Environment Chap# 02.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 35
 02 UNDERSTANDING INTERNAL & EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENTS Sayed Gheyasuddin “SAADAT” sayedbba@gmail. com
02 UNDERSTANDING INTERNAL & EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENTS Sayed Gheyasuddin “SAADAT” sayedbba@gmail. com
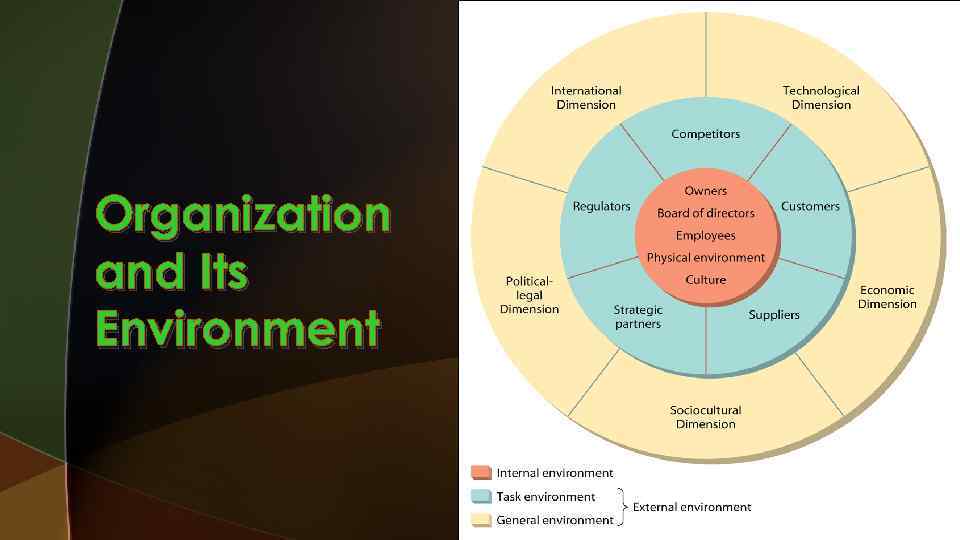 Organization and Its Environment
Organization and Its Environment
 External environment u ‘Major forces outside the organisation with potential to influence significantly a product or service’s likely success. ’ everything outside an organization’s boundaries that might affect it. u 3
External environment u ‘Major forces outside the organisation with potential to influence significantly a product or service’s likely success. ’ everything outside an organization’s boundaries that might affect it. u 3
 External environment is made up of: u. The Mega-environment The broad conditions and trends in societies in which an organisation operates. u. The Task environment Specific outside elements with which an organisation interfaces in the course of conducting its business. 4
External environment is made up of: u. The Mega-environment The broad conditions and trends in societies in which an organisation operates. u. The Task environment Specific outside elements with which an organisation interfaces in the course of conducting its business. 4
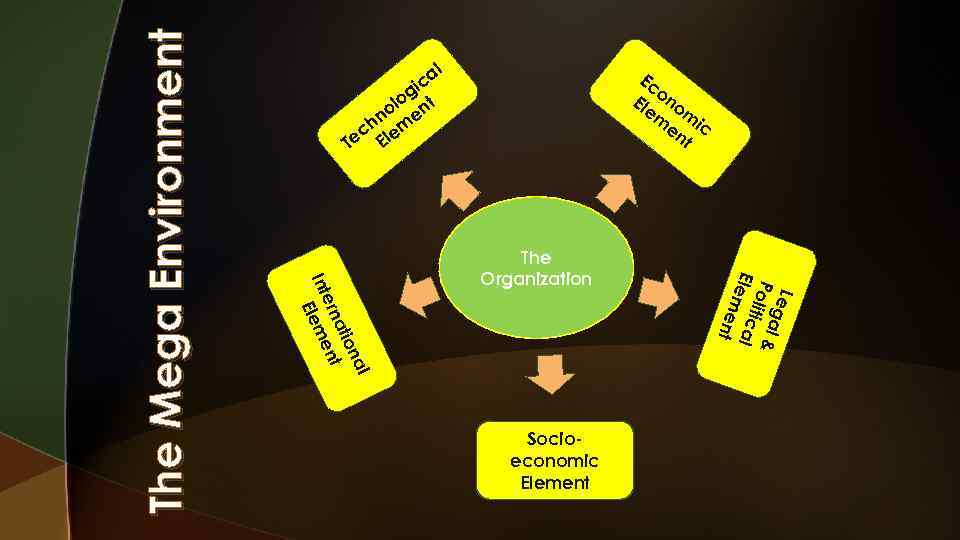 Ec o Ele no m mi en c t The Organization Socioeconomic Element Leg a Poli l & t Elem ical ent al on ati nt ern Int leme E The Mega Environment al c gi o ol ent hn m c Te Ele
Ec o Ele no m mi en c t The Organization Socioeconomic Element Leg a Poli l & t Elem ical ent al on ati nt ern Int leme E The Mega Environment al c gi o ol ent hn m c Te Ele
 The Mega-environment Five major elements: u. Technological element Current state of knowledge regarding production of products & services. Or Methods available for converting resources into products or services. Ex: u CAD (computer-assisted design) techniques u Use of internet in all areas of business 6
The Mega-environment Five major elements: u. Technological element Current state of knowledge regarding production of products & services. Or Methods available for converting resources into products or services. Ex: u CAD (computer-assisted design) techniques u Use of internet in all areas of business 6
 The Mega-environment u. Economic element Overall health and vitality of the economic system in which the organization operates. Usually influenced by economic growth, inflation interest rates and unemployment. u. Legal-political element Refers to government regulation of business and the relationship between business and government. Legal & governmental systems within which an organisation must function.
The Mega-environment u. Economic element Overall health and vitality of the economic system in which the organization operates. Usually influenced by economic growth, inflation interest rates and unemployment. u. Legal-political element Refers to government regulation of business and the relationship between business and government. Legal & governmental systems within which an organisation must function.
