a5782286fb4cd3812f11cb1324e2244f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68
核磁共振光譜與影像導論 Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging Lecture 09 Applications of Solid State NMR (Spring Term, 2011) (Fall Term, 2011) (Spring Term, 2014) (Spring Term, 2015) (Spring Term, 2016) (Spring Term, 2017) Department of Chemistry National Sun Yat-sen University
Applications of Solid State NMR • • Polymers Glasses Porous materials Liquid crystals
Schematic of a typical semicrystallinear polymer
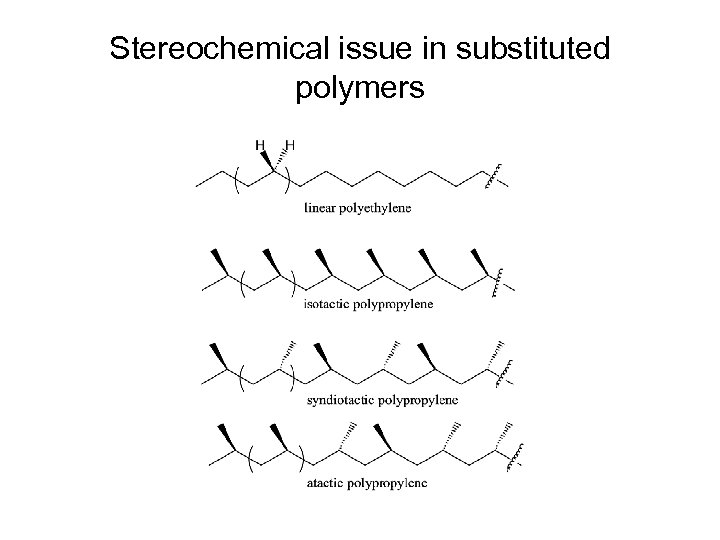
Stereochemical issue in substituted polymers
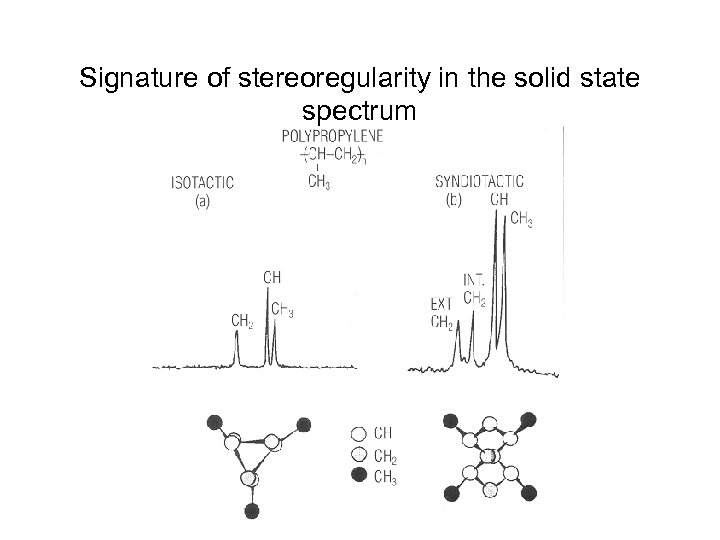
Signature of stereoregularity in the solid state spectrum
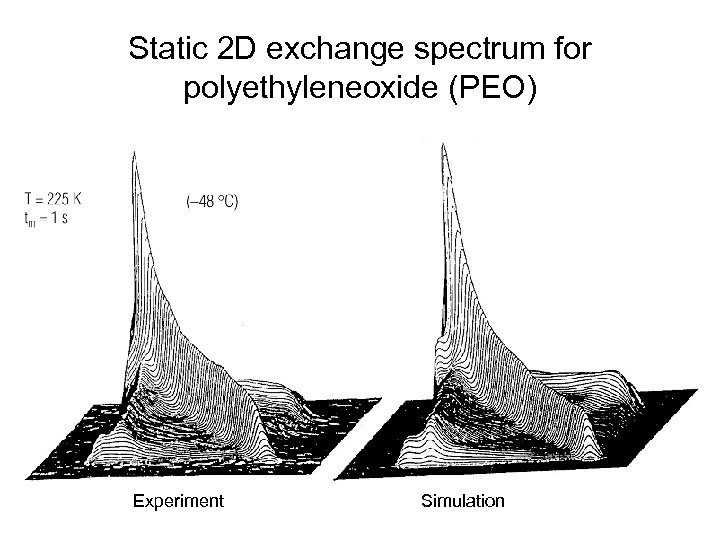
Static 2 D exchange spectrum for polyethyleneoxide (PEO) Experiment Simulation
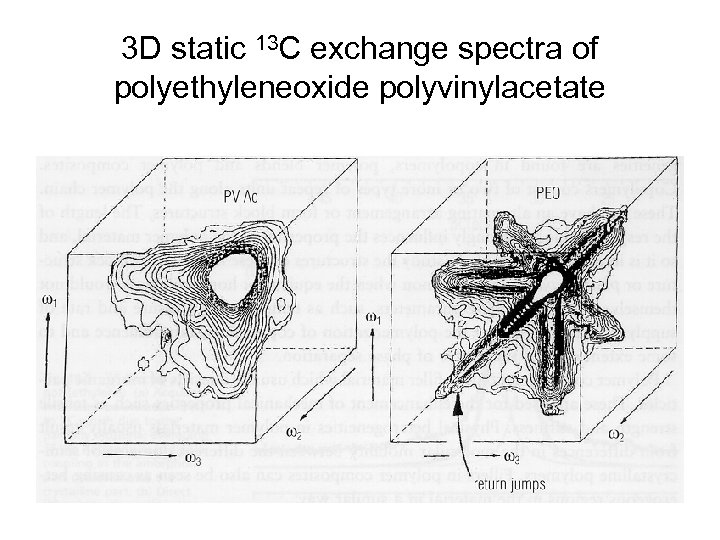
3 D static 13 C exchange spectra of polyethyleneoxide polyvinylacetate

Applications • • Polymers Glasses Porous materials Liquid crystals
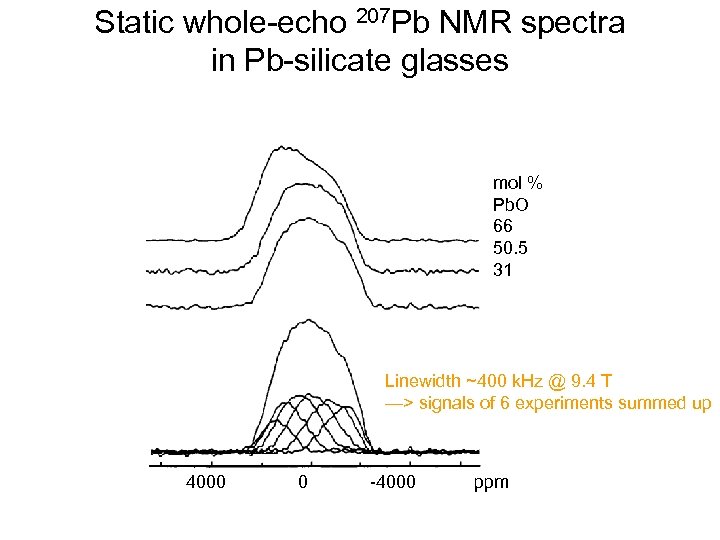
Static whole-echo 207 Pb NMR spectra in Pb-silicate glasses mol % Pb. O 66 50. 5 31 Linewidth ~400 k. Hz @ 9. 4 T —> signals of 6 experiments summed up 4000 0 -4000 ppm
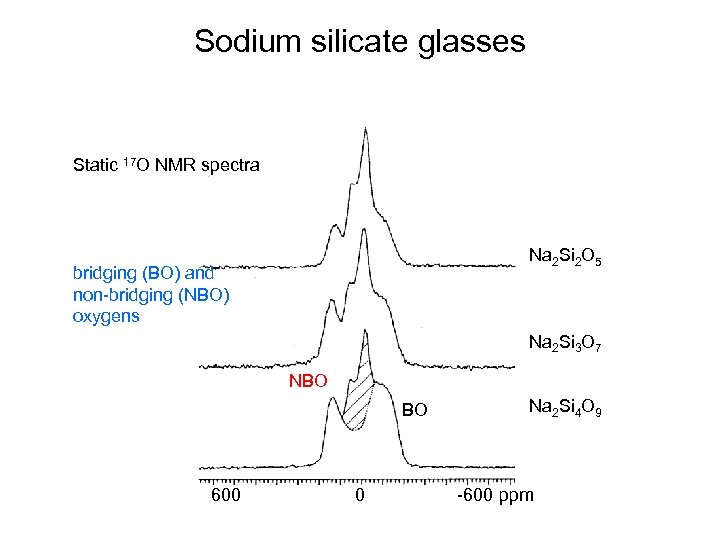
Sodium silicate glasses Static 17 O NMR spectra Na 2 Si 2 O 5 bridging (BO) and non-bridging (NBO) oxygens Na 2 Si 3 O 7 NBO BO 600 0 Na 2 Si 4 O 9 -600 ppm
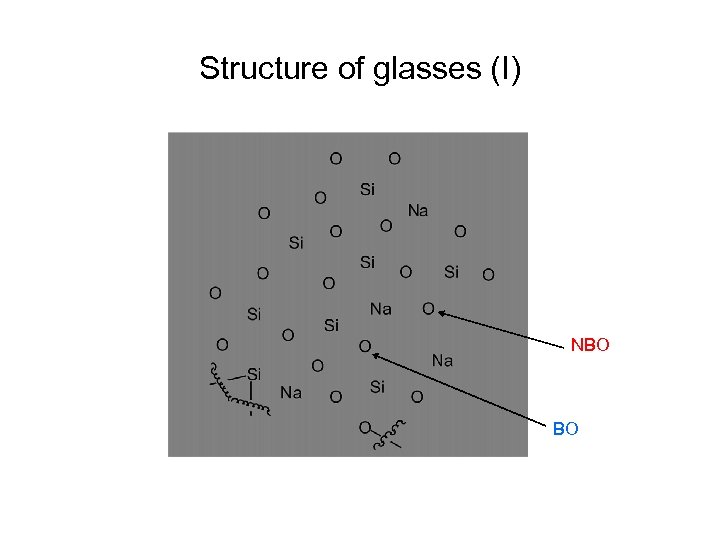
Structure of glasses (I) NBO BO
