0c7d2078822cdd04a0e6711d029629c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

研究室の紹介

Recent progress in aquaporin research • 発現制御 (expression) 分子種間 (among genes) 部位/分化特異性 (tissue/development specific) 環境ストレス応答性 (stress response) 形質転換系 (transgenic) • 活性制御 (activity) リン酸化 (phosphorylation) 分子間相互作用 (intermolecular interaction) 細胞内輸送 (cellular trafficking) • 個体形質との関連 (phenotype)
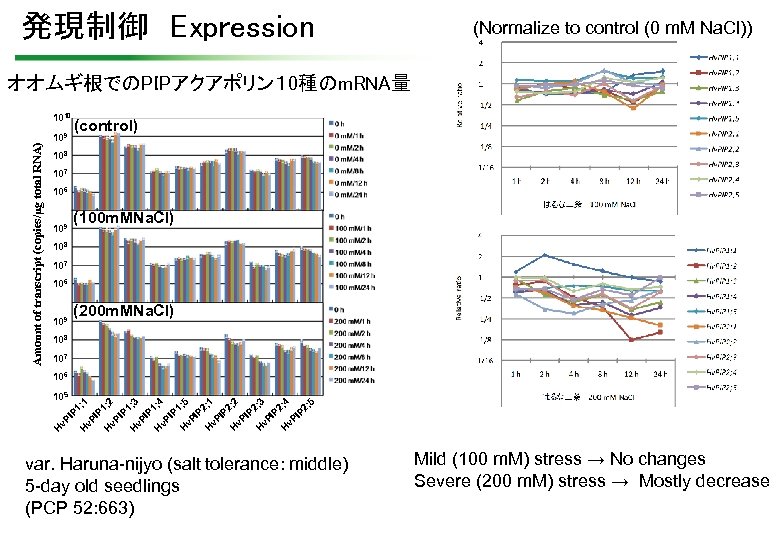
発現制御 Expression (Normalize to control (0 m. M Na. Cl)) オオムギ根でのPIPアクアポリン1 0種のm. RNA量 Amount of transcript (copies/µg total RNA) 1010 109 (control) 108 107 106 109 (100 m. MNa. Cl) 108 107 106 109 (200 m. MNa. Cl) 108 107 ; 5 P 2 ; 4 v. P I P 2 H ; 3 v. P I P 2 H ; 2 P 2 v. P I H v. P I P 2 H ; 5 v. P I P 1 H ; 4 P 1 H v. P I ; 3 P 1 v. P I H ; 2 v. P I P 1 H v. P I H H v. P I P 1 ; 1 105 ; 1 106 var. Haruna-nijyo (salt tolerance: middle) 5 -day old seedlings (PCP 52: 663) Mild (100 m. M) stress → No changes Severe (200 m. M) stress → Mostly decrease
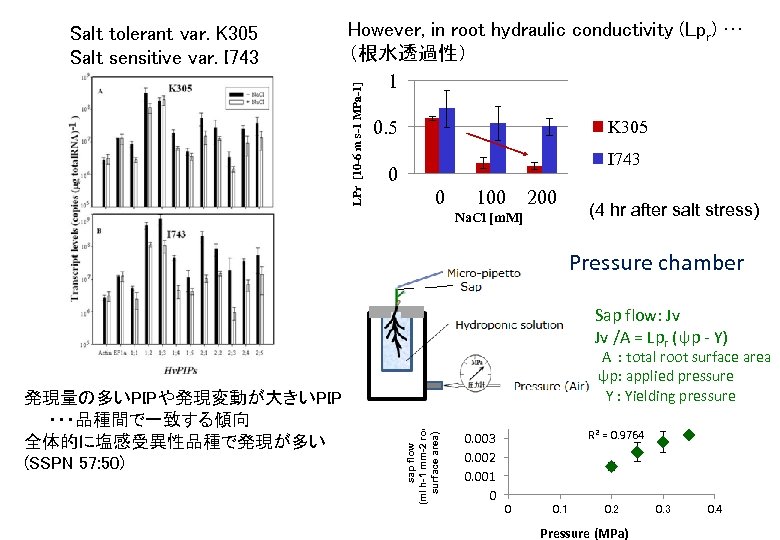
However, in root hydraulic conductivity (Lpr) … (根水透過性) 1 LPr [10 -6 m s-1 MPa-1] Salt tolerant var. K 305 Salt sensitive var. I 743 0. 5 K 305 I 743 0 0 100 200 Na. Cl [m. M] (4 hr after salt stress) Pressure chamber Sap flow: Jv Jv /A = Lpr (ψp - Y) sap flow (ml h-1 mm-2 root surface area) 発現量の多いPIPや発現変動が大きいPIP ・・・品種間で一致する傾向 全体的に塩感受異性品種で発現が多い (SSPN 57: 50) A : total root surface area ψp: applied pressure Y : Yielding pressure 0. 004 0. 003 0. 002 0. 001 0 R 2 = 0. 9764 0 0. 1 0. 2 Pressure (MPa) 0. 3 0. 4
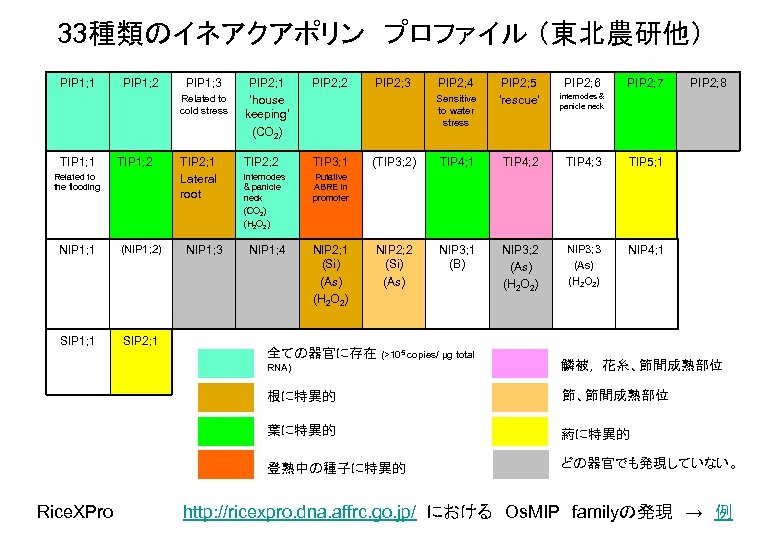
33種類のイネアクアポリン プロファイル (東北農研他) PIP 1; 1 PIP 1; 2 PIP 1; 3 Related to cold stress TIP 1; 1 TIP 1; 2 Related to the flooding NIP 1; 1 (NIP 1; 2) SIP 1; 1 SIP 2; 1 TIP 2; 1 Lateral root NIP 1; 3 PIP 2; 1 ‘house keeping’ (CO 2) PIP 2; 2 TIP 3; 1 internodes & panicle neck (CO 2) (H 2 O 2) Putative ABRE in promoter NIP 1; 4 NIP 2; 1 (Si) (As) (H 2 O 2) PIP 2; 3 PIP 2; 4 Sensitive to water