04_22_2015_JUDAISM.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 53
 04 22 2015 JUDAISM
04 22 2015 JUDAISM
 VIDEO: Matisyahu – King Without a Crown
VIDEO: Matisyahu – King Without a Crown
 Judaism Fact Sheet • FOUNDED: c. 2, 500 BCE in Mesopotamia • FOUNDING FIGURE: Abraham • POPULATION: 14 Million • MAIN LOCATION(s): Israel, Europe, USA • SACRED TEXT: Tanakh, Talmud • SPIRITUAL LEADER: Rabbi • PLACE OF WOSHIP: Synagogue • TYPE: Monotheist, Transcendent
Judaism Fact Sheet • FOUNDED: c. 2, 500 BCE in Mesopotamia • FOUNDING FIGURE: Abraham • POPULATION: 14 Million • MAIN LOCATION(s): Israel, Europe, USA • SACRED TEXT: Tanakh, Talmud • SPIRITUAL LEADER: Rabbi • PLACE OF WOSHIP: Synagogue • TYPE: Monotheist, Transcendent
 Monotheism • Atenism – (Egypt) Pharaoh Akhenaten (18 th Cent BCE) • Zoroastrianism – (Persia) Ahura Mazda, Zarathustra • Marduk – Babylon (Monolateralism – Development of Monotheism from Polytheism) • Ethical Monotheism - Judaism
Monotheism • Atenism – (Egypt) Pharaoh Akhenaten (18 th Cent BCE) • Zoroastrianism – (Persia) Ahura Mazda, Zarathustra • Marduk – Babylon (Monolateralism – Development of Monotheism from Polytheism) • Ethical Monotheism - Judaism
 The Shema – Declaration of Faith Hebrew – שמע ישראל יי אלהנו יי אחד Common transliteration – Shema Yisrael Adonai Eloheinu Adonai Echad English – Hear, O Israel! The Lord is our God! The Lord is One!
The Shema – Declaration of Faith Hebrew – שמע ישראל יי אלהנו יי אחד Common transliteration – Shema Yisrael Adonai Eloheinu Adonai Echad English – Hear, O Israel! The Lord is our God! The Lord is One!
 Abrahamic Religions • Judaism • Christianity • Islam • Baha’i Faith
Abrahamic Religions • Judaism • Christianity • Islam • Baha’i Faith
 Abraham • Patriarch of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam • Covenant • ‘Sacrifice’ of Isaac
Abraham • Patriarch of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam • Covenant • ‘Sacrifice’ of Isaac
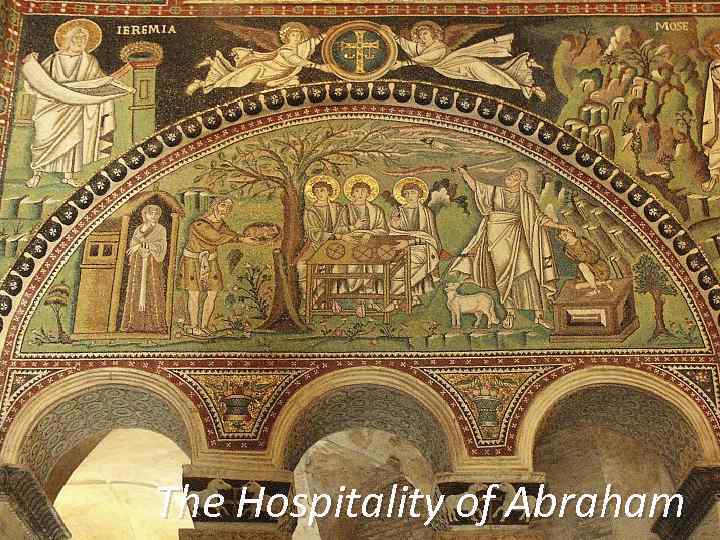
 The Hospitality of Abraham
The Hospitality of Abraham
 • Theophany – An appearance of God, a meeting with the divine, or a sacred disclosure.
• Theophany – An appearance of God, a meeting with the divine, or a sacred disclosure.
 Jacob And he said: 'Thy name shall be called no more Jacob, but Israel; for thou hast striven with God and with men, and hast prevailed. '
Jacob And he said: 'Thy name shall be called no more Jacob, but Israel; for thou hast striven with God and with men, and hast prevailed. '
 The Influence of Judaism
The Influence of Judaism
 Meager Beginnings • In 3000 BCE, Egypt already had pyramids. • The Sumerian and Harappan civilizations had already been established. • The Hebrews were a tiny nomadic people. • Canaan was 150 miles by 50 miles thick at its widest. • Monotonous terrain. • They shared a similar history with other tiny groups of the time of being pushed around by super powers.