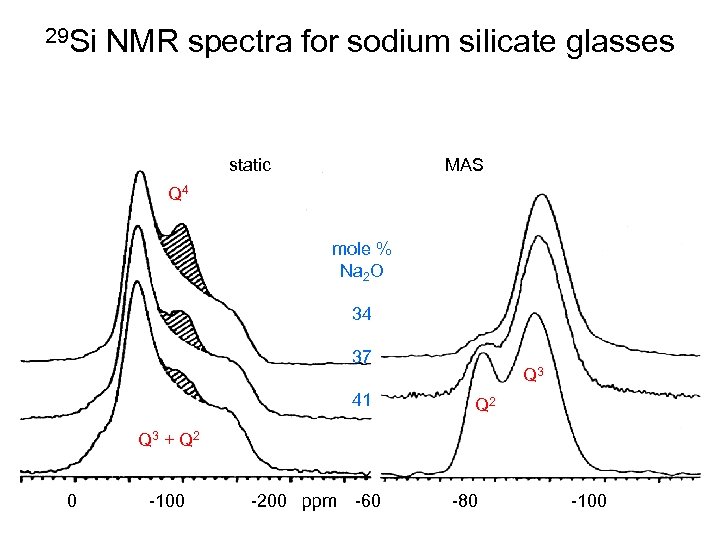
29 Si NMR spectra for sodium silicate glasses static MAS Q 4 mole % Na 2 O 34 37 41 Q 3 Q 2 Q 3 + Q 2 0 -100 -200 ppm -60 -80 -100
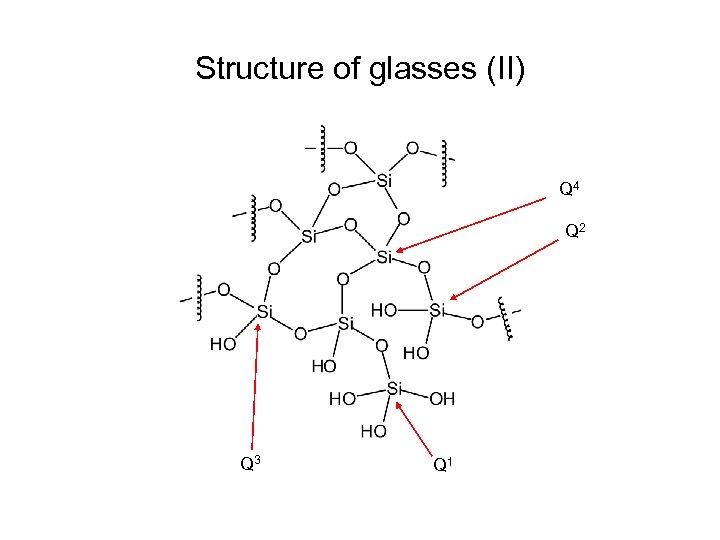
Structure of glasses (II) Q 4 Q 2 Q 3 Q 1
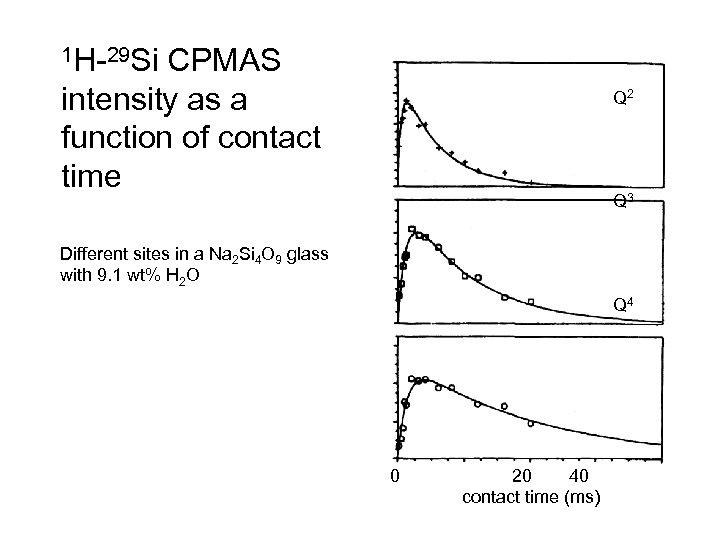
1 H-29 Si CPMAS intensity as a function of contact time Q 2 Q 3 Different sites in a Na 2 Si 4 O 9 glass with 9. 1 wt% H 2 O Q 4 0 20 40 contact time (ms)
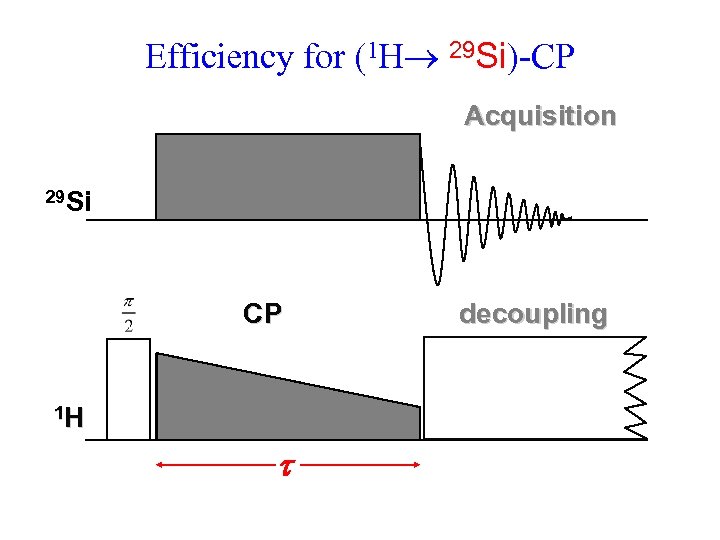
Efficiency for (1 H 29 Si)-CP Acquisition 29 Si CP 1 H t decoupling
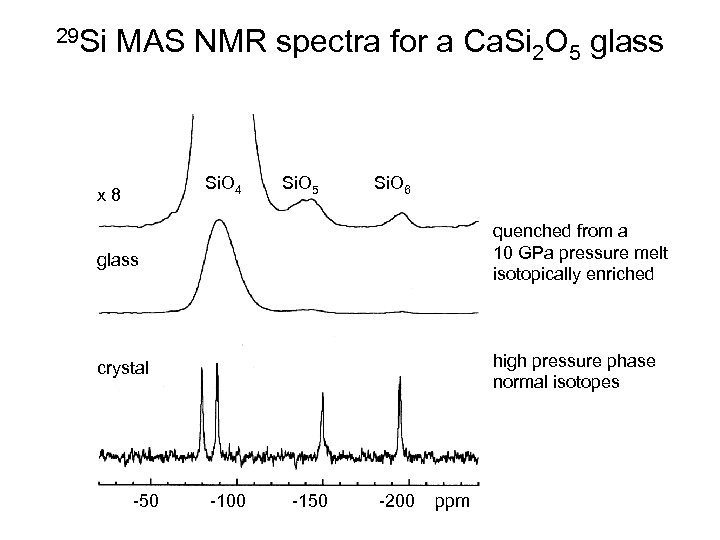
29 Si MAS NMR spectra for a Ca. Si 2 O 5 glass Si. O 4 x 8 Si. O 5 Si. O 6 glass quenched from a 10 GPa pressure melt isotopically enriched crystal high pressure phase normal isotopes -50 -100 -150 -200 ppm
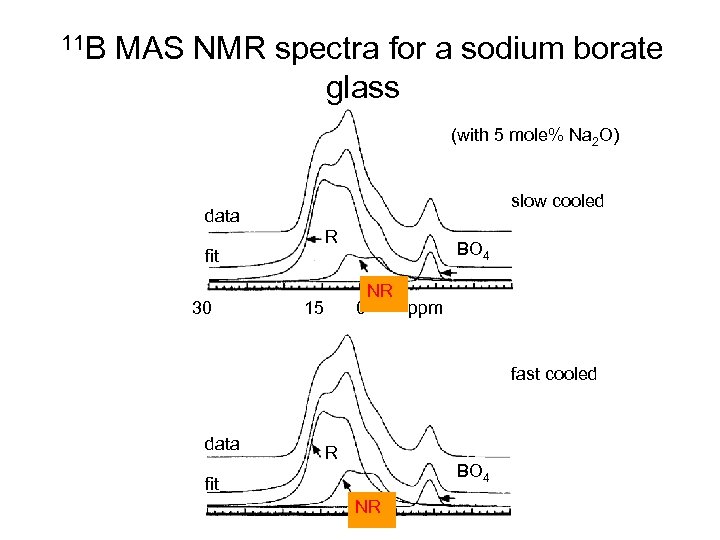
11 B MAS NMR spectra for a sodium borate glass (with 5 mole% Na 2 O) slow cooled data R fit 30 15 BO 4 0 NR ppm fast cooled data R BO 4 fit NR
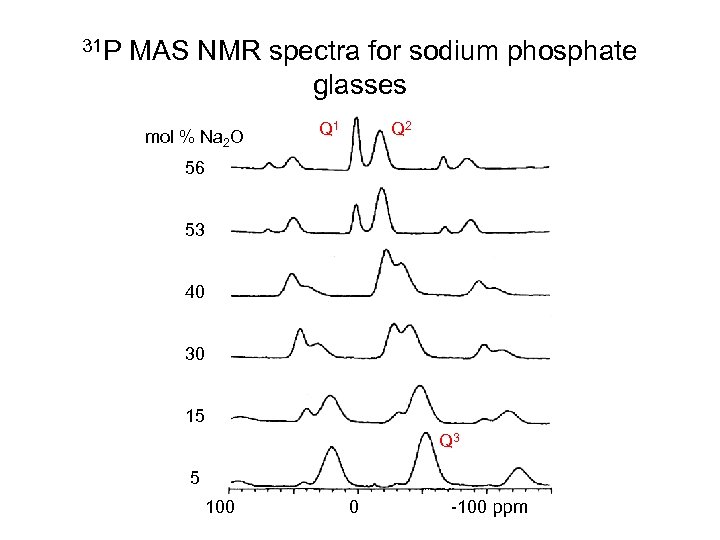
31 P MAS NMR spectra for sodium phosphate glasses mol % Na 2 O Q 1 Q 2 56 53 40 30 15 Q 3 5 100 0 -100 ppm
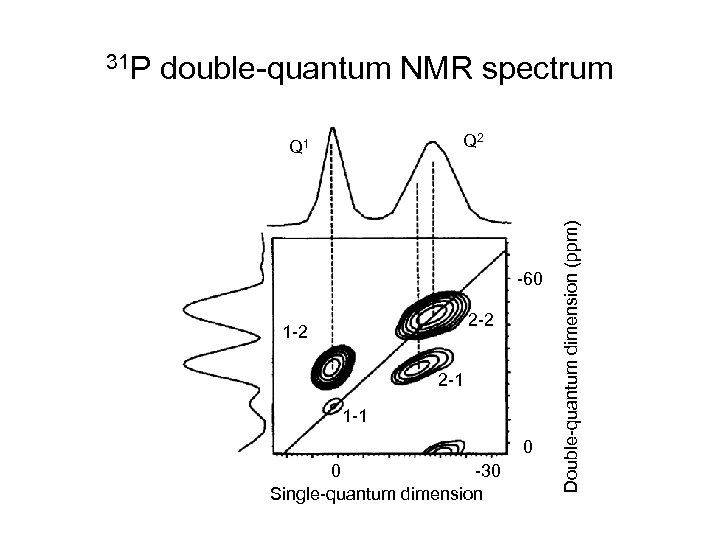
double-quantum NMR spectrum Q 2 Q 1 -60 2 -2 1 -2 2 -1 1 -1 0 0 -30 Single-quantum dimension Double-quantum dimension (ppm) 31 P
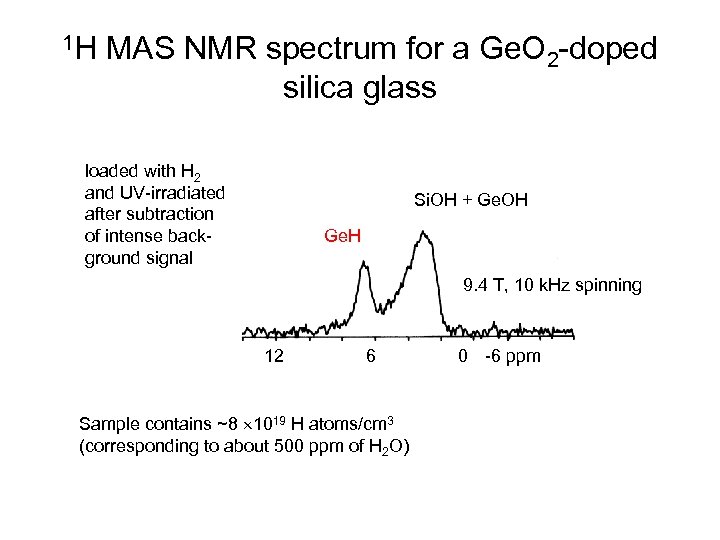
