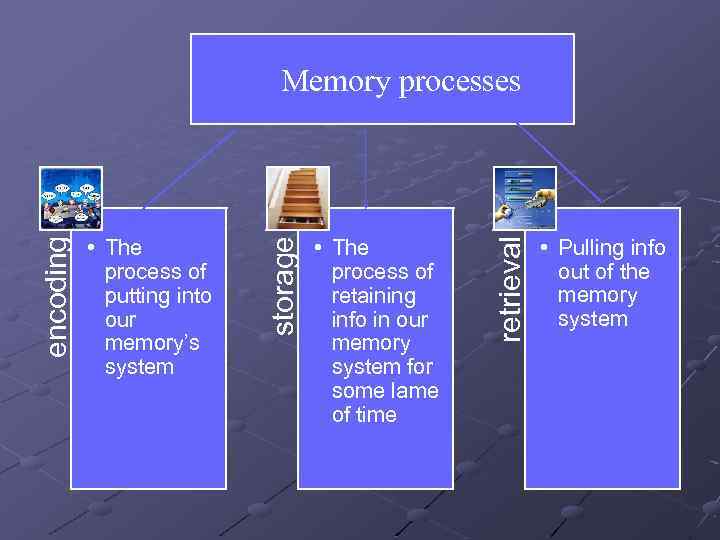 • The process of retaining info in our memory system for some lame of time retrieval • The process of putting into our memory’s system storage encoding Memory processes • Pulling info out of the memory system
• The process of retaining info in our memory system for some lame of time retrieval • The process of putting into our memory’s system storage encoding Memory processes • Pulling info out of the memory system
 Encoding (1 st step) process of putting information into our memory system (like in a computer) Influences on effectiveness 1) Perceive it (hear, see, touch, smell, taste) 2) Motivated to remember 3) Find this info meaningful or relevant to our life 4) Practice or rehearse it
Encoding (1 st step) process of putting information into our memory system (like in a computer) Influences on effectiveness 1) Perceive it (hear, see, touch, smell, taste) 2) Motivated to remember 3) Find this info meaningful or relevant to our life 4) Practice or rehearse it
 Storage (2 nd step) process of retaining information in our memory system for some length of time Sensory 3 memory stores short-term long-term SM (iconic/echoic) STM ( working active/immediate) LTM (semantic/episodic/procedural)
Storage (2 nd step) process of retaining information in our memory system for some length of time Sensory 3 memory stores short-term long-term SM (iconic/echoic) STM ( working active/immediate) LTM (semantic/episodic/procedural)
 Retrieval pulling information out of the memory system. We don’t know what is stored until we retrieve it. Sometimes it is adequately stored but not accessible at the moment. Success depends on effectiveness of encoding and storage.