Meager Beginnings • In 3000 BCE, Egypt already had pyramids. • The Sumerian and Harappan civilizations had already been established. • The Hebrews were a tiny nomadic people. • Canaan was 150 miles by 50 miles thick at its widest. • Monotonous terrain. • They shared a similar history with other tiny groups of the time of being pushed around by super powers.
 What lifts Judaism from obscurity to religious greatness is its passion for meaning.
What lifts Judaism from obscurity to religious greatness is its passion for meaning.
 There is meaning in their concept of God (The Other) • The other as the origin (unmoved mover). • The other as natural power underscoring human limitations. • When combined they form the “wholly other”, the “Big Other”, “O”: the concept of God.
There is meaning in their concept of God (The Other) • The other as the origin (unmoved mover). • The other as natural power underscoring human limitations. • When combined they form the “wholly other”, the “Big Other”, “O”: the concept of God.
 However, this ‘Other’ would be meaningless if it had any of the following characteristics: 1. Prosaic 2. Chaotic 3. Amoral 4. Hostile
However, this ‘Other’ would be meaningless if it had any of the following characteristics: 1. Prosaic 2. Chaotic 3. Amoral 4. Hostile
 In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Prosaic (dull or ordinary) • The universe isn’t dull and meaningless but saturated with meaning. • The universe is more like a mind than a machine.
In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Prosaic (dull or ordinary) • The universe isn’t dull and meaningless but saturated with meaning. • The universe is more like a mind than a machine.
 In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Chaotic • The Hebrews have a unified decision maker. Harmony and Order
In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Chaotic • The Hebrews have a unified decision maker. Harmony and Order
 In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Amoral “ If the gods are as the Romans believed them to be – immoral, vindictive, and capricious – meaningful existence requires that they be opposed or rejected. ” - Lucretius
In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Amoral “ If the gods are as the Romans believed them to be – immoral, vindictive, and capricious – meaningful existence requires that they be opposed or rejected. ” - Lucretius
 In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Hostile Yahweh watches over widows and orphans, and speaks the name “Abraham” lifting his people out of slavery.
In order to be meaningful the concept of God cannot be Hostile Yahweh watches over widows and orphans, and speaks the name “Abraham” lifting his people out of slavery.
 There is meaning in the interpretation of creation: • “God created heaven and the earth, and it was good. ” • Physical realm as meaningful (vs. being illusory, defective, or unimportant).
There is meaning in the interpretation of creation: • “God created heaven and the earth, and it was good. ” • Physical realm as meaningful (vs. being illusory, defective, or unimportant).
 There is meaning in human existence. We are a blend of dust and divinity. • There is meaning in our morality. • There is meaning in our history. • There is meaning in our pain and our suffering.
There is meaning in human existence. We are a blend of dust and divinity. • There is meaning in our morality. • There is meaning in our history. • There is meaning in our pain and our suffering.
 TRADITIONAL JUDAISM The Middle-Eastern Masters of Meaning
TRADITIONAL JUDAISM The Middle-Eastern Masters of Meaning

 Brief History (Ancient) (from the perspective of Judaism) • • C. 1800 BCE - Abraham C. 1250 BCE – Moses (Exodus from Egypt) 975 BCE – King David establishes Israel 967 BCE – King Solomon builds first temple in Jerusalem 565 BCE – Babylonians destroy the temple, exile to Babylonia. 515 BCE – Dedication of Second Temple C. 200 BCE - Completion of the last books of Hebrew scripture. 70 CE – Romans destroy Second Temple.
Brief History (Ancient) (from the perspective of Judaism) • • C. 1800 BCE - Abraham C. 1250 BCE – Moses (Exodus from Egypt) 975 BCE – King David establishes Israel 967 BCE – King Solomon builds first temple in Jerusalem 565 BCE – Babylonians destroy the temple, exile to Babylonia. 515 BCE – Dedication of Second Temple C. 200 BCE - Completion of the last books of Hebrew scripture. 70 CE – Romans destroy Second Temple.
