611989ae8913f7a72f604630d0357713.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 98

ﺩکﺘﺮ ﻣﻬﺮﺯﺍﺩ آﺮﺗﻨگ

Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care 2015

ﻫﻨگﺎﻡ ﺍﺭﺍﺋﻪ ﻣﺮﺍﻗﺒﺖ ﺑﻪ یک ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ ﻗﻠﺒی ﺑﻪ ﻧکﺎﺕ ﺯیﺮ ﺩﻗﺖ کﻨیﻢ : 1. 2. 3. 4. ﺗﺨﻔیﻒ ﺍﺿﻄﺮﺍﺏ ﻭ کﺎﻫﺶ ﺩﺭﺩ ﺟﻠﻮگیﺮی ﺍﺯ ﻫیپﻮکﺴی ﺟﻠﻮگیﺮی ﺍﺯ آﺮیﺘﻤی کﺸﻨﺪﻩ ﻧگﻬﺪﺍﺭی ﺧﻮﻥ ﺭﺳﺎﻧی کﺎﻓی

SUDDEN CARDIAC ARREST • ﻋﺪﻡ ﻟﻤﺲ ﻧﺒﺾ ﺣﺘی ﺑﺎ ﻭﺟﻮﺩ ﺿﺮﺑﺎﻥ ﺩﺍﺭ ﺑﻮﺩﻥ ﻗﻠﺐ

ﻟﻤﺲ کﺪﺍﻡ ﻧﺒﺾ ﻣﻬﻢ ﺍﺳﺖ ؟ ü کﺎﺭﻭﺗیﺪ ü ﻓﻤﻮﺭﺍﻝ ü ﺩﺍﺧﻞ ﺑﺎﺯﻭﺋی )ﺑﺮﺍکیﺎﻝ (

ﻧکﺘﻪ • ﺷﺎیﻌﺘﺮیﻦ آﺮیﺘﻤی ﺩﺭ یک SCA ﻓیﺒﺮیﻼﺳیﻮﻥ ﺑﻄﻨی ) ( VF ﻣی ﺑﺎﺷﺪ. )58% ( • ﺩﻓیﺒﺮﻩ کﺮﺩﻥ ﺯﻭﺩ ﻫﻨگﺎﻡ )کﻤﺘﺮ ﺍﺯ 4 ﺩﻗیﻘﻪ( ﺑﻬﻤﺮﺍﻩ CPR ﺷﺎﻧﺲ ﺑﻘﺎ 03% ﺑﺪﻭﻥ 20% CPR • ﺩﻓیﺒﺮﻩ کﺮﺩﻥ ﺗﺎﺧیﺮی ) 01 ﺩﻗیﻘﻪ ( ﺑﻬﻤﺮﺍﻩ CPR ﺷﺎﻧﺲ ﺑﻘﺎ 8% ﺑﺪﻭﻥ % 2 - 0 CPR
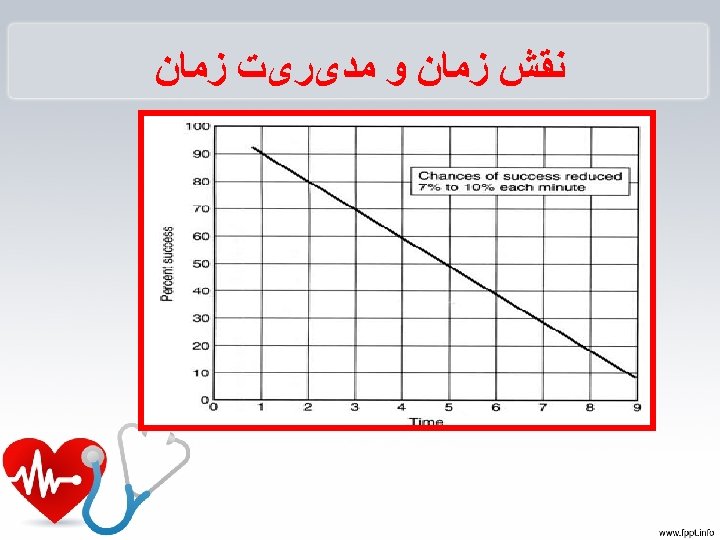
ﻧﻘﺶ ﺯﻣﺎﻥ ﻭ ﻣﺪیﺮیﺖ ﺯﻣﺎﻥ
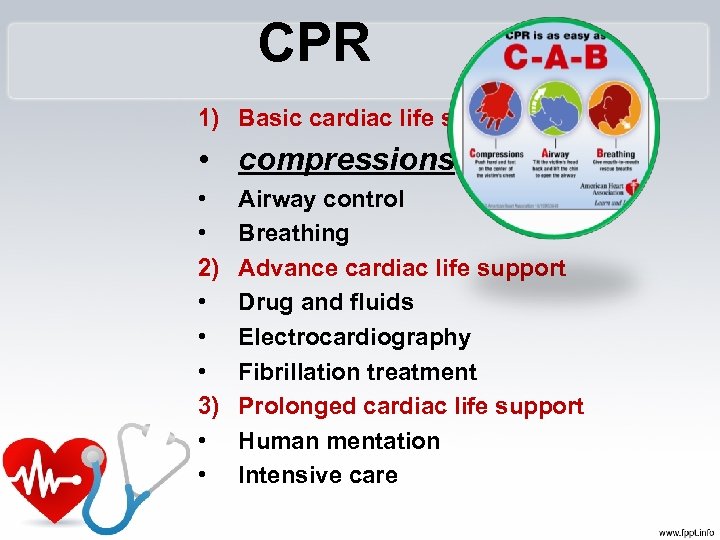
CPR 1) Basic cardiac life support • compressions • • 2) • • • 3) • • Airway control Breathing Advance cardiac life support Drug and fluids Electrocardiography Fibrillation treatment Prolonged cardiac life support Human mentation Intensive care
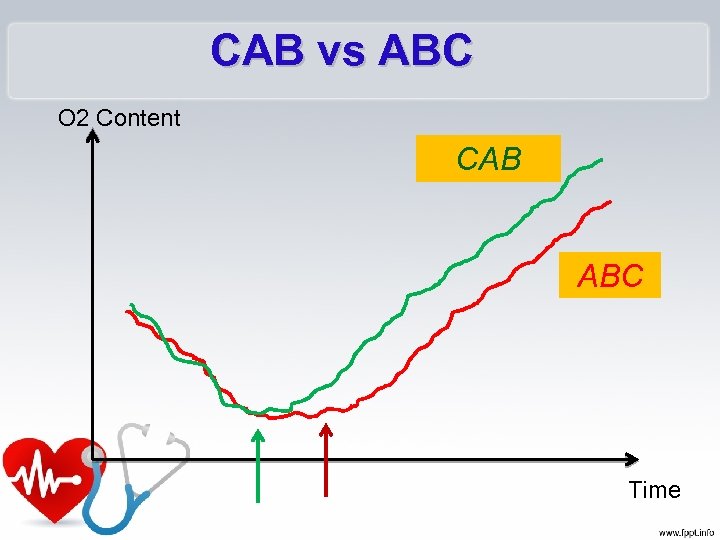
CAB vs ABC O 2 Content CAB ABC Time

Start CPR Immediately • Better chance of survival • Brain damage starts in 4 -6 minutes • Brain damage is certain after 10 minutes without CPR Provides O 2 to the brain until ACLS arrives
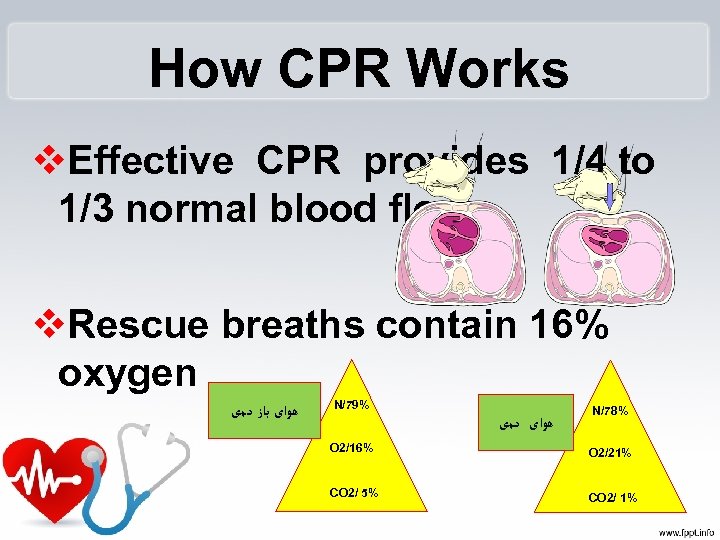
How CPR Works v. Effective CPR provides 1/4 to 1/3 normal blood flow v. Rescue breaths contain 16% oxygen ﻫﻮﺍی ﺑﺎﺯ ﺩﻣی N/79% ﻫﻮﺍی ﺩﻣی N/78% O 2/16% O 2/21% CO 2/ 5% CO 2/ 1%