Retrieval pulling information out of the memory system. We don’t know what is stored until we retrieve it. Sometimes it is adequately stored but not accessible at the moment. Success depends on effectiveness of encoding and storage.
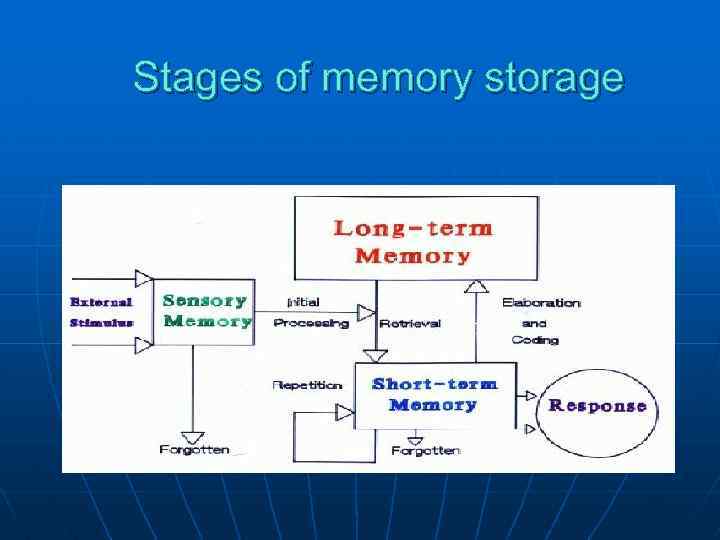 Stages of memory storage
Stages of memory storage
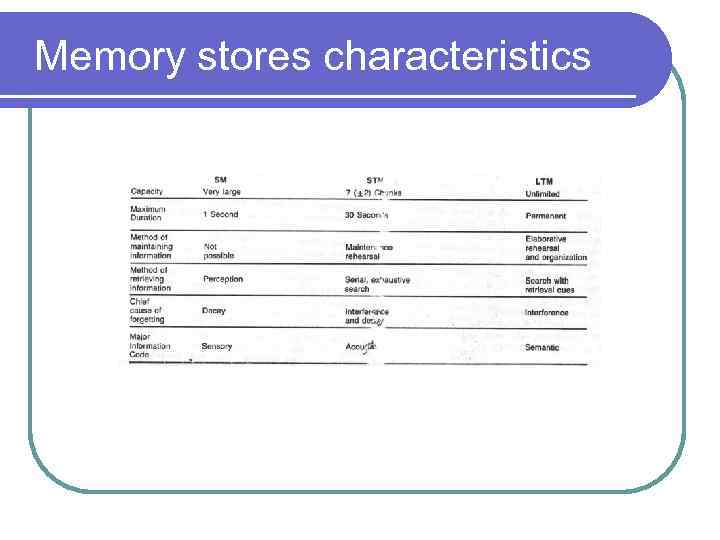 Memory stores characteristics
Memory stores characteristics
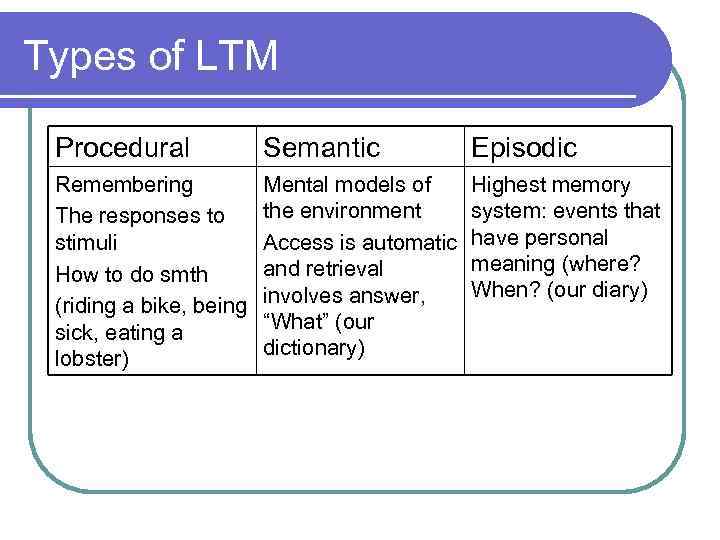 Types of LTM Procedural Semantic Episodic Remembering The responses to stimuli How to do smth (riding a bike, being sick, eating a lobster) Mental models of the environment Access is automatic and retrieval involves answer, “What” (our dictionary) Highest memory system: events that have personal meaning (where? When? (our diary)
Types of LTM Procedural Semantic Episodic Remembering The responses to stimuli How to do smth (riding a bike, being sick, eating a lobster) Mental models of the environment Access is automatic and retrieval involves answer, “What” (our dictionary) Highest memory system: events that have personal meaning (where? When? (our diary)
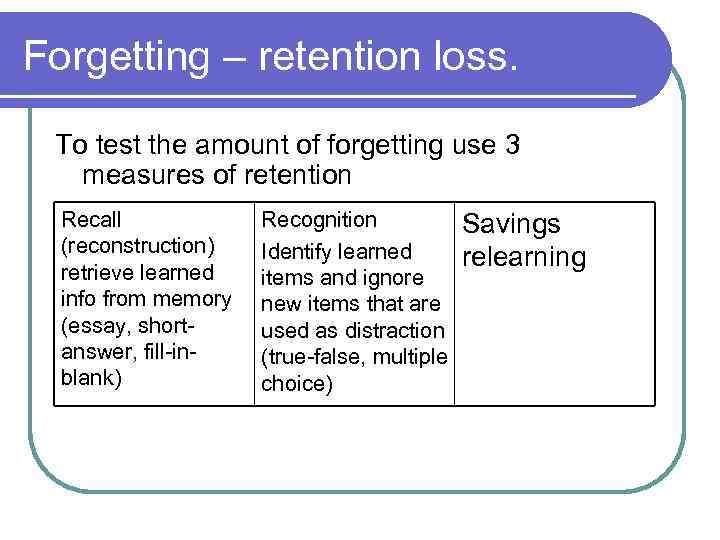 Forgetting – retention loss. To test the amount of forgetting use 3 measures of retention Recall (reconstruction) retrieve learned info from memory (essay, shortanswer, fill-inblank) Recognition Identify learned items and ignore new items that are used as distraction (true-false, multiple choice) Savings relearning
Forgetting – retention loss. To test the amount of forgetting use 3 measures of retention Recall (reconstruction) retrieve learned info from memory (essay, shortanswer, fill-inblank) Recognition Identify learned items and ignore new items that are used as distraction (true-false, multiple choice) Savings relearning
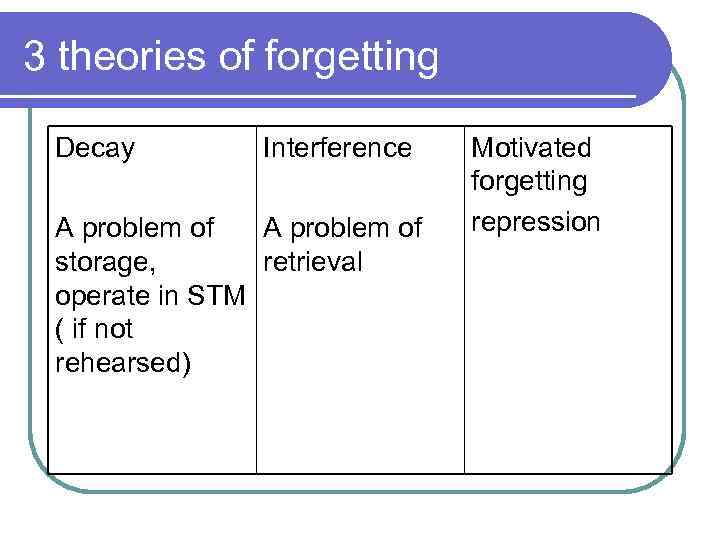 3 theories of forgetting Decay Interference A problem of storage, retrieval operate in STM ( if not rehearsed) Motivated forgetting repression
