 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The main notions of Grammar The word and the morpheme Types of the opposition. Oppositional reduction Types of morphemes Types of words (stems) Means of form-building Рекомендуется к использованию при изучении дисциплины «Теоретическая грамматика английского языка Составитель: Познякова Т. М.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The main notions of Grammar The word and the morpheme Types of the opposition. Oppositional reduction Types of morphemes Types of words (stems) Means of form-building Рекомендуется к использованию при изучении дисциплины «Теоретическая грамматика английского языка Составитель: Познякова Т. М.
 The lexeme (child, children, child’s, children’s) the grammeme (child’s, boys’, bird’s, else’s… boys, children, phenomena, teeth, mice) the grammatical meaning (3 d person, singular number) the grammatical form the paradigm the grammatical category
The lexeme (child, children, child’s, children’s) the grammeme (child’s, boys’, bird’s, else’s… boys, children, phenomena, teeth, mice) the grammatical meaning (3 d person, singular number) the grammatical form the paradigm the grammatical category
 It is obligatory, it must be expressed in speech It must have a form of expression (inflexions, analytical form, word order, intonation). walks – is walking process The system of all grammatical lexemes constitute a It’s a means of expressing grammatical meaning, It may lend variety to speech, Many men – many a man It may convey the information more emotionally He is constantly slamming the door You are being naughty today. forms (grammemes ) of all PARADIGM
It is obligatory, it must be expressed in speech It must have a form of expression (inflexions, analytical form, word order, intonation). walks – is walking process The system of all grammatical lexemes constitute a It’s a means of expressing grammatical meaning, It may lend variety to speech, Many men – many a man It may convey the information more emotionally He is constantly slamming the door You are being naughty today. forms (grammemes ) of all PARADIGM
 a unity of a special grammatical form and a special grammatical meaning. a certain grammatical meaning which is expressed by a grammatical form expressing a special grammatical meaning. It is revealed by the method of binary OPPOSITIONS
a unity of a special grammatical form and a special grammatical meaning. a certain grammatical meaning which is expressed by a grammatical form expressing a special grammatical meaning. It is revealed by the method of binary OPPOSITIONS
 Unmarked (week) Make- – makes+ Marked (strong) Makes+ – making+
Unmarked (week) Make- – makes+ Marked (strong) Makes+ – making+
 Privative Equipollent Gradual Notional Formal Go- – went+ Built+ – was built+ good- – better+ - best+) Tense, gender, number, person Case, gender, order, article determination
Privative Equipollent Gradual Notional Formal Go- – went+ Built+ – was built+ good- – better+ - best+) Tense, gender, number, person Case, gender, order, article determination
 Neutralization Transposition Man is sinful. A rose is a beautiful flower. The train arrives at 5 tomorrow The sun had the Belsey house in her hands. In November an unseen stranger called Pneumonia touched people here and there with his icy fingers.
Neutralization Transposition Man is sinful. A rose is a beautiful flower. The train arrives at 5 tomorrow The sun had the Belsey house in her hands. In November an unseen stranger called Pneumonia touched people here and there with his icy fingers.
 Is one of the central notions of grammatical theory. is the smallest meaningful unit of a word-form (occurs in speech as a part of the word) It constitutes words (MORPHS) Is one of the basic units of language Is a naming unit of language Is the smallest meaningful unit of speech The main features are: -- isolatability -- uninterruptibility -- looseness
Is one of the central notions of grammatical theory. is the smallest meaningful unit of a word-form (occurs in speech as a part of the word) It constitutes words (MORPHS) Is one of the basic units of language Is a naming unit of language Is the smallest meaningful unit of speech The main features are: -- isolatability -- uninterruptibility -- looseness
 The word is a nominative unit of the language formed by morphemes, which enters the lexicon of the language as its elementary component used for the formation of the sentence with other nominative elements.