 The Mega-environment u. Socio-cultural element Attitudes, values, norms, beliefs, behaviours & associated demographic trends characteristic of a given geographic area. Ex: u Consumer tastes change over time – preferences for color, style, taste, etc. change from season to season. 8
The Mega-environment u. Socio-cultural element Attitudes, values, norms, beliefs, behaviours & associated demographic trends characteristic of a given geographic area. Ex: u Consumer tastes change over time – preferences for color, style, taste, etc. change from season to season. 8
 The Mega-environment u. International element Developments in countries outside of an organisation’s home country with potential to influence the organisation. u u Multinational firms are clearly affected by businesses in other countries. [car and aircraft manufacturers, restaurants, electronics firms, etc. ] Virtually every organization is affected by the international dimension of its general environment.
The Mega-environment u. International element Developments in countries outside of an organisation’s home country with potential to influence the organisation. u u Multinational firms are clearly affected by businesses in other countries. [car and aircraft manufacturers, restaurants, electronics firms, etc. ] Virtually every organization is affected by the international dimension of its general environment.
 Mc. Donald’s General Environment
Mc. Donald’s General Environment
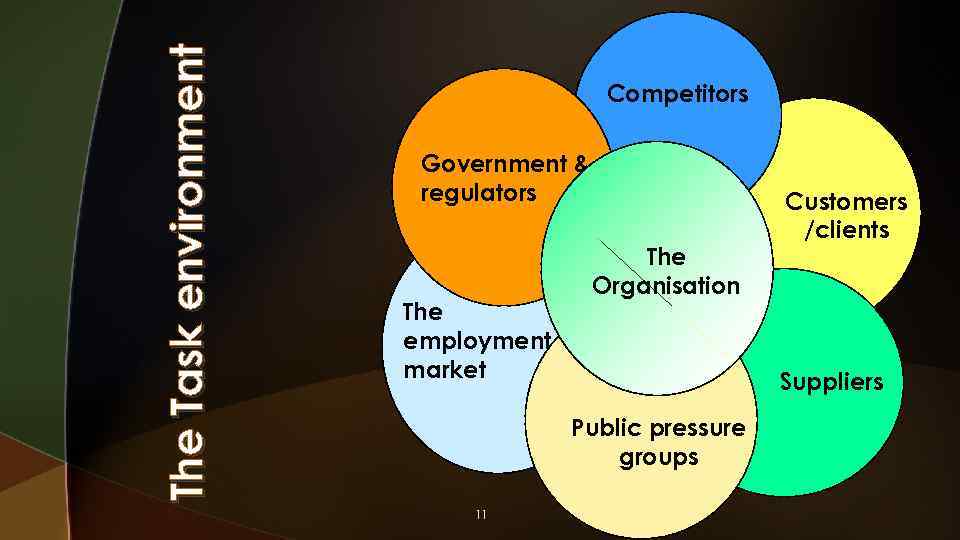 The Task environment Competitors Government & regulators The employment market The Organisation Suppliers Public pressure groups 11 Customers /clients
The Task environment Competitors Government & regulators The employment market The Organisation Suppliers Public pressure groups 11 Customers /clients
 The Task environment Five elements: u. Customers and clients Individuals and organisations purchasing products/services. u. Whoever pays money to acquire an organization’s products or services. u. Customers of major organizations may include: schools, hospitals, government agencies, wholesalers, retailers and manufacturers. u. Companies who expand internationally face critical differences [no beef served in India, alcohol served in Germany and France as a part of the menu]. 12
The Task environment Five elements: u. Customers and clients Individuals and organisations purchasing products/services. u. Whoever pays money to acquire an organization’s products or services. u. Customers of major organizations may include: schools, hospitals, government agencies, wholesalers, retailers and manufacturers. u. Companies who expand internationally face critical differences [no beef served in India, alcohol served in Germany and France as a part of the menu]. 12
 The Task environment u. Competitors Other organisations either offering (or a high potential of offering) rival products/services. u Other organizations that compete with our organization for resources such as raw materials. 13
The Task environment u. Competitors Other organisations either offering (or a high potential of offering) rival products/services. u Other organizations that compete with our organization for resources such as raw materials. 13