1 H MAS NMR spectrum for a Ge. O 2 -doped silica glass loaded with H 2 and UV-irradiated after subtraction of intense background signal Si. OH + Ge. OH Ge. H 9. 4 T, 10 k. Hz spinning 12 6 Sample contains ~8 ´ 1019 H atoms/cm 3 (corresponding to about 500 ppm of H 2 O) 0 -6 ppm
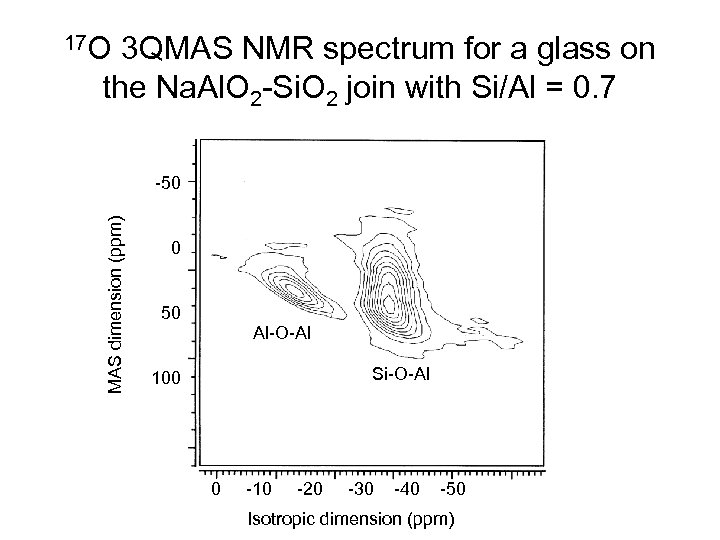
17 O 3 QMAS NMR spectrum for a glass on the Na. Al. O 2 -Si. O 2 join with Si/Al = 0. 7 MAS dimension (ppm) -50 0 50 Al-O-Al Si-O-Al 100 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 Isotropic dimension (ppm)
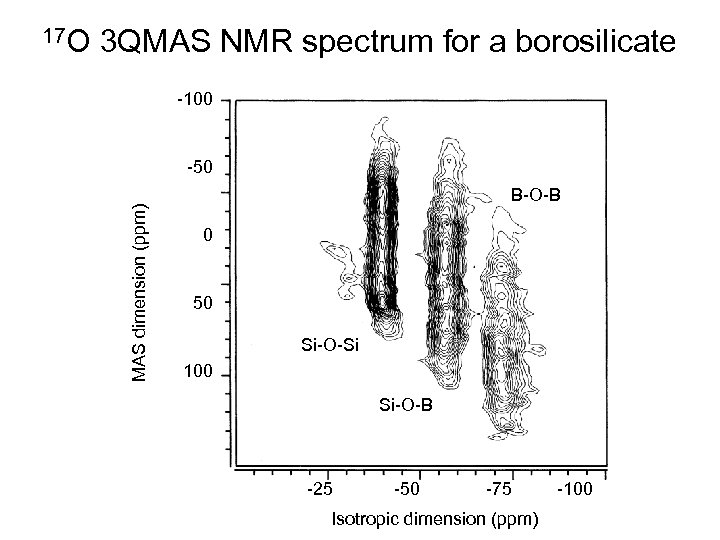
3 QMAS NMR spectrum for a borosilicate -100 -50 MAS dimension (ppm) 17 O B-O-B 0 50 Si-O-Si 100 Si-O-B -25 -50 -75 Isotropic dimension (ppm) -100
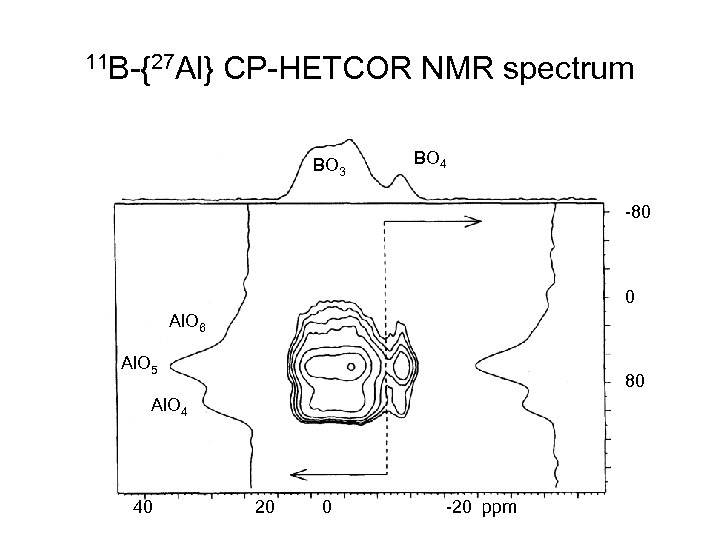
11 B-{27 Al} CP-HETCOR NMR spectrum BO 3 BO 4 -80 0 Al. O 6 Al. O 5 80 Al. O 4 40 20 0 -20 ppm

Applications • • Polymers Glasses Porous materials Liquid crystals
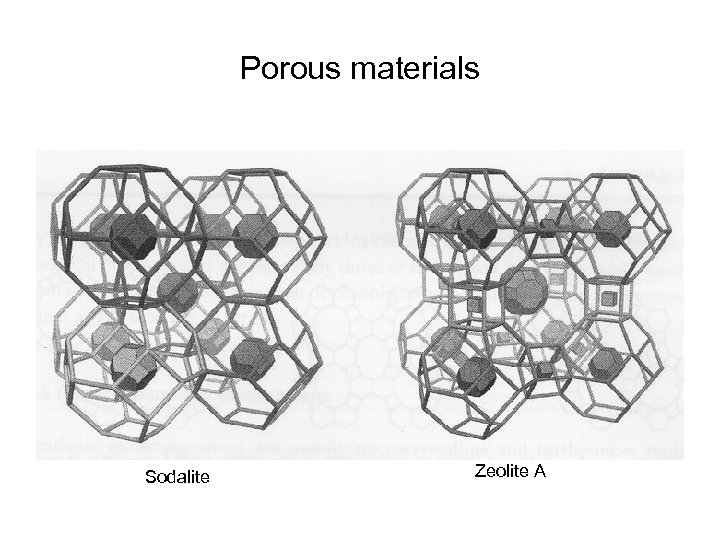
Porous materials Sodalite Zeolite A
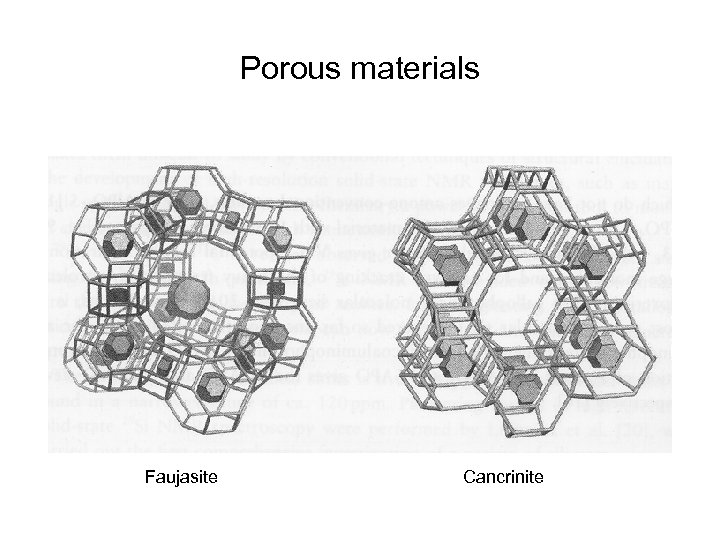
Porous materials Faujasite Cancrinite
Porous materials Zeolite ZK-5 Zeolite Rho
![Zeolite framework projections Al. PO 4 -5 along [001] Al. PO 4 -11 along Zeolite framework projections Al. PO 4 -5 along [001] Al. PO 4 -11 along](https://present5.com/presentation/a5782286fb4cd3812f11cb1324e2244f/image-28.jpg)
Zeolite framework projections Al. PO 4 -5 along [001] Al. PO 4 -11 along [100] VPI-5 along [001]
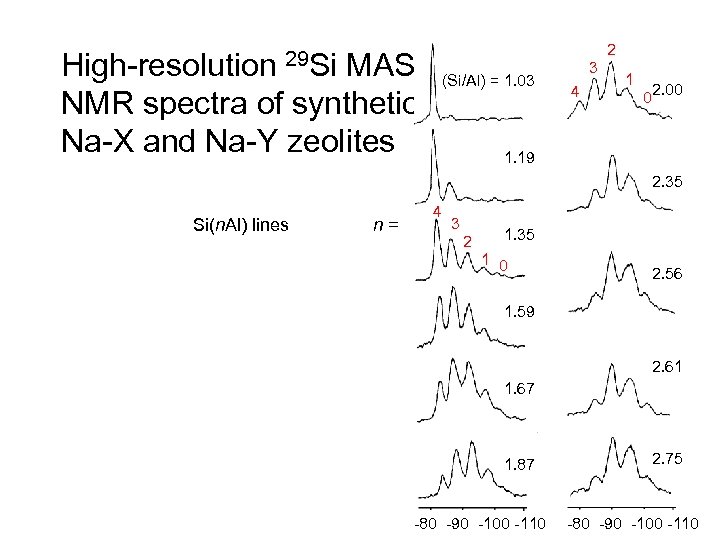