Do Not Move the Victim Until CPR is Given and Qualified Help Arrives… Ø unless the scene dictates otherwise vthreat of fire or explosion vvictim must be on a hard surface v. Place victim level or head slightly lower than body

Survey The Scene, then: R. A. P • R - Responsivenes s – Tap shoulder and shout “Are you ok? ”
R. A. P • A - Activate EMS 115 OR
R. A. P • P - Position on back –All body parts rolled over at the same time • Always be aware of head and spinal cord injuries • Support neck and spinal column

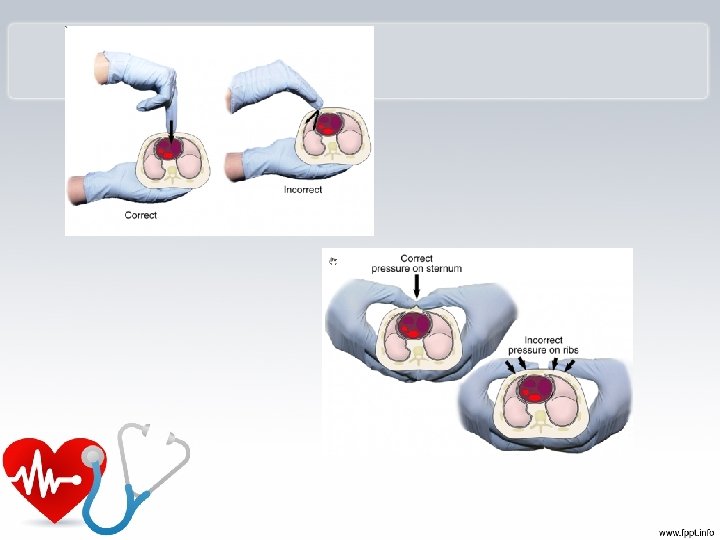
Compressions q. Locate proper hand position for chest compressions q. Place heel of one hand on center of chest between the nipples
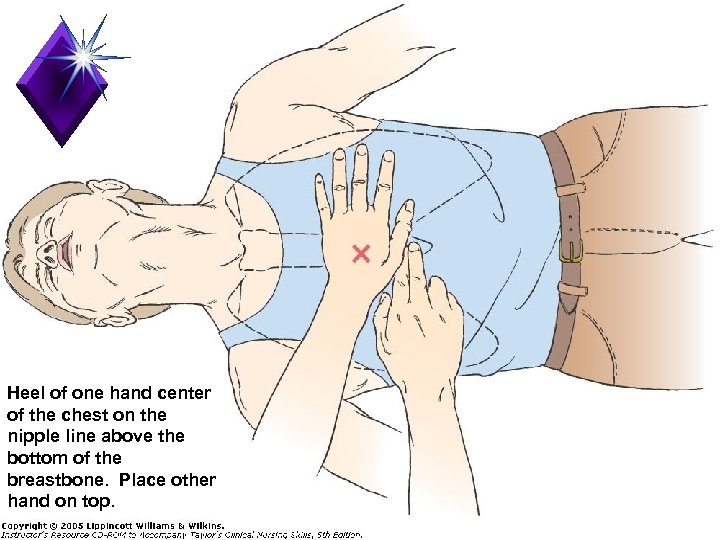
Heel of one hand center of the chest on the nipple line above the bottom of the breastbone. Place other hand on top.


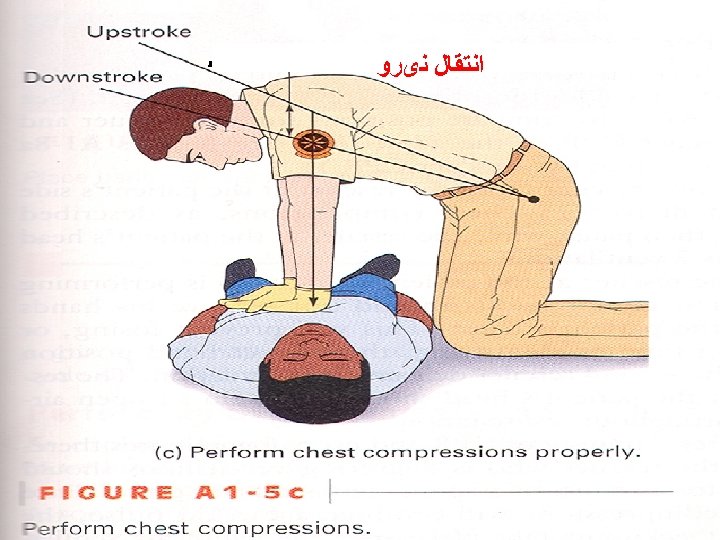
ﺍﻧﺘﻘﺎﻝ ﻧیﺮﻭ -----------------------
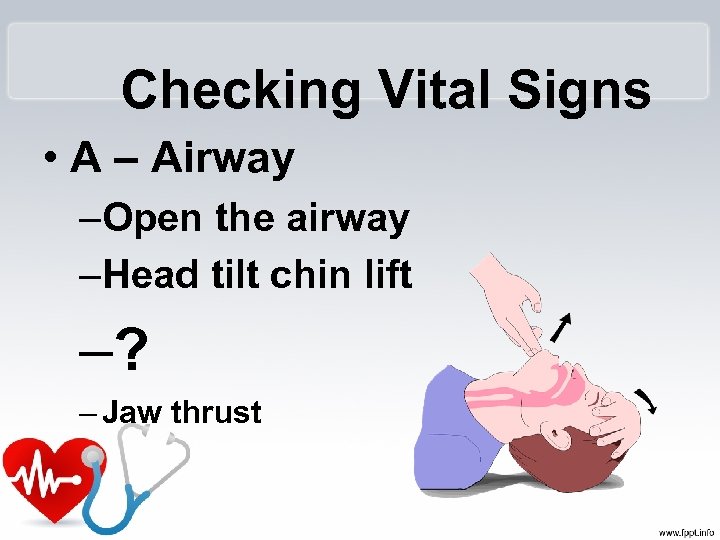
Checking Vital Signs • A – Airway –Open the airway –Head tilt chin lift –? – Jaw thrust
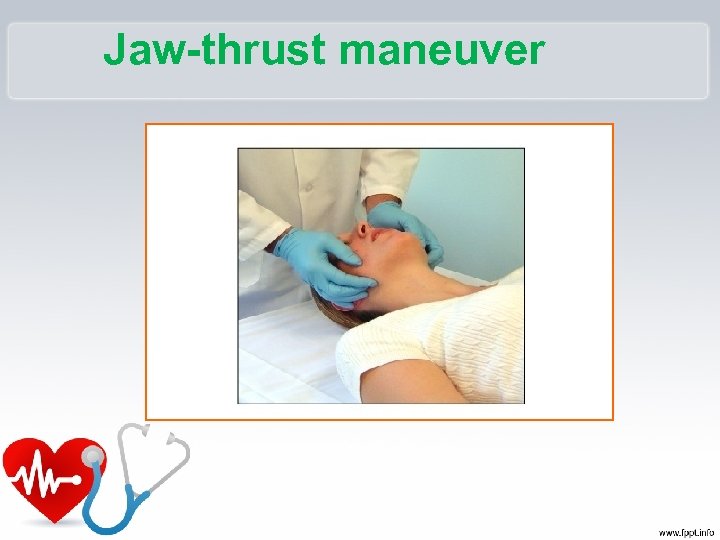
Jaw-thrust maneuver
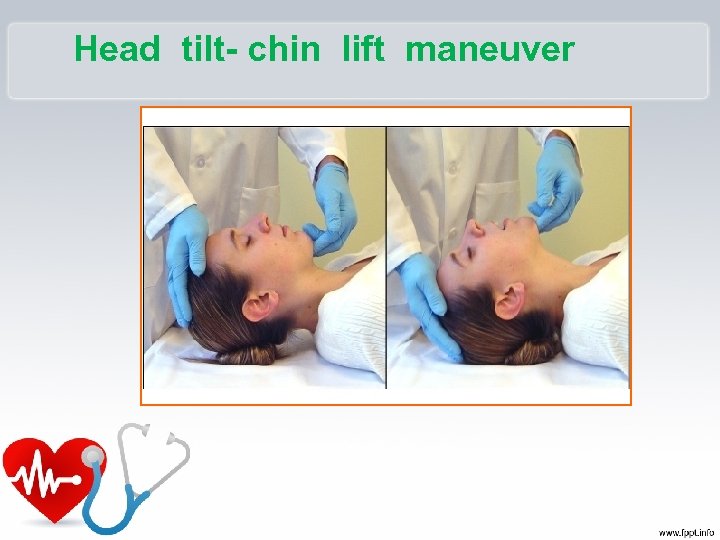
Head tilt- chin lift maneuver