 The Task environment u. Suppliers Organisations and individuals supplying resources an organisation needs to conduct its operations. u. Organizations that provide resources for other organizations. u. Mc. Donald’s depends on Heinz for its ketchup packets and Coca-Cola for its soft drinks. u. Labour supply Individuals potentially employable by an organisation.
The Task environment u. Suppliers Organisations and individuals supplying resources an organisation needs to conduct its operations. u. Organizations that provide resources for other organizations. u. Mc. Donald’s depends on Heinz for its ketchup packets and Coca-Cola for its soft drinks. u. Labour supply Individuals potentially employable by an organisation.
 The Task environment u. Government agencies Agencies providing services and monitoring compliance with laws and regulations at local, State or regional and national levels. u. A unit that has the potential to control, legislate or otherwise influence the organization's policies and practices. u. Regulatory agencies – created by the government to protect the public from certain business practices or to protect organizations from one another.
The Task environment u. Government agencies Agencies providing services and monitoring compliance with laws and regulations at local, State or regional and national levels. u. A unit that has the potential to control, legislate or otherwise influence the organization's policies and practices. u. Regulatory agencies – created by the government to protect the public from certain business practices or to protect organizations from one another.
 Mc. Donald’s Task Environment
Mc. Donald’s Task Environment
 Internal environment Nature of organisational culture: General Conditions existing within an organization. u‘A system of shared values, assumption, beliefs and norms uniting organisational members’ u‘The way we do things around here. ’ u. The ‘glue’ binding the disparate parts (or the oil that keeps them moving). u 17
Internal environment Nature of organisational culture: General Conditions existing within an organization. u‘A system of shared values, assumption, beliefs and norms uniting organisational members’ u‘The way we do things around here. ’ u. The ‘glue’ binding the disparate parts (or the oil that keeps them moving). u 17
 The Internal Environment u. Owner: someone who has legal property rights to a business. u. Board of directors: governing body elected by a corporation’s stockholders and charged with overseeing the general management of the firm. u. Employees: those employed by the organization. u. Physical work environment: the firm’s facilities. 18
The Internal Environment u. Owner: someone who has legal property rights to a business. u. Board of directors: governing body elected by a corporation’s stockholders and charged with overseeing the general management of the firm. u. Employees: those employed by the organization. u. Physical work environment: the firm’s facilities. 18
 Board of Directors u. A board of directors is only required of organizations that are incorporated; however, many other firms have them. The board of directors is elected by the stockholders and is charged with overseeing the general management of the firm to ensure that it is being run in a way that best serves the stockholders' interests.