3 theories of forgetting Decay Interference A problem of storage, retrieval operate in STM ( if not rehearsed) Motivated forgetting repression
 Memory improvement
Memory improvement
 Questions for the seminar: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Define memory Describe encoding, storage, retrieval Iconic/echoic sensory memory Identify ‘attention’ and pattern recognition Characteristics of STM Metamemory Compare 3 types of long-term memory 3 measures of memory retention 3 theories of forgetting Techniques to improve memory
Questions for the seminar: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Define memory Describe encoding, storage, retrieval Iconic/echoic sensory memory Identify ‘attention’ and pattern recognition Characteristics of STM Metamemory Compare 3 types of long-term memory 3 measures of memory retention 3 theories of forgetting Techniques to improve memory
 Essay task: Describe your knowledge of you own memory ability. (how you learn to remember, your ability to encode, store and retrieve, types of memory and techniques to improve your memory) Literature: R. Atkinson. Introduction to Psychology. Ch. 8 pp 288 -330. Volunteer Reports 1. Emotional Factors in forgetting p 309 -311 2. Implicit Memory in amnesia and normal subjects. Pp 311315 3. Improving Memory pp 317 -326 – 3 people.
Essay task: Describe your knowledge of you own memory ability. (how you learn to remember, your ability to encode, store and retrieve, types of memory and techniques to improve your memory) Literature: R. Atkinson. Introduction to Psychology. Ch. 8 pp 288 -330. Volunteer Reports 1. Emotional Factors in forgetting p 309 -311 2. Implicit Memory in amnesia and normal subjects. Pp 311315 3. Improving Memory pp 317 -326 – 3 people.


