d0014007f483c8c9657c7b603017aab4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

ﺑﺴﻢ ﺍﻟﻠﻪ ﺍﻟﺮﺣﻤﻦ ﺍﻟﺮﺣیﻢ

یکی ﺍﺯ ﻣﺴﺎیﻠی کﻪ ﺑیﻤﺎﺭﺳﺘﺎﻧﻬﺎ ﻭ ﻣﺮﺍکﺰ ﺩﺭﻣﺎﻧی ﺑﺎ آﻦ ﺭﻭﺑﺮﻭ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ ﺟﻠﻮگیﺮی ﺍﺯ ﺻﺪﻣﺎﺕ پﻮﺳﺘی ﺩﺭ ﻃﻮﻝ ﻭ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﺯ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﺍﺳﺖ Pressure Ulcer, Bedsore, Trophic Ulcers, Ischemic Ulcer )1 Burn-Like Ulcer )2

ﻋﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﻣﺴﺘﻌﺪ کﻨﻨﺪﻩ ﺻﺪﻣﺎﺕ پﻮﺳﺘی ﻃﻮﻻﻧی ﺑﻮﺩﻥ ﻣﺪﺕ ﺑی ﺗﺤﺮکی ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ کﺎﻫﺶ گﺮﺩﺵ ﺧﻮﻥ ﺩﺭ ﺣیﻦ ﺑی ﻫﻮﺷی ﻭﺿﻌیﺖ ﻋﻤﻮﻣی ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ ﻗﺒﻞ ﺍﺯ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی

PU ﺩﺭ ﻭﺍﻗﻊ ﺳﻮﺧﺘگی ﺍﺯ ﺗﻤﺎﺱ ﺑﺎ ﻣﻨﺒﻊ ﺍﻧﺮژی ﻧﺎﺷی ﻣی ﺷﻮﺩ ﻭ ﺣﺎﻝ آﻨکﻪ ﻧﺘیﺠﻪ ﺗﺸﺪیﺪ ﻓﺸﺎﺭ آﺰﺍﺩ ﻧﺸﺪﻩ ﺍﺳﺖ ﺯﺧﻢ ﻓﺸﺎﺭی ﺳﺎﻋﺎﺗی پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﺗﺎ ﺣﺪﺍکﺜﺮ ﻫﻔﺖ ﺭﻭﺯ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﺯ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﺳﻮﺧﺘگیﻬﺎ آﺴیﺒﻬﺎی ﺑﺎﻓﺘی ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ کﻪ ﺑﻼﻓﺎﺻﻠﻪ پﺲ ﺍﺯ ﺍﺗﻤﺎﻡ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﻗﺎﺑﻞ ﻣﺸﺎﻫﺪﻩ ﻣیﺒﺎﺷﻨﺪ

ﻋﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺳﻮﺧﺘگی ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﺷیﻤیﺎیی ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ ﺍﻟکﺘﺮیکی ﻣﻨﺎﺑﻊ گﺮﻣﺎیی ﻋﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺳﻮﺧﺘگی ﻣﺤﺪﻭﺩ ﺑﻪ ﻣﻮﺍﺭﺩ ﻓﻮﻕ ﻧیﺴﺖ پﺲ ﺩﺭ ﺻﻮﺭﺕ آﺴیﺐ ﻭﺳﺎیﻠی کﻪ ﺩﺭﺣیﻦ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﺍﻣکﺎﻥ ﺍیﺠﺎﺩ ﺍیﻦ ﺩیﺪگی ﺑﺎیﺪ کﻠیﻪ ﻧﻮﻉ آﺴیﺐ ﻫﺎ ﺭﺍ ﺩﺍﺭﻧﺪ ﻣﻮﺭﺩ ﺑﺮﺭﺳی ﻗﺮﺍﺭ گیﺮﻧﺪ
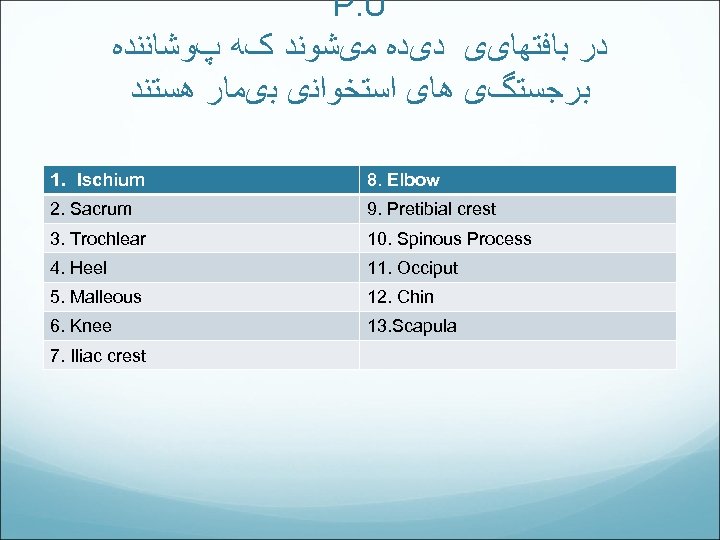
P. U ﺩﺭ ﺑﺎﻓﺘﻬﺎیی ﺩیﺪﻩ ﻣیﺸﻮﻧﺪ کﻪ پﻮﺷﺎﻧﻨﺪﻩ ﺑﺮﺟﺴﺘگی ﻫﺎی ﺍﺳﺘﺨﻮﺍﻧی ﺑیﻤﺎﺭ ﻫﺴﺘﻨﺪ 1. Ischium 8. Elbow 2. Sacrum 9. Pretibial crest 3. Trochlear 10. Spinous Process 4. Heel 11. Occiput 5. Malleous 12. Chin 6. Knee 13. Scapula 7. Iliac crest