stress PIP 2; 5 ‘rescue’ internodes & panicle neck PIP 2; 6 PIP 2; 7 (TIP 3; 2) TIP 4; 1 TIP 4; 2 TIP 4; 3 TIP 5; 1 NIP 2; 2 (Si) (As) NIP 3; 1 (B) NIP 3; 2 (As) (H 2 O 2) NIP 3; 3 (As) (H 2 O 2) PIP 2; 8 NIP 4; 1 全ての器官に存在 (>105 copies/ μg total RNA) 根に特異的 節、節間成熟部位 葉に特異的 葯に特異的 登熟中の種子に特異的 Rice. XPro 鱗被, 花糸、節間成熟部位 どの器官でも発現していない。 http: //ricexpro. dna. affrc. go. jp/ における Os. MIP familyの発現 → 例
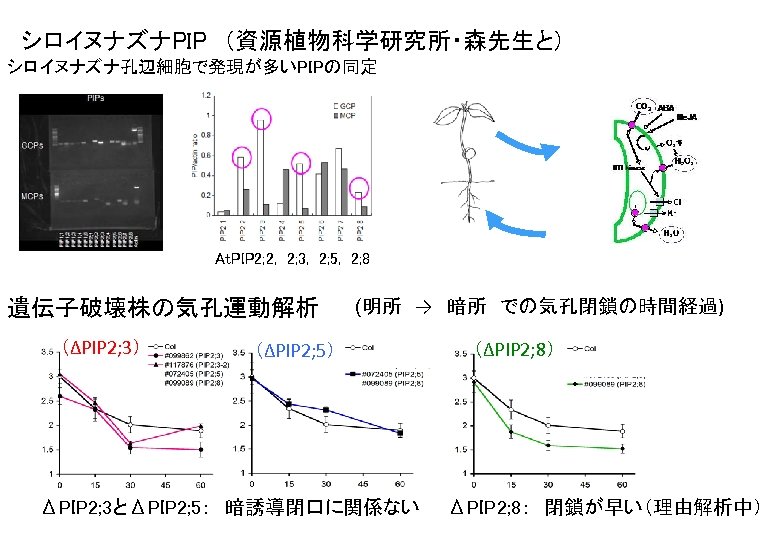
シロイヌナズナPIP (資源植物科学研究所・森先生と) シロイヌナズナ孔辺細胞で発現が多いPIPの同定 At. PIP 2; 2, 2; 3, 2; 5, 2; 8 遺伝子破壊株の気孔運動解析 (ΔPIP 2; 3) (ΔPIP 2; 5) (明所 → 暗所 での気孔閉鎖の時間経過) (ΔPIP 2; 8) ΔPIP 2; 3とΔPIP 2; 5: 暗誘導閉口に関係ない ΔPIP 2; 8: 閉鎖が早い(理由解析中)
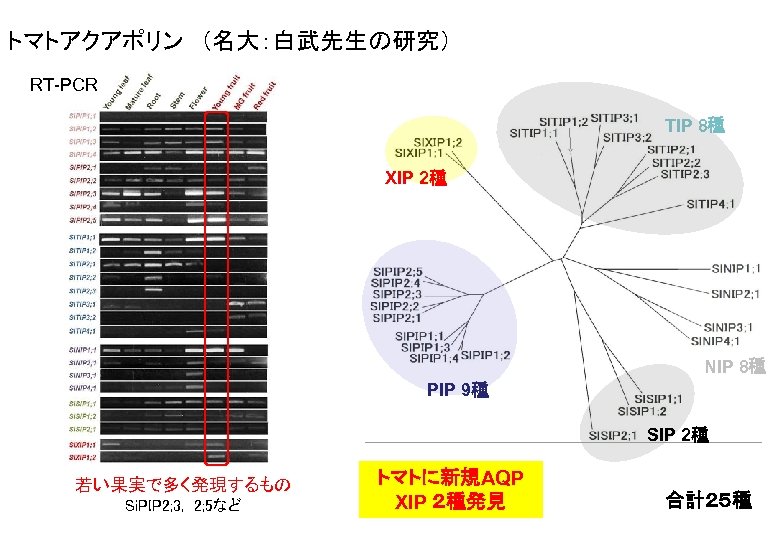
トマトアクアポリン (名大:白武先生の研究) RT-PCR TIP 8種 XIP 2種 NIP 8種 PIP 9種 SIP 2種 若い果実で多く発現するもの Si. PIP 2; 3, 2; 5など トマトに新規AQP XIP 2種発見 合計25種
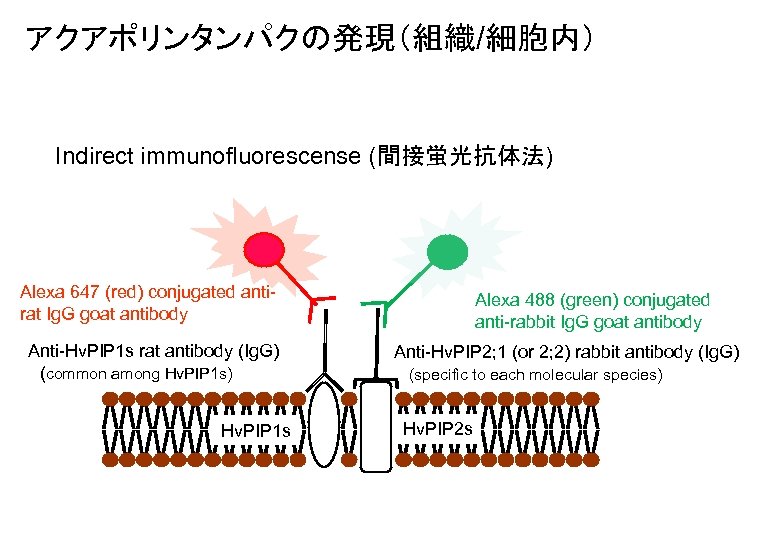
アクアポリンタンパクの発現(組織/細胞内) Indirect immunofluorescense (間接蛍光抗体法) Alexa 647 (red) conjugated antirat Ig. G goat antibody Anti-Hv. PIP 1 s rat antibody (Ig. G) (common among Hv. PIP 1 s) Hv. PIP 1 s Alexa 488 (green) conjugated anti-rabbit Ig. G goat antibody Anti-Hv. PIP 2; 1 (or 2; 2) rabbit antibody (Ig. G) (specific to each molecular species) Hv. PIP 2 s
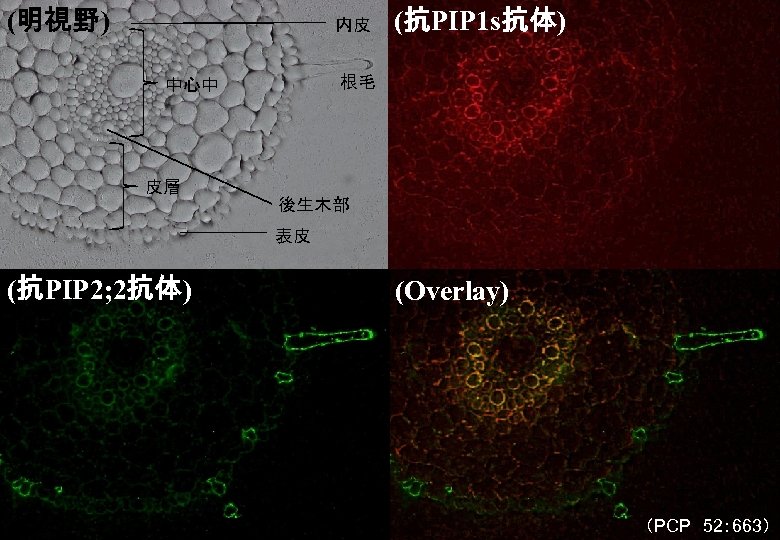
(明視野) 内皮 (抗PIP 1 s抗体) 根毛 中心中 皮層 後生木部 表皮 (抗PIP 2; 2抗体) (Overlay) (PCP 52: 663)
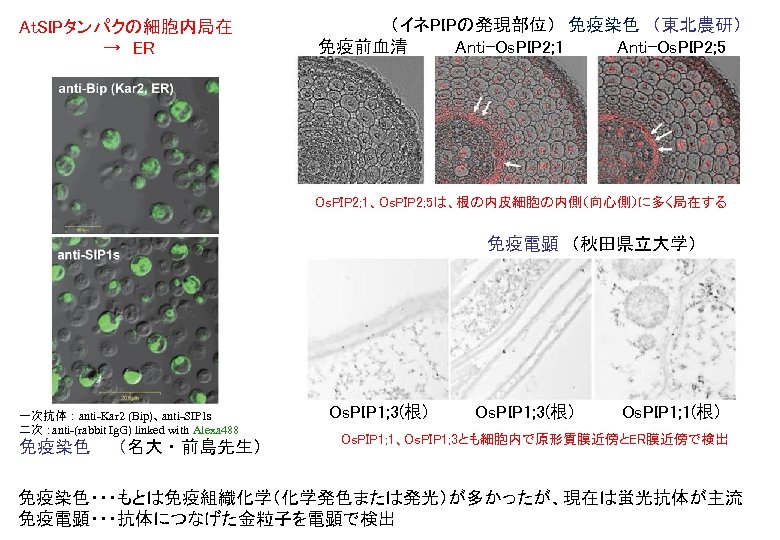
At. SIPタンパクの細胞内局在 → ER (イネPIPの発現部位) 免疫染色 (東北農研) 免疫前血清 Anti-Os. PIP 2; 1 Anti-Os. PIP 2; 5 Os. PIP 2; 1、Os. PIP 2; 5は、根の内皮細胞の内側(向心側)に多く局在する 免疫電顕 (秋田県立大学) 一次抗体:anti-Kar 2 (Bip)、 anti-SIP 1 s 二次: anti-(rabbit Ig. G) linked with Alexa 488 免疫染色 (名大・前島先生) Os. PIP 1; 3(根) Os. PIP 1; 1(根) Os. PIP 1; 1、Os. PIP 1; 3とも細胞内で原形質膜近傍とER膜近傍で検出 免疫染色・・・もとは免疫組織化学(化学発色または発光)が多かったが、現在は蛍光抗体が主流 免疫電顕・・・抗体につなげた金粒子を電顕で検出
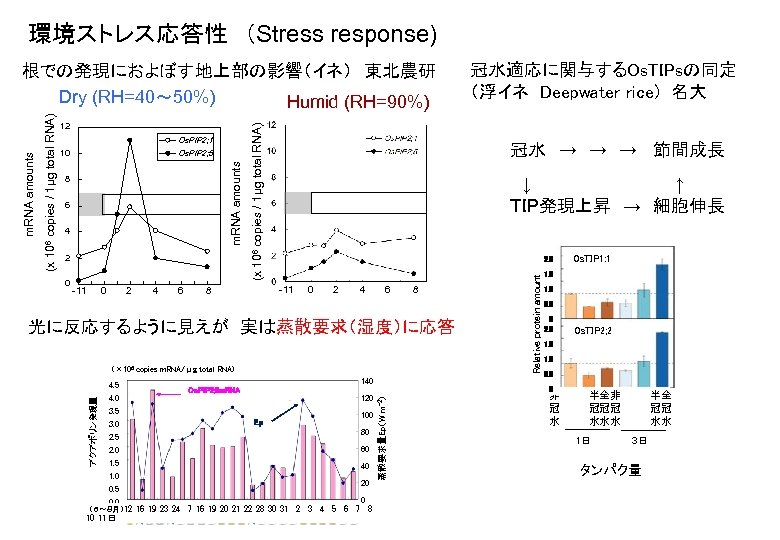