B – Check For Breathing Look, listen and feel for breathing No longer than 10 seconds

Breathing • If the victim is not breathing, give two breaths (1 second or longer) – Pinch the nose – Seal the mouth with yours • If the first two don’t go in, re -tilt and give two more breaths (if breaths still do not go in, suspect choking)

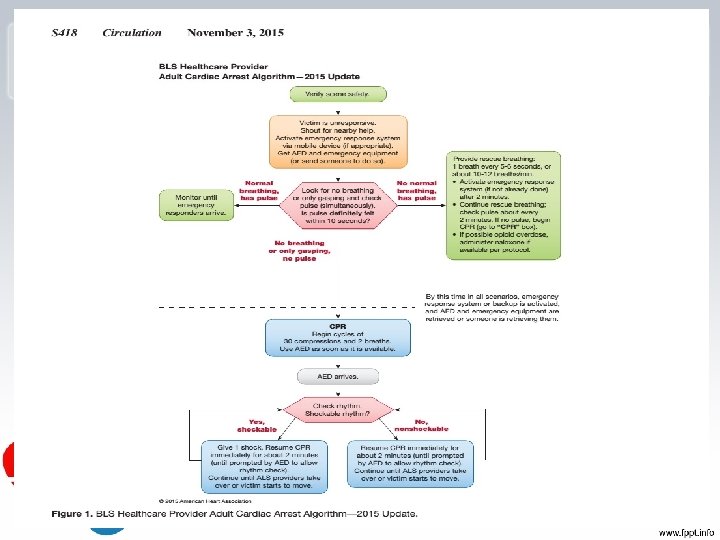
1 Rescuer CPR for Adults • - Check for scene safety (making sure you and the victim is free of danger). • – Check for responsiveness (tapping the shoulders with both hands while saying “are you ok”). • – If no response, yell for help. If someone comes, tell him/her to phone 115 and get an AED. If no one comes, phone 115 immediately and then begin the step of CPR. • A – Open the Airway (head-tilt-chin-lift or Jaw thrust) Look, Listen, Feel for breath (5 – 10 seconds. ). Just say, “I’m looking to see if the chest is rising and listening and feeling for breath” and you’ll be fine. • B –Perform a “head tilt chin lift” and Give 2 breaths (give enough breath to make the chest rise). ***remember to pinch the nose. • Start five cycles of 30 compressions and 2 breaths • Remember—if an AED arrives on the scene (for adult CPR) stop CPR and use AED
Injuries Related to CPR • Rib fractures • Laceration related to the tip of the sternum –Liver, lung, spleen

Stomach Distension


ﻫیپﻮکﺴی ﻭ ﺳﺎکﺸﻦ ﺑﺮﺍی ﺟﻠﻮگیﺮی ﺍﺯ ﺍیﻦ ﻣﺸکﻞ ، ﺳﺎکﺸﻦ کﺮﺩﻥ ﺭﺍ ﺑﻪ 51ﺛﺎﻧیﻪ ﺩﺭ ﺑﺎﻟﻐیﻦ ﻭ 5 ﺛﺎﻧیﻪ ﺩﺭ ﺍﻃﻔﺎﻝ ﻣﺤﺪﻭﺩ کﻨیﺪ. ﺳﺎکﺸﻦ کﺎﻫﺶ ﺿﺮﺑﺎﻥ ﻗﻠﺐ
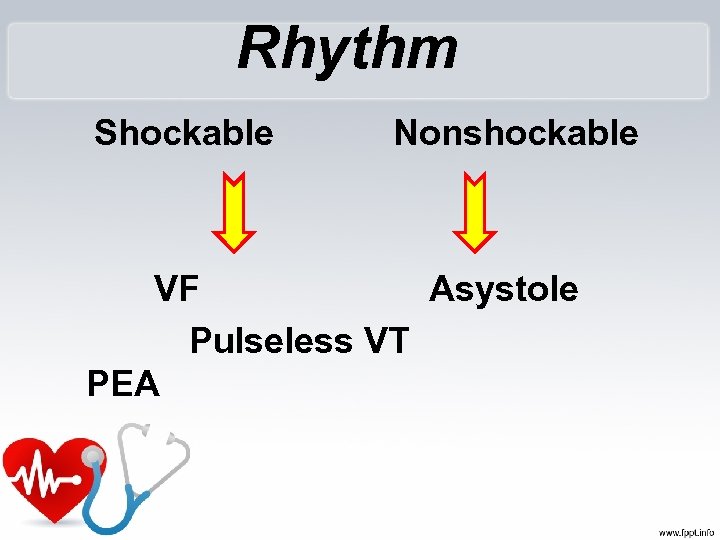
Rhythm Shockable Nonshockable VF Asystole Pulseless VT PEA

Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) • Previously called electromechanical dissociation • PEA is often associated with specific clinical states that can be reversed when identified early and effectively treated. • Survival is poor when the electrical activity is wide and/or slow. • These rhythms may be associated with hyperkalemia, hypothermia, hypoxia, preexisting acidosis, or a variety of drug overdoses (eg, tricyclic antidepressants, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin)
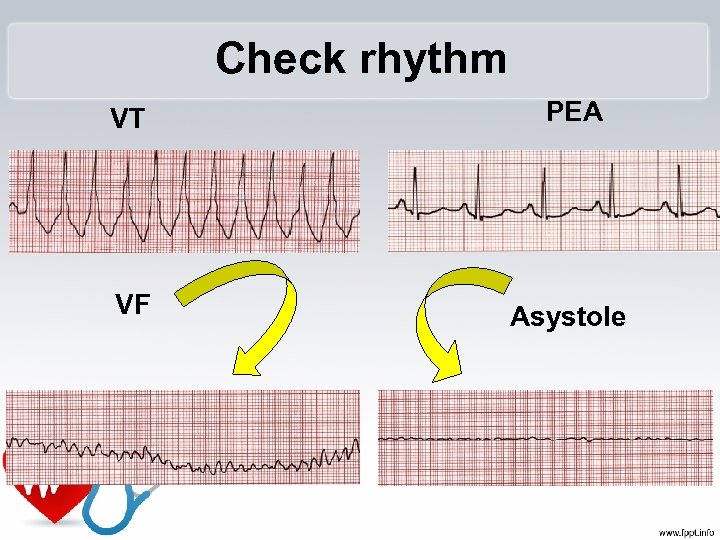
Check rhythm VT VF PEA Asystole
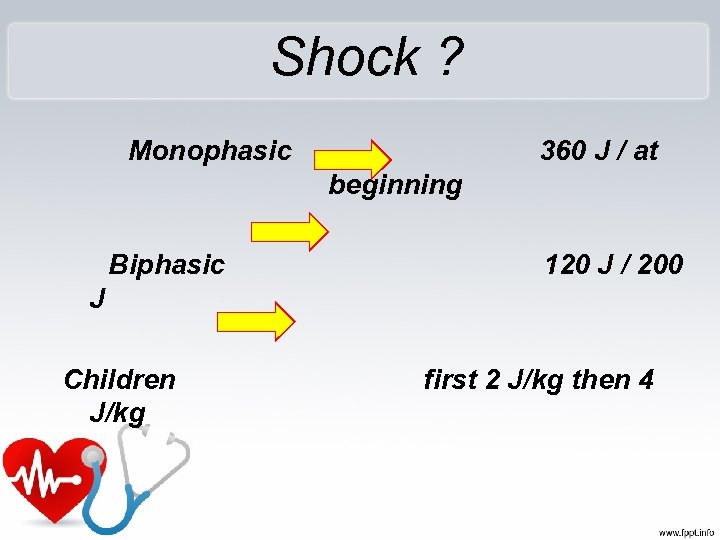
Shock ? Monophasic 360 J / at beginning Biphasic 120 J / 200 J Children J/kg first 2 J/kg then 4