29 Si High-resolution MAS NMR spectra of synthetic Na-X and Na-Y zeolites 2 (Si/Al) = 1. 03 3 4 1 0 2. 00 1. 19 2. 35 Si(n. Al) lines n= 4 3 2 1. 35 1 0 2. 56 1. 59 2. 61 1. 67 1. 87 -80 -90 -100 -110 2. 75 -80 -90 -100 -110
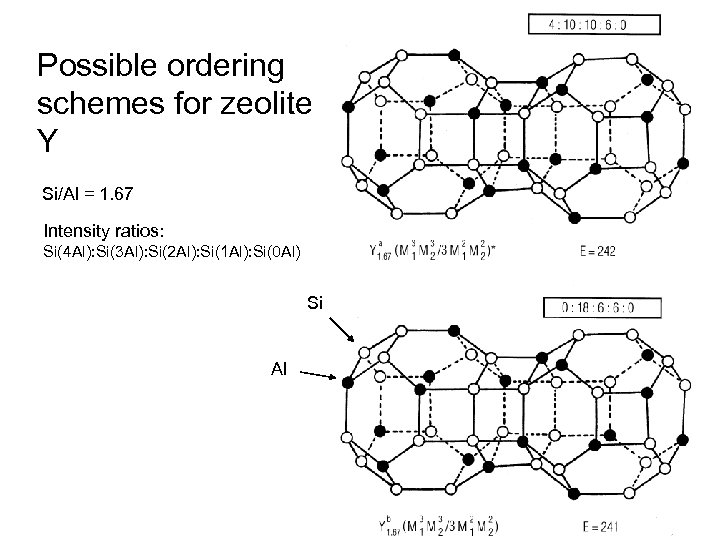
Possible ordering schemes for zeolite Y Si/Al = 1. 67 Intensity ratios: Si(4 Al): Si(3 Al): Si(2 Al): Si(1 Al): Si(0 Al) Si Al
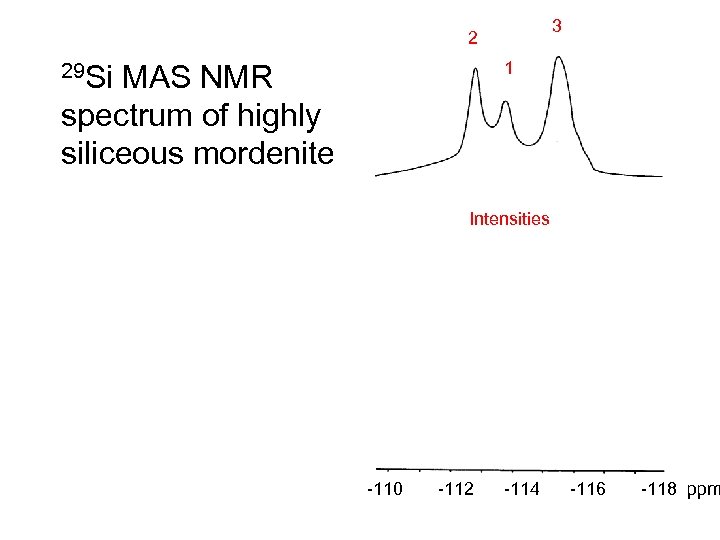
3 2 1 29 Si MAS NMR spectrum of highly siliceous mordenite Intensities -110 -112 -114 -116 -118 ppm
![Mordenite structure along [001] T-site T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 No. Mordenite structure along [001] T-site T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 No.](https://present5.com/presentation/a5782286fb4cd3812f11cb1324e2244f/image-32.jpg)
Mordenite structure along [001] T-site T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 No. per unit cell 16 16 8 8 Neighbouring sites Mean T-O-T bond angle T 1, T 2, T 3 T 1, T 2, T 4 T 1, T 3, T 4 T 2, T 3, T 4 150. 4° 158. 1° 153. 9° 152. 3°
![Mordenite structure along [001] T 1/T 3/T 2+T 4 : 3 cross peaks T Mordenite structure along [001] T 1/T 3/T 2+T 4 : 3 cross peaks T](https://present5.com/presentation/a5782286fb4cd3812f11cb1324e2244f/image-33.jpg)
Mordenite structure along [001] T 1/T 3/T 2+T 4 : 3 cross peaks T 1/T 4/T 2+T 3 : 2 cross peaks T 2/T 3/T 1+T 4 : 2 cross peaks T 2/T 4/T 1+T 3 : 3 cross peaks T-site T 1 T 2 T 3 T 4 No. per unit cell 16 16 8 8 Neighbouring sites Mean T-O-T bond angle T 1, T 2, T 3 T 1, T 2, T 4 T 1, T 3, T 4 T 2, T 3, T 4 150. 4° 158. 1° 153. 9° 152. 3°