Whereas pressure ulcers in adults predominantly appear on the lower body (sacrum, ischium, and heels), they are more common on the upper body of children (occiput and ears)
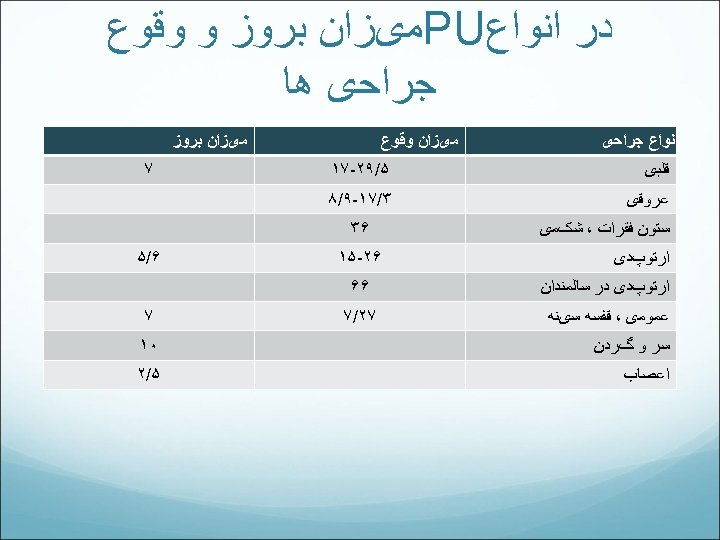
ﺩﺭ ﺍﻧﻮﺍﻉ PU ﻣیﺰﺍﻥ ﺑﺮﻭﺯ ﻭ ﻭﻗﻮﻉ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﻫﺎ ﺍﻧﻮﺍﻉ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﻣیﺰﺍﻥ ﺑﺮﻭﺯ ﻣیﺰﺍﻥ ﻭﻗﻮﻉ ﻗﻠﺒی ۵/۹۲ -۷۱ ﻋﺮﻭﻗی ۳/۷۱ -۹/۸ ﺳﺘﻮﻥ ﻓﻘﺮﺍﺕ ، ﺷکﻤی ﺍﺭﺗﻮپﺪی ۷ ۶۳ ۶۲ -۵۱ ﺍﺭﺗﻮپﺪی ﺩﺭ ﺳﺎﻟﻤﻨﺪﺍﻥ ۶۶ ﻋﻤﻮﻣی ، ﻗﻔﺴﻪ ﺳیﻨﻪ ۷۲/۷ ۶/۵ ۷ ﺳﺮ ﻭ گﺮﺩﻥ ۰۱ ﺍﻋﺼﺎﺏ ۵/۲
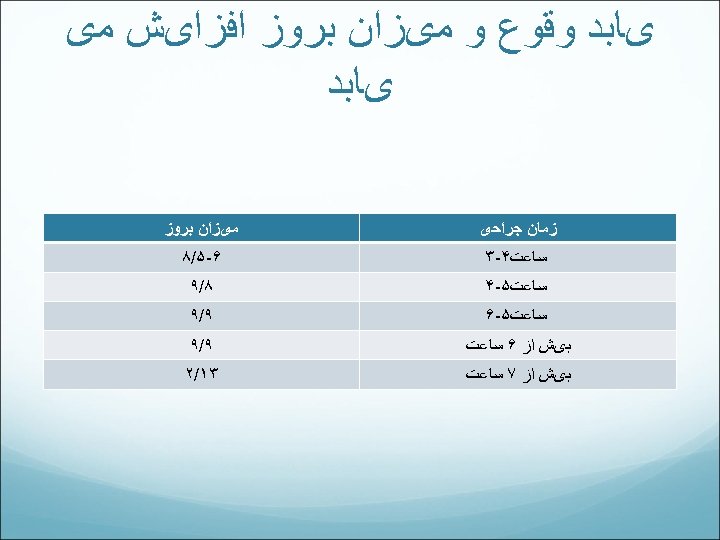
یﺎﺑﺪ ﻭﻗﻮﻉ ﻭ ﻣیﺰﺍﻥ ﺑﺮﻭﺯ ﺍﻓﺰﺍیﺶ ﻣی یﺎﺑﺪ ﺯﻣﺎﻥ ﺟﺮﺍﺣی ﻣیﺰﺍﻥ ﺑﺮﻭﺯ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ۴ -۳ ۶ -۵/۸ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ۵ -۴ ۸/۹ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ۵ -۶ ۹/۹ ﺑیﺶ ﺍﺯ ۶ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ۹/۹ ﺑیﺶ ﺍﺯ ۷ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ۳۱/۲

Electrical Safety
Principles Electricity is the flow of electrons Direct Current-electrons flow in 1 direction Alternating Current-electrons switch directions at regular intervals Capacitance The ability of a capacitor to store a charge.
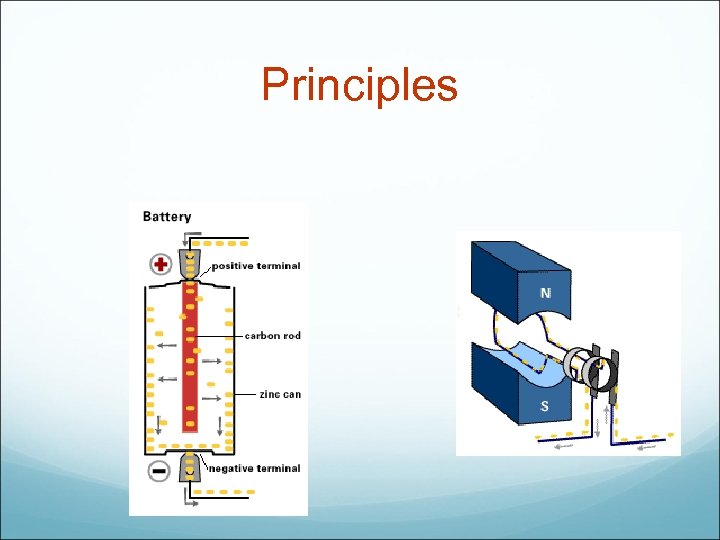
Principles
Principles