Do not check pulse until The rhythm changed

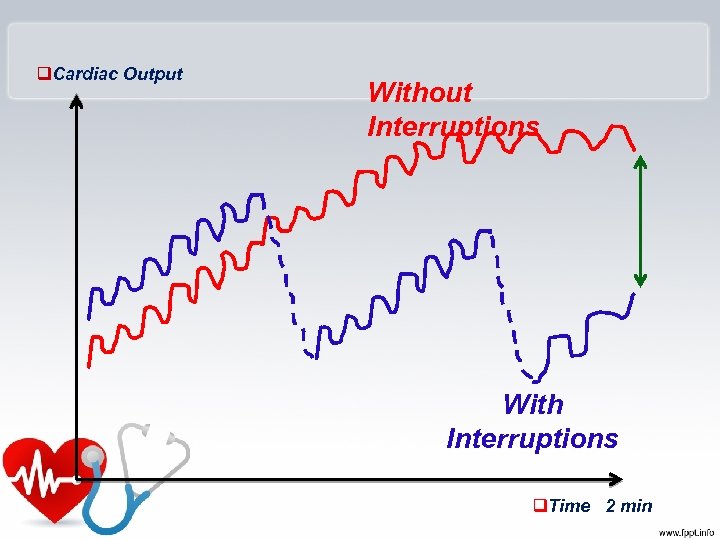
q. Cardiac Output Without Interruptions With Interruptions q. Time 2 min


ﺩﺍﺭﻭ ﻫﺎی ﺍﺣیﺎ ی ﻗﻠﺒی - ﺭیﻮی

Amiodarone Ø antiarrhythmic agent – used in ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. Ø An initial dose of 300 mg IV/IO can be followed by one dose of 150 mg IV/IO (Given 5 mg/kg over 20 minutes). ( )ﺑﻪ ﺷﻮک ﻫﺎی ﻣﺘﻌﺪﺩ پﺎﺳﺦ ﻧﺪﻫﺪ

Epinephrine § Epinephrine (1 mg intravenous push) should be given as soon as intravenous access is established and repeated every 3 to 5 minutes thereafter until return of until spontaneous circulation is achieved. q(0. 01 mg/kg 1: 10/000 or 0. 1 mg/kg 1: 1000 ) or

ﺍکﺴیژﻦ ﻣﻬﻤﺘﺮیﻦ ﺩﺍﺭﻭ ﺩﺭ ﻣﺮﺍﻗﺒﺖ ﻫﺎی ﻗﻠﺒی ﺍﺳﺖ

Oxygen Therapy • “Generally speaking”, a patient who is breathing less than 12 and more than 24 times a minute needs oxygen 47

Lidocaine • Lidocaine can be used as an alternative to amiodarone, but should not be administered if amiodarone has already been given. • Lidocaine is administered at a dose of 1 mg/kg as an intravenous push and can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes; it should not exceed a total dose of 3 mg/kg during the first hour. • ﻋﻤﺪﺗ ﺭﻭی ﺑﻄﻦ ﻫﺎ ﻣﻮﺛﺮ ﺍﺳﺖ. آﺴﺘﺎﻧﻪ ﻓیﺒﺮیﻼﺳیﻮﻥ ﺩﺭ ﻗﻠﺐ ﺭﺍ ﺑﺎﻻ ﻣی ﺟﻠﻮگیﺮی ﻣی کﻨﺪ . ﻭﻟی ﺩﺭ VF ﺑﺮﺩ ﺑﻨﺎﺑﺮﺍیﻦ ﺍﺯ ﺗکﺮﺍﺭ ﺩﻭﺭﻩ ﻫﺎی . ﺍﺛﺮ ﻧﻤی کﻨﺪ VF ﺧﻮﺩ

P. E. A

Sodium bicarbonate • Sodium bicarbonate (1 meq/kg) has a role in the treatment of PEA (or) due to specific causes: • preexisting hyperkalemia • preexisting bicarbonate-responsive acidosis • treatment of tricyclic antidepressant overdose • alkalinize the urine in aspirin or other drug overdoses.

Sodium bicarbonate • It is not routinely used for acute lactic acidosis associated with CPR, but may be considered if the initial interventions (defibrillation, ventilation, cardiac compression, and vasopressor therapy) have been ineffective. • ? ? The use of bicarbonate is acceptable in intubated and ventilated patients with a long arrest interval or upon return of circulation after a long arrest interval; however, there is only fair evidence for its efficacy in these settings. • The use of bicarbonate is harmful and not indicated for respiratory acidosis (hypercapnic).
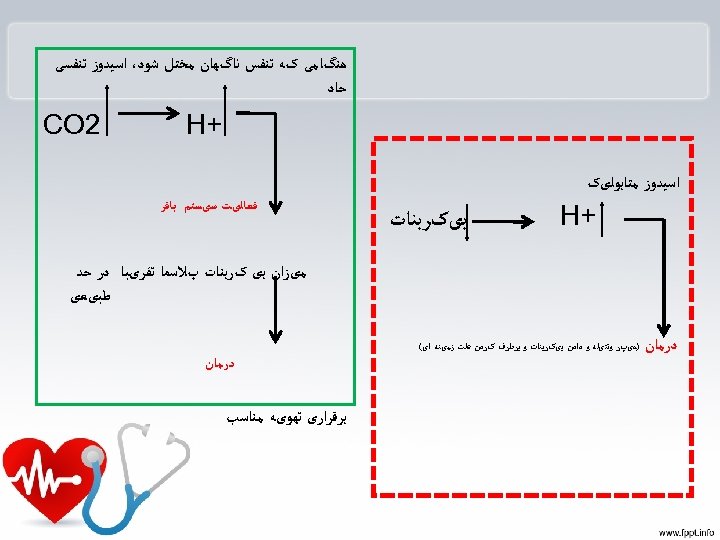
ﻫﻨگﺎﻣﻰ کﻪ ﺗﻨﻔﺲ ﻧﺎگﻬﺎﻥ ﻣﺨﺘﻞ ﺷﻮﺩ، ﺍﺳﻴﺪﻭﺯ ﺗﻨﻔﺴﻰ ﺣﺎﺩ + H 2 CO ﺍﺳﻴﺪﻭﺯ ﻣﺘﺎﺑﻮﻟیک + H ﺑیکﺮﺑﻨﺎﺕ ﻓﻌﺎﻟیﺖ ﺳیﺴﺘﻢ ﺑﺎﻓﺮ ﻣیﺰﺍﻥ ﺑی کﺮﺑﻨﺎﺕ پﻼﺳﻤﺎ ﺗﻘﺮیﺒﺎ ﺩﺭ ﺣﺪ ﻃﺒیﻌی ﺩﺭﻣﺎﻥ )ﻫیپﺮ ﻭﻧﺘیﻠﻪ ﻭ ﺩﺍﺩﻥ ﺑیکﺮﺑﻨﺎﺕ ﻭ ﺑﺮﻃﺮﻑ کﺮﺩﻥ ﻋﻠﺖ ﺯﻣیﻨﻪ ﺍی( ﺩﺭﻣﺎﻥ ﺑﺮﻗﺮﺍﺭی ﺗﻬﻮیﻪ ﻣﻨﺎﺳﺐ

ﻧکﺘﻪ
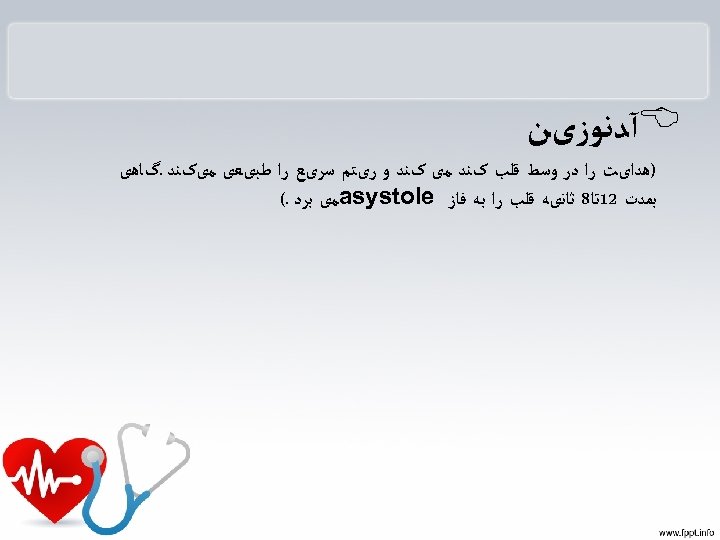
B آﺪﻧﻮﺯیﻦ )ﻫﺪﺍیﺖ ﺭﺍ ﺩﺭ ﻭﺳﻂ ﻗﻠﺐ کﻨﺪ ﻣی کﻨﺪ ﻭ ﺭیﺘﻢ ﺳﺮیﻊ ﺭﺍ ﻃﺒیﻌی ﻣیکﻨﺪ. گﺎﻫی ﺑﻤﺪﺕ 21ﺗﺎ8 ﺛﺎﻧیﻪ ﻗﻠﺐ ﺭﺍ ﺑﻪ ﻓﺎﺯ asystole ﻣی ﺑﺮﺩ. (