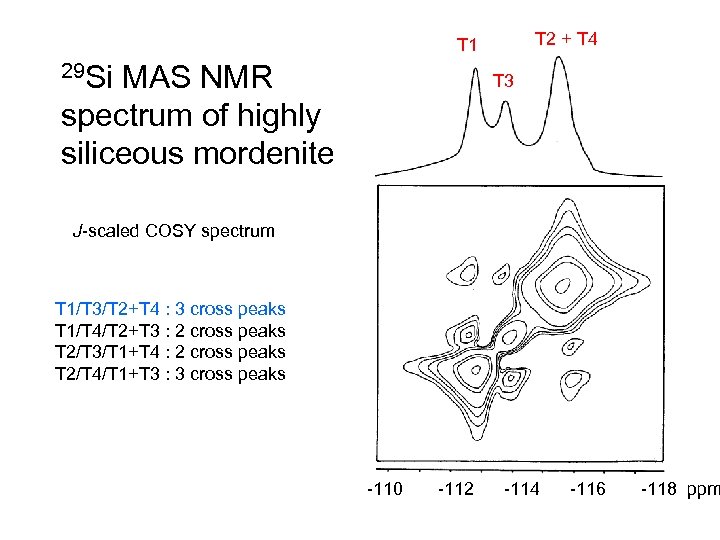
T 2 + T 4 T 1 29 Si MAS NMR spectrum of highly siliceous mordenite T 3 J-scaled COSY spectrum T 1/T 3/T 2+T 4 : 3 cross peaks T 1/T 4/T 2+T 3 : 2 cross peaks T 2/T 3/T 1+T 4 : 2 cross peaks T 2/T 4/T 1+T 3 : 3 cross peaks -110 -112 -114 -116 -118 ppm
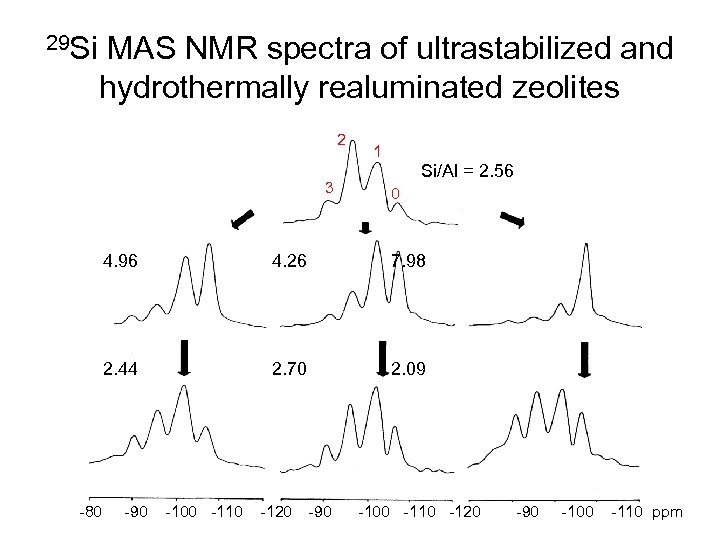
29 Si MAS NMR spectra of ultrastabilized and hydrothermally realuminated zeolites 2 3 1 Si/Al = 2. 56 0 4. 96 7. 98 2. 44 -80 4. 26 2. 70 2. 09 -90 -100 -110 -120 -90 -100 -110 ppm
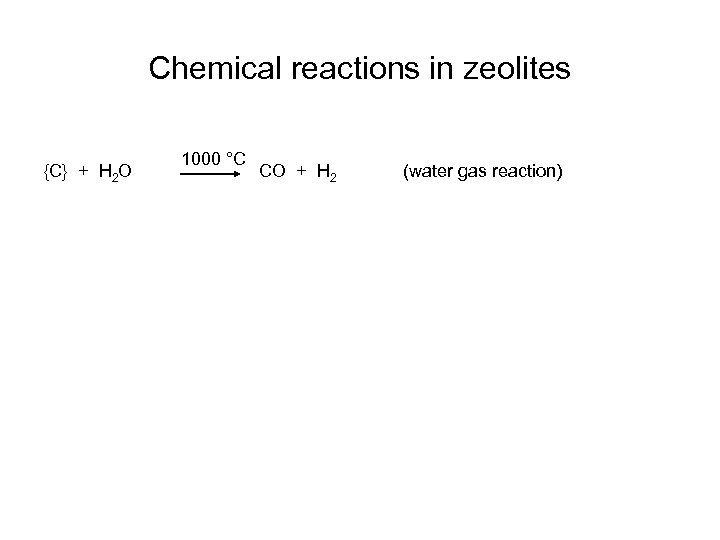
Chemical reactions in zeolites {C} + H 2 O 1000 °C CO + H 2 (water gas reaction)
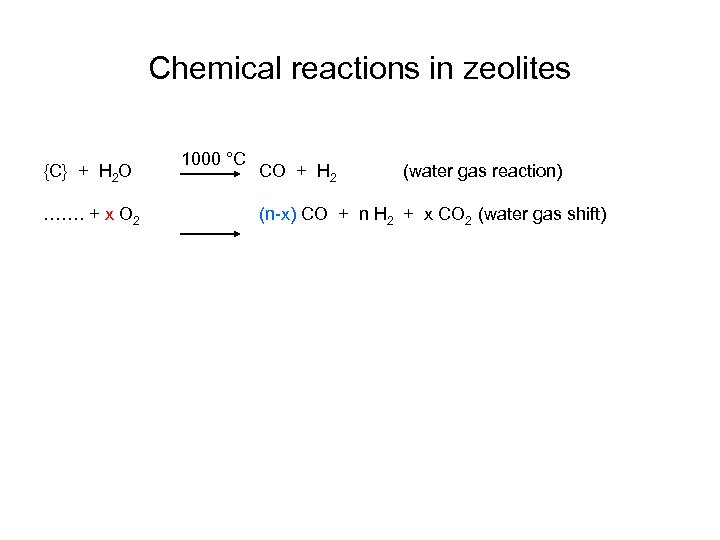
Chemical reactions in zeolites {C} + H 2 O ……. + x O 2 1000 °C CO + H 2 (water gas reaction) (n-x) CO + n H 2 + x CO 2 (water gas shift)
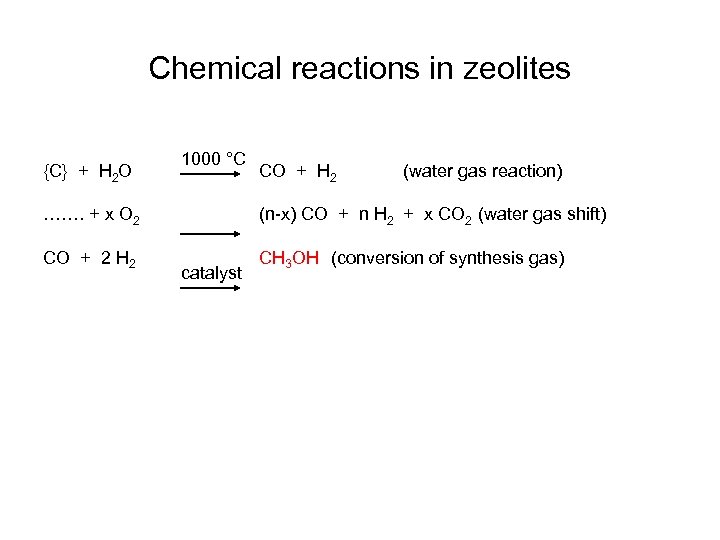
Chemical reactions in zeolites {C} + H 2 O 1000 °C CO + H 2 (water gas reaction) ……. + x O 2 (n-x) CO + n H 2 + x CO 2 (water gas shift) CO + 2 H 2 CH 3 OH (conversion of synthesis gas) catalyst
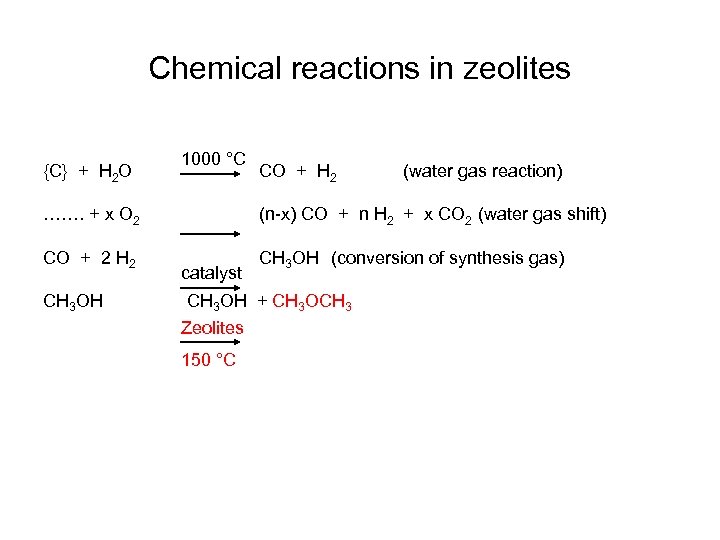
Chemical reactions in zeolites {C} + H 2 O 1000 °C CO + H 2 (water gas reaction) ……. + x O 2 (n-x) CO + n H 2 + x CO 2 (water gas shift) CO + 2 H 2 CH 3 OH (conversion of synthesis gas) CH 3 OH catalyst CH 3 OH + CH 3 OCH 3 Zeolites 150 °C
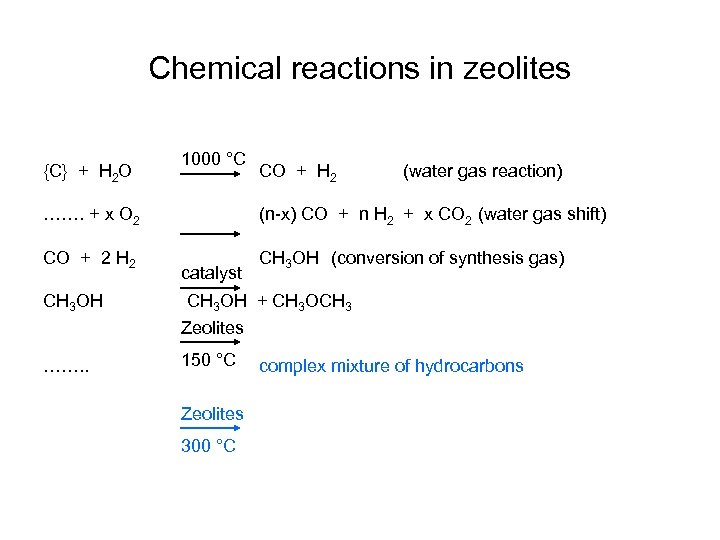