環境ストレス応答性 (Stress response) Os. PIP 2; 5 8 6 4 2 0 -11 0 2 4 6 → → → 冠水 節間成長 ↓ ↑ TIP発現上昇 → 細胞伸長 2. 0 -11 8 0 2 4 6 8 光に反応するように見えが 実は蒸散要求(湿度)に応答 (× 106 copies m. RNA/μg total RNA) 4. 0 140 Os. PIP 2; 5 m. RNA 120 3. 5 3. 0 100 Ep 80 2. 5 2. 0 60 1. 5 40 1. 0 20 0. 5 0. 0 (6~8月)12 16 19 23 24 10 11 日 0 7 16 19 20 21 22 28 30 31 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Os. TIP 1: 1 1. 5 1. 0 0. 5 0 2. 0 Os. TIP 2; 2 1. 5 1. 0 0. 5 0 蒸散要求量Ep(W m-2) アクアポリン発現量 4. 5 冠水適応に関与するOs. TIPsの同定 (浮イネ Deepwater rice) 名大 Relative protein amount Os. PIP 2; 1 10 (x 106 copies / 1μg total RNA) 12 m. RNA amounts (x 106 copies / 1μg total RNA) m. RNA amounts 根での発現におよぼす地上部の影響(イネ) 東北農研 Dry (RH=40~ 50%) Humid (RH=90%) 非 冠 水 半全非 冠冠冠 水水水 1日 3日 タンパク量 半全 冠冠 水水
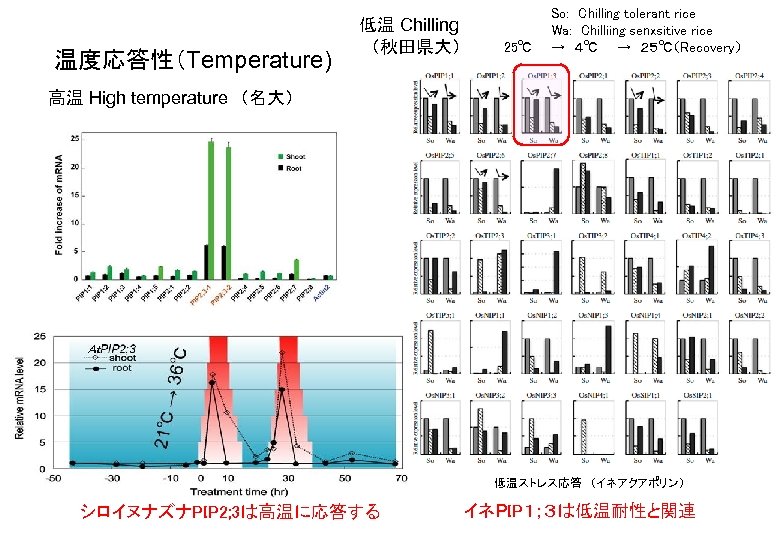
温度応答性(Temperature) 低温 Chilling (秋田県大) So: Chilling tolerant rice Wa: Chilliing senxsitive rice 25℃ → 4℃ → 25℃(Recovery) 高温 High temperature (名大) 低温ストレス応答 (イネアクアポリン) シロイヌナズナPIP 2; 3は高温に応答する イネPIP1;3は低温耐性と関連

低温で根の吸水量が減り、しおれる植物の事例 イネ (春季の低水温) ソラマメ 5ºC Shoot 地下部 25ºC Root 地上部 5ºC → アクアポリンの機能と発現量が低温(冷温)によって低下する
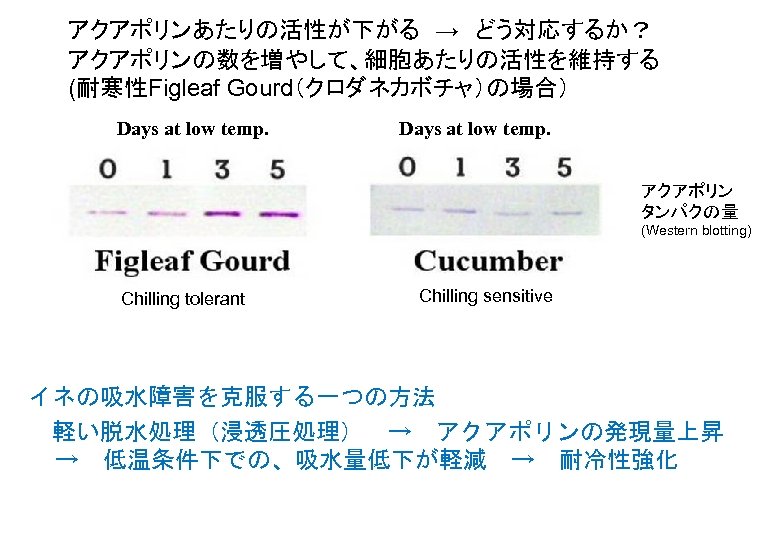
アクアポリンあたりの活性が下がる → どう対応するか? アクアポリンの数を増やして、細胞あたりの活性を維持する (耐寒性Figleaf Gourd(クロダネカボチャ)の場合) Days at low temp. アクアポリン タンパクの量 (Western blotting) Chilling tolerant Chilling sensitive イネの吸水障害を克服する一つの方法 軽い脱水処理(浸透圧処理) → アクアポリンの発現量上昇 → 低温条件下での、吸水量低下が軽減 → 耐冷性強化
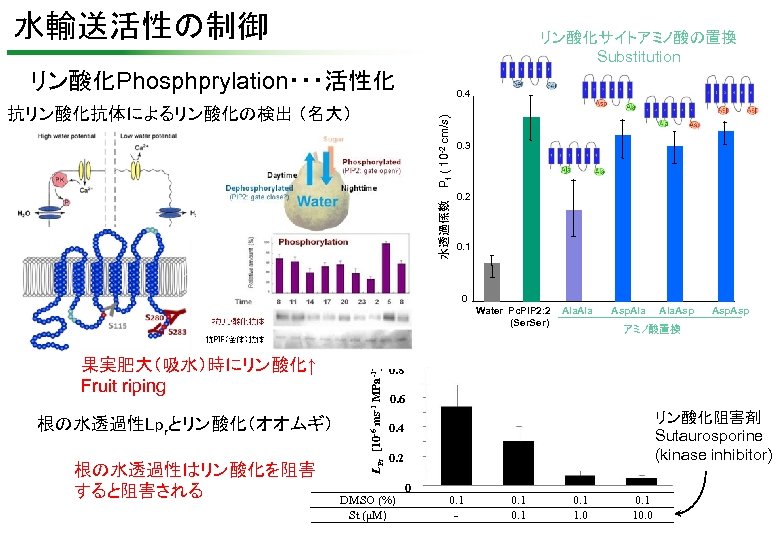
水輸送活性の制御 リン酸化サイトアミノ酸の置換 Substitution リン酸化Phosphprylation・・・活性化 0. 4 水透過係数 Pf ( 10 -2 cm/s) 抗リン酸化抗体によるリン酸化の検出 (名大) 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 果実肥大(吸水)時にリン酸化↑ Fruit riping 根の水透過性Lprとリン酸化(オオムギ) 根の水透過性はリン酸化を阻害 すると阻害される LPr [10 -6 ms-1 MPa-1] Water Pc. PIP 2: 2 (Ser. Ser) Ala Asp. Ala. Asp アミノ酸置換 0. 8 0. 6 リン酸化阻害剤 Sutaurosporine (kinase inhibitor) 0. 4 0. 2 DMSO (%) St (μM) 0 0. 1 - 0. 1 1. 0 0. 1 10. 0
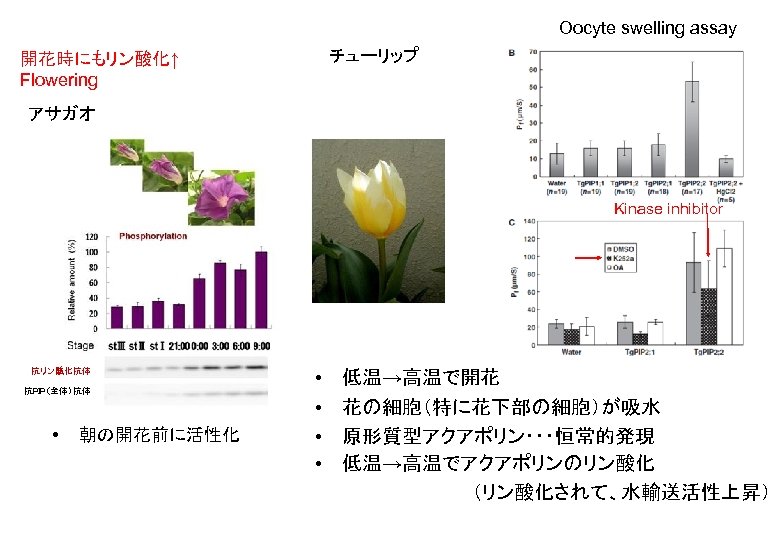
Oocyte swelling assay チューリップ 開花時にもリン酸化↑ Flowering アサガオ Kinase inhibitor 抗リン酸化抗体 抗PIP(全体)抗体 • 朝の開花前に活性化 • • 低温→高温で開花 花の細胞(特に花下部の細胞)が吸水 原形質型アクアポリン・・・恒常的発現 低温→高温でアクアポリンのリン酸化 (リン酸化されて、水輸送活性上昇)
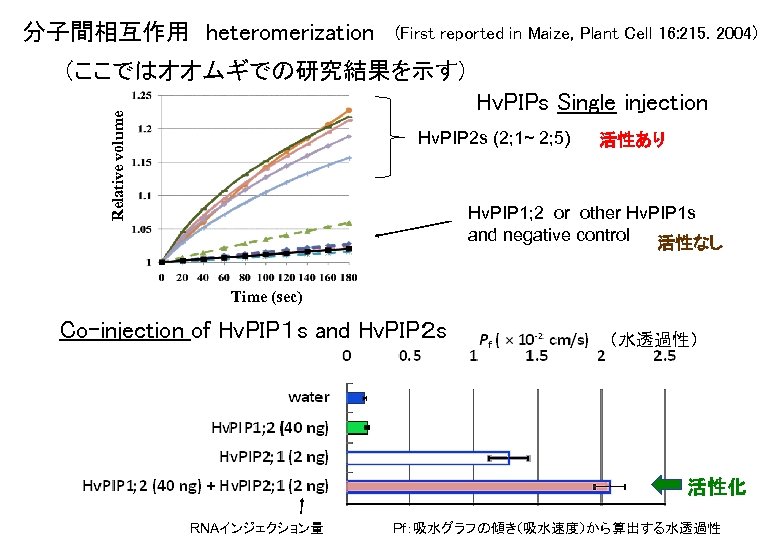