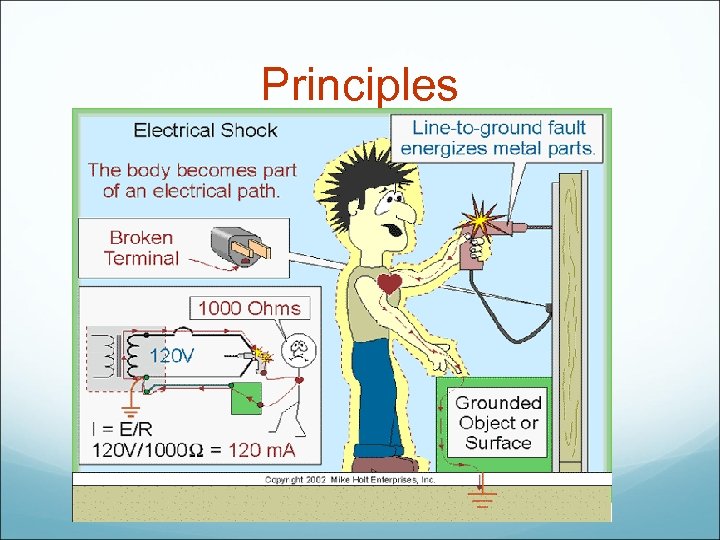
Application: Electrical Shock If electrical systems are not properly wired, persons can be subjected to electric shock.

Application: Electrical Shock People become injured and death occurs when voltage pushes electrons through the human body, particularly through the heart. Damage from electrical current is due to disruption of normal electrical function of cells or dissipation of electrical energy into human bodies (increased temp>burn). Macroshock-large amount of current flow that can cause harm or death Microshock-small amounts of current flow. Dangerous only to electrically susceptible patients

Application: Electrical Shock DC-is less dangerous AC-is more dangerous High frequency current have low penetration and does not tissue excite contractile cells Low frequency current penetrates more

Application: Electrical Shock What levels of current (m. A) is dangerous? Remember 1, 100 macro/100 micro <1 m. A = imperceptable to touch 10 m. A skeletal muscle shock (you can let go) V Fib can be induced by: 100 m. A of macroshock 100 μA (microamperes)of microshock current

Application: Electrical Shock THE MAX LEAKAGE ALLOWED IN OR EQUIPMENT IS 10 μA (microamperes)

Grounding Electrical Power Grounding can exist in two forms GROUNDED UNGROUNDED The National Electrical Code of the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA * ) defines electrical ground as a conducting connection, intentional or accidental, between an electrical circuit or equipment and earth or as a connection to some conducting body that serves in place of the earth.