Chemical reactions in zeolites {C} + H 2 O 1000 °C CO + H 2 (water gas reaction) ……. + x O 2 (n-x) CO + n H 2 + x CO 2 (water gas shift) CO + 2 H 2 CH 3 OH (conversion of synthesis gas) CH 3 OH catalyst CH 3 OH + CH 3 OCH 3 Zeolites ……. . 150 °C Zeolites 300 °C complex mixture of hydrocarbons
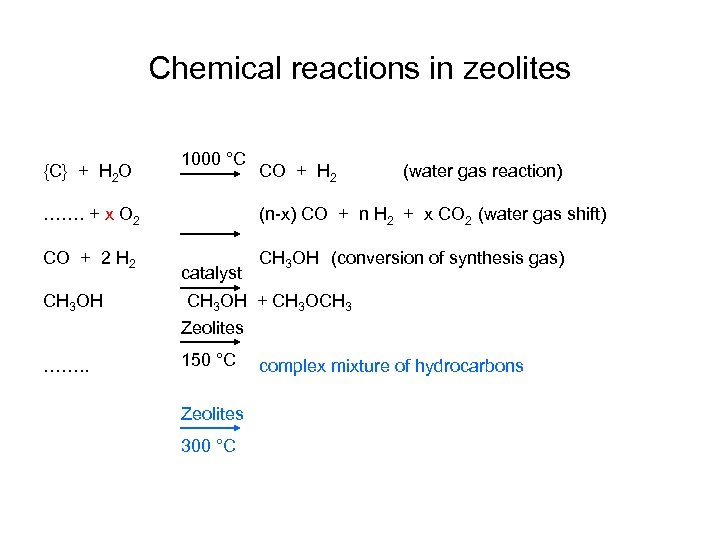
Chemical reactions in zeolites {C} + H 2 O 1000 °C CO + H 2 (water gas reaction) ……. + x O 2 (n-x) CO + n H 2 + x CO 2 (water gas shift) CO + 2 H 2 CH 3 OH (conversion of synthesis gas) CH 3 OH catalyst CH 3 OH + CH 3 OCH 3 Zeolites ……. . 150 °C Zeolites 300 °C complex mixture of hydrocarbons
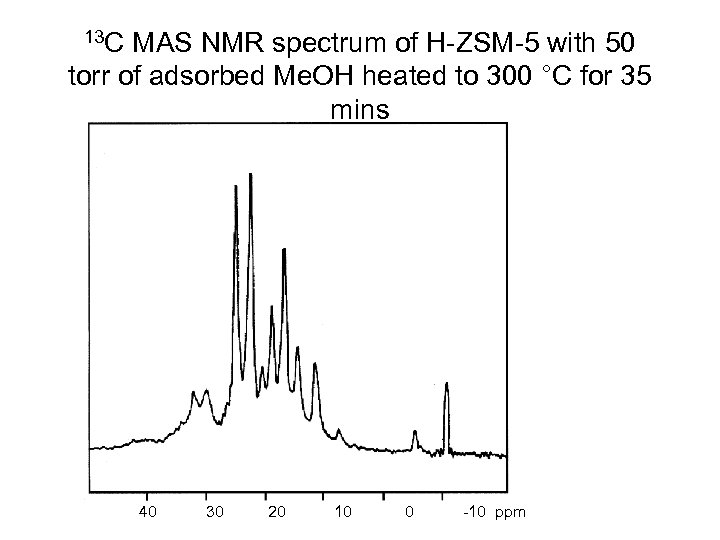
13 C MAS NMR spectrum of H-ZSM-5 with 50 torr of adsorbed Me. OH heated to 300 °C for 35 mins 0 40 30 20 10 -5 -10 0 -15 -10 ppm
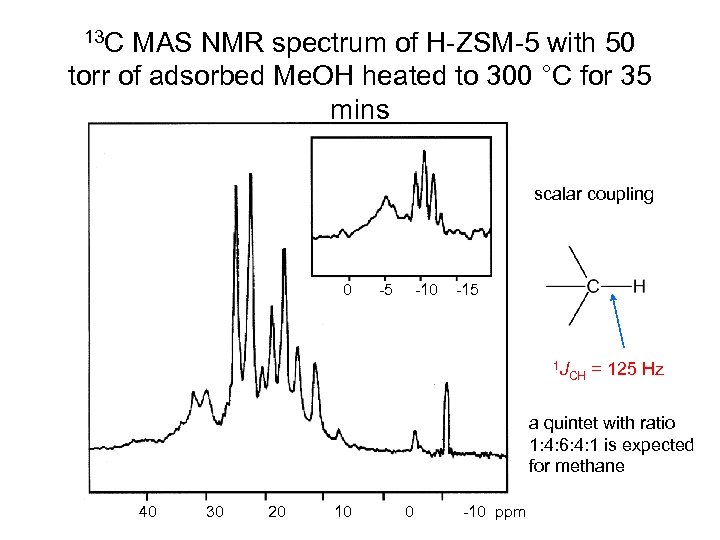
13 C MAS NMR spectrum of H-ZSM-5 with 50 torr of adsorbed Me. OH heated to 300 °C for 35 mins scalar coupling 0 -5 -10 -15 1 J CH = 125 Hz a quintet with ratio 1: 4: 6: 4: 1 is expected for methane 40 30 20 10 0 -10 ppm
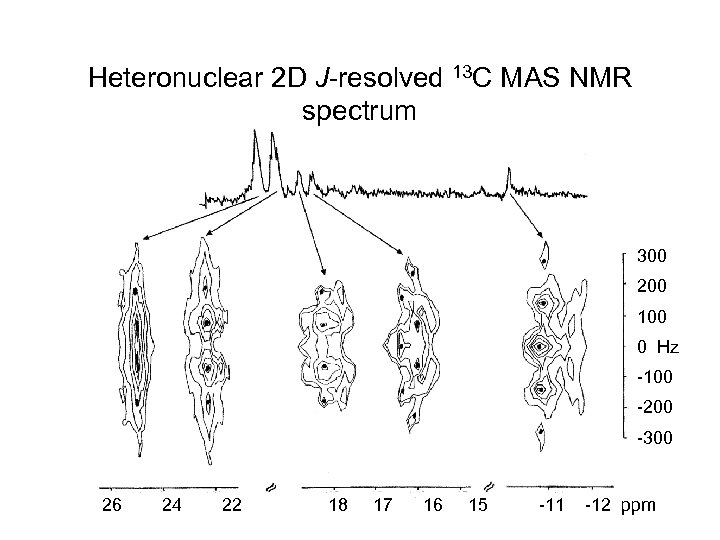
Heteronuclear 2 D J-resolved 13 C MAS NMR spectrum 300 200 100 0 Hz -100 -200 -300 26 24 22 18 17 16 15 -11 -12 ppm
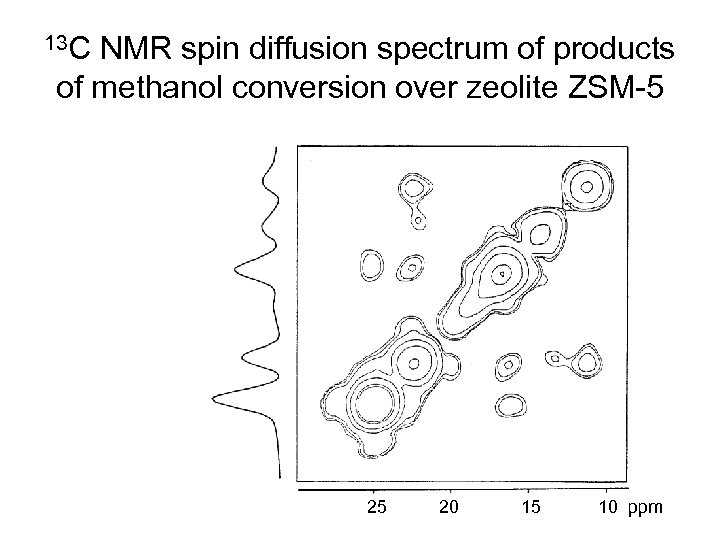
13 C NMR spin diffusion spectrum of products of methanol conversion over zeolite ZSM-5 25 20 15 10 ppm
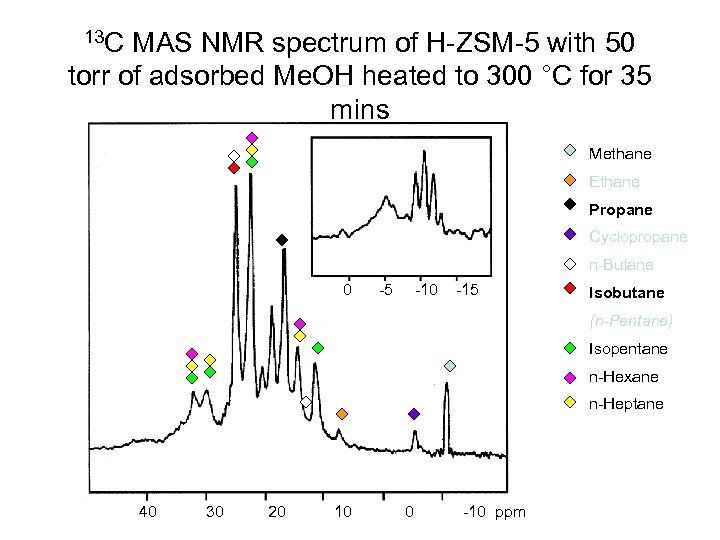