 Moses (10 Commandments)
Moses (10 Commandments)
 The 10 Commandments 1. You shall have no other God but me. (Exclusive) 2. No idols, images, or likenesses of anything in the heavens 3. You shall not take the Lords name in vain (use it incorrectly) 4. Keep the Sabbath 5. Honor your Father and Mother 6. You shall not murder 7. You shall not commit adultery 8. You shall not steal 9. You shall not give false evidence against your neighbor 10. You shall not covet your neighbor's house, wife, livestock
The 10 Commandments 1. You shall have no other God but me. (Exclusive) 2. No idols, images, or likenesses of anything in the heavens 3. You shall not take the Lords name in vain (use it incorrectly) 4. Keep the Sabbath 5. Honor your Father and Mother 6. You shall not murder 7. You shall not commit adultery 8. You shall not steal 9. You shall not give false evidence against your neighbor 10. You shall not covet your neighbor's house, wife, livestock
 King Solomon’s Temple
King Solomon’s Temple
 • Biblical Judaism – Temple Religion • Rabbinical Judaism – after 70 CE and the destruction of the second temple (diaspora).
• Biblical Judaism – Temple Religion • Rabbinical Judaism – after 70 CE and the destruction of the second temple (diaspora).
 Sacred Texts • Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) • Talmud (305) (commentaries, scholarship, paradoxes) - Thou shalt love thy God. - Adam and Eve (the threat of dying)
Sacred Texts • Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) • Talmud (305) (commentaries, scholarship, paradoxes) - Thou shalt love thy God. - Adam and Eve (the threat of dying)
 Judaism Sacred Text Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) – Acronym for the three basic sections (TNK). • Torah (Teachings) – 5 books of Moses: Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, Deuteronomy • Nevi’im (Prophets – Josiah, Judges, Samuel, Isaiah • Ketuvim (Writings) – Psalms, Proverbs, Job
Judaism Sacred Text Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) – Acronym for the three basic sections (TNK). • Torah (Teachings) – 5 books of Moses: Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, Deuteronomy • Nevi’im (Prophets – Josiah, Judges, Samuel, Isaiah • Ketuvim (Writings) – Psalms, Proverbs, Job

 Hellenistic and Roman Era • • Pharisees – strict observance of the laws Sadducees – Family of high priests Essenes – Celibate, vegetarian, ascetic practices Zealots – Opposed Roman occupation
Hellenistic and Roman Era • • Pharisees – strict observance of the laws Sadducees – Family of high priests Essenes – Celibate, vegetarian, ascetic practices Zealots – Opposed Roman occupation
![Medieval Period Persecution in Europe [Bavaria, 1338] Medieval Period Persecution in Europe [Bavaria, 1338]](https://present5.com/presentation/199950391_384685138/image-34.jpg) Medieval Period Persecution in Europe [Bavaria, 1338]
Medieval Period Persecution in Europe [Bavaria, 1338]
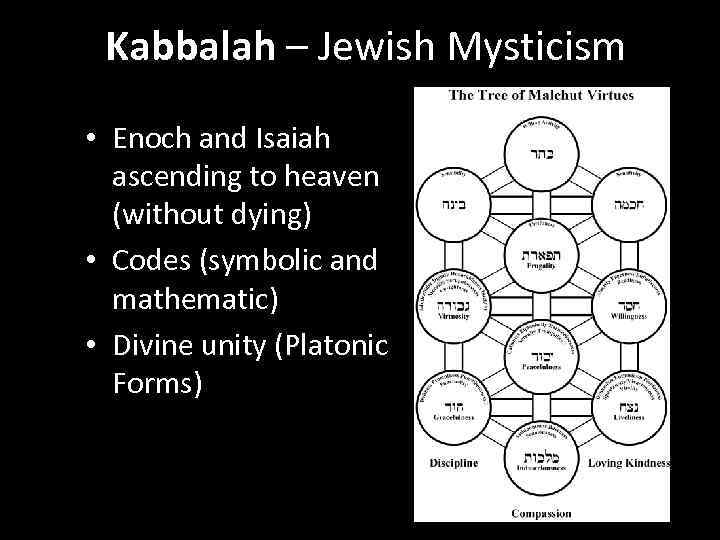 Kabbalah – Jewish Mysticism • Enoch and Isaiah ascending to heaven (without dying) • Codes (symbolic and mathematic) • Divine unity (Platonic Forms)
Kabbalah – Jewish Mysticism • Enoch and Isaiah ascending to heaven (without dying) • Codes (symbolic and mathematic) • Divine unity (Platonic Forms)
 Renaissance (Enlightenment Ideals) • • Human dignity Equality Liberty Reason/ Science “No man has received from nature the right to give orders to others. Freedom is a gift from heaven, and every individual of the same species has the right to enjoy it as soon as he is in enjoyment of his reason. ” – Denis Diderot
Renaissance (Enlightenment Ideals) • • Human dignity Equality Liberty Reason/ Science “No man has received from nature the right to give orders to others. Freedom is a gift from heaven, and every individual of the same species has the right to enjoy it as soon as he is in enjoyment of his reason. ” – Denis Diderot
 In Reaction to the Enlightenment • Hasidism – Reaffirms traditional beliefs, scholarship, devotion, rules. • Reform – Incorporates Enlightenment ideals
In Reaction to the Enlightenment • Hasidism – Reaffirms traditional beliefs, scholarship, devotion, rules. • Reform – Incorporates Enlightenment ideals
 Holidays Hanukkah (winter festival) – Commemorates the rededication of the 2 nd temple. Rosh Hashanah (New Year) – late September- early October (at the end of Harvest season) culminating in Yom Kippur (Day of fasting and atonement). Passover - Seder (meal) Yom Hashoah – Remembrance of the holocaust.