The word is a nominative unit of the language formed by morphemes, which enters the lexicon of the language as its elementary component used for the formation of the sentence with other nominative elements.
 Position in the word -Meaning - Function Root door Prefix in-doors Suffix form-al Infix teeth Lexical day lexical-grammatical Writ-er Grammatical strong-er form-building word-building
Position in the word -Meaning - Function Root door Prefix in-doors Suffix form-al Infix teeth Lexical day lexical-grammatical Writ-er Grammatical strong-er form-building word-building
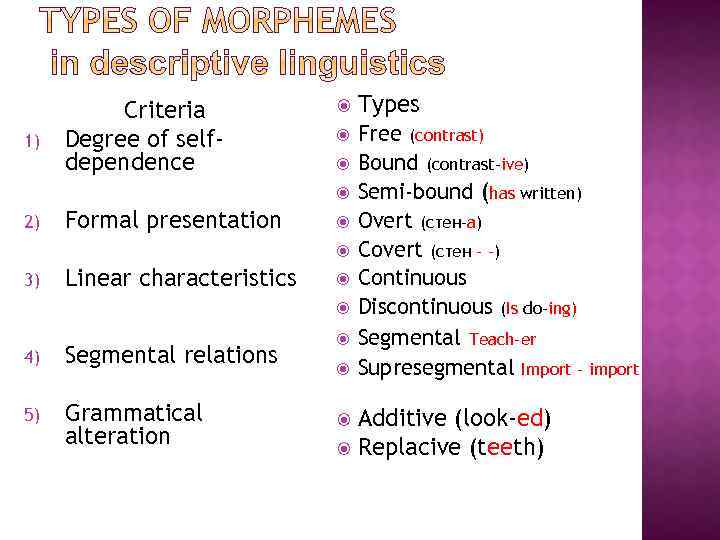 1) Criteria Degree of selfdependence Types Free (contrast) Bound (contrast-ive) Semi-bound (has written) Overt (стен-а) Covert (стен - -) Continuous Discontinuous (Is do-ing) Segmental Teach-er Supresegmental Import – import 2) Formal presentation 3) Linear characteristics 4) Segmental relations 5) Grammatical alteration Additive (look-ed) Replacive (teeth)
1) Criteria Degree of selfdependence Types Free (contrast) Bound (contrast-ive) Semi-bound (has written) Overt (стен-а) Covert (стен - -) Continuous Discontinuous (Is do-ing) Segmental Teach-er Supresegmental Import – import 2) Formal presentation 3) Linear characteristics 4) Segmental relations 5) Grammatical alteration Additive (look-ed) Replacive (teeth)
 Simple Derivative Compound Composite
Simple Derivative Compound Composite
 Synthetic : inner inflexion (teeth, tooth) outer inflexion (tables, doing) suppletivity (went, was) Analytical: possessing discontinuous morphemes bound morphemes (is waiting)
Synthetic : inner inflexion (teeth, tooth) outer inflexion (tables, doing) suppletivity (went, was) Analytical: possessing discontinuous morphemes bound morphemes (is waiting)
 1. A total grammatical meaning is built on the basis of a word combination of all components of the form. Each component in isolation doesn’t possess the information about the total meaning of the given form. 2. Among the components of the analytical form there are no syntactic relations. 3. Syntactic relations are possible for the whole form in total with its surroundings in a sentence 4. Analytical forms are correlated with synthetic forms. There must be at least one synthetic form in the paradigm. 5. Auxiliary elements lose their lexical meaning and can be contracted.
1. A total grammatical meaning is built on the basis of a word combination of all components of the form. Each component in isolation doesn’t possess the information about the total meaning of the given form. 2. Among the components of the analytical form there are no syntactic relations. 3. Syntactic relations are possible for the whole form in total with its surroundings in a sentence 4. Analytical forms are correlated with synthetic forms. There must be at least one synthetic form in the paradigm. 5. Auxiliary elements lose their lexical meaning and can be contracted.