分子間相互作用 heteromerization (First reported in Maize, Plant Cell 16: 215. 2004) (ここではオオムギでの研究結果を示す) Relative volume Hv. PIPs Single injection Hv. PIP 2 s (2; 1~ 2; 5) 活性あり Hv. PIP 1; 2 or other Hv. PIP 1 s and negative control 活性なし Time (sec) Co-injection of Hv. PIP1 s and Hv. PIP2 s (水透過性) 活性化 RNAインジェクション量 Pf:吸水グラフの傾き(吸水速度)から算出する水透過性
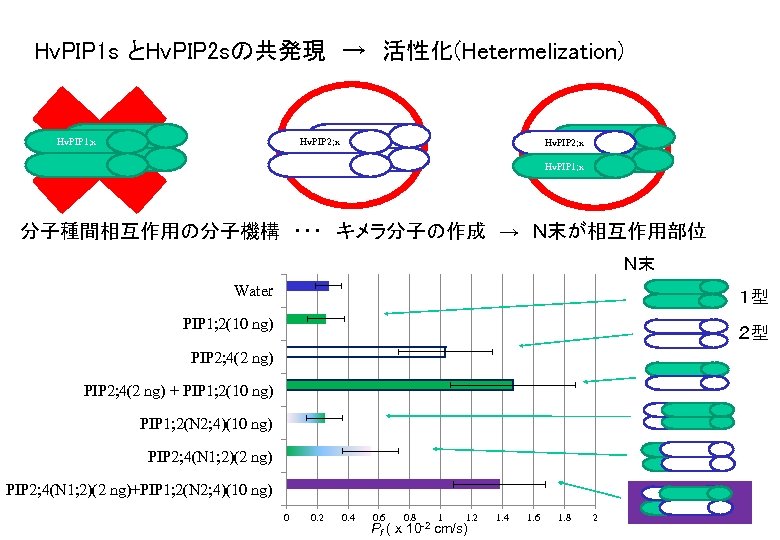
Hv. PIP 1 s とHv. PIP 2 sの共発現 → 活性化(Hetermelization) Hv. PIP 1; x Hv. PIP 2; x Hv. PIP 1; x 分子種間相互作用の分子機構 ・・・ キメラ分子の作成 → N末が相互作用部位 N末 Water 1型 PIP 1; 2(10 ng) 2型 PIP 2; 4(2 ng) + PIP 1; 2(10 ng) PIP 1; 2(N 2; 4)(10 ng) PIP 2; 4(N 1; 2)(2 ng)+PIP 1; 2(N 2; 4)(10 ng) 0 0. 2 0. 4 0. 6 0. 8 1 1. 2 Pf ( x 10 -2 cm/s) 1. 4 1. 6 1. 8 2
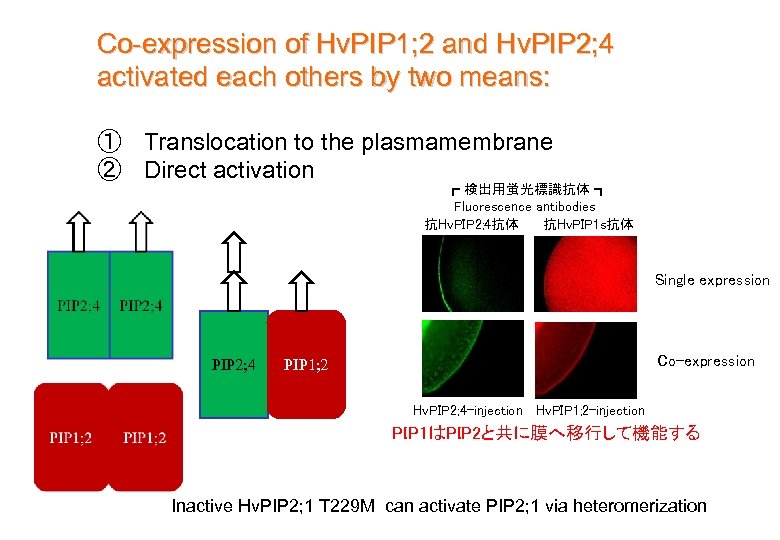
Co-expression of Hv. PIP 1; 2 and Hv. PIP 2; 4 activated each others by two means: ① Translocation to the plasmamembrane ② Direct activation ┏ 検出用蛍光標識抗体 ┓ Fluorescence antibodies 抗Hv. PIP 2; 4抗体 抗Hv. PIP 1 s抗体 Single expression PIP 2; 4 Co-expression PIP 1; 2 Hv. PIP 2; 4 -injection Hv. PIP 1; 2 -injection PIP 1はPIP 2と共に膜へ移行して機能する Inactive Hv. PIP 2; 1 T 229 M can activate PIP 2; 1 via heteromerization
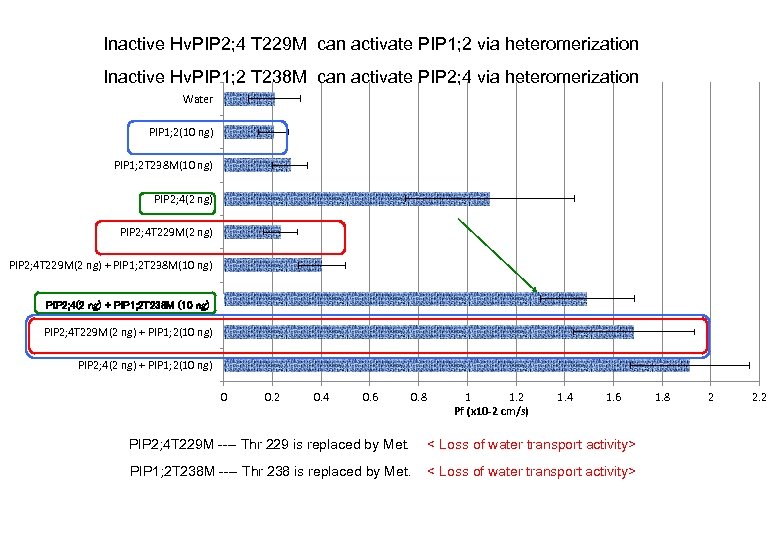
Inactive Hv. PIP 2; 4 T 229 M can activate PIP 1; 2 via heteromerization Inactive Hv. PIP 1; 2 T 238 M can activate PIP 2; 4 via heteromerization Water PIP 1; 2(10 ng) PIP 1; 2 T 238 M(10 ng) PIP 2; 4(2 ng) PIP 2; 4 T 229 M(2 ng) + PIP 1; 2 T 238 M(10 ng) PIP 2; 4(2 ng) + PIP 1; 2 M 238(10 ng) PIP 2; 4(2 ng) + PIP 1; 2 T 238 M (10 ng) PIP 2; 4 T 229 M(2 ng) + PIP 1; 2(10 ng) PIP 2; 4(2 ng) + PIP 1; 2(10 ng) 0 0. 2 0. 4 0. 6 0. 8 1 1. 2 Pf (x 10 -2 cm/s) 1. 4 1. 6 PIP 2; 4 T 229 M ---- Thr 229 is replaced by Met. < Loss of water transport activity> PIP 1; 2 T 238 M ---- Thr 238 is replaced by Met. < Loss of water transport activity> 1. 8 2 2. 2
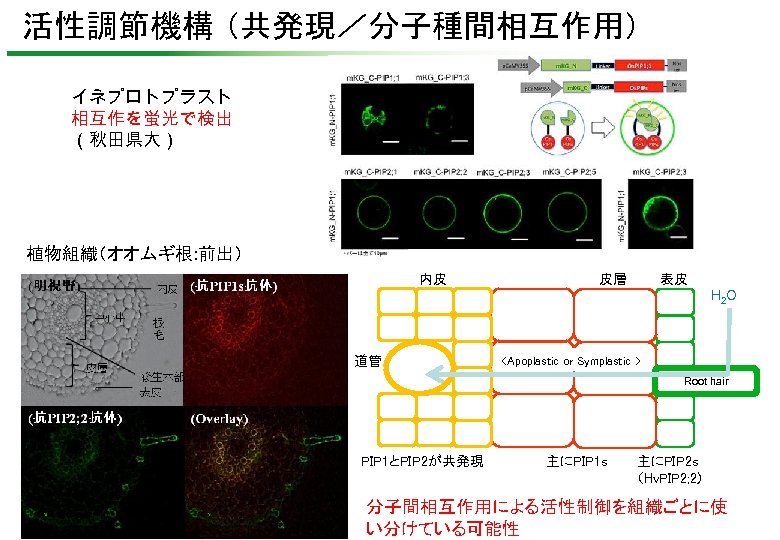