Holidays Hanukkah (winter festival) – Commemorates the rededication of the 2 nd temple. Rosh Hashanah (New Year) – late September- early October (at the end of Harvest season) culminating in Yom Kippur (Day of fasting and atonement). Passover - Seder (meal) Yom Hashoah – Remembrance of the holocaust.
 Rituals • Lighting of the Menorah • Tefillin (Phylacteries) - Leather boxes containing scrolls of verses from the Torah (Video) • Talit – Prayer Shawl • Yarmulke – skull cap • Circumcision • Bar/Bat Mitzvah – Rites of Passage (319) • Mikvaot (Wedding Bath) cleansing
Rituals • Lighting of the Menorah • Tefillin (Phylacteries) - Leather boxes containing scrolls of verses from the Torah (Video) • Talit – Prayer Shawl • Yarmulke – skull cap • Circumcision • Bar/Bat Mitzvah – Rites of Passage (319) • Mikvaot (Wedding Bath) cleansing
 Yamaka (Yarmulke)
Yamaka (Yarmulke)
 Branches of Judaism Cultural Differences • Sephartic (Southern Spain, Mediterranean) • Ashkenazi (Central European) (Yiddish) Observational Differences • Orthodox • Conservative • Reform • Reconstruction
Branches of Judaism Cultural Differences • Sephartic (Southern Spain, Mediterranean) • Ashkenazi (Central European) (Yiddish) Observational Differences • Orthodox • Conservative • Reform • Reconstruction
 Orthodox (Traditional) Judaism Differ on integration with secular society and support of Israel. Hold to tradition practices • Males and Females separate at Synagouge • Quorum (10 Jewish men) necessary for service • Services conducted in Hebrew • Male Rabbis • Talit and Tefillin (every weekday morning) • Only males get Bar Mitzvah-ed • Males must keep head covered • Women – household managers, Men – bread winners • Beards (Men) • Hasidic Black cap and coat • Strict Sabbath rules
Orthodox (Traditional) Judaism Differ on integration with secular society and support of Israel. Hold to tradition practices • Males and Females separate at Synagouge • Quorum (10 Jewish men) necessary for service • Services conducted in Hebrew • Male Rabbis • Talit and Tefillin (every weekday morning) • Only males get Bar Mitzvah-ed • Males must keep head covered • Women – household managers, Men – bread winners • Beards (Men) • Hasidic Black cap and coat • Strict Sabbath rules
 Conservative • Hold Orthodox practices with small variations; will change but reluctant.
Conservative • Hold Orthodox practices with small variations; will change but reluctant.
 Reform Judaism • Moses Mendelssohn (1729 -1786) • Embraces enlightenment ideals: human dignity, equality, individual liberty, democracy, secular education, science. • Native tongue services • Men and Women integrated • Talit and Tefillin (optional) • No traditional garb necessary. • Female Rabbis allowed • Bat Mitzvah
Reform Judaism • Moses Mendelssohn (1729 -1786) • Embraces enlightenment ideals: human dignity, equality, individual liberty, democracy, secular education, science. • Native tongue services • Men and Women integrated • Talit and Tefillin (optional) • No traditional garb necessary. • Female Rabbis allowed • Bat Mitzvah
 Reconstructionist Judaism • Mordecai Kaplan (1881 -1983) • Emphasized the interpretations of individuals • More symbolic readings • And the evolving nature of religion
Reconstructionist Judaism • Mordecai Kaplan (1881 -1983) • Emphasized the interpretations of individuals • More symbolic readings • And the evolving nature of religion
 Jewish Atheism?