13 C MAS NMR spectrum of H-ZSM-5 with 50 torr of adsorbed Me. OH heated to 300 °C for 35 mins Methane Ethane Propane Cyclopropane n-Butane 0 -5 -10 -15 Isobutane (n-Pentane) Isopentane n-Hexane n-Heptane 40 30 20 10 0 -10 ppm
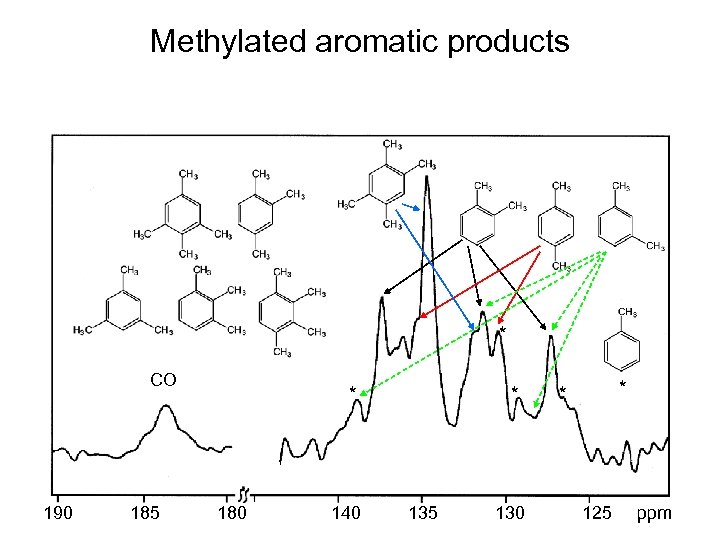
Methylated aromatic products * CO 190 185 * 180 140 * 135 130 * * 125 ppm
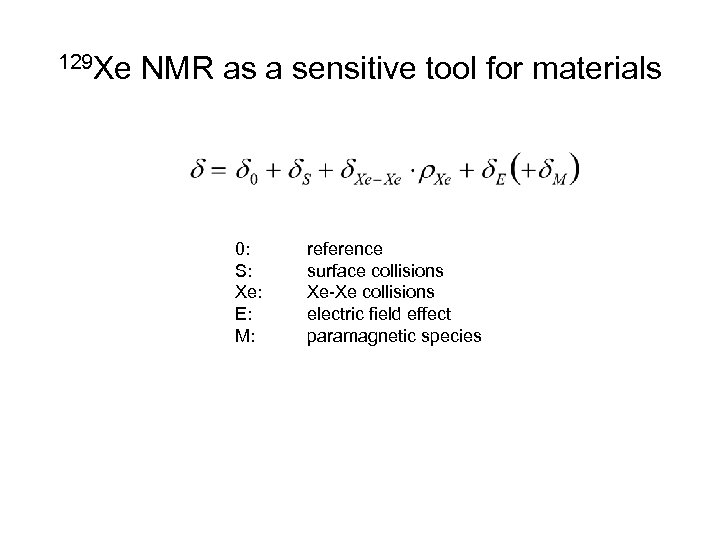
129 Xe NMR as a sensitive tool for materials 0: S: Xe: E: M: reference surface collisions Xe-Xe collisions electric field effect paramagnetic species
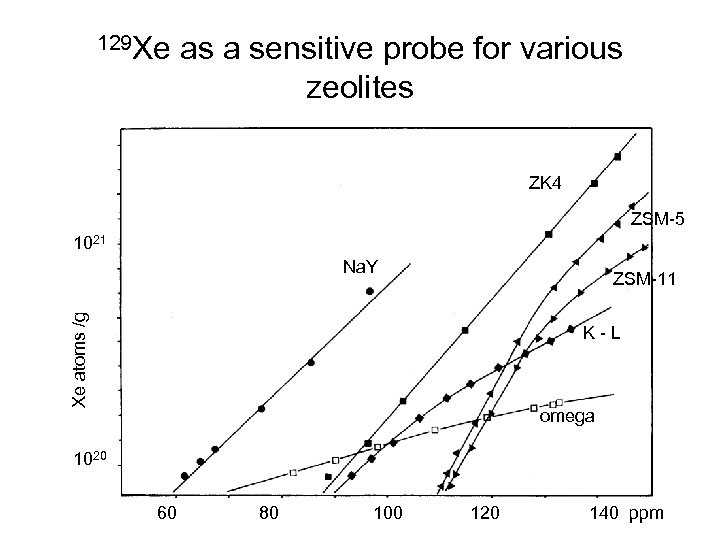
129 Xe as a sensitive probe for various zeolites ZK 4 ZSM-5 1021 Na. Y Xe atoms /g ZSM-11 K-L omega 1020 60 80 100 120 140 ppm

Applications • • Polymers Glasses Porous materials Liquid crystals
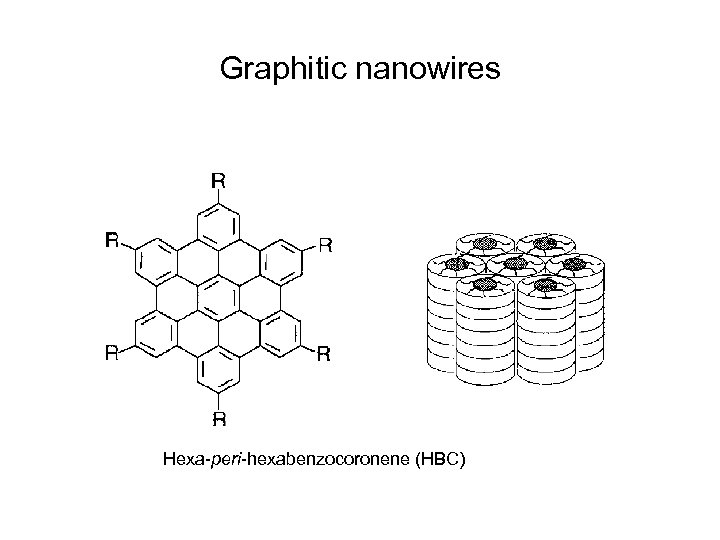
Graphitic nanowires Hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene (HBC)
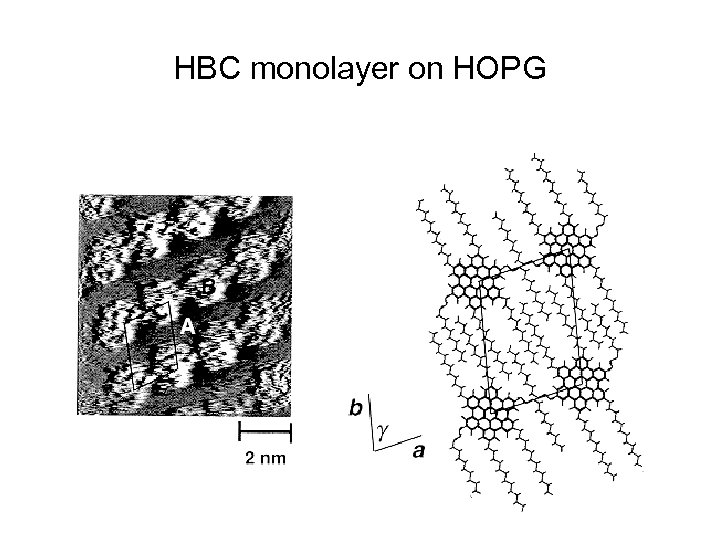
HBC monolayer on HOPG
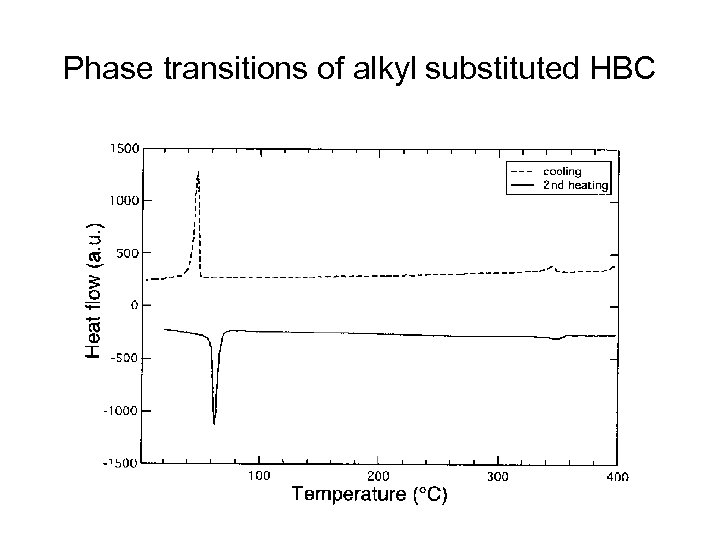
Phase transitions of alkyl substituted HBC
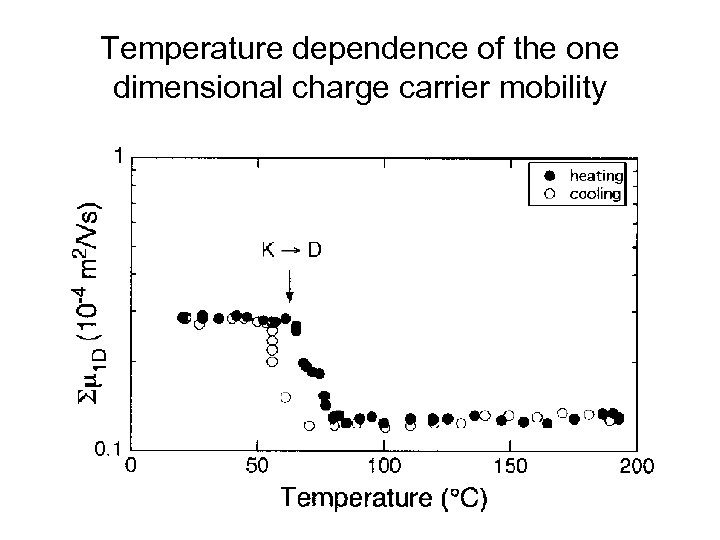
Temperature dependence of the one dimensional charge carrier mobility
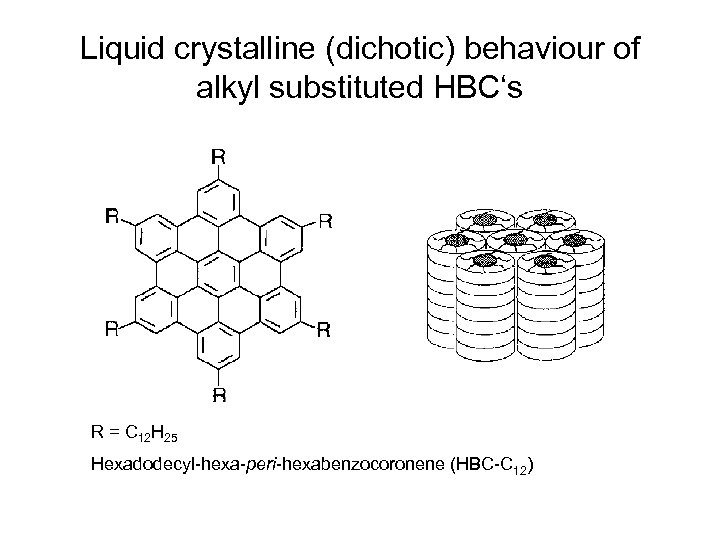
Liquid crystalline (dichotic) behaviour of alkyl substituted HBC‘s R = C 12 H 25 Hexadodecyl-hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene (HBC-C 12)
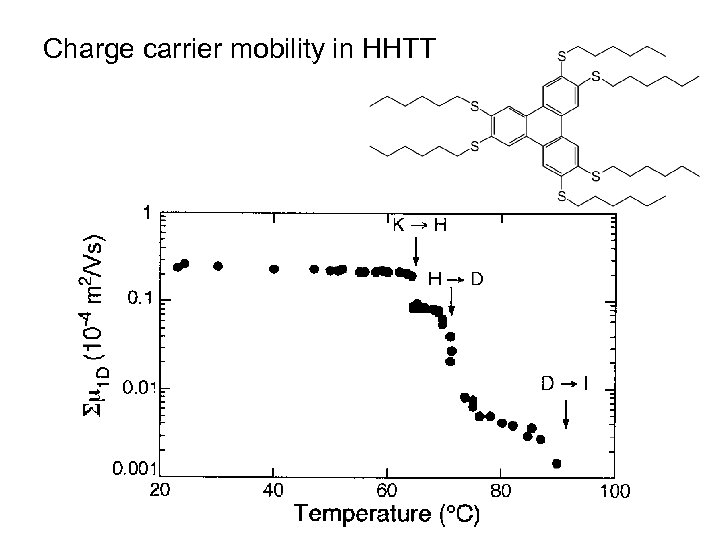
Charge carrier mobility in HHTT
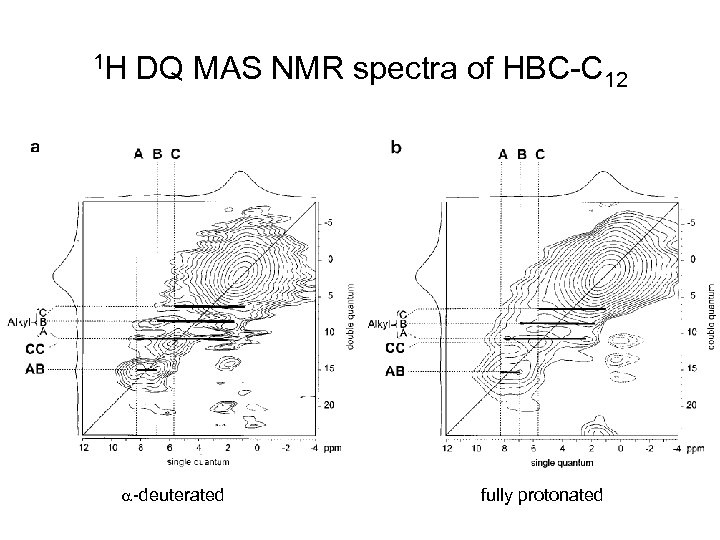
1 H DQ MAS NMR spectra of HBC-C 12 a-deuterated fully protonated