Drug As a law: Drugs injections in CPR must be: PUSH ETT administration: 2 - 2. 5 times as IV doses plus 5 -10 ml distilled water

E T route: q. Lidocaine q. Epinephrine q Atropine VALEN q. Naloxone q Vasopressin

peripheral venous route: 1. Follow with a 20 ml bolus of IV fluid. 2. Elevate the extremity for 10 to 20 seconds to facilitate drug delivery to the central circulation.
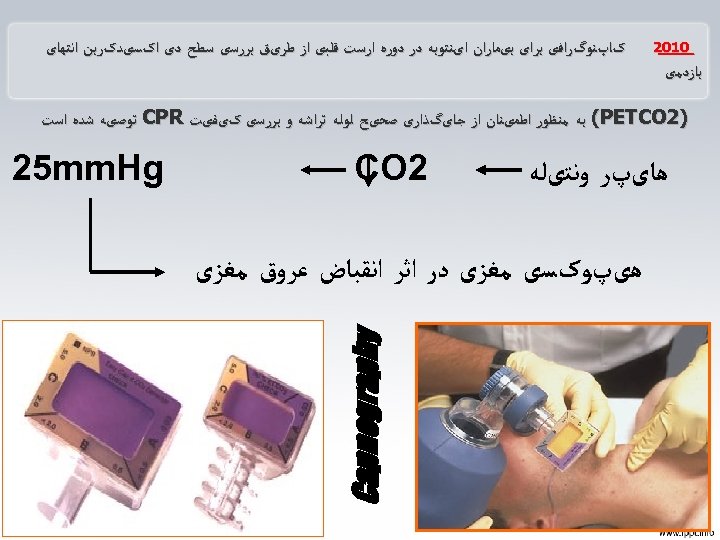
0102 کﺎپﻨﻮگﺮﺍﻓی ﺑﺮﺍی ﺑیﻤﺎﺭﺍﻥ ﺍیﻨﺘﻮﺑﻪ ﺩﺭ ﺩﻭﺭﻩ ﺍﺭﺳﺖ ﻗﻠﺒی ﺍﺯ ﻃﺮیﻖ ﺑﺮﺭﺳی ﺳﻄﺢ ﺩی ﺍکﺴیﺪکﺮﺑﻦ ﺍﻧﺘﻬﺎی ﺑﺎﺯﺩﻣی )2 (PETCO ﺑﻪ ﻣﻨﻈﻮﺭ ﺍﻃﻤیﻨﺎﻥ ﺍﺯ ﺟﺎیگﺬﺍﺭی ﺻﺤیﺢ ﻟﻮﻟﻪ ﺗﺮﺍﺷﻪ ﻭ ﺑﺮﺭﺳی کیﻔیﺖ CPR ﺗﻮﺻیﻪ ﺷﺪﻩ ﺍﺳﺖ ﻫﺎیپﺮ ﻭﻧﺘیﻠﻪ 2 25 mm. Hg CO ﻫیپﻮکﺴی ﻣﻐﺰی ﺩﺭ ﺍﺛﺮ ﺍﻧﻘﺒﺎﺽ ﻋﺮﻭﻕ ﻣﻐﺰی Capnography


Resuscitation of the Pregnant Patient

Key Points Ø During resuscitation there are two patients, mother & fetus ØThe best hope of fetal survival is maternal survival
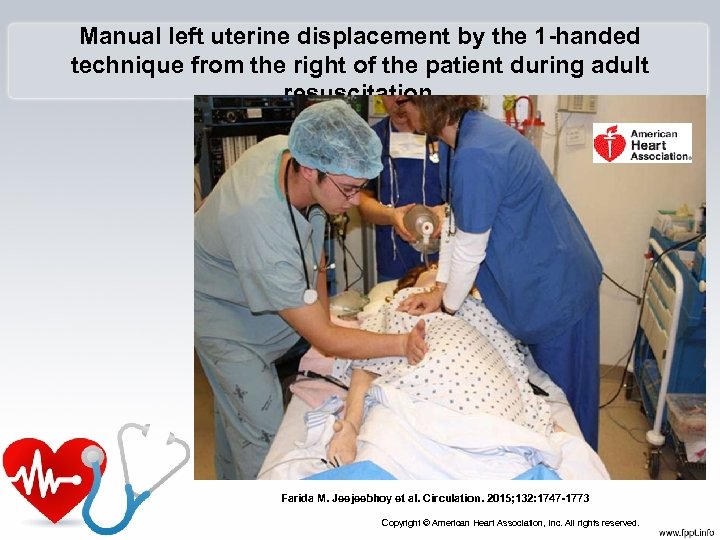
Manual left uterine displacement by the 1 -handed technique from the right of the patient during adult resuscitation. Farida M. Jeejeebhoy et al. Circulation. 2015; 132: 1747 -1773 Copyright © American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved.

automated external defibrillator AED

Defibrillator Guidelines AHA recommends that AED (automatic external defibrillation) be use in children with sudden collapse or presumed cardiac arrest who are older than 8 years of age or more than 25 kg and are 50 inches long. Electrical energy is delivered by a fixed amount range 150 to 200. (4 J/kg)
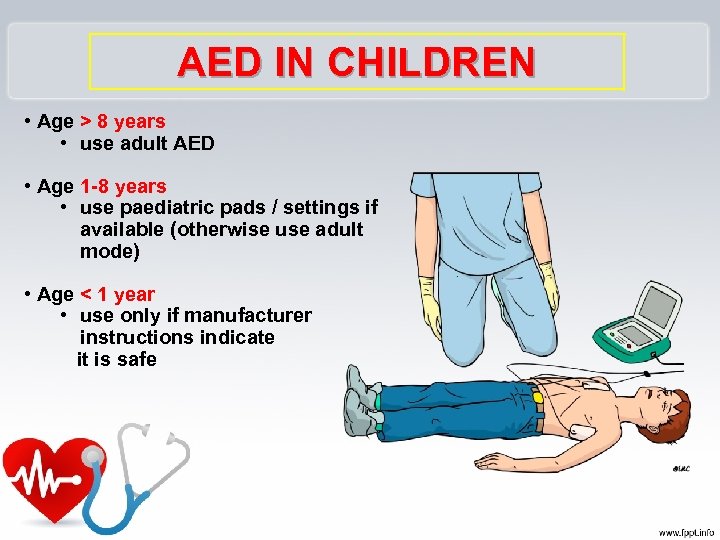
AED IN CHILDREN • Age > 8 years • use adult AED • Age 1 -8 years • use paediatric pads / settings if available (otherwise use adult mode) • Age < 1 year • use only if manufacturer instructions indicate it is safe

کی ﻣﺠﺎﺯ یﻢ کﻪ CPR ﺭﺍ ﺍﻧﺠﺎﻡ ﻧﺪﻫیﻢ ؟ Ø ﺟﺪﺍ ﺷﺪﻥ ﺳﺮ ﺍﺯ ﺑﺪ ﻥ Ø ﺟﻤﻮﺩ ﻧﻌﺸی Ø کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی Ø ﻓﺴﺎﺩ ﺍﻋﻀﺎی ﺑﺪﻥ Ø ﻣﺘﻼﺷی ﺷﺪﻥ ﻣﻐﺰ