Grounding Think about your house: 2 prong outlets = no ground 3 prong outlets = grounded Modern homes have a ground to reduce amount of shock
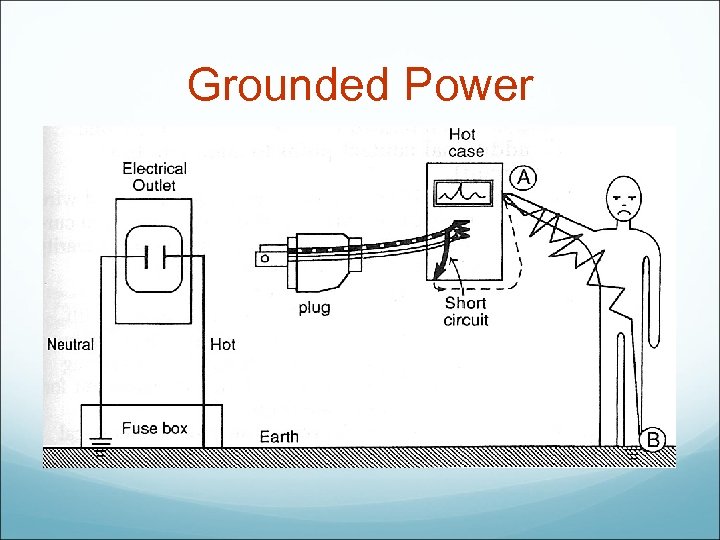
Grounded Power
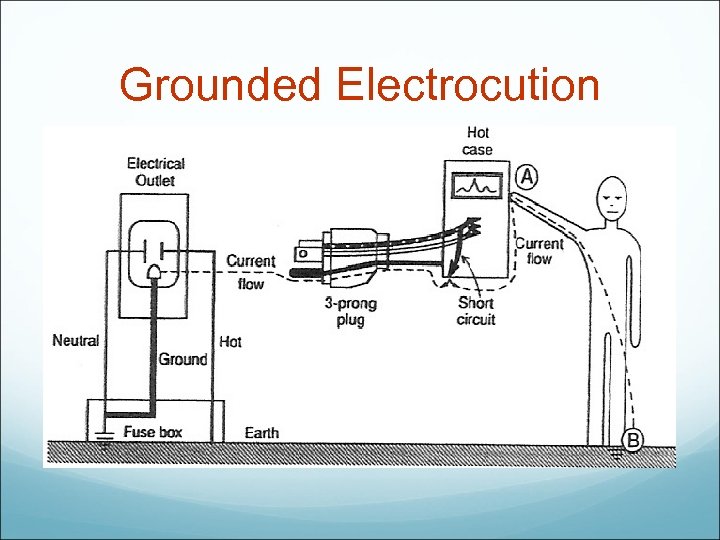
Grounded Electrocution

Why is equipment grounded? Stray Capacitance/Capacitive Coupling: Remember all equipment leaks a small amount of current All OR equipment has 3 prong plug

Ungrounding The OR has many perils that make grounding impracticle. Saline puddles Power cords w/ tears in their insulation (colored part of cord) Numerous electronic devices that risk

Ungrounding This is where the questions are derived: OR uses ungrounded power that is derived from Grounded utilities ISOLATION TRANSFORMER is the answer…
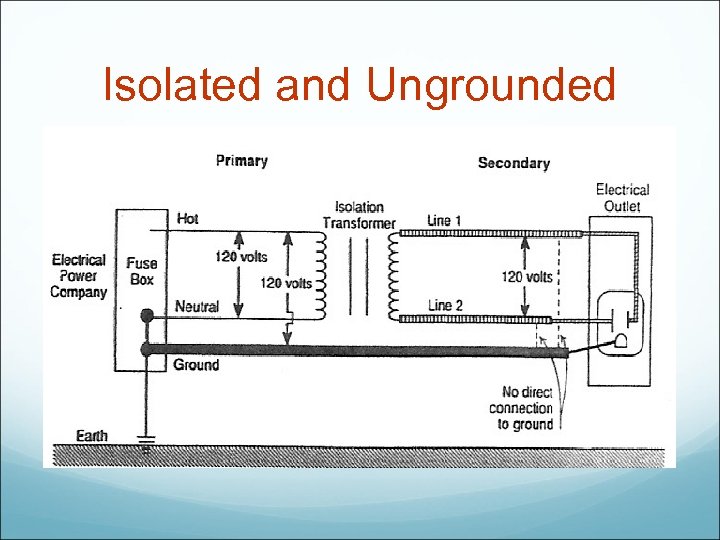
Isolated and Ungrounded

Electrical contacts with “ground” can cause injury if they occur in two different locations such that a circuit is completed and permits a large flow of current through “ground. ” One strategy for ensuring safety is to isolate all electric power sources from “ground, ” thus making it impossible for “ground” to be used as a path for injurious or damaging currents. Traditionally, implementation of this strategy in the operating room has been accomplished by means of isolation transformers, which usually take the form of large wall panels that have outlets and meters. The term isolation transformer comes from the fact that power output is isolated from the electrical ground.