Jewish Atheism?
![Zionism • The nationalistic movement that supports the creation of a Jewish Homeland [Israel] Zionism • The nationalistic movement that supports the creation of a Jewish Homeland [Israel]](https://present5.com/presentation/199950391_384685138/image-48.jpg) Zionism • The nationalistic movement that supports the creation of a Jewish Homeland [Israel] • The Anti-Diaspora • Theodor Herzl (1860 -1904) – The Father of modern Political Zionism • Kabbalah –Zion as The mystical point where reality emerges. • Appropriation by Rastafarianism (Zion – Freedom, Babylonoppression)
Zionism • The nationalistic movement that supports the creation of a Jewish Homeland [Israel] • The Anti-Diaspora • Theodor Herzl (1860 -1904) – The Father of modern Political Zionism • Kabbalah –Zion as The mystical point where reality emerges. • Appropriation by Rastafarianism (Zion – Freedom, Babylonoppression)
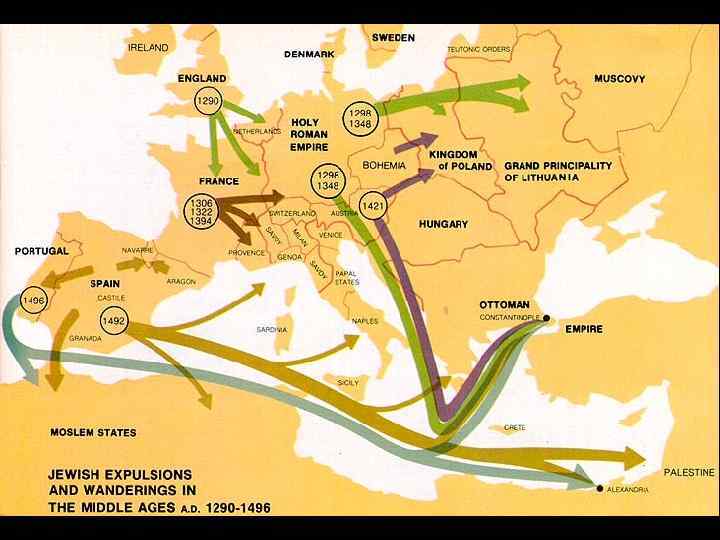
 Modern History • 1090 – Crusades (persecution of Jews in Europe) • Jews banned from England, France, Spain, and Portugal. • 1884 – Zionism : the political movement to regain control of Jerusalem. • 1937 -1945 – The Holocaust (Shoah) • 1948 – The Establishment of the Jewish State of Israel. • 1948 – Present – Continuing violence between Jews and Palestinians.
Modern History • 1090 – Crusades (persecution of Jews in Europe) • Jews banned from England, France, Spain, and Portugal. • 1884 – Zionism : the political movement to regain control of Jerusalem. • 1937 -1945 – The Holocaust (Shoah) • 1948 – The Establishment of the Jewish State of Israel. • 1948 – Present – Continuing violence between Jews and Palestinians.
 Shoah (The Holocaust) Holocaust By 1945, 12 million people had died in concentration camps, an estimated 6 million of them were Jews.
Shoah (The Holocaust) Holocaust By 1945, 12 million people had died in concentration camps, an estimated 6 million of them were Jews.
 ISRAEL
ISRAEL

 1. Catholicism Next 2. Eastern Orthodox 3. Coptic (Egyptian) 4. Mormonism 5. Jehovah’s Witness 6. Quaker 7. Anglican (Episcopalian) 8. Calvinism 9. Methodism 10. Baptism 11. Lutheran 12. Pentecostal up Christianity
1. Catholicism Next 2. Eastern Orthodox 3. Coptic (Egyptian) 4. Mormonism 5. Jehovah’s Witness 6. Quaker 7. Anglican (Episcopalian) 8. Calvinism 9. Methodism 10. Baptism 11. Lutheran 12. Pentecostal up Christianity