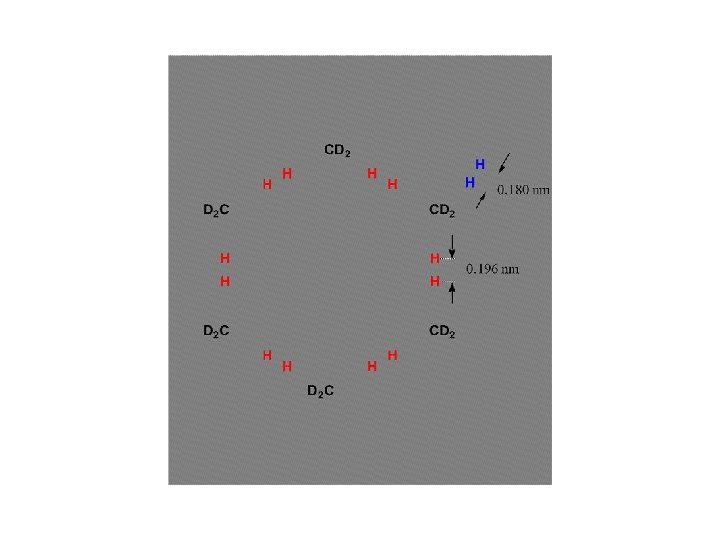
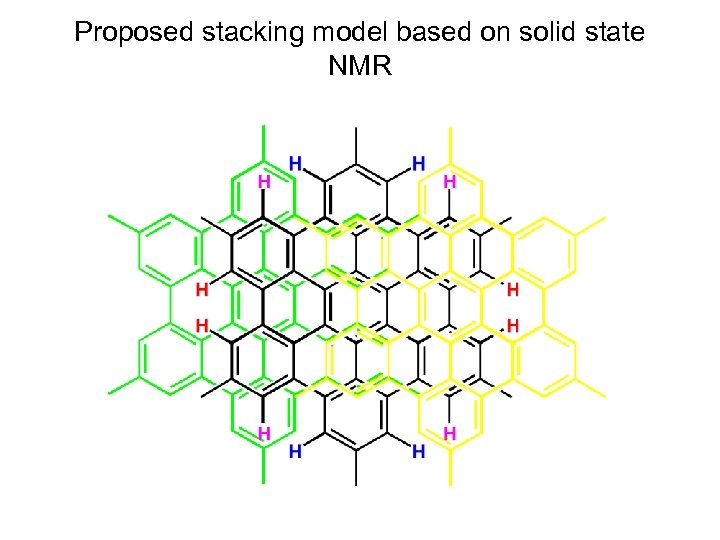
Proposed stacking model based on solid state NMR
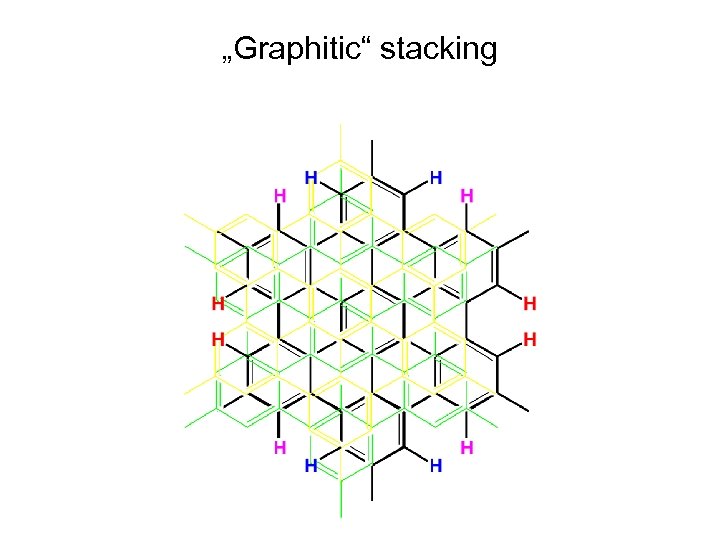
„Graphitic“ stacking
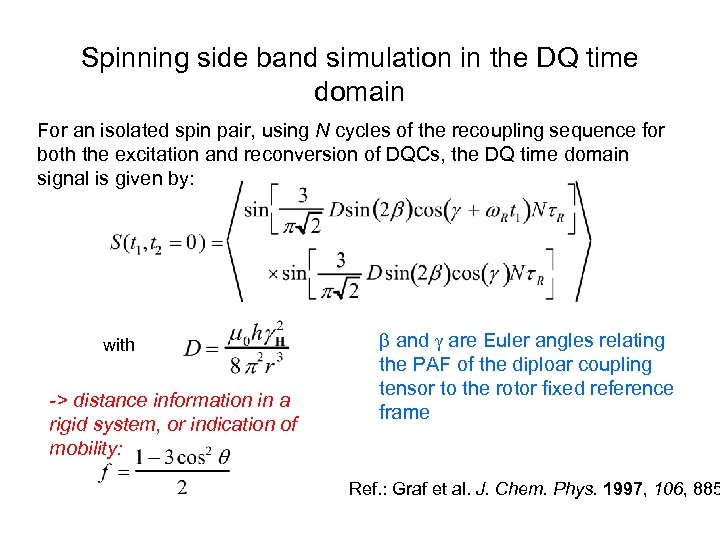
Spinning side band simulation in the DQ time domain For an isolated spin pair, using N cycles of the recoupling sequence for both the excitation and reconversion of DQCs, the DQ time domain signal is given by: with -> distance information in a rigid system, or indication of mobility: b and g are Euler angles relating the PAF of the diploar coupling tensor to the rotor fixed reference frame Ref. : Graf et al. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 106, 885
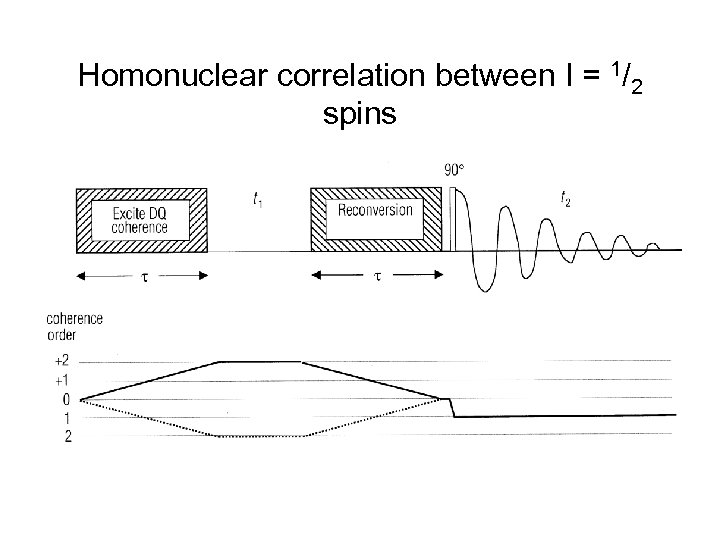
Homonuclear correlation between I = 1/2 spins
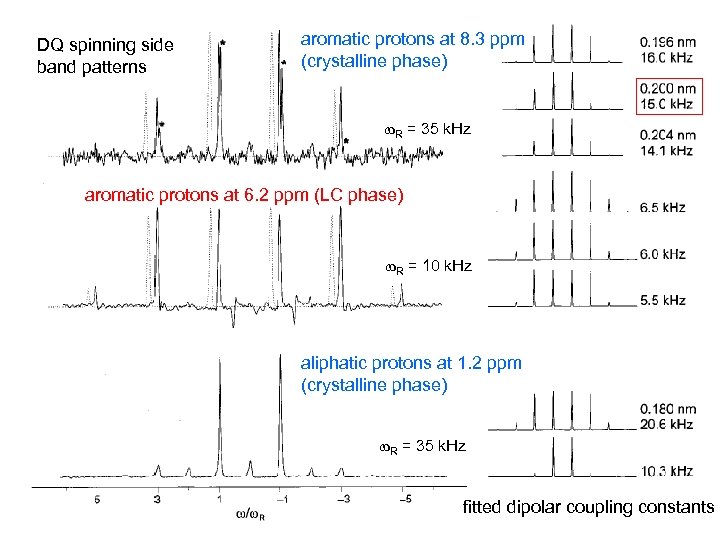
DQ spinning side band patterns aromatic protons at 8. 3 ppm (crystalline phase) w. R = 35 k. Hz aromatic protons at 6. 2 ppm (LC phase) w. R = 10 k. Hz aliphatic protons at 1. 2 ppm (crystalline phase) w. R = 35 k. Hz fitted dipolar coupling constants
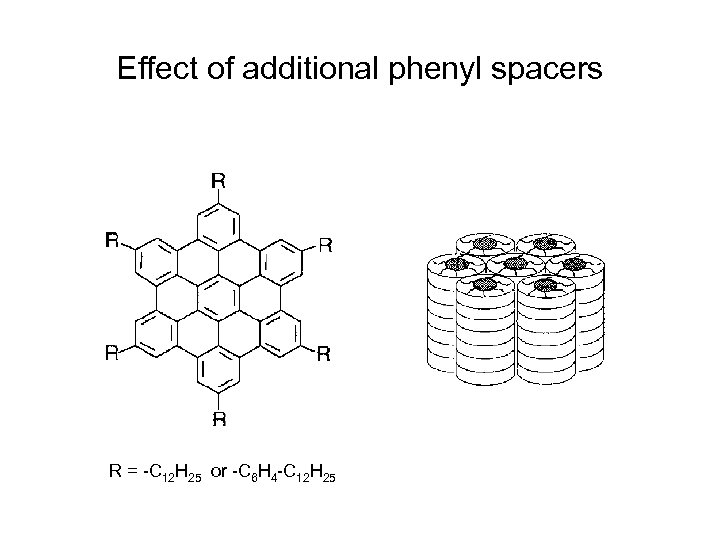
Effect of additional phenyl spacers R = -C 12 H 25 or -C 6 H 4 -C 12 H 25
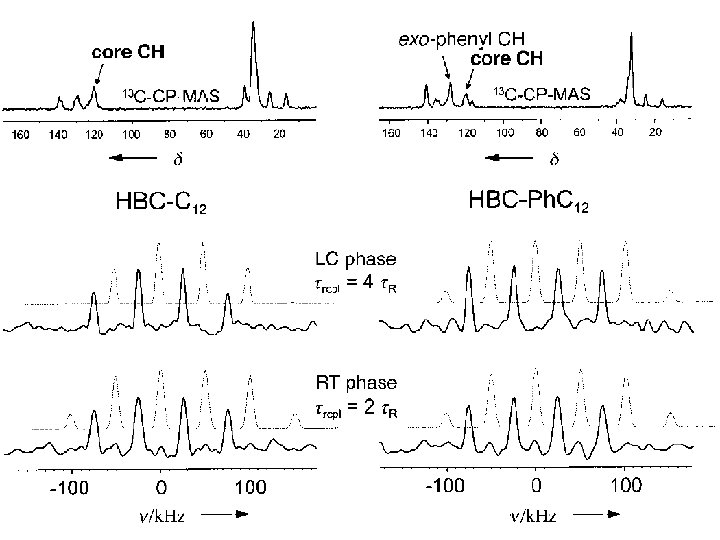
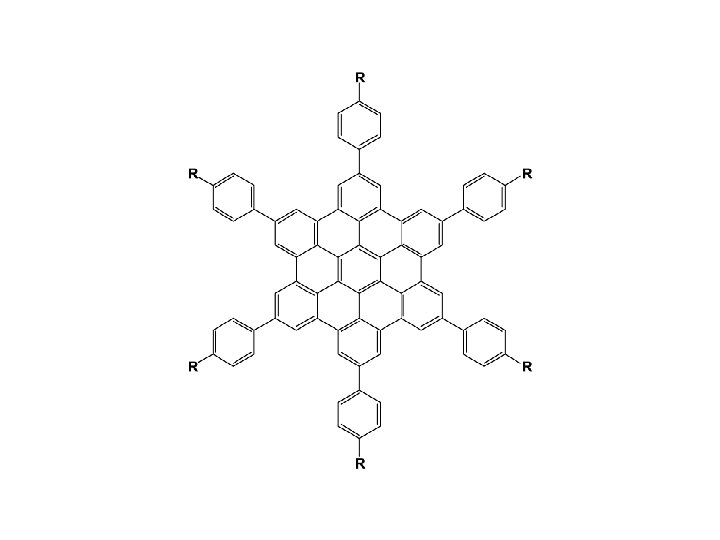
Space filling model for HBC-Ph. C 1
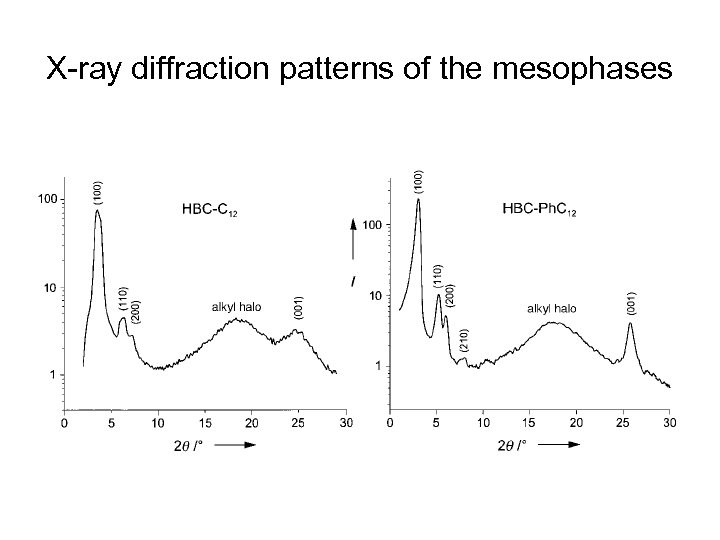
X-ray diffraction patterns of the mesophases
a5782286fb4cd3812f11cb1324e2244f.ppt