Ungrounding: Isolated Power source does not have a ground, the equipment is grounded Isolated Power System provides protection from Macroshock. Faulty equipment plugged into an isolated power system does not present a shock hazard.
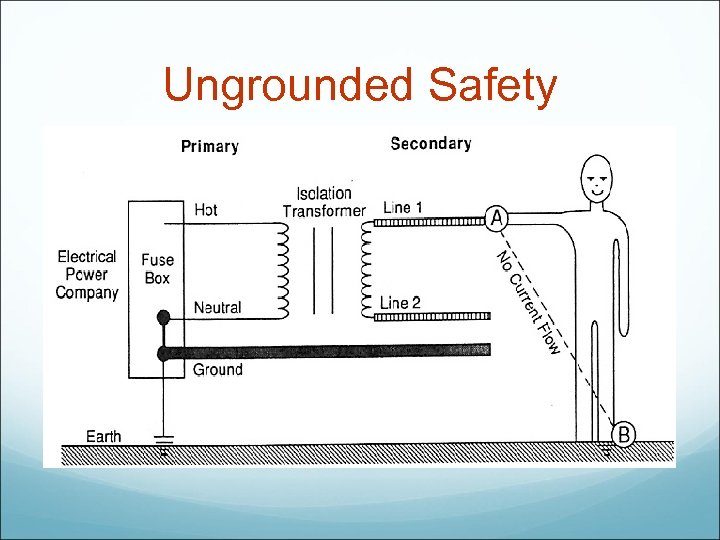
Ungrounded Safety

LIM (Line Isolation Monitor) Alarm is activated if 2 m. A-5 m. A of current is detected.
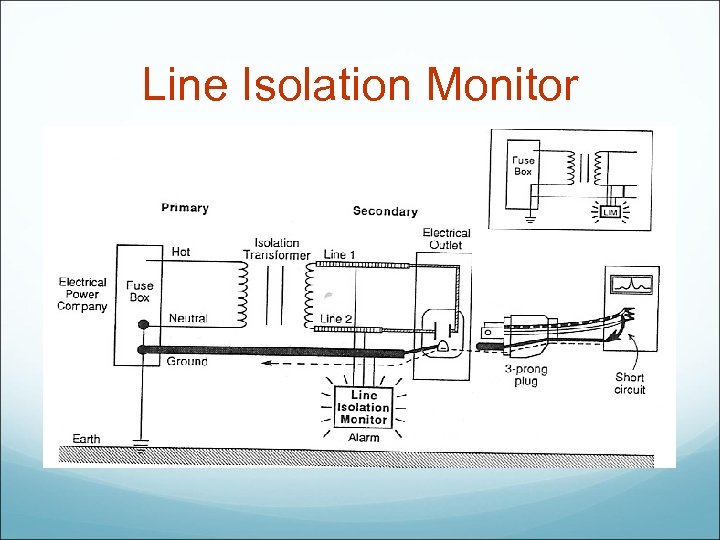
Line Isolation Monitor

electrosurgery Most concerns with electrical safety in the operating room arise from the use of electrosurgical units because they are capable of causing electrical shock, burns, explosions, arrhythmias, and disturbances in pacemaker functioning. During electrosurgery, high currents enter the patient through a small-area surface electrode at the tip of the cutting tool. The combination of high resistance (R), which is attributable to the small area, and high current (I) causes local tissue heating proportional to I 2 R, which produces cutting or coagulation. The tip of the electrode is also designed to produce lower current densities (low I 2 R) at points farther than a few millimeters from the electrode tip.