活性調節機構 (共発現/分子種間相互作用) イネプロトプラスト 相互作を蛍光で検出 (秋田県大) 植物組織(オオムギ根: 前出) 内皮 皮層 表皮 H 2 O 道管 <Apoplastic or Symplastic > Root hair PIP 1とPIP 2が共発現 主にPIP 1 s 主にPIP 2 s (Hv. PIP 2; 2) 分子間相互作用による活性制御を組織ごとに使 い分けている可能性
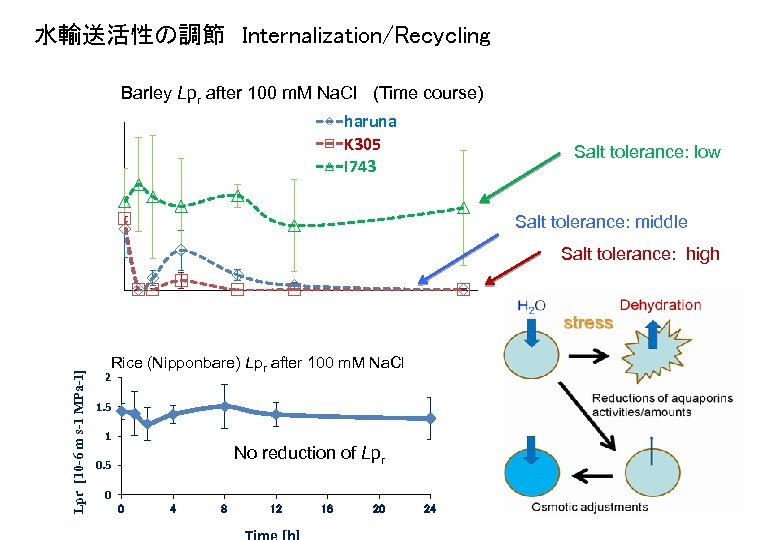
水輸送活性の調節 Internalization/Recycling Barley Lpr after 100 m. M Na. Cl (Time course) haruna K 305 I 743 Lpr [10 -6 m s-1 MPa-1] 1. 4 1. 2 1 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 Salt tolerance: middle Salt tolerance: high 0 Lpr [10 -6 m s-1 MPa-1] Salt tolerance: low 4 8 12 16 Time [h] 20 24 Rice (Nipponbare) Lpr after 100 m. M Na. Cl 2 1. 5 1 No reduction of Lpr 0. 5 0 0 4 8 12 16 20 24
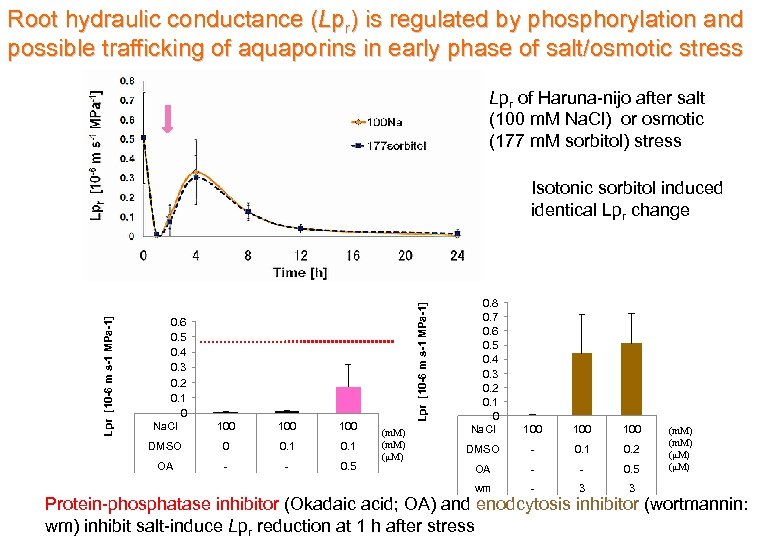
Root hydraulic conductance (Lpr) is regulated by phosphorylation and possible trafficking of aquaporins in early phase of salt/osmotic stress Lpr of Haruna-nijo after salt (100 m. M Na. Cl) or osmotic (177 m. M sorbitol) stress 0. 6 0. 5 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 Na. Cl 100 100 DMSO 0 0. 1 OA - - 0. 5 Lpr [10 -6 m s-1 MPa-1] Isotonic sorbitol induced identical Lpr change (m. M) (μM) 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 0. 5 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 Na. Cl 100 100 DMSO - 0. 1 0. 2 OA - - 0. 5 wm - 3 3 (m. M) (μM) Protein-phosphatase inhibitor (Okadaic acid; OA) and enodcytosis inhibitor (wortmannin: wm) inhibit salt-induce Lpr reduction at 1 h after stress
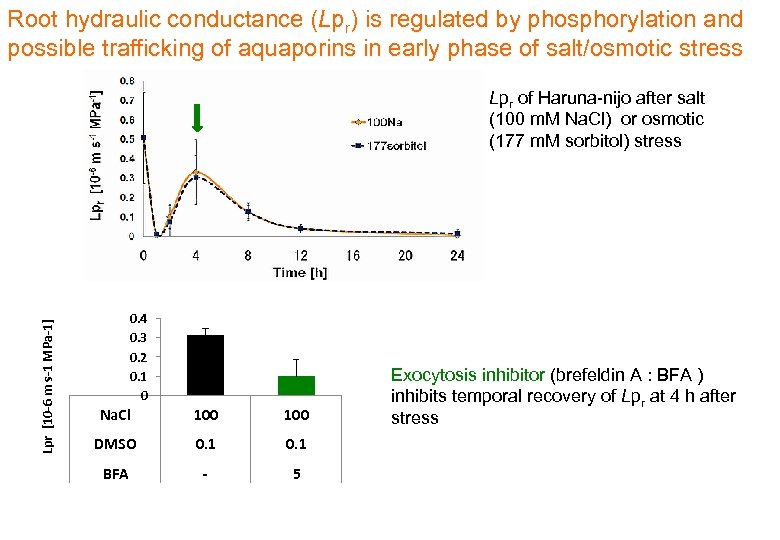
Root hydraulic conductance (Lpr) is regulated by phosphorylation and possible trafficking of aquaporins in early phase of salt/osmotic stress Lpr [10 -6 m s-1 MPa-1] Lpr of Haruna-nijo after salt (100 m. M Na. Cl) or osmotic (177 m. M sorbitol) stress 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 Na. Cl 100 DMSO 0. 1 BFA - 5 Exocytosis inhibitor (brefeldin A : BFA ) inhibits temporal recovery of Lpr at 4 h after stress
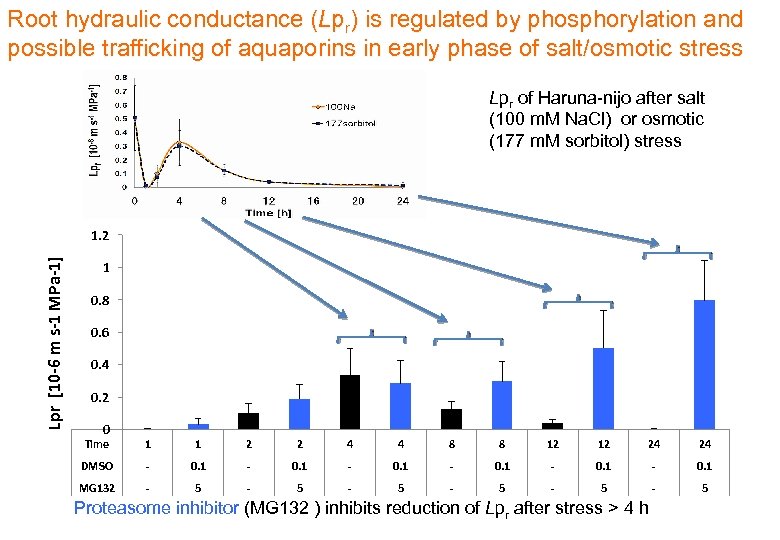