Board of Directors u. A board of directors is only required of organizations that are incorporated; however, many other firms have them. The board of directors is elected by the stockholders and is charged with overseeing the general management of the firm to ensure that it is being run in a way that best serves the stockholders' interests.
 Employees u. When the organization's employees hold the same values and goals as its management, everyone wins. However, when managers and employees work toward different goals everyone suffers. The composition of the organization's employees is changing, and managers must learn how to deal effectively with these changes.
Employees u. When the organization's employees hold the same values and goals as its management, everyone wins. However, when managers and employees work toward different goals everyone suffers. The composition of the organization's employees is changing, and managers must learn how to deal effectively with these changes.
 Culture u. The culture of an organization is the set of values that helps its members understand what the organization stands for, how it does things, and what it considers important. u. A strong organizational culture can shape the firm's overall effectiveness and long-term success and help employees to be more productive.
Culture u. The culture of an organization is the set of values that helps its members understand what the organization stands for, how it does things, and what it considers important. u. A strong organizational culture can shape the firm's overall effectiveness and long-term success and help employees to be more productive.
 Managing Organizational Culture u. The manager must understand the current culture and then decide if it should be maintained or changed. u. Managers must walk a fine line between maintaining a culture that still works effectively versus changing a culture that has become dysfunctional. 22
Managing Organizational Culture u. The manager must understand the current culture and then decide if it should be maintained or changed. u. Managers must walk a fine line between maintaining a culture that still works effectively versus changing a culture that has become dysfunctional. 22
 What is SWOT Analysis ?
What is SWOT Analysis ?
 SWOT Analysis SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats Identification of the threats and opportunities in the external environment and strengths and weaknesses in the internal environment of the firms are the cornerstone of business policy formulation.
SWOT Analysis SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats Identification of the threats and opportunities in the external environment and strengths and weaknesses in the internal environment of the firms are the cornerstone of business policy formulation.
 Strengths • Strengths—internal to the unit; are a unit’s resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for developing a competitive advantage; strength should be realistic and not modest. Your list of strengths should be able to answer: • What are the unit’s advantages? • What does the unit do well? • What relevant resources do you have access to? • What do other people see as your strengths? • What would you want to boast about to someone who knows nothing about this organization and its work?
Strengths • Strengths—internal to the unit; are a unit’s resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for developing a competitive advantage; strength should be realistic and not modest. Your list of strengths should be able to answer: • What are the unit’s advantages? • What does the unit do well? • What relevant resources do you have access to? • What do other people see as your strengths? • What would you want to boast about to someone who knows nothing about this organization and its work?
 • Examples: good reputation among customers, resources, assets, people, : experience, knowledge, data, capabilities • Think in terms of: capabilities; competitive advantages; resources, assets, people • (experience, knowledge); marketing; quality; location; accreditations • qualifications, certifications; processes/systems
• Examples: good reputation among customers, resources, assets, people, : experience, knowledge, data, capabilities • Think in terms of: capabilities; competitive advantages; resources, assets, people • (experience, knowledge); marketing; quality; location; accreditations • qualifications, certifications; processes/systems
 Weaknesses • Weaknesses—internal force that could serve as a barrier to maintain or achieve a competitive advantage; a limitation, fault or defect of the unit; • It should be truthful so that they may be overcome as quickly as possible?
Weaknesses • Weaknesses—internal force that could serve as a barrier to maintain or achieve a competitive advantage; a limitation, fault or defect of the unit; • It should be truthful so that they may be overcome as quickly as possible?