electrosurgery When electrosurgery is in use, a grounding pad should be used that connects the patient to the ground connection provided on the electrosurgery machine. The grounding pad should be well gelled and placed in contact with the patient across a large area. The grounding pad should be inspected during lengthy operations and gelled again or replaced if necessary. The electrosurgical grounding pad should be placed as near the operative site as reasonably possible and as far as possible from any pacemaker wires and ECG wires. When grounding pads are removed, the underlying skin should be inspected for burns.
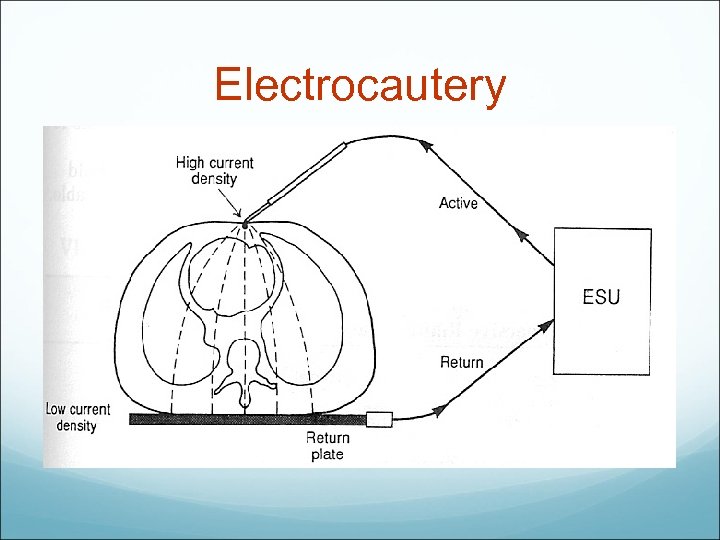
Electrocautery
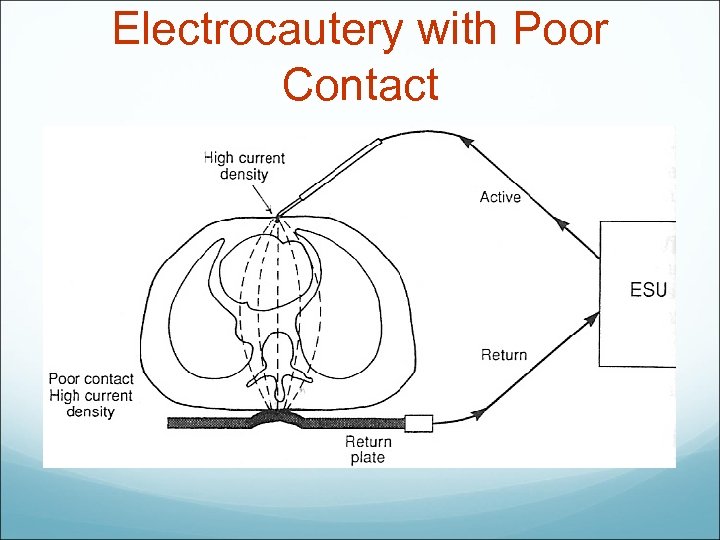
Electrocautery with Poor Contact

Unipolar Electrosurgery In unipolar electrosurgery, the more common of the two, the electric current that enters the patient through one electrode travels throughout the body and is collected outside the surgical field by a large, wide-area, well-jelled grounding pad (i. e. , the dispersive electrode). Skin burns can occur if the grounding pad is dry (i. e. , most of the conducting gel is gone) or is otherwise in poor contact with the patient. Electrical burns have also occurred at the site of ECG leads when the grounding pad was defective and the leads became an alternative path for returning high-frequency electrosurgery currents

Unipolar Electrosurgery Some body locations are never safe for unipolar electrosurgery. This situation is encountered frequently during neurosurgery and in patients with implanted cardiac pacemakers. The solution is bipolar electrosurgery.
Bipolar Electrosurgery Bipolar surgery is performed by two pencil-point electrodes arranged at the tips of a forceps Bipolar devices are required when electrosurgery is performed on an ovary or a fallopian tube Several cases of fatal bowel injury have occurred after female sterilization with unipolar devices

Safe Practice The anesthesiologist should go through the checklists relevant to every case, just as the pilot and the copilot of a commercial airplane do for air travel Years ago the word “vigilance” was used more commonly to describe how anesthesiologists’ eyes and mind are repeatedly and systematically scanning everything in the operating room “Vigilance” is now used more appropriately to describe the virtues of sophisticated electronic monitors and alarms in the operating room

d0014007f483c8c9657c7b603017aab4.ppt