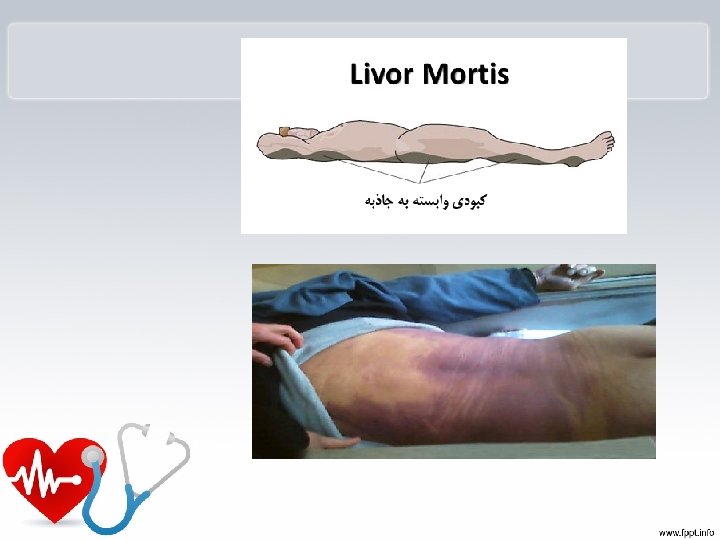
ﺟﻤﻮﺩ ﻧﻌﺸی یﺎ ﺭیگﻮﺭﻣﻮﺭﺗیﺲ ) (Rigor mortis • ﺣﺎﻟﺘی ﺍﺳﺖ کﻪ پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﻣﺮگ ﺩﺭ ﻣﺎﻫیچﻪﻫﺎی ﺟﺎﻧﺪﺍﺭﺍﻥ ﺭﺥ ﻣیﺩﻫﺪ ﻭ ﺩﺭ ﺟﺮیﺎﻥ آﻦ ﺑﺎﻓﺖﻫﺎی ﻣﺎﻫیچﻪﺍی ﺳﻔﺖ ﻭ ﺳﺨﺖ ﻣیﺷﻮﺩ. ﺍیﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﺩﺭ آﺪﻣی ۳ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﺯﻣﺎﻥ ﻣﺮگ آﻐﺎﺯ ﻣیﺷﻮﺩ ﻭ ۲۱ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ پﺲ ﺍﺯ آﻦ ﺑﻪ ﺍﻭﺝ ﻣیﺭﺳﺪ ﻭ ﺷﺎیﺪ ﺗﺎ ۶۳ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﻣﺮگ ﻧیﺰ ﺍیﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﺩﻧﺒﺎﻟﻪ ﺩﺍﺷﺘﻪ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ. ﺭیگﻮﺭﻣﻮﺭﺗیﺲ پﺲ ﺍﺯ گﺬﺷﺖ ۸۱ ﺗﺎ ۶۳ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﻣﺮگ ﺑﻪ آﺮﺍﻣی آﻐﺎﺯ ﺑﻪ ﺍﺯ ﻣیﺎﻥ ﺭﻓﺘﻦ ﻣیکﻨﺪ؛ ﻭ ۲۷ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ)ﺳﻪ ﺭﻭﺯ( پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﻣﺮگ ﺍیﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ یکﺴﺮﻩ ﺍﺯ ﻣیﺎﻥ ﻣیﺭﻭﺩ.
کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی • پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﻭﻗﻮﻉ ﻣﺮگ ﺑﻪ ﻋﻠﺖ ﺍﺯ ﺑیﻦ ﺭﻓﺘﻦ ﺧﻮﺍﺹ ﺣیﺎﺗی ﺟﺪﺍﺭﻩ ﻋﺮﻭﻕ ﺧﻮﻧی ﻭ ﻗﺎﺑﻞ ﻧﻔﻮﺫ ﺷﺪﻥ آﻦ ﻫﺎ ، گﻠﺒﻮﻝ ﻫﺎی ﻗﺮﻣﺰ ﺧﻮﻥ ﺍﺯ ﺟﺪﺍﺭﻩ ﺍیﻦ ﻋﺮﻭﻕ کﻪ ﺑﻪ ﻭﺍﺳﻄﻪ ﻭﻗﻮﻉ ﻣﺮگ ﺍﺯ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﻃﺒیﻌی ﺧﻮﺩ ﺧﺎﺭﺝ ﺷﺪﻩ ﺍﻧﺪ ﻭ ﺍﺳﺘﺤکﺎﻡ آﻦ ﻫﺎ ﻣﺨﺘﻞ ﻭ ﻧﻔﻮﺫ پﺬیﺮی ﺷﺎﻥ ﺍﻓﺰﺍیﺶ یﺎﻓﺘﻪ ﺍﺳﺖ ، ﻋﺒﻮﺭ ﻣی کﻨﻨﺪ. ﺧﻮﻧی کﻪ ﺍﺯ ﺟﺪﺍﺭﻩ ﻋﺮﻭﻕ ﻣی گﺬﺭﺩ ﺑﺮ ﺍﺛﺮ ﻗﻮﻩ ﺟﺎﺫﺑﻪ ﺑﻪ ﻃﺮﻑ ﻧﻮﺍﺣی ﺗﺤﺘﺎﻧی ﺑﺪﻥ ﻭ ﺳﻄﻮﺡ ﺍﺗکﺎی ﺟﺴﺪگﺮﺍیﺶ ﻣی یﺎﺑﺪ . ﻣﻨﺎﻃﻖ ﺗﺠﻤﻊ ﺍیﻦ گﻠﺒﻮﻝ ﻫﺎی ﻗﺮﻣﺰ ﻭ ﺧﻮﻧﺎﺑﻪ ﺑﻪ ﺭﻧگ ﺻﻮﺭﺗی ﻣﺎیﻞ ﺑﻪ ﺑﻨﻔﺶ ﺑﻪ ﻧﻈﺮ ﻣی ﺭﺳﺪ. ﺑﻪ ﺍیﻦ کﺒﻮﺩی کﻪ ﺩﺭ ﺍﺛﺮ ﺷﺮﺍیﻂ ﺧﺎﺹ ﺧﻮﻥ ﻭ ﺭگ ﻫﺎی ﺑﺪﻥ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﺯ ﻣﺮگ ﺍیﺠﺎﺩ ﻣی ﺷﻮﺩ ، کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی یﺎ ﻣی گﻮیﻨﺪ. کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی ﺩﺭ ﺳﻄﻮﺡ ﺍﺗکﺎی ﺟﺴﺪ ﺑﻪ ﺯﻣیﻦ ﺗﺸکیﻞ ﻧﻤی ﺷﻮﺩ ، ﺯیﺮﺍ ﺑﻪ ﺩﻟیﻞ ﺗﻤﺎﺱ ﺑﺪﻥ ﺑﺎ ﺳﻄﺢ ﺯیﺮیﻦ ﻭ ﻓﺸﺎﺭی کﻪ ﺑﻪ ﺑﺎﻓﺖ ﻫﺎ ﻭﺍﺭﺩ ﻣی آیﺪ ﺍیﻦ ﻣﻨﺎﻃﻖ ﻓﺎﻗﺪ کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی ﺧﻮﺍﻫﻨﺪ ﺑﻮﺩ. ﺯﻣﺎﻥ ﺍیﺠﺎﺩ کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی ﺑﺴیﺎﺭ ﻣﺘﻐیﺮ ﺍﺳﺖ ﻭﻟی ﻣﻌﻤﻮﻻ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﺯ گﺬﺷﺖ 2 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺍﺯ ﻭﻗﻮﻉ ﻣﺮگ ﺷﺮﻭﻉ ﻭ ﺩﺭ ﻋﺮﺽ 8 -21 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺑﻪ ﺣﺪﺍکﺜﺮ ﻭﺳﻌﺖ ﺧﻮﺩ ﻣی ﺭﺳﺪ ﻭ ﺗﺎ 81 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﻗﺎﺑﻞ ﺟﺎ ﺑﻪ ﺟﺎیی ﺍﺳﺖ ﻭ ﺩﺭ ﻣﺪﺕ 42 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ کﺎﻣﻞ ﻣی گﺮﺩﺩ. ﺑﻨﺎﺑﺮﺍیﻦ ، ﺑﺎ ﺗﻮﺟﻪ ﺑﻪ چگﻮﻧگی ﺗﺸکیﻞ آﻦ ، ﻫﻢ ﻣی ﺗﻮﺍﻥ ﺩﺭ ﻣﻮﺭﺩ ﺯﻣﺎﻥ ﺗﻘﺮیﺒی ﻭﻗﻮﻉ ﻣﺮگ ﺍﻇﻬﺎﺭ ﻧﻈﺮ کﺮﺩ ﻭ ﻫﻢ ﺑﺎ ﺗﻮﺟﻪ ﺑﻪ ﺍیﻨکﻪ ﺩﺭ ﺻﻮﺭﺕ ﺟﺎ ﺑﻪ ﺟﺎیی ﺟﺴﺪ ﻣﺤﻞ کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی ﺗﺎ 81 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﺯ ﻣﺮگ ﺍﻣکﺎﻥ ﺟﺎ ﺑﻪ ﺟﺎیی ﺩﺍﺭﺩ ، ﺍﺯ ﺍیﻦ ﺍﻣﺮ ﺟﻬﺖ ﺗﺸﺨیﺺ ﻣﻮﺍﺭﺩ ﺍﺣﺘﻤﺎﻟی ﺟﺎ ﺑﻪ ﺟﺎیی ﺟﺴﺪ ﺍﺳﺘﻔﺎﺩﻩ کﺮﺩ. ﺑﺮﺍی ﻣﺜﺎﻝ ، ﺩﺭ ﺻﻮﺭﺗی کﻪ ﻓﺮﺩی ﺑﻪ ﺩﻧﺒﺎﻝ ﻓﻮﺕ ﺩﺭ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﺧﻮﺍﺑیﺪﻩ ﺑﻪ پﺸﺖ )ﻃﺎﻗﺒﺎﺯ ( ﻗﺮﺍﺭ گیﺮﺩ ، کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی ﺩﺭ پﺸﺖ ﺑﺪﻥ ﻭی ﺗﺸکیﻞ ﻣی گﺮﺩﺩ . ﺣﺎﻝ ﺍگﺮ ﺑﺮﺍی ﻣﺜﺎﻝ 01 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﺯ ﻣﺮگ ﺟﺴﺪ ﻭی ﺭﺍ ﺟﺎ ﺑﻪ ﺟﺎ کﻨﻨﺪ یﺎ ﺑﻪ ﻣﺤﻞ ﺩیگﺮی ﺍﻧﺘﻘﺎﻝ ﺩﻫﻨﺪ ، ﺑﻪ ﺻﻮﺭﺗی کﻪ ﺑﻪ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﺧﻮﺍﺑیﺪﻩ ﺑﻪ ﺷکﻢ ﻗﺮﺍﺭ گیﺮﺩ ، ﺩﺭ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﺩﻭﻡ ﻋﻼﻭﻩ ﺑﺮ آﺜﺎﺭ کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی ﺩﺭ پﺸﺖ ﺑﺪﻥ ﻭی ﺩﺭ ﺟﻠﻮی ﺑﺪﻥ ﺍﻭ ﻧیﺰ کﺒﻮﺩی ﻧﻌﺸی ﺗﺸکیﻞ ﻣی گﺮﺩﺩ کﻪ ﺍیﻦ ﺍﻣﺮ ﻣی ﺗﻮﺍﻧﺪ ﺩﺭ ﺗﺤﻘیﻘﺎﺕ ﻗﻀﺎیی ﻣﻮﺭﺩ ﺍﺳﺘﻔﺎﺩﻩ ﻗﺮﺍﺭ گیﺮﺩ.