 Your list of weaknesses should be able to answer: • What can be improved? • What is done poorly? • What should be avoided? • What are you doing as an organization that you feel could be done more effectively/efficiently? • What is this organization NOT doing that you feel it should be doing • If you could change one thing that would help this department function more effectively, what would you change? • Examples: gaps in capabilities, financial, deadlines, morale • lack of competitive
Your list of weaknesses should be able to answer: • What can be improved? • What is done poorly? • What should be avoided? • What are you doing as an organization that you feel could be done more effectively/efficiently? • What is this organization NOT doing that you feel it should be doing • If you could change one thing that would help this department function more effectively, what would you change? • Examples: gaps in capabilities, financial, deadlines, morale • lack of competitive
 Opportunities • Opportunities—any favorable situation present now or in the future in the external environment. Examples: unfulfilled customer need, arrival of new technologies, loosening of regulations, global influences, economic boom, demographic shift • Where are the good opportunities facing you? • What are the interesting trends you are aware of? • Think of: market developments; competitor; vulnerabilities; industry/ lifestyle trends; ; geographical; partnerships
Opportunities • Opportunities—any favorable situation present now or in the future in the external environment. Examples: unfulfilled customer need, arrival of new technologies, loosening of regulations, global influences, economic boom, demographic shift • Where are the good opportunities facing you? • What are the interesting trends you are aware of? • Think of: market developments; competitor; vulnerabilities; industry/ lifestyle trends; ; geographical; partnerships
 Threats • External force that could inhibit the maintenance or attainment of a competitive advantage; any unfavorable situation in the external environment that is potentially damaging now or in the future. • Examples: shifts in consumer tastes, new regulations, political or legislative effects, environmental effects, new technology, loss of key staff, economic downturn, demographic shifts, competitor intent; market demands; sustaining internal capability; insurmountable weaknesses; financial backing
Threats • External force that could inhibit the maintenance or attainment of a competitive advantage; any unfavorable situation in the external environment that is potentially damaging now or in the future. • Examples: shifts in consumer tastes, new regulations, political or legislative effects, environmental effects, new technology, loss of key staff, economic downturn, demographic shifts, competitor intent; market demands; sustaining internal capability; insurmountable weaknesses; financial backing
 Your list of threats should be able to answer: • What obstacles do you face? • What is your competition doing? • Are the required specifications for your job/services changing? • Is changing technology threatening your position? • Do you have financial problems? • Could any of your weaknesses seriously threaten your unit?
Your list of threats should be able to answer: • What obstacles do you face? • What is your competition doing? • Are the required specifications for your job/services changing? • Is changing technology threatening your position? • Do you have financial problems? • Could any of your weaknesses seriously threaten your unit?