Root hydraulic conductance (Lpr) is regulated by phosphorylation and possible trafficking of aquaporins in early phase of salt/osmotic stress Lpr of Haruna-nijo after salt (100 m. M Na. Cl) or osmotic (177 m. M sorbitol) stress Lpr [10 -6 m s-1 MPa-1] 1. 2 1 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 Time 1 1 2 2 4 4 8 8 12 12 24 24 DMSO - 0. 1 MG 132 - 5 - 5 - 5 Proteasome inhibitor (MG 132 ) inhibits reduction of Lpr after stress > 4 h
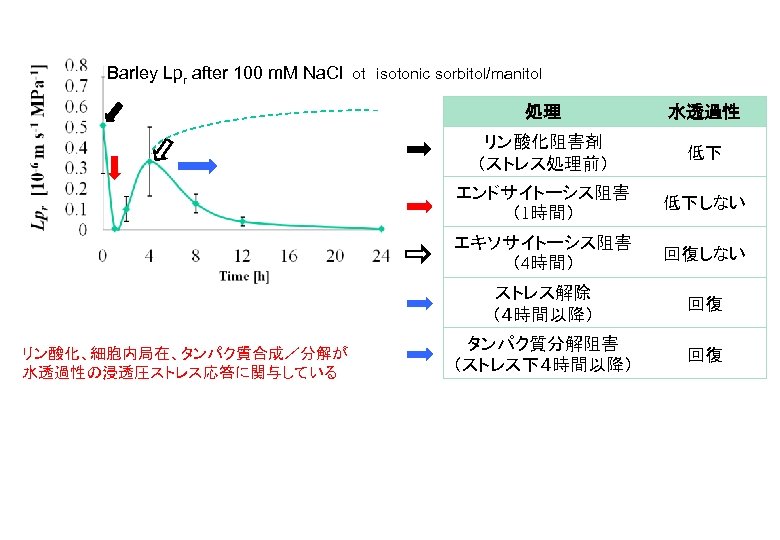
Barley Lpr after 100 m. M Na. Cl ot isotonic sorbitol/manitol 処理 水透過性 リン酸化阻害剤 (ストレス処理前) 低下 エンドサイトーシス阻害 (1時間) 低下しない エキソサイトーシス阻害 (4時間) 回復しない ストレス解除 (4時間以降) リン酸化、細胞内局在、タンパク質合成/分解が 水透過性の浸透圧ストレス応答に関与している 回復 タンパク質分解阻害 (ストレス下4時間以降) 回復
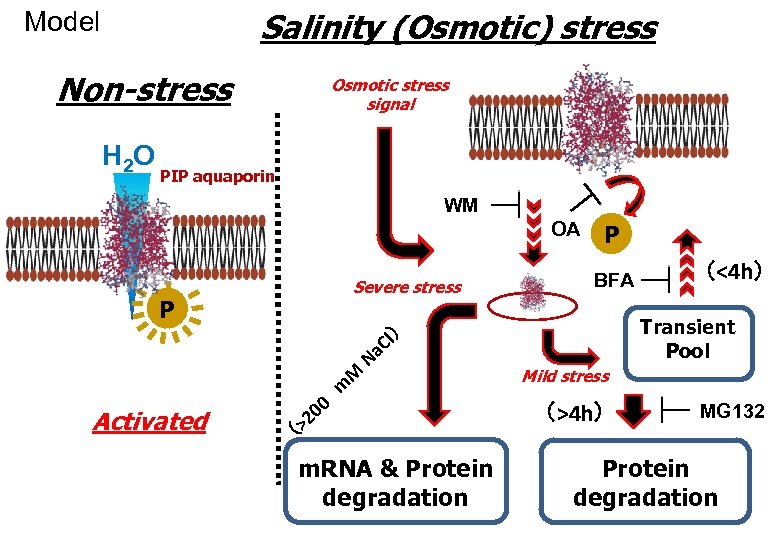
Salinity (Osmotic) stress Model Non-stress H 2 O Osmotic stress signal PIP aquaporin WM OA Severe stress P Activated (> 00 2 m M ) Cl Na m. RNA & Protein degradation P BFA (<4 h) Transient Pool Mild stress (>4 h) MG 132 Protein degradation
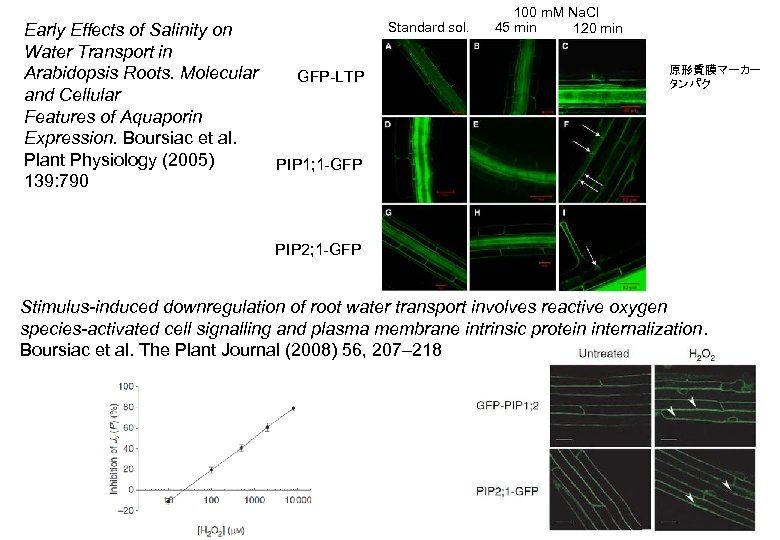
Early Effects of Salinity on Water Transport in Arabidopsis Roots. Molecular and Cellular Features of Aquaporin Expression. Boursiac et al. Plant Physiology (2005) 139: 790 Standard sol. GFP-LTP 100 m. M Na. Cl 45 min 120 min 原形質膜マーカー タンパク PIP 1; 1 -GFP PIP 2; 1 -GFP Stimulus-induced downregulation of root water transport involves reactive oxygen species-activated cell signalling and plasma membrane intrinsic protein internalization. Boursiac et al. The Plant Journal (2008) 56, 207– 218
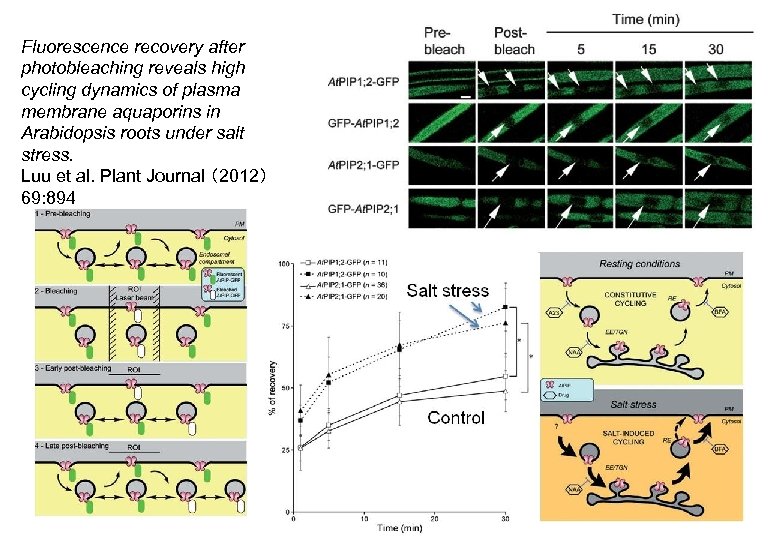
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching reveals high cycling dynamics of plasma membrane aquaporins in Arabidopsis roots under salt stress. Luu et al. Plant Journal (2012) 69: 894
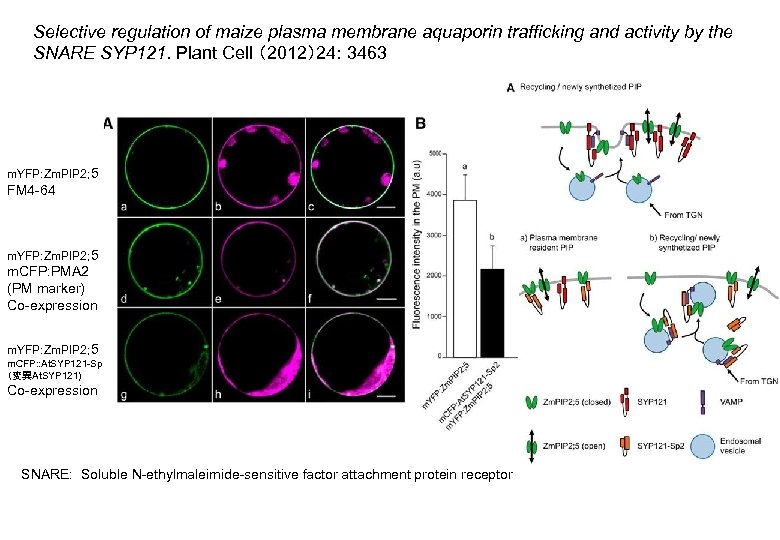
Selective regulation of maize plasma membrane aquaporin trafficking and activity by the SNARE SYP 121. Plant Cell (2012)24: 3463 YFP CFP or FM 4 -64 merge m. YFP: Zm. PIP 2; 5 FM 4 -64 m. YFP: Zm. PIP 2; 5 m. CFP: PMA 2 (PM marker) Co-expression m. YFP: Zm. PIP 2; 5 m. CFP: : At. SYP 121 -Sp 2 (変異At. SYP 121) Co-expression SNARE: Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor
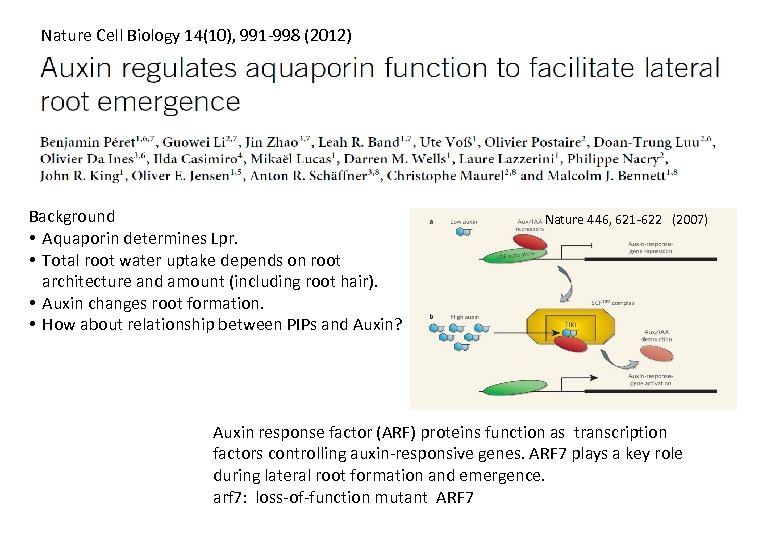
Nature Cell Biology 14(10), 991 -998 (2012) Background • Aquaporin determines Lpr. • Total root water uptake depends on root architecture and amount (including root hair). • Auxin changes root formation. • How about relationship between PIPs and Auxin? Nature 446, 621 -622 (2007) Auxin response factor (ARF) proteins function as transcription factors controlling auxin-responsive genes. ARF 7 plays a key role during lateral root formation and emergence. arf 7: loss-of-function mutant ARF 7
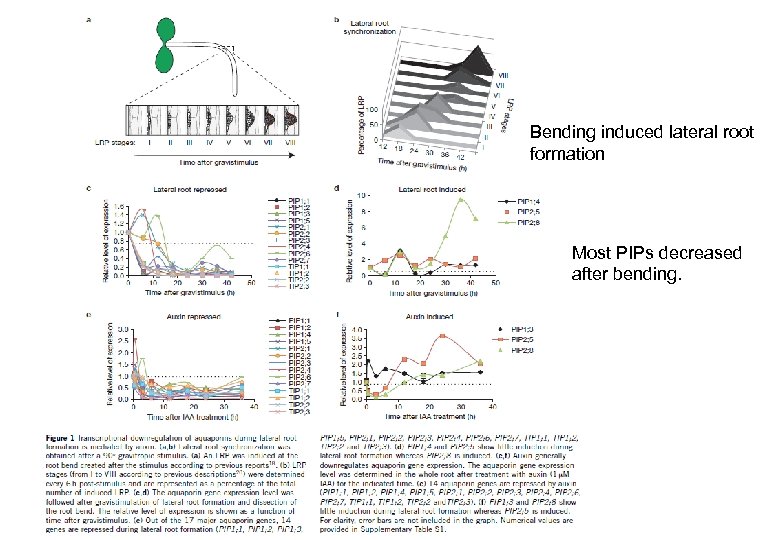
Bending induced lateral root formation Most PIPs decreased after bending. At. PIPsの発現量
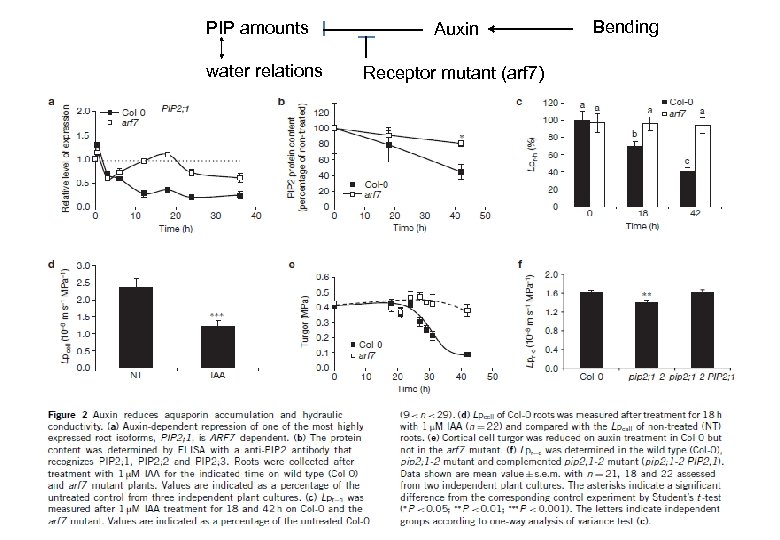
PIP amounts water relations Auxin Receptor mutant (arf 7) Bending
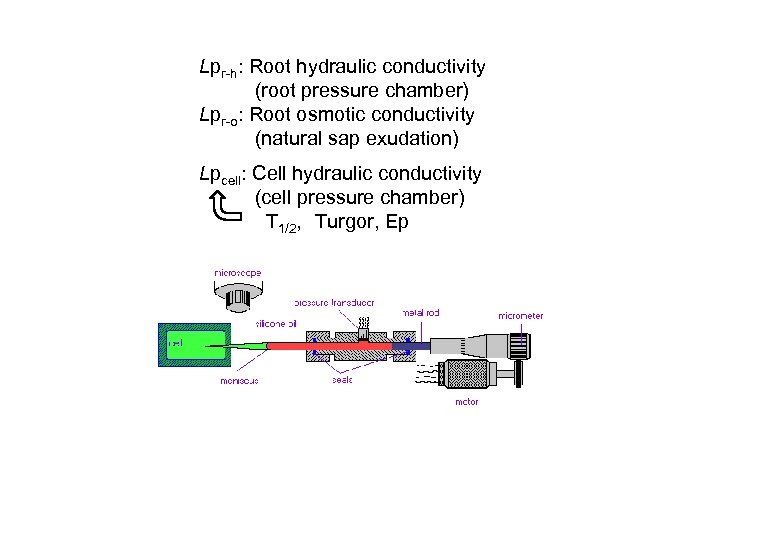
Lpr-h: Root hydraulic conductivity (root pressure chamber) Lpr-o: Root osmotic conductivity (natural sap exudation) Lpcell: Cell hydraulic conductivity (cell pressure chamber) T 1/2, Turgor, Ep
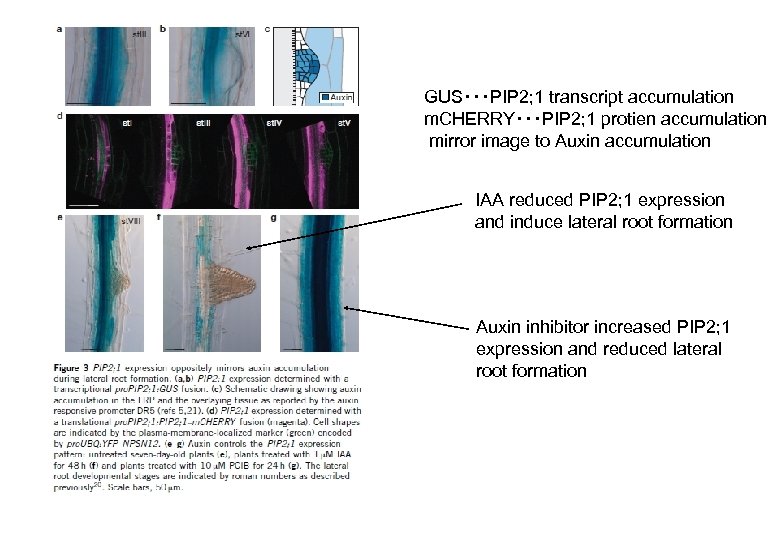
GUS・・・PIP 2; 1 transcript accumulation m. CHERRY・・・PIP 2; 1 protien accumulation mirror image to Auxin accumulation IAA reduced PIP 2; 1 expression and induce lateral root formation Auxin inhibitor increased PIP 2; 1 expression and reduced lateral root formation
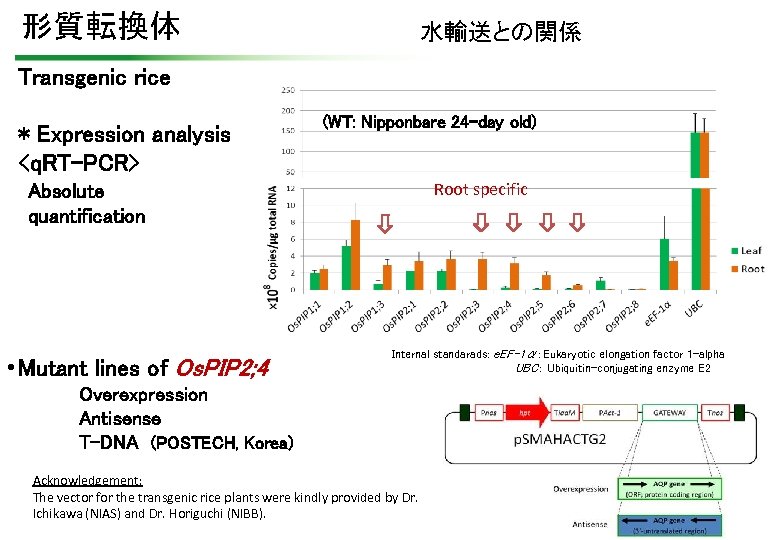
形質転換体 水輸送との関係 Transgenic rice * Expression analysis <q. RT-PCR> (WT: Nipponbare 24 -day old) Root specific Absolute quantification • Mutant lines of Os. PIP 2; 4 Internal standarads: e. EF-1α:Eukaryotic elongation factor 1 -alpha UBC: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E 2 Overexpression Antisense T-DNA (POSTECH, Korea) Acknowledgement: The vector for the transgenic rice plants were kindly provided by Dr. Ichikawa (NIAS) and Dr. Horiguchi (NIBB).