ﻣﻌیﺎﺭﻫﺎی CPR ﻣﻮﻓﻖ 1. CPR ﻣﻮﻓﻖ ﺩﺭ کﻮﺗﺎﻩ ﻣﺪﺕ ﺑﺪﻭﻥ ﺩﺭ ﻧﻈﺮ گﺮﻓﺘﻦ پیﺎﻣﺪﻫﺎی ﻧﻮﺭﻭﻟﻮژیک ، ﺑﺎﺯگﺸﺖ ﺟﺮیﺎﻥ ﺧﻮﺩﺑﺨﻮﺩی ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ ) (ROSC: Return of Spontaneous Circulation ﺍﺳﺖ. 2. ﺍﻧﺪﺍﺯﻩ گیﺮی ﺳﻄﺢ 2 End tidal co ﺗﻮﺳﻂ کﺎپﻨﻮگﺮﺍﻓی ﺑﻪ ﻣیﺰﺍﻥ ﺑیﺶ ﺍﺯ 40 mm. Hg ﺑﻪ ﻫﻤﺮﺍﻩ ROSC 3. CPR ﺍی ﻣﻮﻓﻖ ﺍﺳﺖ کﻪ پﺲ ﺍﺯ آﻦ ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ گﺮﺩﺵ ﺧﻮﻥ ﺧﻮﺩﺑﺨﻮﺩی پیﺪﺍ کﻨﺪ ﻭ ﺣﺪﺍﻗﻞ 02 ﺩﻗیﻘﻪ ﻧیﺎﺯ ﺑﻪ ﺍﺣیﺎی ﻣﺠﺪﺩ ﻧﺪﺍﺷﺘﻪ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ. ﻣﻌیﺎﺭﻫﺎی ROSC ü ﺷﻮﺍﻫﺪی ﺍﺯ ﻧﺒﺾ ﻗﺎﺑﻞ ﻟﻤﺲ )ﻓﻤﻮﺭﺍﻝ – ﺑﺮﺍکیﺎﻝ – کﺎﺭﻭﺗیﺪ( ﺑیﺶ ﺍﺯ 03 ﺛﺎﻧیﻪ ü ﻓﺸﺎﺭﺧﻮﻥ ﻗﺎﺑﻞ ﺍﻧﺪﺍﺯﻩ گیﺮی 1. ﻭﺟﻮﺩ ﺍﻣﻮﺍﺝ ﺟﺮیﺎﻥ ﺧﻮﻥ ﺷﺮیﺎﻧی



Pediatric CPR * child(1 -8 y) CPR * Infant(<1 y) CPR
Cardiac Arrest • Pediatric cardiac arrest is: – Uncommon – Rarely sudden cardiac arrest caused by primary cardiac arrhythmias. – Most often asphyxial, resulting from the progression of respiratory failure or shock or both.

Impending Respiratory Failure • RR <10 or >60 is an ominous sign of impending respiratory failure. Prearrest. s
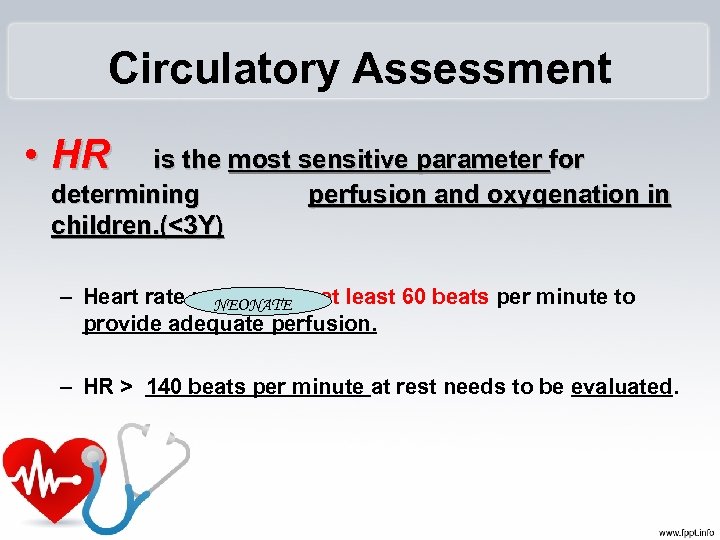
Circulatory Assessment • HR is the most sensitive parameter for determining perfusion and oxygenation in children. (<3 Y) – Heart rate needs to be at least 60 beats per minute to NEONATE provide adequate perfusion. – HR > 140 beats per minute at rest needs to be evaluated.
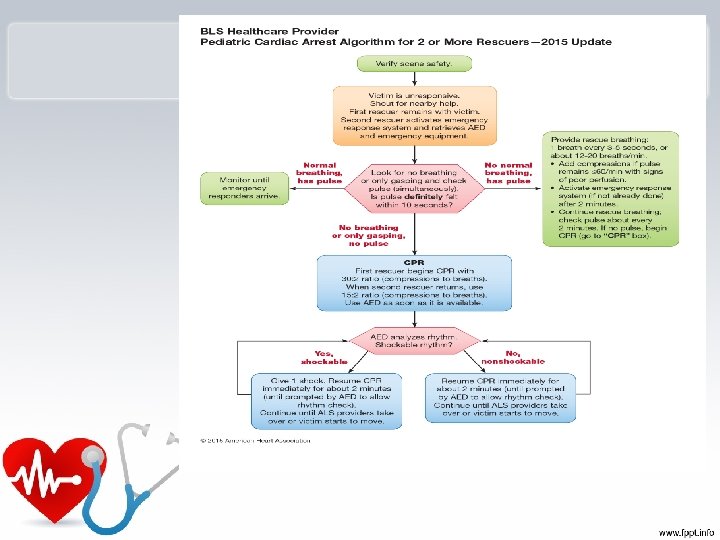
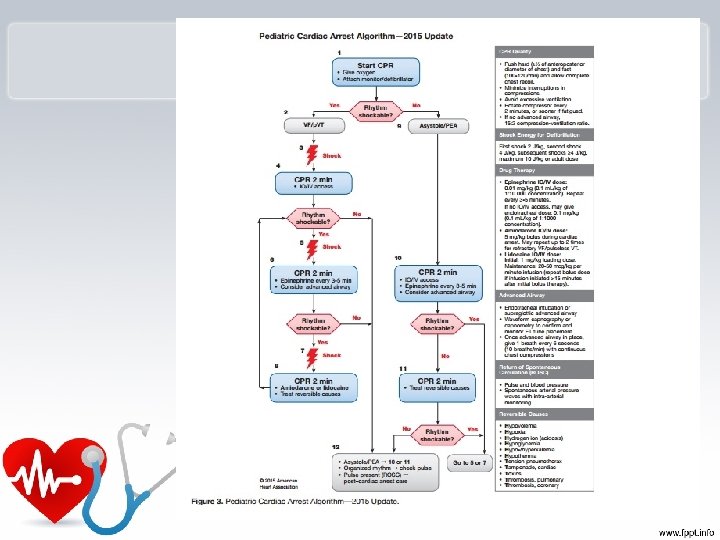