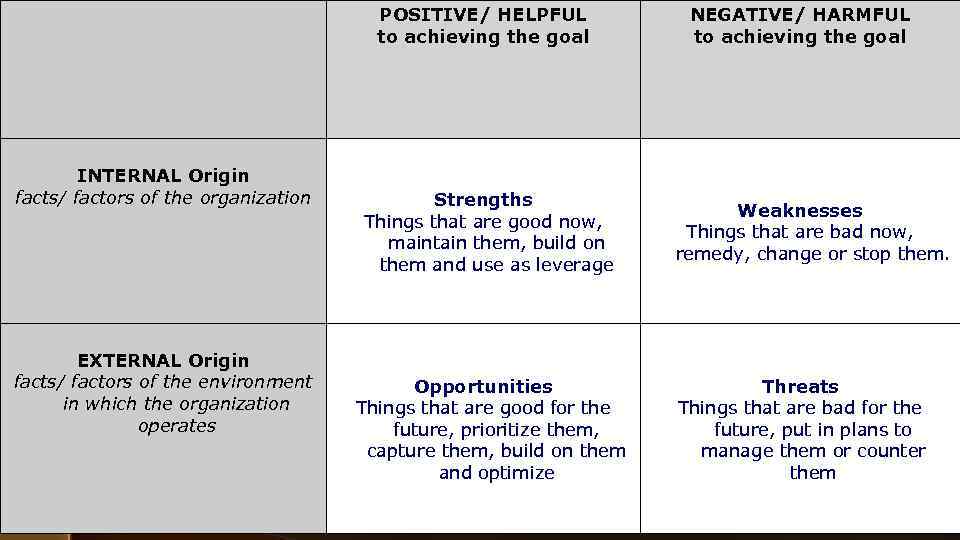 INTERNAL Origin facts/ factors of the organization EXTERNAL Origin facts/ factors of the environment in which the organization operates POSITIVE/ HELPFUL to achieving the goal Strengths Things that are good now, maintain them, build on them and use as leverage Opportunities Things that are good for the future, prioritize them, capture them, build on them and optimize NEGATIVE/ HARMFUL to achieving the goal Weaknesses Things that are bad now, remedy, change or stop them. Threats Things that are bad for the future, put in plans to manage them or counter them
INTERNAL Origin facts/ factors of the organization EXTERNAL Origin facts/ factors of the environment in which the organization operates POSITIVE/ HELPFUL to achieving the goal Strengths Things that are good now, maintain them, build on them and use as leverage Opportunities Things that are good for the future, prioritize them, capture them, build on them and optimize NEGATIVE/ HARMFUL to achieving the goal Weaknesses Things that are bad now, remedy, change or stop them. Threats Things that are bad for the future, put in plans to manage them or counter them
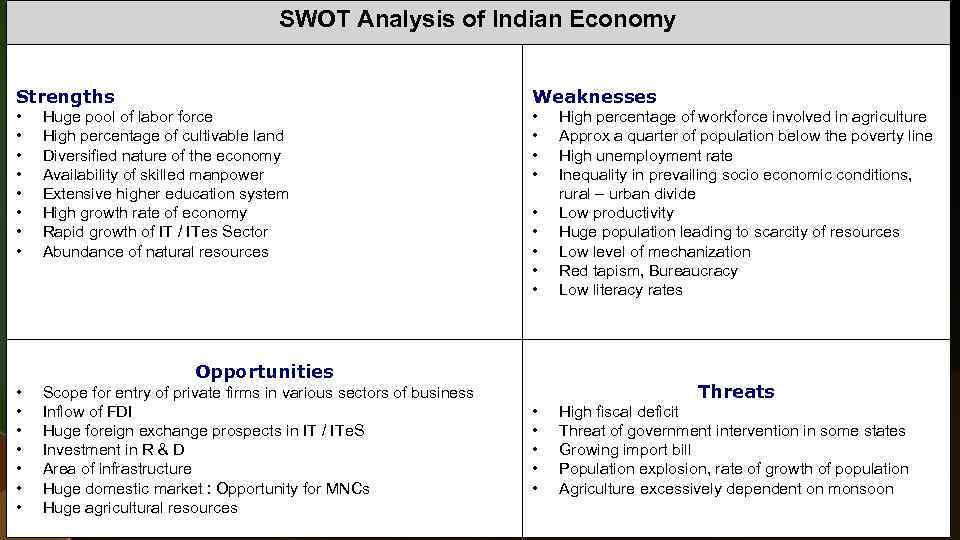 SWOT Analysis of Indian Economy Strengths Weaknesses • • • Huge pool of labor force High percentage of cultivable land Diversified nature of the economy Availability of skilled manpower Extensive higher education system High growth rate of economy Rapid growth of IT / ITes Sector Abundance of natural resources • • • Opportunities • • Scope for entry of private firms in various sectors of business Inflow of FDI Huge foreign exchange prospects in IT / ITe. S Investment in R & D Area of infrastructure Huge domestic market : Opportunity for MNCs Huge agricultural resources High percentage of workforce involved in agriculture Approx a quarter of population below the poverty line High unemployment rate Inequality in prevailing socio economic conditions, rural – urban divide Low productivity Huge population leading to scarcity of resources Low level of mechanization Red tapism, Bureaucracy Low literacy rates Threats • • • High fiscal deficit Threat of government intervention in some states Growing import bill Population explosion, rate of growth of population Agriculture excessively dependent on monsoon
SWOT Analysis of Indian Economy Strengths Weaknesses • • • Huge pool of labor force High percentage of cultivable land Diversified nature of the economy Availability of skilled manpower Extensive higher education system High growth rate of economy Rapid growth of IT / ITes Sector Abundance of natural resources • • • Opportunities • • Scope for entry of private firms in various sectors of business Inflow of FDI Huge foreign exchange prospects in IT / ITe. S Investment in R & D Area of infrastructure Huge domestic market : Opportunity for MNCs Huge agricultural resources High percentage of workforce involved in agriculture Approx a quarter of population below the poverty line High unemployment rate Inequality in prevailing socio economic conditions, rural – urban divide Low productivity Huge population leading to scarcity of resources Low level of mechanization Red tapism, Bureaucracy Low literacy rates Threats • • • High fiscal deficit Threat of government intervention in some states Growing import bill Population explosion, rate of growth of population Agriculture excessively dependent on monsoon
 Questions
Questions
 Thank You
Thank You