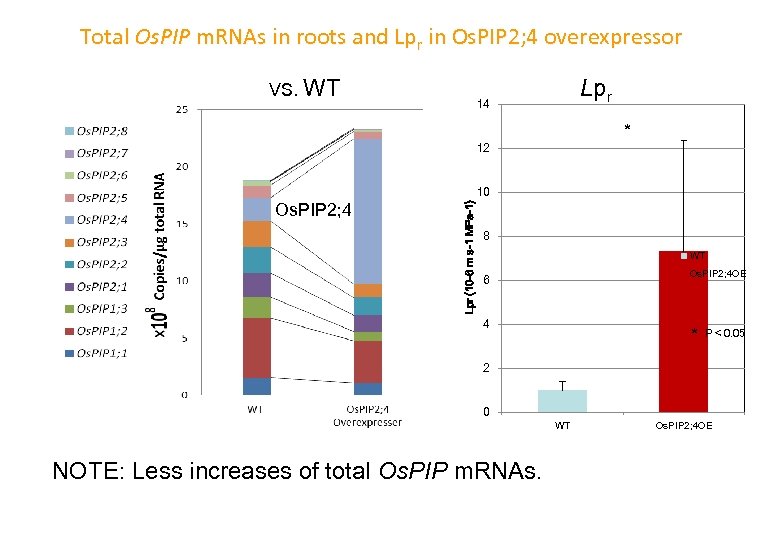
Total Os. PIP m. RNAs in roots and Lpr in Os. PIP 2; 4 overexpressor VS. WT Lpr 14 * 12 Os. PIP 2; 4 Lpr (10 -6 m s-1 MPa-1) 10 8 WT Os. PIP 2; 4 OE 6 4 * P< 0. 05 2 0 NOTE: Less increases of total Os. PIP m. RNAs. WT Os. PIP 2; 4 OE
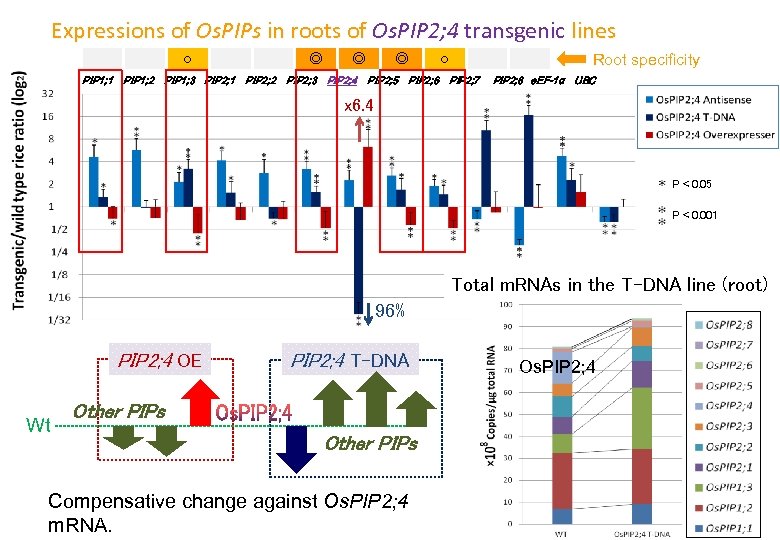
Expressions of Os. PIPs in roots of Os. PIP 2; 4 transgenic lines ○ PIP 1; 1 PIP 1; 2 PIP 1; 3 PIP 2; 1 ◎ PIP 2; 2 ◎ PIP 2; 3 PIP 2; 4 ◎ PIP 2; 5 PIP 2; 6 ○ Root specificity PIP 2; 7 PIP 2; 8 e. EF-1α UBC x 6. 4 P< 0. 05 P< 0. 001 Total m. RNAs in the T-DNA line (root) 96% PIP 2; 4 OE Wt PIP 2; 4 T-DNA Other PIPs Compensative change against Os. PIP 2; 4 m. RNA. Os. PIP 2; 4
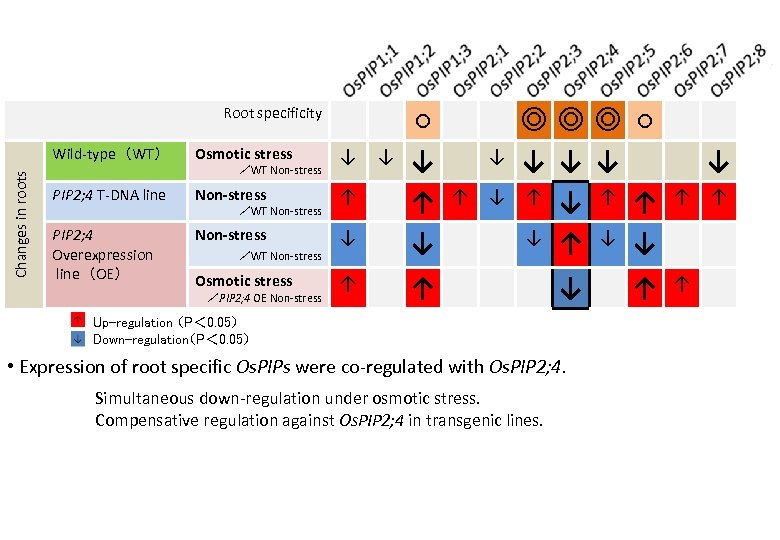
Wild-type(WT) Osmotic stress ↓ ↓ PIP 2; 4 T-DNA line Non-stress ↑ PIP 2; 4 Overexpression line(OE) Non-stress /WT Non-stress ↓ ○ ↓ ↑ ↓ Osmotic stress ↑ ↑ Changes in roots Root specificity /WT Non-stress /PIP 2; 4 OE Non-stress ↓ ↑ ↓ ◎◎◎ ○ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ ↓ Up-regulation (P< 0. 05) Down-regulation(P< 0. 05) • Expression of root specific Os. PIPs were co-regulated with Os. PIP 2; 4. Simultaneous down-regulation under osmotic stress. Compensative regulation against Os. PIP 2; 4 in transgenic lines. ↑ ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑
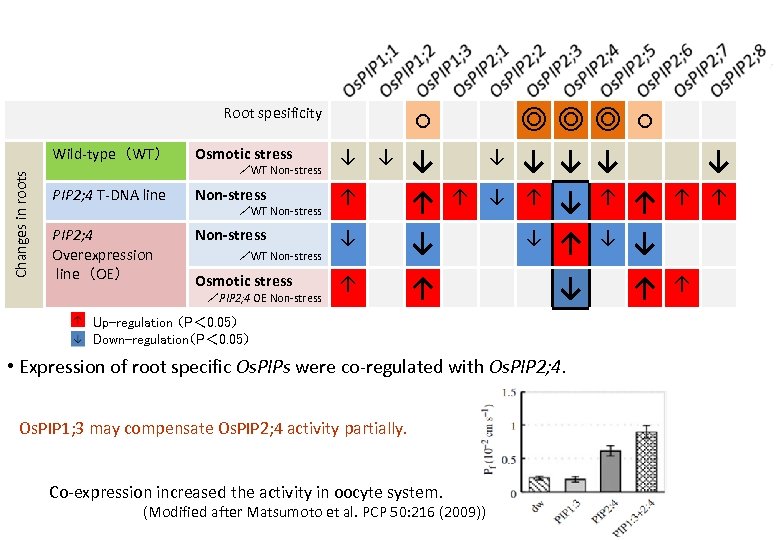
Wild-type(WT) Osmotic stress ↓ ↓ PIP 2; 4 T-DNA line Non-stress ↑ PIP 2; 4 Overexpression line(OE) Non-stress /WT Non-stress ↓ ○ ↓ ↑ ↓ Osmotic stress ↑ ↑ Changes in roots Root spesificity /WT Non-stress /PIP 2; 4 OE Non-stress ↓ ↑ ↓ ◎◎◎ ○ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ ↓ Up-regulation (P< 0. 05) Down-regulation(P< 0. 05) • Expression of root specific Os. PIPs were co-regulated with Os. PIP 2; 4. Os. PIP 1; 3 may compensate Os. PIP 2; 4 activity partially. Co-expression increased the activity in oocyte system. (Modified after Matsumoto et al. PCP 50: 216 (2009)) ↑ ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑
0c7d2078822cdd04a0e6711d029629c8.ppt