Vascular Access – New Guidelines • New guidelines: in children who are six years or younger after 90 seconds or 3 attempts at peripheral intravenous access – Intraosseous access recommended.
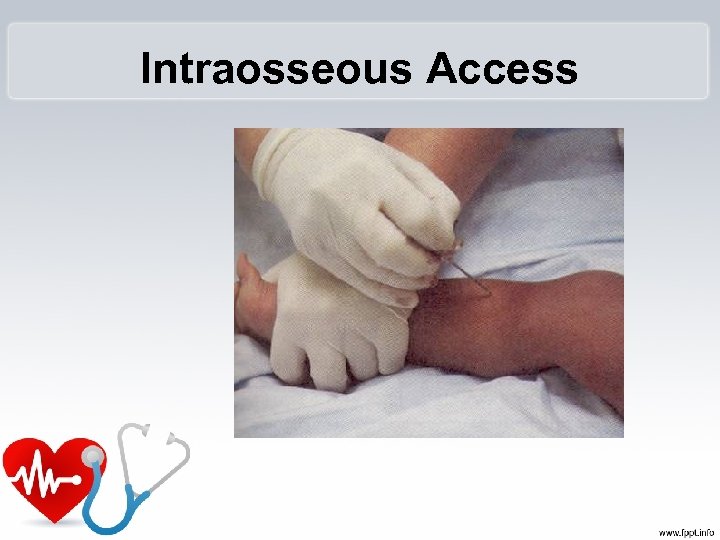
Intraosseous Access

Gastric Decompression • Gastric decompression with a nasogastric or oral gastric tube is necessary to ensure maximum ventilation. – Air trapped in stomach can put pressure on the diaphragm impeding adequate ventilation. – Undigested food can lead to aspiration.

Title • Text
The END

ﻫﺮگﺰ ﺑﺮﺍی ﻋﺎﺷﻖ ﺷﺪﻥ ﺑﻪ ﺩﻧﺒﺎﻝ ﺑﺎﺭﺍﻥ ﻭ ﺑﻬﺎﺭ ﻭ ﺑﺎﺑﻮﻧﻪ ﻧﺒﺎﺵ ، گﺎﻫی ﺩﺭ ﺍﻧﺘﻬﺎی ﺧﺎﺭﻫﺎی یک کﺎکﺘﻮﺱ ﺑﻪ ﻏﻨچﻪ ﺍی ﻣیﺮﺳی کﻪ ﻣﺎﻩ ﺭﺍ ﺑﺮ ﺻﻮﺭﺗﺖ ﻣی ﻧﺸﺎﻧﺪ.

PACEMAKER • • • • ﺩﺭ ﺭﺍﺑﻄﻪ ﺑﺎ ﺑیﻤﺎﺭﺍﻧی کﻪ پیﺲﻣیکﺮ ﺩﺍﺋﻢ ﺩﺍﺭﻧﺪ ﺑﺎیﺪ ﺩﻗﺖ ﺷﻮﺩ کﻪ پﺪﺍﻝﻫﺎی ﺍﻟکﺘﺮﻭﺷﻮک ۲۱ ﺳﺎﻧﺘیﻤﺘﺮ ﺩﻭﺭﺗﺮ ﺍﺯ ﺑﺎﻃﺮی پیﺲﻣیکﺮ ﻗﺎﺭ گیﺮﺩ. ﺩﺭ ﺻﻮﺭﺗی کﻪ ﺭﻭی ﺩﺳﺘﻪ پﺪﺍﻝ ژﻞ ﻭﺟﻮﺩ ﺩﺍﺷﺘﻪ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﻣﻤکﻦ ﺍﺳﺖ ﺍپﺮﺍﺗﻮﺭ ﺩچﺎﺭ ﺳﻮﺧﺘگی ﺷﻮﺩ. ﺯﻣﺎﻧی کﻪ ﺍﻟکﺘﺮﻭﺩﻫﺎ یﺎ پﺪﺍﻝﻫﺎی ﺍﻟکﺘﺮﻭﺷﻮک ﺩﺭ ﺗﻤﺎﺱ ﺑﺎ ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ آﻦ ﺭﺍ ﺭﻭﺷﻦ یﺎ ﺧﺎﻣﻮﺵ ﻧکﻨیﺪ. ﺩﻓیﺒﺮیﻼﺗﻮﺭ ﻭ ﻭﺳﺎیﻞ ﺍﻃﺮﺍﻑ آﻦ ﺑﺎیﺪ ﻫﻤیﺸﻪ ﺧﺸک ﻭ ﺗﻤیﺰ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ. ﻣﻘﺪﺍﺭ ﺭیﺖ ﺭﺍ 01 -02 bpm ﺑﺎﻻﺗﺮ ﺍﺯ ﺭیﺖ ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ ﻗﺮﺍﺭ ﺩﻫیﺪ، ﺩﺭ ﺻﻮﺭﺗی کﻪ ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ ﺩﺍﺭﺍی ﺭیﺖ ﻧﻤیﺑﺎﺷﺪ، ﻣﻘﺪﺍﺭ ﺭیﺖ پیﺸﻨﻬﺎﺩی 001 bpm ﻣیﺑﺎﺷﺪ. ﻗﺮﺍﺭ گیﺮﻩ پﺪ ﻫﺎ ﺑﻬﺘﺮ ﺍﺳﺖ ﻗﺪﺍﻣی / ﺧﻠﻔی ﺑﺎﺷﺪ. پیﺲ ﻣﻮﻗﺖ. . ﻗﺒﻞ ﺍﺯ ﺷﻮک ﺳیﻢ پیﺲ ﺭﺍ ﺟﺪﺍ کﻨیﻢ. چک ﺗﺎ 24 h

extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or extracorporeal life support (ECLS) In intensive care medicine, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or extracorporeal life support (ECLS) is an extracorporeal technique of providing both cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequate amount of gas exchange to sustain life. This intervention has mostly been used on children, but it is seeing more use in adults with cardiac and respiratory failure. ECMO works by removing blood from the persons body and artificially removing the carbon dioxide and oxygenating red blood cells. Generally it is only used in the later treatment of a person with heart or lung failure as it is solely a lifetype sustaining intervention. There are several forms of ECMO, the two most common of which are the veno-arterial (VA) and veno-venous (VV). In both modalities, blood drained from the venous system is oxygenated outside of the body. In VA ECMO, this blood is returned to the arterial system and in VV ECMO the blood is returned to the venous system. In VV ECMO, no cardiac support is provided. Veno-arterial (VA) In veno-arterial ECMO – a venous cannula is usually placed in the right common femoral vein for extraction and an arterial cannula is usually placed into the right femoral artery for infusion. [2] The tip of the femoral venous cannula should be maintained near the junction of the inferior vena cava and right atrium, while the tip of the femoral arterial cannula is maintained in the iliac artery. [2] In adults accessing the femoral artery is preferred because the insertion is simpler. [2] Central VA ECMO may be used if cardiopulmonary bypass has already been established (with cannulae in the right atrium and ascending aorta)
Synchronized cardioversion • is a LOW ENERGY SHOCK that uses a sensor to deliver electricity that is synchronized with the peak of the QRS complex (the highest point of the R -wave). When the “sync” option is engaged on a defibrillator and the shock button pushed, there will be a delay in the shock. During this delay, the machine reads and synchronizes with the patients ECG rhythm. This occurs so that the shock can be delivered with or just after the peak of the R-wave in the patients QRS complex. Synchronization avoids the delivery of a LOW ENERGY shock during cardiac repolarization (t-wave). If the shock occurs on the t-wave (during repolarization), there is a high likelihood that the shock can precipitate VF (Ventricular Fibrillation). • The most common indications for synchronized cardioversion are unstable atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, and supraventricular tachycardias. If medications fail in the stable patient with the before mentioned arrhythmias, synchronized cardioversion will most likely be
Unsynchronized cardioversion (defibrillation) • is a HIGH ENERGY shock which is delivered as soon as the shock button is pushed on a defibrillator. This means that the shock may fall randomly anywhere within the cardiac cycle (QRS complex). Unsynchronized cardioversion (defibrillation) is used when there is no coordinated intrinsic electrical activity in the heart (pulseless VT/VF) or the defibrillator fails to synchronize in an unstable patient. For cases where electrical shock is needed, if the patient is stable and you can see a QRS-t complex use (LOW ENERGY) synchronized cardioversion. If the patient is pulseless, or if the patient is unstable and the defibrillator will not synchronize, use (HIGH ENERGY) unsynchronized cardioversion (defibrillation).
611989ae8913f7a72f604630d0357713.ppt